Abstract
Ionic liquids derived from classical antimalarials are emerging as a new approach towards the cost-effective rescuing of those drugs. Herein, we disclose novel surface-active ionic liquids derived from chloroquine and natural fatty acids whose antimalarial activity in vitro was found to be superior to that of the parent drug. The most potent ionic liquid was the laurate salt of chloroquine, which presented IC50 values of 4 and 110 nM against a chloroquine-sensitive and a chloroquine-resistant strain of Plasmodium falciparum, respectively, corresponding to an 11- and 6-fold increase in potency as compared to the reference chloroquine bisphosphate salt against the same strains. This unprecedented report opens new perspectives in both the fields of malaria chemotherapy and of surface-active ionic liquids derived from active pharmaceutical ingredients.
1. Introduction
Ionic liquids (ILs) are gaining prominence as chemical entities of interest in medicinal chemistry, as well as pharmaceutical science and technology [1,2,3,4]. In fact, ILs can contribute to overcoming the undesirable features of conventional saline forms of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), such as polymorphism, low solubility, and limited bioavailability [5,6]. As such, the development of ILs derived from APIs (API-ILs) is an appealing strategy towards the rescuing of drugs that are falling into disuse due to these and other detrimental traits. With this idea in mind, and following our previous promising findings on cinnamic acid conjugates of classical antimalarial drugs [7,8,9,10], we applied the API-IL concept onto such drugs, by disclosing room temperature ionic liquids (RTILs) derived from primaquine (PQ) and cinnamic acids as triple-stage antimalarial hits [11]. The most remarkable property of these RTILs was their increased activity against blood-stage malaria parasites, on which PQ has a practically negligible action [12]. This might be due to a more efficient interaction of RTILs with membranes of infected erythrocytes than with healthy ones, according to subsequent studies using model lipid membranes [13]. In view of this, we hypothesized that the combination of a blood schizonticide like chloroquine (CQ) with amphiphilic natural fatty acids might deliver new organic salts (Scheme 1) in the form of RTILs with enhanced blood-stage activity, possibly suitable for oral administration, as recently reported for lipid-based formulations of the lumefantrine docusate IL [14].
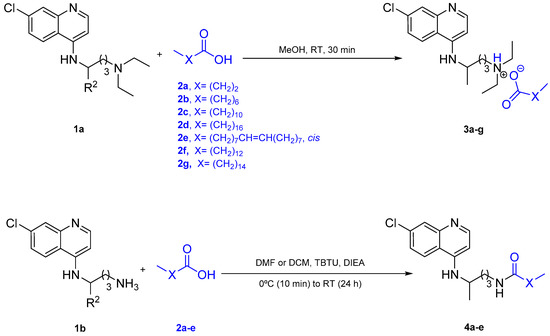
Scheme 1.
Routes towards organic salts 3a–e, derived from chloroquine (CQ) (1a) and fatty acids 2a–e, and their amide covalent counterparts 4a–e, derived from CQ analogue 1b and 2a–e: (i) 1a (1 molar equivalent, eq), 2a–e (1 eq), methanol (MeOH), room temperature (RT), 30 min; (ii) 2a–e (1 eq), O-(benzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N’,N’-tetramethyluronium tetrafluoroborate (TBTU; 1 eq), N-ethyl-N,N-diisopropylamine (DIEA, 2 eq), N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF), 0 °C, 10 min, then addition of 1b (1 eq), RT, 24 h.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemical Synthesis and Thermal Stability
Commercially available CQ phosphate salt was first converted into the free amine form 1a, which then reacted with fatty acids 2a–e via an acid-base neutralization previously reported by us [11], to afford 3a–e (Scheme 1). In parallel, 1b, the primary amine analogue of 1a, was prepared as previously reported by us [7] and conjugated with 2a–e to produce amides 4a–e for comparative assessment of in vitro antimalarial activity alongside salts 3a–e (Scheme 1). The organic salts 3a–e were obtained in nearly quantitative yields as colorless to pale yellow viscous liquids (i.e., 3a–e are all RTILs), whereas amides 4a–e were obtained as white to brownish-yellow solids in moderate to good yields (Table 1). Spectroscopic data, supplied as Supplementary Materials (SM), were in agreement with the expected structures. Notably, although proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR) data are not conclusive regarding protonation of the basic groups in CQ (as spectra were acquired from hexadeuterated dimethylsulfoxide, DMSO-d6, which is an H-bond acceptor), it was possible to confirm complete transfer of the carboxylic acid proton to the aminoquinoline. This is because this proton was observed in the 1H-NMR spectra of solutions of the fatty acids 2a–e in DMSO-d6, but not in the solutions of their respective CQ salts 3a–e in the same solvent (Figure S1 of the SM). This is a remarkable finding, as it has been established by Stoimenovski et al. that a ΔpKa >10 is required to assure complete proton transfer between the proton donor and a tertiary amine [15].

