Identification and Characterization of Circular Intronic RNAs Derived from Insulin Gene
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification and Characterization of Pancreatic Islet CircRNAs
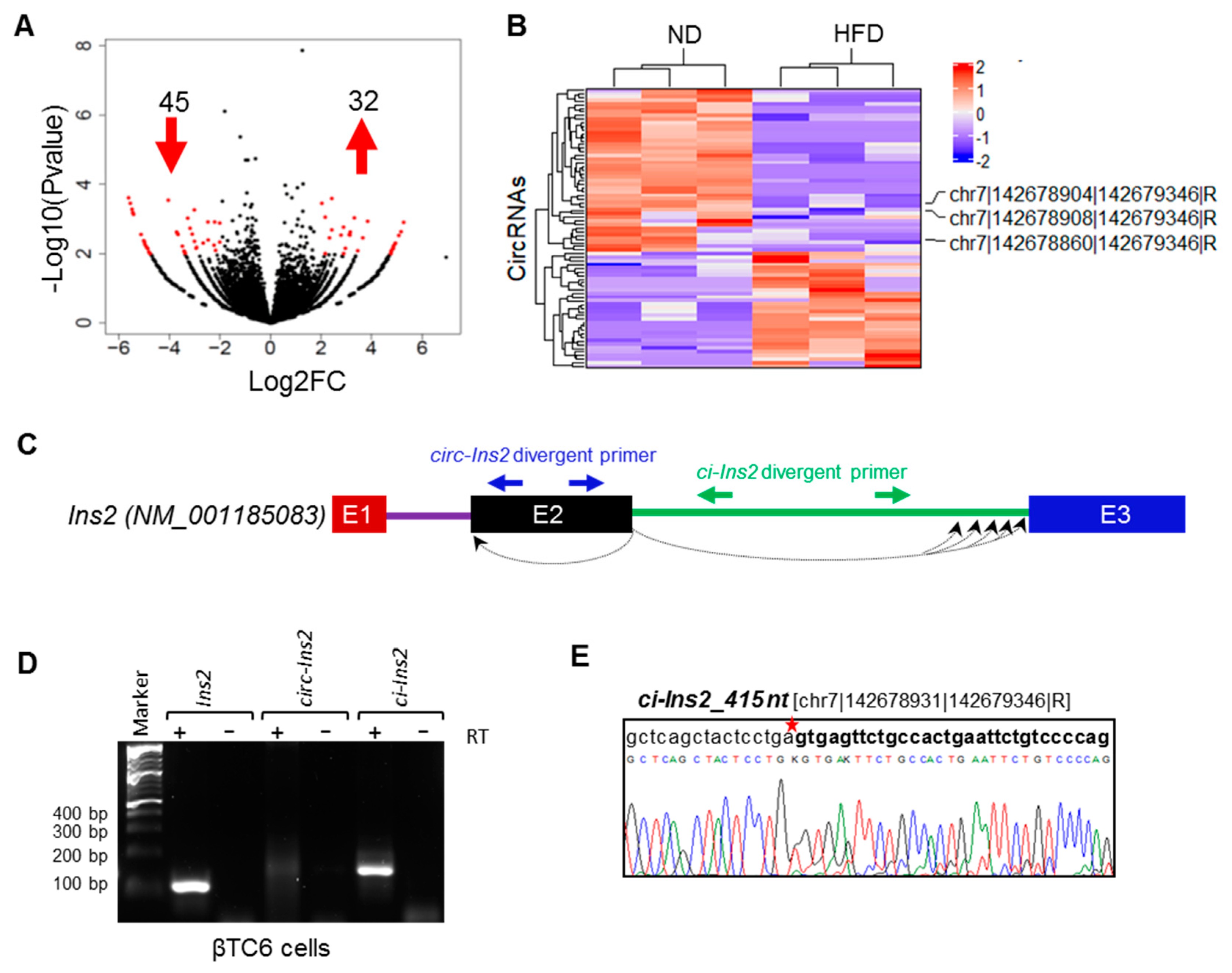
2.2. Identification of Differentially Expressed (DE) CircRNAs
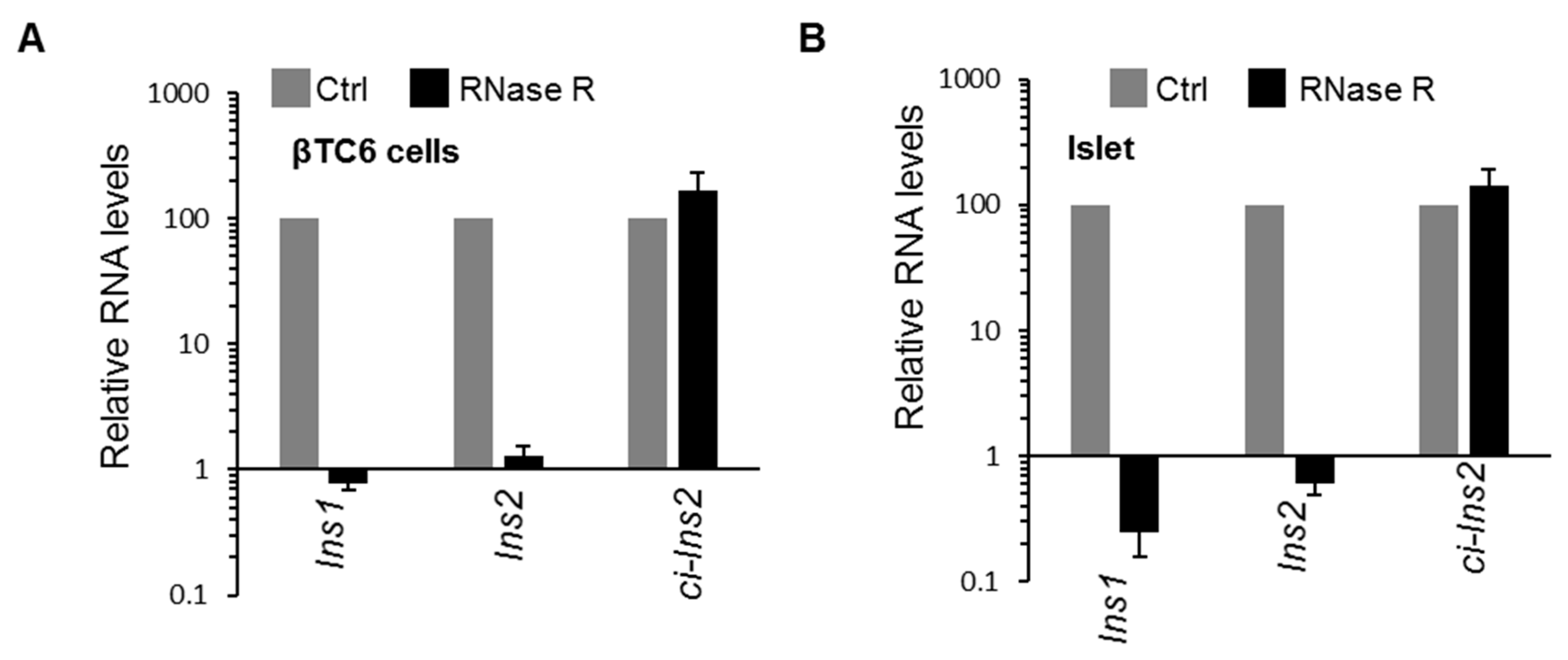
2.3. Multiple Exonic and Intronic CircRNAs are Generated from Ins2 Genes
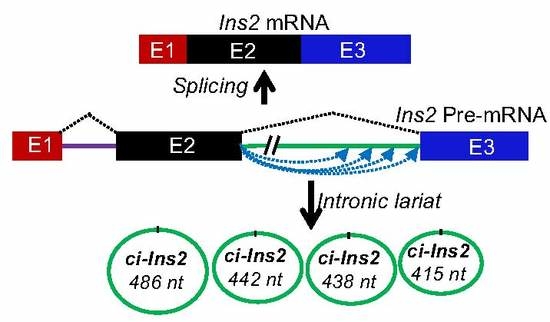
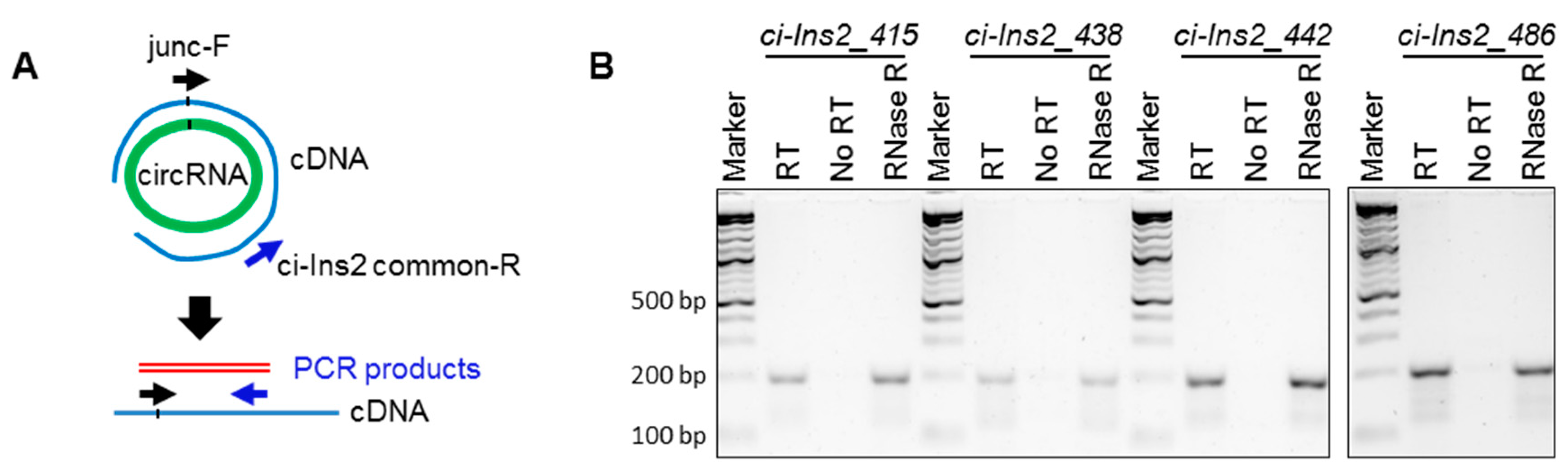
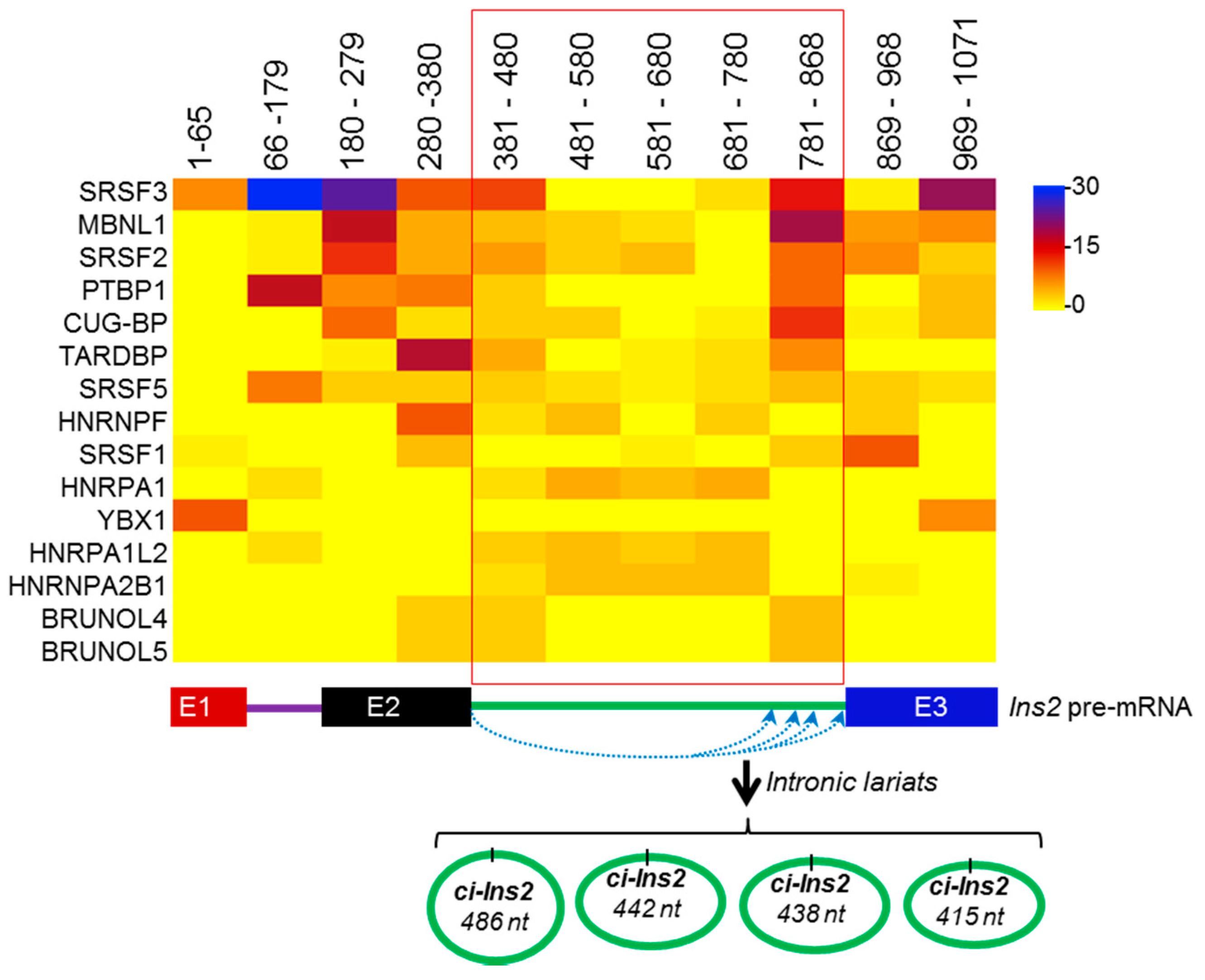
2.4. Alternate Branchpoint Selection Generates Multiple Ci-Ins2 Lariats
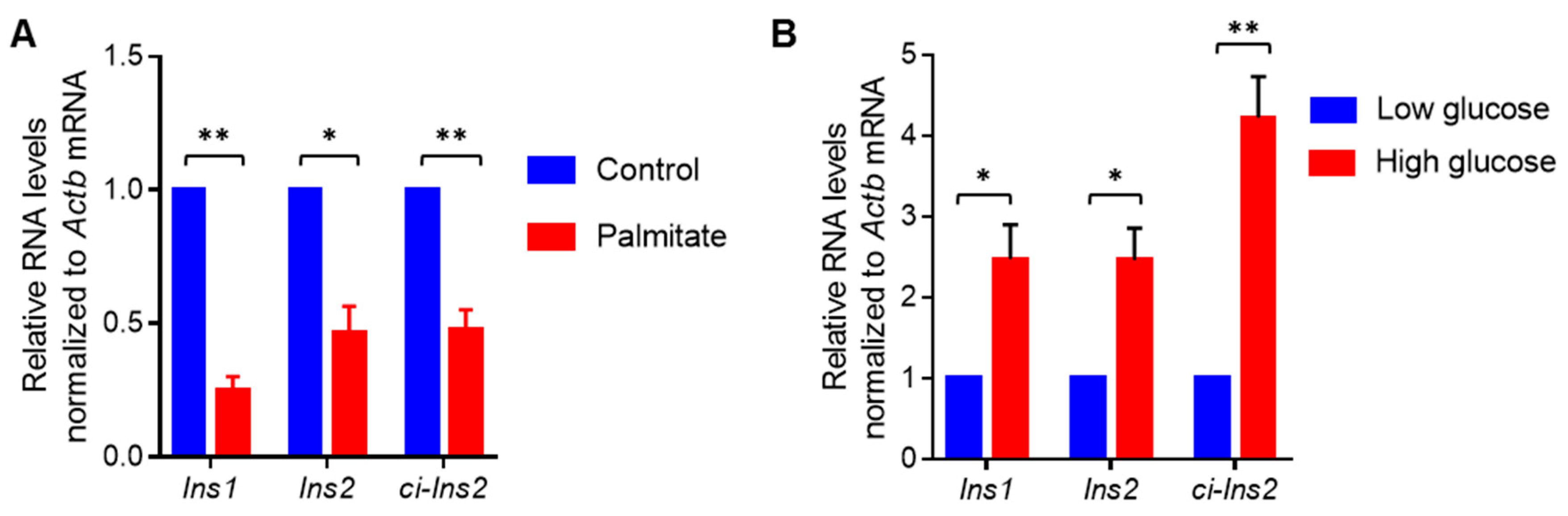
2.5. Exposure of βTC6 Cells to Palmitate and High Glucose Alters the Level of Ci-Ins2
2.6. Splicing Factors are Predicted to Interact with the Ins2 pre-mRNA and ci-Ins2
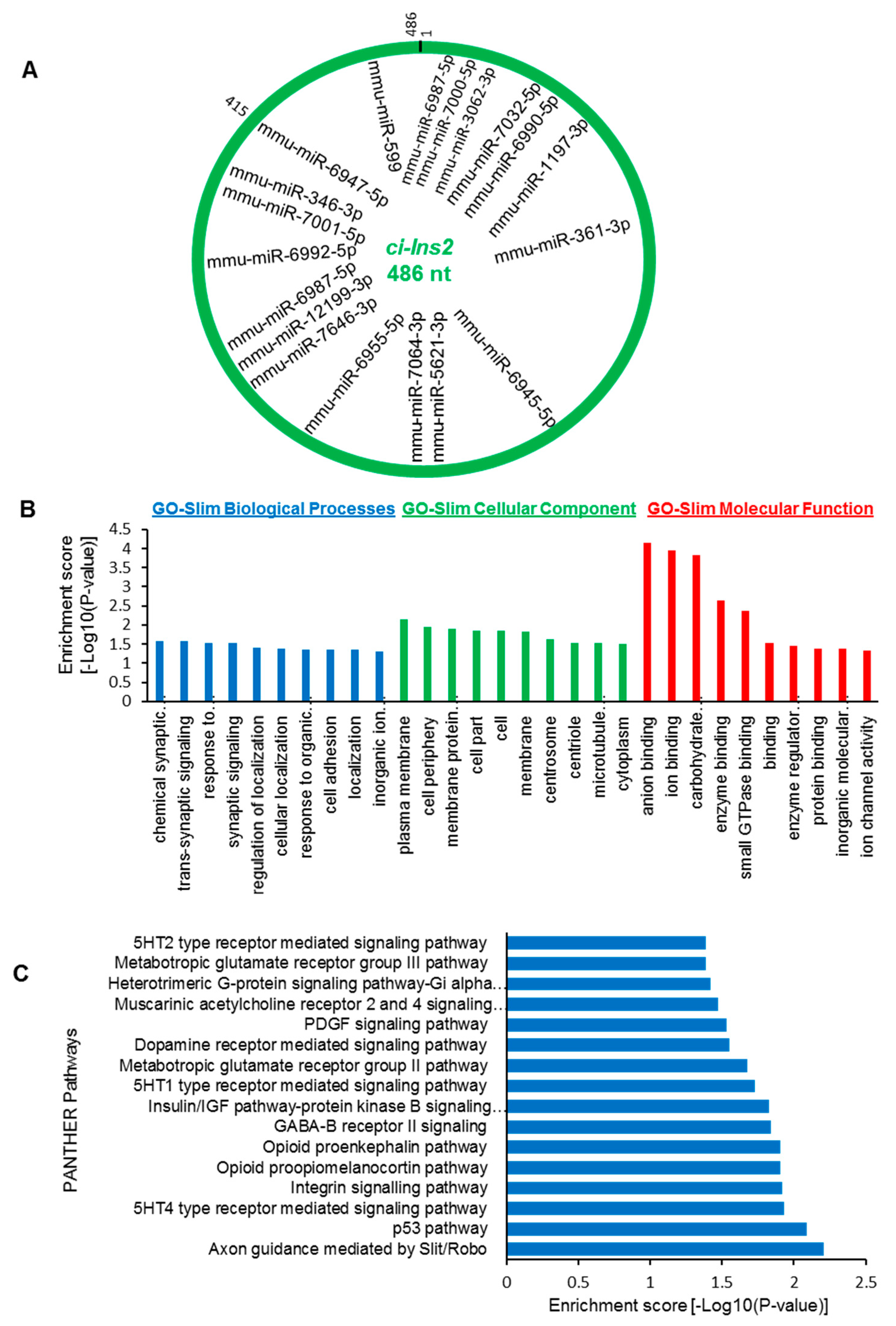
2.7. The ci-Ins2 May Regulate Beta-Cell Physiology by Sponging miRNAs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. CircRNA Annotation
4.2. Animals and Pancreatic Islet Isolation
4.3. βTC6 Cell Culture and In Vitro Treatments
4.4. RNA Isolation, RT-PCR, and Sanger Sequencing
4.5. PCR Product Cloning and DNA Sequencing
4.6. Quantitative (q)PCR Analysis and RNase R Treatment
4.7. Prediction of RBPs, miRNA, and mRNA Targets
4.8. Statistical Analysis and Visualization
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cho, N.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. IDF Diabetes atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harreiter, J.; Roden, M. Diabetes mellitus-definition, classification, diagnosis, screening and prevention. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2019, 131, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laville, M.; Nazare, J.A. Diabetes, insulin resistance and sugars. Obes. Rev. 2009, 10, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plum, L.; Belgardt, B.F.; Bruning, J.C. Central insulin action in energy and glucose homeostasis. J. Clin. Invest. 2006, 116, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melloul, D.; Marshak, S.; Cerasi, E. Regulation of insulin gene transcription. Diabetologia 2002, 45, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.C.; Grammatikakis, I.; Yoon, J.H.; Abdelmohsen, K. Posttranscriptional regulation of insulin family ligands and receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 19202–19229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans-Molina, C.; Garmey, J.C.; Ketchum, R.; Brayman, K.L.; Deng, S.; Mirmira, R.G. Glucose regulation of insulin gene transcription and pre-mRNA processing in human islets. Diabetes 2007, 56, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.C.; Sahu, I.; Kulkarni, S.D.; Martindale, J.L.