Abstract
T cells follow a triphasic distinct pathway of activation, proliferation and differentiation before becoming functionally and phenotypically “exhausted” in settings of chronic infection, autoimmunity and in cancer. Exhausted T cells progressively lose canonical effector functions, exhibit altered transcriptional networks and epigenetic signatures and gain constitutive expression of a broad coinhibitory receptor suite. This review outlines recent advances in our understanding of exhausted T cell biology and examines cellular and molecular mechanisms by which a state of dysfunction or exhaustion is established, and mechanisms by which exhausted T cells may still contribute to pathogen or tumour control. Further, this review describes our understanding of exhausted T cell heterogeneity and outlines the mechanisms by which checkpoint blockade differentially engages exhausted T cell subsets to overcome exhaustion and recover T cell function.
1. T Cell Activation and “Effector” Differentiation—An Overview
T cells are important effector immune cells responsible for inducing cell death of virally transformed or malignant cells, after initiating a highly orchestrated program of differentiation. On initial encounter with mature antigen-presenting cells (APC) bearing their cognate peptide epitope in secondary lymphoid organs, naïve CD8+ T cells integrate and accumulate a signal through their TCR/CD3 complex and associated adaptors, and through constitutively expressed co-stimulatory molecules of the CD28, SLAM and TNFRSF (expertly reviewed elsewhere) [1]. This initial “priming” stimulation is augmented by paracrine cytokine signalling from APC (for example interleukin (IL)-12 [2,3], or Type I interferons (IFN)) [4] and paracrine and autocrine IL-2 signalling [5] and allows T cells to initiate a program of rapid and extensive division and differentiation [6]. T cells receiving peptide:MHC-mediated stimulation through the TCR/CD3 complex alone, and in the absence of additional co-stimulation and IL-2, do not progress through repeated cell cycles and fail to generate effector progeny or participate in an immune response. This failure of activation is described as anergy and is a complex process mediated in part by the CDK2 inhibitor and AP-1 antagonist p27kip1, as well as by PTEN, a negative regulator of PI3K [7]. Anergy is not discussed in this review, but is expertly reviewed elsewhere [8].
Activated T cells undergo epigenetic remodelling to enable de novo transcription of previously silenced genes for effector functions [9]. The contents of cytotoxic granules, including the pore-forming protein perforin, and an array of serine proteases called granzymes, as well as effector cytokines such as TNFα [10] and IFNγ [11] are produced in a division-linked manner [12,13]. These canonical effector cytokines are pleiotropic. TNFα promotes T cell survival and proliferation [14], and can directly induce necrosis of target cells through a TNFR1-JNK signalling cascade that elicits uncontrolled ROS production [15]. IFNγ signalling serves many functions, including inducing IL-12 production by APC, enhancing phagocytosis and enhancing T cell recognition by upregulation of MHC I and II on target cells [16]. Acquisition of effector function is progressive, beginning after 2–3 divisions, but culminating after 6–8 divisions in murine cells [12] and is dependent on transcription factor network changes, epigenetic remodelling and enhanced translational capacity through increased production of ribosomal subunits. Fully realised effector T cells (TEFF) have the capacity to migrate from secondary lymphoid organs (SLO) to areas of tissue inflammation, serially engage and kill target cells, reprogram local tissue resident myeloid cells and produce chemotactic mediators that continue to recruit leukocytes to an area of infection or a tumour.
The interaction between sphingosine-1-phosphates (S1Ps) and their receptors play an essential role in T cell trafficking. Post-activation, T cells transiently down-regulate S1PR1 to render them unresponsive to S1P gradients and trap them in the lymph node (LN) during their signal acquisition phase (~1–4 days), as successive APC contacts are often required for full effector differentiation [17,18]. Following T cell differentiation, S1PR1 expression is restored to allow egress to the periphery along S1P gradients [18]. As naïve CD4+ and CD8+ T cells divide, they alter their chemokine receptor and adhesion molecule expression profiles, to allow repositioning from the paracortical T cell zone to the lymph node periphery through gain of CXCR3 and CXCR4 [19], then to the systemic circulation with the capacity to traffic to and bind inflamed tissue capillary endothelia through expression of CD44, PSGL-1 and CX3CR1 [20,21,22]. Interestingly, the targeting of effector T cell migration can be directed by the source of matured APC they encounter or route of vaccine administration—for instance, programmed homing back to skin or gut via Cutaneous Lymphocyte Antigen (CLA) or α4β7 integrin expression, respectively [23].
The capacity of T cells to form a broad and functional effector compartment and successfully establish immune memory is essential for both acute clearance of a pathogen, and for protection against future exposure. Following clearance of antigen, expanded CD8+ effector T cells massively contract mainly via apoptosis, leaving a small memory population capable of antigen-independent maintenance through responsiveness to homeostatic cytokine signals, self-renewal and robust secondary expansion. Under conditions of prolonged antigen exposure, this canonical naïve-effector-memory spectrum can be perturbed, and T cells instead follow a distinct pathway of differentiation and become functionally and phenotypically “exhausted”.
2. The Discovery and Functional Characterisation of T Cell Exhaustion
T cell exhaustion was originally described as a functional state induced by chronic antigen exposure and integrating signals from other cell types and the tissue microenvironment. Much of our detailed mechanistic knowledge of effector T cell differentiation and fate has come from comparisons of CD8+ T cell phenotype and function in mouse models of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) infection (Figure 1).
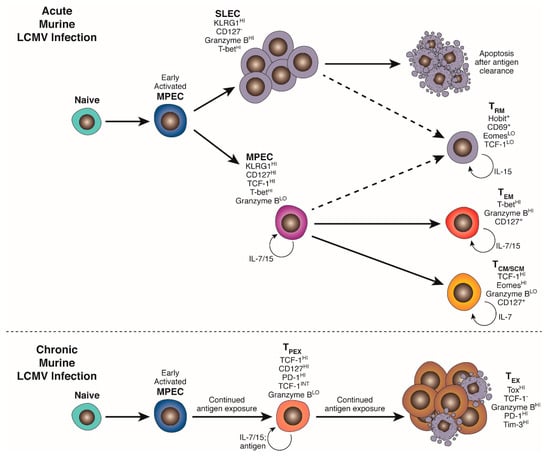
Figure 1.
Acute and chronic infection drive distinct programs of CD8+ T cell differentiation. Activated naïve CD8+ cells initiate a program of metabolic, transcriptional and epigenetic changes that facilitate differentiation into KLRG1HI CD127neg effector and KLRG1neg CD127HI memory precursors (MPEC). In an acute infection, an expanded pool of terminally differentiated cytotoxic effectors (SLEC/TEFF) clear infected cells and subsequently contract, leaving behind a heterogeneous pool of MPEC-derived self-renewing stem-like (TSCM) and central memory (TCM) in secondary lymphoid organs and effector memory (TEM) and resident memory (TRM) in peripheral tissues to provide protection against secondary exposure to the same pathogen. Chronic TCR stimulation, exacerbated by the absence of appropriate CD4+ T cell “help” and co-stimulatory and cytokine signalling, drives an alternative program of differentiation and epigenetic remodeling mediated by NFATc1, BATF, IRF4 and Tox. This gives rise to a TCF-1+PD-1INT pool of self-renewing “precursor” exhausted cells carrying a distinct epigenetic signature (TPEX) that produce and continually replenish an expanded pool of terminally exhausted progeny (TEX) able to partially control, but not fully clear, established infection. TEX maintain the epigenetic signature established in TPEX and exhibit a spectrum of effector function impairment and high expression of a suite of co-inhibitory receptors.
Infection with the Armstrong strain of LCMV results in an acute infection that is typically cleared by a broad and effective CD8+ T cell response within ~8 days. The Clone 13 strain of LCMV differs from Armstrong in only a few amino acid substitutions in the viral polymerase and glycoprotein, conferring enhanced macrophage tropism and allowing disseminated disease to be established in all visceral organs [24]. As such, Clone 13 LCMV infection is not acutely cleared, and will persist for several months with consistently high viral titres [25]. Despite these differences, key immunogenic epitopes in the viral glycoprotein and nucleoprotein are entirely conserved, allowing direct phenotypic and functional comparison of antigen-matched T cells in each setting [26].
Within the first 4–5 days of acute LCMV Armstrong infection, activated CD8+ T cells uniformly acquire effector characteristics, including cytotoxic capacity and IFNγ production, but can be phenotypically partitioned into KLRG1neg CD127+ memory precursor effector cells (MPEC) and KLRG1HI CD127neg/LO short-lived effector cells (SLEC) [27,28,29]. This distinction is mediated by a complex spectrum of transcription factor interactions, and regulated by strength of TCR-mediated signalling, metabolic profile and inflammatory cytokine exposure (for instance IL-12), discussed in further detail in Section 4 and Section 5. [28,30,31] SLEC briefly retain responsiveness to survival signals from IL-15, but are chiefly reliant on continued antigen exposure for their survival, and have been shown to contract mainly by apoptosis after viral clearance, following kinetics programmed during their initial priming [32,33]. MPEC retain responsiveness to both IL-15 and IL-7 and are not reliant on antigen encounter for survival. These cells persist in SLO after differentiation into long-lived but poorly cytotoxic central-memory (TCM) and stem-like memory (TSCM) cells capable of robust secondary expansion, and in peripheral tissues and circulation as effector memory cells (TEM) retaining both proliferative and cytotoxic capacity, governed by patterns of chemokine receptor and adhesion molecule expression. Although IL-7Rα(CD127) expression and IL-7 responsiveness are crucial for the survival of memory T cells, IL-7 signalling alone is not sufficient for an MPEC—memory transition, as overexpression of CD127 in KLRG1+ SLEC does not protect them from contraction [34]. Interestingly, recent cell fate tracking studies suggest that a small proportion of KLRG1+ SLEC exposed to intermediate levels of initial stimulation may downregulate KLRG1 while retaining high cytotoxic capacity and contribute to a pool of peripheral tissue resident memory T cells (TRM) [35].
Tracking of antigen-specific populations in chronic LCMV infection demonstrated that a classical memory compartment failed to form, revealing instead both progressive deletion of high-affinity CD8+ T cells and the persistence of a population of cells that exhibited the partial or complete loss of classical effector functions and contained, but failed to clear virus [26,36,37]. These cells were classified as being exhausted and upon comparison to classical memory or effector cells they exhibit an altered metabolic and transcriptional profile, a unique epigenetic signature, constitutive expression of an array of coinhibitory receptors and an inability to be maintained by homeostatic cytokines [38,39]. The development of this state is dependent on continued high viral antigen load and is exacerbated on CD4+ T cell depletion, demonstrating that CD4+ T cell help, mediated in part by IL-21 production, plays an important role in LCMV control and effector T cell differentiation [40,41,42]. Seminal early studies tracking peptide-specific recall responses over time demonstrated that CD8+ T cell exhaustion is progressive and continual over ~30 days [26,36,41]. Cells sequentially lose the capacity to produce IL-2, TNFα, and finally IFNγ [26,43,44], develop impairment in perforin synthesis [45,46] or effector granule delivery to the immunological synapse [47], lose proliferative potential, and finally exhibit a profound susceptibility to activation-induced cell death [25,48]. Exhausted T cells (TEX) gain high constitutive surface expression of co-inhibitory molecules such as 2B4, CD39, CD160, T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing protein 3 (TIM-3), T cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains (TIGIT), and most notably programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) through a combination of permissive histone modifications, altered Cp DNA methylation status, enhanced chromatin accessibility and transcription factor expression patterns [39,49,50,51,52,53], further detailed in Section 6 and Section 7. Interestingly, through adoptive transfer experiments both Brooks et al. [54] and Angelosanto et al. [55] defined a window of time whereby T cells exhibiting the early hallmarks of exhaustion could be “rescued” on transfer, 5–8 days after priming, into mice with an ongoing LCMV Armstrong infection, instead developing into a normal effector and memory pool. Conversely, T cells primed during an acute LCMV infection then transferred into Clone 13-infected animals developed an exhausted phenotype, demonstrating that continued antigenic encounter, rather than initial signal integration during priming, was responsible for exhaustion and that an exhausted phenotype was not “fixed”, through epigenetic remodelling, until ~14–30 days after infection. Further, this study and others established that only cells within the KLRG1neg MPEC pool were capable of persisting on transfer and progressing to exhaustion [55,56,57], demonstrating that exhausted cells were not simply a linear phenotypic progression from terminally differentiated effector status and that TEX and TEFF were distinct differentiation lineages. This window of phenotypic flexibility was recently confirmed in a murine model of SV40-T-antigen (TAg)-driven hepatocellular carcinoma, whereby TAg-specific T cells isolated and transferred into naïve hosts at day 8 after initial adoptive transfer and tumour exposure could mount a normal secondary response to challenge by Listeria monocytogenes expressing recombinant TAg, while those transferred after 30 days of tumour exposure could not [58].
In addition to other viral infections such as chronic human HIV [59,60], HBV [61,62], HCV [63] and malaria [64], CD8+ T cells exhibiting a similar exhausted phenotype have also been described both in murine tumour models, and in tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) isolated from solid human tumours [65,66,67,68]. The extent of T cell exhaustion in each setting is antigen-dependent, and correlated with viraemia in HIV and HBV. Interestingly, TEX have been described in several autoimmune conditions, including diabetes mellitus type 1, systemic lupus erythematosus and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, and the extent of exhaustion and functional impairment of these cells is inversely correlated with autoimmune damage [69]. Indeed, emerging evidence suggests that CD8+ T cell exhaustion appears to be an evolutionary mechanism to facilitate long-term containment of infection without immune-mediated pathology, and despite displaying a limited range of effector functions, exhausted T cells are not senescent. Importantly, although TEX exhibit impairment of canonical effector function, this is variable across models, and TEX heterogeneously retain some capacity to degranulate and kill target cells while also retaining the capacity to patrol infected tissues and produce high levels of chemoattractant chemokines including MIP1α, MIP1β and RANTES [43,70]. Indeed, deletion of CD8+ T cells in SIV-infected macaques immediately facilitates a rise in viral titre, suggesting that CD8+ T cells unable to completely clear infected cells nonetheless exert sufficient immune pressure to keep chronic viral infection in check and minimize pathology [71,72].