Table 1.
Synthesis yields, thermal degradation data, and in vitro activity against Plasmodium falciparum (Pf) 3D7 and Dd2 strains obtained for room temperature ionic liquids (RTILs) 3a–e and for their covalent analogues 4a–e; thermal degradation data also provided for CQ phosphate and 2a–e; the in vitro activity data obtained for the commercial CQ phosphate salt, for 2c, and for an equimolar mixture of these two compounds are also included.
All compounds were analyzed by simultaneous thermogravimetric analysis (STA), as given in detail in the SM, to assess their thermal stability, an important issue for APIs typically employed in the treatment of diseases, such as malaria, that are endemic to tropical and sub-tropical countries. The temperatures at which thermal degradation events were observed by STA are provided in Table 1, and the corresponding thermograms are provided in the SM. Data show that all the RTILs 3a–e are slightly less thermally stable than the commercial CQ phosphate salt, but still remain unaltered up to about 90 °C (3a) or higher temperatures (3b–e). As expected, covalent amide analogues 4a–e displayed higher thermal stability, with only one thermal degradation event occurring at temperature values that generally increased with the size of the alcanoyl chain, in the 291.3–336.5 °C range. Interestingly, RTIL 3a–c presented two thermal degradation events, whereas 3d and 3e showed only one degradation event in the temperature range of the study (50–500 °C). The possibility that two degradation events might be occurring equally in these two cases, but at very close temperature values, cannot be ruled out at this stage. Still, data from STA clearly show that 3a–e do not behave as the mere sum of their parent compounds, otherwise thermal degradation events would have been observed at the same values recorded for CQ and the relevant fatty acids 2a–e. A deeper study to establish the mechanisms of thermal degradation of RTILs 3a–e is under way, to enable the full profiling of these novel compounds.
2.2. Antimalarial Activity In Vitro
Compounds 3a–e and 4a–e were evaluated in vitro according to previously reported methods (cf. SM) [11], against a CQ-sensitive (3D7) and a CQ-resistant (Dd2) strain of Plasmodium falciparum (Pf). Interestingly, while all RTILs 3a–e did not pose any significant solubility issues in the course of the in vitro assays, only amides 4a–c were sufficiently soluble in the same conditions. Moreover, although accurate values for solubility (log S) are yet to be determined, RTILs 3a–e were also slightly more soluble in water (albeit low) than their covalent analogues 4a–e. More importantly, all RTILs displayed stronger activity than CQ, which is classically formulated as a phosphate salt, against both CQ-sensitive and CQ–resistant strains of Pf, the species responsible for the deadliest form of human malaria. The activities of 3a–e were in the low- to mid-nanomolar ranges against the 3D7 and Dd2 strains, respectively, with 3c (derived from dodecanoic, or lauric, acid 2c) being the most potent of the set. This RTIL was nearly 20-fold more potent than its amide counterpart, 4c, and over 10-fold more potent than the reference drug, against the 3D7 strain. Regarding activity against the Dd2 strain, 3c was virtually comparable to 4c, but nearly five-fold better than CQ phosphate. The in vitro activity of 3c was further compared to those of the parent fatty acid, 2c, and of an equimolar mixture of this acid with the commercial CQ phosphate. Although 2c was completely devoid of antiplasmodial activity, its equimolar mixture with the reference drug was significantly less active than 3c against both strains. These observations further reinforce that 3a–e are chemical entities on their own, and not the simple mixtures of their parent compounds. These data also support that, as originally hypothesized, acid-base pairing of CQ with fatty acids delivers RTILs showing a clear gain over the parent drug concerning in vitro antimalarial activity.
