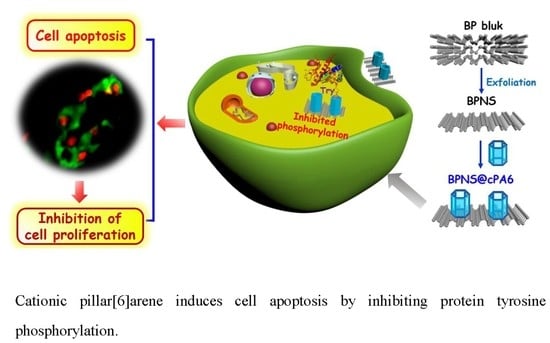
Cationic Pillar[6]arene Induces Cell Apoptosis by Inhibiting Protein Tyrosine Phosphorylation Via Host–Guest Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
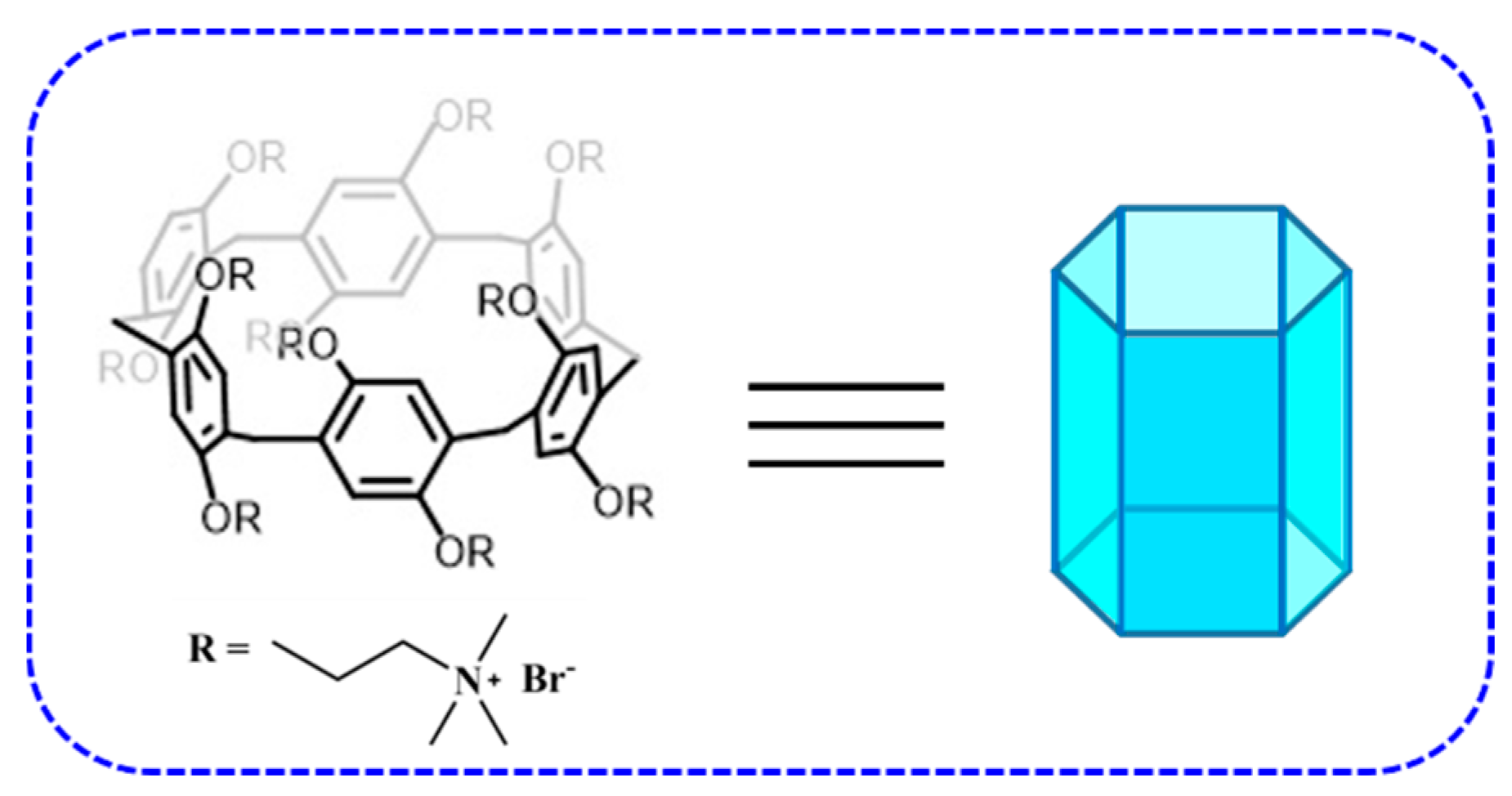
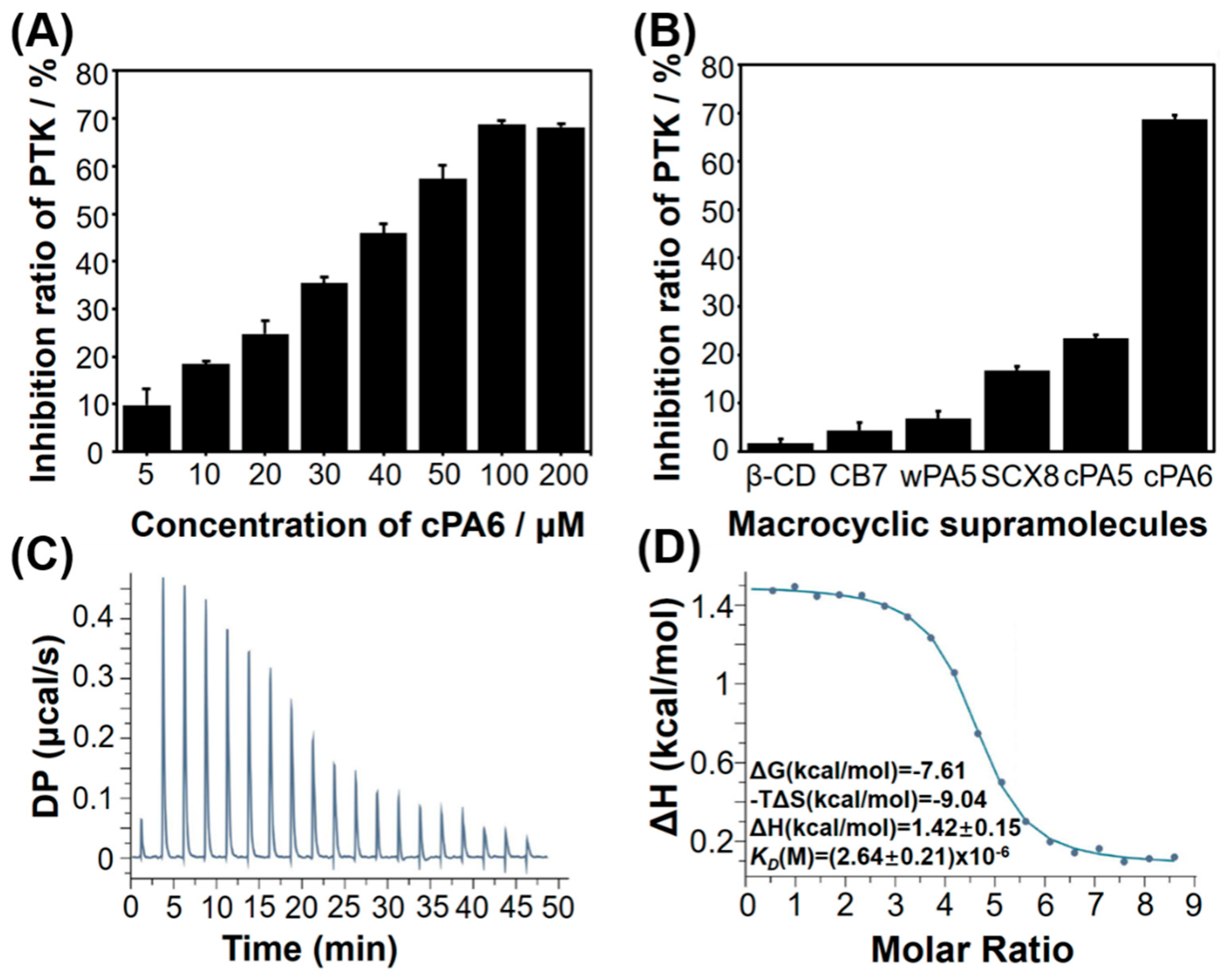
2.1. Inhibition of Tyr Phosphorylation by Macrocyclic Molecules in Vitro
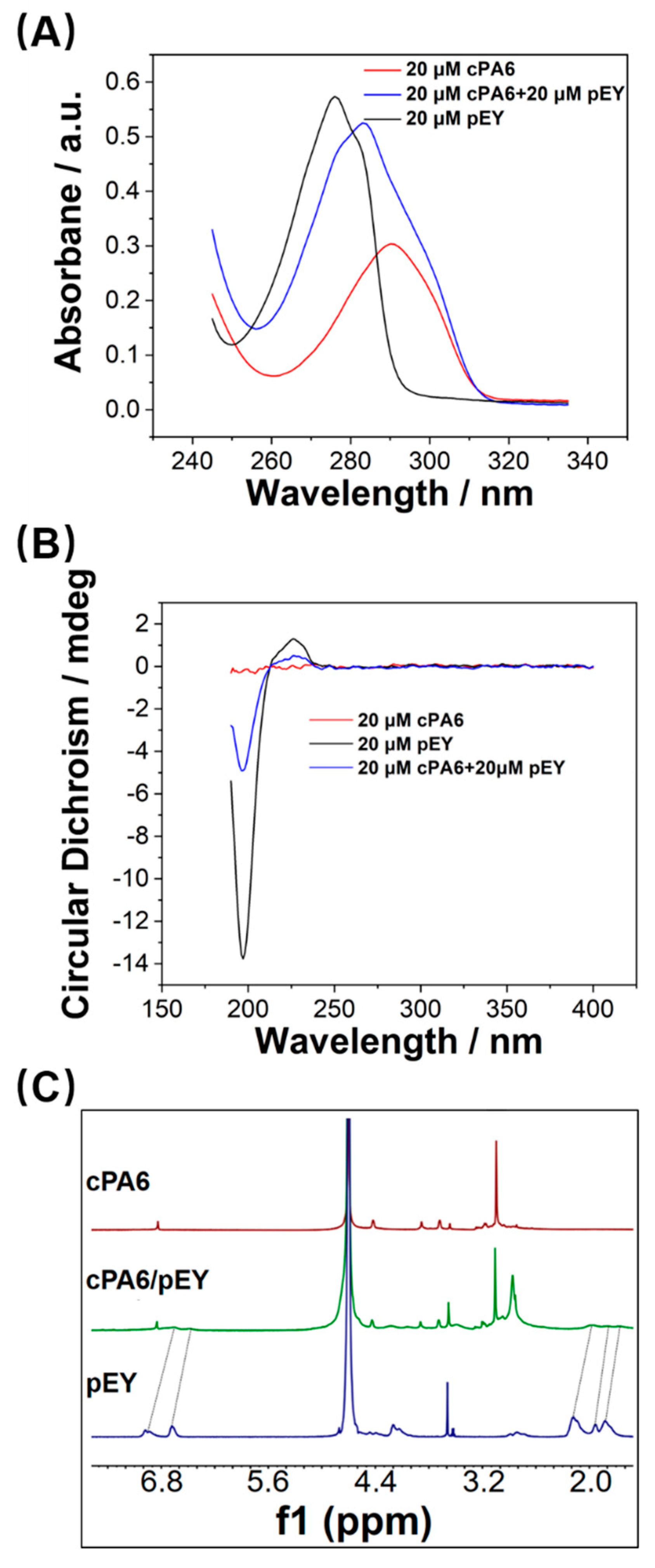
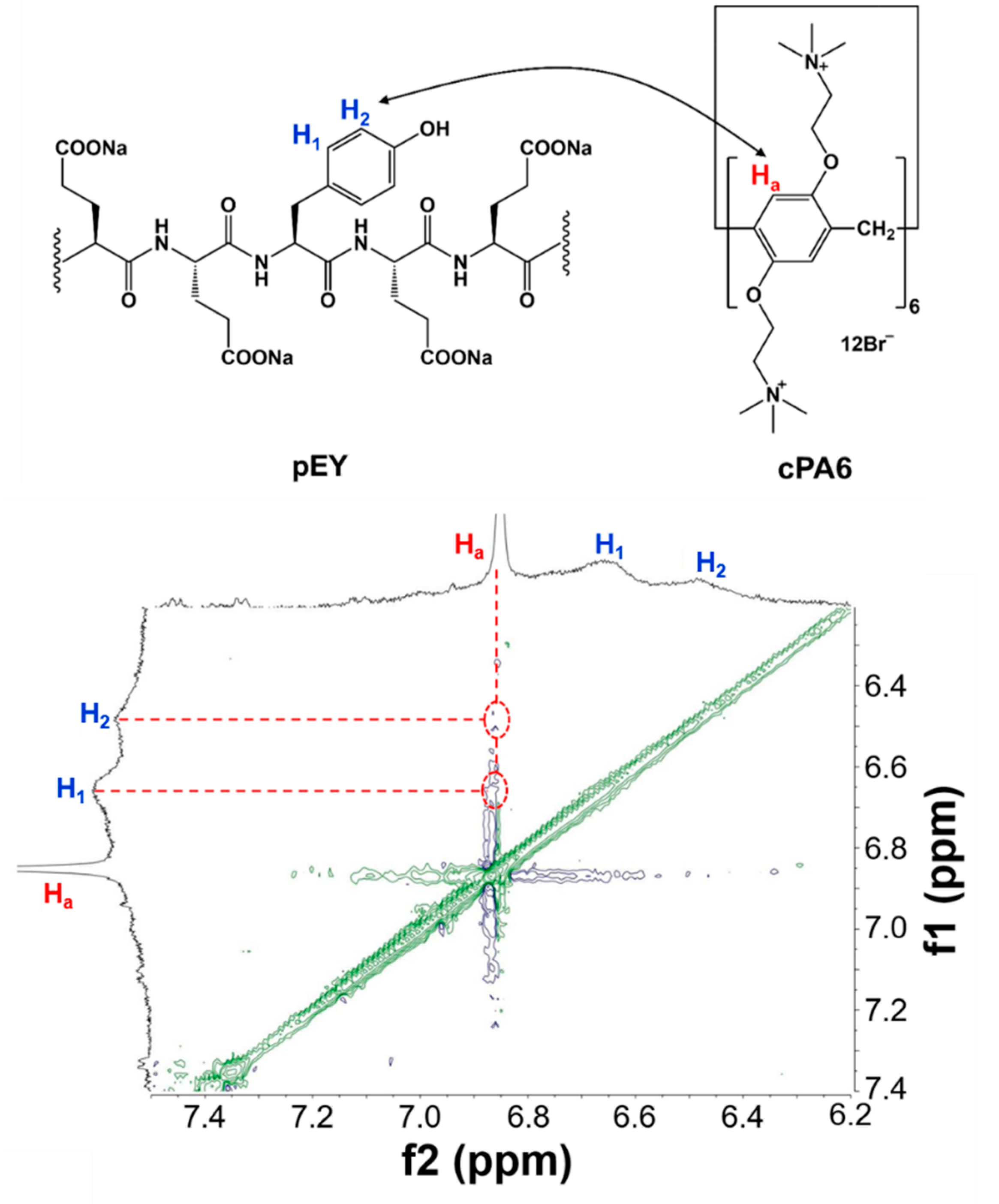
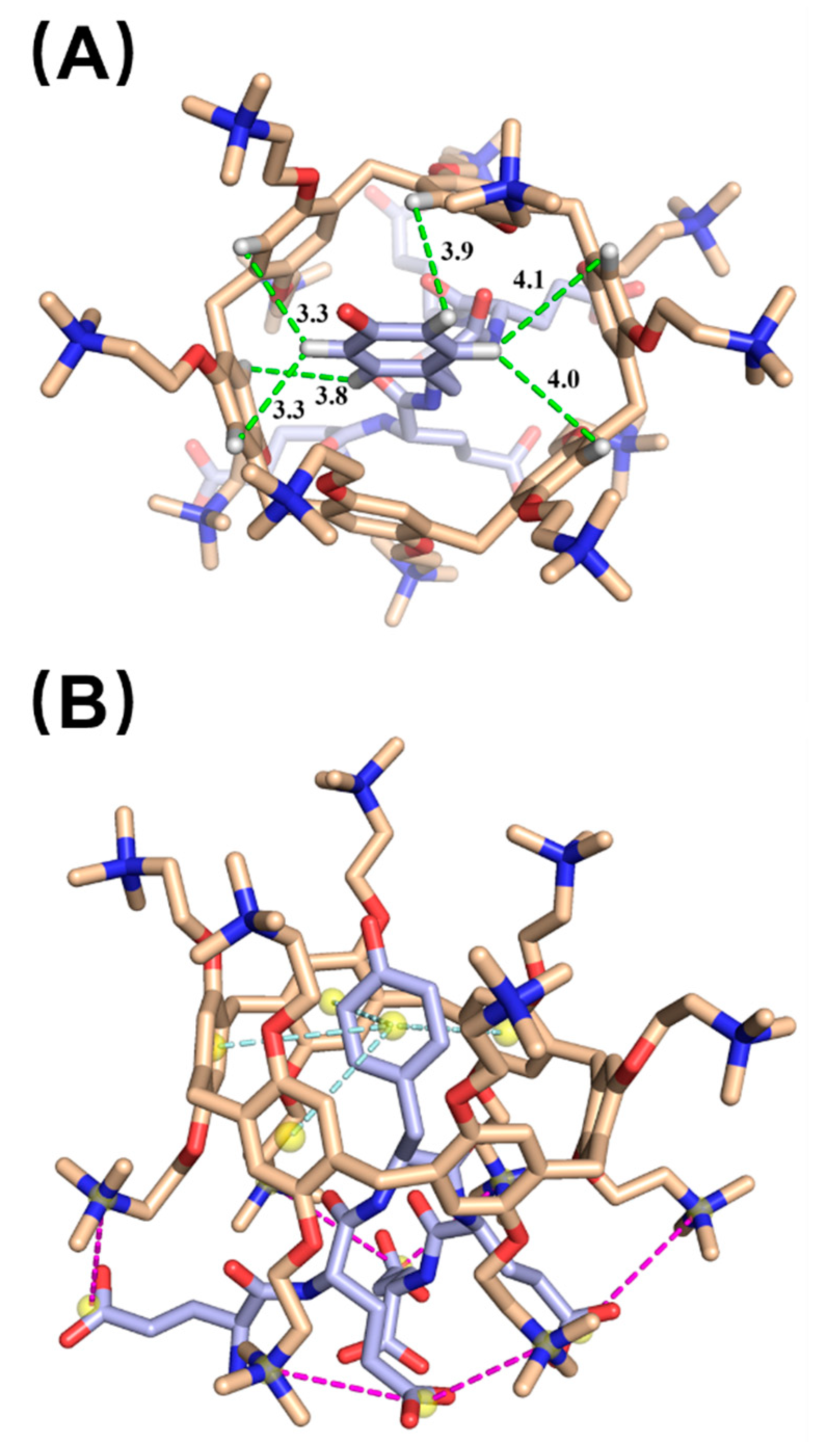
2.2. Host–Guest Interaction between cPA6 and pEY
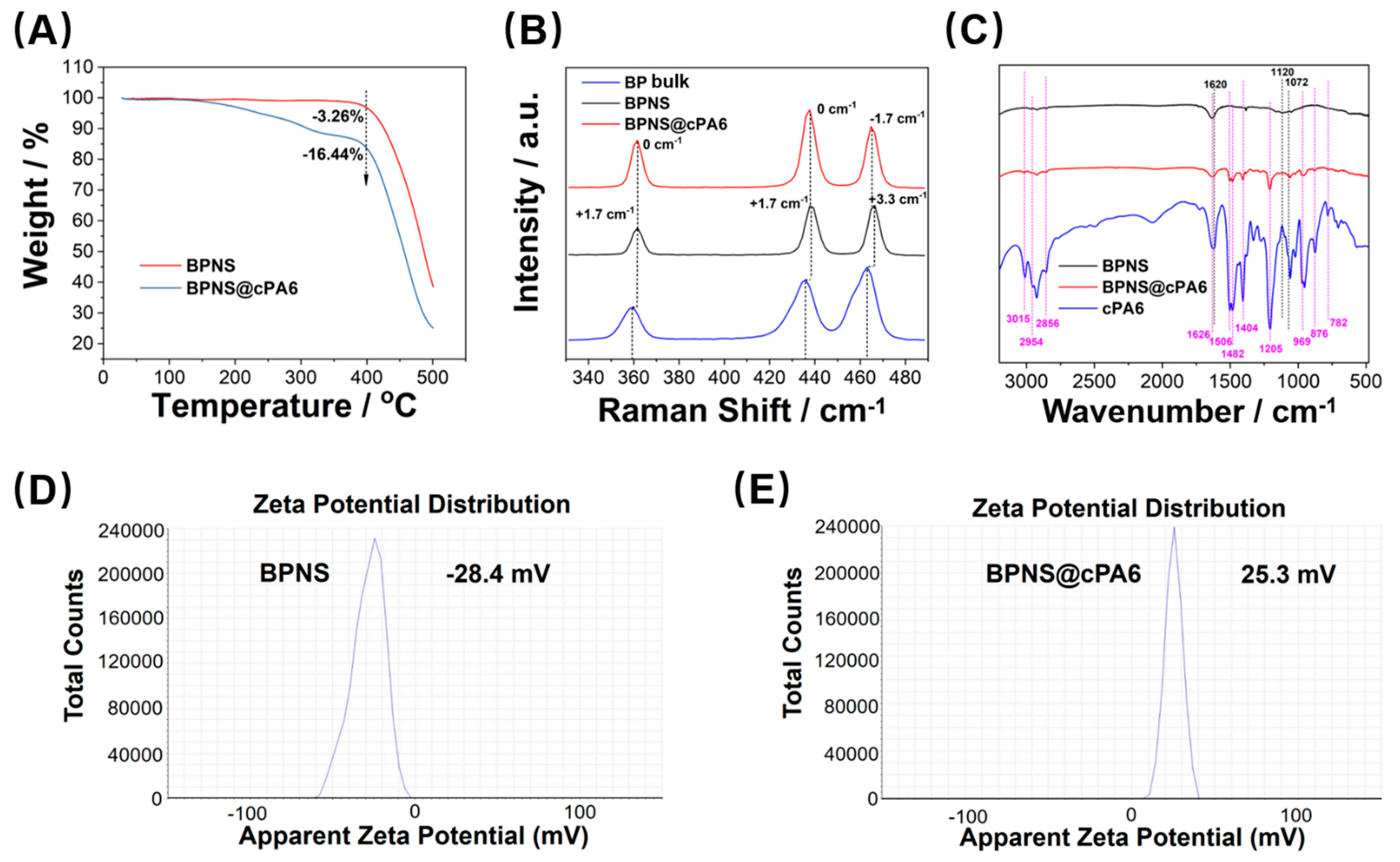
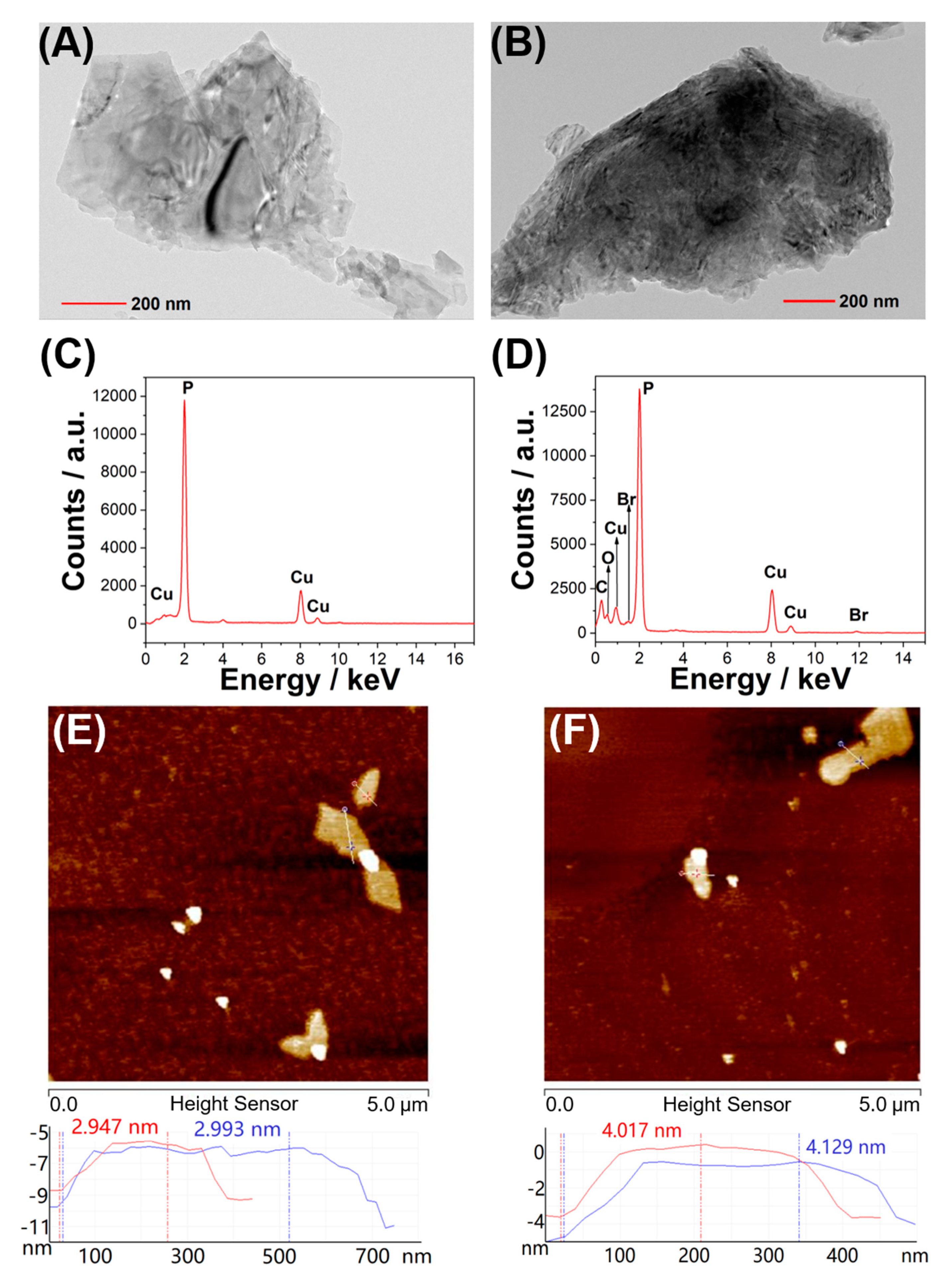
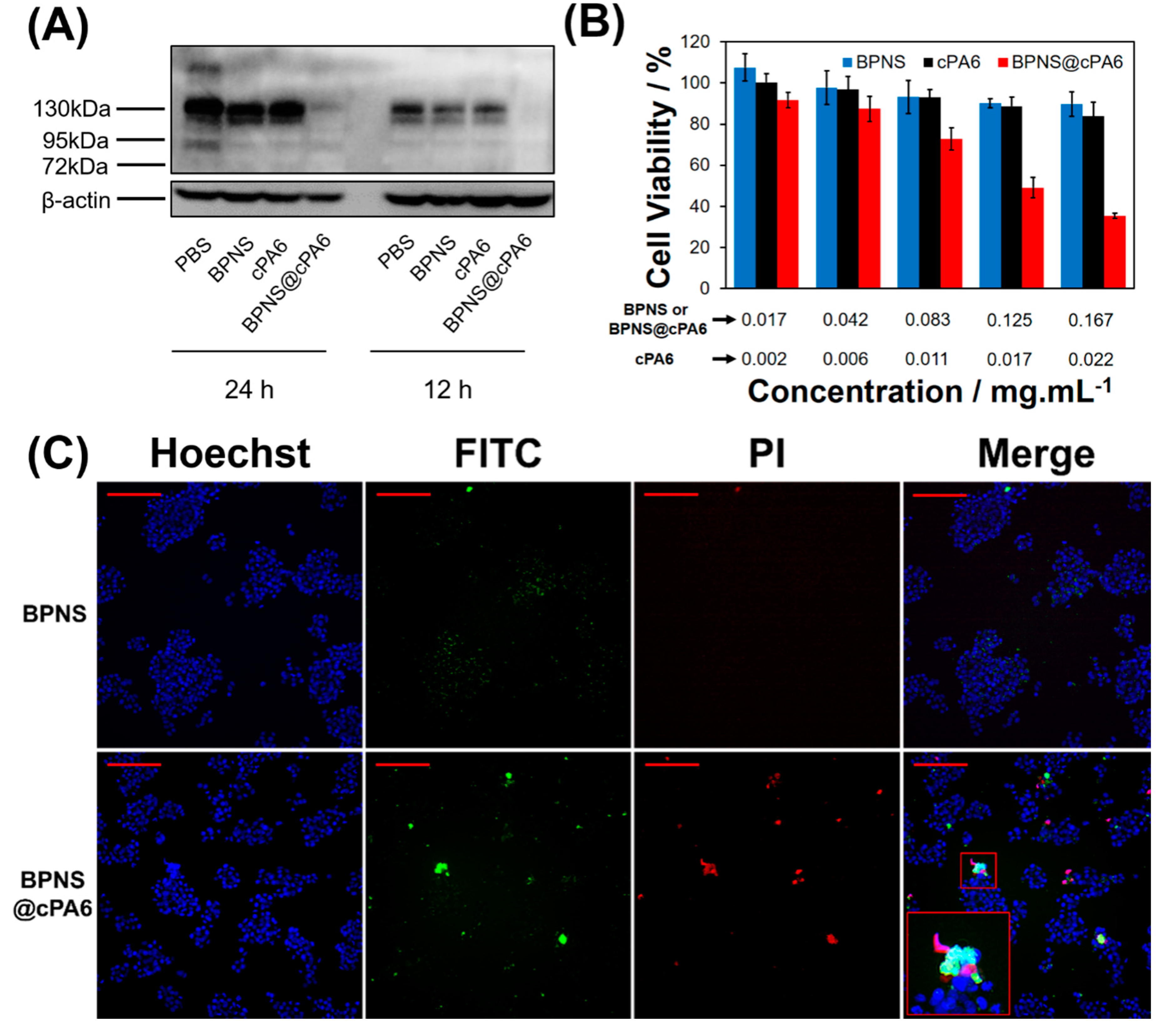
2.3. Effect of cPA6 on Tyr Phosphorylation in Cells
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials, Reagents, and Equipment
4.2. Effect of Macrocyclic Supramolecules on Tyr Phosphorylation
4.3. Molecular Docking
4.4. Synthesis of BPNS
4.5. Synthesis of BPNS @cPA6
4.6. Synthesis of BPNS-PEG-FITC and BPNS @cPA6-PEG-FITC
4.7. Cell Culture
4.8. Uptake of BPNS@cPA6 in Cells
4.9. Western Blot
4.10. Cell Viability
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATP | adenosine triphosphate |
| BPNS | black phosphorus nanosheets |
| ITC | isothermal titration calorimetry |
| PTK | protein tyrosine kinase |
References
- Peczuh, M.W.; Hamilton, A.D. Peptide and protein recognition by designed molecules. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 2479–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashiro, S.; Tominaga, M.; Kawano, M.; Therrien, B.; Ozeki, T.; Fujita, M. Sequence-selective recognition of peptides within the single binding pocket of a self-assembled coordination cage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 