Regulators of Epithelial Sodium Channels in Aldosterone-Sensitive Distal Nephrons (ASDN): Critical Roles of Nedd4L/Nedd4-2 and Salt-Sensitive Hypertension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sodium Reabsorption in Terminal Nephrons
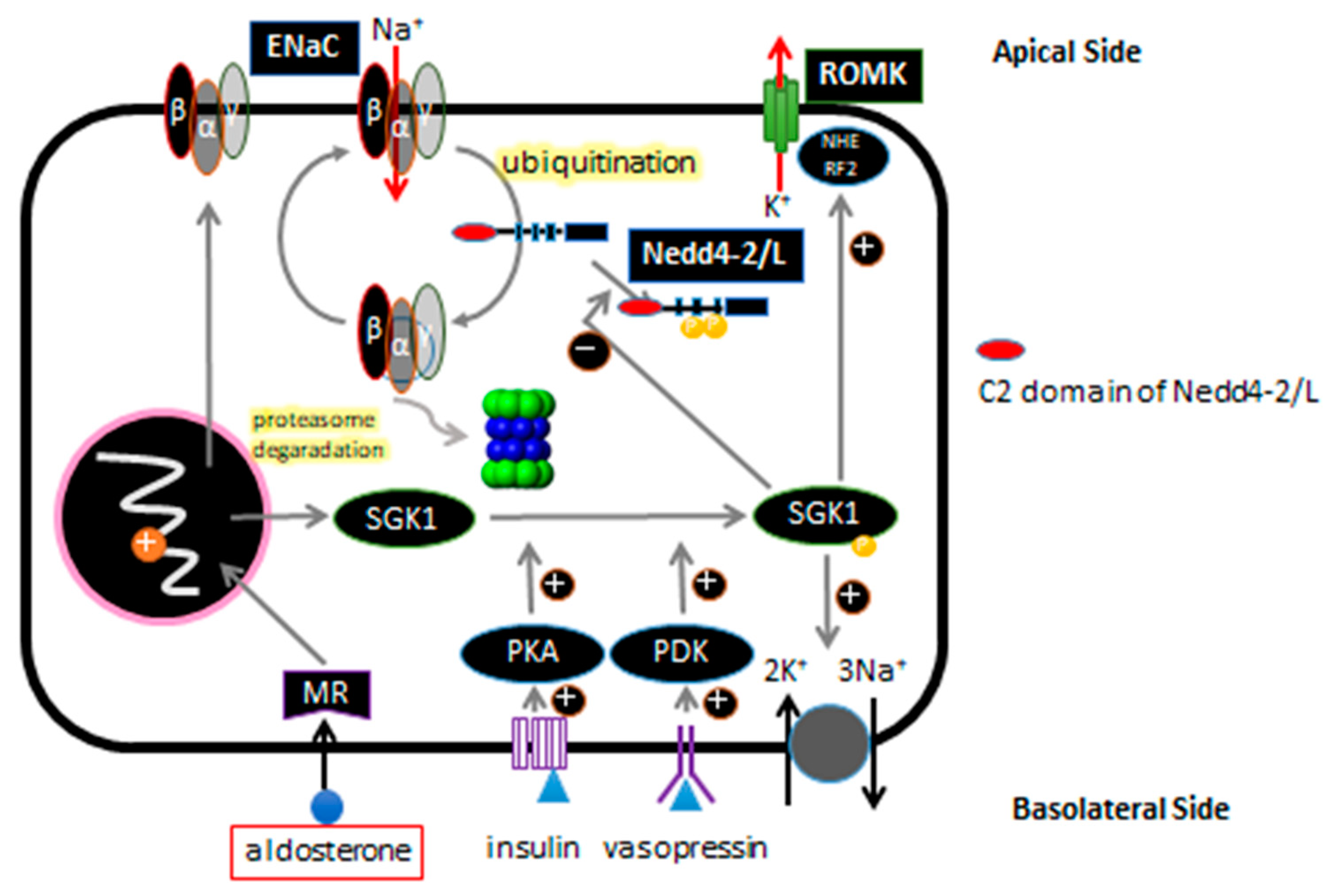
3. ENaC and Regulation of ENaC Expression in Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells
4. Liddle Syndrome and ENaC
5. Background on NEDD4 and NEDD4L/Nedd4-2
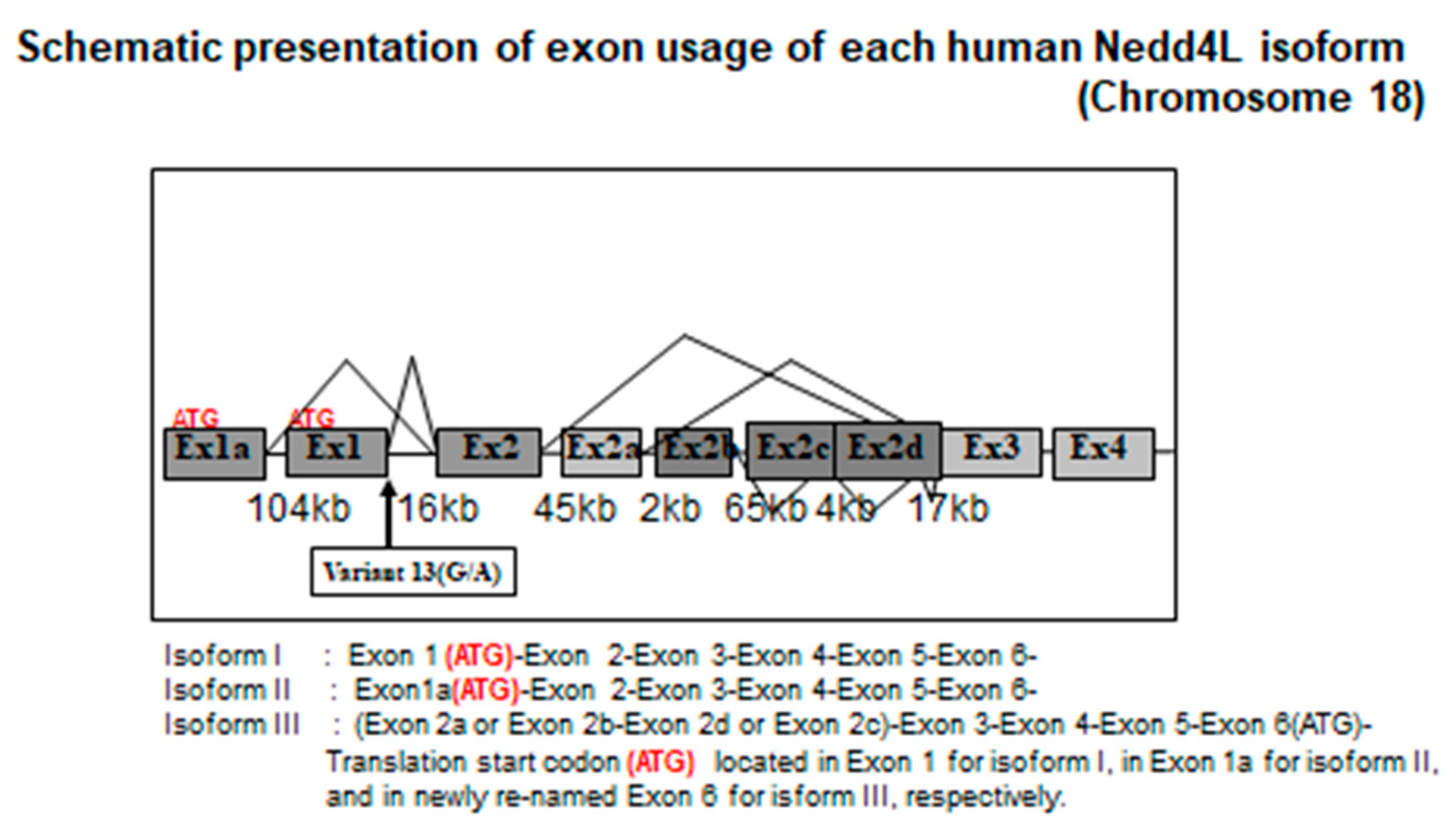
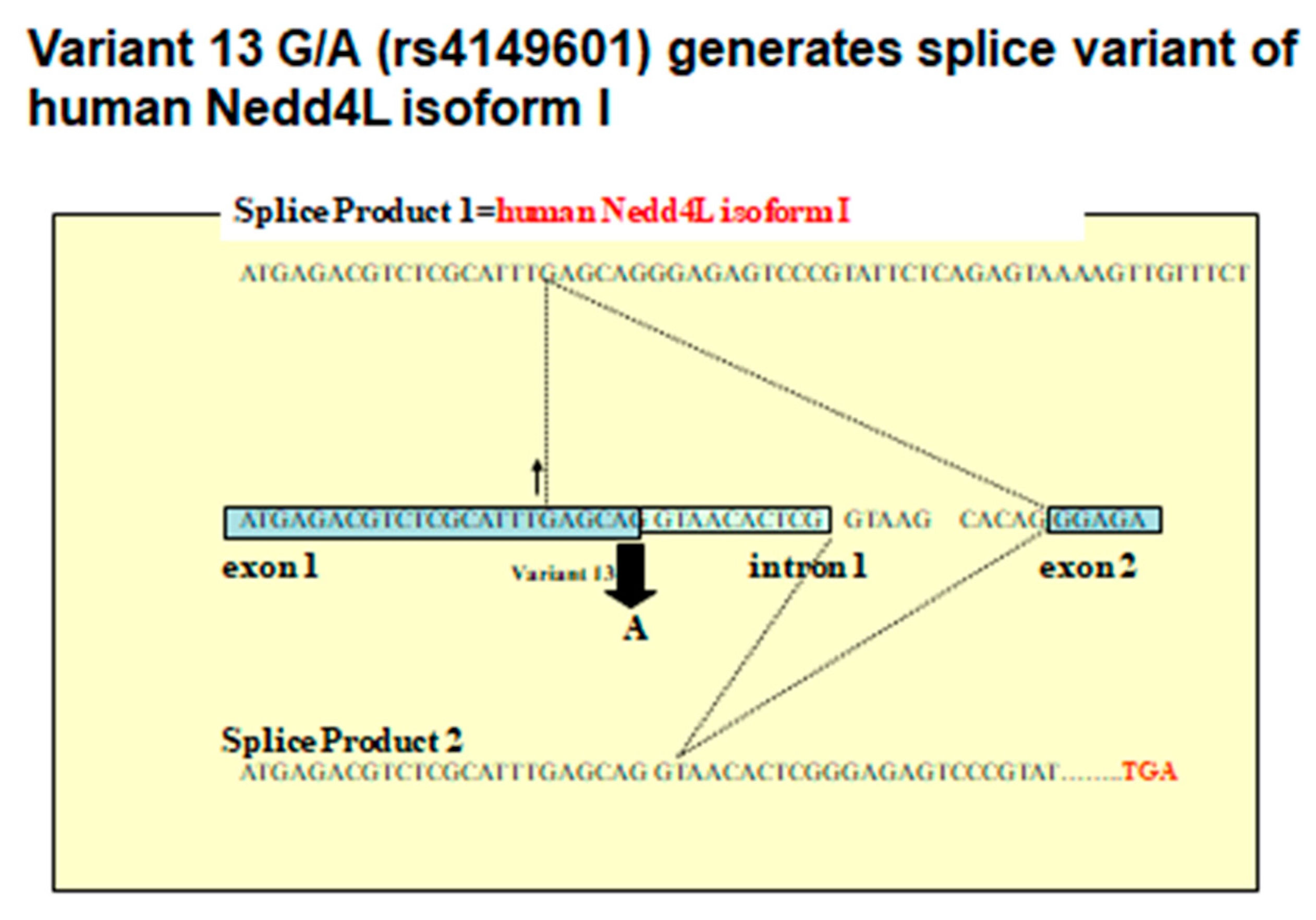
6. Human NEDD4L Is a Causative Gene of Salt-Sensitive Hypertension
7. NEDD4L Is the Causative Protein of Salt-Sensitive Hypertension
8. Generation of Nedd4-2 C2 KO Mice and Discovery of Salt-Sensitive Hypertension with Potential Contributions to Cardio-Renal Involvements
9. Summary
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASDN | Aldosterone Sensitive Distal Nephron |
| ENaC | Epithelial Sodium Channel |
| EPL | Eplerenone |
| DCT | Distal Convoluted Tubule |
| CNT | Conecting Tubule |
| CCD | Cortical Collecting Duct |
| ROMK | Renal outer medullary potassium channel |
| SGK1 | Serum/glucocorticoid regulator kinase 1 |
| MR | Mineral corticoid receptor |
| PKA | cAMP-dependent protein kinase A |
| PDK | Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 |
References
- Intersalt Cooperative Research Group. Intersalt: An international study of electrolyte excretion and blood pressure. Results for 24 hour urinary sodium and potassium excretion. BMJ 1988, 297, 319–328. [Google Scholar]
- Mente, A.; O’Donnell, M.J.; Rangarajan, S.; McQueen, M.J.; Poirier, P.; Wielgosz, A.; Morrison, H.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Di, C.; et al. Association of urinary sodium and potassium excretion with blood pressure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, M.; Mente, A.; Rangarajan, S.; McQueen, M.J.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Yan, H.; Lee, S.F.; Mony, P.; Devanath, A.; et al. Urinary sodium and potassium excretion, mortality, and cardiovascular events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elijovich, F.; Weinberger, M.H.; Anderson, C.A.; Appel, L.J.; Bursztyn, M.; Cook, N.R.; Dart, R.A.; Newton-Cheh, C.H.; Sacks, F.M.; Laffer, C.L.; et al. Salt Sensitivity of Blood Pressure: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Hypertension 2016, 68, e7–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lifton, R.P.; Gharavi, A.G.; Geller, D.S. Molecular mechanisms of human hypertension. Cell 2001, 104, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigami, T.; Umemura, S.; Iwamoto, T.; Tamura, K.; Hibi, K.; Yamaguchi, S.; Nyuui, N.; Kimura, K.; Miyazaki, N.; Ishii, M. Molecular