One interesting observation from in vitro data above was that the laurate salt of CQ, 3c, seemed to possess the optimal size for antiplasmodial activity, which is slightly decreased for compounds 3 with shorter and longer fatty acid chains. Considering the amphiphilicity of fatty acids and derivatives [16], and the probable enhancement of this property when pairing the fatty carboxylates with an amphiphilic cation-like protonated CQ, we anticipated that RTILs 3 could act as surface-active ionic liquids (SAILs) [17], and that such activity might be one factor contributing to their enhanced antiplasmodial potency as compared to the standard formulation of CQ. To test this hypothesis, we carried out surface tension studies as follows (cf. experimental details in the SM, Section 3).
2.3. Surface Tension Studies
The best antimalarial RTIL, 3c, along with one shorter (3b) and two larger (3f and 3g, respectively; X=(CH2)12 and X=(CH2)14 in Scheme 1) analogues, were further studied regarding their surface activity properties, to obtain a finer scrutiny of the effect of alkyl chain size variation on surface activity. The two additional compounds, 3f,g, were synthesized as above described for 3a–e (cf. Scheme 1 and SM).
As mentioned before, compounds 3 display low solubility in water. However, a first indication of their surface activity came from the foaming observed for saturated aqueous solutions of 3c (cf. Figure S2 of the SM) and, particularly, from surface tension measurements at 25.0 °C, which yielded a value of 29.8 ± 0.3 mN·m−1, a considerable decrease from the surface tension of neat water (72.0 mN·m−1), hence indicative of strong adsorption of the compound at the air–solution interface. We also verified that the different SAILs 3b, 3c, 3f and 3g have improved solubility in aqueous solutions of a conventional cationic surfactant, cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB). For comparisons, we evaluated the effect of adding each SAIL at a fixed 0.10 molar fraction, defined as xSAIL = nSAIL/(nSAIL + nCTAB), on the critical micellar concentration (cmc) of the systems and on the surface tension at the cmc (gcmc). The results are shown in Figure 1a and the obtained cmc and gcmc values are presented in Table 2.
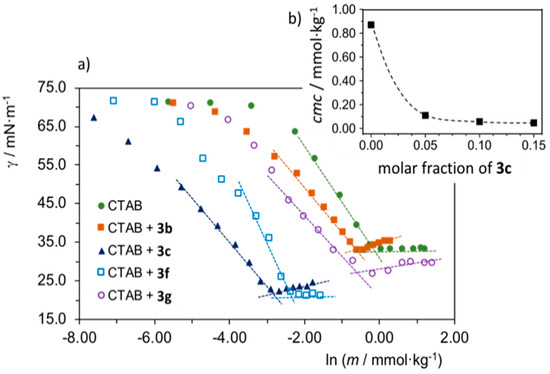
Figure 1.
Surface tension plots and cmc determination at 25 °C of aqueous surface-active ionic liquid (SAIL)/CTAB mixtures: (a) surface tension vs. the logarithm of total SAIL+CTAB concentration expressed in molality; the cmc are obtained from the intersection points of the linear fits in each system; (b) cmc vs. molar fraction of SAIL 3c in mixtures of SAIL 3c/CTAB, showing the marked effect of the SAIL in cmc reduction.

Table 2.
