Single-Cell Analysis of Different Stages of Oral Cancer Carcinogenesis in a Mouse Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Carcinogenesis in the Experimental Animal Model
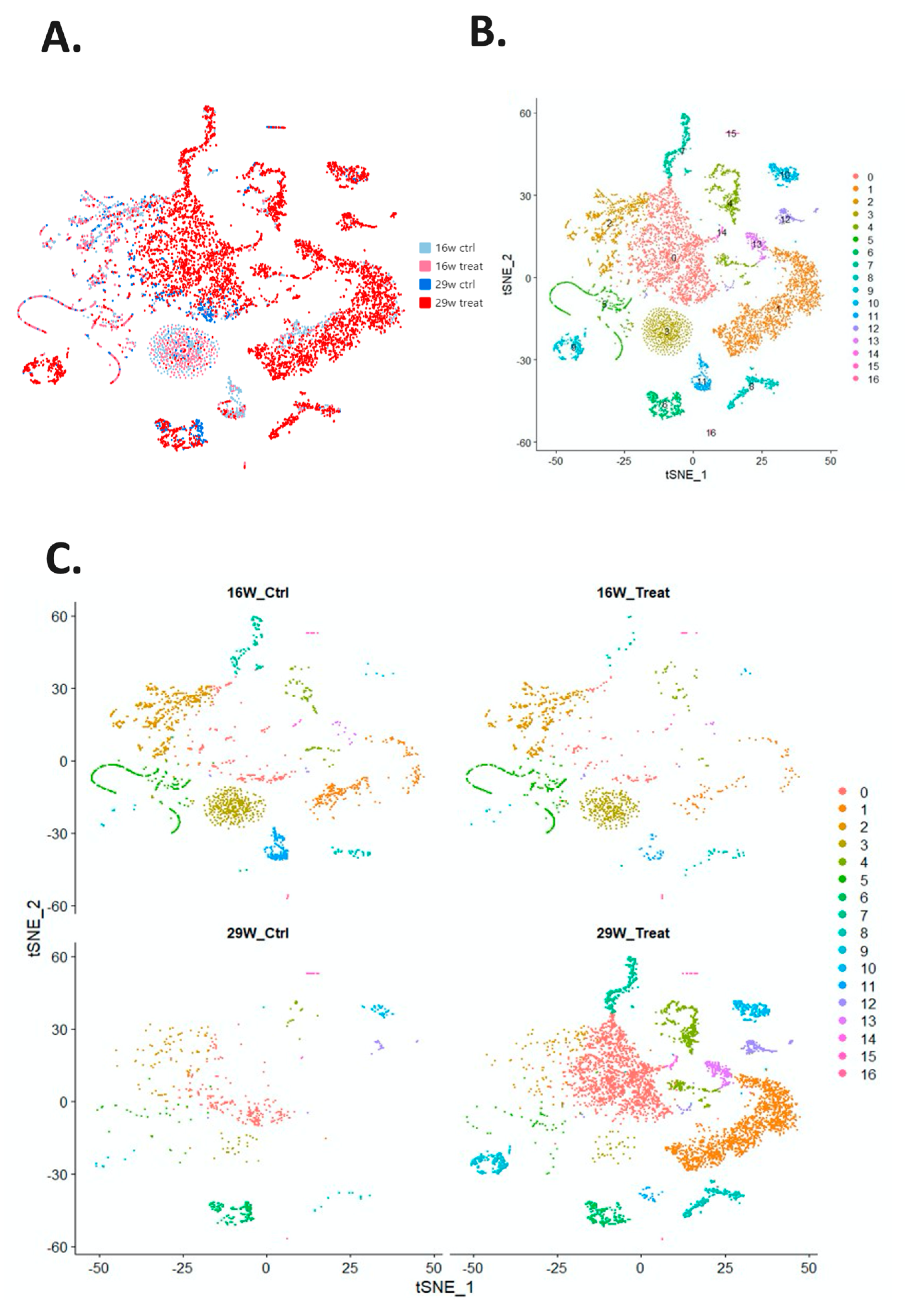
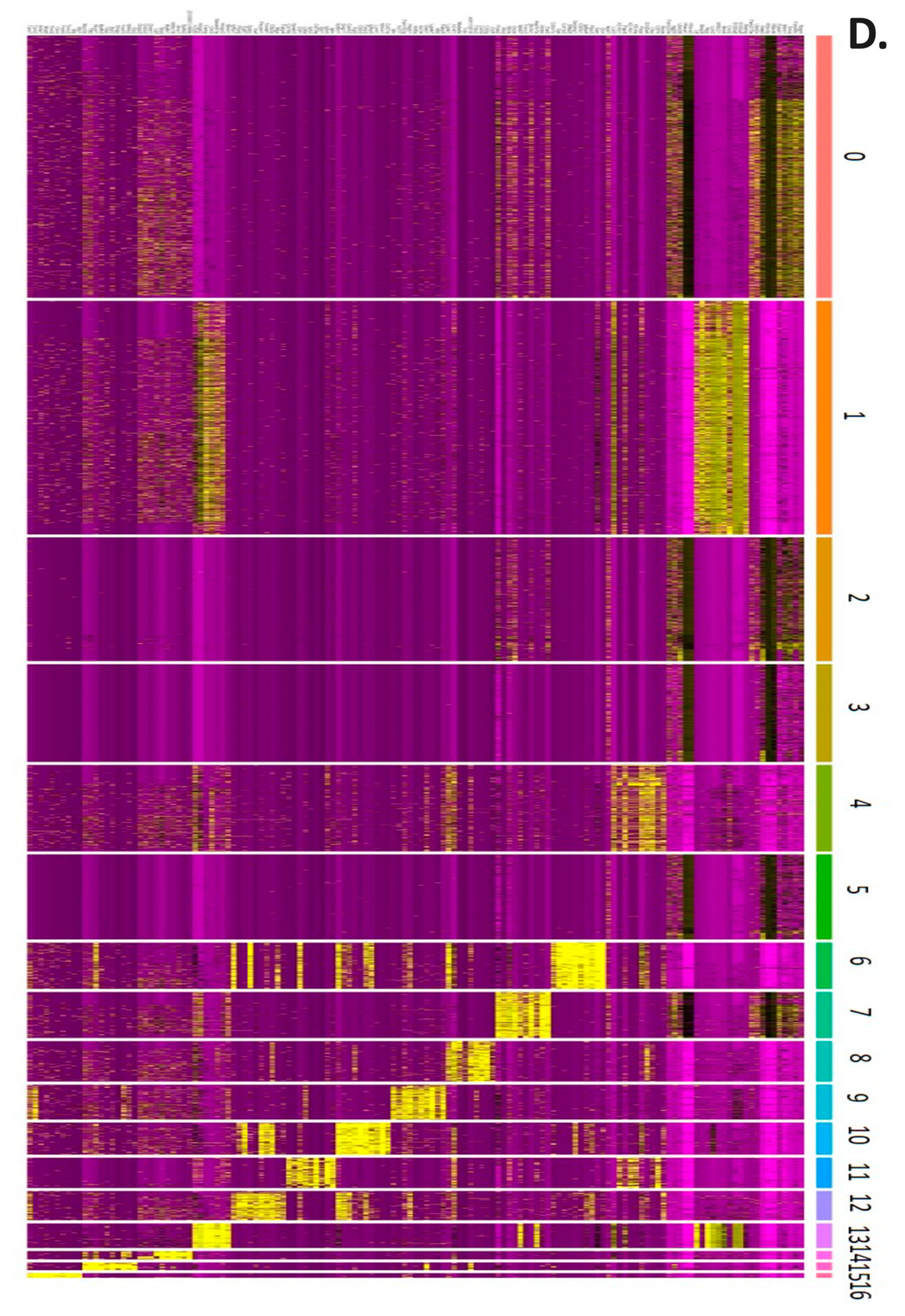
2.2. scRNA-seq in Control and Experimental Groups
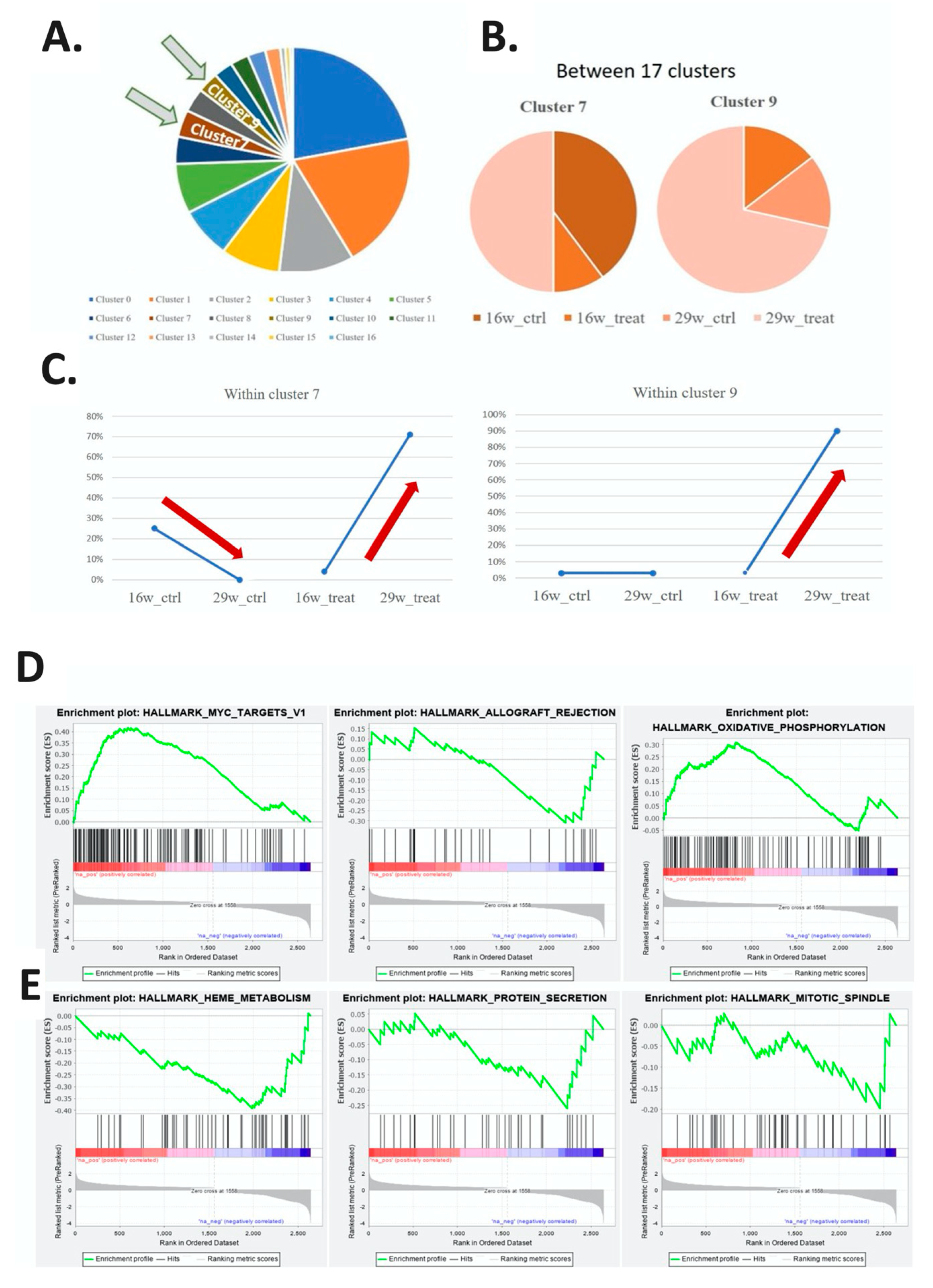
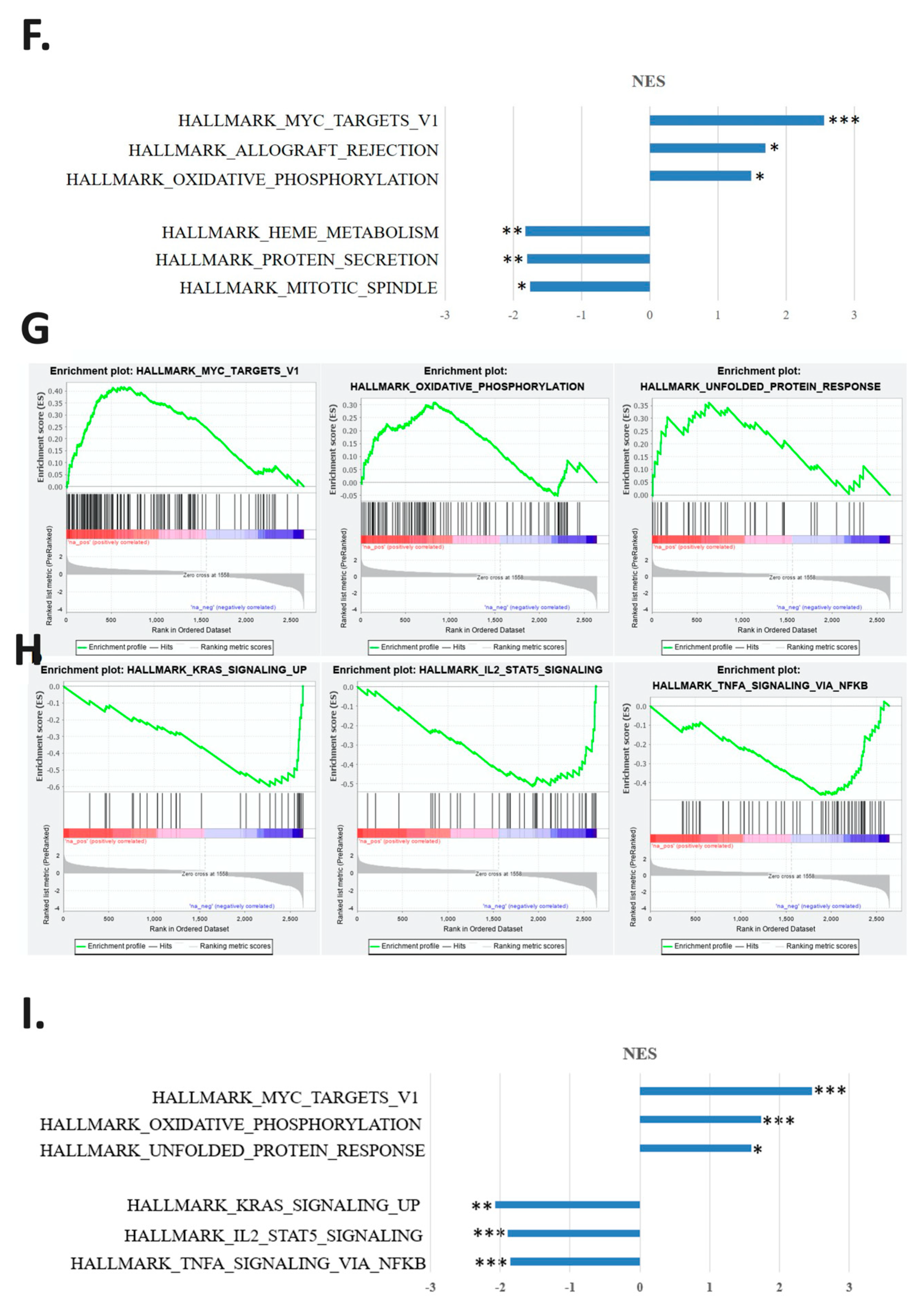
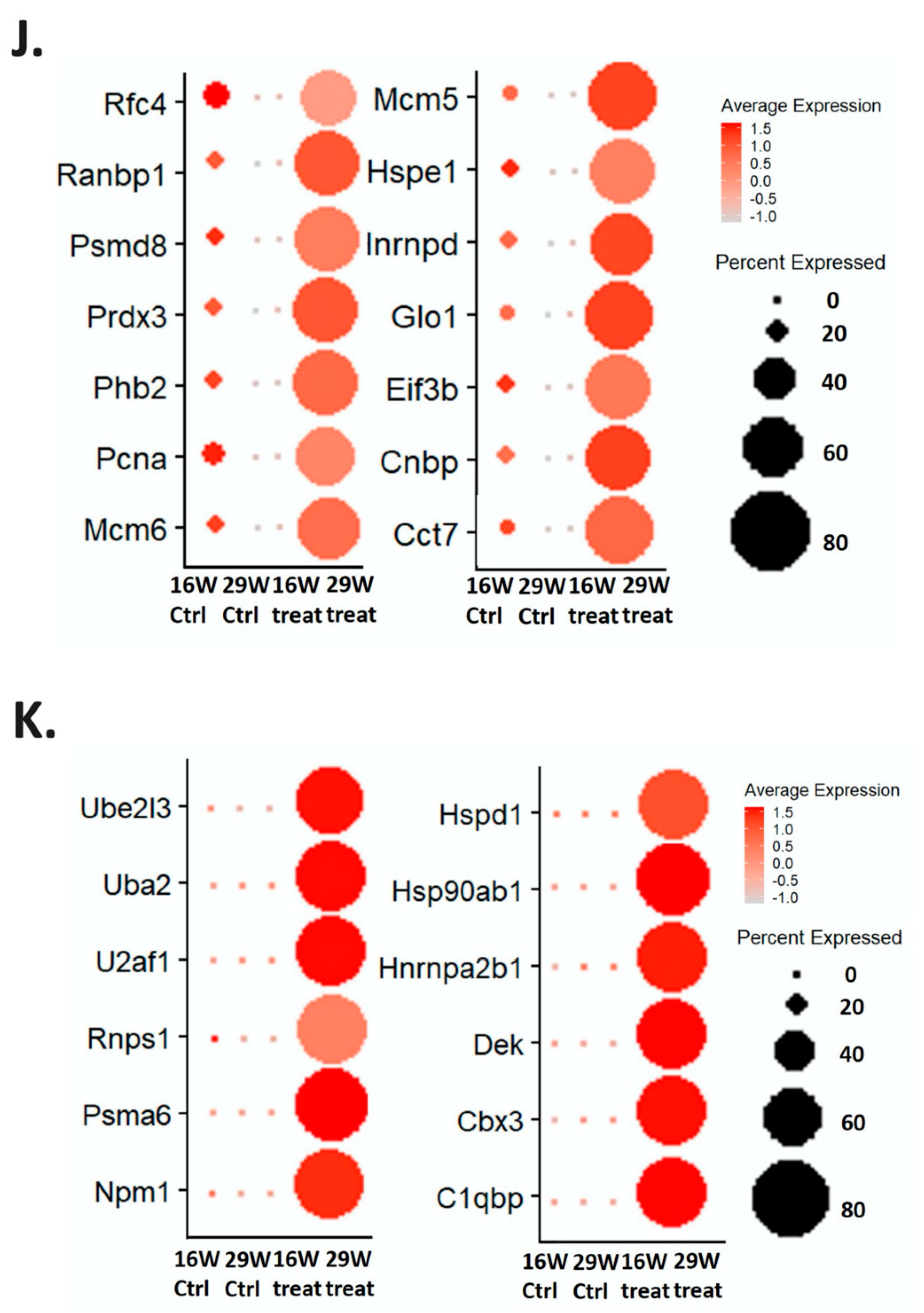
2.3. Regulatory Pathways Involved in the Carcinogenesis of a Mouse Animal Model
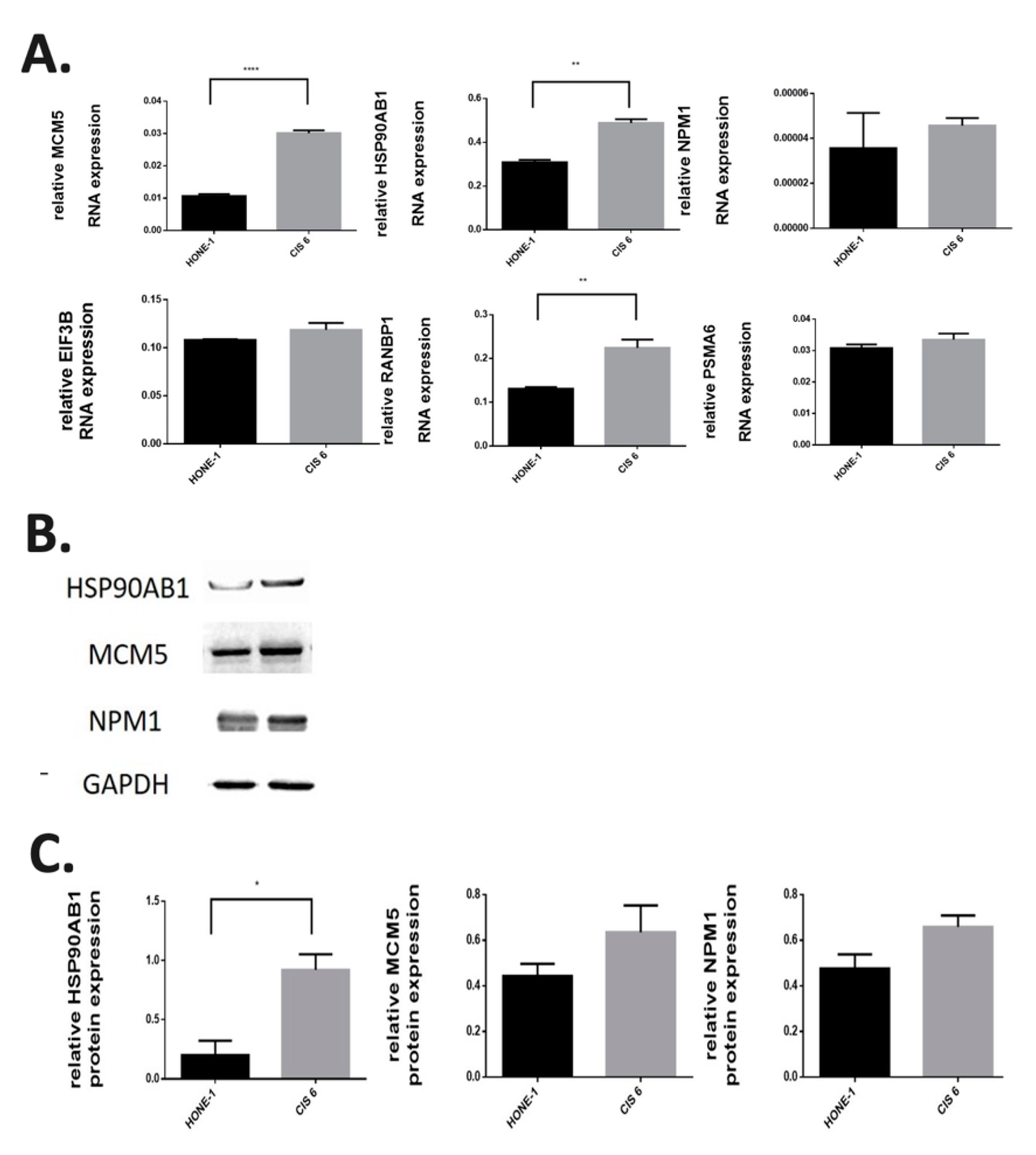
2.4. Validation of the Gene Expression in the Regulatory Pathways in Cisplatin-Resistant Cell Lines
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Establishment of an Experimental Animal Model
4.2. Tongue Cell Isolation
4.3. Next-Generation Sequencing
4.4. Bioinformatic Analysis of Next-Generation Sequencing Data
4.5. Cell Line
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lousada-Fernandez, F.; Rapado-Gonzalez, O.; Lopez-Cedrun, J.L.; Lopez-Lopez, R.; Muinelo-Romay, L.; Suarez-Cunqueiro, M.M. Liquid Biopsy in Oral Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, M.; Nanavati, R.; Modi, T.G.; Dobariya, C. Oral cancer: Etiology and risk factors: A review. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2016, 12, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.; Wiesenfeld, D. Oral Cancer. Aust. Dent. J. 2018, 63 (Suppl. 1), S91–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Dong, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Dong, W. Identification of Potential Biomarkers and Survival Analysis for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Using Bioinformatics Strategy: A Study Based on TCGA and GEO Datasets. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7376034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zevallos, J.P.; Mazul, A.L.; Walter, V.; Hayes, D.N. Gene Expression Subtype Predicts Nodal Metastasis and Survival in Human Papillomavirus-Negative Head and Neck Cancer. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suva, M.L.; Tirosh, I. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing in Cancer: Lessons Learned and Emerging Challenges. Mol. Cell 2019, 75, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valihrach, L.; Androvic, P.; Kubista, M. Platforms for Single-Cell Collection and Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salomon, R.; Kaczorowski, D.; Valdes-Mora, F.; Nordon, R.E.; Neild, A.; Farbehi, N.; Bartonicek, N.; Gallego-Ortega, D. Droplet-based single cell RNAseq tools: A practical guide. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 1706–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirosh, I.; Izar, B.; Prakadan, S.M.; Wadsworth, M.H., 2nd; Treacy, D.; Trombetta, J.J.; Rotem, A.; Rodman, C.; Lian, C.; Murphy, G.; et al. Dissecting the multicellular ecosystem of metastatic melanoma by single-cell RNA-seq. Science 2016, 352, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, C.; Zheng, L.; Yoo, J.K.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Kang, B.; Hu, R.; Huang, J.Y.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Landscape of Infiltrating T Cells in Liver Cancer Revealed by Single-Cell Sequencing. Cell 2017, 169, 1342–1356.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winterhoff, B.J.; Maile, M.; Mitra, A.K.; Sebe, A.; Bazzaro, M.; Geller, M.A.; Abrahante, J.E.; Klein, M.; Hellweg, R.; Mullany, S.A.; et al. Single cell sequencing reveals heterogeneity within ovarian cancer epithelium and cancer associated stromal cells. Gynecol. Oncol. 2017, 144, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venteicher, A.S.; Tirosh, I.; Hebert, C.; Yizhak, K.; Neftel, C.; Filbin, M.G.; Hovestadt, V.; Escalante, L.E.; Shaw, M.L.; Rodman, C.; et al. Decoupling genetics, lineages, and microenvironment in IDH-mutant gliomas by single-cell RNA-seq. Science 2017, 355, eaai8478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puram, S.V.; Tirosh, I.; Parikh, A.S.; Patel, A.P.; Yizhak, K.; Gillespie, S.; Rodman, C.; Luo, C.L.; Mroz, E.A.; Emerick, K.S.