Does Allergy Break Bones? Osteoporosis and Its Connection to Allergy
Abstract
1. Introduction
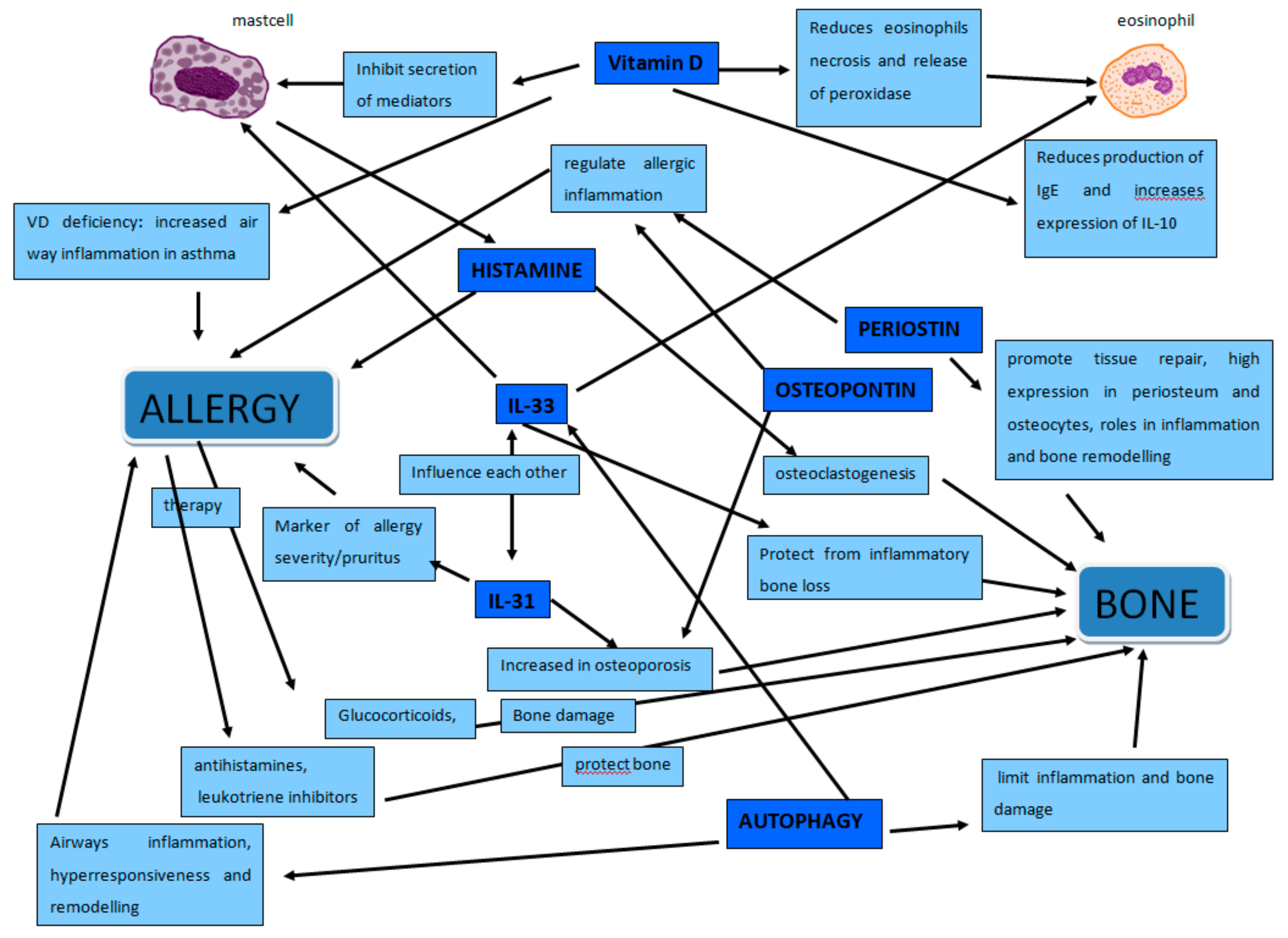
2. Osteoporosis and Allergy
2.1. Osteoimmunology
2.2. Inflammation
2.3. Osteopontin and Periostin
3. IL-33/IL-31 Axis
Autophagy
4. Vitamin D
5. Histamine
6. Mast Cells
7. Pollen-Allergy
8. Asthma
9. Atopic Dermatitis
10. Chronic Urticaria
11. Milk-Allergy
12. Mastocytosis
13. Hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome
14. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M. Osteoimmunology and Beyond. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 3754–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martinis, M.; Sirufo, M.M.; Ginaldi, L. Allergy and aging: An old/new emerging health issue. Aging Dis. 2017, 8, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martinis, M.; Sirufo, M.M.; Ginaldi, L. Food allergies and ageing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 8, 5580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Martinis, M.; Sirufo, M.M.; Ginaldi, L. Food allergy insights: A changing landscape Archivum Immunologie et Therapiae Experimentalis. AITE 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, K.E.; Mansfield, K.E.; Delmestri, A.; Smeeth, L.; Roberts, A.; Abuabara, K.; Prieto-Alhambra, D.; Langan, S.M. Atopic eczema and fracture risk in adults: A population-based cohort study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, N.; Silverberg, J.I. Association between eczema and increased fracture and bone or joint injury in adults a us population-based study. JAMA Dermatol. 2015, 151, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Ramsook, A.H.; Coxson, H.O.; Bon, J.; Reid, W.D. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Osteoporosis in Individuals with COPD: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Chest 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccarelli, F.; Martinis, M.; Ginaldi, L. Glucocorticoids in Patients with Rheumatic Diseases: Friends or Enemies of Bone? Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Anouti, F.; Taha, Z.; Shamim, S.; Khalaf, K.; Al Kaabi, L.; Alsafar, H. An insight into the paradigms of osteoporosis: From genetics to biomechanics. Bone Rep. 2019, 11, 100216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucci, S.; Incorvaia, C. Allergy as an organ and a systemic disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 153, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrick, B.J.; Jalan, S.; Tollefson, M.M.; Milbrandt, T.A.; Larson, A.N.; Rank, M.A.; Lohse, C.M.; Davis, D.M.R. Associations of self-reported allergic diseases and musculoskeletal problems in children: A US population-based study. Ann. Allergy Asthma. Immunol. 2017, 119, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zupan, J.; Jeras, M.; Marc, J. Osteoimmunology and the influence of pro-inflammatory cytokines on osteoclasts. Biochem. Medica 2013, 23, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Qi, X. Cytokine signaling in the differentiation of innate effector cells. JAK-STAT 2013, 2, e23531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, G.; D’Amelio, P.; Faccio, R.; Brunetti, G. The Interplay between the Bone and the Immune System. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madel, M.-B.; Ibáñez, L.; Wakkach, A.; De Vries, T.J.; Teti, A.; Apparailly, F.; Blin-Wakkach, C. Immune Function and Diversity of Osteoclasts in Normal and Pathological Conditions. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponzetti, M.; Rucci, N. Updates on Osteoimmunology: What’s New on the Cross-Talk between Bone and Immune System. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansfield, L.E. Allergy and the bone. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2011, 107, 188–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.M.M.; Rahman, S.; Hubeau, C.; Ma, H.-L. Cytokine Pathways in Allergic Disease. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 40, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martinis, M.; Franceschi, C.; Monti, D.; Ginaldi, L. Apoptosis remodeling in immunosenescence: Implications for strategies to delay ageing. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, U.; Teichmann, J.; Schett, G.; Neumann, E.; Müller-Ladner, U. Osteoimmunology: How inflammation influences bone metabolism. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 2013, 138, 1845–1849. [Google Scholar]