4546–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaver, J.E.; Waters, M.L. Molecular recognition of Lys and Arg methylation. Acs Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamuro, Y.; Calama, M.C.; Park, H.S.; Hamilton, A.D. A calixarene with four peptide loops: An antibody mimic for recognition of protein surfaces. Angew. Chem. 1997, 36, 2680–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uekama, K.; Hirayama, F.; Irie, T. Cyclodextrin drug carrier systems. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 2045–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinalli, R.; Pedrini, A.; Dalcanale, E. Biochemical sensing with macrocyclic receptors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 7006–7026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bontempi, N.; Biavardi, E.; Bordiga, D.; Candiani, G.; Alessandri, I.; Bergese, P.; Dalcanale, E. Probing lysine mono-methylation in histone H3 tail peptides with an abiotic receptor coupled to a non-plasmonic resonator. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 8639–8646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Perez, L.; Mettry, M.; Easley, C.J.; Hooley, R.J.; Zhong, W. Self-aggregating deep cavitand acts as a fluorescence displacement sensor for lysine methylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 10746–10749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Perez, L.; Gill, A.D.; Mettry, M.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Hooley, R.J.; Zhong, W. Site-selective sensing of histone methylation enzyme activity via an arrayed supramolecular tandem assay. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 10964–10967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaker, S.A.; Daze, K.D.; Ma, M.C.F.; Hof, F. Antibody-free reading of the histone code using a simple chemical sensor array. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 11674–11680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadmard, R.; Schrader, T. Nanomolar protein sensing with embedded receptor molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guagnini, F.; Antonik, P.M.; Rennie, M.L.; O’Byrne, P.; Khan, A.R.; Pinalli, R.; Dalcanale, E.; Crowley, P.B. Cucurbit[7]uril-dimethyllysine recognition in a model protein. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7126–7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wagner, H.; Still, W.C. Fluorescent, sequence-selective peptide detection by synthetic small molecules. Science 1998, 279, 851–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmuck, C. How to improve guanidinium cations for oxoanion binding in aqueous solution? The design of artificial peptide receptors. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2006, 250, 3053–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekharsky, M.V.; Yamamura, H.; Inoue, C.; Kawai, M.; Osaka, I.; Arakawa, R.; Shiba, K.; Sato, A.; Ko, Y.H.; Selvapalam, N. Chiral recognition in cucurbituril cavities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 14871–14880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitmann, L.M.; Taylor, A.B.; Hart, P.J.; Urbach, A.R. Sequence-specific recognition and cooperative dimerization of N-terminal aromatic peptides in aqueous solution by a synthetic host. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 12574–12581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennig, A.; Ghale, G.; Nau, W.M. Effects of cucurbit[7]uril on enzymatic activity. Chem. Commun. 