Abstract
Hunter syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis II; MPS II) is caused by a defect of the iduronate-2-sulfatase (IDS) gene. Few studies have reported integrated mutation data of Taiwanese MPS II phenotypes. In this study, we summarized genotype and phenotype correlations of confirmed MPS II patients and asymptomatic MPS II infants in Taiwan. Regular polymerase chain reaction and DNA sequencing were used to identify genetic abnormalities of 191 cases, including 51 unrelated patients with confirmed MPS II and 140 asymptomatic infants. IDS activity was analyzed in individual novel IDS variants using in vitro expression studies. Nineteen novel mutations were identified, in which the percentages of IDS activity of the novel missense mutations c.137A>C, c.311A>T, c.454A>C, c.797C>G, c.817C>T, c.998C>T, c.1106C>G, c.1400C>T, c.1402C>T, and c.1403G>A were significantly decreased (p < 0.001), c.254C>T and c.1025A>G were moderately decreased (p < 0.01), and c.851C>T was slightly decreased (p < 0.05) comparing with normal enzyme activity. The activities of the other six missense mutations were reduced but were insignificant. The results of genomic studies and their phenotypes were highly correlated. A greater understanding of the positive correlations may help to prevent the irreversible manifestations of Hunter syndrome, particularly in infants suspected of having asymptomatic MPS II. In addition, urinary glycosaminoglycan assay is important to diagnose Hunter syndrome since gene mutations are not definitive (could be non-pathogenic).
1. Introduction
Hunter syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis II; MPS II) (OMIM 309900) is an X-linked recessive lysosomal storage disorder (LSD). MPS II is caused by a deficiency in iduronate-2-sulfatase activity (IDS gene; Hunter: OMIM#309900; EC 3.1.6.13), which is involved in the lysosomal degradation of heparan sulfate (HS) and dermatan sulfate (DS). There are two major clinical forms, including mild and severe forms based on age at onset and severity of clinical manifestations [1,2,3,4]. The heterogeneity of the syndrome is assumed to reflect different mutations at the IDS locus affecting the expression of the IDS protein (enzyme), stability, and catalyzation function. The severe form of MPS II is characteristic by early somatic abnormalities together with skeletal deformities, hepatosplenomegaly, and progressive cardiopulmonary deterioration. In the severe form of MPS II, neurological damage presents progressively and prominently as developmental delay and intellectual disability, often concomitant with neurodegeneration; whereas patients with the mild form of MPS II usually have the attenuated somatic complications without mental disability. MPS II is the most common type of MPS, accounting for 52% of all diagnosed MPS cases in Taiwan, and the prevalence in northeast Asia is very similar [5,6,7]. The birth prevalence of MPS II in different populations was varied, i.e., 1.07 per 100,000 live births in Taiwan [7,8]; 0.84 per 100,000 live births in Japan; 0.74 per 100,000 live births in South Korea; 0.29 per 100,000 live births in the United States; 0.27, 1.09, and 0.67 per 100,000 live births in Denmark, Portugal, and The Netherlands, respectively [8]. However, integrated mutation data of the Taiwanese MPS II phenotype are currently lacking.
The human IDS gene has been mapped to chromosome Xq28.1, spans approximately 24 kb, and contains 9 exons [9]. The whole IDS gene has been sequenced, and an IDS-like pseudogene, comprising copies of exons 2 and 3 and intron 7, has been located about 20 kb from the active gene [10,11,12]. The full-length cDNA is 1650 bp encoding a 550 amino-acid polypeptide, which has shown a high degree of homology with the sulfatase protein family [13]. To date, more than 541 different mutations underlying MPS II have been identified [www.HGMD.cf.ac.uk/]. The frequency of large alterations (complete or partial gene deletions and large rearrangements) is about 28.2%, however, the majority of the identified mutations (71.8%) are small deletions, insertions, or single base substitutions (missense mutations, nonsense mutations, and mutations affecting splicing). Haplotype analysis has shown that mutations occur more frequently in male meiosis. Even though the disease is almost reported in males, rare sporadic cases in females do occur. Affected females generally have low levels of IDS activity associated with a mild clinical phenotype. The result of either an X chromosome anomaly or homozygosity for the mutated gene, but most frequently, is the consequence of skewed X chromosome inactivation [14,15].
Accurate knowledge of the specific mutations involved in this disease may help to clarify the relationships between genotype and phenotype in individual patients and allow for the identification of female carriers. To characterize the biochemical and molecular defects in IDS-deficient patients and their families, this study was designed to identify IDS gene mutations in a group of Taiwanese patients with MPS II. We analyzed the genotype–phenotype relationships in all 51 IDS variants currently known in Taiwan using integrated clinical data with in vitro expression studies and a mass spectrometry-based assay of urinary glycosaminoglycans (uGAGs) to investigate and predict the likelihood of novel IDS variants for the severe or attenuated phenotype.
2. Results
2.1. Mutations of the IDS Gene by Sequencing Analysis
Sequencing data were obtained by scanning through the data to identify anomalies using Applied Biosystems Sequence Scanner Software v2.0 Sequence Trace Viewer and Editor (Applied Biosystems Co., CA, USA) and manual progressive alignment. A total of 51 mutations of the IDS gene from the 191 cases, including the confirmed patients (n = 51) and infants suspected of having MPS II (n = 140) that were identified. The suspected MPS II infants were classified into two groups: Those with either 1) “positive” uGAG biochemistry examinations, reduction in leukocyte IDS enzyme activity, and identified IDS variations (n = 7); or 2) “negative” uGAG biochemistry examinations, reduction in leukocyte IDS enzyme activity and identified IDS variations (n = 133). The 51 mutations of the IDS gene included 32 missense (62.7%), 3 nonsense (5.9%), 2 silent (3.9%), 6 splicing (11.8%), 4 small deletions (7.8%), 3 gross deletions (5.9%), and 1 complex inversion (2%) (Table 1). Of these mutations, 35 were reported and verified as being pathogenic for MPS II with varying degrees of severity or non-pathogenic [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36], and the other 16 were novel mutations (Figure 1), which needed to be verified according to individual IDS activity by using in vitro expression studies.

Table 1.
Mutations of the iduronate-2-sulfatase (IDS) gene underlying Taiwanese Hunter syndrome by sequencing analysis.
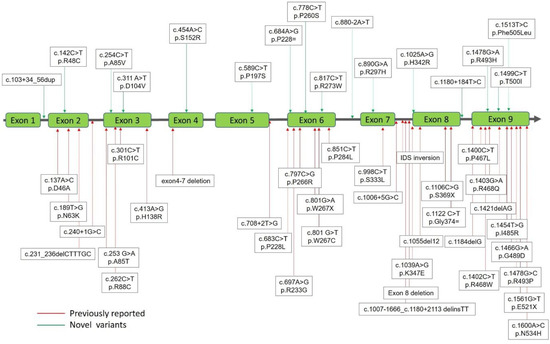
Figure 1.
Mutations of the iduronate-2-sulfatase (IDS) gene underlying Taiwanese Hunter syndrome. A total of 51 mutations of the IDS gene underlying Taiwanese Hunter syndrome were found, in those 35 have been reported previously (red lines with arrows) and the other 16 were novel mutations (green lines with arrows).