variant of angiotensinogen gene is associated with coronary atherosclerosis. Circulation 1995, 91, 951–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigami, T.; Umemura, S.; Tamura, K.; Hibi, K.; Nyui, N.; Kihara, M.; Yabana, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Sumida, Y.; Nagahara, T.; et al. Essential hypertension and 5’ upstream core promoter region of human angiotensinogen gene. Hypertension 1997, 30, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar]
- Ishigami, T.; Tamura, K.; Fujita, T.; Kobayashi, I.; Hibi, K.; Kihara, M.; Toya, Y.; Ochiai, H.; Umemura, S. Angiotensinogen gene polymorphism near transcription start site and blood pressure: Role of a T-to-C transition at intron I. Hypertension 1999, 34, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantelme, P.; Rohrwasser, A.; Gociman, B.; Hillas, E.; Cheng, T.; Petty, G.; Thomas, J.; Xiao, S.; Ishigami, T.; Herrmann, T.; et al. Effects of dietary sodium and genetic background on angiotensinogen and Renin in mouse. Hypertension 2002, 39, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Jorde, L.B.; Ishigami, T.; Umemura, S.; Emi, M.; Lalouel, J.M.; Inoue, I. Nucleotide diversity and haplotype structure of the human angiotensinogen gene in two populations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 70, 108–123. [Google Scholar]
- Rohrwasser, A.; Ishigami, T.; Gociman, B.; Lantelme, P.; Morgan, T.; Cheng, T.; Hillas, E.; Zhang, S.; Ward, K.; Bloch-Faure, M.; et al. Renin and kallikrein in connecting tubule of mouse. Kidney Int. 2003, 64, 2155–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gociman, B.; Rohrwasser, A.; Lantelme, P.; Cheng, T.; Hunter, G.; Monson, S.; Hunter, J.; Hillas, E.; Lott, P.; Ishigami, T.; et al. Expression of angiotensinogen in proximal tubule as a function of glomerular filtration rate. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 2153–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, T.; Wooding, S.; Sakagami, T.; Emi, M.; Tokunaga, K.; Tamiya, G.; Ishigami, T.; Umemura, S.; Munkhbat, B.; Jin, F.; et al. Natural selection and population history in the human angiotensinogen gene (AGT): 736 complete AGT sequences in chromosomes from around the world. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 74, 898–916. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rohrwasser, A.; Morgan, T.; Dillon, H.F.; Zhao, L.; Callaway, C.W.; Hillas, E.