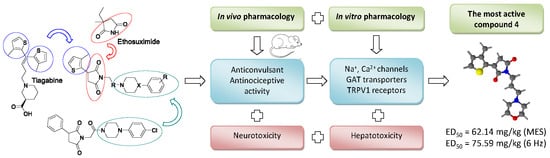
Synthesis, Anticonvulsant and Antinociceptive Activity of New Hybrid Compounds: Derivatives of 3-(3-Methylthiophen-2-yl)-pyrrolidine-2,5-dione
Abstract
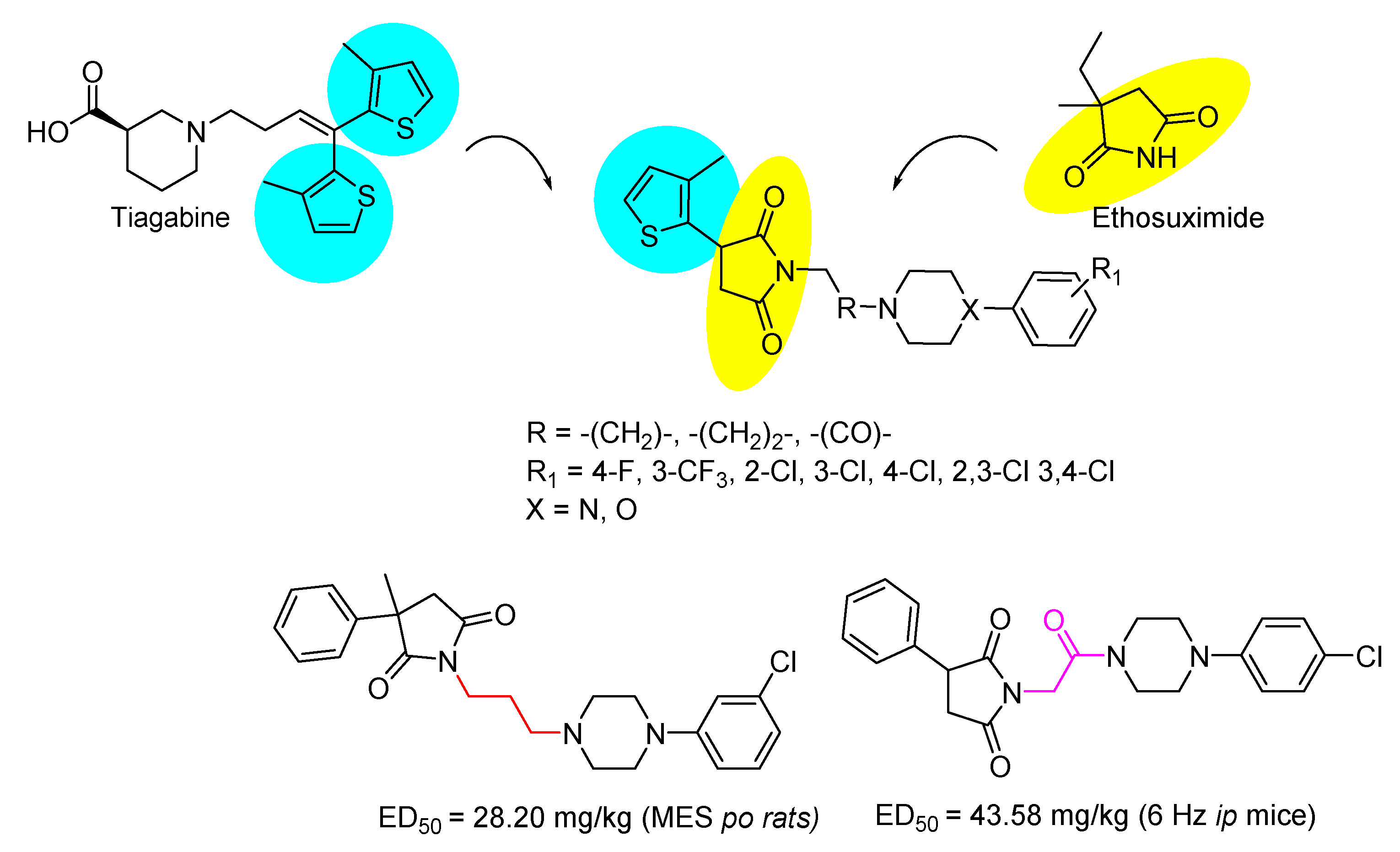
1. Introduction
2. Results
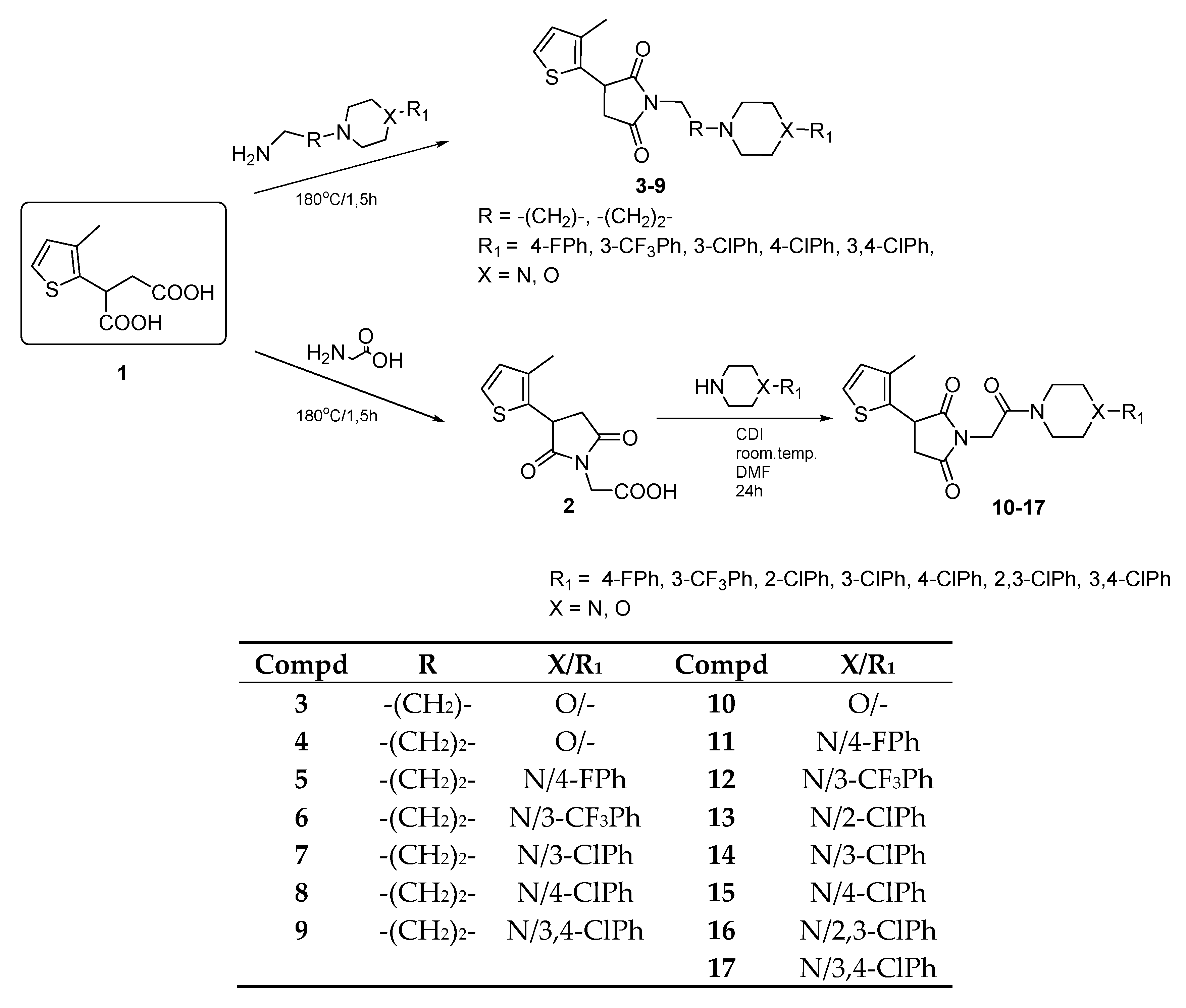
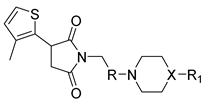
2.1. Chemical Synthesis and Drug Likeness Properties
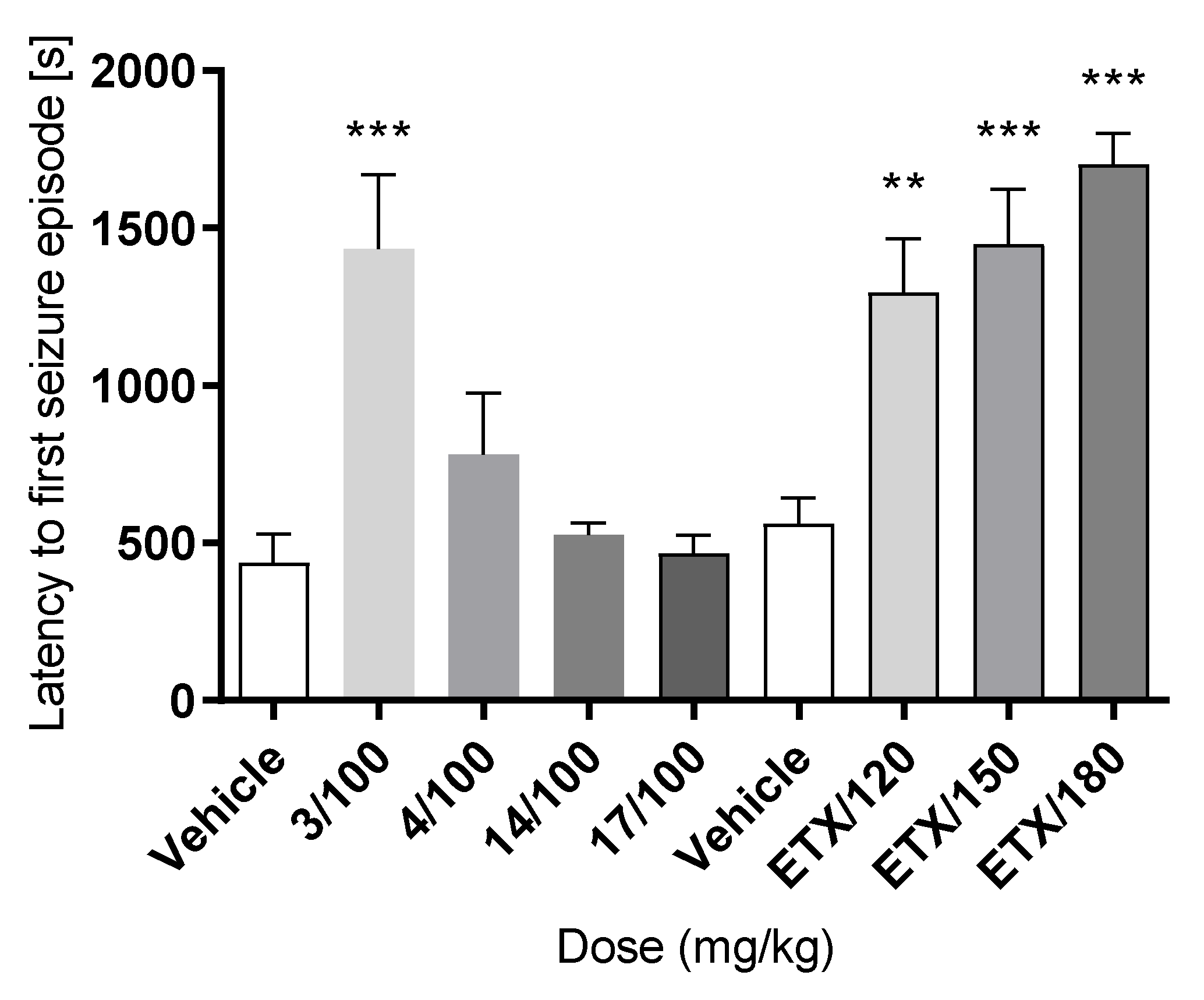
2.2. Anticonvulsant Activity
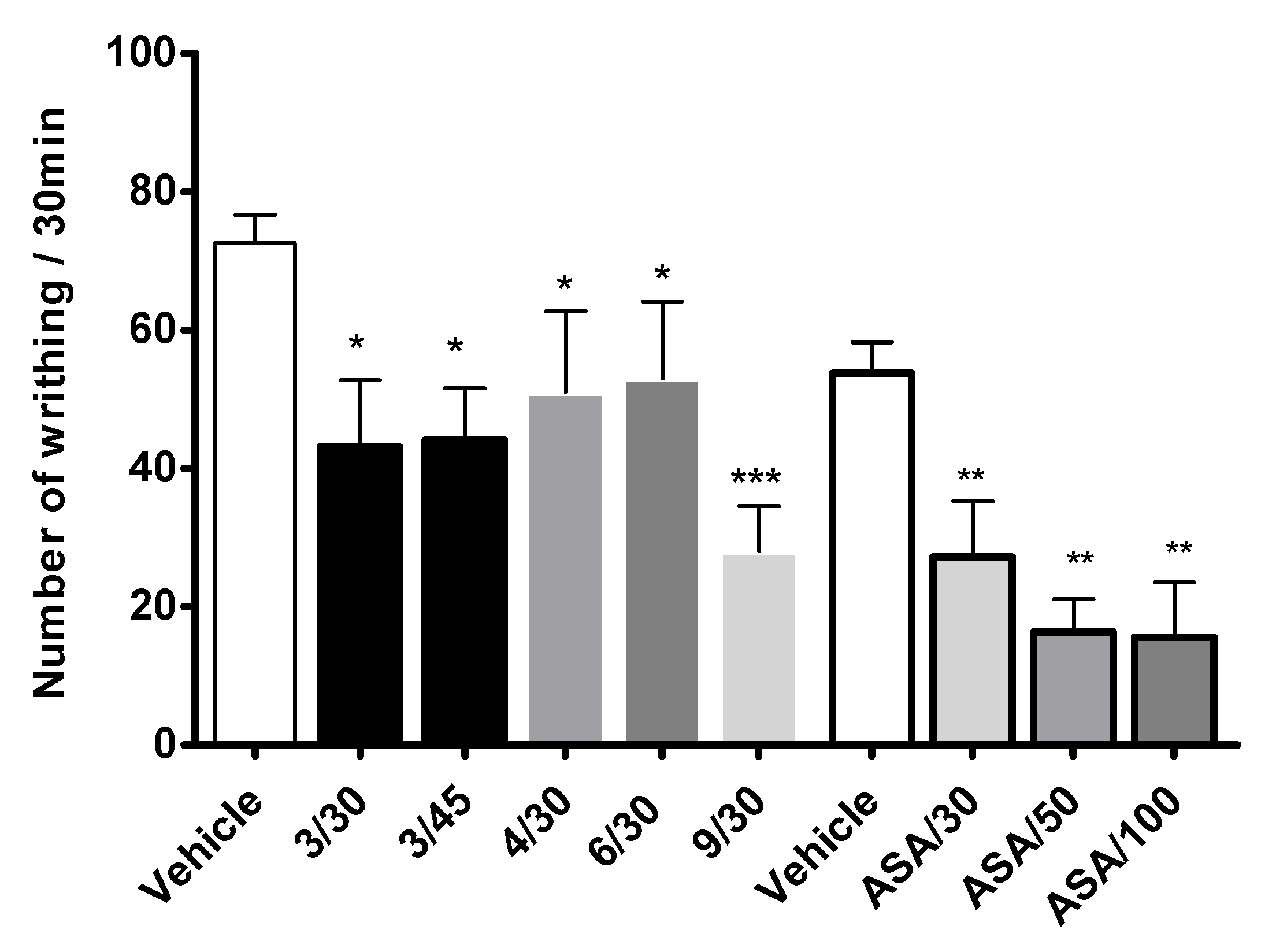
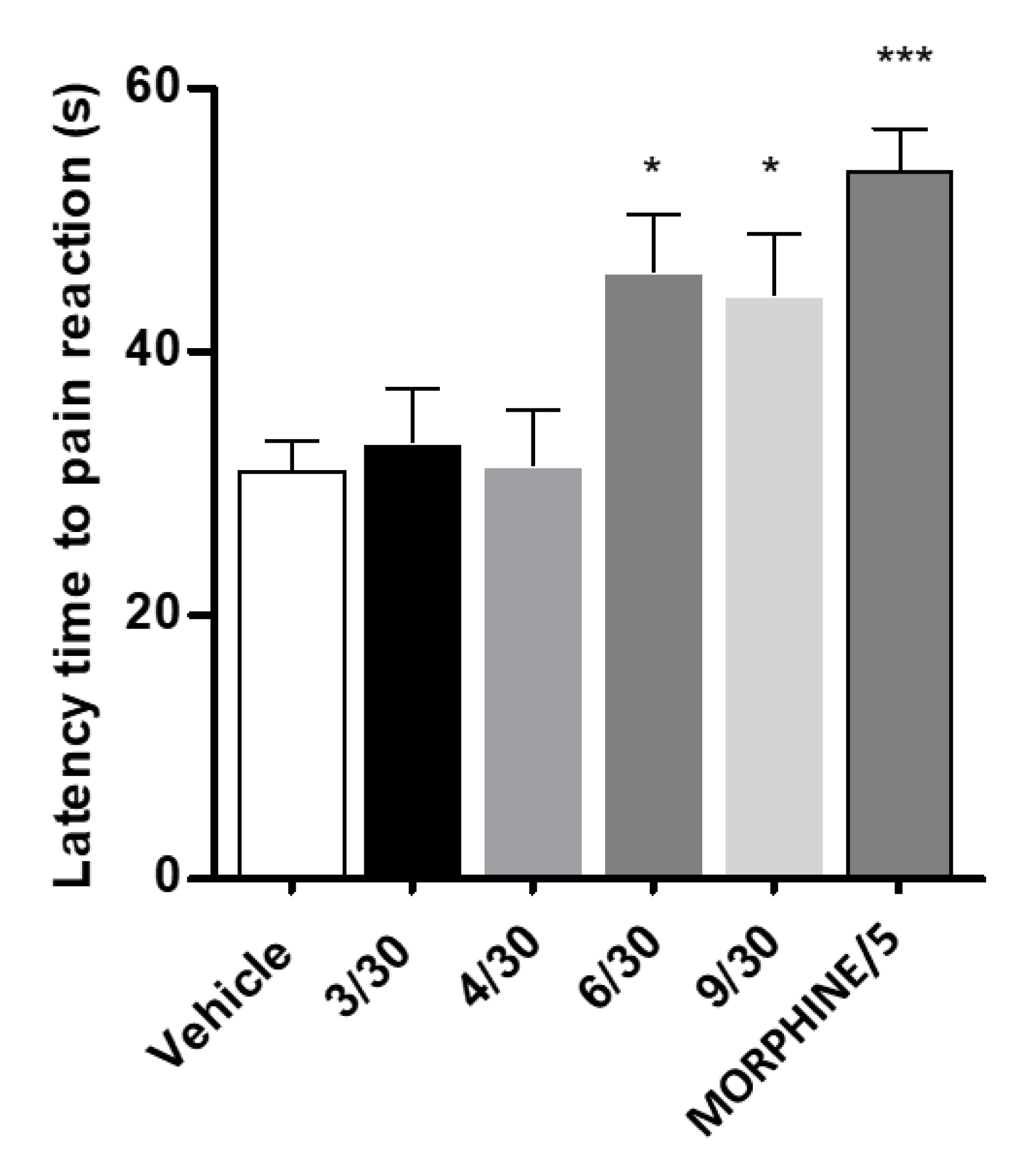
2.3. Antinociceptive Activity
2.4. In Vitro Radioligand Binding Studies
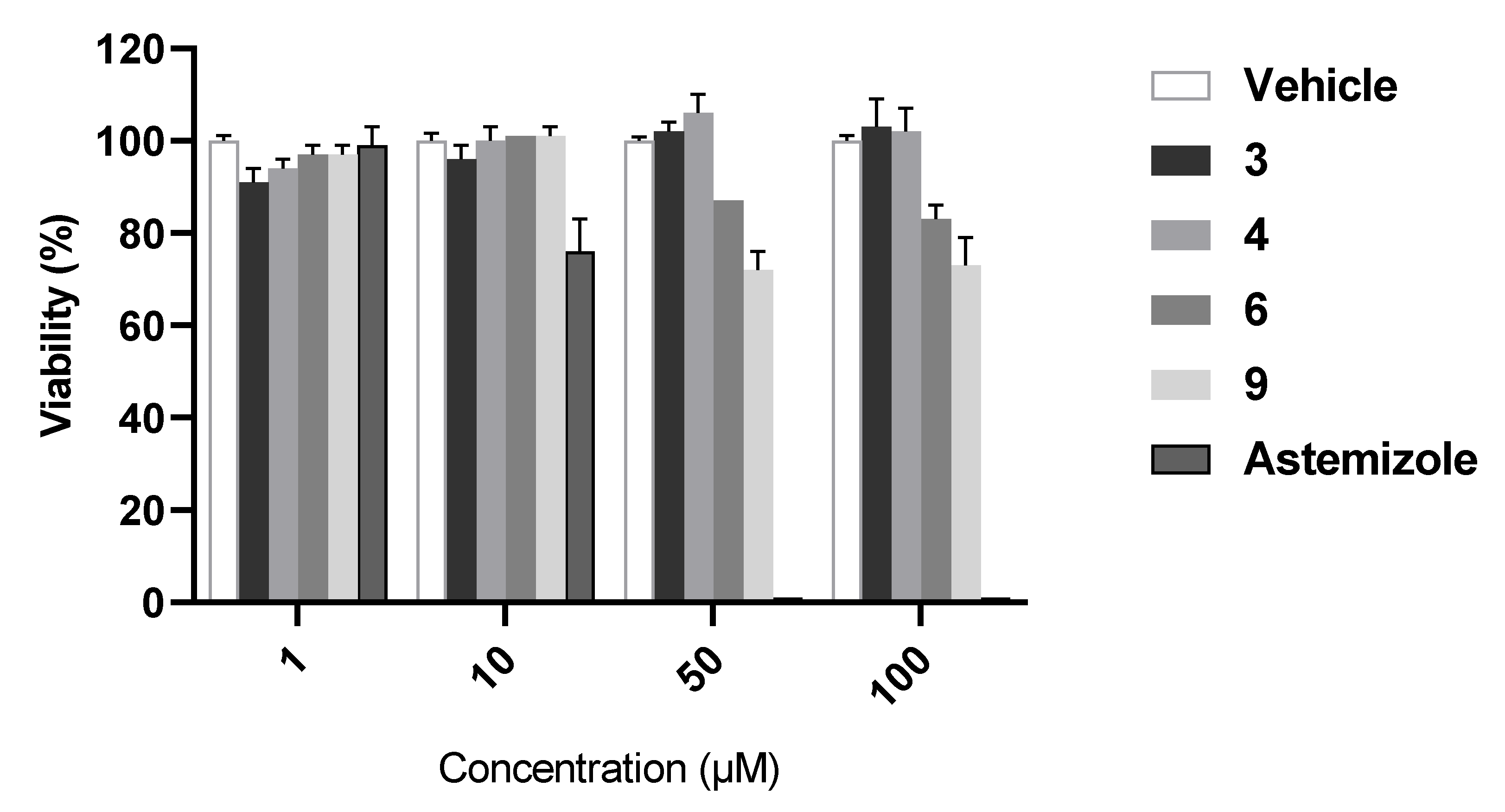
2.5. Hepatotoxicity Study
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry
4.1.1. General Remarks
4.1.2. Synthesis and Structural Characterization
General Procedure for the Synthesis of 2-(3-methylthiophen-2-yl)succinic acid (1) and 2-(3-(3-methylthiophen-2-yl)-2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)acetic acid (2)
(R,S)-2-(3-(3-methylthiophen-2-yl)-2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)acetic acid (2)
General Procedure for the Preparation of 1-(3-aminopropyl)-4-arylpiperazines
General Procedure for the Synthesis of Compounds 3–9
(R,S)-3-(3-Methylthiophen-2-yl)-1-(2-morpholinoethyl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione hydrochloride (3)
(R,S)-3-(3-Methylthiophen-2-yl)-1-(3-morpholinopropyl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione hydrochloride (4)
(R,S)-1-(3-(4-(4-Fluorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl)propyl)-3-(3-methylthiophen-2-yl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione hydrochloride (5)