Critical micellar concentration (cmc) and surface tension at the cmc (©cmc) for CTAB and different CTAB/SAIL solutions with a molar fraction of SAIL, xSAIL, equal to 0.10.
It is clear that all SAILs form mixed micelles with CTAB and induce a marked decrease in cmc compared to neat CTAB, even at the low xSAIL studied (equal to a SAIL/CTAB molecular ratio of 1:9). Table 2 also shows that there is seemingly a U-shaped variation of cmc with an increasing chain length of fatty acids, a somewhat unexpected trend that, on the other hand, demonstrates that surface activities observed are not solely due to the presence of the fatty carboxylate. Significantly, the laurate derivative, 3c, is the SAIL that brings about the highest decrease in cmc, with the mixture’s cmc being ca. 15 times smaller than that of neat CTAB. The corresponding gcmc for 3c is also very low, 22 mN·m−1, consistent with a strong surface adsorption for this mixture. We further tested the effect of increasing the molar fraction of 3c on the cmc of the mixture (cf. surface tension curves in Figure S3 of the SM). Figure 1b shows that the cmc continually decreases with increasing x3c, again confirming the high interfacial activity of 3c.
Taken together, these findings not only demonstrate that the 3 RTILs used in the surface activity assays do behave as SAILs, but also suggest that surface activity may influence the antimalarial action of these compounds, as the compound with the most potent antimalarial activity, 3c, was also the one with a most dramatic effect in lowering cmc and surface tension of CTAB, in comparison to the effects exhibited by its counterparts derived from shorter (3b) or longer (3f,g) fatty acids. A more in-depth interpretation of this observation requires further studies, namely by including the butyric (3a) and caprylic (3b) acid derivatives, among others, in the surface activity assays, in particular because 3a was also quite active in vitro, despite the fact that butyrate salts are not usually associated with self-assembling properties. Still, the “counterion” to butyrate is, in 3a, a protonated hydrophobic 4-aminoquinoline, and is hence quite different to counterions used in most common butyrate salts, e.g., sodium butyrate. Moreover, distinct concentration ranges are used in the in vitro assays vs. the surface activity ones, which might put into question the comparability of data from both types of study.
3. Concluding Remarks
The observed parallelism between surface activity and antimalarial activity hardly seems coincidental, meaning that this activity, despite being due primarily to the bioactive cation, (i.e., protonated CQ), is also significantly influenced by the amphipathicity and surface activity conveyed by the fatty carboxylate. To the best of our knowledge, this is a first-time disclosure of CQ-derived SAILs whose antimalarial activity is (i) higher than that of CQ, (ii) modulated by the amphipathic anion used, and (iii) influenced by surface activity. Furthermore, the ability of CQ-derived SAILs to co-assemble into colloidal nanostructures (in this case, mixed micelles with CTAB), strongly suggests that these systems could potentially act both as drugs and as enhanced drug delivery systems. We are aware that this may be speculative at this stage, but ongoing studies will shed light onto this and other open questions. Further physico-chemical, biophysical, and biological, including in vivo, studies are under way, which will allow us to fully validate the reported CQ-derived SAILs as a new antimalarial chemotype. Although ILs derived from API have been thoroughly explored over recent years [18,19,20], validation of drug-derived SAILs acting as therapeutic agents that are able to promote their own intracellular delivery will represent a noteworthy development in molecular pharmacology.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical Synthesis
4.1.1. Conversion of Chloroquine Phosphate into 1a
Commercial chloroquine phosphate was converted into its free base form 1a as previously described by us for primaquine [11]. Briefly, triethylamine (1.5 mL) was added to a suspension of chloroquine bisphosphate (1.06 g, 2.05 mmol) in dichloromethane (DCM), and the mixture was stirred for 30 min at room temperature (RT). The organic layer was washed with water (10 mL × 3), dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, and evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure, to afford 1a (0.63 g, 1.97 mmol) in nearly quantitative yield (93%), and with correct 1H-NMR spectral data, as given in the SM.