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Vindu, A.; Joseph, J.; Gorospe, M.; Seshadri, V. miR-196b-mediated translation regulation of mouse insulin2 via the 5’UTR. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.D.; Muralidharan, B.; Panda, A.C.; Bakthavachalu, B.; Vindu, A.; Seshadri, V. Glucose-stimulated translation regulation of insulin by the 5’ UTR-binding proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 14146–14156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guria, A.; Sharma, P.; Natesan, S.; Pandi, G. Circular RNAs-the road less traveled. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2019, 6, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.; Wu, W.; Chen, S.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, H.; Yan, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, P.; et al. Expanded expression landscape and prioritization of circular RNAs in mammals. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 3444–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glazar, P.; Papavasileiou, P.; Rajewsky, N. circBase: A database for circular RNAs. RNA 2014, 20, 1666–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vromman, M.; Vandesompele, J.; Volders, P.J. Closing the circle: Current state and perspectives of circular RNA databases. Brief. Bioinform. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.O.; Dong, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.L.; Yang, L. Diverse alternative back-splicing and alternative splicing landscape of circular RNAs. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xue, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.L.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. The biogenesis of nascent circular RNAs. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.O.; Chen, T.; Xiang, J.F.; Yin, Q.F.; Xing, Y.H.; Zhu, S.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell. 2013, 51, 792–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.C.; De, S.; Grammatikakis, I.; Munk, R.; Yang, X.; Piao, Y.; Dudekula, D.B.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Gorospe, M. High-purity circular RNA isolation method (RPAD) reveals vast collection of intronic circRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Bao, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Zhong, G.; Yu, B.; Hu, W.; Dai, L.; et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, N.E. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 2013, 19, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamudurti, N.R.; Bartok, O.; Jens, M.; Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Stottmeister, C.; Ruhe, L.; Hanan, M.; Wyler, E.; Perez-Hernandez, D.; Ramberger, E.; et al. Translation of CircRNAs. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, A.C. Circular RNAs Act as miRNA sponges. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1087, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, P.R.; Yang, J.H.; Tsitsipatis, D.; Panda, A.C.; Noh, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Munk, R.; Nicholson, T.; Hanniford, D.; Argibay, D.; et al. circSamd4 represses myogenic transcriptional activity of PUR proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Meyer, M.; Pamudurti, N.R.; Ivanov, A.; Bartok, O.; Hanan, M.; Evantal, N.; Memczak, S.; Rajewsky, N.; Kadener, S. circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmohsen, K.; Panda, A.C.; De, S.; Grammatikakis, I.; Kim, J.; Ding, J.; Noh, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Mattison, J.A.; de Cabo, R.; et al. Circular RNAs in monkey muscle: Age-dependent changes. Aging 2015, 7, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.C.; Grammatikakis, I.; Kim, K.M.; De, S.; Martindale, J.L.; Munk, R.; Yang, X.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Gorospe, M. Identification of senescence-associated circular RNAs (SAC-RNAs) reveals senescence suppressor CircPVT1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 4021–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Das, A.; Das, D.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Panda, A.C. Circular RNAs in myogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2019, 194372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Das, A.; Panda, A.C. Emerging role of long noncoding RNAs and circular RNAs in pancreatic β cells. Non Coding RNA Investig. 2018, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.; Harries, L.W. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) in health and disease. Genes 2017, 8, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, D.; Pu, W.; Wang, J.; Peng, Y. Circular RNAs in cancer: Biogenesis, function, and clinical significance. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.L.; Xu, Z.H.; Yang, S.M.; Yu, C.; Zhang, F.; Qin, M.C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhong, Z.G.; Wu, D.P. Identification of differentially expressed profiles of Alzheimer’s disease associated circular RNAs in a panax notoginseng saponins-treated Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoll, L.; Sobel, J.; Rodriguez-Trejo, A.; Guay, C.; Lee, K.; Veno, M.T.; Kjems, J.; Laybutt, D.R.; Regazzi, R. Circular RNAs as novel regulators of beta-cell functions in normal and disease conditions. Mol. Metab. 