- De Martinis, M.; Sirufo, M.M.; Ginaldi, L. Osteoporosis: Current and emerging therapies targeted to immunological checkpoints. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. Pathophysiology of allergic inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 242, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irelli, A.; Sirufo, M.M.; Scipioni, T.; De Pietro, F.; Pancotti, A.; Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M. Breast cancer patients receiving denosumab during adjuvant aromatase inhibitors treatment: Who are the “inadequate responders” patients to denosumab? J. Buon 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Irelli, A.; Sirufo, M.M.; Scipioni, T.; De Pietro, F.; Pancotti, A.; Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M. mTOR Links Tumor Immunity and Bone Metabolism: What are the Clinical Implications? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Shi, X. Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 (cysLT1R) regulates osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46 (Suppl. 3), S64–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Chi, M.; Zhang, M.; Shan, H.; Zhang, Q.-H.; Zhang, J.; Shi, J.; Zhang, J.-Z.; Wu, R.-M.; et al. Osteoprotegerin mediate RANK/RANKL signaling inhibition eases asthma inflammatory reaction by affecting the survival and function of dendritic cells. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2019, 47, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, D.; Bondor, C.; Albu, A.; Simon, S.P.; Craciun, A.; Muntean, L. The value of osteopontin in the assessment of bone mineral density status in postmenopausal women. J. Investig. Med. 2013, 61, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, S.; Kurokawa, M.; Uede, T.; Nishimura, M.; Huang, S.-K. Role of osteopontin, a multifunctional protein, in allergy and asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2011, 41, 1360–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idolazzi, L.; Ridolo, E.; Fassio, A.; Gatti, D.; Montagni, M.; Caminati, M.; Martignago, I.; Incorvaia, C.; Senna, G. Periostin: The bone and beyond. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 38, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izuhara, K.; Nunomura, S.; Nanri, Y.; Ono, J.; Mitamura, Y.; Yoshihara, T.; Ogawa, M. Periostin in inflammation and allergy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 4293–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdaca, G.; Greco, M.; Tonacci, A.; Negrini, S.; Borro, M.; Puppo, F.; Gangemi, S. IL-33/IL-31 Axis in Immune-Mediated and Allergic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, K.D.; Agrawal, D.K. Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells in Inflammation and Allergy. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M.; Ciccarelli, F.; Saitta, S.; Imbesi, S.; Mannucci, C.; Gangemi, S. Increased levels of interleukin 31 (IL-31) in osteoporosis. BMC Immunol. 2015, 16, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takatori, H.; Makita, S.; Ito, T.; Matsuki, A.; Nakajima, H. Regulatory Mechanisms of IL-33-ST2-Mediated Allergic Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulo, E.L.; McKernan, E.M.; Fichtinger, P.S.; Mathur, S.K. Comparison of IL-33 and IL-5 family mediated activation of human eosinophils. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M.; Saitta, S.; Sirufo, M.M.; Mannucci, C.; Casciaro, M.; Ciccarelli, F.; Gangemi, S. Interleukin-33 serum levels in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martinis, M.; Sirufo, M.M.; Suppa, M.; Ginaldi, L. IL-33/IL-31 axis in osteoporosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Shang, Q.; Wong, C.