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, T.; Inagami, T.; Ward, K.; et al. Elements of a paracrine tubular renin-angiotensin system along the entire nephron. Hypertension 1999, 34, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeunemaitre, X.; Soubrier, F.; Kotelevtsev, Y.V.; Lifton, R.P.; Williams, C.S.; Charru, A.; Hunt, S.C.; Hopkins, P.N.; Williams, R.R.; Lalouel, J.M.; et al. Molecular basis of human hypertension: Role of angiotensinogen. Cell 1992, 71, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, S.; Mullins, J.J.; Bunnemann, B.; Metzger, R.; Hilgenfeldt, U.; Zimmermann, F.; Jacob, H.; Fuxe, K.; Ganten, D.; Kaling, M. High blood pressure in transgenic mice carrying the rat angiotensinogen gene. Embo. J. 1992, 11, 821–827. [Google Scholar]
- Tanimoto, K.; Sugiyama, F.; Goto, Y.; Ishida, J.; Takimoto, E.; Yagami, K.; Fukamizu, A.; Murakami, K. Angiotensinogen-deficient mice with hypotension. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 31334–31337. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, I.; Nakajima, T.; Williams, C.S.; Quackenbush, J.; Puryear, R.; Powers, M.; Cheng, T.; Ludwig, E.H.; Sharma, A.M.; Hata, A.; et al. A nucleotide substitution in the promoter of human angiotensinogen is associated with essential hypertension and affects basal transcription in vitro. J. Clin. Invest. 1997, 99, 1786–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, K.; Saito, T.; Hirota, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Murakami, K.; Fukamizu, A. Molecular variation of the human angiotensinogen core promoter element located between the TATA box and transcription initiation site affects its transcriptional activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 30558–30562. [Google Scholar]
- Davisson, R.L.; Ding, Y.; Stec, D.E.; Catterall, J.F.; Sigmund, C.D. Novel mechanism of hypertension revealed by cell-specific targeting of human angiotensinogen in transgenic mice. Physiol. Genomics 1999, 1, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jeunemaitre, X.; Inoue, I.; Williams, C.; Charru, A.; Tichet, J.; Powers, M.; Sharma, A.M.; Gimenez-Roqueplo, A.P.; Hata, A.; Corvol, P.; et al. Haplotypes of angiotensinogen in essential hypertension. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1997, 60, 1448–1460. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ishigami, T.; Iwamoto, T.; Tamura, K.; Yamaguchi, S.; Iwasawa, K.; Uchino, K.; Umemura, S.; Ishii, M. Angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) gene polymorphism and essential hypertension in Japan. Ethnic difference of ACE genotype. Am. J. Hypertens 1995, 8, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigami, T.; Kino, T.; Chen, L.; Minegishi, S.; Araki, N.; Umemura, M.; Abe, K.; Sasaki, R.; Yamana, H.; Umemura, S. Identification of bona fide alternative renin transcripts expressed along cortical tubules and potential roles in promoting insulin resistance in vivo without significant plasma renin activity elevation. Hypertension 2014, 64, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guyton, A.C. Blood pressure control—Special role of the kidneys and body fluids. Science 1991, 252, 1813–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shaughnessy, K.M.; Karet, F.E. Salt handling and hypertension. J. Clin. Invest. 