(R,S)-3-(3-Methylthiophen-2-yl)-1-(3-(4-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)piperazin-1-yl)propyl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione hydrochloride (6)
(R,S)-1-(3-(4-(3-Chlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl)propyl)-3-(3-methylthiophen-2-yl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione hydrochloride (7)
(R,S)-1-(3-(4-(4-Chlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl)propyl)-3-(3-methylthiophen-2-yl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione hydrochloride (8)
(R,S)-1-(3-(4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl)propyl)-3-(3-methylthiophen-2-yl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione hydrochloride (9)
General Procedure for the Synthesis of Compounds 10–17
(R,S)-3-(3-Methylthiophen-2-yl)-1-(2-morpholino-2-oxoethyl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione (10)
(R,S)-1-(2-(4-(4-Fluorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-2-oxoethyl)-3-(3-methylthiophen-2-yl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione (11)
(R,S)-3-(3-Methylthiophen-2-yl)-1-(2-oxo-2-(4-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)piperazin-1-yl)ethyl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione (12)
(R,S)-1-(2-(4-(2-Chlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-2-oxoethyl)-3-(3-methylthiophen-2-yl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione (13)
(R,S)-1-(2-(4-(3-Chlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-2-oxoethyl)-3-(3-methylthiophen-2-yl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione (14)