3. Heterogeneity and Lineage Relationships in Exhausted T Cells
A major advance in our understanding of T cell exhaustion was the recent discovery that rather than being a homogenous, poorly proliferative compartment incapable of forming immunological memory, exhausted cells could be demarcated into distinct phenotypic and functional subsets in an analogous way to classical memory and effector cells. Following the identification of PD-1 as both an essential marker and mediator of T cell exhaustion and the landmark demonstration that blockade of the PD-1:PD-L1 signalling axis could ameliorate functional exhaustion, restoring effector cytokine production and enabling viral control, several studies provided evidence that responsiveness to PD-1 or PD-L1 blockade was heterogenous, with only a subset of T cells undergoing a proliferative burst (Figure 2). Blackburn et al. [73] demarcated TEX into PD-1INT CD44HI and PD-1HI CD44INT subset, with the PD-1INT CD44HI subset being enriched for cells responsive to anti-PD-1 in clone 13 infection [73,74] and only the PD-1HI CD44INT subset displaying co-expression of PD-1, CD244, CD160 and LAG-3 [74]. Paley et al. found that anti-PD-1 responsive TEX could be identified by high levels of expression of the T-box transcription factor T-bet and by intermediate surface intensity of PD-1. These cells were relatively rare and typically localised to the spleen. By contrast, in this study a larger, poorly proliferative and systemically distributed TEX population expressed intermediate T-bet but high levels of the related T-box transcription factor Eomes, and exhibited high surface co-expression of PD-1, 2B4 and TIM-3 [75]. Utzschneider et al. [76] subsequently demonstrated that the PD-1+ population could be divided by expression of TCF-1 (TCF7), typically found in naïve, stem-like and central memory cells, but lost in SLEC [77,78]. TCF-1 complexes with β-catenin to signal through the Wnt pathway and is a marker of self-renewal capacity [77]. This finding suggested a potential precursor-progeny relationship between rare T-bet+/PD-1INT/TCF-1+ and PD-1HI/TCF-1neg subsets. Importantly, subsequent single-cell sequencing studies in in LCMV and murine tumour models have suggested that T-bet and Eomes expression are heterogenous across TCF-1+ and TCF-1neg subsets [79,80,81], suggesting that TCF-1 expression is a more accurate means of discriminating precursor and terminally differentiated exhausted cells. Interestingly, although depletion of either subset inhibited control of LCMV viraemia, only ablation of the TCF-1+ compartment abrogated responsiveness to PD-1 blockade, suggesting that the proliferative burst provided by disinhibited T-bet+ PD-1INT TCF-1+ cells was responsible for therapeutic efficacy [76,80,82]. Adoptive transfer studies of both subsets have revealed that only the T-bet+ PD-1INT TCF-1+ population could survive on transfer into naïve animals and provide protection against subsequent infection or indeed tumour challenge [76,78,80,81]. Further transcriptomic and proteomic analyses have shown that these less differentiated cells exhibit low or no expression of additional co-inhibitory markers such as TIM-3 and 2B4 or cytotoxic mediators such as granzyme B, and express memory associated markers SLAMF6, BCL-6, FOXO-1 and CXCR5, while their terminally exhausted progeny express lack these markers but express high levels of granzyme B and TIM-3. These less-differentiated exhausted cells have been variously described as “stem-like-“ [78,80], “memory-like-” [83,84], “progenitor-” [85], “follicular-” [82] or “precursor-”-exhausted cells [86]. Interestingly, as this self-renewing subset has limited differentiation capacity, only giving rise to terminally exhausted progeny that retain a fixed epigenetic signature of exhaustion, this review utilises the nomenclature recently coined by Kallies, et al. defining PD-1INT TCF-1HI as “precursor exhausted” cells (TPEX) and their PD-1HI TIM-3HI progeny as being terminally exhausted (TEX) [86]. Single cell RNA sequencing studies through the course of clone 13 infection have recently added complexity to this lineage schema, suggesting that activated TPEX may initially give rise to “transitory” TEX (TTEX) that are KLRG1NEG, PD-1HI, CD101NEG CX3CR1HI (suggesting an early window where TEX are capable of trafficking in response to fractalkine cues). These TTEX develop linearly into KLRG1NEG PD-1HI CD101+ CX3CR1NEG terminal TEX [42,87,88]. CD101 is a coinhibitory receptor that has been shown to perturb TCR/CD3-mediated calcium flux to disrupt T cell proliferation [89]. Anti-PD-1 therapy rapidly and transiently increases the frequency of this TTEX population, suggesting they may be the immediate progeny of a TPEX proliferative burst [42,88]. On transfer of TPEX isolated from B16-OVA melanoma into new tumour-bearing mice, Miller et al. found that TCF-1+ SLAMF6+ TIM3- TPEX could both self-renew and give rise to SLAMF6+ TIM3+ and SLAMF6-TIM3+ progeny over 14 days, adding to the model of a phenotypic spectrum among TTEX [85]. By contrast, transferred TCF-1NEG SLAMF6NEG TIM3HI TEX remained phenotypically fixed. The crucial role of TPEX in providing the proliferative burst and producing a large pool of responsive cells following checkpoint blockade is of crucial importance for our understanding of how checkpoint blockade therapies in human tumour settings may operate. This phenomenon has been confirmed in several murine tumour and viral models and has been shown to be CD28 dependent [90], highlighting the importance of retention of co-stimulatory signalling capacity in TPEX. Further, TCF-1+ PD-1INT and TCF-1+ CXCR5+ gene signatures in both TIL and circulating T cells have been shown to have predictive prognostic value in human melanoma and lung cancer patients, and in chronic viral disease, highlighting the therapeutic potential of this lineage [81,85,91,92,93,94]. Differential polarisation into TPEX/TEX among particular epitope-responsive T cell populations, or TCR-disparate but epitope-matched clones, may be responsible for the clonal replacement observed within TIL following anti-PD-1 treatment, and indeed, Miller et al. found that in B16-OVA TIL, the TPEX compartment contained a far broader spread of TCR clonotypes than did the co-infiltrating TEX compartment [85]. These studies highlight the need to consider each TEX subset when designing therapeutic approaches to target exhausted T cells, and more work is required to understand their dynamic regulation.
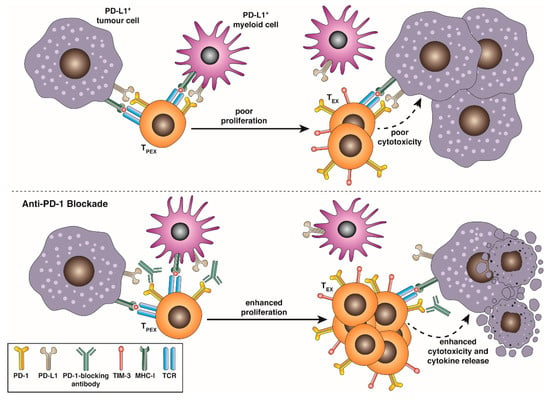
Figure 2.
TPEX respond to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 blockade. TCF-1HI intratumoral or virus-specific precursor-exhausted T cells (TPEX) expressing intermediate surface levels of PD-1 continually replenish and maintain a pool of cytotoxic granzyme BHI TCF-1NEG PD-1HI TIM-3HI exhausted progeny (TEX) when they are stimulated. PD-1:PD-L1 interactions impair activation and proliferation of TPEX and activation cytokine production and direct cytotoxicity of TEX. Blockade of these interactions using monoclonal antibodies allows the expansion of a larger tumour- or virus-reactive TEX pool, and enhances direct cytotoxicity against transformed or virus-infected cells.
4. Activation and TCR-Proximal Signal Transduction in Exhaustion
The establishment and progression of T cell exhaustion is dependent on repeated TCR stimulation [57], during which Nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT)c1 and NFATc2 are activated by the calcium-dependent phosphatase calcineurin facilitating translocation to the nucleus [95,96]. NFATc1 induces the expression of basic leucine zipper transcription factor (BATF) and interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4), and these transcription factors establish a positive feedback cycle that maintains both their and NFATc1 expression [50,97,98]. BATF competitively regulates the expression and functional pairing of AP-1 family members c-fos and c-jun, which normally interact with NFATc1 during SLEC differentiation to tune its control of transcriptional profiles [96]. Further, BATF and IRF4 can directly compete with heterodimeric AP-1 complexes for binding sites, including at the IL2 locus [99]. c-fos is normally induced by costimulatory signalling and by IL-2, and as such, in situations of repeated TCR ligation where costimulation might be absent and IL-2 production poor, BATF skews the NFAT:AP-1 ratio, and partnerless NFATc1 is able to directly induce the expression of several co-inhibitory receptors, including LAG-3, TIM-3 and PD-1 [95,100]. The Pdcd1(PD-1) locus contains a direct NFATc1 binding site −3.7 kb upstream from the promoter. Overexpression of a mutant NFATc1 unable to partner with AP-1 factors exacerbates T cell exhaustion [95], and miR-155 promotes partnerless NFAT activity by degrading mRNA of the AP-1 family member fosl2 [101]. Interestingly, this signalling pathway has been targeted as a means of preventing exhaustion in chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells, a potent adoptive immunotherapy. Lynn et al. [102] demonstrated that CAR constructs exhibiting continuous tonic signalling promoted exhaustion in CAR-T, resulting in loss of IL-2 production and poor cytotoxicity and proliferation on stimulation. Engineering of constitutive c-jun expression alleviated this exhaustion and restored full effector function. Interestingly, even in non-tonically signalling CAR-T cells c-jun expression maintained superior proliferation and anti-tumour efficacy, by countering the regulatory activity of BATF and IRF4 and maintaining an AP-1 mediated transcriptional profile. Utzschneider et al. have recently shown that TPEX early in chronic LCMV (docile) infection could be identified by high expression of BTB and CNC homolog 2 (BACH2), a basic leucine zipper transcription factor that exerts an oppositional transcriptional program to BATF, and by higher levels of accessible chromatin bearing BACH2 binding sites than TEX. In this study, BACH2 knockout depleted the TPEX pool and promoted TEX formation, reinforcing the role of BATF in driving T cell exhaustion [103].
NFATc1 signalling induces the expression of nuclear receptor (NR)4A family members and thymocyte selection-associated high mobility group box protein (Tox) family members, transcriptional regulators which have recently emerged as both a key marker and mediator of exhausted T cell phenotype and function [104,105]. In comparisons of acute vs. chronic LCMV infection, Tox expression clearly demarcates TMEM and TPEX at the single-cell sequencing level [18,106]. Tox promotes the progression of an exhausted phenotype and its level is greatest in cells co-expressing high PD-1 and TIM-3 [50,105,107,108]. Interestingly, Tox expression is critical for differentiation and maintenance of both TEX and TPEX, as Tox overexpression promotes TPEX formation in chronic LCMV infection [106]. Conversely, Tox knockout mice do not form an exhausted compartment, and on conditional knockout after the establishment of TPEX and TEX populations these cells are rapidly depleted [50]. Therefore, although the mechanism for this depletion is yet to be clarified, Tox knockdown has been shown to reduce surface expression of several co-inhibitory receptors, including PD-1, TIM-3, TIGIT and CTLA-4 and so it is possible that TPEX and TEX are deleted by activation induced cell death as they lose their capacity to “detune” continual TCR signalling [50,108]. In fact, TEX with high-affinity TCR have been shown to be susceptible to deletion by this mechanism during the course of a normal chronic LCMV infection [25]. Indeed, several studies have demonstrated that TPEX and TEX exhibit loss of positive signal adaptors, including TRAF family members [109], and express higher levels of negative signal regulators such as Diacyl-glycerol-kinase; inhibitory phosphatases such as PTPN2 [110]; and E3 ubiquitin ligases [111]—suggesting that exhausted T cells are impaired in accumulating activating signals, which acts both to diminish their immediate effector capacity and protect them from death on stimulation. Interestingly, conditional knockout of PTPN2 greatly increases the generation, persistence and cytotoxic capacity of TIM-3HI TEX TIL in a murine MC38 model, facilitating enhance tumour clearance [110].
Although several groups have shown that Tox is induced by NFAT, Tox subsequently promotes the expression of NR4A1-3, and these cooperate to maintain Tox expression in an NFAT-independent feedback loop, possibly explaining why Tox expression is maintained in relatively quiescent TPEX [50,104,107]. NR4A family members themselves further promote IRF4 and Runx1 expression, and both Tox and NR4A family members appear to cooperate in order to enforce an exhaustion-specific program of chromatin accessibility [50]. Importantly, Tox directly mediates the acquisition of an exhaustion specific open enhancer region far distal (-23.8kb) to the Pdcd1 locus and plays an important role in constitutive PD-1 expression on TPEX and TEX [49]. The Tox-NR4A axis has been identified as a potential engineering target in adoptive cell therapies, as both Tox1/2 double knockout [104] and NR4A1-3 triple knockout CAR-T [112] cells exhibited enhanced effector function, cytokine production and tumour clearance in B16-hCD19 tumours, alongside increased chromatin accessibility in genes bound by AP-1 complexes.
Interestingly, although Tox expression was initially identified as being exhaustion-restricted on the basis of acute vs chronic LCMV sequencing comparisons, Sekine et al. have recently demonstrated that Tox expression can also be found in circulating human effector memory T cells specific for latent EBV and CMV antigens [113]. It should be noted that these TEM do also commonly express a poly-inhibitory suite, especially in older individuals, and that cells of these specificities may face periods of antigen resurgence and repeated stimulation on periodic latent viral reactivation [114]. Importantly, Tox expression was not observed in Influenza-virus-specific TCM, and was constitutive in circulating HIV, HBV and HCV-specific T cells [113,115]. Similarly, in acute LCMV low and transient expression of Tox can be detected in some cells, consistent with early NFAT-mediated, but not late NR4A-maintained, expression [50]. Nonetheless, in human melanoma and NSCLC TIL Tox expression is highest in cells that exhibit high PD-1, TIM-3 and CD39 co-expression, and Tox expression itself is a predictor of responsiveness to anti-PD-1 therapy [108]. As NFAT, IRF4 and BATF upregulation and signalling are a natural consequence of TCR-mediated signalling under conditions promoting SLEC and TEX formation [39], the precise balance of signals, or frequency and nature of repeated stimulation events required to direct cells down either pathway of differentiation remain to be completely characterized. These studies highlight that a deep understanding of the molecular pathways regulating T cell exhaustion may lead to the identification of further targets for a combined therapeutic approach in T cell redirection immunotherapy, a field still in its infancy.
5. Transcriptional Control of Exhaustion
Effector T cell differentiation, memory formation and T cell exhaustion are mediated by a complex interplay of transcription factor, transcriptional coactivator and corepressor networks often involving synergistic or mutually antagonistic signalling pairs.