4.1.2. Synthesis of Chloroquine Analogue 1b
The synthesis of 1b was performed as previously described by us [7]. Briefly, 1,4-diaminobutane (1.12 g, 12.7 mmol) and 4,7-dichloroquinoline (0.25 g, 1.27 mmol) were stirred at 100 °C for 3 h. After cooling to RT, the mixture was diluted with DCM (25 mL), and the solution was washed with 5% aqueous Na2CO3 (25 mL × 3). The organic layer was separated, dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered, and concentrated to afford 1b (0.22, 0.87) without need for further purification. Spectroscopic data were in agreement with previous reports [7].
4.1.3. Synthesis of Ionic Liquids 3
All compounds 3 were synthesized by exactly the same experimental procedure, using the amounts of reactants included in Table S1 of the SM. Briefly, compound 1a (1 molar equivalent, eq) was dissolved in methanol (10 mL). In parallel, the convenient fatty acid 2a–g (1 eq) was dissolved in methanol (10 mL). The methanolic solution of 1a was placed under magnetic stirring and the methanolic solution of the convenient fatty acid 2 was added dropwise. Upon addition of the acid, the reaction mixture was kept under stirring for 30 min, at RT. The solvent was removed by evaporation under reduced pressure in the rotary evaporator, and finally dried at high vacuum. The residue obtained was analyzed by 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR, allowing for verification of the identity of the desired salt, with an anion/cation stoichiometry of 1:1, according to the 1H-NMR data given in the SM.
4.1.4. Synthesis of Amides 4
All compounds 4 were synthesized by exactly the same experimental procedure, using the amounts of reactants included in Table S2 of the SM. Briefly, compound 1b (1 eq) was dissolved in either dimethylformamide DMF or DCM. In parallel, 1.1 eq of the convenient fatty acid 2a–e, 1.1 eq of O-(benzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N′,N′-tetramethyluronium tetrafluoroborate (TBTU), and 2 eq of N,N-diisopropylethylamine (DIEA) were dissolved in DMF or DCM; this solution was placed under magnetic stirring for 10 min at RT, and the solution of 1b was added dropwise. Stirring was prolonged for 24 h more, at RT in the dark. The mixture was diluted with DCM, and washed 3 times with 5% aqueous Na2CO3. The organic layer was separated, dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, and filtered. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure by rotatory evaporation, and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography. Chromatographically homogeneous fractions collected were pooled, and the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure, to afford the final compound. Structural data obtained by 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, and ESI-IT MS are given in the SM.
4.2. Simultaneous Thermogravimetric Analysis
The thermal stability of the compounds was evaluated using STA equipment from Scancsi, model 7200RV, following the manufacturer’s instructions. The compounds were subjected to heating from room temperature to 500 °C at a speed of 5 °C/min, obtaining the thermograms provided in the SM. For a better visualization of the degradative events, the derivatives of the thermogravimetric curves are also displayed in the thermograms.
4.3. Surface Tension Measurements
A DCAT11 tensiometer from Dataphysics GmbH with a Wilhelmy plate was used, and all measurements were performed at 25.0 °C ± 0.5 °C, using a thermostated Julabo F20 circulating bath. The measurements for the cmc determination of the CTAB/SAIL solutions were performed by adding aliquots from a stock mixed CTAB/SAIL solution to the solution in the measuring vessel (starting initially with neat water). No dynamic surface tension effects were observed in any measurements.