(R,S)-1-(2-(4-(4-Chlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-2-oxoethyl)-3-(3-methylthiophen-2-yl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione (15)
(R,S)-1-(2-(4-(2,3-Dichlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-2-oxoethyl)-3-(3-methylthiophen-2-yl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione (16)
(R,S)-1-(2-(4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-2-oxoethyl)-3-(3-methylthiophen-2-yl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione (17)
4.2. In Vivo Experiments
4.2.1. Animals
4.2.2. The Maximal Electroshock Seizure Test (MES Test)
4.2.3. The 6 Hz Psychomotor Seizure Test
4.2.4. PTZ Seizure Test
4.2.5. Rotarod Test
4.2.6. Writhing Test
4.2.7. Hot Plate Test
4.3. In Vitro Experiments
4.3.1. Binding and Functional Assays
4.3.2. Analysis of Hepatotoxicity using Cellular Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fisher, R.S.; Cross, J.H.; French, J.A.; Higurashi, N.; Hirsch, E.; Jansen, F.E.; Lagae, L.; Moshé, S.L.; Peltola, J.; Roulet Perez, E.; et al. Operational classification of seizure types by the International League Against Epilepsy: Position Paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/epilepsy (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- De Oliveira Pedrosa, M.; Duarte da Cruz, R.M.; De Oliveira Viana, J.; De Moura, R.O.; Ishiki, H.M.; Barbosa Filho, J.M.; Diniz, M.F.F.M.; Scotti, M.T.; Scotti, L.; Bezerra Mendonca, F.J. Hybrid Compounds as Direct Multitarget Ligands: A Review. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1044–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, K.E.; Braestrup, C.; Grønwald, F.C.; Jørgensen, A.S.; Nielsen, E.B.; Sonnewald, U.; Sørensen, P.O.; Suzdak, P.D.; Knutsen, L.J. The synthesis of novel GABA uptake inhibitors. 