2018, 9, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motterle, A.; Gattesco, S.; Peyot, M.L.; Esguerra, J.L.S.; Gomez-Ruiz, A.; Laybutt, D.R.; Gilon, P.; Burdet, F.; Ibberson, M.; Eliasson, L.; et al. Identification of islet-enriched long non-coding RNAs contributing to beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 1407–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Ji, P.; Zhao, F. CircAtlas: An integrated resource of one million highly accurate circular RNAs from 1070 vertebrate transcriptomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, T.R.; Clark, M.B.; Andersen, S.B.; Brunck, M.E.; Haerty, W.; Crawford, J.; Taft, R.J.; Nielsen, L.K.; Dinger, M.E.; Mattick, J.S. Genome-wide discovery of human splicing branchpoints. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.Q.; Malhotra, A.; Mayeda, A. Characterization of RNase R-digested cellular RNA source that consists of lariat and circular RNAs from pre-mRNA splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, J.M.B.; Bradley, R.K. Most human introns are recognized via multiple and tissue-specific branchpoints. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelpe, C.L.; Moore, P.C.; Parazzoli, S.D.; Wicksteed, B.; Rhodes, C.J.; Poitout, V. Palmitate inhibition of insulin gene expression is mediated at the transcriptional level via ceramide synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 30015–30021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz-Laser, B.; Meda, P.; Constant, I.; Klages, N.; Charollais, A.; Morales, A.; Magnan, C.; Ktorza, A.; Philippe, J. Glucose-induced preproinsulin gene expression is inhibited by the free fatty acid palmitate. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 4005–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briaud, I.; Harmon, J.S.; Kelpe, C.L.; Segu, V.B.; Poitout, V. Lipotoxicity of the pancreatic beta-cell is associated with glucose-dependent esterification of fatty acids into neutral lipids. Diabetes 2001, 50, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacqueminet, S.; Briaud, I.; Rouault, C.; Reach, G.; Poitout, V. Inhibition of insulin gene expression by long-term exposure of pancreatic beta cells to palmitate is dependent on the presence of a stimulatory glucose concentration. Metabolism 2000, 49, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Sheng, Q.; Liu, Q.; Shyr, Y. beRBP: Binding estimation for human RNA-binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillmar, L.; Welsh, N. Hypoxia may increase rat insulin mRNA levels by promoting binding of the polypyrimidine tract-binding protein (PTB) to the pyrimidine-rich insulin mRNA 3’-untranslated region. Mol. Med. 2002, 8, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araki, K.; Araki, A.; Honda, D.; Izumoto, T.; Hashizume, A.; Hijikata, Y.; Yamada, S.; Iguchi, Y.; Hara, A.; Ikumi, K.; et al. TDP-43 regulates early-phase insulin secretion via CaV1.2-mediated exocytosis in islets. J. Clin. Invest. 