2007, 16, 1614–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logsdon, L.A.; Urbach, A.R. Sequence-specific inhibition of a nonspecific protease. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 11414–11416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Smith, L.C.; Leach, D.G.; Blaylock, B.E.; Ali, O.A.; Urbach, A.R. Sequence-specific, nanomolar peptide binding via cucurbit[8]uril-induced folding and inclusion of neighboring side chains. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 3663–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ding, F. Efficient fluorescent sensors of oligopeptides by dithiobis(2-benzoylamide)-bridged bis(β-cyclodextrin)s: Structure in solution, binding behavior, and thermodynamic origin. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcgovern, R.E.; Fernandes, H.; Khan, A.R.; Power, N.P.; Crowley, P.B. Protein camouflage in cytochrome c–calixarene complexes. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogoshi, T.; Kanai, S.; Fujinami, S.; Yamagishi, T.; Nakamoto, Y. Para-Bridged symmetrical pillar[5]arenes: Their lewis acid catalyzed synthesis and host–guest property. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5022–5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogoshi, T.; Yamagishi, T.; Nakamoto, Y. Pillar-shaped macrocyclic hosts pillar[n]arenes: New key players for supramolecular chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 7937–8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Pei, Y.; Wen, J.; Pei, Z. Recent advances in pillar[n]arenes: Synthesis and applications based on host–guest interactions. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 9316–9326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ma, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Shu, X.; Li, J.; Jia, X. Molecular selective binding of basic amino acids by a water-soluble pillar[5]arene. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 1924–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, D.X.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Tan, L.; Weiss, P.S.; Yang, Y. Viologen-mediated assembly of and sensing with carboxylatopillar[5]arene-modified gold nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1570–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Fu, D.; Wu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Tan, L.; Zhou, T.; Ma, S.; Zha, X.; Yang, Y. Efficient inhibition of human papillomavirus 16 L1 pentamer formation by a carboxylatopillarene and a p-sulfonatocalixarene. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 3201–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, D.X.; Wang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Stoddart, J.F. Mechanized silica nanoparticles based on pillar[5]arenes for on-command cargo release. Small 2013, 9, 3224–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiyajith, C.; Shaikh, R.R.; Han, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Meguellati, K.; Yang, Y. Biological and related applications of pillar[n]arenes. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 677–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbera, L.; De Plano, L.M.; Franco, D.; Gattuso, G.; Guglielmino, S.P.P.; Lando, G.; Notti, A.; Parisi, M.F.; Pisagatti, I. Antiadhesive and antibacterial properties of pillar[5]arene-based multilayers. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 10203–10206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, R.; Naugolny, A.; Feldman, M.; Herzog, I.M.; Fridman, M.; Cohen, Y. Cationic pillararenes potently inhibit biofilm formation without affecting bacterial growth and viability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 754–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.M.; Wang, D.; Cole, P.A. Chemical rescue of a mutant protein-tyrosine kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 38127–38130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Schlessinger, J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 2000, 141, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regad, T. Targeting RTK signaling pathways in cancer. Cancers 2015, 7, 1758–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, P. Protein kinases—the major drug targets of the twenty-first century? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haskell, M.D.; Slack, J.K.; Parsons, J.T.; Parsons, S.J. C-Src tyrosine phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor, P190 RhoGAP, and focal adhesion kinase regulates diverse cellular processes. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 2425–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocco, E.; Scaltriti, M.; Drilon, A. NTRK fusion-positive cancers and TRK inhibitor therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 731–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, L. Non-kinase targets of protein kinase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 424–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggi, E.; Perez, Y.; Luis, S.V.; Alfonso, I. Supramolecular protection from the enzymatic tyrosine phosphorylation in a polypeptide. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 8142–8145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Fan, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Mei, L. 2D Black phosphorus–based biomedical applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Wang, H.; Jia, Y. Rediscovering black phosphorus as an anisotropic layered material for optoelectronics and electronics. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, T.; Grinstein, S. Lipid signaling and the modulation of surface charge during phagocytosis. Immunol. Rev. 2007, 219, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotnik, T.; Pucihar, G.; Miklavcic, D. Induced transmembrane voltage and its correlation with electroporation-mediated molecular transport. J. Membr. Biol. 2010, 236, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagrintseva, K.; Schwab, R.; Kohl, T.M.; Schnittger, S.; Eichenlaub, S.; Ellwart, J.W.; Hiddemann, W.; Spiekermann, K. Mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of FLT3 define a new molecular mechanism of acquired drug resistance to PTK inhibitors in FLT3-ITD transformed hematopoietic cells. Blood 2004, 103, 2266–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Jie, K.; Huang, F. Supramolecular amphiphiles based on host–guest molecular recognition motifs. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 7240–7303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Yang, Y.; Chi, X.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, F. Pillararenes, a new class of macrocycles for supramolecular chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 1294–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Qin, S.; Yao, C.; Li, Y.; Cao, D.; Peng, L.; Wang, L. Controllable construction of biocompatible supramolecular micelles and vesicles by water-soluble phosphate pillar[5,6]arenes for selective anti-cancer drug delivery. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 3778–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cell Type | Cell Line | IC50 (mg·mL−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Cancer cell | HepG2 | 0.1229 |