The 32 missense mutations are listed in Table 1. Most of the missense variations were verified as being pathogenic genes for Hunter syndrome [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39], except for 12 novel mutations, i.e., c.142C>T (p.R48C), c.254C>T (p.A85V), c.311A>T (p.D104V), c.454A>C (p.S152R), c.589C>T (p.P197S), c.778C>T (p.P260S), c.817C>T (p.R273W), c.890G>A (p.R297H), c.1025A>G (p.H342R), c.1478G>A (p.R493H), c.1499C>T (p.T500I), and c.1513T>C (p.F505L). Most of these missense mutations have been identified by the NBS program for MPS in Taiwan since August 2015. The phenotypes of the confirmed MPS II patients varied from the attenuated (mild form) to the severe form according to the IQ test, DQ tests, and WeeFIM questionnaire scores. The phenotypes of missense mutations (14/32) from the NBS program were uncertain due to the patients being asymptomatic during the infantile period, and the sequence variant classification, according to the American College of Medical Genetics (ACMG) criteria, were also demonstrated in Table 1. The ACMG Standards and Guidelines can provide an interpretation for evaluating evidence for sequence variants observed in patients with suspected MPS II (primarily Mendelian) [40]. Two of the missense mutations (c.301C>T, p.R101C and c.851C>T, p.P284L) have been reported to be non-pathogenic IDS mutations and are regarded as being the attenuated form [21,24]. In the current study, 6 infants had the c.301C>T mutation in which the construct expressed a high activity of about 97% ± 9% of the wild-type activity reported by Keeratichamroen et al. [18]. The predictive ability for the onset of MPS signs or symptoms for infants with this variant may be extraordinarily low or even unremarkable, as suggested by our analysis showing normal leukocyte IDS activity, ranging from 7.74 to 43.9 (25.82 ± 9.04) μmol/g protein/4 h, and negative uGAG tests, particularly the quantities of DS and HS (less than the cut-off values, <0.80 μg/mL for DS and < 0.78 μg/mL for HS). The diagnosis in these cases could be because the mutation was non-pathogenic and may or may not cause MPS signs or symptoms, however, further studies are needed to clarify this issue. Kosuga et al. previously verified that the disease phenotype of the missense mutation c.851C>T (p.P284L) is the attenuated form [24]. Another missense mutation c.1400C>T (p.P467L) has been reported to be pathogenic to cause severe MPS manifestations [27,28]. The infant and another highly suspected infant with the novel missense mutation c.311A>T (p.D104V) who did not have pre-symptoms received Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) (idursulfase) or ERT plus hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) at the ages of 1.11 and 0.55 years old, respectively, due to definite evidence of a family history.
The nonsense mutations, c.801G>A (W267X) and c.1561G>T (E521X), have been reported previously [17], and showed the severe phenotype due to protein alteration in Trp-Stop and Glu-Stop, respectively. Another nucleotide alteration, c.1561G>T was confirmed to be a phenotype of the mild form, which was consistent with the study by Lualdi et al. [33].
Two silent mutations were identified in this study, c.684A>G (p.Pro228 =) and c.1122C>T (p.Gly374 =). The case with the nucleotide alteration, c.684A>G (p.Pro228 =), was referred from the NBS program and was confirmed to be a novel mutation and to be one of the combinations of the IDS mutations mentioned above. Another mutation, c.1122C>T (p.Gly374 =), has been reported to be pathogenic for the attenuated phenotype [20].
Six splicing mutations including c.103 + 34_56dup, c.240 + 1G>C, c.708 + 2T>G, c.880-2A>T, c.1006 + 5G>C, and c.1180 + 184T>C were identified, of which three were novel IDS mutation genes and the other three were pathogenic for either the severe form or the attenuated form of MPS II. As mentioned above, the variation allele, c.103 + 34_56dup, a novel IDS variation located between exon 1 and exon 2 (intron-1) downstream of the 34 to 56 regions, had a repeat sequence, CCTTCCTCCCTCCCTTCCTTCCT. The cDNA sequencing analysis was normal, and there was no significant difference in RNA expression in real-time PCR analysis [41]. Most of the cases also showed other IDS mutations, including c.851C>T (P284L) in exon 6, c.1180 + 184T>C (splicing) in intron 8, and c.684A>G (p.Pro228 =) in exon 5 (silent mutation). The patients with these combinations of variation alleles had pseudo-deficiencies of leukocyte IDS enzyme activities, ranging from 0.56 to 14.69 μmol/g protein/4 h, but no significant signs or symptoms were noted when surveying the family members who had the same variation alleles [41]. Chang et al. reported that the c.240 + 1G>C variation in intron 2 resulted in false splicing that caused the deletion of 105 amino acids and caused the severe form of MPS II [14]. The splicing mutation, c.708 + 2T>G has been reported to lead to the loss of a splice site that introduces 12 new AA then termination, with the base change of Aggt → AGGG [22]. In general, a severe phenotype was confirmed. Birot et al. reported that another splicing mutation, c.1006 + 5G>C, would lead to splicing in 22 nucleotides in intron 7 and cause the attenuated form of MPS II [11].
Four small deletions were found in our study, including c.231_236delCTTTGC, c.1055del12, c.1184delG, and c.1421delAG, all of which have been reported previously [17]. Mutation c.231del6 resulted in the loss of F78 and A79 and led to the severe form of MPS II according to clinical judgment. Mutation c.1055del12 caused a 12 bp deletion that caused protein alterations including the loss of V353-H356 and a severe phenotype. Mutation c.1184delG caused a 1 bp deletion resulting in the alteration of 44 amino acids by frame shift to stop codon, and a severe phenotype was observed. Mutation c.1421delAG caused a 2 bp deletion that led to the alteration of 17 amino acids by frame shift to termination, and a severe phenotype was also observed. The severe forms caused by these small deletions all corresponded well with the clinical symptoms and manifestations of the MPS II patients in our hospital.
Three gross deletions, exon 4–7 deletion, c.1007-1666_c.1180 + 2113delinsTT, and exon 8 deletions were found and were associated with the attenuated form of MPS II [11], except for one infant with an exon 8 deletion who was referred from the NBS program with no MPS pre-symptoms. A sequence of exon 8 linking c.1007-1666 and c.1180 + 2113, a total of 3953 bp, had been completely deleted, and TT insertion was observed in the deleted region between intron 7 and 8 (Figure 2A,B).
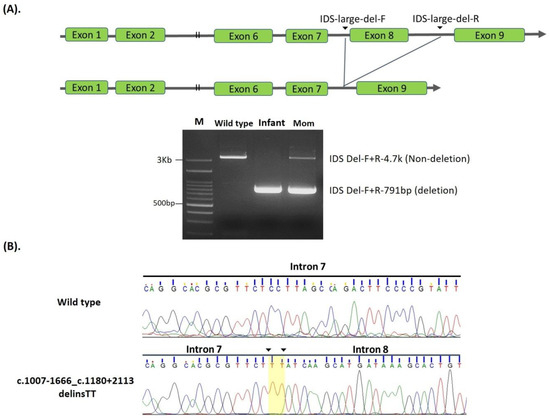
Figure 2.