-K.; Li, E.K.; Kun, E.W.; Cheng, I.T.; Li, M.; Li, T.K.; Zhu, T.Y.; Yu, C.-M.; et al. Carotid plaque and bone density and microarchitecture in psoriatic arthritis: The correlation with soluble ST2. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massimini, M.; Palmieri, C.; De Maria, R.; Romanucci, M.; Malatesta, D.; De Martinis, M.; Maniscalco, L.; Ciccarelli, A.; Ginaldi, L.; Buracco, P.; et al. 17-AAG and Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Mitophagy in Canine Osteosarcoma Cell Lines. Veter Pathol. 2016, 54, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Huang, M.; Yao, Y.-M. Autophagy and proinflammatory cytokines: Interactions and clinical implications. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018, 43, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y. Autophagy is involved in allergic rhinitis by inducing airway remodeling. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 1346–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdeva, K.; Do, D.C.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Gao, P. Environmental Exposures and Asthma Development: Autophagy, Mitophagy, and Cellular Senescence. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, M.; Wang, C.-J.; Yu, F.; Xie, K.; Lin, S.-H.; Xu, F. Different intensity of autophagy regulate interleukin-33 to control the uncontrolled inflammation of acute lung injury. Inflamm. Res. 2019, 68, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Xiao, Y. The Autophagy in Osteoimmonology: Self-Eating, Maintenance, and Beyond. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florencio-Silva, R.; Sasso, G.R.; Simões, M.J.; Simões, R.S.; Baracat, M.C.; Sasso-Cerri, E.; Cerri, P.S. Osteoporosis and autophagy: What is the relationship? Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2017, 63, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bivona, G.; Agnello, L.; Ciaccio, M. The immunological implication of the new vitamin D metabolism. Central Eur. J. Immunol. 2018, 43, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccarelli, F.; De Martinis, M.; Sirufo, M.M.; Ginaldi, L. Psoriasis Induced by Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Agents: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. ADC 2016, 24, 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Muehleisen, B.; Gallo, R.L. Vitamin D in allergic disease: Shedding light on a complex problem. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillon, R.; Marcocci, C.; Carmeliet, G.; Bikle, D.; White, J.H.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Lips, P.; Munns, C.F.; Lazaretti-Castro, M.; Giustina, A.; et al. Skeletal and Extraskeletal Actions of Vitamin D: Current Evidence and Outstanding Questions. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 1109–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, R.; Misra, M. Extra-Skeletal Effects of Vitamin D. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, C.; Passalacqua, G. Italian Vitamin D Allergy Group Vitamin D levels and allergic diseases. An Italian cross-sectional multicenter survey. Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 49, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Souto Filho, J.T.D.; de Andrade, A.S.; Ribeiro, F.M.; Alves, P.A.S.; Simonini, V.R.F. Impact of vitamin D deficiency on increased blood eosinophil counts. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Ther. 2018, 11, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biosse-Duplan, M.; Baroukh, B.; Dy, M.; De Vernejoul, M.-C.; Saffar, J.-L. Histamine Promotes Osteoclastogenesis through the Differential Expression of Histamine Receptors on Osteoclasts and Osteoblasts. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 1426–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-W.; Kim, B.-M.; Lee, K.-A.; Lee, S.-H.; Firestein, G.S.; Kim, H.