4.4. In Vitro Assays
Laboratory-adapted Pf 3D7 (chloroquine- and mefloquine-sensitive), Dd2 (chloroquine-resistant and mefloquine-resistant) were continuously cultured and sorbitol synchronized, as previously described [21]. Staging and parasitemia were determined by light microscopy of Giemsa-stained thin blood smears. Anti-malarial activity was determined using the SYBR Green I assay, as previously described [22]. Briefly, early ring stage parasites (> 80% of rings) were challenged with a 1:3 serial dilution in medium from a stock solution of each compound in DMSO, with final concentrations ranging from 10,000–0.169 nM. Fluorescence intensity was measured with a multi-mode microplate reader (Triad, Dynex Technologies), with excitation and emission wavelengths of 485 and 535 nm, respectively, and analyzed by nonlinear regression using GraphPad Prism to determine IC50 values.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/15/5334/s1, Table S1: amounts of reactants used for the synthesis of 3a–g; spectral data and traces for compounds 3a–g; Table S2: amounts of reactants used for the synthesis of 4a–e; spectral data and traces for compounds 4a–e; Figure S1: superimposed 1H NMR spectra of octanoic acid 2b, basic chloroquine 1a, and their derived ionic liquid 3b; thermograms for ionic liquids 3; thermograms for amides 4; Figure S2: appearance of a saturated solution of 3c in water, displaying turbidity and foam formation; Figure S3: surface tension plots and cmc determination, at 25.0 °C, of aqueous CTAB/SAIL 3c mixtures for increasing molar fraction of 3c; Table S4: values for cmc and surface tension at the cmc (γcmc) for CTAB/SAIL 3c with increasing molar fraction of 3c.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.N., E.F.M., P.G.; Investigation, A.T.S., J.G., I.S.O., L.L., C.T., R.F.; Writing—Original Draft, A.T.S., L.L., I.S.O., E.F.M., P.G.; Writing—Review & Editing, F.N., R.F., E.F.M., P.G.; Supervision, F.N., R.F., E.F.M., P.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (FCT, Portugal), through grants UIDB/50006/2020 (to LAQV-REQUIMTE Research Unit), UIDB/00081/2020 (to CIQ-UP Research Unit), UID/Multi/04413/2013 (to GHTM Research Unit), and also for project grant PTDC/BTM-SAL/29786/2017. Thanks are due to FCT for doctoral grants to I.S.O. (SFRH/BD/108629/2015) and to A.T.S. (SFRH/BD/150649/2020.
Acknowledgments
Thanks are also due to the Portuguese NMR network (RNRMN) for supporting the Laboratory for Structural Elucidation (LAE) of the Materials Centre of the University of Porto (CEMUP).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| API | Active pharmaceutical ingredient |
| CQ | Chloroquine |
| CTAB | Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide |
| DCM | Dichloromethane |
| DIEA | N-ethyl-N,N-diisopropylamine |
| DMF | Dimethylformamide |
| DMSO | Dimethylsulfoxide |
| DMSO-d6 | Hexadeuterated dimethylsulfoxide |
| eq | Molar equivalent |
| ESI-IT MS | Electrospray ionization-ion trap mass spectrometry |
| IC50 | Half-maximal inhibitory concentration |
| IL | Ionic liquid |
| MeOH | Methanol |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| Pf | Plasmodium falciparum |
| PQ | Primaquine |
| RT | Room temperature |
| RTIL | Room temperature ionic liquid |
| SAIL | Surface-active ionic liquid |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SM | Supplementary materials |
| STA | Simultaneous thermogravimetric analysis |
| TBTU | O-(benzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N′,N′-tetramethyluronium tetrafluoroborate |
References
- Marrucho, I.M.; Branco, L.C.; Rebelo, L.P.N. Ionic liquids in pharmaceutical applications. Ann. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2014, 5, 527–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshina, J.L.; Barber, P.S.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic liquids in drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 1367–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Cláudio, A.F.M.; Valega, M.; Domingues, F.M.J.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Rogers, R.D.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Switchable (pH-driven) aqueous biphasic systems formed by ionic liquids as integrated production–separation platforms. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 2768–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, M.; Almeida, M.R.; Silva, F.A.; Domingues, P.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Novel biocompatible and self-buffering ionic liquids for biopharmaceutical applications. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 4781–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamshina, J.L.; Rogers, R.D. Overcoming the problems of solid state drug formulations with ionic liquids. Ther. Deliv. 