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis of Primary and Metastatic Tumor Ecosystems in Head and Neck Cancer. Cell 2017, 171, 1611–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, N.W.; Pei, R.J.; Tseng, H.C.; Yeh, K.T.; Chan, H.C.; Lee, M.R.; Lin, C.; Hsieh, W.T.; Kao, M.C.; Tsai, M.H.; et al. Co-treating with arecoline and 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide to establish a mouse model mimicking oral tumorigenesis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 183, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzén, O.; Gan, L.-M.; Björkegren, J.L.M. PanglaoDB: A web server for exploration of mouse and human single-cell RNA sequencing data. Database 2019, 2019, baz046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, B.J.; Chan, M.Y.; Hsiao, H.Y.; Chang, C.H.; Hsu, L.P.; Lin, P.T. Relationship of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome in Patients with Oral Cancer. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 9303094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketabat, F.; Pundir, M.; Mohabatpour, F.; Lobanova, L.; Koutsopoulos, S.; Hadjiiski, L.; Chen, X.; Papagerakis, P.; Papagerakis, S. Controlled Drug Delivery Systems for Oral Cancer Treatment-Current Status and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kreso, A.; Dick, J.E. Evolution of the cancer stem cell model. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Picelli, S. Single-cell RNA-sequencing: The future of genome biology is now. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.; Gao, R.; Sei, E.; Brandt, R.; Hartman, J.; Hatschek, T.; Crosetto, N.; Foukakis, T.; Navin, N.E. Chemoresistance Evolution in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Delineated by Single-Cell Sequencing. Cell 2018, 173, 879–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Izar, B.; Tirosh, I.; Stover, E.H.; Wakiro, I.; Cuoco, M.S.; Alter, I.; Rodman, C.; Leeson, R.; Su, M.J.; Shah, P.; et al. A single-cell landscape of high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.Y.; Tu, H.F.; Kao, S.Y.; Chang, K.W.; Lin, S.C. The increase of oncogenic miRNA expression in tongue carcinogenesis of a mouse model. Oral Oncol. 