Transcriptome Sequencing Revealed an Inhibitory Mechanism of Aspergillus flavus Asexual Development and Aflatoxin Metabolism by Soy-Fermenting Non-Aflatoxigenic Aspergillus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
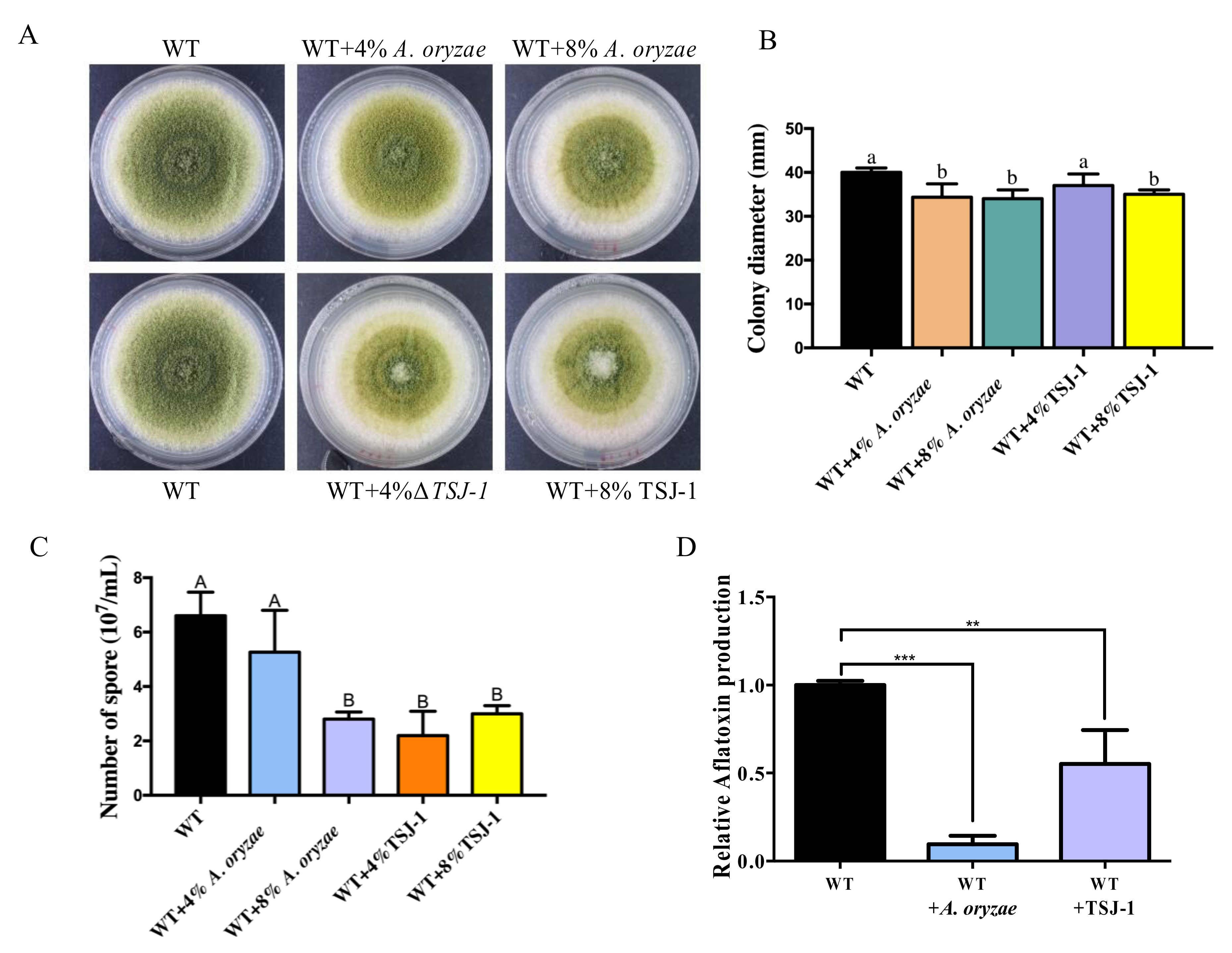
2.1. The Effect of Non-Aflatoxigenic Aspergilli on A. flavus Growth and Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) Production by Co-Cultivation with A. flavus
2.2. Cell-Free Concentrated Filtrates of Non-Aflatoxigenic Aspergilli inhibit A. flavus Asexual Development and AFB1 Accumulation
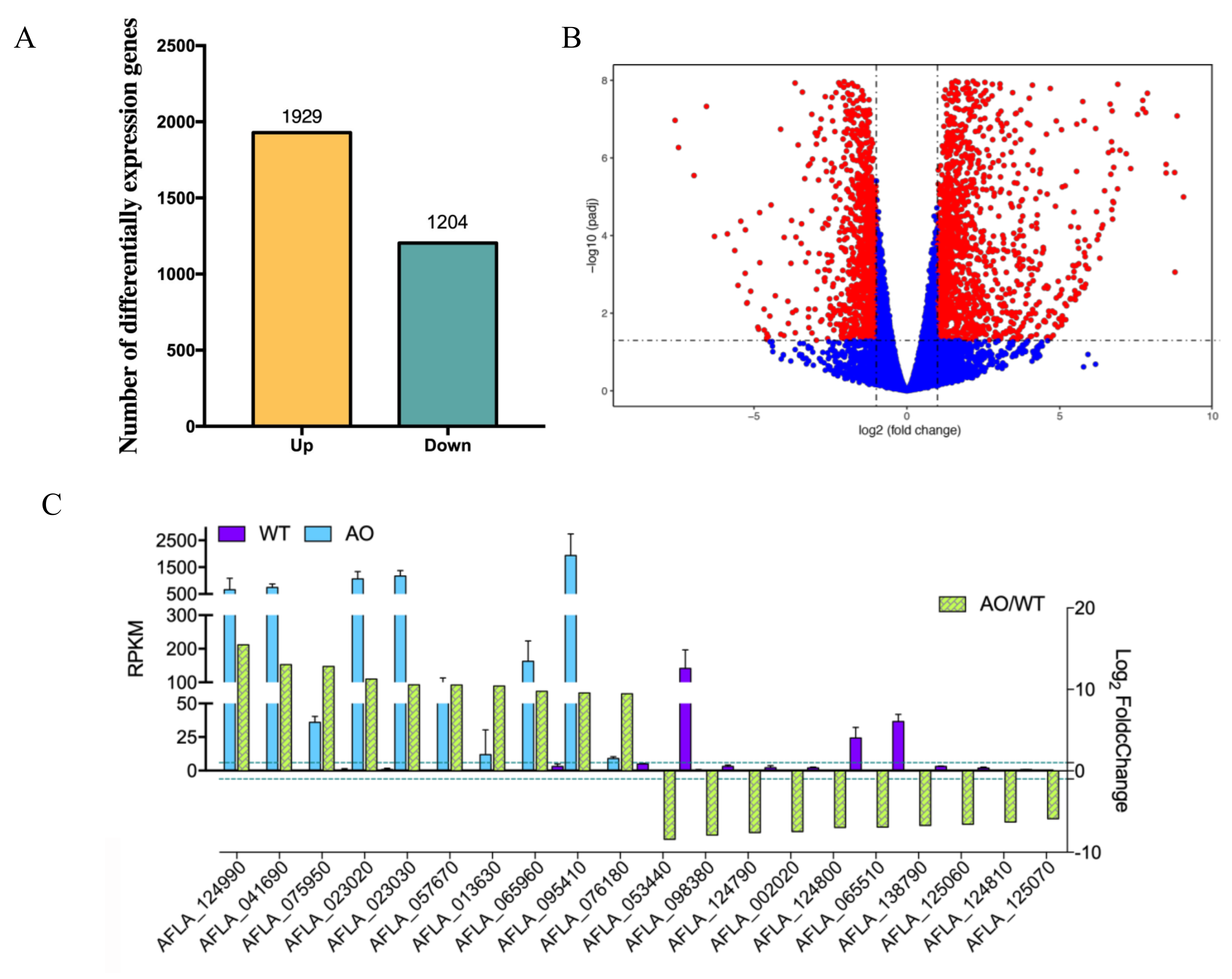
2.3. RNA-seq Analysis of A. flavus by the Treatment of A. oryzae Culture Filtrate
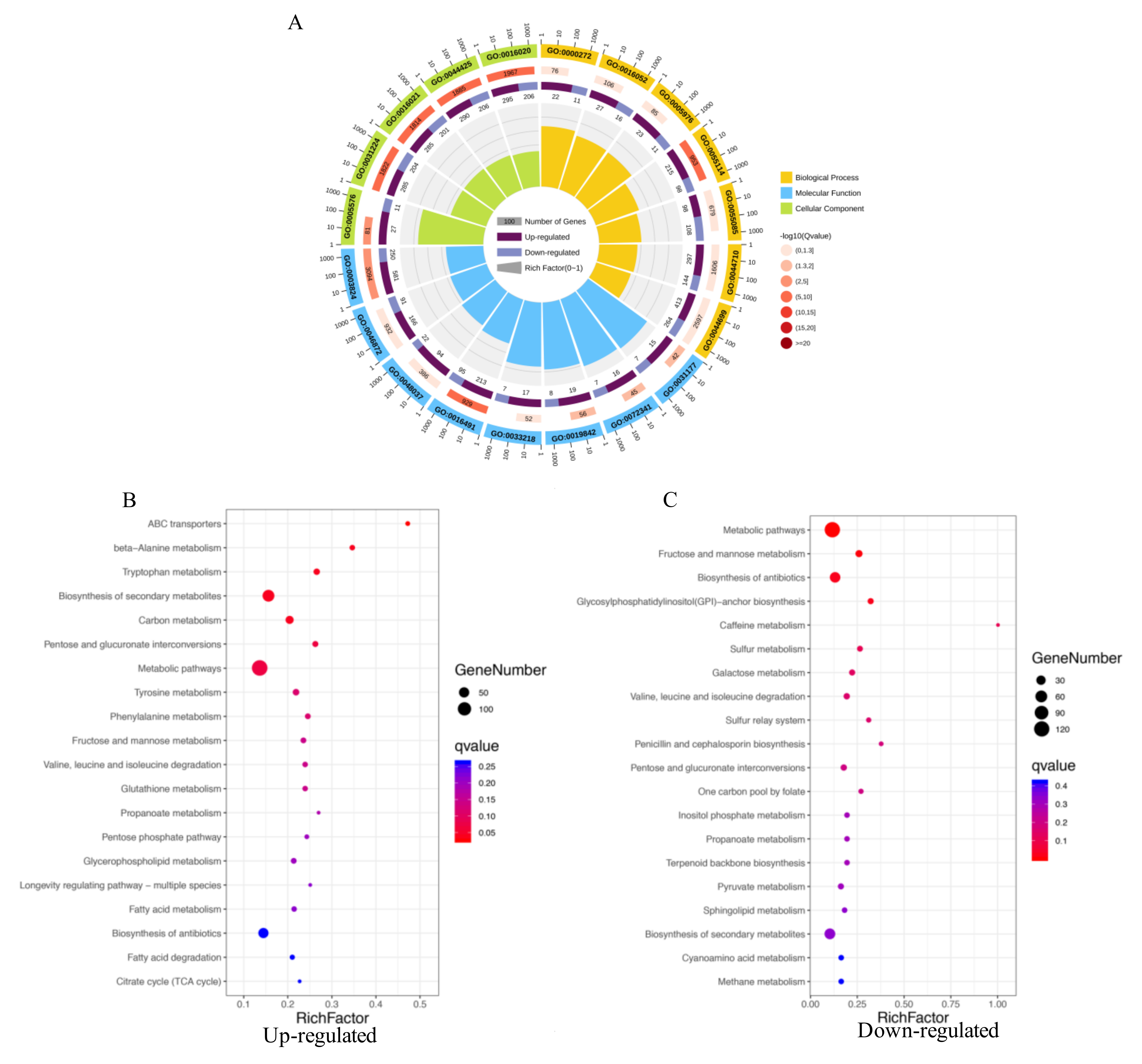
2.4. GO Enrichment and KEGG Pathways Analysis of DEGs
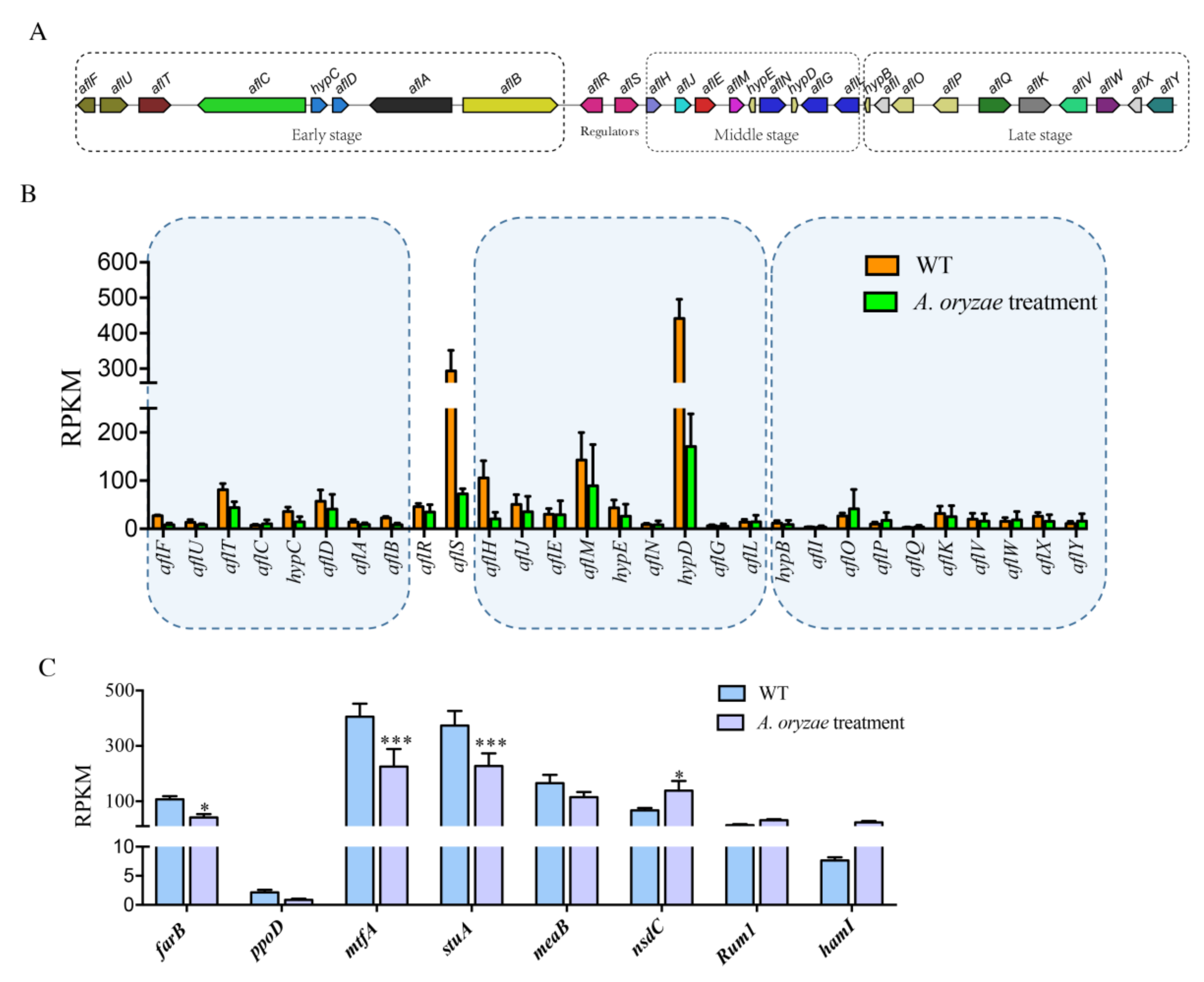
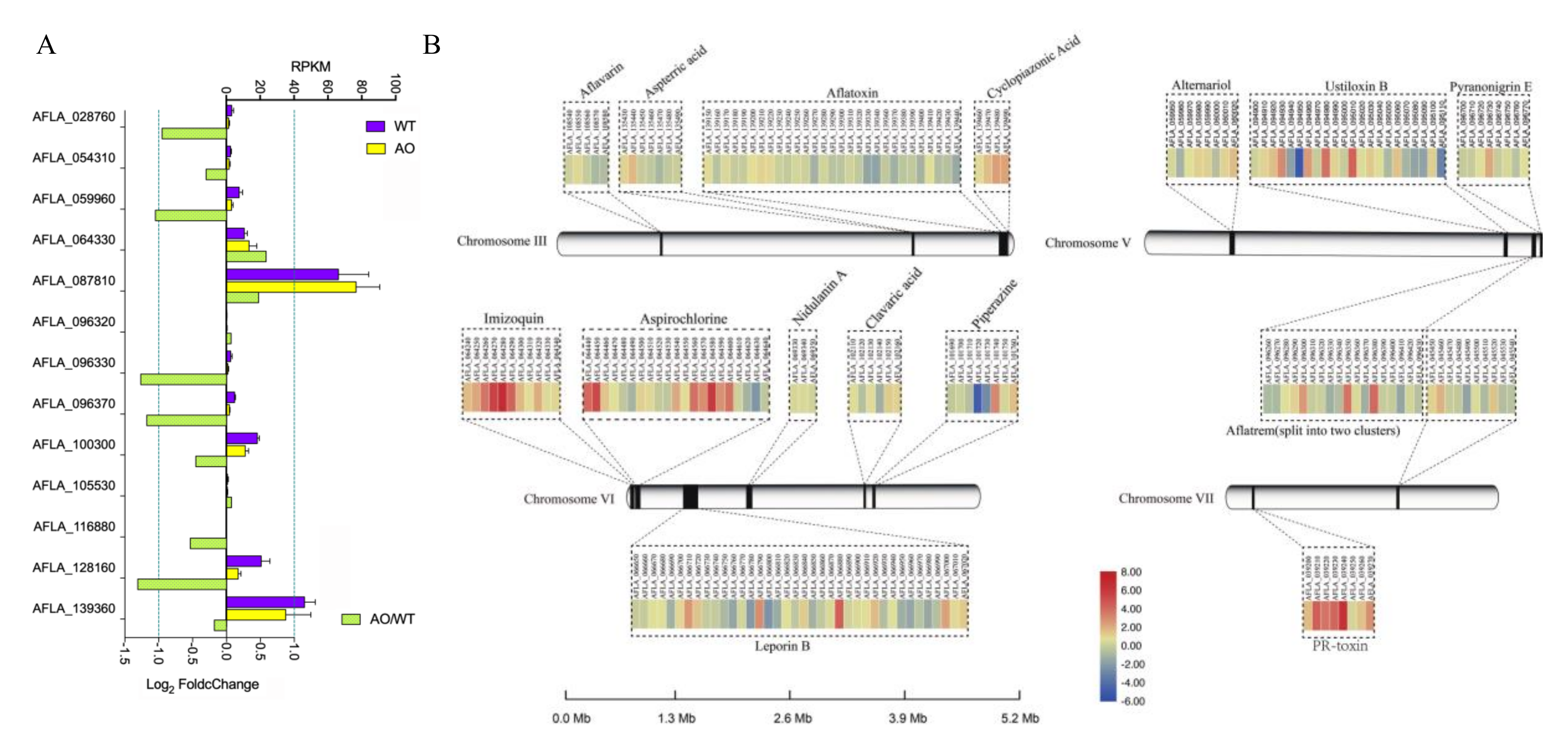
2.5. Inhibition of Aflatoxin Biosynthesis Gene Cluster by the Treatment of A. oryzae Filtrates
2.6. The Effect of A. oryzae Filtrates on the Expression of Biosynthetic Gene Clusters (BGCs)
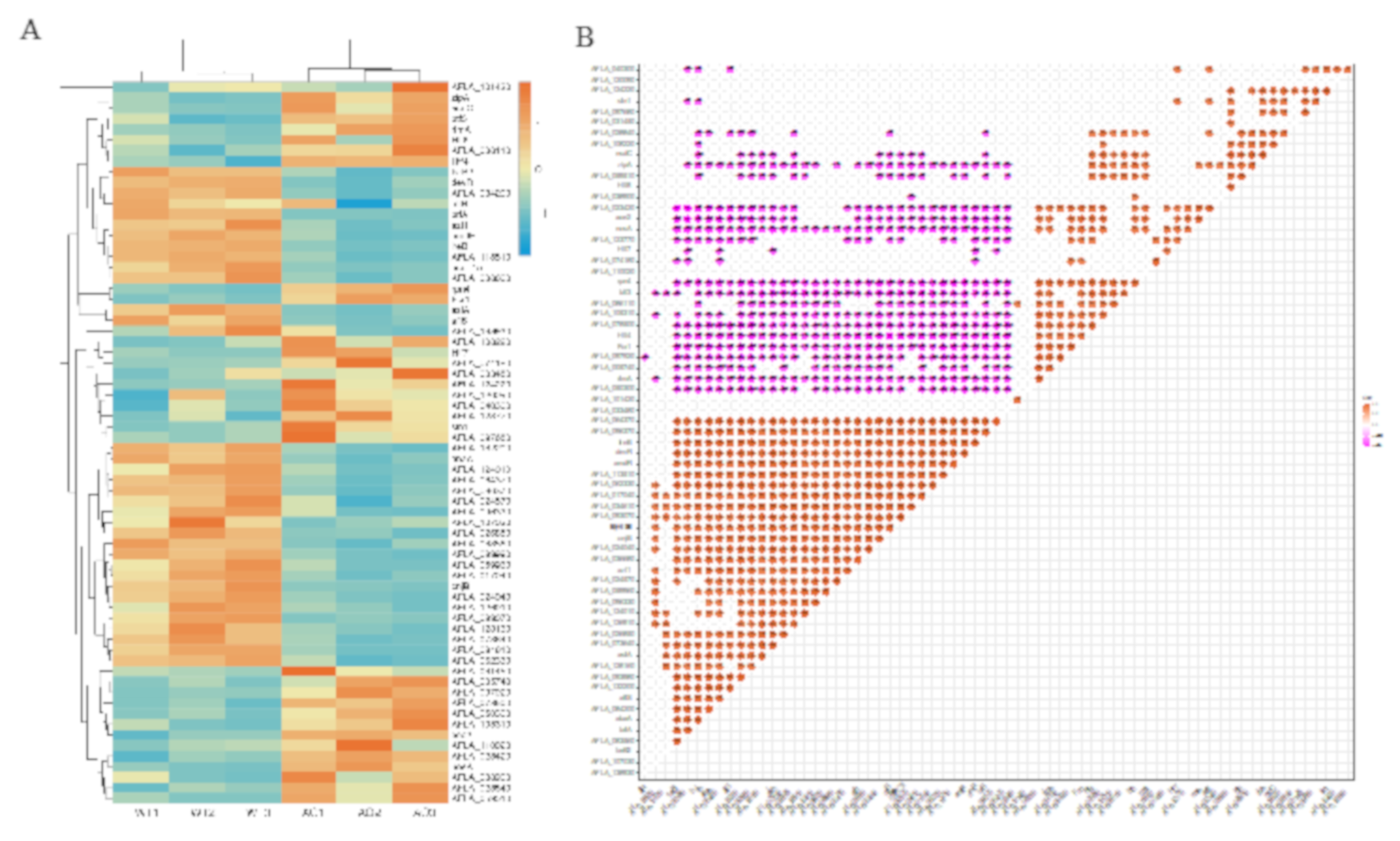
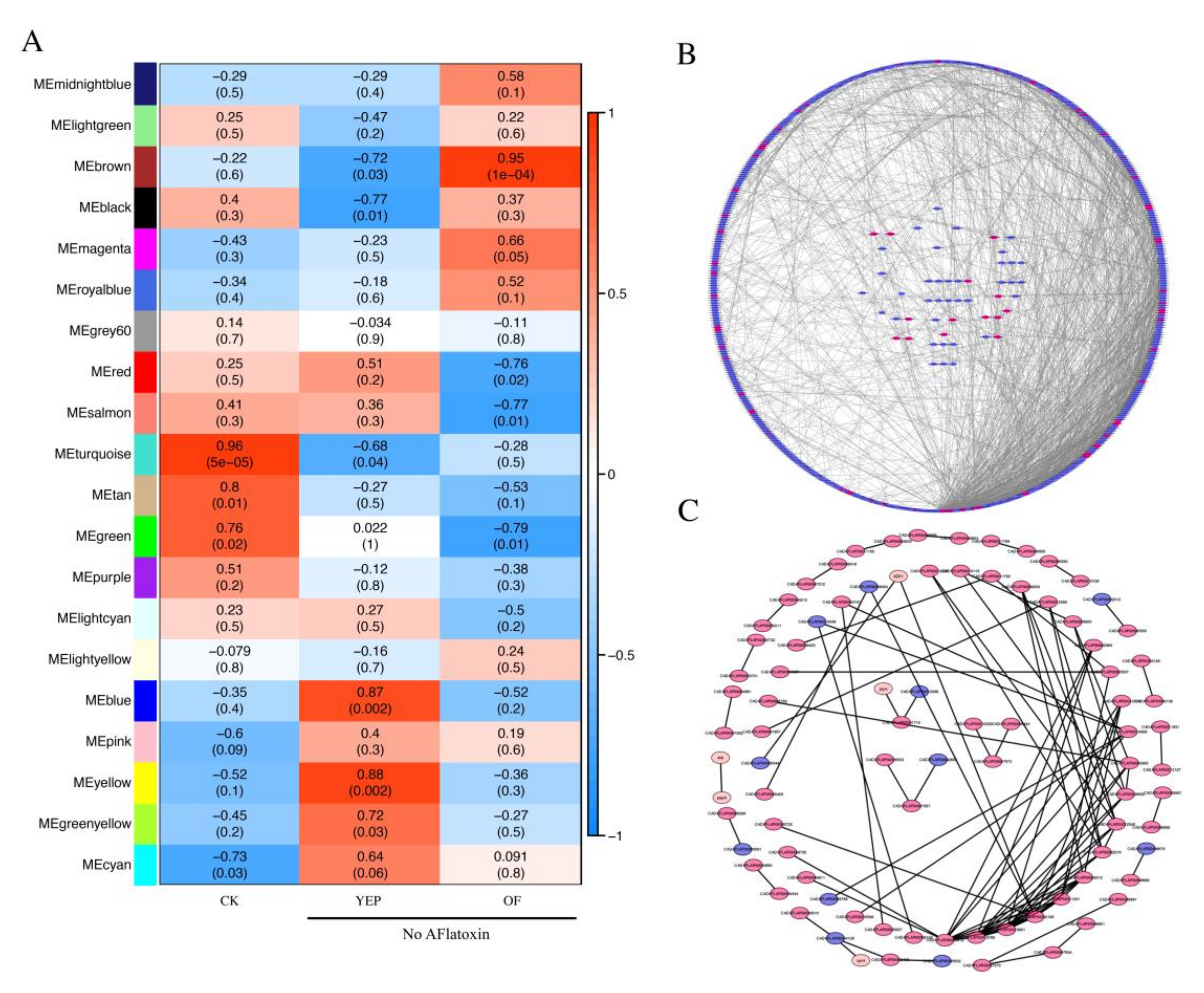
2.7. Co-Regulated Gene Expression Network between Aflatoxigenic and Non-Aflatoxigenic Conditions
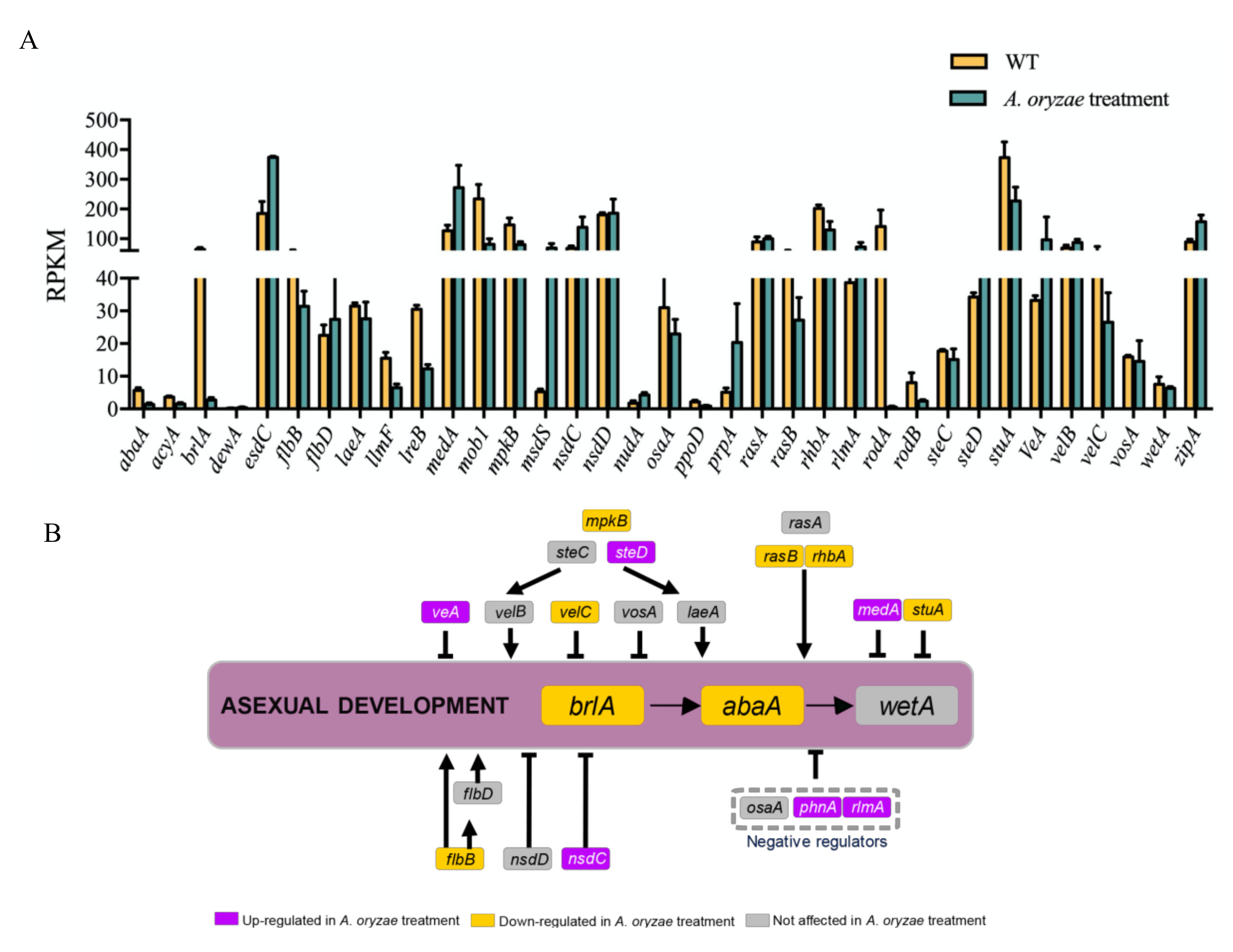
2.8. Inhibitory Regulation of Asexual Development Genes by the Treatment of A. oryzae Filtrates
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strains and Culture Conditions
4.2. Effect of Co-Cultivation of Non-Aflatoxigenic Aspergilli on the Growth of A. flavus and AFB1 Production
4.3. Effect of the Culture Filtrate of Non-Aflatoxigenic Aspergilli Strains on A. flavus Development and AFB1 Production
4.4. RNA Isolation
4.5. RNA-Seq and Enrichment Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes
4.6. Weighted Correlation Network Analysis (WGCNA) of Co-Expression Gene Network
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AF | Aflatoxin |