Scheme for generating a delins c.1007-1666_c.1180 + 2113delinsTT between intron 7 and intron 8. (A): Scheme for generating a delins c.1007-1666_c.1180 + 2113delinsTT between intron 7 and intron 8, leading to the loss of exon 8 in open reading frames. PCR using a primer pair flanking the delins site was used to detect this mutation in one infant and the carrier mother. Lanes M, wild-type, infant, and mom, corresponding to DNA size markers, wild type control, infant, and the mother. (B): Electropherogram showing the sequences of PCR products flanking the breakpoint created in this delins; note a dinucleotide TT insertion is shadowed.
One complex rearrangement, IDS inversion, was identified. Recombination between the IDS gene and its putative pseudogene, IDS-2, resulted in an inversion of the intervening DNA. This inversion, which may have been the consequence of an intra-chromosomal mispairing, was caused by homologous recombination between sequences located in intron 7 of the IDS gene and sequences located distal of exon 3 in IDS-2 [38,39]. IDS inversion led to the attenuated form of MPS II (Figure 3A,B).
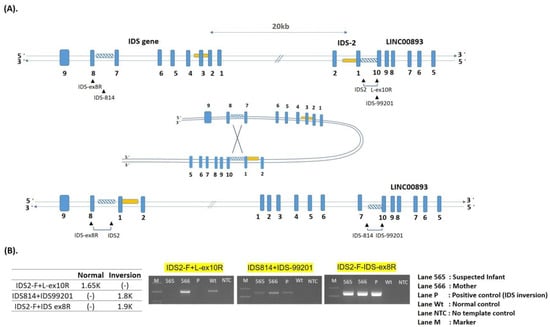
Figure 3.
Scheme for generating a complex inversion in the IDS gene and IDS-2 pseudogene. The created inversions were identified by PCR. (A): The supposed folding structure was formed by homologous sequences (twill line boxes) in the IDS gene and IDS-2 pseudogene. The rearrangement of the IDS gene was inverted from the homolog in intron 7 to the homolog in distal IDS-2-LINC00893 region. (B): Three sets of primer pairs, as illustrated in Figure A that flanked the breakpoints of recombination were used; the lengths of the amplified fragments of created inversions were 1.9 kb in IDS-2, and 1.8 kb in IDS. PCR products of the affected infant and mother were resolved by electrophoresis, lanes 565, 566, P, Wt, NTC, and M, corresponding to the infant, mother, positive control, wild-type control, template control, and 100 bp ladder DNA size marker.
2.2. The IDS Activity in Extracts of COS-7 Cells Expressing Novel Mutant cDNA
A total of 19 mutant cDNA expression clones were constructed and analyzed for IDS activity in extracts of COS-7 cells in order to verify the influence of individual IDS variants found in the MPS II patients with different severities (Table S1). From the 19 mutants, 11 were novel mutants, which have not been reported and analyzed for enzyme activity in COS-7 cells, i.e., c.142C>T, c.254C>T, c.311A>T, c.454A>C, c.589C>T, c.778C>T, c.817C>T, c.890G>A, c.1025A>G, c.1478G>C and c.1499C>T. Six mutants have been reported previously but the IDS in vitro study has not been performed, i.e., c.137A>C, c.797C>G, c.851C>T, c.998C>T, c.1106C>G, and c.1400C>T. The rest two mutants, i.e., c.1402C>T and c.1403G>A, have been reported previously [17,21,29,30]. The IDS activities in wild-type, PCMV6-vector, vehicle, COS-7 cells (mock), and positive controls (c.928C>T, p.Q310Ter) were 768.49 (± 72.92), 59.66 (± 11.84), 91.80 (± 14.30), 72.99 (± 17.28), and 53.83 (± 10.79) μmol/g protein/4 h, respectively. The percentages of IDS activity expressed in transfected COS-7 cells of individual novel missense mutations for c.137A>C, c.311A>T, c.454A>C, c.797C>G, c.817C>T, c.998C>T, c.1106C>G, c.1400C>T, c.1402C>T, and c.1403G>A ranged from 0% to 2.2%, and were extremely significant compared to the wild type (p <0.001). In addition, the IDS activity expressions were 22.6% and 41.8% for c.254C>T and c.1025A>G mutations, respectively, which were highly significant compared to the wild type (p < 0.01), and the IDS activity expression of c.851C>T was 62.3% which was significant compared to the wild type (p < 0.05). The percentages of IDS activity expressed in transfected COS-7 cells of the other missense mutations, i.e., c.142C>T, c.589C>T, c.778C>T, c.890G>A, c.1478G>C, and c.1499C>T were 83.6%, 74.9%, 84.5%, 98.9%, 86.5%, and 77.5%, respectively, and there were no significant differences. The variations between repetitions of the enzyme activity tests were valid and acceptable, and the IDS values were the average of three different transfections (Figure 4). The results corresponded well with the quantities of uGAG-derived disaccharides and the IDS activities in leukocytes (Table 2). In Table 2, the missense mutations, i.e., c.254C>T, c.311A>T, c.817C>T, c.1025A>G, and c.1400C>T showed “positive” uGAG test results (DS: 11.59–45.95 μg/mL and HS: 11.43–30.01 μg/mL) and a deficiency in IDS enzyme activity (0.20–0.83 μmol/g protein/4 h) in leukocytes, which agrees with the disease prediction of the severe phenotype. In contrast, the infants with the other novel missense mutations, i.e., c.142C>T, c.589C>T, c.778C>T, c.890G>A, c.1478G>A, c.1499C>T, and c.1513T>C, showed “negative” uGAG test results and reductions in leukocyte IDS activities, indicating that the phenotype of these mutation variants could cause the attenuated form of MPS II disease. Intensive long-term follow-up examinations for asymptomatic MPS II infants are very important. In addition to the severe form found in the patients with missense mutations, six confirmed MPS II patients with the mutations c.253G>A, c.683C>T, c.697A>G, c.797C>G, c.801G>T, and c.1600A>C were diagnosed and confirmed to have the attenuated phenotype characterized by somatic problems, including developmental delays, stiffness of the joints, short stature, coarse facial features, especially the lips, nostrils, and tongue, enlargement of the head, progressive hearing loss, broad chest, and short neck, but without neuronopathic findings [17,18,22,32].
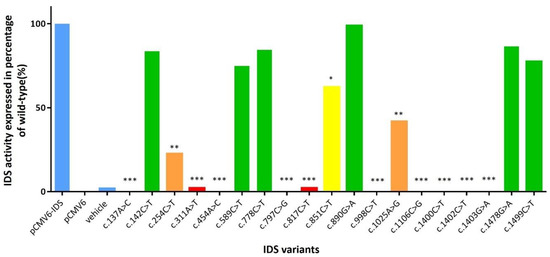
Figure 4.
The percentages of IDS activity expressed in transfected COS-7 cells of individual novel missense mutations (n = 17), and previously reported missense mutation (n = 2). A p-value < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant (*); p-value < 0.01 was considered to be highly significant (**); and a p-value < 0.001 was considered to be extremely significant (***).