2019, 130, 3578–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X. miRDB: An online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D127–D131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loher, P.; Rigoutsos, I. Interactive exploration of RNA22 microRNA target predictions. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3322–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.W.; Bartel, D.P. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Li, J.; Huang, K.Y.; Shrestha, S.; Hong, H.C.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Y.G.; Jin, C.N.; Yu, Y.; et al. miRTarBase 2020: Updates to the experimentally validated microRNA-target interaction database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D148–D154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.; Muruganujan, A.; Ebert, D.; Huang, X.; Thomas, P.D. PANTHER version 14: More genomes, a new PANTHER GO-slim and improvements in enrichment analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D419–D426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerf, M.E. Beta cell dysfunction and insulin resistance. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erion, K.; Corkey, B.E. Beta-cell failure or beta-cell abuse? Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, A.; Memczak, S.; Wyler, E.; Torti, F.; Porath, H.T.; Orejuela, M.R.; Piechotta, M.; Levanon, E.Y.; Landthaler, M.; Dieterich, C.; et al. Analysis of intron sequences reveals hallmarks of circular RNA biogenesis in animals. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, F. Circular RNA identification based on multiple seed matching. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 19, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.C.; Kulkarni, S.D.; Muralidharan, B.; Bakthavachalu, B.; Seshadri, V. Novel splice variant of mouse insulin2 mRNA: Implications for insulin expression. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 1169–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.C.; Gorospe, M. Detection and analysis of circular RNAs by RT-PCR. Bio Protoc. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M. Complex heatmaps reveal patterns and correlations in multidimensional genomic data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2847–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| CircRNA_ID | Name of Isoform | Name of Gene | Splice Length | Type of CircRNA | logFC (HFD vs. ND) | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr16|20422304|20422485|R | NM_013790 | Abcc5 | 181 | circRNA | −2.9989 | 0.0044 |