2014, 5, 489–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, R.; Teixeira, V.; Rodrigues, D.; Fernandes, R.; Prudêncio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Petrovski, Ž.; Branco, L.C. Antibacterial activity of ionic liquids based on ampicillin against resistant bacteria. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 4301–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, B.; Teixeira, C.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Gomes, J.R.B.; Gomes, P. Cinnamic acid/chloroquinoline conjugates as potent agents against chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum. Chem. Med. Chem. 2012, 7, 1537–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, A.; Pérez, B.; Albuquerque, I.; Machado, M.; Nogueira, F.; Prudêncio, M.; Teixeira, C.; Gomes, P. N-cinnamoylation of antimalarial classics: Quinacrine analogues with decreased toxicity and dual-stage activity. Chem. Med. Chem. 2014, 9, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.; Machado, M.; Lobo, L.; Nogueira, F.; Prudêncio, M.; Teixeira, C.; Gomes, P. N-Cinnamoylation of antimalarial classics: Effects of using acyl groups other than cinnamoyl toward dual-stage antimalarials. Chem. Med. Chem. 2015, 10, 1344–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.; Fernandes, I.; Teixeira, C.; Mateus, N.; Sottomayor, M.J.; Gomes, P. A quinacrine analogue selective against gastric cancer cells: Insight from biochemical and biophysical studies. Chem. Med. Chem. 2016, 11, 2703–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, R.; Noronha, J.; Murtinheira, F.; Nogueira, F.; Machado, M.; Prudêncio, M.; Parapini, S.; D’Alessandro, S.; Teixeira, C.; Gomes, A.; et al. Primaquine-based ionic liquids as a novel class of antimalarial hits. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 56134–56138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, C.; Vale, N.; Pérez, B.; Gomes, A.; Gomes, J.R.B.; Gomes, P. “Recycling” classical drugs for malaria. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11164–11220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz, R.; Pinheiro, M.; Teixeira, C.; Gomes, A.; Prudêncio, C.; Reis, S.; Gomes, A. Effects of novel triple-stage antimalarial ionic liquids on lipid membrane models. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 4190–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, E.; Nguyen, T.-H.; Ford, L.; Williams, H.D.; Benameur, H.; Scammells, P.J.; Porter, C.J.H. Ionic liquid forms of the antimalarial lumefantrine in combination with LFCS Type IIIB lipid-based formulations preferentially increase lipid solubility, in vitro solubilization behavior and in vivo exposure. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoimenovski, J.; Izgorodina, E.I.; MacFarlane, D.R. Ionicity and proton transfer in protic ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 10341–10347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fameau, A.-L.; Arnould, A.; Lehmann, M.; von Klitzing, R. Photoresponsive self-assemblies based on fatty acids. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 2907–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Kaur, M.; Drechsler, M.; Kang, T.S. Unprecedented self-assembled architectures of surface-active ionic liquids in aqueous medium. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 2432–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoimenovski, J.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Bica, K.; Rogers, R.D. Crystalline versus ionic liquid salt forms of active pharmaceutical ingredients: A position paper. Pharm. Res. 2009, 27, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, K.S.; Gordeev, E.G.; Ananikov, V.P. Biological activity of ionic liquids and their application in pharmaceutics and medicine. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7132–7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.M.; Raposo, L.R.; Carrera, G.V.S.M.; Costa, A.; Dionísio, M.; Baptista, P.V.; Fernandes, A.R.; Branco, L.C. Ionic liquids and salts from ibuprofen as promising innovative formulations of an old drug. Chem. Med. Chem. 2019, 14, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, F.; Diez, A.; Radfar, A.; Pérez-Benavente, S.; do Rosário, V.E.; Puyet, A.; Bautista, J.M. Early transcriptional response to chloroquine of the Plasmodium falciparum antioxidant defence in sensitive and resistant clones. Acta Trop. 2010, 114, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, M.; Murtinheira, F.; Lobo, E.N.F. Whole-cell SYBR Green I assay for antimalarial activity assessment. Ann. Clin. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 2, 1010. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).