Rocuronium Has a Suppressive Effect on Platelet Function via the P2Y12 Receptor Pathway In Vitro That Is Not Reversed by Sugammadex
Abstract
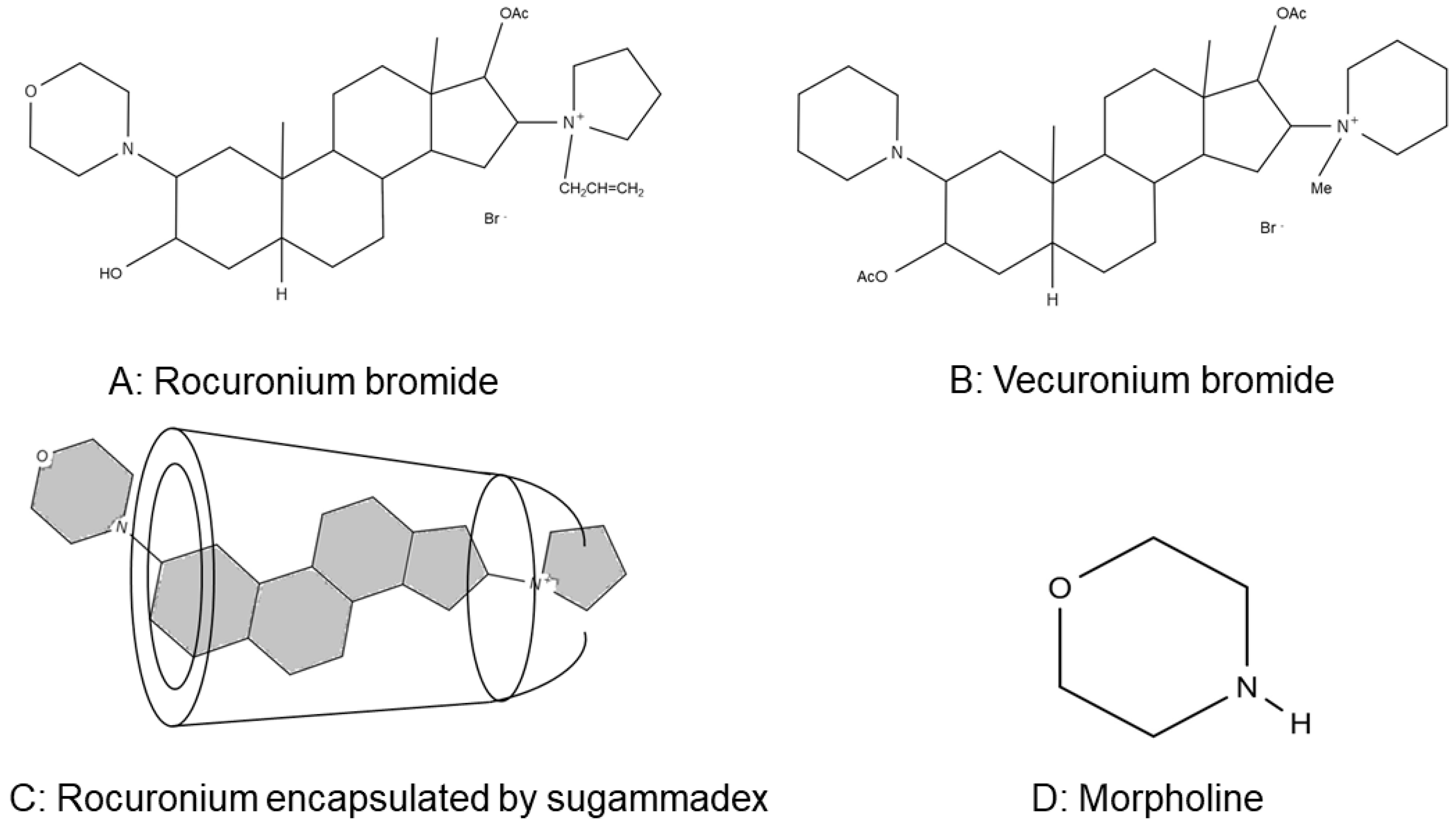
1. Introduction
2. Results
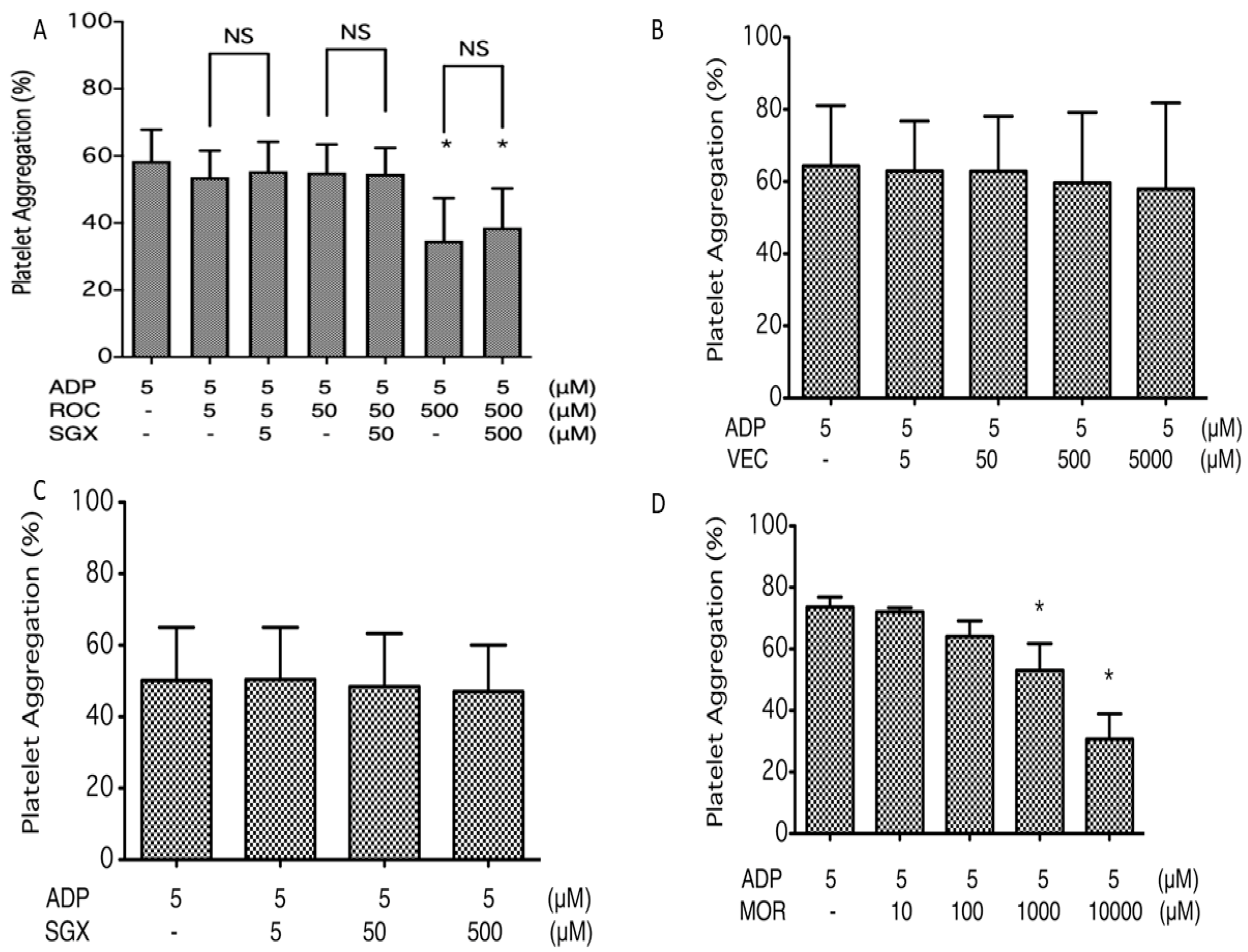
2.1. Platelet Aggregation
2.2. Flow Cytometry Analysis of P-Selectin Expression on ADP-Stimulated Platelets
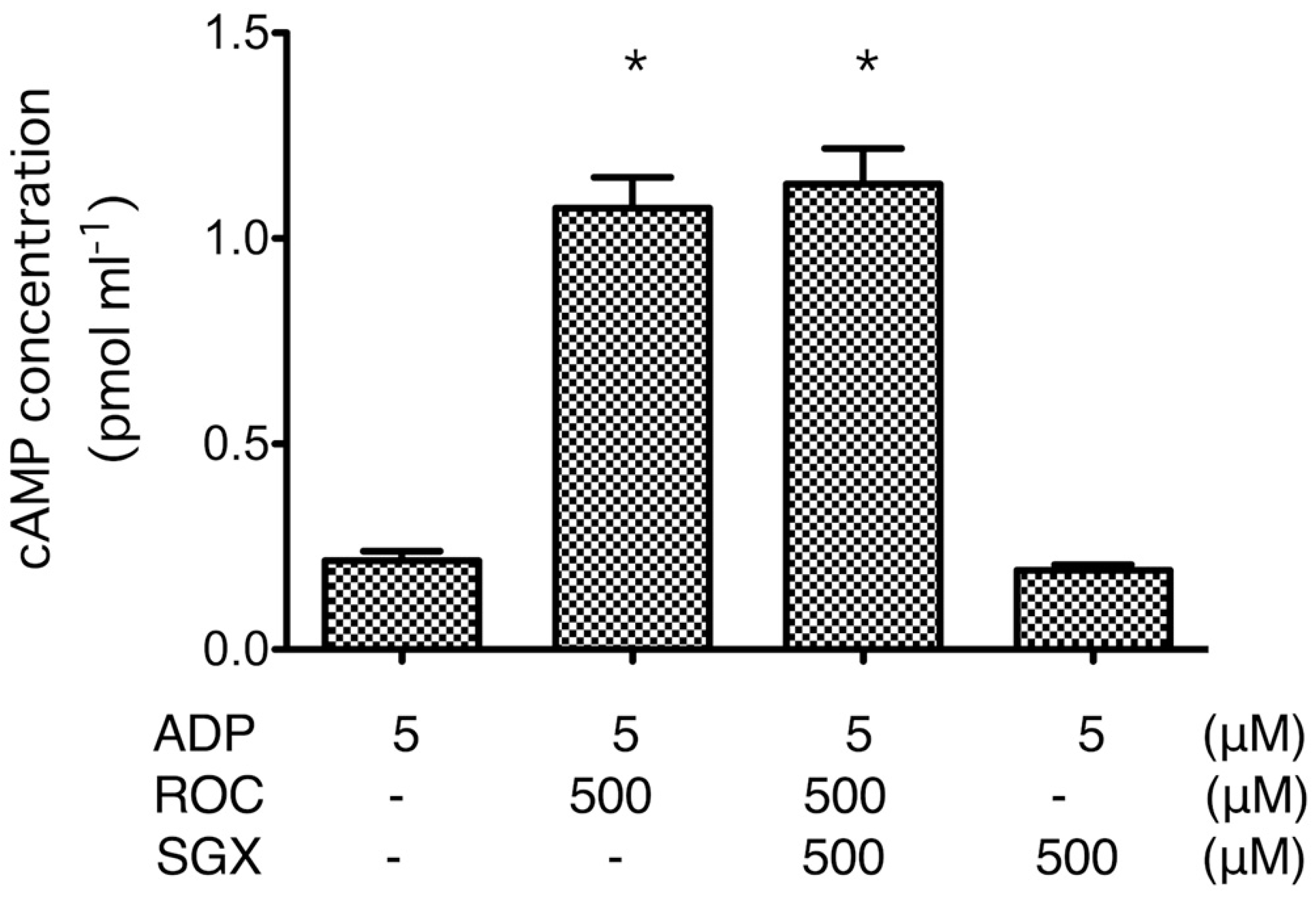
2.3. cAMP Formation
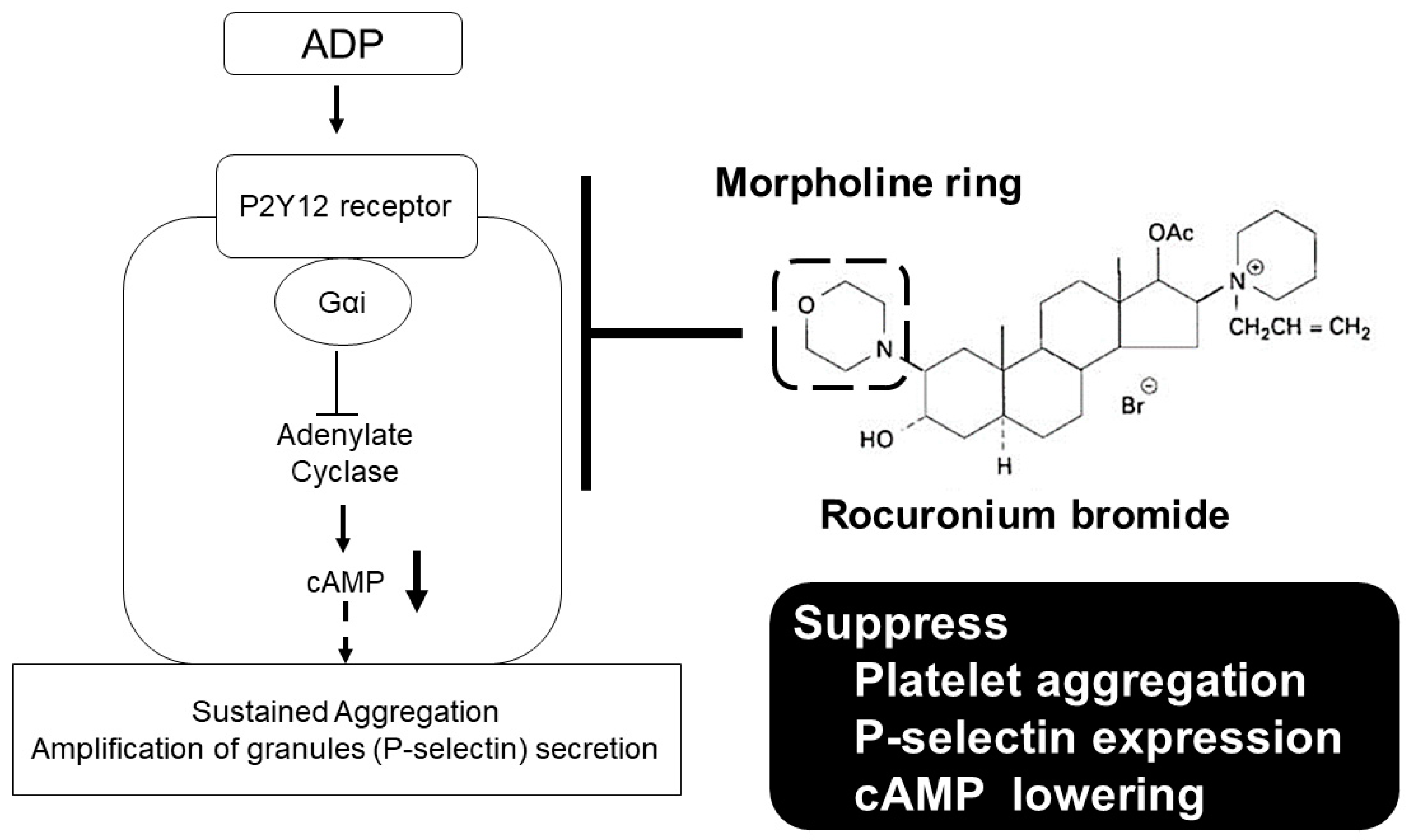
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Platelet Preparation
4.2. Chemicals and Drugs
4.3. Measurement of ADP-Induced Platelet Aggregation
4.4. Flow Cytometry Analysis of P-Selectin Expression on ADP-Stimulated Platelets
4.5. cAMP Assay
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADP | Adenosine diphosphate |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| FACS | Fluorescence-activated cell sorting |
| HEPES | N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-N′-2′-ethanesulfonic acid |
| MFI | Mean fluorescent intensity |
| MOR | Morpholine |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PE | Phycoerythrin |
| PerCP | Peridinin Chlorophyll Protein |
| PPP | Platelet-poor plasma |
| PRP | Platelet-rich plasma |
| ROC | Rocuronium |
| SGX | Sugammadex |
| VEC | Vecuronium |
References
- Hirakata, H.; Hatano, Y.; Ushikubi, F.; Mori, K.; Narumiya, S.; Nakamura, K. The Effect of Inhaled Anesthetics on the Platelet Aggregation and the Ligand-Binding Affinity of the Platelet Thromboxane A2 Receptor. Anesth. Analg. 