Advances in Oligonucleotide Aptamers for NSCLC Targeting
Abstract
1. Introduction
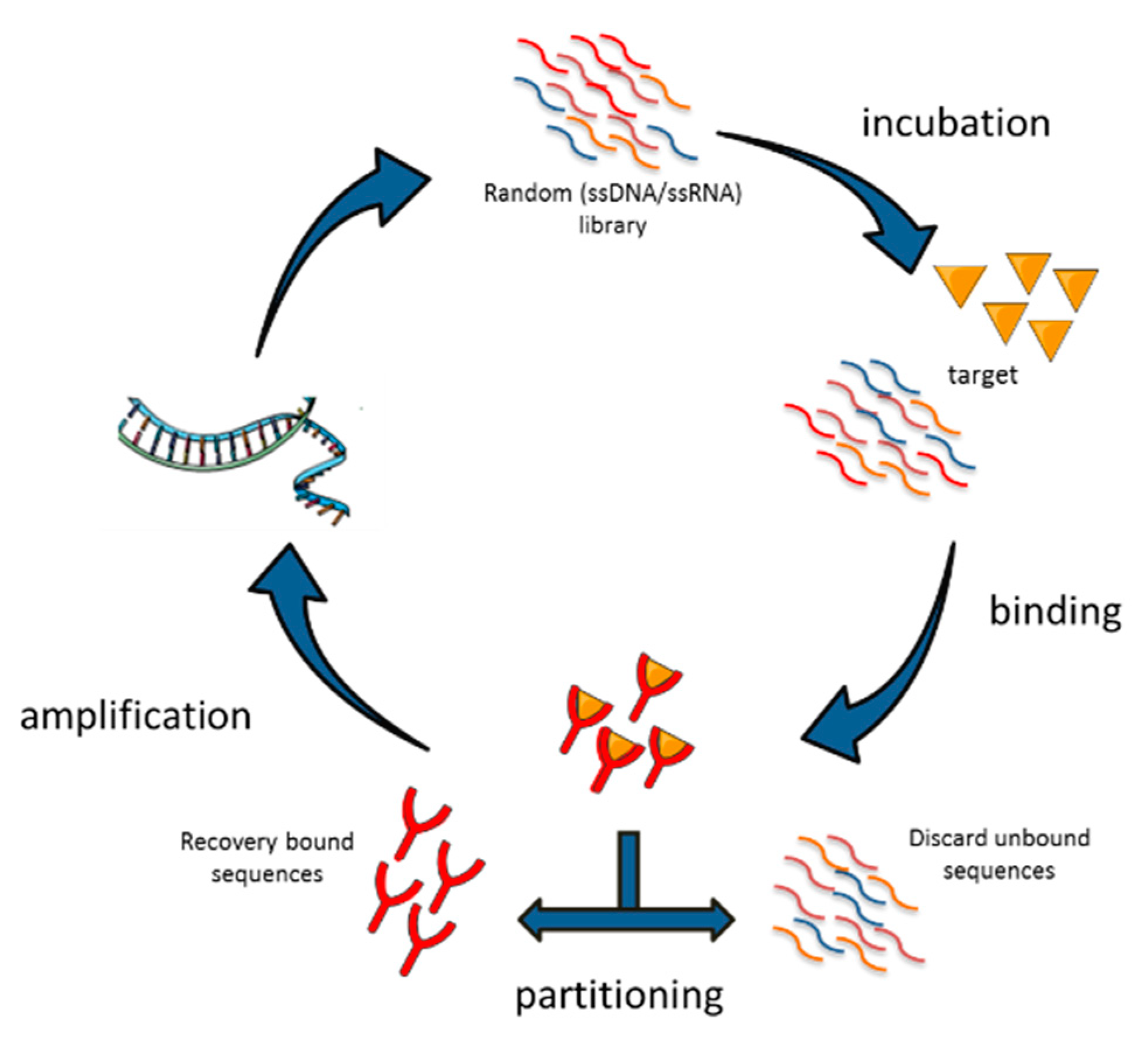
2. SELEX Technologies to Generate NSCLC Targeting Aptamers
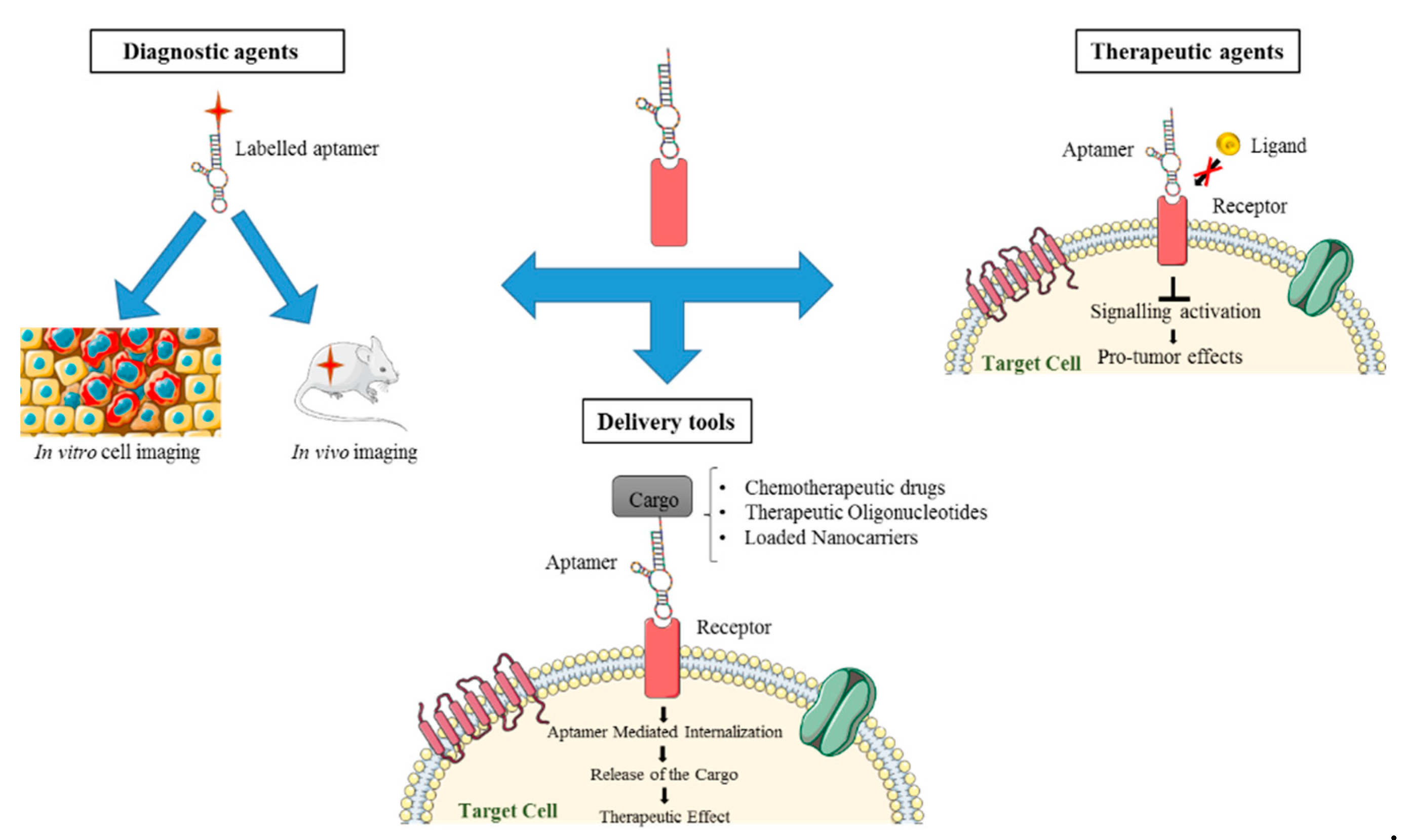
3. Nucleic Acid Aptamers for NSCLC Detection
4. Nucleic Acid Aptamers for NSCLC Therapy
5. Aptamer-Based Conjugates for Targeted Delivery in NSCLC
5.1. Aptamer-Small Molecule Conjugates
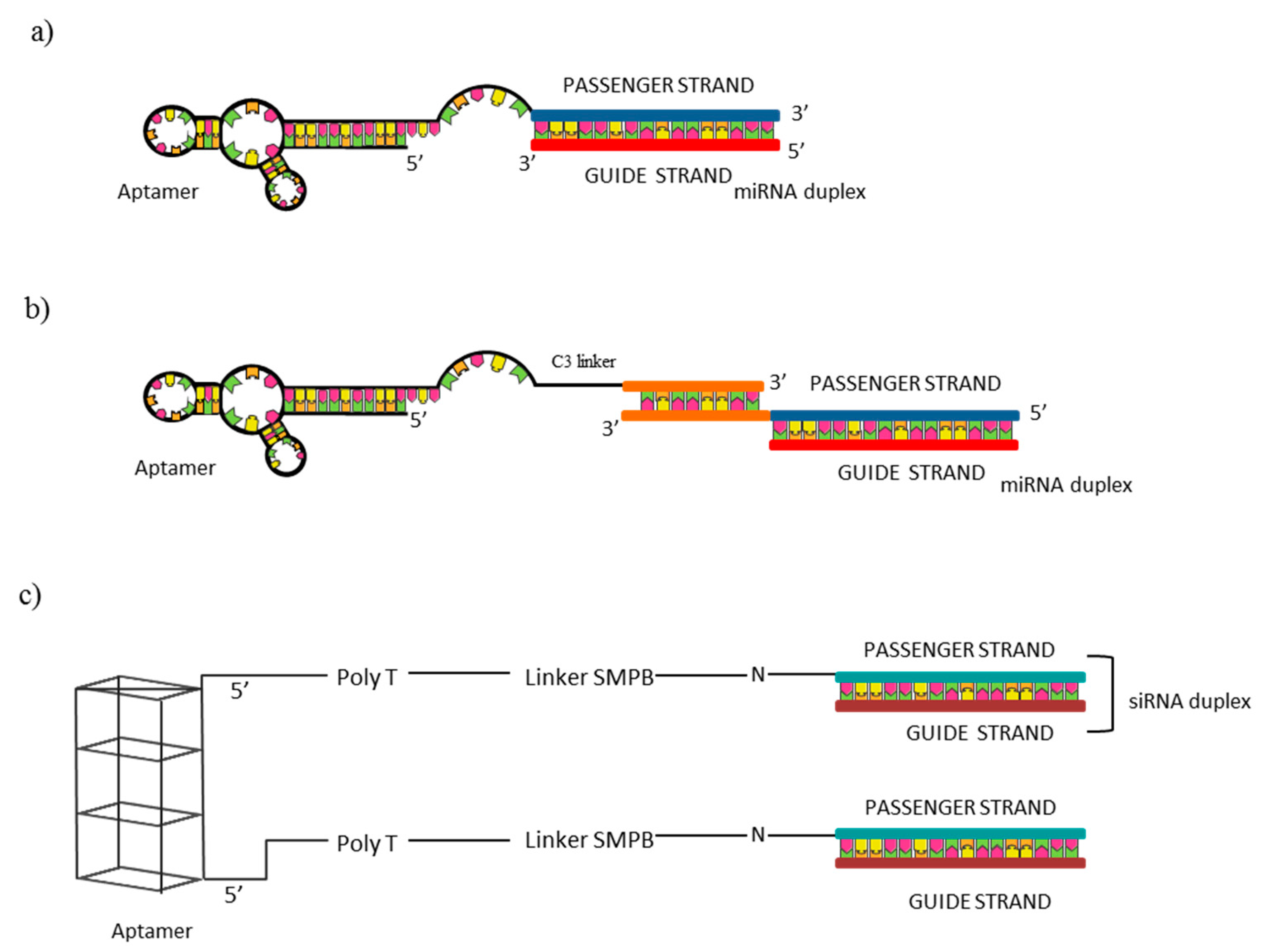
5.2. Aptamer-Therapeutic RNA Conjugates
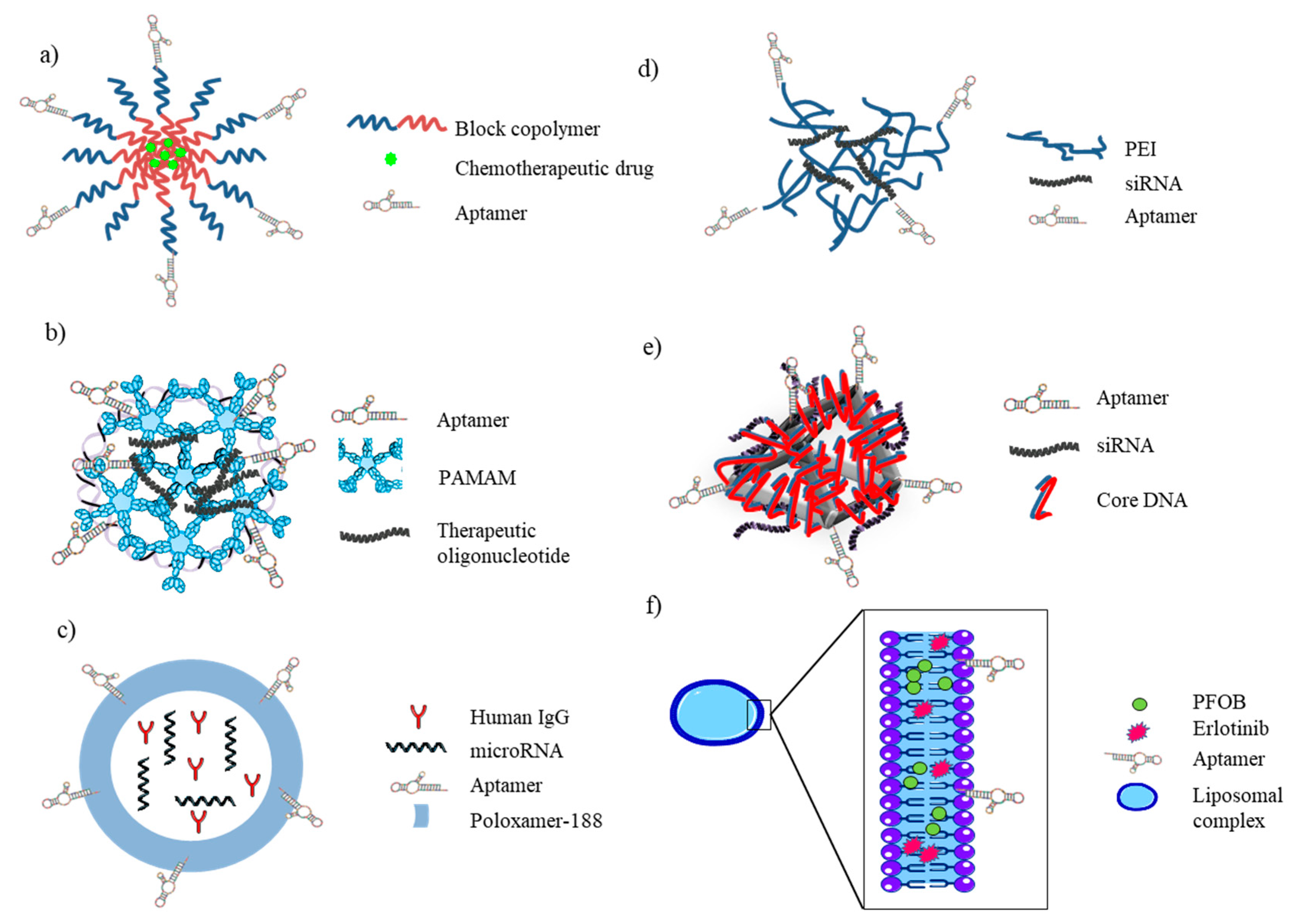
5.3. Aptamer–Nanomaterial Conjugated Systems
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, A.S.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Bunn, P.A., Jr.; Carbone, D.P.; Warren, G.W.; Bai, C.; De Koning, H.J.; Yousaf-Khan, A.U.; McWilliams, A.; Tsao, M.S. Scientific advances in lung cancer 2015. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 613–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, U.; Castelli, G.; Pelosi, E. Lung cancers: Molecular characterization, clonal heterogeneity and evolution, and cancer stem cells. Cancers 2018, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Huang, L.-L.; Chen, J.-H.; Wu, J.; Xu, Q. The emerging treatment landscape of targeted therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Signal. Transduct. Targ. Ther. 2019, 4, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, C.J.; Mok, T.; Postmus, P.E. Targeted agents in the third-/fourth-line treatment of patients with advanced (stage III/IV) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Cancer Treat. Rev. 2013, 39, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomi, P.D. Treatment of Stage IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Prog. Respir. Res. 1997, 29, 56–72. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, B.; Zhang, X. Aptamers as Versatile Ligands for Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Xiang, J. Aptamers, the Nucleic Acid Antibodies, in Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Rossi, J. Aptamers as targeted therapeutics: Current potential and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catuogno, S.; Esposito, C.L.; de Franciscis, V. Aptamer-Mediated Targeted Delivery of Therapeutics: An Update. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catuogno, S.; Esposito, C.L. Aptamer Cell-Based Selection: Overview and Advances. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Xu, L.; Shi, X.; Tan, W.; Fang, X.; Shangguan, D. Recognition of subtype non-small cell lung cancer by DNA aptamers selected from living cells. Analyst 2009, 134, 1808–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidic, M.; Smuc, T.; Janez, N.; Blank, M.; Accetto, T.; Mavri, J.; Nascimento, I.C.; Nery, A.A.; Ulrich, H.; Lah, T.T. In Silico Selection Approach to Develop DNA Aptamers for a Stem-like Cell Subpopulation of Non-small Lung Cancer Adenocarcinoma Cell Line A549. Radiol. Oncol. 2018, 52, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Luo, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, B.; Wang, Y.; Bian, X. Identification of CD90 as a marker for lung cancer stem cells in A549 and H446 cell lines. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 2733–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, C.L.; Passaro, D.; Longobardo, I.; Condorelli, G.; Marotta, P.; Affuso, A.; de Franciscis, V.; Cerchia, L. A neutralizing RNA aptamer against EGFR causes selective apoptotic cell death. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catuogno, S.; Esposito, C.L.; de Franciscis, V. Developing Aptamers by Cell-Based SELEX. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1380, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamay, G.S.; Kolovskaya, O.S.; Zamay, T.N.; Glazyrin, Y.E.; Krat, A.V.; Zubkova, O.; Spivak, E.; Wehbe, M.; Gargaun, A.; Muharemagic, D.; et al. Aptamers Selected to Postoperative Lung Adenocarcinoma Detect Circulating Tumor Cells in Human Blood. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 1486–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamay, G.; Kolovskaya, O.; Ivanchenko, T.; Zamay, T.; Veprintsev, D.; Grigorieva, V.; Garanzha, I.; Krat, A.; Glazyrin, Y.; Gargaun, A.; et al. Development of DNA Aptamers to Native EpCAM for Isolation of Lung Circulating Tumor Cells from Human Blood. Cancers 2019, 11, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeuerle, P.A.; Gires, O. EpCAM (CD326) finding its role in cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joosse, S.A.; Pantel, K. Biologic challenges in the detection of circulating tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Qin, M.; Ding, X.; Liu, R.; Jiang, Y. In Vivo SELEX of an Inhibitory NSCLC-Specific RNA Aptamer from PEGylated RNA Library. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 10, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; He, W.; Jiang, H.; Wu, L.; Xiong, W.; Li, B.; Zhou, Z.; Qian, Y. In vivo SELEX of bone targeting aptamer in prostate cancer bone metastasis model. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Chen, Y.H.; Lennox, K.A.; Behlke, M.A.; Davidson, B.L. In vivo SELEX for Identification of Brain-penetrating Aptamers. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2013, 2, e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civit, L.; Theodorou, I.; Frey, F.; Weber, H.; Lingnau, A.; Grober, C.; Blank, M.; Dambrune, C.; Stunden, J.; Beyer, M.; et al. Targeting hormone refractory prostate cancer by in vivo selected DNA libraries in an orthotopic xenograft mouse model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Tang, C.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Hu, H.; Cheng, S.; Zhou, W.; Huang, M.; Fong, A.; et al. Enhanced and Differential Capture of Circulating Tumor Cells from Lung Cancer Patients by Microfluidic Assays Using Aptamer Cocktail. Small 2016, 12, 1072–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, M.G.; Sloane, R.; Priest, L.; Lancashire, L.; Hou, J.-M.; Greystoke, A.; Ward, T.H.; Ferraldeschi, R.; Hughes, A.; Clack, G.; et al. Evaluation and Prognostic Significance of Circulating Tumor Cells in Patients With Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1556–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W. Capturing Cancer: Emerging Microfluidic Technologies for the Capture and Characterization of Circulating Tumor Cells. Small 2015, 11, 3850–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalik, A.; Kowalewska, M.; Gozdz, S. Current approaches for avoiding the limitations of circulating tumor cells detection methods-implications for diagnosis and treatment of patients with solid tumors. Transl. Res. 2017, 185, 58–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Xu, L.; Zhao, L.; Wu, D.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ouyang, W.H.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Song, M.; et al. Specific capture and release of circulating tumor cells using aptamer-modified nanosubstrates. Adv. Mat. 2013, 25, 2368–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Tang, C.; Zhao, L.; Xu, J.; Yayun, W.; Tang, X.; Zhou, W.; He, R.; Zhao, R.; Xu, L.; et al. A Microwell-Assisted Multiaptamer Immunomagnetic Platform for Capture and Genetic Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells. Adv. Healthc. Mat. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, P.; Li, J.; Ji, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, K. A recognition-before-labeling strategy for sensitive detection of lung cancer cells with a quantum dot–aptamer complex. Analyst 2015, 140, 6100–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xiang, J.; Mao, Z.; Shen, G.; Yang, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Du, N.; Zhang, J. Ultrasensitive and high specific detection of non-small-cell lung cancer cells in human serum and clinical pleural effusion by aptamer-based fluorescence spectroscopy. Talanta 2018, 179, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Xiang, J.; Yang, S.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Guan, A.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Y.; Xu, G. Verification of specific G-quadruplex structure by using a novel cyanine dye supramolecular assembly: II. The binding characterization with specific intramolecular G-quadruplex and the recognizing mechanism. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 1022–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mir, T.A.; Yoon, J.H.; Gurudatt, N.G.; Won, M.S.; Shim, Y.B. Ultrasensitive cytosensing based on an aptamer modified nanobiosensor with a bioconjugate: Detection of human non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamay, G.S.; Ivanchenko, T.I.; Zamay, T.N.; Grigorieva, V.L.; Glazyrin, Y.E.; Kolovskaya, O.S.; Garanzha, I.V.; Barinov, A.A.; Krat, A.V.; Mironov, G.G.; et al. DNA Aptamers for the Characterization of Histological Structure of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 6, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehan, M.R.; Ostroff, R.; Wilcox, S.K.; Steele, F.; Schneider, D.; Jarvis, T.C.; Baird, G.S.; Gold, L.; Janjic, N. Highly multiplexed proteomic platform for biomarker discovery, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 735, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.J.; Oh, I.-J.; Kim, Y.; Jung, J.H.; Seok, M.; Lee, W.; Park, C.K.; Lim, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-C.; Kim, W.-S.; et al. Clinical Validation of a Protein Biomarker Panel for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Kor. Med. Sci. 2018, 33, 1109814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.J.; Katilius, E.; Ostroff, R.M.; Kim, Y.; Seok, M.; Lee, S.; Jang, S.; Kim, W.S.; Choi, C.-M. Development of a Protein Biomarker Panel to Detect Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer in Korea. Clin. Lung Cancer 2017, 18, e99–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdian-Robati, R.; Ramezani, M.; Khedri, M.; Ansari, N.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M. An aptamer for recognizing the transmembrane protein PDL-1 (programmed death-ligand 1), and its application to fluorometric single cell detection of human ovarian carcinoma cells. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 4029–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunath, Y.; Upparahalli, S.V.; Avella, D.M.; Deroche, C.B.; Kimchi, E.T.; Staveley-O’Carroll, K.F.; Smith, C.J.; Li, G.; Kaifi, J.T. PD-L1 Expression with Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition of Circulating Tumor Cells Is Associated with Poor Survival in Curatively Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, P.J.; Laber, D.A.; Miller, D.M.; Thomas, S.D.; Trent, J.O. Discovery and development of the G-rich oligonucleotide AS1411 as a novel treatment for cancer. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009, 86, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Reyes, E.M.; Šalipur, F.R.; Shams, M.; Forsthoefel, M.K.; Bates, P.J. Mechanistic studies of anticancer aptamer AS1411 reveal a novel role for nucleolin in regulating Rac1 activation. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 1392–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltese, W.A.; Overmeyer, J.H. Methuosis: Nonapoptotic cell death associated with vacuolization of macropinosome and endosome compartments. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 1630–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanot, H.; Young, A.M.; Overmeyer, J.H.; Maltese, W.A. Induction of nonapoptotic cell death by activated Ras requires inverse regulation of Rac1 and Arf6. Mol. Cancer Res. 2010, 8, 1358–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerchia, L.; Esposito, C.L.; Camorani, S.; Rienzo, A.; Stasio, L.; Insabato, L.; Affuso, A.; De Franciscis, V. Targeting Axl with an high-affinity inhibitory aptamer. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 2291–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamay, T.N.; Kolovskaya, O.S.; Glazyrin, Y.E.; Zamay, G.S.; Kuznetsova, S.A.; Spivak, E.A.; Wehbe, M.; Savitskaya, A.G.; Zubkova, O.A.; Kadkina, A.; et al. DNA-aptamer targeting vimentin for tumor therapy in vivo. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2014, 24, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.Y.; Huang, B.T.; Wang, J.W.; Lin, P.Y.; Yang, P.C. A Novel PD-L1-targeting Antagonistic DNA Aptamer with Antitumor Effects. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajona, D.; Ortiz-Espinosa, S.; Moreno, H.; Lozano, T.; Pajares, M.J.; Agorreta, J.; Bertolo, C.; Lasarte, J.J.; Vicent, S.; Hoehlig, K.; et al. A Combined PD-1/C5a Blockade Synergistically Protects against Lung Cancer Growth and Metastasis. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodeus, A.; Abdul-Wahid, A.; Fischer, N.W.; Huang, E.H.; Cydzik, M.; Gariépy, J. Targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 Immune Evasion Axis with DNA Aptamers as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy for the Treatment of Disseminated Cancers. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2015, 4, e237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangavelu Devaraj, S.G.; Ganesh Lakshmana Rao, L.; Zu, Y.; Chang, J.; Iyer, S.P. DNA Aptamer Against Anti- Programmed Cell Death-1 (Anti-PD1-Apt) Induces Robust Anti-Leukemic Activity In Vitro and In Vivo Humanized NSG Mice with Myeloid Leukemia Xenografts. Blood 2017, 130, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qin, M.; Liu, R.; Ding, X.; Chen, I.S.Y.; Jiang, Y. Characterization of A Bifunctional Synthetic RNA Aptamer and A Truncated Form for Ability to Inhibit Growth of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieleba, I.; Wojas-Krawczyk, K.; Krawczyk, P. Aptamers in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, K.; Min, S.W.; Sung, H.J.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Choi, B.K.; Han, S.; Chung, S.; Lee, E.S.; et al. An aptamer-antibody complex (oligobody) as a novel delivery platform for targeted cancer therapies. J. Control. Release 2016, 229, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera-Puente, O.; Rodriguez-Antolin, C.; Salgado-Figueroa, A.; Michalska, P.; Pernia, O.; Reid, B.M.; Rosas, R.; Garcia-Guede, A.; Sacristán, S.; Jimenez, J.; et al. MAFG is a potential therapeutic target to restore chemosensitivity in cisplatin-resistant cancer cells by increasing reactive oxygen species. Transl. Res. 2018, 200, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelberg, S.; Netzer, E.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Livney, Y.D. Selective eradication of human non-small cell lung cancer cells using aptamer-decorated nanoparticles harboring a cytotoxic drug cargo. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Bobbin, M.L.; Burnett, J.C.; Rossi, J.J. Current progress of RNA aptamer-based therapeutics. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Duan, J.; Zhan, Q.; Wang, F.; Lu, X.; Yang, X.D. Novel MUC1 aptamer selectively delivers cytotoxic agent to cancer cells in vitro. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganson, N.J.; Povsic, T.J.; Sullenger, B.A.; Alexander, J.H.; Zelenkofske, S.L.; Sailstad, J.M.; Rusconi, C.P.; Hershfield, M.S. Pre-existing anti-polyethylene glycol antibody linked to first-exposure allergic reactions to pegnivacogin, a PEGylated RNA aptamer. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1610–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povsic, T.J.; Lawrence, M.G.; Lincoff, A.M.; Mehran, R.; Rusconi, C.P.; Zelenkofske, S.L.; Huang, Z.; Sailstad, J.; Armstrong, P.W.; Steg, P.G.; et al. Pre-existing anti-PEG antibodies are associated with severe immediate allergic reactions to pegnivacogin, a PEGylated aptamer. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1712–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, A.; Pitoc, G.A.; Ganson, N.J.; Layzer, J.M.; Hershfield, M.S.; Tarantal, A.F.; Sullenger, B.A. Anti-PEG Antibodies Inhibit the Anticoagulant Activity of PEGylated Aptamers. Cell Chem. Biol. 2019, 26, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, S.-I.; Herrera, A.; Rossi, J.J.; Zhou, J. Current advances in aptamers for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Cancers 2018, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, Z.; Yu, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Lu, A.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, B. Recent Advances in SELEX Technology and Aptamer Applications in Biomedicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, C.L.; Cerchia, L.; Catuogno, S.; De Vita, G.; Dassie, J.P.; Santamaria, G.; Swiderski, P.; Condorelli, G.; Giangrande, P.H.; de Franciscis, V. Multifunctional aptamer-miRNA conjugates for targeted cancer therapy. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 1151–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaboni, M.; Russo, V.; Fontanella, R.; Roscigno, G.; Fiore, D.; Donnarumma, E.; Esposito, C.L.; Quintavalle, C.; Giangrande, P.H.; de Franciscis, V. Aptamer-miRNA-212 conjugate sensitizes NSCLC cells to TRAIL. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, V.; Paciocco, A.; Affinito, A.; Roscigno, G.; Fiore, D.; Palma, F.; Galasso, M.; Volinia, S.; Fiorelli, A.; Esposito, C.L.; et al. Aptamer-miR-34c Conjugate Affects Cell Proliferation of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 13, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzzo, S.; Catuogno, S.; Capuozzo, M.; Fiorelli, A.; Swiderski, P.; Boccella, S.; de Nigris, F.; Esposito, C.L. Axl-Targeted Delivery of the Oncosuppressor miR-137 in Non-small-Cell Lung Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 17, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.-Y.; Wang, W.-Y.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-J.; Yang, P.-C.; Peck, K. Synergistic inhibition of lung cancer cell invasion, tumor growth and angiogenesis using aptamer-siRNA chimeras. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 2905–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhu, X.; Lu, P.Y.; Rosato, R.R.; Tan, W.; Zu, Y. Oligonucleotide aptamers: New tools for targeted cancer therapy. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelberg, S.; Modrejewski, J.; Walter, J.G.; Livney, Y.D.; Assaraf, Y.G. Cancer cell-selective, clathrin-mediated endocytosis of aptamer decorated nanoparticles. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 20993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, X.; Guo, C.; Ren, D.