2015, 51, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, S.H.; Yang, C.C.; Yu, E.H.; Chang, C.; Lee, Y.S.; Liu, C.J.; Chang, K.W.; Lin, S.C. K14-EGFP-miR-31 transgenic mice have high susceptibility to chemical-induced squamous cell tumorigenesis that is associating with Ku80 repression. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandak, R.M.; Chandak, M.G.; Rawlani, S.M. Current Concepts about Areca Nut Chewing. J. Contemp. Dent. 2013, 3, 78–81. [Google Scholar]
- Liberzon, A.; Subramanian, A.; Pinchback, R.; Thorvaldsdottir, H.; Tamayo, P.; Mesirov, J.P. Molecular signatures database (MSigDB) 3.0. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1739–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberzon, A.; Birger, C.; Thorvaldsdottir, H.; Ghandi, M.; Mesirov, J.P.; Tamayo, P. The Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) hallmark gene set collection. Cell Syst. 2015, 1, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rounbehler, R.J.; Fallahi, M.; Yang, C.; Steeves, M.A.; Li, W.; Doherty, J.R.; Schaub, F.X.; Sanduja, S.; Dixon, D.A.; Blackshear, P.J.; et al. Tristetraprolin impairs myc-induced lymphoma and abolishes the malignant state. Cell 2012, 150, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.J.; Wu, Y.L.; Tanaka, Y.; Zhang, W. Small molecules targeting c-Myc oncogene: Promising anti-cancer therapeutics. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 1084–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, U.; Huber, J.; Nilsson, J.A.; Fallahi, M.; Hall, M.A.; Peschel, C.; Cleveland, J.L. Myc suppression of Nfkb2 accelerates lymphomagenesis. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seitz, V.; Butzhammer, P.; Hirsch, B.; Hecht, J.; Gutgemann, I.; Ehlers, A.; Lenze, D.; Oker, E.; Sommerfeld, A.; von der Wall, E.; et al. Deep sequencing of MYC DNA-binding sites in Burkitt lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fallah, Y.; Brundage, J.; Allegakoen, P.; Shajahan-Haq, A.N. MYC-Driven Pathways in Breast Cancer Subtypes. Biomolecules 2017, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ma, Y.M.; Zheng, P.S.; Zhang, P. GDF15 promotes the proliferation of cervical cancer cells by phosphorylating AKT1 and Erk1/2 through the receptor ErbB2. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrzypczak, M.; Goryca, K.; Rubel, T.; Paziewska, A.; Mikula, M.; Jarosz, D.; Pachlewski, J.; Oledzki, J.; Ostrowski, J. Modeling oncogenic signaling in colon tumors by multidirectional analyses of microarray data directed for maximization of analytical reliability. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollaoglu, G.; Guthrie, M.R.; Bohm, S.; Bragelmann, J.; Can, I.; Ballieu, P.M.; Marx, A.; George, J.; Heinen, C.; Chalishazar, M.D.; et al. MYC Drives Progression of Small Cell Lung Cancer to a Variant Neuroendocrine Subtype with Vulnerability to Aurora Kinase Inhibition. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 270–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, W.; Kim, J.; Park, J.; Lee, D.H.; Hwang, D.; Kim, J.H.; Ashktorab, H.; Smoot, D.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, C.; et al. YAP/TAZ Initiates Gastric Tumorigenesis via Upregulation of MYC. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3306–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.H.; Wang, H.K.; Yeh, K.T.; Tai, H.C.; Wang, H.Y.; Huang, L.R.; Chiu, C.W.; Chung, C.M.; Velmurugan, B.K. c-MYC expression in T (III/IV) stage oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) patients. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 5163–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Ouyang, M.; Rao, J.N.; Zou, T.; Xiao, L.; Chung, H.K.; Wu, J.; Donahue, J.M.; Gorospe, M.; Wang, J.Y. Competition between RNA-binding proteins CELF1 and HuR modulates MYC translation and intestinal epithelium renewal. Mol. Biol. Cell 2015, 26, 1797–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koh, C.M.; Sabo, A.; Guccione, E. Targeting MYC in cancer therapy: RNA processing offers new opportunities. Bioessays 2016, 38, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kress, T.R.; Sabo, A.; Amati, B. MYC: Connecting selective transcriptional control to global RNA production. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.; Meng, L.; Jia, B.; Han, W. Expression of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit B in liver cancer and its prognostic significance. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiger, G.; Mayor, T. Perilous journey: A tour of the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adams, J. Potential for proteasome inhibition in the treatment of cancer. Drug Discov. Today 2003, 8, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adele Di Matteo, M.F. Sara Chiarella, Serena Rocchio, Carlo Travaglini-Allocatelli and Luca Federici, Molecules that target nucleophosmin for cancer treatment: An update. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 44821–44840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.L.; Boone, D.; Hann, S.R. Nucleophosmin interacts directly with c-Myc and controls c-Myc-induced hyperproliferation and transformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18794–18799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teng, S.C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Su, Y.N.; Chou, P.C.; Chiang, Y.C.; Tseng, S.F.; Wu, K.J. Direct activation of HSP90A transcription by c-Myc contributes to c-Myc-induced transformation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 14649–14655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Simone, M.; Rossetti, G.; Pagani, M. Chromium 10x Single-Cell 3’ mRNA Sequencing of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1979, 87–110. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.W.; Dawood, M.; Johnson, C.A.; Schmitz, R. RNA Sequencing in B-Cell Lymphomas. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1956, 283–303. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, W.; Su, W.; Tang, H.; Le, W.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Xie, L.; Li, J.; Ye, J.; et al. Immune cell profiling of COVID-19 patients in the recovery stage by single-cell sequencing. Cell Discov. 2020, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermayer, B.; Holtgrewe, M.; Nieminen, M.; Messerschmidt, C.; Beule, D. SCelVis: Exploratory single cell data analysis on the desktop and in the cloud. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrall-Fairbanks, M.C.; Ball, M.; Padron, E.; Altrock, P.M. Leveraging Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Experiments to Model Intratumor Heterogeneity. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2019, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.W.; Abedini, M.R.; Yang, L.X.; Ding, A.A.; Figeys, D.; Chang, J.Y.; Tsang, B.K.; Shieh, D.B. Gelsolin regulates cisplatin sensitivity in human head-and-neck cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 2760–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Type | Mean Reads per Cell | Reads Mapped to Genome |
|---|---|---|
| 16W_CONTROL_1 | 3,779,830 | 95.9% |
| 16W_CONTROL_2 | 120,426 | 94.3% |
| 16W_CONTROL_3 | 71,885 | 93.4% |
| 16W_TREAT_1 | 5,963,561 | 95.9% |
| 16W_TREAT_2 | 205,687 | 92.6% |
| 16W_TREAT_3 | 112,034 | 92.7% |
| 29W_CONTROL_1 | 2,995,150 | 98.4% |
| 29W_CONTROL_2 | 32,436 | 94.7% |
| 29W_TREAT_1 | 1,335,636 | 97.7% |
| 29W_TREAT_2 | 23,521 | 92.6% |
| 29W_TREAT_3 | 14,880 | 92.9% |
| Cell Number | 2271 | 2022 | 1069 | 847 | 749 | 737 | 401 | 399 | 351 | 303 | 276 | 262 | 254 | 214 | 72 | 68 | 39 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subtype | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| 16W_CTRL | 192 | 239 | 521 | 440 | 109 | 325 | 2 | 98 | 38 | 10 | 5 | 201 | 6 | 14 | 7 | 12 | 9 |
| 16W_TREAT | 118 | 82 | 354 | 340 | 47 | 332 | 1 | 16 | 26 | 9 | 5 | 29 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 8 | 24 |
| 29W_CTRL | 224 | 1 | 85 | 27 | 31 | 33 | 173 | 1 | 11 | 10 | 33 | 0 | 26 | 0 | 2 | 18 | 1 |
| 29W_TREAT | 1717 | 1700 | 109 | 40 | 562 | 47 | 225 | 284 | 276 | 274 | 233 | 32 | 215 | 195 | 60 | 30 | 5 |
| Within Cluster | |||||||||||||||||
| 16W_CTRL | 8% | 12% | 49% | 52% | 15% | 44% | 0% | 25% | 11% | 3% | 2% | 77% | 2% | 7% | 10% | 18% | 23% |
| 16W_TREAT | 5% | 4% | 33% | 40% | 6% | 45% | 0% | 4% | 7% | 3% | 2% | 11% | 3% | 2% | 4% | 12% | 62% |
| 29W_CTRL | 11% | 0% | 8% | 3% | 4% | 4% | 43% | 0% | 3% | 3% | 12% | 0% | 10% | 0% | 3% | 26% | 3% |