The T-box transcription factors T-bet (Tbx21) and Eomes (Eomesodermin) are both induced following TCR ligation and the timing and relative intensity of their expression plays a well-characterised role in the acquisition of canonical effector functions and in the formation of memory T cells [28,29,116,117]. T-bet expression is induced early and promoted by IL-2- and IL-12- and mTOR/AKT-mediated signalling pathways [117,118,119]. T-bet directly promotes IFNγ, TNFα and CXCR3 expression, and promotes IL-12Rβ2 expression, establishing a positive IL-12- and IFNγ-mediated signalling loops [19,28,119,120,121]. Interestingly, T-bet is associated with a loss of CD127 expression in early SLEC [28,29], but also directly binds to and partially represses the PDCD1 locus, impairing PD-1 expression in both SLEC and in TPEX [70,122]. Partial and complete knockout studies have demonstrated T-bet to be essential in the differentiation of TEFF [28], and the maintenance of both TPEX and TEX in chronic LCMV infection [70]. T-bet levels are lower in MPEC and T-bet is dispensable for a transition to long-lived memory [27,120]. Interestingly, T-bet expression is indirectly maintained by miR-155, which acts to target SHIP-1 (an inhibitory phosphatase that plays a role in T-bet repression) mRNA for degradation [123]. Accordingly, overexpression of miR-155 in chronic LCMV has been shown to promote the survival and activity of TEX [124]. Interestingly, T-bet can induce the expression of the zinc-finger corepressor Zeb2, which binds to and blockades binding sites for the E-box transcription factors E2A and HEB, including CD127 and IL-2 [125]. As such, T-bet and Zeb2 cooperatively enforce effector differentiation, but the role of Zeb2 in TPEX and TEX is less well characterised, and decoupled Zeb2 expression may contribute to T-bet+ TPEX retaining expression of memory associated genes.
Eomes is also induced following T cell activation, but early exposure to IL-12 impairs Eomes induction, transiently establishing a T-betHI/EomesLO window during T cell priming [28,119]. Eomes expression is subsequently driven by FOXO1, TCF-1, Runx3 and Notch1 [118,126,127]. Eomes cooperates with T-bet and Runx1 in maintaining IFNγ expression, and Eomes, Runx3 and Notch1 are each important in binding to and directly promoting perforin and granzyme B expression, whereas T-bet knockout cells show no defect in perforin production [29,118,126,128]. Continued Eomes or Runx1/3 expression in TEX may play an important role in retention of some cytotoxic capacity in these cells, but Eomes also directly upregulates some co-inhibitory receptors, notably TIM-3 [129]. Eomes plays an indispensable role in the transition of MPEC to stem-like and central memory cells, by promoting IL-2Rβ expression to allow responsiveness to homeostatic IL-15, and by driving CD62L and CXCR4 expression to allow localisation to SLO and bone marrow [116,120,130]. Interestingly, a comparison of the transcriptional networks and interaction modules in acute vs chronic LCMV has shown that T-bet and Eomes signalling and interaction modules are distinct and somewhat dysregulated in TPEX and TEX when compared to classical TMEM and TEFF cells, contributing to decoupling of TCF-1 and Eomes expression in TEX [131]. Interestingly, Miller et al. recently demonstrated that in both LCMV Clone 13 infection and in B16 melanoma TIL, high Eomes expression was not observed in TCF-1- TEX but high Runx1/3 expression were, mediated by enhanced chromatin accessibility. Runx1/3 were absent from TCF-1+ TPEX in this study, suggesting that Runx3 expression may demarcate TCF-1- PD-1HI cytotoxic TEX more accurately than Eomes [85]. As such, the transcriptional network controlled by Eomes, and its role in demarcating subsets of exhausted cells remains an active and incompletely resolved area of investigation.
FOXO1 is essential for induction and maintenance of TCF-1 expression, and for the long-term survival of both TMEM and TPEX compartments through regulation of the CD127 and BCL-2 [132,133]. Indeed, conditional FOXO1 deletion during chronic LCMV infection led to a rapid loss of TPEX [83,134]. FOXO1 also acts to inhibit expression of cytotoxic mediators and promotes PD-1 expression through binding to a proximal promoter site -1.1 kb from the Pdcd1 locus [122,134]. As such, expression of FOXO1 may play an important role in establishing the granzyme BLOW, PD-1INT phenotype of TPEX, through competition with T-bet.
The transcriptional co-repressor BLIMP-1 plays an important role in maintenance of cytotoxic capacity in SLEC, but is not involved in memory T cell formation. Complete or partial BLIMP-1 knockout drives greater accumulation of TSCM/CM in acute LCMV infection or TPEX in chronic LCMV infection, with impairment in effector generation and migration [135,136]. BLIMP-1 expression in chronic LCMV is highest on TEX co-expressing PD-1, 2B4, LAG-3 and CD160, and lowest or absent in TPEX, as TCF-1 and BLIMP-1 are mutually antagonistic [78,92,117,137]. Interestingly, while BLIMP-1 acts to directly upregulate the coinhibitory receptor TIGIT, it actually impairs PD-1 expression in a similar way to T-bet, binding in a proximal upstream location at the Pdcd1 locus and displacing NFATc1 [122,138]. BLIMP-1 acts to recruit histone modifying machinery, including both histone deacetylases and methyltransferases [139]. Exogenous expression of BLIMP-1 in T cells post activation has been shown to silence PD-1 expression though facilitating trimethylation at H3K27 and H3K9, but these repressive marks are lost in exhausted cells even in the presence of BLIMP-1 expression, suggesting an eventual dysregulation of histone methylation machinery. Similarly, BLIMP-1 silences expression of CD27, CD25 and IL-2 through targeted recruitment of HDAC2, resulting in deacetylation and then H3K9 trimethylation at these loci [139].
Finally, the transcriptional regulators inhibitor of DNA binding (ID)2 and ID3 are expressed in effector and memory T cell populations, respectively [140]. These act by binding to and sequestering E-box transcription factor such as E2A and HEB to prevent them controlling a transcriptional program [141], as such ID2 acts to indirectly inhibit the expression of memory related markers and enable effector differentiation. This pattern of expression is conserved in exhaustion, with TEX exhibiting high ID2 expression, and TPEX exhibiting high ID3 expression [80,82,85], although the complex networks of interactivity mediated by ID2 and ID3 in these subsets still need to be fully elucidated.
Overall, notable overlap exists between the transcriptional programs that underlie the TMEM-TEFF and TPEX-TEX differentiation axes, although the interconnectedness of transcriptional modules in acute and chronic infections appears to be distinct [131].
6. The Epigenetic Landscape of T Cell Exhaustion
Despite superficially expressing similar patterns and programs of transcriptional regulators to effector and memory T cells, exhausted T cells exhibit entirely distinct patterns of epigenetic modification and chromatin accessibility with a state-specific epigenetic landscape. The epigenetic signatures of exhausted T cell subsets are typically determined by analysis of permissive and repressive histone acetylation and trimethylation respectively, typically at H3K27 and H3K9, while higher order chromatin accessibility or sequestration into lamina-associated heterochromatin is determined by ATAC-SEQ [51,142]. Recent whole genome studies have determined that TPEX and TEX exhibit several thousand differentially accessible loci when compared to effector or memory T cells [49,143], although this was determined using bulk sequenced populations, and single-cell TPEX/TEX analyses and thus a complete understanding of the heterogeneity of the exhausted epigenetic signature remain an active area of investigation. The epigenetic signature of exhausted T cells in chronic LCMV infection appears to be largely the same as that observed in HCV-specific TEX [143]. Interestingly, exhaustion is characterised by a large increase in chromatin accessibility [50,53,85,143], enabling constitutive expression of a various co-inhibitory receptors, and this increased accessibility may be responsible for the differences observed in transcription factor network interactivity described by Doering et al. [131]. The roles of Tox, NR4A and BLIMP-1 in recruiting histone modifying machinery have been previously discussed, and exhausted cells generally exhibit higher levels of DNA Methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1), Methyltransferase 3B (MT3B) and the polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) subunit EZH2 than TMEM or TEFF [144,145]. Repeated TCR stimulation is essential [145,146] in promoting the continuous and progressive accumulation of histone trimethylation from an early stage in chronic LCMV or on tumour exposure, as exhaustion specific methylation patterns are evident in early TPEX and inherited by their TEX progeny [43,53,57,58,145]. Gonheim et al. demonstrated that inhibition of this progressive methylation by DNMT3A knockout preserved effector function even in LCMV Clone 13 infection, and that inhibition of methylation together with PD-1 blockade synergistically enhanced proliferation of virus-specific cells, mediated in part through prevention of methylation at the myc locus that would normally act to prevent TEX from initiating cell cycling [145]. Importantly, although PD-1/PD-L1 blockade can alter transcriptional networks and transiently reinvigorate exhausted T cell effector function, several studies have shown that it induces no epigenetic remodelling and as such does not fundamentally alleviate exhaustion [49,145,146,147]. By contrast, treatment of LCMV-specific TEX with HDAC inhibitors during ex vivo restimulation can restore histone modification to a pre-exhausted state and restore effector function on adoptive transfer into LCMV-infected mice [148]. A such, epigenetic modification may play an important future role in ‘reconditioning’ chronic virus-specific- or tumour-isolated TEX in adoptive cellular therapy protocols.
7. Extrinsic Mediators of T Cell Exhaustion
7.1. Soluble Factors
Extrinsic cell-mediated and soluble signals also contribute to the pathways controlling T cell exhaustion. Metabolic changes in the local environment can promote T cell exhaustion. Tumour cells that deplete their microenvironment of available glucose have been shown to impose metabolic stress on TEX reliant on glycolysis for their metabolic demands. Further, excess potassium flux from necrotic tumour cells [149], buildup of extracellular adenosine [150] and tumour release of kynurenine as a metabolic byproduct of tryptophan metabolism by indoleamine 2.3-dioxygenase (IDO) [151] all impair T cell stimulation, effector function and survival. Therefore, IDO and the Adenosine A2A receptor (A2AR) are active targets of small molecule inhibition to alleviate these suppressive axes [152,153]. One of the main classes of soluble mediators influencing exhaustion are immunosuppressive cytokines. Tumour cells, tumour-associated macrophages and infiltrating myeloid-derived suppressor cells can inhibit T cell function through release of TGFβ and IL-10 - these cytokines repress T-bet expression and upregulate the pro-apoptotic factor Bim. Blockade of either these cytokines or their receptors can synergistically enhance LCMV control in combination with either anti-PD-L1 blockade or vaccination [154,155]. Whether blocking these immunosuppressive cytokines reverses T cell exhaustion or not is yet to be precisely determined. Type I interferons play an essential role in primary T cell activation, and in viral control; however, there is evidence to suggest that prolonged exposure to type I interferon signalling exacerbates T cell exhaustion [78], and that blocking IFNα/β during LCMV Clone 13 infection reversed T cell exhaustion [156].
7.2. Coinhibitory Receptor Contribution to T Cell Exhaustion
Tumour cells, tumour-associated macrophages, infiltrating myeloid-derived suppressor cells and, in the liver, infected hepatocytes [157] have all been shown to express an array of ligands for co-inhibitory receptors borne by exhausted cells. These ligand:receptor interactions are key in dampening TCR- mediated and co-stimulatory signalling and imposing T cell dysfunction in situ, and targeted blockade of these interactions has revolutionised our approach to cancer therapy.
Therapeutic targeting of T cell exhaustion has been a topic of intense research for decades, recently celebrated with the 2018 Nobel prize in Physiology and Medicine to Allison and Honjo. Their approach to understand how negative regulators influence T cell function led to the development of immunotherapy as a bone fide treatment for cancer. In both cancer and viral infections, several immune checkpoint molecules have since been identified, some of which are amendable to targeted therapy. As outlined in the previous sections, sustained expression of these inhibitory receptors is one of the cardinal features of TEX cells. Most of these receptors are induced by T cell activation, and their co-expression can exert cumulative inhibitory effects on T cells in cancer and chronic viral infection. Therefore, antagonization of these receptors or their ligands has emerged as a valuable strategy in counteracting T cell exhaustion.
Arguably, the most impressive clinical benefit for immune checkpoint inhibition has been obtained by targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway. PD-1, first described in 1992 [158], is a cell-surface receptor inhibiting T cell effector functions. Interaction of PD-1 ligands (programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PDL1) and PDL2) with the extracellular domain of PD-1 leads to recruitment of the tyrosine-protein phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2 [159,160]. This leads to inhibition of ZAP70, the PI3K-AKT and RAS-MEK-ERK pathways, perturbing both TCR-mediated and CD28-mediated signalling [90] and thereby inhibiting cytokine production, leading to cell cycle arrest, and to decreased expression of cell survival proteins such as Bcl-XL [161]. Although often described in the context of T cell exhaustion, T cells transiently upregulate PD-1 upon activation, and its expression is therefore not entirely exhaustion-specific. The transcriptional and epigenetic control of PD-1 expression is complex, and is expertly reviewed elsewhere [122]. Other cell types have also been found to express PD-1, including B cells, NK cells, NKT cells, some myeloid cells and cancer cells [161]. Additionally, metabolically active and clonally expanding PD-1+CD8+ cells can be found in the blood of healthy humans and at sites of chronic inflammation, and they are thought to resemble effector memory T cells rather than exhausted cells [162,163]. Interestingly, although expression of PD-1 is a defining phenotypic marker of all exhausted T cells, PD-1 signalling is dispensable in the differentiation of TPEX and TEX and the formation of an exhausted compartment in chronic LCMV, as this occurs normally in PD-1 knockout mice. In fact, in this system progression to terminal exhaustion is exacerbated, and PD-1-/-TEX exhibit greater susceptibility to clearance via apoptosis [164], consistent with a role of PD-1 in maintaining exhausted T cell survival by modulating stimulatory signal integration.