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, W.; Jiao, W. Aptamer-dendrimer bioconjugates for targeted delivery of miR-34a expressing plasmid and antitumor effects in non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiggins, J.F.; Ruffino, L.; Kelnar, K.; Omotola, M.; Patrawala, L.; Brown, D.; Bader, A.G. Development of a lung cancer therapeutic based on the tumor suppressor microRNA-34. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 5923–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, C.; Matthews, C.; Missailidis, S. DNA aptamers that bind to MUC1 tumour marker: Design and characterization of MUC1-binding single-stranded DNA aptamers. Tumor Biol. 2006, 27, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M.J.; Margue, C.; Behrmann, I.; Kreis, S. MiRNA-29: A microRNA family with tumor-suppressing and immune-modulating properties. Curr. Mol. Med. 2013, 13, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perepelyuk, M.; Maher, C.; Lakshmikuttyamma, A.; Shoyele, S.A. Aptamer-hybrid nanoparticle bioconjugate efficiently delivers miRNA-29b to non-small-cell lung cancer cells and inhibits growth by downregulating essential oncoproteins. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 3533. [Google Scholar]
- Perepelyuk, M.; Sacko, K.; Thangavel, K.; Shoyele, S.A. Evaluation of MUC1-aptamer functionalized hybrid nanoparticles for targeted delivery of miRNA-29b to nonsmall cell lung cancer. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacko, K.; Thangavel, K.; Shoyele, S.A. Codelivery of genistein and miRNA-29b to A549 cells using aptamer-hybrid nanoparticle bioconjugates. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosaki, T.; Higuchi, N.; Kawakami, S.; Higuchi, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Kitahara, T.; Hashida, M.; Sasaki, H. Self-assemble gene delivery system for molecular targeting using nucleic acid aptamer. Gene 2012, 491, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, D.; Xu, Z.; Huang, C.; Zhang, C.; He, B.; Mao, C.; Wang, G.; Qian, H. Targeted delivery of Rab26 siRNA with precisely tailored DNA prism for lung cancer therapy. ChemBioChem 2019, 20, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarian, S.; Abnous, K.; Taghavi, S.; Oskuee, R.K.; Ramezani, M. Cellular delivery of shRNA using aptamer-conjugated PLL-alkyl-PEI nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayatollahi, S.; Salmasi, Z.; Hashemi, M.; Askarian, S.; Oskuee, R.K.; Abnous, K.; Ramezani, M. Aptamer-targeted delivery of Bcl-xL shRNA using alkyl modified PAMAM dendrimers into lung cancer cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2017, 92, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibolandi, M.; Ramezani, M.; Abnous, K.; Hadizadeh, F. AS1411 Aptamer-Decorated Biodegradable Polyethylene Glycol-Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanopolymersomes for the Targeted Delivery of Gemcitabine to Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer In Vitro. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Shi, Y.S.; Wu, X.D.; Liang, H.Y.; Gao, Y.B.; Li, S.J.; Zhang, X.M.; Wang, F.; Gao, T.M. DNA aptamers that target human glioblastoma multiforme cells overexpressing epidermal growth factor receptor variant III in vitro. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Mei, H.; Gao, Y.; Xie, X.; Nie, H.; Li, T.; Zhang, H.; Jia, L. Co-delivery of oxygen and erlotinib by aptamer-modified liposomal complexes to reverse hypoxia-induced drug resistance in lung cancer. Biomaterials 2017, 145, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altieri, D.C. Survivin, cancer networks and pathway-directed drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krepela, E.; Dankova, P.; Moravcikova, E.; Krepelova, A.; Prochazka, J.; Cermak, J.; Schutzner, J.; Zatloukal, P.; Benkova, K. Increased expression of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins, survivin and XIAP, in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 35, 1449–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; Li, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Gao, Y. Chloroquine in combination with aptamer modified nanocomplexes for tumor vessel normalization and efficient erlotinib/Survivin-shRNA co-delivery to overcome drug resistance in EGFR-mutated NSCLC. Acta Biomater. 2018, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigdar, S.; Lin, J.; Yu, Y.; Pastuovic, M.; Wei, M.; Duan, W. RNA aptamer against a cancer stem cell marker epithelial cell adhesion molecule. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibolandi, M.; Ramezani, M.; Abnous, K.; Sadeghi, F.; Atyabi, F.; Asouri, M.; Ahmadi, A.A.; Hadizadeh, F. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of therapy targeting epithelial-cell adhesion-molecule aptamers for non-small cell lung cancer. J. Control Release 2015, 209, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibolandi, M.; Ramezani, M.; Sadeghi, F.; Abnous, K.; Hadizadeh, F. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule aptamer conjugated PEG-PLGA nanopolymersomes for targeted delivery of doxorubicin to human breast adenocarcinoma cell line in vitro. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 479, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigdar, S.; Qiao, L.; Zhou, S.F.; Xiang, D.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Lim, L.Y.; Kong, L.; Li, L.; Duan, W. RNA aptamers targeting cancer stem cell marker CD133. Cancer Lett. 2013, 330, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ababneh, N.; Alshaer, W.; Allozi, O.; Mahafzah, A.; El-Khateeb, M.; Hillaireau, H.; Noiray, M.; Fattal, E.; Ismail, S. In vitro selection of modified RNA aptamers against CD44 cancer stem cell marker. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2013, 23, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Wan, J.; Leng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S. Dual-targeting nanomicelles with CD133 and CD44 aptamers for enhanced delivery of gefitinib to two populations of lung cancer-initiating cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Morgensztern, D.; Boshoff, C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 2018, 553, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laber, D.A.; Taft, B.S.; Kloecker, G.H.; Bates, P.J.; Trent, J.O.; Miller, D.M. Extended phase I study of AS1411 in renal and non-small cell lung cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 13098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Type of SELEX | Type of Library | Counter-Selection Target | Selection Target | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Differential-cell SELEX | ssDNAs | HLAMP cells | A549 cells | [14] |
| Differential-cell SELEX | ssDNAs | Human blood cells | CD90+ A549 cells | [15] |
| Differential-cell SELEX | 2′F-Py-RNAs | H460 cells | A549 cells | [17] |
| Differential-cell SELEX | ssDNAs | Cells from healthy lung tissues and blood cells from healthy person | Lung cells derived from postoperative adenocarcinoma tissues | [19] |
| Competitive-cell SELEX | ssDNAs | – | Primary lung cancer cells overexpressing EpCAM | [20] |
| In vivo SELEX | 2′F-Py-PEG-RNAs | – | NCI-H460 tumor xenograft mice | [23] |
| Aptamer | Target | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Aptamer Pool | NSCLC Subtypes | [14] |
| S1, S6, S11e, S15 | Lung adenocarcinoma cells | |