Table 2.
Mutations of the iduronate-2-sulfatase (IDS) gene found in suspected MPS II infants referred from newborn screening program for MPS in Taiwan.
2.3. The Quantitative Analysis of Urinary GAG-Derived Disaccharides by Liquid Chromatography /Tandem Mass Spectrometry Assay
The values of DS and HS of the confirmed MPS II patients and the suspected MPS II infants calculated using the CS-normalized method varied widely, from 0.01 to 45.95 μg/mL for DS and from 0.09 to 203.35 μg/mL for HS. The relationships between uGAG-derived disaccharide levels, including DS and HS and the severity of the phenotype, were investigated, and the values of DS and HS closely matched the phenotypes of MPS. The MPS II patients with mental retardation had significantly higher levels of HS than those without mental retardation, and the DS values in the MPS II patients with hernia, hepatosplenomegaly, claw hands, coarse face, valvular heart disease, and joint stiffness were higher than in those without the symptoms reported by Lin et al. [42]. In the current study, “positive” uGAG tests indicated that the Dimethylmethylene Blue/creatinine (DMB/Cre.) ratio was increased, and distinct patterns of DS and HS separations were found on cellulose acetate sheet by two-dimensional electrophoresis (2-DEP), and the quantities of urinary DS and HS were significantly elevated in the MS/MS-based method. The confirmed MPS II patients and the seven highly suspected infants closely matched the diagnostic criteria of the MPS II phenotype.
3. Discussion
The relationship between the phenotype and genotype of MPS type II has been widely discussed, and the issue is of particular importance since the initiation of the NBS program for MPS in Taiwan. Almost none of the suspected MPS infants in this study had MPS pre-symptoms, although the first-line biochemistry examinations, IDS enzymatic assays, and IDS mutation gene analyses exhibited positive results. Infants in Taiwan are not permitted to receive ERT for Hunter syndrome unless their clinical and laboratory findings meet the guidelines for treatment issued by the National Health Insurance Bureau of Taiwan, which include the onset of one or more MPS signs or symptoms, deficiency of leukocyte IDS activity, identification of IDS variants, elevated urinary GAG levels, and definite evidence of a family history. The nationwide NBS program for MPS was officially launched in 1 August 2015, and up to 31 July 2019, a total of 324,426 infants had been screened in two newborn screening centers of Taiwan (Chinese Foundation of Health; CFOH and Taipei Institute of Pathology; TIP). In those, a total of 154 suspected infants who were referred to MacKay Memorial Hospital for confirmation due to the lower IDS enzyme activities in dried blood spot (DBS), which was measured by tandem mass spectrometry in the first test and the second recall test. The cut-off values of the first and the second test were < 6.5 and < 2.2 μmol/L/h, respectively. Genotyping was also performed when the second newborn screening specimen again had decreased enzyme activity [37]. In this study, seven infants were confirmed as MPS II based on the results of confirmatory diagnosis including a “positive” in uGAG biochemistry examinations, deficiency in leukocyte IDS enzyme activity, and identification of IDS variant. Of these seven infants, two were enrolled in ERT Program for MPS II; one received ERT (Elaprase; Shire Human Genetic Therapies, Boston, MA, USA) and another received ERT plus HSCT at the age of 1.11 and 0.55 years, respectively, due to definite evidence of family history. In order to achieve the goal of the NBS program for MPS, namely “Early detection, making an early diagnosis, giving them early therapy and preventing the onset of irreversible symptoms”, a comprehensive understanding of genotype–phenotype correlations is important by analyzing the genomic findings via in vitro expression studies. In this study, we evaluated the genotype–phenotype relationships of all 51 IDS variants currently known in Taiwan by integrating clinical data with in vitro expression studies and mass spectrometry-based assays of uGAGs to investigate and predict the likelihood of novel IDS variants, which can cause the severe or attenuated phenotype.
A total of 191 cases were enrolled in this study, including 51 confirmed MPS II patients (aged from 3.5 to 48.3 years) and 140 suspected MPS II infants who were referred from the NBS program for MPS. Of these cases, 66 had missense mutations, 3 had nonsense mutations, 4 had silent mutations, 106 had splicing mutations, 5 had small deletions, 3 had gross deletions, and 4 had complex rearrangements (IDS inversion). Twelve missense mutations including c.137A>C, c.189T>G, c.262C>T, c.413A>G, c.454A>C, c.998C>T, c.1039A>G, c.1402C>T, c.1403G>A, c.1454T>G, c.1466G>A, and c.1478G>C have been reported to cause the severe phenotype [13,14,16,17,18,22,23,26,27,28,29] according to clinical manifestations of neuronopathic with intellectual disabilities and cognitive decline with hyperactive and aggressive behavior, as well as in vitro expression studies [23,43]. Of these mutations, only one missense mutation, c.454A>C, was a novel variant that showed 0.0% IDS activity of the wild type (extremely significance, p < 0.001). Of the missense mutations, all of the novel variants except c.454A>C were found in infants from the NBS program and showed varied IDS activities in the extracts of COS-7 cells, i.e., c.142C>T (83.6%), c.254C>T (22.6%), c.311A>T (2.2%), c.589C>T (74.9%), c.778C>T (84.5%), c.817C>T (2.2%), c.890G>A (98.9%), c.1025A>G (41.8%), c.1478G>A (86.5%), c.1499C>T (77.5%), and c.1513T>C (not showed in this report) (Figure 4).
In order to investigate and assess the consequences of IDS missense variants on clinical phenotypes, the tertiary structure of IDS was constructed using the arylsulfatase structure as a template in homology modeling analysis. Structural analysis indicated that the residues of the mutations found in the severe phenotype had direct interactions with the active site residues or broke the hydrophobic core domain of IDS, whereas residues of the missense mutations found in the attenuated phenotype were located in the peripheral region as reported by Kato et al. [6]. The putative active site residues i.e., D45 (c.133-135GAT), D46 (c.136-138GAC), C84 (c.250-252TGC), K135 (c.403-405AAA), and D334 (c.1000-1002GAT) would lead to a severe phenotype of Hunter syndrome. In the current study, a 3D structural analysis was performed by simulating 6 missense residues, i.e., c.253G>A (p.A85T), c.262C>T (p.R88C), c.311A>T (p.D104V), c.817C>T (p.R273W), c.851C>T (p.P284L), and c.1402C>T (p.R468W) in the automated protein structure homology-modeling server, SWISS-MODEL (https://swissmodel.expasy.org) (Figure 5). Figure 5 shows that P284L residue on the loop (random coil) located at the peripheral region of the IDS structure that was far from the active site and was considered to be less conserved residue, and thus the variant would not have a strong influence on IDS protein configuration and function. R273W residue on the folding α-helix located between the peripheral region and active site of IDS structure was considered to be a conserved residue that would affect IDS protein function. According to our in vitro expression study, variants of the IDS gene would conserve about 2.2% of IDS activity of the wild type. R468 was adjacent to the positively charged active site residue. According to Kato et al., R468L or R468W, that is, the changes from the positively charged residue, Arginine, to large hydrophobic residues, Leucine or Tryptophan, should result in modification of the active site geometry and also in a significant change in substrate affinity [6]. R88 mutations were related to the severe phenotype. According to the structural analysis reported by Kato et al., the R88C residue itself was one of the most important active site residues. This finding suggests that any type of amino acid substitution would affect enzymatic activity in the severe phenotype, as observed in our patients [6,18,27,44,45]. In addition, there was no clear phenotype/genotype relationship associated with the A85T mutation; however, the location of this variant residue was adjacent to the active site domain and the changes in the non-polar amino acid, Alanine, to the polar amino acid with hydroxyl group, Threonine, which was extremely non-conserved and may result in the severe form of Hunter syndrome [6,27,46].