| DEGs | differentially expressed genes |
| RPKM | Reads Per Kilobase per Million mapped reads |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| WGCNA | Weighted correlation network analysis |
References
- Diener, U.L.; Cole, R.J.; Sanders, T.; Payne, G.A.; Lee, L.S.; Klich, M.A. Epidemiology of aflatoxin formation by Aspergillus flavus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1987, 25, 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Yang, K.; Chen, L.; Liu, M.; Geng, Q.; He, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tian, J. Cinnamaldehyde, a promising natural preservative against Aspergillus flavus. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Shadkchan, Y.; Tannous, J.; Landero Figueroa, J.A.; Wiemann, P.; Osherov, N.; Wang, S.; Keller, N.P. Contribution of ATPase copper transporters in animal but not plant virulence of the crossover pathogen Aspergillus flavus. Virulence 2018, 9, 1273–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, F.; Ding, N.; Liu, X.; Selvaraj, J.N.; Wang, L.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Variation in fungal microbiome (mycobiome) and aflatoxins during simulated storage of in-shell peanuts and peanut kernels. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchese, S.; Polo, A.; Ariano, A.; Velotto, S.; Costantini, S.; Severino, L. Aflatoxin B1 and M1: Biological properties and their involvement in cancer development. Toxins 2018, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Gan, Y.; Pan, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Tang, X.; Peng, X. Nerol-induced apoptosis associated with the generation of ROS and Ca(2+) overload in saprotrophic fungus Aspergillus flavus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 6659–6672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Geng, Q.; Wang, X.; Gao, X.; He, X.; Zhao, W.; Lan, H.; Tian, J.; Yang, K.; Wang, S. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry profiling of volatile compounds reveals metabolic changes in a non-aflatoxigenic Aspergillus flavus induced by 5-azacytidine. Toxins 2020, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Huang, B.; Luo, X.; Zeng, H.; Ban, X.; He, J.; Wang, Y. The control of Aspergillus flavus with Cinnamomum jensenianum Hand.-Mazz essential oil and its potential use as a food preservative. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Li, M.; Hu, H.; Ma, Y.; Chen, X.; Ni, J.; Zhao, W.; Huang, S.; et al. Biological degradation of aflatoxin B(1) by cell-free extracts of Bacillus velezensis DY3108 with broad PH stability and excellent thermostability. Toxins 2018, 10, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, J.F.; Engelbrecht, Y.; Steyn, P.S.; Holzapfel, W.H.; van Zyl, W.H. Biological degradation of aflatoxin B1 by Rhodococcus erythropolis cultures. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 109, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teniola, O.D.; Addo, P.A.; Brost, I.M.; Farber, P.; Jany, K.D.; Alberts, J.F.; van Zyl, W.H.; Steyn, P.S.; Holzapfel, W.H. Degradation of aflatoxin B(1) by cell-free extracts of Rhodococcus erythropolis and Mycobacterium fluoranthenivorans sp. nov. DSM44556(T). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 105, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Mao, J.; Li, P. Control of aflatoxigenic molds by antagonistic microorganisms: Inhibitory behaviors, bioactive compounds, related mechanisms, and influencing factors. Toxins 2020, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damann, J. Atoxigenic Aspergillus flavus biological control of aflatoxin contamination: What is the mechanism? World Mycotoxin J. 2015, 8, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, Q.; Lyu, A.; Zhang, J.; Wu, M.; Li, G.; Hsiang, T.; Yang, L. Biocontrol of Aspergillus flavus on peanut kernels using Streptomyces yanglinensis 3-10. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorner, J.W.; Cole, R.J.; Blankenship, P.D. Use of a biocompetitive agent to control preharvest aflatoxin in drought stressed peanuts. J. Food Prot. 1992, 55, 888–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, R.; Rehm, H.-J. Degradation products from aflatoxin B1 by Corynebacterium rubrum, Aspergillus niger, Trichoderma viride and Mucor ambiguus. Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1976, 2, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S.S.T.; Sarreal, S.B.L.; Chang, P.K.; Yu, J. Transcriptional regulation of aflatoxin biosynthesis and conidiation in Aspergillus flavus by Wickerhamomyces anomalus WRL-076 for reduction of aflatoxin contamination. Toxins 2019, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khoury, R.; Caceres, I.; Puel, O.; Bailly, S.; Atoui, A.; Oswald, I.P.; El Khoury, A.; Bailly, J.D. Identification of the anti-aflatoxinogenic activity of Micromeria graeca and elucidation of its molecular mechanism in Aspergillus flavus. Toxins 2017, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Folly, Y.M.E.; Chang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y. Morphological and transcriptomic analysis of the inhibitory effects of Lactobacillus plantarum on Aspergillus flavus Growth and Aflatoxin Production. Toxins 2019, 11, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Yue, Y.; Fu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Ma, G.; Wang, S. Exploration of the regulatory mechanism of secondary metabolism by comparative transcriptomics in Aspergillus flavus. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cary, J.W.; Harris-Coward, P.Y.; Ehrlich, K.C.; Mack, B.M.; Kale, S.P.; Larey, C.; Calvo, A.M. NsdC and NsdD affect Aspergillus flavus morphogenesis and aflatoxin production. Eukaryot. Cell 2012, 11, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Affeldt, K.J.; Keller, N.P. Characterization of the Far transcription factor family in Aspergillus flavus. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2016, 6, 3269–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Z.; Lohmar, J.M.; Satterlee, T.; Cary, J.W.; Calvo, A.M. The master transcription factor mtfA governs aflatoxin production, morphological development and pathogenicity in the fungus Aspergillus flavus. Toxins 2016, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.Y.; Mead, M.E.; Lee, M.K.; Ostrem Loss, E.M.; Kim, S.C.; Rokas, A.; Yu, J.H. Systematic dissection of the evolutionarily conserved WetA developmental regulator across a genus of filamentous fungi. mBio 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inglis, D.O.; Binkley, J.; Skrzypek, M.S.; Arnaud, M.B.; Cerqueira, G.C.; Shah, P.; Wymore, F.; Wortman, J.R.; Sherlock, G. Comprehensive annotation of secondary metabolite biosynthetic genes and gene clusters of Aspergillus nidulans, A. fumigatus, A. niger and A. oryzae. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools, a Toolkit for Biologists integrating various biological data han- dling tools with a user-friendly interface. bioRxiv 2018, 289660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drott, M.T.; Satterlee, T.R.; Skerker, J.M.; Pfannenstiel, B.T.; Glass, N.L.; Keller, N.P.; Milgroom, M.G. The Frequency of Sex: Population genomics reveals differences in recombination and population structure of the aflatoxin-producing fungus. mBio 2020, 11, e00963-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.M. Aspergillus flavus grown in peptone as the carbon source exhibits spore density- and peptone concentration-dependent aflatoxin biosynthesis. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaike, S.; Keller, N.P. Aspergillus flavus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2011, 49, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudramurthy, S.M.; Seyedmousavi, S.; Dhaliwal, M.; Chakrabarti, A.; Meis, J.F.; Mouton, J.W. Pharmacodynamics of voriconazole against wild-type and azole-Resistant Aspergillus flavus isolates in a nonneutropenic murine model of disseminated aspergillosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Shi, Z.-Q.; Hu, L.-B.; Cheng, L.-G.; Wang, F. Antifungal compounds from Bacillus subtilis B-FS06 inhibiting the growth of Aspergillus flavus. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 24, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Sun, C.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, A.; Peng, X. Perillaldehyde, a promising antifungal agent used in food preservation, triggers apoptosis through a metacaspase-dependent pathway in Aspergillus flavus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7404–7413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Li, Y.X.; Yang, K.; Famous, E.; Ma, Y.; He, X.; Geng, Q.; Liu, M.; Tian, J. The molecular mechanism of perillaldehyde inducing cell death in Aspergillus flavus by inhibiting energy metabolism revealed by transcriptome sequencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshannaq, A.F.; Gibbons, J.G.; Lee, M.K.; Han, K.H.; Hong, S.B.; Yu, J.H. Controlling aflatoxin contamination and propagation of Aspergillus flavus by a soy-fermenting Aspergillus oryzae strain. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, F.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Selvaraj, J.N.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y. Aflatoxin B1 inhibition in Aspergillus flavus by Aspergillus niger through downregulating expression of major biosynthetic genes and AFB1 degradation by atoxigenic A. flavus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 256, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Sun, X. Inhibition of non-toxigenic Aspergillus niger FS10 isolated from Chinese fermented soybean on growth and aflatoxin B1 production by Aspergillus flavus. Food Control 2013, 32, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shantha, T.; Rati, E. Isolation and characterization of an aflatoxin-inhibiting metabolite from A. niger. Curr. Sci. 1990, 59, 326–327. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, J.; Owens, R.; Doyle, S.; Núñez, F.; Asensio, M. Quantitative proteomics reveals new insights into calcium-mediated resistance mechanisms in Aspergillus flavus against the antifungal protein PgAFP in cheese. Food Microbiol. 2017, 66, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.G.; Shin, S.Y.; Maeng, C.-Y.; Jin, Z.Z.; Kim, K.L.; Hahm, K.-S. Isolation and characterization of a novel antifungal peptide from Aspergillus niger. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 263, 646–651. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Kong, Q.; Liang, Y. Three newly identified peptides from Bacillus megaterium strongly inhibit the growth and aflatoxin B 1 production of Aspergillus flavus. Food Control 2018, 21, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, U.; Oberparleiter, C.; Meyer, V.; Marx, F. The antifungal protein PAF interferes with PKC/MPK and cAMP/PKA signalling of Aspergillus nidulans. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 75, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raksha Rao, K.; Vipin, A.V.; Venkateswaran, G. Mechanism of inhibition of aflatoxin synthesis by non-aflatoxigenic strains of Aspergillus flavus. Microb. Pathog. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, A.L.; Lim, F.Y.; Soukup, A.A.; Keller, N.P.; Rokas, A. An LaeA- and BrlA-dependent cellular network governs tissue-specific secondary metabolism in the human pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. mSphere 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, L.; Xie, R.; Lan, H.; Fasoyin, O.E.