Exhausted T cells can also co-express PD-1 together with Lymphocyte-activation gene 3 (LAG-3, also known as CD223) a membrane protein of the Ig superfamily discovered in 1990 [165]. In effector T cells, LAG-3 cross-links with CD3, leading to inhibition of proliferation and cytokine production [166]. In addition, LAG-3 has been shown to have a role as a metabolic regulator [167] and while the intracellular motif necessary for signalling has been discovered in CD4+ T cells [168], the exact downstream signalling pathway remains elusive [169]. Similar to PD-1, its expression is not limited to activated T cells (including Tregs [170]), but can also be found on NK cells [165], B cells [171] and pDCs [172]. Its best-known ligand is MHC Class II, to which it binds with higher affinity than CD4 [173,174], selectively binding to stable complexes of peptide and MHC class II [175]. As LAG-3 also regulates CD8+ T cell and NK cell function, both of which do not interact with MHC Class II [169], alternate ligands have long been proposed. Indeed, the C-type lectin receptor LSECtin, expressed in the liver and on many tumors, has recently been identified as another ligand of LAG-3 [176]. Additional studies have added galectin-3 [177] and FGL-1 [178] to the list of putative ligands in the context of immunoregulation. The fact that FGL-1 levels in the blood of cancer patients correlates with poor prognosis and resistance to anti-PD-1/B7-H1 therapy suggests FGL-1 as a major contributor to LAG-3 immunoregulation [178]. A soluble form of LAG-3 has also been described [179], resulting from metalloprotease cleavage of the membrane-bound form [180], potentially representing an additional layer of post-translational regulation. Although membrane-bound LAG-3 can inhibit DC function [181], soluble LAG-3 has been described as an activator of antigen-presenting cells [182,183], and it has been used in vaccinations as an adjuvant [184,185]. The clinical activity of soluble LAG-3 (IMP321) has also been tested in renal cell carcinoma [186] and metastatic melanoma [187] with comparably mild side effects. In chronic LCMV infection, LAG-3 expression is co-expressed with PD-1 on exhausted/dysfunctional virus-specific CD8+ T cells [188], and it is closely associated to the severity of infection [74]. Similar findings have been described in human cancers such as ovarian cancer [189] and non-small cell lung cancer [190], where LAG-3 expression correlated with PD-1 expression in exhausted/dysfunctional T cells.
A more recently identified immune checkpoint is TIM-3, first described in 2002 [191]. Similar to LAG-3, it is a transmembrane protein belonging to the Ig superfamily. First identified on Th1 and CD8+ cytotoxic T cells, it is now known to be expressed also on Tregs [192], NK cells [193], mast cells [194], DCs and monocytes [195], and it can also be expressed by cancer cells such as acute myeloid leukemia stem cells [196,197]. Its role in immunological tolerance [198] has been proposed to be induced by its soluble ligand galectin-9 [199]. Over time, additional ligands have been identified, including membrane-bound phosphatidyl serine (PtdSer) [200] and the soluble ligand high mobility group protein B1 (HMGB1) [201], both of which are mainly important for innate immune responses. The most recently described ligand of TIM-3 is Ceacam-1. It is co-expressed with TIM-3 on CD8+ exhausted/dysfunctional T cells, and they can bind both in cis and trans, leading to induction of tolerance and inhibiting anti-tumor function [202]. TIM-3 mediated signalling seems to be dependent on the balance of intracellular binding partners: In its “permissive” state, the cytoplasmatic tail of TIM-3 is bound by Bat3, which represses the inhibitory function of TIM-3 [203]. Fyn, a known inducer of T cell anergy [204], can bind to the same region as Bat3, potentially competing with it for TIM-3 binding [169,205]. A soluble isoform of TIM-3 has also been described [206]. Similar to the other immune checkpoints, TIM-3 is expressed by a multitude of cells of both the innate and the adaptive immune system, including NK cells [193], DCs [201] and macrophages [207]. Therefore, any therapeutic blockade of TIM-3 could potentially increase the immune function of T cells via both direct and indirect mechanisms.
TIGIT is an Ig superfamily transmembrane receptor first identified in 2009, has been described by several groups under different names, including TIGIT [208,209], Vstm3 [210] and WUCAM [211]. Initially found to be expressed by T cells and NK cells, it has since shown to be expressed by follicular T cells [211] and a functionally distinct subset of Tregs [212]. In T cells, TIGIT binds three targets: CD112, CD113 and CD155 [208,209]. CD112 and CD113 are bound with lower affinity than CD155, and the functional relevance of CD112 and CD113 for T cell dysfunction is not yet clear. TIGIT binding of CD155 (Poliovirus receptor, PVR) on the surface of DCs induces production of the anti-inflammatory IL-10 in these DCs [208]. This process has also been reported after TIGIT binding to macrophage-bound CD155 [213]. In addition to its inhibitory effects on myeloid cells, TIGIT can also intrinsically suppress T cell function. Its affinity to CD155 is higher than CD226 (DNAM-1), which is a known co-stimulatory molecule in T cells [214], thereby competitively inhibiting the immunostimulatory function of CD226. Furthermore, TIGIT can impede the homodimerization of CD226, additionally restricting CD226 signalling [215]. In NK cells it has the cytoplasmatic tail of TIGIT has been shown to transmit inhibitory signals upon ligand binding, inhibiting the PI3K and MAPK pathway [216] and suppression of IFN-γ via NF-κB [217] however, this has not been demonstrated in T cells to date. In T cells, TIGIT activation leads to attenuation of TCR signalling [218]. Preclinical cancer models show that TIGIT is highly upregulated in tumor infiltrating lymphocytes, where it marks a exhausted/dysfunctional T cell population able to produce IL-10 [219]. Also in persistent viral infection, TIGIT is co-expressed with PD-1, Tim-3 and Lag-3 in exhausted, dysfunctional T cells [131,215]. As TIGIT is expressed in multiple cell types, therapeutic TIGIT-blockade might affect T cell function both directly and indirectly.
Several other co-inhibitory receptors have been identified as being expressed on TEX in recent years. B- and T- cell lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA), discovered in 2003 [220], is another transmembrane member of the Ig-superfamily, expressed after T cell activation. Its ligand has been proposed to be HVEM, [221] interestingly a receptor of the TNFR (and not the Ig) family. Similar to other immune checkpoints, BTLA expression is not exclusive for T cells, but also found on B cells, NKTs, DCs, and splenic macrophages [222]. Soon thereafter, CD160 was found to also inhibit T cell function, binding to the same ligand [223]. Both Ig-superfamily receptors (BTLA and CD160) inhibit T cell functions, and together with the stimulatory ligand LIGHT (binding to HVEM) form part of an intricate, bidirectional signalling network (BTLA, CD160, LIGHT, HVEM) [224].
7.3. Conclusions and Future Directions
Advances in recent years have shed light on the functional state of T cell exhaustion, which has revealed that it is not an inert and non-functional state, but rather the T cells display a residual level of impeded function. Given the recent evidence that T cell exhaustion can be rescued, it highlights the clinical relevance for understanding the molecular mechanisms driving it. Certainly in the case of chronic infections, exhausted T cells play an important role in controlling disease and, further, immunopathology. It is tempting to speculate that T cell exhaustion has evolved as a strategy to protect us from pathogenic but latent viruses, and thereby a balancing the host-pathogen interaction. But in the case of cancer this work highlights a potential role for targeting and reinvigorating exhausting T cells within a tumour. Sustained expression of inhibitory receptors is one of the cardinal features of an exhausted T cell, and therefore antagonization of these receptors or their ligands has emerged as a valuable strategy in overcoming exhaustion. In fact, antibody-based blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction leads to durable clinical responses in several types of cancers [225,226,227,228,229] and reviewed elsewhere [230], and has exhibited a therapeutic benefit in chronic HBV and HCV infection [231,232]. These positive responses led to the rapid FDA approval of six checkpoint inhibitor antibodies to date, including 3 anti-PD-L1 and 3 anti-PD-1 antibodies. Although impressive response rates have led to increased overall survival after checkpoint blockade, the majority of patients in these trials did not achieve durable remissions, and PD-1 alone is not sufficient to overcome T cell exhaustion [164]. Therefore, it has been no surprise that combination therapies targeting several inhibitory receptors simultaneously have shown increased response rates in several cancers. The targeting of T cell exhaustion through cytokines has been shown to be effective [233], as has epigenetic targeting and using small molecules to modulate receptor signalling (reviewed in [234]). So, whilst researchers have begun to investigate the metabolic targets, transcriptional regulators and epigenetic targets of T cell exhaustion, the field is still in its infancy, and future studies should focus on combination therapies to rescue T cell function, without compromising T cell persistence. In summary, more research is urgently required into how to overcome a state of T cell exhaustion, and clinical studies should be focused on combination multi-model targeting of the various signals that induce exhaustion for therapeutic intervention of future immunotherapies.
Author Contributions
D.J.V., M.M., and M.R.J. contributed to the conception, drafting, writing, and revision of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge the support of the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research. M.M. is funded by the German Cancer Aid (Mildred Scheel Postdoctoral Fellowship). M.R.J. is funded by NHMRC, The Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research Suzanne Cory Fellowship, RCD Foundation and Cancer Australia.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ryan Cross and members of the Jenkins Lab for useful discussion. The authors thank Peter Maltezos at The Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research for generation of graphics.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| APC | Antigen Presenting Cell |
| BTLA | B- and T- cell lymphocyte attenuator |
| BATF | Basic leucine zipper transcription factor |
| CAR | Chimeric antigen receptor |
| TCM | Central-memory T cells |
| TEFF | Effector |
| TEM | Effector memory T cells |
| TEX | Exhausted T cells |
| HIV | Human Immunodeficiency virus |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| IFN | Interferon |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IRF4 | Interferon regulatory factor 4 |
| LAG3 | Lymphocyte activation gene 3 protein |
| LN | Lymph node |
| LCMV | Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus |
| MPEC | Memory precursor effector cells |
| MHC | Major Histocompatibility Complex |
| NFAT | Nuclear Factor for activation T cells |
| TPEX | Precursor exhausted T cells |
| PD-1 | Programmed cell death protein 1 |
| TRM | Resident memory T cells |
| SLO | Secondary Lymphoid Organ |
| SLEC | Short-lived effector cells |
| S1Ps | Sphingosine-1-phosphates |
| TSCM | Stem-like memory T cells |
| TCR | T cell receptor |
| TIM3 | T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing protein 3 |
| TIGIT | T cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains |
| TTEX | Transitional exhausted T cells |
References
- Chen, L.; Flies, D.B. Molecular mechanisms of T cell co-stimulation and co-inhibition. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, C.J.; Ornelles, D.A.; Mitchell, L.M.; Brzoza-Lewis, K.L.; Hiltbold, E.M. IL-12 Produced by Dendritic Cells Augments CD8+ T cell Activation through the Production of the Chemokines CCL1 and CCL171. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 8576–8584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Montero, C.M.; El-Naggar, S.A.; Al Khami, A.; El Naggar, R.; Montero, A.J.; Cole, D.J.; Salem, M.L. Priming of naive CD8+ T cells in the presence of IL-12 selectively enhances the survival of CD8+CD62Lhi cells and results in superior anti-tumor activity in a tolerogenic murine model. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2007, 57, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, H.J.; Davis, A.M.; Cole, A.G.; Schatzle, J.D.; Forman, J.; Farrar, J.D. Reciprocal responsiveness to interleukin-12 and interferon-α specifies human CD8+ effector versus central memory T-cell fates. Blood 2009, 113, 5516–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redeker, A.; Welten, S.P.; Baert, M.R.M.; Vloemans, S.A.; Tiemessen, M.M.; Staal, F.J.T.; Arens, R. The Quantity of Autocrine IL-2 Governs the Expansion Potential of CD8+ T Cells. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 4792–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gett, A.V.; Hodgkin, P.D. A cellular calculus for signal integration by T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2000, 1, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussiotis, V.A.; Freeman, G.J.; Taylor, P.A.; Berezovskaya, A.; Grass, I.; Blazar, B.R.; Nadler, L.M. p27kip1 functions as an anergy factor inhibiting interleukin 2 transcription and clonal expansion of alloreactive human and mouse helper T lymphocytes. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, R.H. T Cell Anergy. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 21, 305–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, A.E.; Russ, B.E.; Doherty, P.C.; Rao, S.; Turner, S.J. Differentiation-dependent functional and epigenetic landscapes for cytokine genes in virus-specific CD8+ T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15306–15311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehm, M.A.; Daniels, K.A.; Welsh, R.M. Rapid Production of TNF-α following TCR Engagement of Naive CD8 T Cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 5043–5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, H.; Hosoi, A.; Ueha, S.; Abe, J.; Fujieda, N.; Tomura, M.; Maekawa, R.; Matsushima, K.; Ohara, O.; Kakimi, K. Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Block Tumor Growth Both by Lytic Activity and IFN -Dependent Cell-Cycle Arrest. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 3, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, M.R.; Mintern, J.D.; La Gruta, N.L.; Kedzierska, K.; Doherty, P.C.; Turner, S.J. Cell cycle-related acquisition of cytotoxic mediators defines the progressive differentiation to effector status for virus-specific CD8+ T cells. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 3818–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, M.R.; Kedzierska, K.; Doherty, P.C.; Turner, S.J. Heterogeneity of effector phenotype for acute phase and memory influenza A virus-specific CTL. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, E.M.; Fulton, R.B.; Sampson, J.F.; Muda, M.; Camblin, A.; Richards, J.; Koshkaryev, A.; Tang, J.; Kurella, V.; Jiao, Y.; et al. Antibody-mediated targeting of TNFR2 activates CD8+ T cells in mice and promotes antitumor immunity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaax0720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.J.; Kim, Y.-S.; Liu, Z.-G. TNFα and reactive oxygen species in necrotic cell death. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, F.; Cardoso, A.P.; Gonçalves, R.; Serre, K.; Oliveira, M.J. Interferon-Gamma at the Crossroads of Tumor Immune Surveillance or Evasion. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeyens, A.; Fang, V.; Chen, C.; Schwab, S.R. Exit Strategies: S1P Signaling and T Cell Migration. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benechet, A.P.; Menon, M.; Xu, D.; Samji, T.; Maher, L.; Murooka, T.T.; Mempel, T.R.; Sheridan, B.S.; Lemoine, F.M.; Khanna, K.M. T cell-intrinsic S1PR1 regulates endogenous effector T-cell egress dynamics from lymph nodes during infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2182–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groom, J.; Luster, A.D. CXCR3 in T cell function. Exp. Cell Res. 2011, 317, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, M.; Umehara, H.; Nakayama, T.; Yoneda, O.; Hieshima, K.; Kakizaki, M.; Dohmae, N.; Yoshie, O.; Imai, T. Dual functions of fractalkine/CX3C ligand 1 in trafficking of perforin+/granzyme B+ cytotoxic effector lymphocytes that are defined by CX3CR1 expression. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 6173–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, C.; Moseman, E.A.; Loughhead, S.M.; Alvarez, D.; Zwijnenburg, A.J.; Waanders, L.; Garg, R.; De La Torre, J.C.; Von Andrian, U.H. The Chemokine Receptor CX3CR1 Defines Three Antigen-Experienced CD8 T Cell Subsets with Distinct Roles in Immune Surveillance and Homeostasis. Immunity 2016, 45, 1270–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, K.; Kansas, G.S. Selectins in T-cell recruitment to non-lymphoid tissues and sites of inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudda, J.C.; Lembo, A.; Bachtanian, E.; Huehn, J.; Siewert, C.; Hamann, A.; Kremmer, E.; Förster, R.; Martin, S.F. Dendritic cells govern induction and reprogramming of polarized tissue-selective homing receptor patterns of T cells: Important roles for soluble factors and tissue microenvironments. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 1056–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matloubian, M.; Kolhekar, S.R.; Somasundaram, T.; Ahmed, R. Molecular determinants of macrophage tropism and viral persistence: Importance of single amino acid changes in the polymerase and glycoprotein of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 7340–7349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskophidis, D.; Lechner, F.; Pircher, H.; Zinkernagel, R.M. Virus persistence in acutely infected immunocompetent mice by exhaustion of antiviral cytotoxic effector T cells. Nature 1993, 362, 758–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wherry, E.J.; Blattman, J.N.; Murali-Krishna, K.; Van Der Most, R.; Ahmed, R. Viral Persistence Alters CD8 T-Cell Immunodominance and Tissue Distribution and Results in Distinct Stages of Functional Impairment. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 4911–4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaech, S.M.; Tan, J.T.; Wherry, E.J.; Konieczny, B.T.; Surh, C.D.; Ahmed, R. Selective expression of the interleukin 7 receptor identifies effector CD8 T cells that give rise to long-lived memory cells. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.; Cui, W.; Chandele, A.; Lee, H.K.; Urso, D.R.; Hagman, J.; Gapin, L.; Kaech, S.M. Inflammation Directs Memory Precursor and Short-Lived Effector CD8+ T Cell Fates via the Graded Expression of T-bet Transcription Factor. Immunity 2007, 27, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaech, S.M.; Cui, W. Transcriptional control of effector and memory CD8+ T cell differentiation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuneu, H.; Lemaitre, F.; Deguine, J.; Moreau, H.D.; Bouvier, I.; Garcia, Z.; Albert, M.L.; Bousso, P. Visualizing the Functional Diversification of CD8+ T Cell Responses in Lymph Nodes. Immunity 2010, 33, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snook, J.P.; Kim, C.; Williams, M.A. TCR signal strength controls the differentiation of CD4 + effector and memory T cells. Sci. Immunol. 2018, 3, eaas9103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Althaus, C.L.; Ganusov, V.V.; De Boer, R.J. Dynamics of CD8+ T cell responses during acute and chronic lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 2944–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinzel, S.; Giang, T.B.; Kan, A.; Marchingo, J.M.; Lye, B.K.; Corcoran, L.M.; Hodgkin, P.D. A Myc-dependent division timer complements a cell-death timer to regulate T cell and B cell responses. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hand, T.W.; Morre, M.; Kaech, S.M. Expression of IL-7 receptor alpha is necessary but not sufficient for the formation of memory CD8 T cells during viral infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11730–11735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herndler-Brandstetter, D.; Ishigame, H.; Shinnakasu, R.; Plajer, V.; Stecher, C.; Zhao, J.; Lietzenmayer, M.; Kroehling, L.; Takumi, A.; Kometani, K.; et al. KLRG1+ Effector CD8+ T Cells Lose KLRG1, Differentiate into All Memory T Cell Lineages, and Convey Enhanced Protective Immunity. Immunity 2018, 48, 716–729.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajac, A.J.; Blattman, J.N.; Murali-Krishna, K.; Sourdive, D.J.; Suresh, M.; Altman, J.D.; Ahmed, R. Viral Immune Evasion Due to Persistence of Activated T Cells Without Effector Function. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallimore, A.M.; Glithero, A.; Godkin, A.; Tissot, A.C.; Plückthun, A.; Elliott, T.; Hengartner, H.; Zinkernagel, R. Induction and Exhaustion of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus–specific Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Visualized Using Soluble Tetrameric Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I–Peptide Complexes. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 1383–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wherry, E.J.; Barber, D.L.; Kaech, S.M.; Blattman, J.N.; Ahmed, R. Antigen-independent memory CD8 T cells do not develop during chronic viral infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16004–16009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wherry, E.J.; Kurachi, M. Molecular and cellular insights into T cell exhaustion. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrends, T.; Spanjaard, A.; Pilzecker, B.; Bąbała, N.; Bovens, A.; Xiao, Y.; Jacobs, H.; Borst, J. CD4+ T Cell Help Confers a Cytotoxic T Cell Effector Program Including Coinhibitory Receptor Downregulation and Increased Tissue Invasiveness. Immunity 2017, 47, 848–861.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, M.J.; Khanolkar, A.; Tebo, A.E.; Zajac, A.J. Maintenance, loss, and resurgence of T cell responses during acute, protracted, and chronic viral infections. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 4204–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zander, R.; Schauder, D.; Xin, G.; Nguyen, C.; Wu, X.; Zajac, A.; Cui, W. CD4+ T Cell Help Is Required for the Formation of a Cytolytic CD8+ T Cell Subset that Protects against Chronic Infection and Cancer. Immunity 2019, 51, 1028–1042.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wherry, E.J.; Ha, S.-J.; Kaech, S.M.; Haining, W.N.; Sarkar, S.; Kalia, V.; Subramaniam, S.; Blattman, J.N.; Barber, D.L.; Ahmed, R. Molecular Signature of CD8+ T Cell Exhaustion during Chronic Viral Infection. Immunity 2007, 27, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackerness, K.J.; Cox, M.A.; Lilly, L.M.; Weaver, C.T.; Harrington, L.E.; Zajac, A.J. Pronounced Virus-Dependent Activation Drives Exhaustion but Sustains IFN-γ Transcript Levels. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 3643–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Shankar, P.; Xu, Z.; Harnisch, B.; Chen, G.; Lange, C.; Lee, S.J.; Valdez, H.; Lederman, M.M.; Lieberman, J. Most antiviral CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection do not express high levels of perforin and are not directly cytotoxic. Blood 2003, 101, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelinskyy, G.; Robertson, S.J.; Schimmer, S.; Messer, R.J.; Hasenkrug, K.J.; Dittmer, U. CD8+ T-Cell Dysfunction due to Cytolytic Granule Deficiency in Persistent Friend Retrovirus Infection. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 10619–10626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoja, S.; Saio, M.; Schaer, D.; Koneru, M.; Vukmanović, S.; Frey, A.B. CD8(+) tumor-infiltrating T cells are deficient in perforin-mediated cytolytic activity due to defective microtubule-organizing center mobilization and lytic granule exocytosis. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 5042–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoja, S.; Saio, M.; Frey, A.B. CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are primed for Fas-mediated activation-induced cell death but are not apoptotic in situ. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 6074–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauken, K.E.; Sammons, M.A.; Odorizzi, P.M.; Manne, S.; Godec, J.; Khan, O.; Drake, A.M.; Chen, Z.; Sen, D.R.; Kurachi, M.; et al. Epigenetic stability of exhausted T cells limits durability of reinvigoration by PD-1 blockade. Science 2016, 354, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, O.; Giles, J.R.; McDonald, S.; Manne, S.; Ngiow, S.F.; Patel, K.P.; Werner, M.T.; Huang, A.C.; Alexander, K.A.; Wu, J.E.; et al. TOX transcriptionally and epigenetically programs CD8+ T cell exhaustion. Nature 2019, 571, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngblood, B.; Hale, J.S.; Ahmed, R. T-cell memory differentiation: Insights from transcriptional signatures and epigenetics. Immunology 2013, 139, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLane, L.M.; Abdel-Hakeem, M.S.; Wherry, E.J. CD8 T Cell Exhaustion During Chronic Viral Infection and Cancer. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 37, 457–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, M.; Fairchild, L.; Sun, L.; Horste, E.L.; Camara, S.; Shakiba, M.; Scott, A.; Viale, A.; Lauer, P.; Merghoub, T.; et al. Chromatin states define tumour-specific T cell dysfunction and reprogramming. Nature 2017, 545, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, D.G.; McGavern, D.B.; Oldstone, M.B. Reprogramming of antiviral T cells prevents inactivation and restores T cell activity during persistent viral infection. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1675–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelosanto, J.M.; Blackburn, S.D.; Crawford, A.; Wherry, E.J. Progressive Loss of Memory T Cell Potential and Commitment to Exhaustion during Chronic Viral Infection. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 8161–8170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utzschneider, D.T.; Legat, A.; Marraco, S.A.F.; Carrié, L.; Luescher, I.; E Speiser, D.; Zehn, D. T cells maintain an exhausted phenotype after antigen withdrawal and population reexpansion. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utzschneider, D.T.; Alfei, F.; Roelli, P.; Barras, D.; Chennupati, V.; Darbre, S.; Delorenzi, M.; Pinschewer, D.D.; Zehn, D. High antigen levels induce an exhausted phenotype in a chronic infection without impairing T cell expansion and survival. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 1819–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schietinger, A.; Philip, M.; Krisnawan, V.E.; Chiu, E.Y.; Delrow, J.J.; Basom, R.S.; Lauer, P.; Brockstedt, D.G.; Knoblaugh, S.E.; Hämmerling, G.J.; et al. Tumor-Specific T Cell Dysfunction Is a Dynamic Antigen-Driven Differentiation Program Initiated Early during Tumorigenesis. Immunity 2016, 45, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, P.; Russo, M.; Harnisch, B.; Patterson, M.; Skolnik, P.; Lieberman, J. Impaired function of circulating HIV-specific CD8(+) T cells in chronic human immunodeficiency virus infection. Blood 2000, 96, 3094–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostense, S.; Vandenberghe, K.; Joling, J.; Van Baarle, D.; Nanlohy, N.; Manting, E.; Miedema, F. Persistent numbers of tetramer+ CD8+ T cells, but loss of interferon-γ+ HIV-specific T cells during progression to AIDS. Blood 2002, 99, 2505–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisicaro, P.; Boni, C.; Barili, V.; Laccabue, D.; Ferrari, C. Strategies to overcome HBV-specific T cell exhaustion: Checkpoint inhibitors and metabolic re-programming. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisicaro, P.; Barili, V.; Montanini, B.; Acerbi, G.; Ferracin, M.; Guerrieri, F.; Salerno, D.; Boni, C.; Massari, M.; Cavallo, M.C.; et al. Targeting mitochondrial dysfunction can restore antiviral activity of exhausted HBV-specific CD8 T cells in chronic hepatitis B. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruener, N.H.; Lechner, F.; Jung, M.-C.; Diepolder, H.; Gerlach, T.; Lauer, G.; Walker, B.; Sullivan, J.; Phillips, R.; Pape, G.R.; et al. Sustained Dysfunction of Antiviral CD8+ T Lymphocytes after Infection with Hepatitis C Virus. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 5550–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wykes, M.N.; Horne-Debets, J.M.; Leow, C.-Y.; Karunarathne, D.S. Malaria drives T cells to exhaustion. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baitsch, L.; Baumgaertner, P.; Devevre, E.; Raghav, S.K.; Legat, A.; Barba, L.; Wieckowski, S.; Bouzourene, H.; Deplancke, B.; Romero, P.; et al. Exhaustion of tumor-specific CD8⁺ T cells in metastases from melanoma patients. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2350–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadzadeh, M.; Johnson, L.A.; Heemskerk, B.; Wunderlich, J.R.; Dudley, M.E.; White, N.E.; Rosenberg, S.A. Tumor antigen–specific CD8 T cells infiltrating the tumor express high levels of PD-1 and are functionally impaired. Blood 2009, 114, 1537–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.P.; Yee, C.; Savage, P.A.; Fong, L.; Brockstedt, D.; Weber, J.S.; Johnson, D.; Swetter, S.; Thompson, J.; Greenberg, P.D.; et al. Characterization of circulating T cells specific for tumor-associated antigens in melanoma patients. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zippelius, A.; Batard, P.; Rubio-Godoy, V.; Bioley, G.; Liénard, D.; Lejeune, F.; Rimoldi, D.; Guillaume, P.; Meidenbauer, N.; Mackensen, A.; et al. Effector function of human tumor-specific CD8 T cells in melanoma lesions: A state of local functional tolerance. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 2865–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, E.F.; Lee, J.C.; Jayne, D.R.; Lyons, P.A.; Smith, K.G. T-cell exhaustion, co-stimulation and clinical outcome in autoimmunity and infection. Nature 2015, 523, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.; Oestreich, K.J.; Paley, M.A.; Crawford, A.; Angelosanto, J.M.; Ali, M.