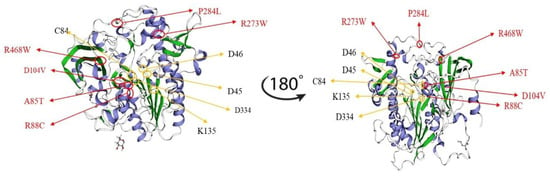
Figure 5.
3D structure analysis by simulating six missense residues, i.e., c.253G>A (p.A85T), c.262C>T (p.R88C), c.311A>T (p.D104V), c.817C>T (p.R273W), c.851C>T (p.P284L), and c.1402C>T (p.R468W), was performed using SWISS-MODEL. The location and the residues of A85T and P284L may have had less influence on the structure of IDS protein and its function and were considered to cause the attenuated phenotype. The altered residues that may have strongly influenced the confirmation of the active site on IDS protein were identified by 3D structure analysis, i.e., R88C, D104V, R273W, and D104V variants may have been pathogenic variations for the severe phenotype of Hunter syndrome.
Interestingly, a complex rearrangement (IDS inversion) was found in four unrelated patients, in whom one case was referred from the NBS program for MPS. The pseudogene (I2S2/IDSP1) located on the telomeric side of IDS has been shown to undergo homologous recombination leading to large complex genomic/genetic rearrangements, which comprise about 13% of mutations [10,36]. Patients with this mutation had the attenuated phenotype. The region of IDS gene was inverted as a recombination from intron 7 to the distal part of exon 3 in IDS-2. The IDS inversion was not found after sequencing all nine exons of the IDS gene and their intro-exon junctions using conventional PCR-based method [47]. However, when using three pairs of designed primers, i.e., IDS2-F + L-ex10R, IDS814 + IDS-99201, and IDS2-F + IDS-ex8R, as indicated in Figure 3A for PCR-based analysis that flanked the breaking points of these two inversions, the inverse mutations were easily resolved. The length of PCR products in the suspected infant (Figure 3B, lane 565) and the mother (Figure 3B, lane 566) were 1.8 kb in IDS inversion and 1.9 kb in IDS2 inversion, respectively. These PCR fragments were not detected from the wild IDS loci, however, the primer pair (IDS2-F + ex10R), which crossed the homolog of IDS2 and LINC00893 junction resulted in a 1.65-kb PCR product (Figure 3B, lane Wt) [38,39]. In this study, the mother (lane 566) was confirmed to be a carrier and was positive in all PCRs.
One suspected infant had the c.1007-1666_c.1180 + 2113delinsTT mutation. In this case, a 3953 bp deletion and a dinucleotide TT insertion, which removed all exon 8 linking between c.1007-1666 and c.1180 + 2113 were observed (Figure 2A). The primers located in intron 7 and 8, respectively, successfully detected the large deletion, and the sequences of the PCR products showed the breaking point and TT insertion (Figure 2B). The phenotype of this infant with the gross deletion was indefinite, and further studies to predict the disease-causing potential of this novel variant are necessary to confirm the clinical significance and determine the effect of the variation on IDS protein function.
Five of the patients had small deletions (i.e., c.231_236delCTTTGC, c.1055del12, c.1184delG, and c.1421delAG) and they had the severe form phenotype. The patients were unrelated except for a male sibling with c.1421delAG. In general, small deletions of the IDS gene led to the loss of amino acids and the occurrence of frame shift to termination when in translation a stop codon was interpreted that may have altered the normal arrangement or sequence of amino acids in the IDS gene, resulting in serious defects of IDS protein structure and function.
A total of 99 suspected infants were identified with the variation allele, c.103 + 34_56dup, which was linked with other variants, including c.851C>T (P284L) in exon 6, c.1180 + 184T>C (splicing) in intron 8, and c.684A>G (p.Pro228 =) in exon 5 (silent mutation). For those cases, all the results showed “negative” in urinary first-line biochemistry examinations and “reduction” of leukocyte IDS activities varied from 0.56 to 14.69 μmol/g protein/4 h, which did not exactly meet the confirmatory criteria for a typical MPS II diagnosis. According to our cDNA sequencing and RNA real-time PCR analyses, the combinative variation alleles, c.103 + 34_56dup plus c.1180 + 184T>C, showed normal in cDNA sequences and no significant difference of mRNA levels; besides, the silent mutation, c.684A>G (p.Pro228 =) in exon 5, that would not cause the change of the amino acid Proline that was defined as non-pathogenic, not leading to the defect of IDS protein. In addition, the only variation that would cause pseudo-deficiency of IDS enzyme activity was c.851C>T (P284L), in which the in vitro expression of IDS activity was 62.3% of the wild type. The single nucleotide change, and the deduced amino acid substitution might produce a steric effect that mildly influences the stability of mRNA and/or folding of IDS protein. In summary, the frequency of the Taiwanese population carried with the combination of above four variants was high, about 70.7% of referred cases (99/140), and the infants with these combined variations might not show up any notable MPS presentations, but it is still required for a long-term follow-up inspection of disease progression, even though the male family members with the same variations via maternal inheritance have been thoroughly investigated. In our study, an additional two suspected cases were notable; one had the c.103 + 34_56dup variation accompanied with c.851C>T (P284L), and another had the variation allele c.851C>T plus c.1180 + 184 T>C. Variation c.851C>T (P284L) was reported by Sawada et al. that this substitution might cause pseudo-deficiency of IDS and might result in a structural modeling of the enzyme (http://www.aismme.org/pdf/ACIMD.pdf). From the report, IDS with c.851C > T (P284L) confirmed that this amino acid substitution was non-pathogenic. In addition, another study reported that the missense mutation c.851C > T (P284L) could cause an attenuated phenotype of Hunter syndrome according to the exhibition of some clinical presentations [24].
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Samples
A total of 191 cases were enrolled and analyzed in this study. These cases included 51 patients diagnosed with MPS II since the 1990s in Taiwan, and 140 infants suspected of having MPS II after being screened by the Newborn Screening (NBS) Program for MPS. This screening program was established in Taiwan in August 2015, and all children suspected of having MPS were then referred to MacKay Memorial Hospital to confirm the diagnosis. The samples required for the assays included urine (10–20 mL) and EDTA blood (2 tubes, 3–5 mL in each). Urine samples were stored at −20 °C prior to GAG analyses, and the blood samples were kept at room temperature and 4 °C before leukocyte isolation for enzymatic assay and molecular DNA analysis, respectively. All procedures were performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committees on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Declaration of Helsinki of 1975, as revised in 2000. The Institutional Review Board of MacKay Memorial Hospital approved this study (14MMHIS281, approval date: 30 March 2015; 16MMHIS152, approval date: 22 June 2017; and 17MMHIS176, approval date: 30 August 2018), and written informed consent was obtained from all of the patients or their parents.