-R. Histamine and Histamine H4 Receptor Promotes Osteoclastogenesis in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folwarczna, J.; Janas, A.; Pytlik, M.; Sliwinski, L.; Wiercigroch, M.; Brzęczek, A. Modifications of histamine receptor signaling affect bone mechanical properties in rats. Pharmacol. Rep. 2014, 66, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folwarczna, J.; Konarek, N.; Freier, K.; Karbowniczek, D.; Londzin, P.; Janas, A. Effects of loratadine, a histamine H1 receptor antagonist, on the skeletal system of young male rats. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 3357–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasarød, K.M.; Stunes, A.K.; Mosti, M.P.; Ramezanzadehkoldeh, M.; Viggaklev, B.I.; Reseland, J.E.; Skallerud, B.H.; Fossmark, R.; Syversen, U. Effects of the Histamine 1 Receptor Antagonist Cetirizine on the Osteoporotic Phenotype in H+/K+ATPase Beta Subunit KO Mice. J. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 117, 2089–2096. [Google Scholar]
- Kinjo, M.; Setoguchi, S.; Solomon, D.H. Antihistamine therapy and bone mineral density: Analysis in a population-based US sample. Am. J. Med. 2008, 121, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Solomon, D.H.; Diem, S.J.; Ruppert, K.; Lian, Y.J.; Liu, C.-C.; Wohlfart, A.; Greendale, G.A.; Finkelstein, J.S. Bone mineral density changes among women initiating proton pump inhibitors or H2 receptor antagonists: A SWAN cohort study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2015, 30, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikawa, Y.; Yonekawa, T.; Ohkuni, Y.; Kuribayashi, M.; Fukino, K.; Ueno, K. A comparative study of histamine activities on differentiation of osteoblasts and osteoclasts. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 32, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renke, J.; Kędzierska-Mieszkowska, S.; Lange, M.; Nedoszytko, B.; Wasilewska, E.; Liberek, A.; Renke, M.; Niedoszytko, M.; Witkowski, J.; Skórko-Glonek, J.; et al. Mast cells in mastocytosis and allergy—Important player in metabolic and immunological homeostasis. Adv. Med Sci. 2019, 64, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader-Meunier, B.; Livideanu, C.B.; Larroche, C.; Durieu, I.; Artru, L.; Beucher, A.; Cormier, G.; Cornec, D.; DeLarco, M.; Dubost, J.-J.; et al. Association of mastocytosis with inflammatory joint diseases: A series of 31 patients. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 44, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redegeld, F.A.; Yu, Y.; Kumari, S.; Charles, N.; Blank, U. Non-IgE mediated mast cell activation. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 282, 87–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferencz, V.; Mészáros, S.; Csupor, E.; Tóth, E.; Bors, K.; Falus, A.; Horvath, C. Increased bone fracture prevalence in postmenopausal women suffering from pollen-allergy. Osteoporos. Int. 2006, 17, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.G.; Kong, I.G. Association between chronic rhinosinusitis and osteoporosis: A case-control study using a National sample color. Int. Forum. Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelardi, M.; Barbara, F.; Covelli, I.; Damiani, M.A.; Plantone, F.; Notarnicola, A.; Moretti, B.; Quaranta, N.; Ciprandi, G. Long-Term Therapy with Corticosteroids in Nasal Polyposis: A Bone Metabolism Assessment. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 71, 2050–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljubran, S.A.; Whelan, G.J.; Glaum, M.C.; Lockey, R.F. Osteoporosis in the at-risk asthmatic. Allergy 2014, 69, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.-W.; Kang, H.-R.; Kim, J.-Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, S.S.; Cho, S.H. Are asthmatic patients prone to bone loss? Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014, 112, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Min, K.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Shim, J.J.; Kang, K.H.; Hur, G.Y. Osteoporosis in Patients with Asthma–Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Overlap Syndrome. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2018, 81, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.R.; Wala, S.M. Inflammation, allergy and asthma, complex immune origin diseases: Mechanisms and therapeutic agents. Recent Patents Inflamm. Allergy Drug Discov. 2013, 7, 62–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Lim, H.; Lee, D.; Yim, M. Montelukast inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and bone loss via CysLTR1 and P2Y12. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 2387–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirufo, M.M.; De Martinis, M.; Ginaldi, L. Omalizumab an effective and safe alternative therapy in severe refractory atopic dermatitis. A case report. Medicine 2018, 97, e10897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, N.K.; Silverberg, J.I. Eczema is associated with osteoporosis and fractures in adults: A US population-based study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 1085–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkwright, P.D.; Mughal, M.Z. Vertebral, pelvic, and hip fracture risk in adults with severe atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, K.; Okawa, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Ono, J.; Inoue, Y.; Kohno, M.; Matsukura, S.; Kambara, T.; Ohta, S.; Izuhara, K.; et al. Periostin levels correlate with disease severity and chronicity in patients with atopic dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 171, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalom, G.; Kridin, K.; Babaev, M. Chronic urticaria and osteoporosis: A longitudinal community-based color study of 11944 patients. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 180, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martinis, M.; Sirufo, M.M.; Ginaldi, L. A “Stadium” Urticaria, Cold Urticaria Is Still a Mostly Unknown Disease, with a Wide Spectrum of Severity Degrees and Few Therapeutic Certainties: Is Omalizumab One of These? Reflections from a Clinical Case Report. Iran Red Cresc Med. J. 2019, 21, e84250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martinis, M.; Sirufo, M.M.; Ginaldi, L. Solar urticaria, a disease with many dark sides: Is omalizumab the right therapeutic response? Reflections from a clinical case report. Open Med. 2019, 14, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirufo, M.M.; Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M. Asthma, urticaria and omalizumab in children: Reflections from a clinical case report. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaney, R.P. Dairy and Bone Health. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2009, 28, 82S–90S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachshon, L.; Goldberg, M.R.; Schwartz, N.; Sinai, T.; Amitzur-Levy, R.; Elizur, A.; Eisenberg, E.; Katz, Y. Decreased bone mineral density in young adult IgE-mediated cow’s milk–allergic patients. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 1108–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, M.R.; Nachshon, L.; Sinai, T.; Epstein-Rigbi, N.; Oren, Y.; Eisenberg, E.; Katz, Y.; Elizur, A. Risk factors for reduced bone mineral density measurements in milk-allergic patients. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 29, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Toit, G.; Elizur, A.; Nadeau, K.C. Cow’s Milk and Vitamin D Supplementation in Infants-Timing Is Everything. JAMA Pediatr. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardecka, I.; Łoś-Rycharska, E.; Gawryjołek, J.; Toporowska-Kowalska, E.; Krogulska, A. FOXP3 expression, vitamins D and C in the prediction of tolerance acquisition in infants with cow’s milk allergy. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garla, V.V.; Chaudhary, K.U.Q.; Yaqub, A. Systemic mastocytosis: A rare cause of osteoporosis. Pan Afr. Med J. 2019, 32, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossini, M.; Zanotti, R.; Viapiana, O.; Tripi, G.; Orsolini, G.; Idolazzi, L.; Bonadonna, P.; Schena, D.; Escribano, L.; Adami, S.; et al. Bone Involvement and Osteoporosis in Mastocytosis. Immunol. Allergy Clin. North Am. 2014, 34, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsolini, G.; Viapiana, O.; Rossini, M.; Bonifacio, M.; Zanotti, R. Bone Disease in Mastocytosis. Immunol. Allergy Clin. North Am. 2018, 38, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabenhorst, A.; Christopeit, B.; Leja, S.; Gerbaulet, A.; Kleiner, S.; Forster, A.; Raap, U.; Wickenhauser, C.; Hartmann, K. Serum levels of bone cytokines are increased in indolent systemic mastocytosis associated with osteopenia or osteoporosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 1234–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuerman, O.; Hoffer, V.; Cohen, A.H.; Woellner, C.; Grimbacher, B.; Garty, B.-Z. Reduced Bone Density in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Hyper-IgE Syndrome. J. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 33, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowerwine, K.J.; Shaw, P.A.; Gu, W.; Ling, J.C.; Collins, M.T.; Darnell, D.N.; Anderson, V.L.; Davis, J.; Hsu, A.; Welch, P.; et al. Bone density and fractures in autosomal dominant hyper IgE syndrome. J. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 34, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Solal, M.; Prieur, A.; Prin, L.; Denne, M.; Launay, J.; Graulet, A.; Brazier, M.; Griscelli, C.; De Vernejoul, M. Cytokine-Mediated Bone Resorption in Patients with the Hyperimmunoglobulin E Syndrome. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1995, 76, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minegishi, Y. Hyper-IgE syndrome. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2009, 21, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczawinska-Poplonyk, A.; Kycler, Z.; Pietrucha, B.; Heropolitanska-Pliszka, E.; Breborowicz, A.; Gerreth, K. The hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome-clinical manifestation diversity in primary immune deficiency. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2011, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.H.; Pajarinen, J.; Lu, L.; Nabeshima, A.; Cordova, L.A.; Yao, Z.; Goodman, S.B. NF-κB as a Therapeutic Target in Inflammatory-Associated Bone Diseases. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2017, 107, 117–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| IL-31 | IL-33 | |
|---|---|---|
| Bone | Involvement in postmenopausal osteoporosis | Protective |
| Atopic dermatitis | Involvement in impairment of skin barrier function | Modulate eosinophil function. IL-33 inhibition: reduced IgE serum IgE levels, and mast cells and eosinophils infiltration |
| Asthma and allergic rhinitis | Asthma exacerbation | Inflammation and fibrotic damage. IL-33 inhibition: asthma improvement |
| Allergic contact dermatitis | Pruritus | Early warning system of skin damage. Inhibit contact hypersensitivity and induce Treg; IL-33 blockade worsens contact hypersensitivity. |
| Chronic spontaneous urticaria | Pruritus | |
| Food allergy | Th2 response promotion. IL-33 inhibition: FA improvement |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sirufo, M.M.; Suppa, M.; Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M. Does Allergy Break Bones? Osteoporosis and Its Connection to Allergy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030712
Sirufo MM, Suppa M, Ginaldi L, De Martinis M. Does Allergy Break Bones? Osteoporosis and Its Connection to Allergy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(3):712. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030712
Chicago/Turabian StyleSirufo, Maria Maddalena, Mariano Suppa, Lia Ginaldi, and Massimo De Martinis. 2020. "Does Allergy Break Bones? Osteoporosis and Its Connection to Allergy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 3: 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030712
APA StyleSirufo, M. M., Suppa, M., Ginaldi, L., & De Martinis, M. (2020). Does Allergy Break Bones? Osteoporosis and Its Connection to Allergy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(3), 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030712