| chr1|155601453|155677234|F | NM_028250 | Acbd6 | 310 | circRNA | −3.0915 | 0.0027 |
| chr1|82893582|82894474|F | NM_001347077 | Agfg1 | 892 | ciRNA | −3.6744 | 0.0026 |
| chr1|177102961|177109738|R | NM_011785 | Akt3 | 257 | circRNA | 2.3388 | 0.0035 |
| chr1|177031649|177067333|R | NM_011785 | Akt3 | 658 | circRNA | −4.9995 | 0.0043 |
| chr1|58059034|58065366|F | NM_009676 | Aox1 | 797 | circRNA | −4.7680 | 0.0096 |
| chr13|94493668|94532066|F | NM_009680 | Ap3b1 | 497 | circRNA | 5.1675 | 0.0023 |
| chr9|44751215|44752275|R | NM_145985 | Arcn1 | 314 | circRNA | 3.1211 | 0.0028 |
| chr8|11781154|11785914|F | NM_001113517 | Arhgef7 | 418 | circRNA | 3.3226 | 0.0009 |
| chr12|101932967|101945919|R | NM_029705 | Atxn3 | 638 | circRNA | −3.7032 | 0.0024 |
| chr2|59932104|59960105|R | NM_001001182 | Baz2b | 1064 | circRNA | 2.7952 | 0.0029 |
| chr19|36986454|36992584|F | NM_001080706 | Btaf1 | 1233 | circRNA | 3.8481 | 0.0012 |
| chr8|124597498|124600487|F | NM_023709 | Capn9 | 339 | circRNA | −4.8492 | 0.0071 |
| chr13|24164800|24178257|R | NM_001311122 | Carmil1 | 233 | circRNA | −3.4788 | 0.0061 |
| chr10|41654941|41656332|R | NM_001358562 | Ccdc162 | 423 | circRNA | 4.7722 | 0.0084 |
| chr6|147507783|147562712|F | NM_001355714 | Ccdc91 | 759 | circRNA | −4.9599 | 0.0054 |
| chr17|42805159|42830105|R | NM_009847 | Cd2ap | 1267 | circRNA | −2.2265 | 0.0056 |
| chr8|105643515|105666792|F | NM_001358924 | Ctcf | 1212 | circRNA | 4.7654 | 0.0098 |
| chr9|3454539|3460131|F | NM_027545 | Cwf19l2 | 567 | circRNA | 4.9208 | 0.0052 |
| chr7|55873445|55875088|F | NM_001164661 | Cyfip1 | 362 | circRNA | −5.5388 | 0.0004 |
| chr8|111010720|111011462|R | NM_001190800 | Ddx19b | 416 | circRNA | −3.2670 | 0.0009 |
| chr11|86784878|86793261|R | NM_026191 | Dhx40 | 609 | circRNA | 3.6590 | 0.0035 |
| chr4|99070177|99079849|R | NM_001290636 | Dock7 | 646 | circRNA | −2.9306 | 0.0070 |
| chr14|66824344|66834376|R | NM_009955 | Dpysl2 | 498 | circRNA | −2.4682 | 0.0012 |
| chr15|12878657|12890547|F | NM_001130149 | Drosha | 811 | circRNA | −3.3908 | 0.0091 |
| chr4|59690143|59691338|F | NM_153158 | E130308A19Rik | 1195 | circRNA | 2.9678 | 0.0070 |
| chr4|58872588|58885498|R | NM_001355696 | Ecpas | 689 | circRNA | 4.7628 | 0.0099 |
| chr18|33874141|33891476|R | NM_013512 | Epb41l4a | 591 | circRNA | −2.0009 | 0.0013 |
| chr11|26407547|26434500|F | NM_001277273 | Fancl | 267 | circRNA | −4.7565 | 0.0099 |
| chr9|78098345|78104354|R | NM_023605 | Fbxo9 | 401 | circRNA | 4.8614 | 0.0061 |
| chr6|99162838|99435345|R | NM_001347345 | Foxp1 | 491 | circRNA | −3.1755 | 0.0018 |