4.2. DNA Isolation, Amplification, and Sequencing
Genomic DNA was extracted using a QIAamp DNA Blood Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions, from peripheral leukocytes of all patients. All IDS gene exons and flanking intronic regions were amplified by PCR using Taq DNA polymerase 2X Master Mix Red (containing Tris-HCl pH 8.5, (NH4)2SO4, 3 mM MgCl2, 0.2% Tween 20, 0.4 mM dNTPs, 0.2 units/µL Ampliqon Taq DNA polymerase, inert red dye and stabilizer; Ampliqon, Denmark), 10 pmol of each forward and reverse primer, and 75 ng of template DNA in a final volume of 30 µL. The PCR conditions were as follows: 94 °C for 5 min, 33 cycles of 94 °C for 40 s, 58–62 °C for 40 s and 72 °C for 40 s, and a final extension time of 72 °C for 10 min. The PCR products were analyzed by 2.5% agarose gel electrophoresis, stained with SYBER green, and then visualized under a UV trans-illuminator. Sequencing of PCR products was performed at Genomics Inc. sequencing services (New Taipei City, Taiwan) on an ABI 3730XL DNA analyzer (Applied Biosystems).
4.3. Constructing Mutant DNA by Site-Directed Mutagenesis
Plasmids expressing IDS protein were made by cloning the IDS cDNA into a pCMV6-Entry based Myc-DDK tagging vector (ORIGENE, RC219187) (Figure S1). Nineteen mutations of the IDS gene, including c.137C>A (p.D46A), c.142C>T (p.R48C), c.254C>T (p.A85V), c.311A>T (p.D104V), c.454A>C (p.S152R), c.589C>T (p.P197S), c.778C>T (p.P260S), c.797C>G (p.P266R), c.817C>T (p.R273W), c.851C>T (p.P284L), c.890G>A (p.R297H), c.998C>T (p.S333L), c.1106C>G (p.S369X), c.1025A>G (p.H342R), c.1400C>T (p.P467L), c.1402C>T (p.R468W), c.1403G>A (p.R468Q), c.1478G>A (p.R493H), and c.1499C>T (p.T500I) were introduced into the wild-type IDS cDNA by site-directed mutagenesis. Table S2 lists the primers used for site-directed mutagenesis. PCR was carried out with initial denaturation at 95 °C for 2 min, 18 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 20 s, annealing at 60 °C for 10 s, and extension at 68˚C for 30 s followed by a final extension for 5 min. The reaction mixture contained 10 ng DNA template, 125 ng of oligonucleotide primers, 5 µL of 10X Reaction Buffer, 1 µL of dNTP, 1.5 µL of QuikSolution reagent and 1 µl of QuikChange Lightning Enzyme (QuikChange Lightning Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The constructs were verified by direct DNA sequencing.
4.4. Cell Culture and Transient Transfection
COS-7 cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s MEM (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Grand Island, NJ, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Grand Island, NJ, USA) and penicillin-streptomycin mixture (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Grand Island, NJ, USA) at 37 °C in 5% CO2. The COS-7 cells were transfected by pCMV6-Entry plasmids of wild-type IDS cDNA and the 19 mutants using Lipofectamine 3000 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) following the manufacture’s protocol. After 24 h of incubation at 37 °C, the cells were harvested for IDS enzyme assays. These experiments were performed in triplicate.
4.5. Enzyme Assay for MPS II
Leukocyte enzyme assay for MPS II was described previously [40,48]. The enzymatic liberation of fluorochrome from 4MU-α-L-iduronide-2-sulfate required the sequential action of IDS and α-iduronidase. The rate of fluorescence increase was directly proportional to enzyme activity. Leukocyte isolation and protein determination were required prior to performing an enzyme assay. Leukocytes were isolated from EDTA blood by centrifugation through Ficoll-Paque (Sigma-Aldrich, Inc., St. Louis, MO, USA) at 18 °C for 40 min at 2500 rpm. By removing the upper layer, the white cell ring from the interface was removed and transferred to a 5 mL centrifuge tube, followed by the addition of 0.9% NaCl to the top, mixing, and centrifugation for 10 min at 2000 rpm at 4 °C. Cell lysates were prepared by suspending leukocyte pellets in 0.2 mL of 0.85% NaCl and disrupted by 6 cycles of freeze-thawing. Proteins were determined using Coomassie Plus protein assay (Pierce, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). The assay for individual enzyme activity was performed using 4-methylumbelliferyl substrate, with the enzyme activity being proportional to the amount of liberated fluorescence detected (μmol enzyme activity/g protein/hour). Individual enzyme activity, which was 5% lower than normal was defined as a marked reduction in that enzyme activity. The principle of the assay has been illustrated previously [41,48,49]. The enzymatic liberation of fluorochrome from 4MU-α-L-iduronide-2-sulfate required the sequential action of IDS and α-iduronidase, and a normal level of α-iduronidase activity was insufficient to complete hydrolysis of the reaction intermediate 4-methylumbelliferyl-α-iduronide formed by IDS. In performing IDS enzymatic assay, at least one additional sulfatase is recommended to analyze to differentiate from multiple sulfatase deficiency. In our study, one additional enzyme, i.e., α-L-iduronidase (IDUA), was analyzed by 4-MU fluorometric assay to ensure the quality assurance of the cell supernatant sample.
4.6. The Quantification of uGAG-Derived Disaccharides by Tandem Mass Spectrometry Assay
The Tandem mass spectrometry (liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry; LC-MS/MS) (4000 QTRAP LC-MS/MS System; AB Sciex, Foster City, CA, USA) assay for relevant GAG-derived disaccharides was performed using methanolysis for chondroitin sulfate (CS), DS and HS [50,51,52], and the mass to charge(m/z) of the parent ion and its daughter ion after collision was 426.1→236.2 for DS and 384.2→161.9 for HS. The quantities of urinary DS and HS were determined by applying the CS-normalized method reported by Lin et al., and the reference cut-off values were < 0.80 μg/mL for DS and < 0.78 μg/mL for HS [53].
4.7. MPS II Phenotype Determination
The clinical signs and symptoms of MPS II were heterogeneous, and the disorder should be regarded as two broad groups, the severe and attenuated forms, according to the severity of symptoms and whether or not the patients are neuronopathic with intellectual disability. Neuronopathic with intellectual disability was assessed according to the scores for IQ and DQ tests and the Functional Independence Measure for Children (WeeFIM) questionnaire for the parents [54]. Individuals with attenuated MPS II were most often diagnosed between the ages of 4 and 8 years, and survival to adulthood was common. Patients with the more severe form of MPS II exhibited a chronic and progressive disease involving multiple organs and tissues. The age at diagnosis was usually between 18 and 36 months, and death from a combination of neurological deterioration and cardio-respiratory failure usually occurred in the mid-teenage years [14]. Patients who underwent an HSCT or ERT could prolong their life and dramatically change the natural history of this disease. For this reason, it was mandatory to have a correlation between the severity of MPS II and genotype to decide the appropriate treatment.