2004, 113, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peti-Peterdi, J.; Warnock, D.G.; Bell, P.D. Angiotensin II directly stimulates ENaC activity in the cortical collecting duct via AT(1) receptors. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar]
- Komlosi, P.; Fuson, A.L.; Fintha, A.; Peti-Peterdi, J.; Rosivall, L.; Warnock, D.G.; Bell, P.D. Angiotensin I conversion to angiotensin II stimulates cortical collecting duct sodium transport. Hypertension 2003, 42, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beutler, K.T.; Masilamani, S.; Turban, S.; Nielsen, J.; Brooks, H.L.; Ageloff, S.; Fenton, R.A.; Packer, R.K.; Knepper, M.A. Long-term regulation of ENaC expression in kidney by angiotensin II. Hypertension 2003, 41, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Gormley, K.; Dong, Y.; Sagnella, G.A. Regulation of the epithelial sodium channel by accessory proteins. Biochem. J. 2003, 371, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Booth, R.E.; Johnson, J.P.; Stockand, J.D. Aldosterone. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2002, 26, 8–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kamynina, E.; Staub, O. Concerted action of ENaC, Nedd4-2, and Sgk1 in transepithelial Na(+) transport. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2002, 283, F377–F387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneton, P.; Loffing, J.; Warnock, D.G. Sodium and potassium handling by the aldosterone-sensitive distal nephron: The pivotal role of the distal and connecting tubule. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2004, 287, F593–F601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, F.H.; Disse-Nicodeme, S.; Choate, K.A.; Ishikawa, K.; Nelson-Williams, C.; Desitter, I.; Gunel, M.; Milford, D.V.; Lipkin, G.W.; Achard, J.M.; et al. Human hypertension caused by mutations in WNK kinases. Science 2001, 293, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallon, V.; Wulff, P.; Huang, D.Y.; Loffing, J.; Volkl, H.; Kuhl, D.; Lang, F. Role of Sgk1 in salt and potassium homeostasis. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2005, 288, R4–R10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhargava, A.; Wang, J.; Pearce, D. Regulation of epithelial ion transport by aldosterone through changes in gene expression. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2004, 217, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.S.; Grunder, S.; Hanukoglu, A.; Rosler, A.; Mathew, P.M.; Hanukoglu, I.; Schild, L.; Lu, Y.; Shimkets, R.A.; Nelson-Williams, C.; et al. Mutations in subunits of the epithelial sodium channel cause salt wasting with hyperkalaemic acidosis, pseudohypoaldosteronism type 1. Nat. Genet. 1996, 12, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, J.H.; Nelson-Williams, C.; Suzuki, H.; Schild, L.; Shimkets, R.; Lu, Y.; Canessa, C.; Iwasaki, T.; Rossier, B.; Lifton, R.P. Hypertension caused by a truncated epithelial sodium channel gamma subunit: Genetic heterogeneity of Liddle syndrome. Nat. Genet. 1995, 11, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimkets, R.A.; Warnock, D.G.; Bositis, C.M.; Nelson-Williams, C.; Hansson, J.H.; Schambelan, M.; Gill, J.R., Jr.; Ulick, S.; Milora, R.V.; Findling, J.W.; et al. Liddle’s syndrome: Heritable human hypertension caused by mutations in the beta subunit of the epithelial sodium channel. Cell 1994, 79, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schild, L.; Lu, Y.; Gautschi, I.; Schneeberger, E.; Lifton, R.P.; Rossier, B.C. Identification of a PY motif in the epithelial Na channel subunits as a target sequence for mutations causing channel activation found in Liddle syndrome. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 2381–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staub, O.; Dho, S.; Henry, P.; Correa, J.; Ishikawa, T.; McGlade, J.; Rotin, D. WW domains of Nedd4 bind to the proline-rich PY motifs in the epithelial Na+ channel deleted in Liddle’s syndrome. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 2371–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant, P.J.; Yeger, H.; Staub, O.; Howard, P.; Rotin, D. The C2 domain of the ubiquitin protein ligase Nedd4 mediates Ca2+-dependent plasma membrane localization. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 32329–32336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staub, O.; Gautschi, I.; Ishikawa, T.; Breitschopf, K.; Ciechanover, A.; Schild, L.; Rotin, D. Regulation of stability and function of the epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) by ubiquitination. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 6325–6336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abriel, H.; Loffing, J.; Rebhun, J.F.; Pratt, J.H.; Schild, L.; Horisberger, J.D.; Rotin, D.; Staub, O. Defective regulation of the epithelial Na+ channel by Nedd4 in Liddle’s syndrome. J. Clin. Invest. 