| chr5|71623854|71642326|R | NM_001359041 | Gabra4 | 929 | circRNA | 2.4293 | 0.0003 |
| chr7|19164639|19164967|R | NM_001080815 | Gipr | 328 | ciRNA | −4.9741 | 0.0046 |
| chr6|86717385|86722665|R | NM_011818 | Gmcl1 | 374 | circRNA | −4.9008 | 0.0063 |
| chr3|88880070|88887645|F | NM_001242372 | Gon4l | 390 | circRNA | 4.9467 | 0.0049 |
| chr3|20058898|20076584|F | NM_001355097 | Hltf | 1131 | circRNA | −4.8942 | 0.0064 |
| chr16|4762558|4763846|F | NM_001136066 | Hmox2 | 237 | circRNA | 3.1462 | 0.0029 |
| chr6|51465178|51466222|R | NM_016806 | Hnrnpa2b1 | 144 | circRNA | −5.4402 | 0.0006 |
| chr7|142678908|142679346|R | NM_001185083 | Ins2 | 438 | ciRNA | −2.6556 | 0.0050 |
| chr7|142678860|142679346|R | NM_001185083 | Ins2 | 486 | ciRNA | −3.3804 | 0.0094 |
| chr7|142678904|142679346|R | NM_001185083 | Ins2 | 442 | ciRNA | −3.3891 | 0.0090 |
| chr13|44731712|44848421|F | NM_001205044 | Jarid2 | 482 | circRNA | 5.2731 | 0.0012 |
| chr4|149251740|149253751|R | NM_001290995 | Kif1b | 156 | circRNA | −5.1133 | 0.0028 |
| chr12|111785271|111785502|F | NM_001361611 | Klc1 | 118 | circRNA | −3.6522 | 0.0028 |
| chr1|134475787|134485913|F | NM_001311136 | Klhl12 | 418 | circRNA | 2.1707 | 0.0099 |
| chr18|56739820|56743315|F | NM_010721 | Lmnb1 | 552 | circRNA | 5.0791 | 0.0030 |
| chr7|72161139|72185865|R | NM_001024703 | Mctp2 | 503 | circRNA | −5.0067 | 0.0042 |
| chr4|87840681|87880148|R | NM_027326 | Mllt3 | 935 | circRNA | 2.8933 | 0.0017 |
| chr11|62419597|62423067|R | NM_001252313 | Ncor1 | 376 | circRNA | −2.0002 | 0.0045 |
| chr8|61086398|61089799|F | NM_001293637 | Nek1 | 418 | circRNA | −2.9191 | 0.0065 |
| chr5|24692806|24695590|F | NM_001305264 | Nub1 | 301 | circRNA | −4.7608 | 0.0098 |
| chr2|121429453|121434093|F | NM_007952 | Pdia3 | 665 | circRNA | 4.8197 | 0.0076 |
| chr5|65663855|65666311|R | NM_001081321 | Pds5a | 389 | circRNA | 4.7741 | 0.0096 |
| chr8|109876802|109895641|F | NM_001122594 | Phlpp2 | 415 | circRNA | −4.8009 | 0.0090 |
| chr6|65862914|65901859|F | NM_027547 | Prdm5 | 758 | circRNA | −3.0054 | 0.0005 |
| chr6|112665277|112681676|R | NM_001167730 | Rad18 | 761 | circRNA | 2.0348 | 0.0004 |
| chr17|65857661|65864732|R | NM_001198949 | Ralbp1 | 1103 | circRNA | 3.1595 | 0.0024 |
| chr4|135418379|135420419|R | NM_022980 | Rcan3 | 346 | circRNA | −2.1644 | 0.0079 |
| chr5|63924734|63938033|R | NM_145923 | Rell1 | 734 | circRNA | 2.1681 | 0.0009 |
| chr17|29634660|29636022|F | NM_021419 | Rnf8 | 313 | circRNA | 3.4555 | 0.0082 |
| chr7|97616842|97653207|F | NM_001081267 | Rsf1 | 546 | circRNA | −5.4669 | 0.0005 |
| chr3|130040673|130041447|R | NM_207209 | Sec24b | 774 | circRNA | 2.8977 | 0.0098 |
| chr6|4707073|4719496|R | NM_001130188 | Sgce | 553 | circRNA | −2.4581 | 0.0040 |