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis (Students t-test) was performed to compare values of IDS activity obtained from individual variants to those of the wild type. P values were calculated using Excel 2010 (Microsoft Office), and a p-value < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant, a p-value < 0.01 was considered to be highly significant, and p-value < 0.001 was considered to be extremely significant.
5. Conclusions
Awareness of the specific mutations involved in MPS II may help to clarify the relationship between genotype and phenotype in individual patients and allow for the identification of female carriers. To characterize the biochemical and molecular defects in IDS-deficient patients and their families, this study was designed to identify IDS gene mutations in a group of Taiwanese patients with MPS II. Sixteen novel variants were found, and these cases were all referred from the NBS program for MPS in the past 4 years. Because such patients were too young to manifest signs or symptoms, the investigation of genotype–phenotype relationships was especially important. In this study, clinical data were integrated with in vitro expression studies as well as a mass spectrometry-based assay of uGAGs to predict the likelihood of novel IDS variants, which can cause the severe or attenuated phenotype. Further molecular investigations with a reliable intelligence or developmental disability score should be performed to better understand the genotype–phenotype correlation for future therapeutic approaches.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Materials can be found at https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/1/114/s1.
Author Contributions
H.-Y.L., R.-Y.T., S.-R.C., and C.-K.C. conceptualized the study design, performed data analysis, interpreted results, drafted the initial manuscript, and reviewed and revised the manuscript. S.-P.L. provided the confirmed MPS patients and non-MPS controls, coordinated and supervised data, and critically reviewed the manuscript. Y.-T.L., S.F., F.-J.W., S.-F.H., S.-Y.T., Y.-H.C., and C.-L.L. carried out the laboratory experiments including the sample collection and preparation, biochemistry examinations of MPS diagnosis, tandem mass spectrometry analysis, data collection, data analysis, and statistical analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by research grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology, Executive Yuan, Taiwan (MOST-106-2314-B-195-015-MY2, MOST-105-2628-B-195-001-MY3, MOST-108-2314-B-195-014, and MOST-108-2314-B-195-012), and from MacKay Memorial Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan (MMH-E-108-16).
Acknowledgments
The authors express their sincere thanks to the staff of the Department of Clinical Laboratory, Rare Disease Center, and the Department of Pediatrics of MacKay Memorial Hospital for sample collection, clinical and genetic counseling, and experimental laboratory work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no financial or non-financial interests.
References
- Besley, G.T.N.; Wraith, J.E. Lysosomal disorders. Curr. Paediatr. 1997, 7, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wraith, J.E. Mucopolysaccharidoses. Curr. Paediatr. 1996, 6, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufeld, E.; Muenzer, J. The mucopolysaccharidoses. In Scriver’s Online Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease; Valle, D., Beaudet, A., Vogelstein, B., Kinzler, K., Antonarakis, S., Ballabio, A., Eds.; McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 2465–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Chuang, C.K.; Chen, M.R.; Chiu, P.C.; Ke, Y.Y.; Niu, D.M.; Tsai, F.J.; Hwu, W.L.; Lin, J.L.; Lin, S.P. Natural history and clinical assessment of Taiwanese patients with mucopolysaccharidosis IVA. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Hwang, H.Z.; Song, S.M.; Paik, K.H.; Kwon, E.K.; Moon, K.B.; Yoon, J.H.; Han, C.K.; Jin, D.K. Mutational spectrum of the iduronate 2 sulfatase gene in 25 unrelated Korean Hunter syndrome patients: Identification of 13 novel mutations. Hum. Mutat. 2003, 21, 449–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Kato, Z.; Kuratsubo, I.; Tanaka, N.; Ishigami, T.; Kajihara, J.; Sukegawa-Hayasaka, K.; Orii, K.; Isogai, K.; Fukao, T.; et al. Mutational and structural analysis of Japanese patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type II. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 50, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.Y.; Lin, S.P.; Chuang, C.K.; Niu, D.M.; Chen, M.R.; Tsai, F.J.; Chao, M.C.; Chiu, P.C.; Lin, S.J.; Tsai, L.P.; et al. Incidence of the mucopolysaccharidoses in Taiwan, 1984–2004. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2009, 149, 960–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Peracha, H.; Ballhausen, D.; Wiesbauer, A.; Rohrbach, M.; Gautschi, M.; Mason, R.W.; Giugliani, R.; Suzuki, Y.; Orii, K.E.; et al. Epidemiology of mucopolysaccharidoses. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 121, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.J.; Meaney, C.A.; Hopwood, J.J.; Morris, C.P. Sequence of the human iduronate 2-sulfatase (IDS.) gene. Genomics 1993, 17, 773–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timms, K.M.; Lu, F.; Shen, Y.; Pierson, C.A.; Muzny, D.M.; Gu, Y.; Nelson, D.L.; Gibbs, R.A. 130 kb of DNA sequence reveals 2 new genes and a regional duplication distal to the human iduronate-2-sulfate sulfatase locus. Genome Res. 1995, 5, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birot, A.M.; Bouton, O.; Froissart, R.; Maire, I.; Bozon, D. IDS Gene-pseudogene exchange responsible for an intragenic deletion in a Hunter patient. Hum. Mutat. 1996, 8, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondeson, M.L.; Malmgren, H.; Dahl, N.; Carlberg, B.M.; Pettersson, U. Presence of an IDS-related locus (IDS2) in Xq28 complicates the mutational analysis of Hunter syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 1995, 3, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, P.J.; Morris, C.P.; Anson, D.S.; Occhiodoro, T.; Bielicki, J.; Clements, P.R.; Hopwood, J.J. Hunter syndrome: Isolation of an iduronate-2-sulfatase cDNA clone and analysis of patient DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 8531–8535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wraith, J.E.; Scarpa, M.; Beck, M.; Bodamer, O.A.; De Meirleir, L.; Guffon, N.; Meldgaard Lund, A.; Malm, G.; Van der Ploeg, A.T.; Zeman, J. Mucopolysaccharidosis type II (Hunter syndrome): A clinical review and recommendations for treatment in the era of enzyme replacement therapy. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2008, 167, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cudry, S.; Tigaud, I.; Froissart, R.; Bonnet, V.; Maire, I.; Bozon, D. MPS II in females: Molecular basis of two different cases. J. Med. Genet. 2000, 37, E29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pollard, L.M.; Jones, J.R.; Wood, T.C. Molecular characterization of 355 mucopolysaccharidosis patients reveals 104 novel mutations. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2013, 36, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.H.; Lin, S.P.; Lin, S.C.; Tseng, K.L.; Li, C.L.; Chuang, C.K.; Lee-Chen, G.J. Expression studies of mutations underlying Taiwanese Hunter syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis type II). Hum. Genet. 