1995, 81, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hirakata, H.; Ushikubi, F.; Toda, H.; Nakamura, K.; Sai, S.; Urabe, N.; Hatano, Y.; Narumiya, S.; Mori, K. Sevoflurane inhibits human platelet aggregation and thromboxane A 2 formation, possibly by suppression of cyclooxygenase activity. Anesthesiology 1996, 85, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirakata, H.; Nakamura, K.; Sai, S.; Okuda, H.; Hatano, Y.; Urabe, N.; Mori, K. Platelet aggregation is impaired during anaesthesia with sevoflurane but not with isoflurane. Can. J. Anaesth. 1997, 44, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hirakata, H.; Nakamura, K.; Yokubol, B.; Toda, H.; Hatano, Y.; Urabe, N.; Mori, K. Propofol Has Both Enhancing and Suppressing Eflects on Human Platelet Aggregation. Anesthesiology 1999, 91, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, T.; Hirakata, H.; Sato, M.; Nakamura, K.; Hatano, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Fukuda, K. Ketamine suppresses platelet aggregation possibly by suppressed inositol triphosphate formation and subsequent suppression of cytosolic calcium increase. Anesthesiology 2002, 96, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, S.; Hirakata, H.; Sugita, N.; Fukuda, K. Bidirectional effects of dexmedetomidine on human platelet functions in vitro. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 766, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamoto, S.; Fukuda, K. Dexmedetomidine increases human platelet-derived microparticles via the α2-adrenoceptor. J. Jpn. Soc. Intensive Care Med. 2018, 25, 457–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.M. Rocuronium: The newest aminosteroid neuromuscular blocking drug. Br. J. Anaesth. 1996, 76, 481–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, S.S. Cyclodextrins: Emerging Medicines of the New Millennium. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welliver, M.; McDonough, J.; Kalynych, N.; Redfern, R. Discovery, development, and clinical application of sugammadex sodium, a selective relaxant binding agent. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2008, 2, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahner, B.N.; Shankar, H.; Murugappan, S.; Prasad, G.L.; Kunapuli, S.P. Nucleotide receptor signaling in platelets. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 2317–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gachet, C. P2 receptors, platelet function and pharmacological implications. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 99, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keularts, I.M.L.W.; van Gorp, R.M.A.; Feijge, M.A.H.; Vuist, W.M.J.; Heemskerk, J.W.M. α 2A-Adrenergic Receptor Stimulation Potentiates Calcium Release in Platelets by Modulating cAMP Levels. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 1763–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabinger, I.; Thaler, J.; Ay, C. Biomarkers for prediction of venous thromboembolism in cancer. Blood 2013, 122, 2011–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merten, M.; Thiagarajan, P. P-Selectin Expression on Platelets Determines Size and Stability of Platelet Aggregates. Circulation 2000, 102, 1931–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christersson, C.; Johnell, M.; Siegbahn, A. Tissue factor and IL8 production by P-selectin-dependent platelet-monocyte aggregates in whole blood involves phosphorylation of Lyn and is inhibited by IL10. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, S.; Ikeda, H.; Haramaki, N.; Yasukawa, H.; Murohara, T.; Imaizumi, T. Platelet P-selectin plays an important role in arterial thrombogenesis by forming large stable platelet-leukocyte aggregates. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 45, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naim, M.J.; Alam, O.; Alam, M.J.; Alam, P.; Shrivastava, N. A review on pharmacological profile of Morpholine derivatives. Int. J. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 3, 40–51. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.M.; Xin, M.H.; Xu, J.; Kang, B.R.; Li, Y.; Lu, S.M.; Zhang, S.Q. Synthesis and antitumor activities evaluation of m-(4-morpholinoquinazolin-2-yl)benzamides in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 96, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senwar, K.R.; Sharma, P.; Reddy, T.S.; Jeengar, M.K.; Nayak, V.L.; Naidu, V.G.M.; Kamal, A.; Shankaraiah, N. Spirooxindole-derived morpholine-fused-1,2,3-triazoles: Design, synthesis, cytotoxicity and apoptosis inducing studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 102, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smelcerovic, A.; Rangelov, M.; Smelcerovic, Z.; Veljkovic, A.; Cherneva, E.; Yancheva, D.; Nikolic, G.M.; Petronijevic, Z.; Kocic, G. Two 6-(propan-2-yl)-4-methyl-morpholine-2,5-diones as new non-purine xanthine oxidase inhibitors and anti-inflammatory agents. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 55, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanum, S.A.; Begum, B.A.; Girish, V.; Khanum, N.F. Synthesis and evaluation of benzophenone-n-ethyl morpholine ethers as anti-inflammatory agents. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 6, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Kuettel, S.; Zambon, A.; Kaiser, M.; Brun, R.; Scapozza, L.; Perozzo, R. Synthesis and evaluation of antiparasitic activities of new 4-[5-(4-phenoxyphenyl)-2H-pyrazol-3-yl]morpholine derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5833–5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, H.D.; Kim, T.H.; Park, M.C.; Choi, G.; Kim, S. Identification of a new morpholine scaffold as a P2Y12 receptor antagonist. Molecules 2016, 21, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Saeki, S.; Takeda, J.; Ozaki, M.; Iwao, Y. Neuromuscular blocking effects, pharmacokinetics and safety of Org 9426 (rocuronium bromide) in Japanese patients. Masui 2006, 55, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bevan, D.R. Rocuronium bromide and organ function. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. Suppl. 1994, 9, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Magorian, T.; Wood, P.; Caldwell, J.; Fisher, D.; Segredo, V.; Szenohradszky, J.; Sharma, M.; Gruenke, L.; Miller, R. The Pharmacokinetics and Neuromuscular Effects of Rocuronium Bromide in Patients with Liver Disease. Anesth. Analg. 1995, 80, 754–759. [Google Scholar]
- Szenohradszky, J.; Fisher, D.M.; Segredo, V.; Caldwell, J.E.; Bragg, P.; Sharma, M.L.; Gruenke, L.D.; Miller, R.D. Pharmacokinetics of Rocuronium Bromide (ORG 9426) in Patients with Normal Renal Function or Patients Undergoing Cadaver Renal Transplantation. Anesthesiology 1992, 77, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteo, R.S.; Ornstein, E.; Schwartz, A.E.; Ostapkovich, N.; Stone, J.G. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Rocuronium (Org 9426) in Elderly Surgical Patients. Anesth. Analg. 