| chr11|52236836|52243758|F | NM_011543 | Skp1a | 315 | circRNA | −3.4104 | 0.0085 |
| chr6|142101591|142133232|R | NM_023718 | Slco1a6 | 936 | circRNA | 4.8197 | 0.0076 |
| chr17|71455604|71465669|R | NM_028887 | Smchd1 | 452 | circRNA | −5.4092 | 0.0007 |
| chr1|192930477|192986882|R | NM_001301370 | Syt14 | 1103 | circRNA | 2.4311 | 0.0021 |
| chr10|56087530|56089839|R | NM_001033385 | Tbc1d32 | 326 | circRNA | −4.8798 | 0.0066 |
| chr11|121602987|121611748|F | NM_029878 | Tbcd | 871 | circRNA | −5.4350 | 0.0007 |
| chr1|135304429|135309198|R | NM_001360857 | Timm17a | 304 | circRNA | −2.2046 | 0.0012 |
| chr1|37783816|37811027|R | NM_207228 | Tsga10 | 732 | circRNA | 4.9306 | 0.0051 |
| chr5|92166530|92167333|F | NM_019490 | Uso1 | 260 | circRNA | 4.8256 | 0.0075 |
| chr11|85077264|85083894|R | NM_001029934 | Usp32 | 385 | circRNA | −3.3658 | 0.0095 |
| chr11|23333438|23345217|F | NM_001190401 | Usp34 | 690 | circRNA | 4.8640 | 0.0069 |
| chr7|99065799|99099473|R | NM_178635 | Uvrag | 320 | circRNA | −5.6041 | 0.0002 |
| chr3|108618489|108638757|F | NM_001358053 | Wdr47 | 2071 | circRNA | −4.0332 | 0.0003 |
| chr8|107483331|107485642|F | NM_025830 | Wwp2 | 235 | circRNA | −3.4087 | 0.0083 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Das, D.; Das, A.; Sahu, M.; Mishra, S.S.; Khan, S.; Bejugam, P.R.; Rout, P.K.; Das, A.; Bano, S.; Mishra, G.P.; et al. Identification and Characterization of Circular Intronic RNAs Derived from Insulin Gene. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4302. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124302
Das D, Das A, Sahu M, Mishra SS, Khan S, Bejugam PR, Rout PK, Das A, Bano S, Mishra GP, et al. Identification and Characterization of Circular Intronic RNAs Derived from Insulin Gene. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(12):4302. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124302
Chicago/Turabian StyleDas, Debojyoti, Aniruddha Das, Mousumi Sahu, Smruti Sambhav Mishra, Shaheerah Khan, Pruthvi R. Bejugam, Pranita K. Rout, Arundhati Das, Shehnaz Bano, Gyan Prakash Mishra, and et al. 2020. "Identification and Characterization of Circular Intronic RNAs Derived from Insulin Gene" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 12: 4302. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124302
APA StyleDas, D., Das, A., Sahu, M., Mishra, S. S., Khan, S., Bejugam, P. R., Rout, P. K., Das, A., Bano, S., Mishra, G. P., Raghav, S. K., Dixit, A., & Panda, A. C. (2020). Identification and Characterization of Circular Intronic RNAs Derived from Insulin Gene. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(12), 4302. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124302