| Ap1, Ap2, Ap3, Ap4 aptamer cocktails | NSCLC CTCs | [27] |
| Ap1–MNP, ap2–MNP cocktail | A549 cells, A549D cells, NSCLC CTCs | [32] |
| LC-183, LC17, LC-18, LC-110 | Lung adenocarcinoma CTCs | [19] |
| ECM-APT-01 ECM-APT-02 | EpCAM+ CTCs | [20] |
| A155_18 | CD90+ A549 cells | [15] |
| S11e-QDs | Lung adenocarcinoma cells | [33] |
| S6–cyM | Lung adenocarcinoma cells | [34] |
| apt/TTBA/AuNP + Hyd/AuNP/Apt | MUC1+ NSCLC cells | [36] |
| Aptamer | Target | Therapeutic Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| AS1411 | Nucleolin | Antiproliferative activity in vitro | [44] |
| CL4 | EGFR | Induction of cell death in vitro and tumor growth inhibition in vivo | [17] |
| GL21.T | Axl | Inhibition of cell viability, migration and colony formation in vitro and tumor growth inhibition in vivo | [47] |
| NAS-24 | vimentin | Induction of apoptosis in vitro and in Ehrlich ascites adenocarcinoma mouse models of the aptamer linked to a natural polysaccharide arabinogalactan | [48] |
| aptPD–L1 | PD–L1 | Inhibition of PD–1–PD–L1 interaction and of tumor growth in vivo | [49] |
| C5a aptamer | C5a | Inhibition of C5a signaling and synergistic reduction of tumor growth and metastasis in combination with anti-PD1 antibody in vivo | [50] |
| RA16 and its truncated form S3 | NSCLC NCI-H460 cells (specific target not been identified) | Inhibition of cancer cell proliferation both in vitro and in vivo | [53] |
| apMAFG6F | MAFG | Restoration of cisplatin sensitivity | [56] |
| Pegaptanib | VEGF-165 | Reduction of tumor growth with good tumor penetration and extended pharmacokinetics in vivo when complexed to the anti-cotinine antibody | [55] |
| Aptamer | Conjugated System | Cargo | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| MUC1 | Chemotherapeutic drug | doxorubicin (DOX) | [59] |
| Loaded nanoparticle | microRNA-29 | [76,77] | |
| microRNA-29 and genistein | [78] | ||
| pDNA | [79] | ||
| rab26 siRNA | [80] | ||
| RA16 | Chemotherapeutic drug | epirubicin (EPI) | [23] |
| GL21.T | Therapeutic oligonucleotide | let-7 g miRNA | [65] |
| miR-212 | [66] | ||
| miR-137 | [62] | ||
| miR-34c | [67] | ||
| S15 | Loaded nanoparticle | paclitaxel (PTX) | [57] |
| S6 | Loaded nanoparticle | miR-34a | [72] |
| AS1411 | Therapeutic oligonucleotide | SLUGsiR and NRP1siR | [69] |
| Loaded nanoparticle | Bcl-xL shRNA | [81,82] | |
| gemcitabine (GEM) | [83] | ||
| anti-EGFR | Loaded nanoparticle | erlotinib & PFOB | [85] |
| erlotinib & Survivin shRNA | [88] | ||
| anti-EpCAM | Loaded nanoparticle | doxorubicin (DOX) | [90] |
| CD133 and CD44 | Loaded nanoparticle | gefitinib (Gef) | [94] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rotoli, D.; Santana-Viera, L.; Ibba, M.L.; Esposito, C.L.; Catuogno, S. Advances in Oligonucleotide Aptamers for NSCLC Targeting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176075
Rotoli D, Santana-Viera L, Ibba ML, Esposito CL, Catuogno S. Advances in Oligonucleotide Aptamers for NSCLC Targeting. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(17):6075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176075
Chicago/Turabian StyleRotoli, Deborah, Laura Santana-Viera, Maria L. Ibba, Carla L. Esposito, and Silvia Catuogno. 2020. "Advances in Oligonucleotide Aptamers for NSCLC Targeting" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 17: 6075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176075
APA StyleRotoli, D., Santana-Viera, L., Ibba, M. L., Esposito, C. L., & Catuogno, S. (2020). Advances in Oligonucleotide Aptamers for NSCLC Targeting. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(17), 6075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176075