1. Elucidation of the structure-activity studies leading to the choice of (R)-1-[4,4-bis(3-methyl-2-thienyl)-3-butenyl]-3-piperidinecarboxylic acid (tiagabine) as an anticonvulsant drug candidate. J. Med. Chem. 1993, 36, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogensen, S.B.; Jørgensen, L.; Madsen, K.K.; Jurik, A.; Borkar, N.; Rosatelli, E.; Nielsen, B.; Ecker, G.F.; Schousboe, A.; Clausen, R.P. Structure activity relationship of selective GABA uptake inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 2480–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, G.; Rasool, N.; Rizwan, K.; Imran, I.; Zahoor, A.F.; Zubair, M.; Sadiq, A.; Rashid, U. Synthesis, in-vitro cholinesterase inhibition, in-vivo anticonvulsant activity and in-silico exploration of N-(4-methylpyridin-2-yl)thiophene-2-carboxamide analogs. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 92, 103216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulandasamy, R.; Adhikari, A.V.; Stables, J.P. A new class of anticonvulsants possessing 6Hz activity: 3,4-Dialkyloxy thiophene bishydrazones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 4376–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Mathew, G.; Suresh, J.; Jaseel, M.; Usman, D.; Subramanyan, P.; Safna, K.; Vilapurathu, J. Psychomotor Seizure Screening and in vitro Neuroprotection Assay of Hydrazones Derived from 2-Acetyl Thiophene. Central Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sałat, K.; Podkowa, A.; Kowalczyk, P.; Kulig, K.; Dziubina, A.; Filipek, B.; Librowski, T. Anticonvulsant