| 29W_TREAT | 76% | 84% | 10% | 5% | 75% | 6% | 56% | 71% | 79% | 90% | 84% | 12% | 85% | 91% | 83% | 44% | 13% |
| Between Cluster | |||||||||||||||||
| 16W_CTRL | 9% | 11% | 23% | 20% | 5% | 15% | 0% | 4% | 2% | 0% | 0% | 9% | 0% | 1% | 0% | 1% | 0% |
| 16W_TREAT | 8% | 6% | 25% | 24% | 3% | 24% | 0% | 1% | 2% | 1% | 0% | 2% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 1% | 2% |
| 29W_CTRL | 35% | 0% | 12% | 4% | 4% | 5% | 25% | 0% | 2% | 1% | 5% | 0% | 4% | 0% | 0% | 3% | 0% |
| 29W_TREAT | 29% | 28% | 2% | 1% | 9% | 1% | 4% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 4% | 1% | 4% | 3% | 1% | 0% | 0% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, L.-Y.; Hsieh, Y.-P.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Hwang, D.-Y.; Jiang, S.S.; Huang, W.-T.; Chiang, W.-F.; Liu, K.-J.; Huang, T.-T. Single-Cell Analysis of Different Stages of Oral Cancer Carcinogenesis in a Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8171. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218171
Huang L-Y, Hsieh Y-P, Wang Y-Y, Hwang D-Y, Jiang SS, Huang W-T, Chiang W-F, Liu K-J, Huang T-T. Single-Cell Analysis of Different Stages of Oral Cancer Carcinogenesis in a Mouse Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(21):8171. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218171
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Ling-Yu, Yi-Ping Hsieh, Yen-Yun Wang, Daw-Yang Hwang, Shih Sheng Jiang, Wen-Tsung Huang, Wei-Fan Chiang, Ko-Jiunn Liu, and Tze-Ta Huang. 2020. "Single-Cell Analysis of Different Stages of Oral Cancer Carcinogenesis in a Mouse Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 21: 8171. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218171
APA StyleHuang, L.-Y., Hsieh, Y.-P., Wang, Y.-Y., Hwang, D.-Y., Jiang, S. S., Huang, W.-T., Chiang, W.-F., Liu, K.-J., & Huang, T.-T. (2020). Single-Cell Analysis of Different Stages of Oral Cancer Carcinogenesis in a Mouse Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(21), 8171. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218171