-A.A.; Intlekofer, A.M.; Boss, J.M.; Reiner, S.L.; Weinmann, A.S.; et al. Transcription factor T-bet represses expression of the inhibitory receptor PD-1 and sustains virus-specific CD8+ T cell responses during chronic infection. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Bauer, D.E.; Tuttleton, S.E.; Lewin, S.R.; Gettie, A.; Blanchard, J.; Irwin, C.E.; Safrit, J.T.; Mittler, J.; Weinberger, L.; et al. Dramatic Rise in Plasma Viremia after CD8+ T Cell Depletion in Simian Immunodeficiency Virus–infected Macaques. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, J.E.; Kuroda, M.J.; Santra, S.; Sasseville, V.G.; Simon, M.A.; Lifton, M.A.; Racz, P.; Tenner-Racz, K.; Dalesandro, M.; Scallon, B.J.; et al. Control of viremia in simian immunodeficiency virus infection by CD8+ lymphocytes. Science 1999, 283, 857–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackburn, S.D.; Shin, H.; Freeman, G.J.; Wherry, E.J. Selective expansion of a subset of exhausted CD8 T cells by PD-L1 blockade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15016–15021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackburn, S.D.; Shin, H.; Haining, W.N.; Zou, T.; Workman, C.J.; Polley, A.; Betts, M.R.; Freeman, G.J.; Vignali, D.A.A.; Wherry, E.J. Coregulation of CD8+ T cell exhaustion by multiple inhibitory receptors during chronic viral infection. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paley, M.A.; Kroy, D.C.; Odorizzi, P.M.; Johnnidis, J.B.; Dolfi, D.V.; Barnett, B.E.; Bikoff, E.K.; Robertson, E.J.; Lauer, G.M.; Reiner, S.L.; et al. Progenitor and Terminal Subsets of CD8+ T Cells Cooperate to Contain Chronic Viral Infection. Science 2012, 338, 1220–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utzschneider, D.T.; Charmoy, M.; Chennupati, V.; Pousse, L.; Ferreira, D.P.; Calderon-Copete, S.; Danilo, M.; Alfei, F.; Hofmann, M.; Wieland, D.; et al. T Cell Factor 1-Expressing Memory-like CD8+ T Cells Sustain the Immune Response to Chronic Viral Infections. Immunity 2016, 45, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattinoni, L.; Zhong, X.-S.; Palmer, D.; Ji, Y.; Hinrichs, C.S.; Yu, Z.; Wrzesinski, C.; Boni, A.; Cassard, L.; Garvin, L.M.; et al. Wnt signaling arrests effector T cell differentiation and generates CD8+ memory stem cells. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Ji, Y.; Moseman, E.A.; Xu, H.C.; Manglani, M.; Kirby, M.; Anderson, S.M.; Handon, R.; Kenyon, E.; Elkahloun, A.; et al. The TCF1-Bcl6 axis counteracts type I interferon to repress exhaustion and maintain T cell stemness. Sci. Immunol. 2016, 1, eaai8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ji, Z.; Ngiow, S.F.; Manne, S.; Cai, Z.; Huang, A.C.; Johnson, J.; Staupe, R.P.; Bengsch, B.; Xu, C.; et al. TCF-1-Centered Transcriptional Network Drives an Effector versus Exhausted CD8 T Cell-Fate Decision. Immunity 2019, 51, 840–855.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, S.J.; Hashimoto, M.; Gerner, M.Y.; Lee, J.; Kissick, H.T.; Burger, M.C.; Shan, Q.; Hale, J.S.; Lee, J.; Nasti, T.H.; et al. Defining CD8+ T cells that provide the proliferative burst after PD-1 therapy. Nature 2016, 537, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, I.; Schaeuble, K.; Chennupati, V.; Marraco, S.A.F.; Calderon-Copete, S.; Ferreira, D.P.; Carmona, S.J.; Scarpellino, L.; Gfeller, D.; Pradervand, S.; et al. Intratumoral Tcf1+PD-1+CD8+ T Cells with Stem-like Properties Promote Tumor Control in Response to Vaccination and Checkpoint Blockade Immunotherapy. Immunity 2019, 50, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Hou, S.; Liu, C.; Zhang, A.; Bai, Q.; Han, M.; Yang, Y.; Wei, G.; Shen, T.; Yang, X.; et al. Follicular CXCR5-expressing CD8+ T cells curtail chronic viral infection. Nature 2016, 537, 412–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utzschneider, D.T.; Delpoux, A.; Wieland, D.; Huang, X.; Lai, C.-Y.; Hofmann, M.; Thimme, R.; Hedrick, S.M. Active Maintenance of T Cell Memory in Acute and Chronic Viral Infection Depends on Continuous Expression of FOXO1. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 3454–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snell, L.M.; MacLeod, B.L.; Law, J.C.; Osokine, I.; Elsaesser, H.J.; Hezaveh, K.; Dickson, R.J.; Gavin, M.A.; Guidos, C.J.; McGaha, T.L.; et al. CD8+ T Cell Priming in Established Chronic Viral Infection Preferentially Directs Differentiation of Memory-like Cells for Sustained Immunity. Immunity 2018, 49, 678–694.e675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.C.; Sen, D.R.; Al Abosy, R.; Bi, K.; Virkud, Y.V.; LaFleur, M.W.; Yates, K.B.; Lako, A.; Felt, K.; Naik, G.S.; et al. Subsets of exhausted CD8+ T cells differentially mediate tumor control and respond to checkpoint blockade. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallies, A.; Zehn, D.; Utzschneider, D.T. Precursor exhausted T cells: Key to successful immunotherapy? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 20, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, V.R.; Busch, D.H. Back to the Future: Effector Fate during T Cell Exhaustion. Immunity 2019, 51, 970–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, W.H.; Gensheimer, J.; Hashimoto, M.; Wieland, A.; Valanparambil, R.M.; Li, P.; Lin, J.-X.; Konieczny, B.T.; Im, S.J.; Freeman, G.J.; et al. Proliferating Transitory T Cells with an Effector-like Transcriptional Signature Emerge from PD-1+ Stem-like CD8+ T Cells during Chronic Infection. Immunity 2019, 51, 1043–1058.e1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, L.R.; Tsavaler, L.; Rivas, A.; Engleman, E.G. V7 (CD101) ligation inhibits TCR/CD3-induced IL-2 production by blocking Ca2+ flux and nuclear factor of activated T cell nuclear translocation. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 209–217. [Google Scholar]
- Kamphorst, A.O.; Wieland, A.; Nasti, T.H.; Yang, S.; Zhang, R.; Barber, D.L.; Konieczny, B.T.; Daugherty, C.Z.; Koenig, L.; Yu, K.; et al. Rescue of exhausted CD8 T cells by PD-1–targeted therapies is CD28-dependent. Science 2017, 355, 1423–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamphorst, A.O.; Pillai, R.N.; Yang, S.; Nasti, T.H.; Akondy, R.S.; Wieland, A.; Sica, G.L.; Yu, K.; Koenig, L.; Patel, N.T.; et al. Proliferation of PD-1+ CD8 T cells in peripheral blood after PD-1-targeted therapy in lung cancer patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4993–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brummelman, J.; Mazza, E.M.; Alvisi, G.; Colombo, F.S.; Grilli, A.; Mikulak, J.; Mavilio, D.; Alloisio, M.; Ferrari, F.; Lopci, E.; et al. High-dimensional single cell analysis identifies stem-like cytotoxic CD8+ T cells infiltrating human tumors. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 2520–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, P.S.; Ahmed, R. Features of responding T cells in cancer and chronic infection. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2010, 22, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sade-Feldman, M.; Yizhak, K.; Bjorgaard, S.L.; Ray, J.P.; De Boer, C.G.; Jenkins, R.W.; Lieb, D.J.; Chen, J.H.; Frederick, D.T.; Barzily-Rokni, M.; et al. Defining T Cell States Associated with Response to Checkpoint Immunotherapy in Melanoma. Cell 2018, 175, 998–1013.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, G.J.; Pereira, R.M.; Aijo, T.; Kim, E.Y.; Marangoni, F.; Pipkin, M.E.; Togher, S.; Heissmeyer, V.; Zhang, Y.C.; Crotty, S.; et al. The transcription factor NFAT promotes exhaustion of activated CD8⁺ T cells. Immunity 2015, 42, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macian, F.; García-Rodríguez, C.; Rao, A. Gene expression elicited by NFAT in the presence or absence of cooperative recruitment of Fos and Jun. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 4783–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurachi, M.; Barnitz, R.A.; Yosef, N.; Odorizzi, P.M.; Dilorio, M.A.; Lemieux, M.E.; Yates, K.; Godec, J.; Klatt, M.G.; Regev, A.; et al. The transcription factor BATF operates as an essential differentiation checkpoint in early effector CD8+ T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, K.; Gabriel, S.S.; Liao, Y.; Gloury, R.; Preston, S.; Henstridge, D.C.; Pellegrini, M.; Zehn, D.; Berberich-Siebelt, F.; Febbraio, M.A.; et al. Transcription Factor IRF4 Promotes CD8+ T Cell Exhaustion and Limits the Development of Memory-like T Cells during Chronic Infection. Immunity 2017, 47, 1129–1141.e1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Glover, J.N.M.; Hogan, P.G.; Rao, A.; Harrison, S.C. Structure of the DNA-binding domains from NFAT, Fos and Jun bound specifically to DNA. Nature 1998, 392, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oestreich, K.J.; Yoon, H.; Ahmed, R.; Boss, J.M. NFATc1 Regulates Programmed Death-1 Expression Upon T Cell Activation1. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 4832–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelekati, E.; Chen, Z.; Manne, S.; Kurachi, M.; Ali, M.-A.; Lewy, K.; Cai, Z.; Nzingha, K.; McLane, L.M.; Hope, J.L.; et al. Long-Term Persistence of Exhausted CD8 T Cells in Chronic Infection Is Regulated by MicroRNA-155. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 2142–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynn, R.C.; Weber, E.W.; Sotillo, E.; Gennert, D.; Xu, P.; Good, Z.; Anbunathan, H.; Lattin, J.; Jones, R.; Tieu, V.; et al. c-Jun overexpression in CAR T cells induces exhaustion resistance. Nature 2019, 576, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utzschneider, D.T.; Gabriel, S.S.; Chisanga, D.; Gloury, R.; Gubser, P.M.; VasanthaKumar, A.; Shi, W.; Kallies, A. Early precursor T cells establish and propagate T cell exhaustion in chronic infection. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 1256–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, H.; Chen, J.; Gonzalez-Avalos, E.; Samaniego-Castruita, D.; Das, A.; Wang, Y.H.; Lopez-Moyado, I.F.; Georges, R.O.; Zhang, W.; Onodera, A.; et al. TOX and TOX2 transcription factors cooperate with NR4A transcription factors to impose CD8(+) T cell exhaustion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 12410–12415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.C.; Dündar, F.; Zumbo, P.; Chandran, S.S.; Klebanoff, C.A.; Shakiba, M.; Trivedi, P.; Menocal, L.; Appleby, H.; Camara, S.J.; et al. TOX is a critical regulator of tumour-specific T cell differentiation. Nature 2019, 571, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Sun, H.-W.; Lacey, N.E.; Ji, Y.; Moseman, E.A.; Shih, H.-Y.; Heuston, E.F.; Kirby, M.; Anderson, S.; Cheng, J.; et al. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals TOX as a key regulator of CD8+ T cell persistence in chronic infection. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 890–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfei, F.; Kanev, K.; Hofmann, M.; Wu, M.; Ghoneim, H.E.; Roelli, P.; Utzschneider, D.T.; Von Hoesslin, M.; Cullen, J.G.; Fan, Y.; et al. TOX reinforces the phenotype and longevity of exhausted T cells in chronic viral infection. Nature 2019, 571, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Park, S.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, G.; Park, S.M.; Cho, J.-W.; Kim, D.H.; Park, Y.M.; Koh, Y.W.; Kim, H.R.; et al. Single-cell transcriptome analysis reveals TOX as a promoting factor for T cell exhaustion and a predictor for anti-PD-1 responses in human cancer. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; McPherson, A.J.; Jones, R.B.; Kawamura, K.S.; Lin, G.H.; Lang, P.A.; Ambagala, T.; Pellegrini, M.; Calzascia, T.; Aidarus, N.; et al. Loss of the signaling adaptor TRAF1 causes CD8+ T cell dysregulation during human and murine chronic infection. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 209, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaFleur, M.W.; Nguyen, T.H.; Coxe, M.A.; Miller, B.C.; Yates, K.B.; Gillis, J.E.; Sen, D.R.; Gaudiano, E.F.; Al Abosy, R.; Freeman, G.J.; et al. PTPN2 regulates the generation of exhausted CD8+ T cell subpopulations and restrains tumor immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, R.; Zhang, M.; Huang, L.; Moskophidis, D. Control of Virus-Specific CD8+ T-Cell Exhaustion and Immune-Mediated Pathology by E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Cbl-b during Chronic Viral Infection. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3353–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; López-Moyado, I.F.; Seo, H.; Lio, C.-W.J.; Hempleman, L.J.; Sekiya, T.; Yoshimura, A.; Scott-Browne, J.; Rao, A. NR4A transcription factors limit CAR T cell function in solid tumours. Nature 2019, 567, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekine, T.; Potti, A.P.; Nguyen, S.; Gorin, J.-B.; Wu, V.H.; Gostick, E.; Llewellyn-Lacey, S.; Hammer, Q.; Falck-Jones, S.; Vangeti, S.; et al. TOX is expressed by exhausted and polyfunctional human effector memory CD8+ T cells. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eaba7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klenerman, P.; Oxenius, A. T cell responses to cytomegalovirus. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utzschneider, D.T.; Kallies, A. Human effector T cells express TOX—Not so “TOX”ic after all. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabc8272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, E.L.; Mullen, A.C.; Martins, G.A.; Krawczyk, C.M.; Hutchins, A.S.; Zediak, V.P.; Banica, M.; DiCioccio, C.B.; Gross, D.A.; Mao, C.-A.; et al. Control of Effector CD8+ T Cell Function by the Transcription Factor Eomesodermin. Science 2003, 302, 1041–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, A.; Masson, F.; Liao, Y.; Preston, S.; Guan, T.; Gloury, R.; Olshansky, M.; Lin, J.-X.; Li, P.; Speed, T.P.; et al. A molecular threshold for effector CD8+ T cell differentiation controlled by transcription factors Blimp-1 and T-bet. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipkin, M.E.; Sacks, J.A.; Cruz-Guilloty, F.; Lichtenheld, M.G.; Bevan, M.J.; Rao, A. Interleukin-2 and Inflammation Induce Distinct Transcriptional Programs that Promote the Differentiation of Effector Cytolytic T Cells. Immunity 2010, 32, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemoto, N.; Intlekofer, A.M.; Northrup, J.T.; Wherry, E.J.; Reiner, S.L. Cutting Edge: IL-12 Inversely Regulates T-bet and Eomesodermin Expression during Pathogen-Induced CD8+ T Cell Differentiation. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 7515–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intlekofer, A.M.; Takemoto, N.; Wherry, E.J.; A Longworth, S.; Northrup, J.T.; Palanivel, V.R.; Mullen, A.C.; Gasink, C.R.; Kaech, S.M.; Miller, J.D.; et al. Effector and memory CD8+ T cell fate coupled by T-bet and eomesodermin. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 1236–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lighvani, A.A.; Frucht, D.M.; Jankovic, D.; Yamane, H.; Aliberti, J.; Hissong, B.D.; Nguyen, B.V.; Gadina, M.; Sher, A.; Paul, W.E.; et al. T-bet is rapidly induced by interferon-gamma in lymphoid and myeloid cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 15137–15142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bally, A.P.R.; Austin, J.W.; Boss, J.M. Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation of PD-1 Expression. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 2431–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, R.M.; Chaudhuri, A.A.; Rao, D.S.; Baltimore, D. Inositol phosphatase SHIP1 is a primary target of miR-155. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7113–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Usatorre, A.; Sempere, L.F.; Carmona, S.J.; Carretero-Iglesia, L.; Monnot, G.; Speiser, D.E.; Rufer, N.; Donda, A.; Zehn, D.; Jandus, C.; et al. MicroRNA-155 Expression Is Enhanced by T-cell Receptor Stimulation Strength and Correlates with Improved Tumor Control in Melanoma. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, C.X.; Amezquita, R.A.; Guan, T.; Marshall, H.D.; Joshi, N.; Kleinstein, S.H.; Kaech, S.M. The transcription factors ZEB2 and T-bet cooperate to program cytotoxic T cell terminal differentiation in response to LCMV viral infection. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 2041–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Guilloty, F.; Pipkin, M.E.; Djuretic, I.M.; Levanon, D.; Lotem, J.; Lichtenheld, M.G.; Groner, Y.; Rao, A. Runx3 and T-box proteins cooperate to establish the transcriptional program of effector CTLs. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delpoux, A.; Lai, C.Y.; Hedrick, S.M.; Doedens, A.L. FOXO1 opposition of CD8(+) T cell effector programming confers early memory properties and phenotypic diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8865–E8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, O.H.; Shin, H.M.; Miele, L.; Golde, T.E.; Fauq, A.; Minter, L.M.; Osborne, B. Notch Regulates Cytolytic Effector Function in CD8+ T Cells1. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 3380–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, Y.; Hao, J.; Ni, L.; Dong, C. High Levels of Eomes Promote Exhaustion of Anti-tumor CD8+ T Cells. Front. Immunol 2018, 9, 2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Gordon, S.M.; Intlekofer, A.M.; Paley, M.A.; Mooney, E.C.; Lindsten, T.; Wherry, E.J.; Reiner, S.L. Cutting edge: The transcription factor eomesodermin enables CD8+ T cells to compete for the memory cell niche. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 4988–4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doering, T.A.; Crawford, A.; Angelosanto, J.M.; Paley, M.A.; Ziegler, C.G.; Wherry, E.J. Network Analysis Reveals Centrally Connected Genes and Pathways Involved in CD8+ T Cell Exhaustion versus Memory. Immunity 2012, 37, 1130–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delpoux, A.; Michelini, R.H.; Verma, S.; Lai, C.-Y.; Omilusik, K.D.; Utzschneider, D.T.; Redwood, A.J.; Goldrath, A.W.; Benedict, C.A.; Hedrick, S.M. Continuous activity of Foxo1 is required to prevent anergy and maintain the memory state of CD8+ T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 215, 575–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejera, M.M.; Kim, E.H.; Sullivan, J.A.; Plisch, E.H.; Suresh, M. FoxO1 controls effector-to-memory transition and maintenance of functional CD8 T cell memory. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staron, M.M.; Gray, S.M.; Marshall, H.D.; Parish, I.A.; Chen, J.H.; Perry, C.J.; Cui, G.; Li, M.O.; Kaech, S.M. The transcription factor FoxO1 sustains expression of the inhibitory receptor PD-1 and survival of antiviral CD8(+) T cells during chronic infection. Immunity 2014, 41, 802–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallies, A.; Xin, A.; Belz, G.T.; Nutt, S.L. Blimp-1 Transcription Factor Is Required for the Differentiation of Effector CD8+ T Cells and Memory Responses. Immunity 2009, 31, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.; Blackburn, S.D.; Intlekofer, A.M.; Kao, C.; Angelosanto, J.M.; Reiner, S.L.; Wherry, E.J. A Role for the Transcriptional Repressor Blimp-1 in CD8+ T Cell Exhaustion during Chronic Viral Infection. Immunity 2009, 31, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutishauser, R.L.; Martins, G.A.; Kalachikov, S.; Chandele, A.; Parish, I.A.; Meffre, E.; Jacob, J.; Calame, K.; Kaech, S.M. Transcriptional Repressor Blimp-1 Promotes CD8+ T Cell Terminal Differentiation and Represses the Acquisition of Central Memory T Cell Properties. Immunity 2009, 31, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Youngblood, B.A.; Austin, J.W.; Mohammed, A.U.R.; Butler, R.; Ahmed, R.; Boss, J.M. Blimp-1 represses CD8 T cell expression of PD-1 using a feed-forward transcriptional circuit during acute viral infection. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.M.; Kapoor, V.N.; Guan, T.; Kaech, S.M.; Welsh, R.M.; Berg, L.J. Epigenetic Modifications Induced by Blimp-1 Regulate CD8+ T Cell Memory Progression during Acute Virus Infection. Immunity 2013, 39, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.Y.; Best, J.A.; Knell, J.; Yang, E.; Sheridan, A.D.; Jesionek, A.K.; Li, H.S.; Rivera, R.R.; Lind, K.C.; D’Cruz, L.M.; et al. The transcriptional regulators Id2 and Id3 control the formation of distinct memory CD8+ T cell subsets. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, F.; Minnich, M.; Olshansky, M.; Bilic, I.; Mount, A.M.; Kallies, A.; Speed, T.P.; Busslinger, M.; Nutt, S.L.; Belz, G.T. Id2-Mediated Inhibition of E2A Represses Memory CD8+ T Cell Differentiation. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 4585–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buenrostro, J.D.; Wu, B.; Chang, H.Y.; Greenleaf, W.J. ATAC-seq: A Method for Assaying Chromatin Accessibility Genome-Wide. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2015, 109, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, D.R.; Kaminski, J.; Barnitz, R.A.; Kurachi, M.; Gerdemann, U.; Yates, K.B.; Tsao, H.-W.; Godec, J.; LaFleur, M.W.; Brown, F.D.; et al. The epigenetic landscape of T cell exhaustion. Science 2016, 354, 1165–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Liu, Y.; Meng, L.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Ji, Y.; Purushe, J.; Chen, P.; Li, C.; Madzo, J.; et al. Ezh2 phosphorylation state determines its capacity to maintain CD8+ T memory precursors for antitumor immunity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, H.E.; Fan, Y.; Moustaki, A.; Abdelsamed, H.A.; Dash, P.; Dogra, P.; Carter, R.; Awad, W.; Neale, G.; Thomas, P.G.; et al. De Novo Epigenetic Programs Inhibit PD-1 Blockade-Mediated T Cell Rejuvenation. Cell 2017, 170, 142–157.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mognol, G.P.; Spreafico, R.; Wong, V.; Scott-Browne, J.P.; Togher, S.; Hoffmann, A.; Hogan, P.G.; Rao, A.; Trifari, S. Exhaustion-associated regulatory regions in CD8(+) tumor-infiltrating T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E2776–E2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.C.; Postow, M.A.; Orlowski, R.J.; Mick, R.; Bengsch, B.; Manne, S.; Xu, W.; Harmon, S.; Giles, J.R.; Wenz, B.; et al. T-cell invigoration to tumour burden ratio associated with anti-PD-1 response. Nature 2017, 545, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhou, X.; DiSpirito, J.R.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Shen, H. Epigenetic Manipulation Restores Functions of Defective CD8+ T Cells From Chronic Viral Infection. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 1698–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eil, R.; Vodnala, S.K.; Clever, D.; Klebanoff, C.A.; Sukumar, M.; Pan, J.H.; Palmer, D.; Gros, A.; Yamamoto, T.N.; Patel, S.J.; et al. Ionic immune suppression within the tumour microenvironment limits T cell effector function. Nature 2016, 537, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, R.D.; Emens, L.A. Targeting adenosine for cancer immunotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornyák, L.; Dobos, N.; Koncz, G.; Karanyi, Z.; Pall, D.; Szabo, Z.; Halmos, G.; Székvölgyi, L. The Role of Indoleamine-2,3-Dioxygenase in Cancer Development, Diagnostics, and Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günther, J.; Däbritz, J.; Wirthgen, E. Limitations and Off-Target Effects of Tryptophan-Related IDO Inhibitors in Cancer Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beavis, P.A.; Henderson, M.A.; Giuffrida, L.; Mills, J.K.; Sek, K.; Cross, R.S.; Davenport, A.J.; John, L.B.; Mardiana, S.; Slaney, C.Y.; et al. Targeting the adenosine 2A receptor enhances chimeric antigen receptor T cell efficacy. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinoco, R.; Alcalde, V.; Yang, Y.; Sauer, K.; Zúñiga, E.I. Cell-Intrinsic Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling Mediates Virus-Specific CD8+ T Cell Deletion and Viral Persistence In Vivo. Immunity 2009, 31, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, D.G.; Ha, S.J.; Elsaesser, H.; Sharpe, A.H.; Freeman, G.J.; Oldstone, M.B. IL-10 and PD-L1 operate through distinct pathways to suppress T-cell activity during persistent viral infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20428–20433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, E.B.; Yamada, D.H.; Elsaesser, H.; Herskovitz, J.; Deng, J.; Cheng, G.; Aronow, B.J.; Karp, C.L.; Brooks, D.G. Blockade of Chronic Type I Interferon Signaling to Control Persistent LCMV Infection. Science 2013, 340, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mühlbauer, M.; Fleck, M.; Schütz, C.; Weiss, T.S.; Froh, M.; Blank, C.; Schölmerich, J.; Hellerbrand, C. PD-L1 is induced in hepatocytes by viral infection and by interferon-α and -γ and mediates T cell apoptosis. J. Hepatol. 2006, 45, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, Y.; Agata, Y.; Shibahara, K.; Honjo, T. Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 3887–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemnitz, J.M.; Parry, R.V.; Nichols, K.E.; June, C.H.; Riley, J.L. SHP-1 and SHP-2 associate with immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif of programmed death 1 upon primary human T cell stimulation, but only receptor ligation prevents T cell activation. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Xu, C. Immune checkpoint signaling and cancer immunotherapy. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, A.H.; Pauken, K.E. The diverse functions of the PD1 inhibitory pathway. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 18, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duraiswamy, J.; Ibegbu, C.C.; Masopust, D.; Miller, J.D.; Araki, K.; Doho, G.H.; Tata, P.; Gupta, S.K.; Zilliox, M.J.; I Nakaya, H.; et al. Phenotype, function, and gene expression profiles of programmed death-1(hi) CD8 T cells in healthy human adults. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 4200–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrelli, A.; Mijnheer, G.; Van Konijnenburg, D.P.H.; Van Der Wal, M.M.; Giovannone, B.; Mocholi, E.; Vazirpanah, N.; Broen, J.C.A.; Hijnen, D.; Oldenburg, B.; et al. PD-1+CD8+ T cells are clonally expanding effectors in human chronic inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4669–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odorizzi, P.M.; Pauken, K.E.; Paley, M.A.; Sharpe, A.; Wherry, E.J. Genetic absence of PD-1 promotes accumulation of terminally differentiated exhausted CD8+ T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 1125–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triebel, F.; Jitsukawa, S.; Baixeras, E.; Roman-Roman, S.; Genevée, C.; Viegas-Pequignot, E.; Hercend, T. LAG-3, a novel lymphocyte activation gene closely related to CD4. J. Exp. Med. 1990, 171, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannier, S.; Tournier, M.; Bismuth, G.; Triebel, F. CD3/TCR complex-associated lymphocyte activation gene-3 molecules inhibit CD3/TCR signaling. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 4058–4065. [Google Scholar]
- Previte, D.M.; Martins, C.P.; O’Connor, E.C.; Marre, M.L.; Coudriet, G.M.; Beck, N.W.; Menk, A.V.; Wright, R.H.; Tse, H.M.; Delgoffe, G.M.; et al. Lymphocyte Activation Gene-3 Maintains Mitochondrial and Metabolic Quiescence in Naive CD4+ T Cells. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 129–141.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workman, C.J.; Rice, D.S.; Dugger, K.J.; Kurschner, C.; Vignali, D.A.A. Phenotypic analysis of the murine CD4-related glycoprotein, CD223 (LAG-3). Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 2255–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.C.; Joller, N.; Kuchroo, V.K. Lag-3, Tim-3, and TIGIT: Co-inhibitory Receptors with Specialized Functions in Immune Regulation. Immunity 2016, 44, 989–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-T.; Workman, C.J.; Flies, D.; Pan, X.; Marson, A.L.; Zhou, G.; Hipkiss, E.L.; Ravi, S.; Kowalski, J.; Levitsky, H.I.; et al. Role of LAG-3 in Regulatory T Cells. Immunity 2004, 21, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisielow, M.; Kisielow, J.; Karjalainen, K.; Capoferri-Sollami, G. Expression of lymphocyte activation gene 3 (LAG-3) on B cells is induced by T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 2081–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Workman, C.J.; Wang, Y.; El Kasmi, K.C.; Pardoll, E.M.; Murray, P.J.; Drake, C.G.; Vignali, D.A. LAG-3 regulates plasmacytoid dendritic cell homeostasis. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 1885–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huard, B.; Prigent, P.; Tournier, M.; Bruniquel, D.; Triebel, F. CD4/major histocompatibility complex class II interaction analyzed with CD4- and lymphocyte activation gene-3 (LAG-3)-Ig fusion proteins. Eur. J. Immunol. 1995, 25, 2718–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baixeras, E.; Huard, B.; Miossec, C.; Jitsukawa, S.; Martin, M.; Hercend, T.; Auffray, C.; Triebel, F.; Piatier-Tonneau, D. Characterization of the lymphocyte activation gene 3-encoded protein. A new ligand for human leukocyte antigen class II antigens. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 176, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruhashi, T.; Okazaki, I.-M.; Sugiura, D.; Takahashi, S.; Maeda, T.K.; Shimizu, K.; Okazaki, T. LAG-3 inhibits the activation of CD4+ T cells that recognize stable pMHCII through its conformation-dependent recognition of pMHCII. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Liu, J.; Liu, D.; Liu, B.; Wang, M.; Hu, Z.; Du, X.; Tang, L.; He, F. LSECtin Expressed on Melanoma Cells Promotes Tumor Progression by Inhibiting Antitumor T-cell Responses. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3418–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouo, T.; Huang, L.; Pucsek, A.B.; Cao, M.; Solt, S.; Armstrong, T.; Jaffee, E.M. Galectin-3 Shapes Antitumor Immune Responses by Suppressing CD8+ T Cells via LAG-3 and Inhibiting Expansion of Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Datar, I.; Su, T.T.; Ji, L.; Sun, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, G.; Yin, W.; et al. Fibrinogen-like Protein 1 Is a Major Immune Inhibitory Ligand of LAG-3. Cell 2019, 176, 334–347.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Workman, C.J.; Martin, S.M.; Vignali, D.A. Biochemical analysis of the regulatory T cell protein lymphocyte activation gene-3 (LAG-3; CD223). J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 6806–6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Forbes, K.; Vignali, K.M.; Heale, B.S.; Saftig, P.; Hartmann, D.; A Black, R.; Rossi, J.J.; Blobel, C.P.; et al. Metalloproteases regulate T-cell proliferation and effector function via LAG-3. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Workman, C.; Lee, J.; Chew, C.; Dale, B.M.; Colonna, L.; Flores, M.; Li, N.; Schweighoffer, E.; Greenberg, S.; et al. Regulatory T Cells Inhibit Dendritic Cells by Lymphocyte Activation Gene-3 Engagement of MHC Class II. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 5916–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triebel, F. LAG-3: A regulator of T-cell and DC responses and its use in therapeutic vaccination. Trends Immunol. 2003, 24, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreae, S.; Buisson, S.; Triebel, F. MHC class II signal transduction in human dendritic cells induced by a natural ligand, the LAG-3 protein (CD223). Blood 2003, 102, 2130–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brignone, C.; Grygar, C.; Marcu, M.; Perrin, G.; Triebel, F. IMP321 (sLAG-3) safety and T cell response potentiation using an influenza vaccine as a model antigen: A single-blind phase I study. Vaccine 2007, 25, 4641–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brignone, C.; Grygar, C.; Marcu, M.; Perrin, G.; Triebel, F. IMP321 (sLAG-3), an immunopotentiator for T cell responses against a HBsAg antigen in healthy adults: A single blind randomised controlled phase I study. J. Immune Based Ther. Vaccines 2007, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brignone, C.; Escudier, B.; Grygar, C.; Marcu, M.; Triebel, F. A Phase I Pharmacokinetic and Biological Correlative Study of IMP321, a Novel MHC Class II Agonist, in Patients with Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6225–6231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legat, A.; Hajjami, H.M.-E.; Baumgaertner, P.; Cagnon, L.; Maillard, S.A.; Geldhof, C.; Iancu, E.M.; Lebon, L.; Guillaume, P.; Dojcinovic, D.; et al. Vaccination with LAG-3Ig (IMP321) and Peptides Induces Specific CD4 and CD8 T-Cell Responses in Metastatic Melanoma Patients—Report of a Phase I/IIa Clinical Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 22, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, K.; Agnellini, P.; Oxenius, A. On the role of the inhibitory receptor LAG-3 in acute and chronic LCMV infection. Int. Immunol. 2010, 22, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, J.; Gnjatic, S.; Mhawech-Fauceglia, P.; Beck, A.; Miller, A.; Tsuji, T.; Eppolito, C.; Qian, F.; Lele, S.; Shrikant, P.; et al. Tumor-infiltrating NY-ESO-1-specific CD8+ T cells are negatively regulated by LAG-3 and PD-1 in human ovarian cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 7875–7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datar, I.J.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Wang, J.; Henick, B.S.; Choi, J.; Badri, T.; Dong, W.; Mani, N.; Toki, M.; Mejías, L.D.; et al. Expression Analysis and Significance of PD-1, LAG-3, and TIM-3 in Human Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Spatially Resolved and Multiparametric Single-Cell Analysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4663–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monney, L.; Sabatos, C.A.; Gaglia, J.L.; Ryu, A.; Waldner, H.; Chernova, T.; Manning, S.; Greenfield, E.A.; Coyle, A.J.; Sobel, R.A.; et al. Th1-specific cell surface protein Tim-3 regulates macrophage activation and severity of an autoimmune disease. Nature 2002, 415, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, G.; Huang, H.; Zhang, G.; Wang, F.; Sun, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, X.-G.; Lu, B. TIM-3 Expression Characterizes Regulatory T Cells in Tumor Tissues and Is Associated with Lung Cancer Progression. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndhlovu, L.C.; Lopez-Vergès, S.; Barbour, J.D.; Jones, R.B.; Jha, A.R.; Long, B.R.; Schoeffler, E.C.; Fujita, T.; Nixon, D.F.; Lanier, L.L. Tim-3 marks human natural killer cell maturation and suppresses cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Blood 2012, 119, 3734–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phong, B.L.; Avery, L.; Sumpter, T.L.; Gorman, J.V.; Watkins, S.C.; Colgan, J.D.; Kane, L. Tim-3 enhances FcεRI-proximal signaling to modulate mast cell activation. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 2289–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, A.C.; Anderson, D.E.; Bregoli, L.; Hastings, W.D.; Kassam, N.; Lei, C.; Chandwaskar, R.; Karman, J.; Su, E.W.; Hirashima, M.; et al. Promotion of Tissue Inflammation by the Immune Receptor Tim-3 Expressed on Innate Immune Cells. Science 2007, 318, 1141–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikushige, Y.; Shima, T.; Takayanagi, S.-I.; Urata, S.; Miyamoto, T.; Iwasaki, H.; Takenaka, K.; Teshima, T.; Tanaka, T.; Inagaki, Y.; et al. TIM-3 Is a Promising Target to Selectively Kill Acute Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 7, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Feng, Z.; Ma, J.; Ling, S.; Cao, Y.; Gurung, B.; Wu, Y.; Katona, B.W.; O’Dwyer, K.P.; Siegel, D.L.; et al. Bispecific and split CAR T cells targeting CD13 and TIM3 eradicate acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2020, 135, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Fueyo, A.; Tian, J.; Picarella, D.; Domenig, C.; Zheng, X.X.; Sabatos, C.A.; Manlongat, N.; Bender, O.; Kamradt, T.; Kuchroo, V.K.; et al. Tim-3 inhibits T helper type 1-mediated auto- and alloimmune responses and promotes immunological tolerance. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Anderson, A.C.; Schubart, A.; Xiong, H.; Imitola, J.; Khoury, S.; Zheng, X.X.; Strom, T.B.; Kuchroo, V.K. The Tim-3 ligand galectin-9 negatively regulates T helper type 1 immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, E.; Zang, X.; Ramagopal, U.A.; Mukhopadhaya, A.; Fedorov, A.; Fedorov, E.; Zencheck, W.D.; Lary, J.W.; Cole, J.L.; Deng, H.; et al. T Cell Immunoglobulin Mucin-3 Crystal Structure Reveals a Galectin-9-Independent Ligand-Binding Surface. Immunity 2007, 26, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, S.; Baghdadi, M.; Akiba, H.; Yoshiyama, H.; Kinoshita, I.; Dosaka-Akita, H.; Fujioka, Y.; Ohba, Y.; Gorman, J.V.; Colgan, J.D.; et al. Tumor-infiltrating DCs suppress nucleic acid–mediated innate immune responses through interactions between the receptor TIM-3 and the alarmin HMGB1. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Zhu, C.; Kondo, Y.; Anderson, A.C.; Gandhi, A.; Russell, A.; Dougan, S.K.; Petersen, B.-S.; Melum, E.; Pertel, T.; et al. CEACAM1 regulates TIM-3-mediated tolerance and exhaustion. Nature 2015, 517, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangachari, M.; Zhu, C.; Sakuishi, K.; Xiao, S.; Karman, J.; Chen, A.; Angin, M.; Wakeham, A.; Greenfield, E.A.; Sobel, R.A.; et al. Bat3 promotes T cell responses and autoimmunity by repressing Tim-3–mediated cell death and exhaustion. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, D.; Schraven, B.; Veillette, A. PAG-Associated FynT Regulates Calcium Signaling and Promotes Anergy in T Lymphocytes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 1960–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.; Rangachari, M.; Kuchroo, V.K. Tim-3: A co-receptor with diverse roles in T cell exhaustion and tolerance. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 42, 101302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatos, C.A.; Chakravarti, S.; Cha, E.; Schubart, A.; Sanchez-Fueyo, A.; Zheng, X.X.; Coyle, A.J.; Strom, T.B.; Freeman, G.J.; Kuchroo, V.K. Interaction of Tim-3 and Tim-3 ligand regulates T helper type 1 responses and induction of peripheral tolerance. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocaña-Guzman, R.; Torre-Bouscoulet, L.; Sada-Ovalle, I. TIM-3 Regulates Distinct Functions in Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Harden, K.; Gonzalez, L.C.; Francesco, M.; Chiang, E.; Irving, B.; Tom, I.; Ivelja, S.; Refino, C.J.; Clark, H.; et al. The surface protein TIGIT suppresses T cell activation by promoting the generation of mature immunoregulatory dendritic cells. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 10, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanietsky, N.; Simic, H.; Arapovic, J.; Toporik, A.; Levy, O.; Novik, A.; Levine, Z.; Beiman, M.; Dassa, L.; Achdout, H.; et al. The interaction of TIGIT with PVR and PVRL2 inhibits human NK cell cytotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17858–17863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, S.D.; Taft, D.W.; Brandt, C.S.; Bucher, C.; Howard, E.D.; Chadwick, E.M.; Johnston, J.; Hammond, A.; Bontadelli, K.; Ardourel, D.; et al. Vstm3 is a member of the CD28 family and an important modulator of T-cell function. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 902–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boles, K.S.; Vermi, W.; Facchetti, F.; Fuchs, A.; Wilson, T.J.; Diacovo, T.G.; Cella, M.; Colonna, M. A novel molecular interaction for the adhesion of follicular CD4 T cells to follicular DC. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joller, N.; Lozano, E.; Burkett, P.R.; Patel, B.; Xiao, S.; Zhu, C.; Xia, J.; Tan, T.G.; Sefik, E.; Yajnik, V.; et al. Treg cells expressing the coinhibitory molecule TIGIT selectively inhibit proinflammatory Th1 and Th17 cell responses. Immunity 2014, 40, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Lu, P.-H.; Liu, L.; Fang, Z.-M.; Duan, W.; Liu, Z.-L.; Wang, C.-Y.; Zhou, P.; Yu, X.; He, W.-T. TIGIT negatively regulates inflammation by altering macrophage phenotype. Immunobiology 2016, 221, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilfillan, S.; Chan, C.J.; Cella, M.; Haynes, N.M.; Rapaport, A.S.; Boles, K.S.; Andrews, D.M.; Smyth, M.J.; Colonna, M. DNAM-1 promotes activation of cytotoxic lymphocytes by nonprofessional antigen-presenting cells and tumors. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 2965–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, R.J.; Comps-Agrar, L.; Hackney, J.A.; Yu, X.; Huseni, M.; Yang, Y.; Park, S.; Javinal, V.; Chiu, H.; Irving, B.; et al. The Immunoreceptor TIGIT Regulates Antitumor and Antiviral CD8 + T Cell Effector Function. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 923–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Hu, D.; Li, C.; Ge, B.; Jin, B.; Fan, Z. Recruitment of Grb2 and SHIP1 by the ITT-like motif of TIGIT suppresses granule polarization and cytotoxicity of NK cells. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xia, P.; Du, Y.; Liu, S.; Huang, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Hou, N.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, L.; et al. T-cell Immunoglobulin and ITIM Domain (TIGIT) Receptor/Poliovirus Receptor (PVR) Ligand Engagement Suppresses Interferon-γ Production of Natural Killer Cells via β-Arrestin 2-mediated Negative Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 17647–17657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joller, N.; Hafler, J.P.; Brynedal, B.; Kassam, N.; Spoerl, S.; Levin, S.D.; Sharpe, A.H.; Kuchroo, V.K. Cutting edge: TIGIT has T cell-intrinsic inhibitory functions. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 1338–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtulus, S.; Sakuishi, K.; Ngiow, S.-F.; Joller, N.; Tan, D.J.; Teng, M.W.; Smyth, M.J.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Anderson, A.C. TIGIT predominantly regulates the immune response via regulatory T cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 4053–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, N.; Gavrieli, M.; Sedy, J.R.; Yang, J.; Fallarino, F.; Loftin, S.K.; Hurchla, M.A.; Zimmerman, N.; Sim, J.; Zang, X.; et al. BTLA is a lymphocyte inhibitory receptor with similarities to CTLA-4 and PD-1. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šedý, J.R.; Gavrieli, M.; Potter, K.G.; Hurchla, M.A.; Lindsley, R.C.; Hildner, K.; Scheu, S.; Pfeffer, K.; Ware, C.F.; Murphy, T.L.; et al. B and T lymphocyte attenuator regulates T cell activation through interaction with herpesvirus entry mediator. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 6, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, P.; Goularte, O.D.; Rufner, K.; Wilkinson, B.; Kaye, J. An Inhibitory Ig Superfamily Protein Expressed by Lymphocytes and APCs Is Also an Early Marker of Thymocyte Positive Selection. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 5931–5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, G.; Anumanthan, A.; Brown, J.A.; Greenfield, E.A.; Zhu, B.; Freeman, G.J. CD160 inhibits activation of human CD4+ T cells through interaction with herpesvirus entry mediator. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Mao, R.; Su, Z.; Zhang, J.-M. BTLA/HVEM Signaling: Milestones in Research and Role in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmer, J.R.; Tykodi, S.S.; Chow, L.Q.; Hwu, W.-J.; Topalian, S.L.; Hwu, P.; Drake, C.G.; Camacho, L.H.; Kauh, J.; Odunsi, K.; et al. Safety and Activity of Anti–PD-L1 Antibody in Patients with Advanced Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalian, S.L.; Hodi, F.S.; Brahmer, J.R.; Gettinger, S.N.; Smith, D.C.; McDermott, D.F.; Powderly, J.D.; Carvajal, R.D.; Sosman, J.A.; Atkins, M.B.; et al. Safety, Activity, and Immune Correlates of Anti–PD-1 Antibody in Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, C.; Ribas, A.; Wolchok, J.D.; Hodi, F.S.; Hamid, O.; Kefford, R.F.; Weber, J.S.; Joshua, A.M.; Hwu, W.-J.; Gangadhar, T.C.; et al. Anti-programmed-death-receptor-1 treatment with pembrolizumab in ipilimumab-refractory advanced melanoma: A randomised dose-comparison cohort of a phase 1 trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, C.; Long, G.V.; Brady, B.; Dutriaux, C.; Maio, M.; Mortier, L.; Hassel, J.C.; Rutkowski, P.; McNeil, C.; Kalinka-Warzocha, E.; et al. Nivolumab in Previously Untreated Melanoma without BRAF Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.; Chow, L.Q.; Vokes, E.E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, A.; Wolchok, J.D. Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science 2018, 359, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gane, E.; Verdon, D.J.; Brooks, A.E.S.; Gaggar, A.; Nguyen, A.H.; Subramanian, G.M.; Schwabe, C.; Dunbar, P.R. Anti-PD-1 blockade with nivolumab with and without therapeutic vaccination for virally suppressed chronic hepatitis B: A pilot study. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardiner, D.; Lalezari, J.; Lawitz, E.; DiMicco, M.; Ghalib, R.; Reddy, K.R.; Chang, K.-M.; Sulkowski, M.; Marro, S.O.; Anderson, J.; et al. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Assessment of BMS-936558, a Fully Human Monoclonal Antibody to Programmed Death-1 (PD-1), in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarhini, A.A.; Lin, Y.; Lin, H.; Rahman, Z.; Vallabhaneni, P.; Mendiratta, P.; Pingpank, J.F.; Holtzman, M.P.; Yusko, E.C.; Rytlewski, J.; et al. Neoadjuvant ipilimumab (3 mg/kg or 10 mg/kg) and high dose IFN-α2b in locally/regionally advanced melanoma: Safety, efficacy and impact on T-cell repertoire. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henning, A.N.; Roychoudhuri, R.; Restifo, N.P. Epigenetic control of CD8+ T cell differentiation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 340–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).