active inhibitor of GABA transporter subtype 1, tiagabine, with activity in mouse models of anxiety, pain and depression. Pharmacol. Rep. 2015, 67, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czapiński, P.; Blaszczyk, B.; Czuczwar, S.J. Mechanisms of action of antiepileptic drugs. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2005, 5, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obniska, J.; Rapacz, A.; Rybka, S.; Góra, M.; Żmudzki, P.; Kamiński, K. Synthesis and Anticonvulsant Properties of New 3,3-Diphenyl-2,5-dioxo-pyrrolidin-1-yl-acetamides and 3,3-Diphenyl-propionamides: Anticonvulsant Activity of Imide/Amide Derivatives. Archiv Pharm. 2017, 350, 1600368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obniska, J.; Rapacz, A.; Rybka, S.; Góra, M.; Kamiński, K.; Sałat, K.; Żmudzki, P. Synthesis, and anticonvulsant activity of new amides derived from 3-methyl- or 3-ethyl-3-methyl-2,5-dioxo-pyrrolidin-1-yl-acetic acids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiński, K.; Obniska, J.; Chlebek, I.; Wiklik, B.; Rzepka, S. Design, synthesis and anticonvulsant properties of new N-Mannich bases derived from 3-phenylpyrrolidine-2,5-diones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 6821–6830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapacz, A.; Obniska, J.; Wiklik-Poudel, B.; Rybka, S.; Sałat, K.; Filipek, B. Anticonvulsant and antinociceptive activity of new amides derived from 3-phenyl-2,5-dioxo-pyrrolidine-1-yl-acetic acid in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 781, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obniska, J.; Chlebek, I.; Kamiński, K.; Bojarski, A.J.; Satała, G. Synthesis, anticonvulsant