1999, 103, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulet, C.C.; Volk, K.A.; Adams, C.M.; Prince, L.S.; Stokes, J.B.; Snyder, P.M. Inhibition of the epithelial Na+ channel by interaction of Nedd4 with a PY motif deleted in Liddle’s syndrome. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 30012–30017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, D.M.; Ishigami, T.; Pankow, J.; von Niederhausern, A.; Alder, J.; Hunt, S.C.; Leppert, M.F.; Lalouel, J.M.; Weiss, R.B. Common variant of human NEDD4L activates a cryptic splice site to form a frameshifted transcript. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 47, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Tomooka, Y.; Noda, M. Identification of a set of genes with developmentally down-regulated expression in the mouse brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 185, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, K.; Nagase, T.; Nakajima, D.; Seki, N.; Ohira, M.; Miyajima, N.; Tanaka, A.; Kotani, H.; Nomura, N.; Ohara, O. Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. VIII. 78 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro. DNA Res. 1997, 4, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, K.F.; Dinudom, A.; Cook, D.I.; Kumar, S. The Nedd4-like protein KIAA0439 is a potential regulator of the epithelial sodium channel. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 8597–8601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ross, C.A.; Wang, N.; Huo, Y.; MacKinnon, D.F.; Potash, J.B.; Simpson, S.G.; McMahon, F.J.; DePaulo, J.R., Jr.; McInnis, M.G. NEDD4L on human chromosome 18q21 has multiple forms of transcripts and is a homologue of the mouse Nedd4-2 gene. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 9, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamynina, E.; Debonneville, C.; Hirt, R.P.; Staub, O. Liddle’s syndrome: A novel mouse Nedd4 isoform regulates the activity of the epithelial Na(+) channel. Kidney Int. 2001, 60, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamynina, E.; Debonneville, C.; Bens, M.; Vandewalle, A.; Staub, O. A novel mouse Nedd4 protein suppresses the activity of the epithelial Na+ channel. FASEB J 2001, 15, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamynina, E.; Tauxe, C.; Staub, O. Distinct characteristics of two human Nedd4 proteins with respect to epithelial Na(+) channel regulation. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2001, 281, F469–F477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishigami, T.; Araki, N.; Umemura, S. Human Nedd4L rs4149601 G allele generates evolutionary new isoform I with C2 domain. Hypertension 2010, 55, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishigami, T.; Araki, N.; Minegishi, S.; Umemura, M.; Umemura, S. Genetic variation in NEDD4L, salt sensitivity, and hypertension: Human NEDD4L rs4149601 G allele generates evolutionary new isoform I with C2 domain. J. Hypertens. 