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S. Cyclase-associated protein Cap with multiple domains contributes to mycotoxin biosynthesis and fungal virulence in Aspergillus flavus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4200–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, K.; Geng, Q.; Song, F.; He, X.; Hu, T.; Wang, S.; Tian, J. Transcriptome Sequencing Revealed an Inhibitory Mechanism of Aspergillus flavus Asexual Development and Aflatoxin Metabolism by Soy-Fermenting Non-Aflatoxigenic Aspergillus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21196994
Yang K, Geng Q, Song F, He X, Hu T, Wang S, Tian J. Transcriptome Sequencing Revealed an Inhibitory Mechanism of Aspergillus flavus Asexual Development and Aflatoxin Metabolism by Soy-Fermenting Non-Aflatoxigenic Aspergillus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(19):6994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21196994
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Kunlong, Qingru Geng, Fengqin Song, Xiaona He, Tianran Hu, Shihua Wang, and Jun Tian. 2020. "Transcriptome Sequencing Revealed an Inhibitory Mechanism of Aspergillus flavus Asexual Development and Aflatoxin Metabolism by Soy-Fermenting Non-Aflatoxigenic Aspergillus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 19: 6994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21196994
APA StyleYang, K., Geng, Q., Song, F., He, X., Hu, T., Wang, S., & Tian, J. (2020). Transcriptome Sequencing Revealed an Inhibitory Mechanism of Aspergillus flavus Asexual Development and Aflatoxin Metabolism by Soy-Fermenting Non-Aflatoxigenic Aspergillus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(19), 6994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21196994