activity and 5-HT1A/5-HT7 receptors affinity of 1-[(4-arylpiperazin-1-yl)-propyl]-succinimides. Pharmacol. Rep. 2012, 64, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löscher, W.; Hönack, D.; Fassbender, C.P.; Nolting, B. The role of technical, biological and pharmacological factors in the laboratory evaluation of anticonvulsant drugs. III. Pentylenetetrazole seizure models. Epilepsy Res. 1991, 8, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löscher, W.; Schmidt, D. Modern antiepileptic drug development has failed to deliver: Ways out of the current dilemma. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 657–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, C.S.; West, P.J.; Thomson, K.E.; Edwards, S.F.; Smith, M.D.; White, H.S.; Wilcox, K.S. Development and pharmacologic characterization of the rat 6 Hz model of partial seizures. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeijón, P.; Blanco, J.M.; Fernández, F.; García, M.D.; López, C. Synthesis of Two Precursors of Heterocarbocyclic Nucleoside Analogues. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 2006, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybka, S.; Obniska, J.; Żmudzki, P.; Koczurkiewicz, P.; Wójcik-Pszczoła, K.; Pękala, E.; Bryła, A.; Rapacz, A. Synthesis and Determination of Lipophilicity, Anticonvulsant Activity, and Preliminary Safety of 3-Substituted and 3-Unsubstituted N -[(4-Arylpiperazin-1-yl)alkyl]pyrrolidine-2,5-dione Derivatives. ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SwissAdme. Available online: http://www.swissadme.ch/ (accessed on 25 June 2020).