2014, 32, 1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishigami, T.; Umemura, M.; Araki, N.; Hirawa, N.; Tamura, K.; Uchino, K.; Umemura, S.; Rohrwasser, A.; Lalouel, J.M. NEDD4L protein truncating variant (v13(G/A):rs4149601) is associated with essential hypertension (EH) in a sample of the Japanese population. Geriatrics Geront. Int. 2007, 7, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlberg, J.; Nilsson, L.O.; von Wowern, F.; Melander, O. Polymorphism in NEDD4L is associated with increased salt sensitivity, reduced levels of P-renin and increased levels of Nt-proANP. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, C.; von Wowern, F.; Berglund, G.; Carlson, J.; Hedblad, B.; Rosberg, L.; Burri, P.; Almgren, P.; Melander, O. 24-h ambulatory blood pressure is linked to chromosome 18q21-22 and genetic variation of NEDD4L associates with cross-sectional and longitudinal blood pressure in Swedes. Kidney Int. 2006, 70, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson-Farbom, P.; Wahlstrand, B.; Almgren, P.; Dahlberg, J.; Fava, C.; Kjeldsen, S.; Hedner, T.; Melander, O. A functional variant of the NEDD4L gene is associated with beneficial treatment response with beta-blockers and diuretics in hypertensive patients. J. Hypertens 2011, 29, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemura, M.; Ishigami, T.; Tamura, K.; Sakai, M.; Miyagi, Y.; Nagahama, K.; Aoki, I.; Uchino, K.; Rohrwasser, A.; Lalouel, J.M.; et al. Transcriptional diversity and expression of NEDD4L gene in distal nephron. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 339, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, N.; Umemura, M.; Miyagi, Y.; Yabana, M.; Miki, Y.; Tamura, K.; Uchino, K.; Aoki, R.; Goshima, Y.; Umemura, S.; et al. Expression, transcription, and possible antagonistic interaction of the human Nedd4L gene variant: Implications for essential hypertension. Hypertension 2008, 51, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, N.; Ishigami, T.; Ushio, H.; Minegishi, S.; Umemura, M.; Miyagi, Y.; Aoki, I.; Morinaga, H.; Tamura, K.; Toya, Y.; et al. Identification of NPC2 protein as interaction molecule with C2 domain of human Nedd4L. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 388, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Minegishi, S.; Ishigami, T.; Kino, T.; Chen, L.; Nakashima-Sasaki, R.; Araki, N.; Yatsu, K.; Fujita, M.; Umemura, S. An isoform of Nedd4-2 is critically involved in the renal adaptation to high salt intake in mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henshall, T.L.; Manning, J.A.; Alfassy, O.S.; Goel, P.; Boase, N.A.; Kawabe, H.; Kumar, S. Deletion of Nedd4-2 results in progressive kidney disease in mice. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 2150–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, J.A.; Shah, S.S.; Henshall, T.L.; Nikolic, A.; Finnie, J.; Kumar, S. Dietary sodium modulates nephropathy in Nedd4-2-deficient mice. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 27, 1832–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kino, T.; Ishigami, T.; Murata, T.; Doi, H.; Nakashima-Sasaki, R.; Chen, L.; Sugiyama, M.; Azushima, K.; Wakui, H.; Minegishi, S.; et al. Eplerenone-Resistant Salt-Sensitive Hypertension in Nedd4-2 C2 KO Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minegishi, S.; Ishigami, T.; Kawamura, H.; Kino, T.; Chen, L.; Nakashima-Sasaki, R.; Doi, H.; Azushima, K.; Wakui, H.; Chiba, Y.; et al. An Isoform of Nedd4-2 Plays a Pivotal Role in Electrophysiological Cardiac Abnormalities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1268. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ishigami, T.; Kino, T.; Minegishi, S.; Araki, N.; Umemura, M.; Ushio, H.; Saigoh, S.; Sugiyama, M. Regulators of Epithelial Sodium Channels in Aldosterone-Sensitive Distal Nephrons (ASDN): Critical Roles of Nedd4L/Nedd4-2 and Salt-Sensitive Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21113871
Ishigami T, Kino T, Minegishi S, Araki N, Umemura M, Ushio H, Saigoh S, Sugiyama M. Regulators of Epithelial Sodium Channels in Aldosterone-Sensitive Distal Nephrons (ASDN): Critical Roles of Nedd4L/Nedd4-2 and Salt-Sensitive Hypertension. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(11):3871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21113871
Chicago/Turabian StyleIshigami, Tomoaki, Tabito Kino, Shintaro Minegishi, Naomi Araki, Masanari Umemura, Hisako Ushio, Sae Saigoh, and Michiko Sugiyama. 2020. "Regulators of Epithelial Sodium Channels in Aldosterone-Sensitive Distal Nephrons (ASDN): Critical Roles of Nedd4L/Nedd4-2 and Salt-Sensitive Hypertension" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 11: 3871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21113871
APA StyleIshigami, T., Kino, T., Minegishi, S., Araki, N., Umemura, M., Ushio, H., Saigoh, S., & Sugiyama, M. (2020). Regulators of Epithelial Sodium Channels in Aldosterone-Sensitive Distal Nephrons (ASDN): Critical Roles of Nedd4L/Nedd4-2 and Salt-Sensitive Hypertension. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(11), 3871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21113871