1993, 77, 1193–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, S.; Nair, A.B. Cyclodextrin complexes: Perspective from drug delivery and formulation. Drug Dev. Res. 2018, 79, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.C.; Sadleir, P.H.M.; Platt, P.R. The role of sugammadex in the development and modification of an allergic response to rocuronium: Evidence from a cutaneous model. Anaesthesia 2012, 67, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limbird, L.E. Receptors linked to inhibition of adenylate cyclase: Additional signaling mechanisms. FASEB J. 1988, 2, 2686–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murata, Y.; Kawamoto, S.; Fukuda, K. Rocuronium Has a Suppressive Effect on Platelet Function via the P2Y12 Receptor Pathway In Vitro That Is Not Reversed by Sugammadex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176399
Murata Y, Kawamoto S, Fukuda K. Rocuronium Has a Suppressive Effect on Platelet Function via the P2Y12 Receptor Pathway In Vitro That Is Not Reversed by Sugammadex. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(17):6399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176399
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurata, Yutaka, Shuji Kawamoto, and Kazuhiko Fukuda. 2020. "Rocuronium Has a Suppressive Effect on Platelet Function via the P2Y12 Receptor Pathway In Vitro That Is Not Reversed by Sugammadex" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 17: 6399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176399
APA StyleMurata, Y., Kawamoto, S., & Fukuda, K. (2020). Rocuronium Has a Suppressive Effect on Platelet Function via the P2Y12 Receptor Pathway In Vitro That Is Not Reversed by Sugammadex. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(17), 6399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176399