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings1PII of original article: S0169-409X(96)00423-1. The article was originally published in Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 23 (1997) 3–25.1. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veber, D.F.; Johnson, S.R.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Smith, B.R.; Ward, K.W.; Kopple, K.D. Molecular properties that influence the oral bioavailability of drug candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2615–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybka, S.; Obniska, J.; Rapacz, A.; Filipek, B.; Żmudzki, P. Synthesis and anticonvulsant activity of new N-mannich bases derived from benzhydryl- and isopropyl-pyrrolidine-2,5-dione. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abram, M.; Zagaja, M.; Mogilski, S.; Andres-Mach, M.; Latacz, G.; Baś, S.; Łuszczki, J.J.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K.; Kamiński, K. Multifunctional Hybrid Compounds Derived from 2-(2,5-Dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)-3-methoxypropanamides with Anticonvulsant and Antinociceptive Properties. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 8565–8579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, S.H.; Woodhead, J.H.; Wilcox, K.S.; Stables, J.P.; Kupferberg, H.J.; Wolf, H.H. Discovery and preclinical development of antiepileptic drugs. In Antiepileptic Drugs, 5th ed.; Levy, R.H., Mattson, R.H., Meldrum, B.S., Perucca, E., Eds.; Lippincott: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002; pp. 36–48. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, G. 3H-batrachotoxinin-A benzoate binding to voltage-sensitive sodium channels: Inhibition by the channel blockers tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin. J. Neurosci. 1986, 6, 2064–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, R.J.; Murphy, K.M.; Snyder, S.H. [3H]nitrendipine-labeled calcium channels discriminate inorganic calcium agonists and antagonists. PNAS 1982, 79, 3656–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shank, R.P.; Baldy, W.J.; Mattucci, L.C.; Villani, F.J. Ion and Temperature Effects on the Binding of γ-Aminobutyrate to Its Receptors and the High-Affinity Transport System. J. Neurochem. 1990, 54, 2007–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanovic-Petrovic, R.M.; Tomic, M.A.; Vuckovic, S.M.; Paranos, S.; Ugresic, N.D.; Prostran, M.S.; Milovanovic, S.; Boskovic, B. The antinociceptive effects of anticonvulsants in a mouse visceral pain model. Anesth. Analg. 2008, 106, 1897–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, D.; West, P.J.; Smith, M.D.; Yagen, B.; Bialer, M.; Devor, M.; White, H.S.; Brennan, K.C. sec-Butylpropylacetamide (SPD), a New Amide Derivative of Valproic Acid for the Treatment of Neuropathic and Inflammatory Pain. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 117, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiliç, F.S.; Sirmagul, B.; Yildirim, E.; Oner, S.; Erol, K. Antinociceptive effects of gabapentin & its mechanism of action in experimental animal studies. Indian J. Med Res. 2012, 135, 630–635. [Google Scholar]
- Shamsi Meymandi, M.; Keyhanfar, F. Assessment of the antinociceptive effects of pregabalin alone or in combination with morphine during acetic acid-induced writhing in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2013, 110, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.D.; Woodhead, J.H.; Handy, L.J.; Pruess, T.H.; Vanegas, F.; Grussendorf, E.; Grussendorf, J.; White, K.; Bulaj, K.K.; Krumin, R.K.; et al. Preclinical Comparison of Mechanistically Different Antiseizure, Antinociceptive, and/or Antidepressant Drugs in a Battery of Rodent Models of Nociceptive and Neuropathic Pain. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 1995–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepanovic-Petrovic, R.M.; Micov, A.M.; Tomic, M.A.; Kovacevic, J.M.; Boškovic, B.D. Antihyperalgesic/antinociceptive effects of ceftriaxone and its synergistic interactions with different analgesics in inflammatory pain in rodents. Anesthesiology 2014, 120, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomić, M.A.; Pecikoza, U.B.; Micov, A.M.; Stepanović-Petrović, R.M. The Efficacy of Eslicarbazepine Acetate in Models of Trigeminal, Neuropathic, and Visceral Pain: The Involvement of 5-HT1B/1D Serotonergic and CB1/CB2 Cannabinoid Receptors. Anesth. Analg. 2015, 121, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Listos, J.; Talarek, S.; Orzelska, J.; Fidecka, S.; Wujec, M.; Plech, T. The antinociceptive effect of 4-substituted derivatives of 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione in mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol. 2014, 387, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzanares, J.; Julian, M.; Carrascosa, A. Role of the cannabinoid system in pain control and therapeutic implications for the management of acute and chronic pain episodes. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2006, 4, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laughlin, T.M.; Tram, K.V.; Wilcox, G.L.; Birnbaum, A.K. Comparison of antiepileptic drugs tiagabine, lamotrigine, and gabapentin in mouse models of acute, prolonged, and chronic nociception. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 302, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogawski, M.A.; Löscher, W. The neurobiology of antiepileptic drugs. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meldrum, B.S.; Chapman, A.G. Basic mechanisms of gabitril (tiagabine) and future potential developments. Epilepsia 1999, 40 (Suppl. S9), S2–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazıroğlu, M. TRPV1 Channel: A Potential Drug Target for Treating Epilepsy. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2015, 13, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, E.; Yoon, J.; Pae, A.N.; Rhim, H.; Park, W.-K.; Kong, J.Y.; Park Choo, H.-Y. Synthesis and biological evaluation of (phenylpiperazinyl-propyl)arylsulfonamides as selective 5-HT2A receptor antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 1665–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Koh, H.Y.; Seo, S.H.; Baek, Y.Y.; Rhim, H.; Cho, Y.S.; Choo, H.; Pae, A.N. Synthesis and biological evaluation of oxazole derivatives as T-type calcium channel blockers. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 4219–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, D.; Kang, S.Y.; Park, W.-K.; Kim, H.J.; Jung, M.E.; Son, E.-J.; Pae, A.N.; Kim, J.; Lee, J. Arylpiperazine-containing pyrimidine 4-carboxamide derivatives targeting serotonin 5-HT(2A), 5-HT(2C), and the serotonin transporter as a potential antidepressant. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 6439–6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obniska, J.; Rapacz, A.; Rybka, S.; Powroźnik, B.; Pękala, E.; Filipek, B.; Żmudzki, P.; Kamiński, K. Design, synthesis and biological activity of new amides derived from 3-methyl-3-phenyl-2,5-dioxo-pyrrolidin-1-yl-acetic acid. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 102, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litchfield, J.T.; Wilcoxon, F. A simplified method of evaluating dose-effect experiments. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1949, 96, 99–113. [Google Scholar]