| BT474 | 0.1586 | |
| LNCaP | 0.1901 | |
| Normal cell | L-02 | 0.2752 |
| MCF10A | 0.2833 | |
| 293T | 0.2791 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.-P.; Lu, Y.-X.; Zi, C.-T.; Zhao, Y.-T.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.-P. Cationic Pillar[6]arene Induces Cell Apoptosis by Inhibiting Protein Tyrosine Phosphorylation Via Host–Guest Recognition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4979. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144979
Li C-P, Lu Y-X, Zi C-T, Zhao Y-T, Zhao H, Zhang Y-P. Cationic Pillar[6]arene Induces Cell Apoptosis by Inhibiting Protein Tyrosine Phosphorylation Via Host–Guest Recognition. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(14):4979. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144979
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Can-Peng, Yu-Xun Lu, Cheng-Ting Zi, Yu-Ting Zhao, Hui Zhao, and Ya-Ping Zhang. 2020. "Cationic Pillar[6]arene Induces Cell Apoptosis by Inhibiting Protein Tyrosine Phosphorylation Via Host–Guest Recognition" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 14: 4979. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144979
APA StyleLi, C.-P., Lu, Y.-X., Zi, C.-T., Zhao, Y.-T., Zhao, H., & Zhang, Y.-P. (2020). Cationic Pillar[6]arene Induces Cell Apoptosis by Inhibiting Protein Tyrosine Phosphorylation Via Host–Guest Recognition. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(14), 4979. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144979