- Rapacz, A.; Kamiński, K.; Obniska, J.; Koczurkiewicz, P.; Pękala, E.; Filipek, B. Analgesic, antiallodynic, and anticonvulsant activity of novel hybrid molecules derived from N-benzyl-2-(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)propanamide and 2-(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)butanamide in animal models of pain and epilepsy. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2017, 390, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelps, P.T.; Anthes, J.C.; Correll, C.C. Cloning and functional characterization of dog transient receptor potential vanilloid receptor-1 (TRPV1). Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 513, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerets, H.H.J.; Tilmant, K.; Gerin, B.; Chanteux, H.; Depelchin, B.O.; Dhalluin, S.; Atienzar, F.A. Characterization of primary human hepatocytes, HepG2 cells, and HepaRG cells at the mRNA level and CYP activity in response to inducers and their predictivity for the detection of human hepatotoxins. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2012, 28, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 3–17 are available from the authors. |
| Comps | Lipinski Rules | Veber Rules | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MW ≤ 500 | LogP ≤ 5 | NHD ≤ 5 a | NHA ≤ 10 b | Violations of Rules | NBR ≤ 10 c | TPSA ≤ 140 d | |
| 3 | 308.40 | 2.81 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 78.09 |
| 4 | 322.42 | 3.01 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 5 | 78.09 |
| 5 | 415.52 | 3.66 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 6 | 72.10 |
| 6 | 465.53 | 3.77 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 7 | 72.10 |
| 7 | 431.98 | 3.65 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 6 | 72.10 |
| 8 | 431.98 | 3.82 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 6 | 72.10 |
| 9 | 466.62 | 3.94 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 6 | 72.10 |
| 10 | 318.43 | 2.99 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 61.02 |
| 11 | 415.48 | 3.19 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 5 | 89.17 |
| 12 | 465.49 | 3.16 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 89.17 |
| 13 | 431.94 | 3.12 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 89.17 |
| 14 | 431.94 | 3.52 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 89.17 |
| 15 | 431.94 | 3.33 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 89.17 |
| 16 | 466.38 | 3.34 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 89.17 |
| 17 | 466.38 | 3.53 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 89.17 |
| Compd | R | X/R1 | Intraperitoneal Administration in Mice | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MES a | 6 Hz b | NT c | |||
| 3 | -CH2- | O/- | 1/4 | 4/4 | 0/4 |
| 4 | -(CH2)2- | O/- | 3/4 | 3/4 | 0/4 |
| 5 | -(CH2)2- | N/4-FPh | 0/4 | 0/4 | 4/4 |
| 6 | -(CH2)2- | N/3-CF3Ph | 1/4 | 3/4 | 4/4 |
| 7 | -(CH2)2- | N/3-ClPh | 0/4 | 0/4 | 2/4 |
| 8 | -(CH2)2- | N/4-ClPh | 1/4 | 1/4 | 0/4 |
| 9 | -(CH2)2- | N/3,4-ClPh | 2/4 | 2/4 | 0/4 |
| 10 | -(CO)- | O/- | 0/4 | 1/4 | 0/4 |
| 11 | -(CO)- | N/4-FPh | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 |
| 12 | -(CO)- | N/3-CF3Ph | 0/4 | 0/4 | 1/4 |
| 13 | -(CO)- | N/2-ClPh | 0/4 | 1/4 | 0/4 |
| 14 | -(CO)- | N/3-ClPh | 0/4 | 2/4 | 0/4 |
| 15 | -(CO)- | N/4-ClPh | 0/4 | 1/4 | 0/4 |
| 16 | -(CO)- | N/2,3-ClPh | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/4 |
| 17 | -(CO)- | N/3,4-ClPh | 0/4 | 2/4 | 0/4 |
| Compd | TPE a | MES ED50 b (mg/kg) | 6 Hz ED50 b (mg/kg) | NT TD50 b (mg/kg) | PI c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 0.5 | - | 74.32 (64.91–85.09) | > 200 | > 2.69 |
| 4 | 0.5 | 62.14 (43.30–89.20) | 75.59 (65.39–87.39) | < 200* | < 3.21 (MES) < 2.65 (6 Hz) |
| 6 | 0.5 | - | 78.30 (65.82–93.13) | < 100 | < 1.28 |
| 9 | 0.5 | > 130 | > 130 | > 300 | - |
| 14 | 0.5 | - | 153.25 (130.70–179.68) | > 300 | > 1.95 (6 Hz) |
| 17 | 0.5 | - | > 150 | - | - |
| ETX d | 0.25 | > 500 | 221.7 (183.0–268.5) | 722.1 (647.0–805.8) | 3.2 (6 Hz) |
| VPA d | 0.5 | 252.7 (220.1–290.2) | 130.6 (117.6–145.2) | 430.8 (407.9–454.9) | 1.7 (MES) 3.3 (6 Hz) |
| Compd | % Inhibition of Control Specific Binding a | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage-Sensitive Na+ Channel (site 2) b | Voltage-Sensitive Ca2+ Channel L-typ c | GABA Transporter (GAT) d | |
| 3 | 15.6% | −1.1% | −1.1% |
| 4 | 42.1% | 39.7% | −3.2% |
| 6 | 96.7% | 69.9% | - |
| 9 | 78.8% | −9.5% | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Góra, M.; Czopek, A.; Rapacz, A.; Dziubina, A.; Głuch-Lutwin, M.; Mordyl, B.; Obniska, J. Synthesis, Anticonvulsant and Antinociceptive Activity of New Hybrid Compounds: Derivatives of 3-(3-Methylthiophen-2-yl)-pyrrolidine-2,5-dione. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165750
Góra M, Czopek A, Rapacz A, Dziubina A, Głuch-Lutwin M, Mordyl B, Obniska J. Synthesis, Anticonvulsant and Antinociceptive Activity of New Hybrid Compounds: Derivatives of 3-(3-Methylthiophen-2-yl)-pyrrolidine-2,5-dione. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(16):5750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165750
Chicago/Turabian StyleGóra, Małgorzata, Anna Czopek, Anna Rapacz, Anna Dziubina, Monika Głuch-Lutwin, Barbara Mordyl, and Jolanta Obniska. 2020. "Synthesis, Anticonvulsant and Antinociceptive Activity of New Hybrid Compounds: Derivatives of 3-(3-Methylthiophen-2-yl)-pyrrolidine-2,5-dione" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 16: 5750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165750
APA StyleGóra, M., Czopek, A., Rapacz, A., Dziubina, A., Głuch-Lutwin, M., Mordyl, B., & Obniska, J. (2020). Synthesis, Anticonvulsant and Antinociceptive Activity of New Hybrid Compounds: Derivatives of 3-(3-Methylthiophen-2-yl)-pyrrolidine-2,5-dione. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(16), 5750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165750