2005, 116, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathmann, M.; Bunge, S.; Beck, M.; Kresse, H.; Tylki-Szymanska, A.; Gal, A. Mucopolysaccharidosis type II (Hunter syndrome): Mutation hot spots in the iduronate-2-sulfatase gene. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1996, 59, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Rathmann, M.; Bunge, S.; Steglich, C.; Schwinger, E.; Gal, A. Evidence for an iduronate-sulfatase pseudogene near the functional Hunter syndrome gene in Xq27.3-q28. Hum. Genet. 1995, 95, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, S.; Mangas, M.; Prata, M.J.; Ribeiro, G.; Lopes, L.; Ribeiro, H.; Pinto-Basto, J.; Lima, M.R.; Lacerda, L. Molecular characterization of Portuguese patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type II shows evidence that the IDS gene is prone to splicing mutations. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2006, 29, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeratichamroen, S.; Cairns, J.R.; Wattanasirichaigoon, D.; Wasant, P.; Ngiwsara, L.; Suwannarat, P.; Pangkanon, S.; Kuptanon, J.; Tanpaiboon, P.; Rujirawat, T.; et al. Molecular analysis of the iduronate-2-sulfatase gene in Thai patients with Hunter syndrome. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2008, 31, S303–S311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafiadaki, E.; Cooper, A.; Heptinstall, L.E.; Hatton, C.E.; Thornley, M.; Wraith, J.E. Mutation analysis in 57 unrelated patients with MPS II (Hunter’s disease). Arch. Dis. Child. 1998, 79, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Kuzenkova, L.M.; Savost’anov, K.V.; Gevorkyan, A.K.; Pushkov, A.A.; Nikitin, A.G.; Vashakmadze, N.D.; Zhurkova, N.V.; Podkletnova, T.V.; Namazova-Baranova, L.S.; et al. Genetic analysis of 17 children with Hunter syndrome: Identification and functional characterization of four novel mutations in the iduronate-2-sulfatase gene. J. Genet. Genom. 2014, 41, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosuga, M.; Mashima, R.; Hirakiyama, A.; Fuji, N.; Kumagai, T.; Seo, J.H.; Nikaido, M.; Saito, S.; Ohno, K.; Sakuraba, H.; et al. Molecular diagnosis of 65 families with mucopolysaccharidosis type II (Hunter syndrome) characterized by 16 novel mutations in the IDS gene: Genetic, pathological, and structural studies on iduronate-2-sulfatase. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2016, 118, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flomen, R.H.; Green, P.M.; Bentley, D.R.; Giannelli, F.; Green, E.P. Detection of point mutations and a gross deletion in six Hunter syndrome patients. Genomics 1992, 13, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollebregt, A.A.M.; Hoogeveen-Westerveld, M.; Kroos, M.A.; Oussoren, E.; Plug, I.; Ruijter, G.J.; van der Ploeg, A.T.; Pijnappel, W.W.M.P. Genotype-phenotype relationship in mucopolysaccharidosis II: Predictive power of IDS variants for the neuronopathic phenotype. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2017, 59, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froissart, R.; Maire, I.; Millat, G.; Cudry, S.; Birot, A.M.; Bonnet, V.; Bouton, O.; Bozon, D. Identification of iduronate sulfatase gene alterations in 70 unrelated Hunter patients. Clin. Genet. 1998, 53, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, A.; D’Avanzo, F.; Rigon, L.; Rampazzo, A.; Concolino, D.; Barone, R.; Volpi, N.; Santoro, L.; Lualdi, S.; Bertola, F.; et al. Molecular diagnosis of patients affected by mucopolysaccharidosis: A multicenter study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2019, 178, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotty, P.L.; Braun, S.E.; Anderson, R.A.; Whitley, C.B. Mutation R468W of the iduronate-2-sulfatase gene in mild Hunter syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis type II) confirmed by in vitro mutagenesis and expression. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1992, 1, 755–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitley, C.B.; Anderson, R.A.; Aronovich, E.L.; Crotty, P.L.; Anyane-Yeboa, K.; Russo, D.; Warburton, D. Caveat to genotype-phenotype correlation in mucopolysaccharidosis type II: Discordant clinical severity of R468W and R468Q mutations of the iduronate-2-sulfatase gene. Hum. Mutat. 1993, 2, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, W.; Wulff, K.; Wehnert, M.; Seidlitz, G.; Herrmann, F.H. Mutations of the iduronate-2-sulfatase (IDS.) gene in patients with Hunter syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis II). Hum. Mutat. 1994, 4, 128–131. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhzouz, C.; Lazea, C.; Bucerzan, S.; Nascu, I.; Kiss, E.; Denes, C.L.; Grigorescu-Sido, P. Clinical and Genetic Characteristics of Romanian Patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II. JIMD Rep. 2017, 33, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lualdi, S.; Di Rocco, M.; Corsolini, F.; Spada, M.; Bembi, B.; Cotugno, G.; Battini, R.; Stroppiano, M.; Gabriela Pittis, M.; Filocamo, M. Identification of nine new IDS alleles in mucopolysaccharidosis II. Quantitative evaluation by real-time RT-PCR of mRNAs sensitive to nonsense-mediated and nonstop decay mechanisms. Biochim. Acta 2006, 1762, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lissens, W.; Seneca, S.; Liebaers, I. Molecular analysis in 23 Hunter disease families. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1997, 20, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Bellows, A.B.; Thompson, J.N. Molecular basis of iduronate-2-sulphatase gene mutations in patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type II (Hunter syndrome). J. Med. Genet. 1999, 36, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uttarilli, A.; Ranganath, P.; Matta, D.; Md Nurul Jain, J.; Prasad, K.; Babu, A.S.; Girisha, K.M.; Verma, I.C.; Phadke, S.R.; Mandal, K.; et al. Identification and characterization of 20 novel pathogenic variants in 60 unrelated Indian patients with mucopolysaccharidoses type I and type II. Clin. Genet. 2016, 90, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, W.; Ye, J.; Han, L.; Gao, X.; Gu, X. Analysis of the IDS gene in 38 patients with Hunter syndrome: The c.879G>A (p.Gln293Gln) synonymous variation in a female create exonic splicing. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerstedt, K.; Karsten, S.L.; Carlberg, B.M.; Kleijer, W.J.; Tönnesen, T.; Pettersson, U.; Bondeson, M.L. Double-strand breaks may initiate the inversion mutation causing the Hunter syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1997, 6, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, G.; Sakura, N.; Kosuga, M.; Okuyama, T.; Kobayashi, M. Effects of idursulfase enzyme replacement therapy for Mucopolysaccharidosis type II when started in early infancy: Comparison in two siblings. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2013, 108, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of medical genetics and genomics and the association for molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.K.; Lin, H.Y.; Wang, T.J.; Huang, Y.H.; Chan, M.J.; Liao, H.C.; Lo, Y.T.; Wang, L.Y.; Tu, R.Y.; Fang, Y.Y.; et al. Status of newborn screening and follow up investigations for Mucopolysaccharidoses I and II in Taiwan. Orphanet J. Rare. Dis 2018, 13, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Lee, C.L.; Lo, Y.T.; Wang, T.J.; Huang, S.F.; Chen, T.L.; Wang, Y.S.; Niu, D.M.; Chuang, C.K.; Lin, S.P. The relationships between urinary glycosaminoglycan levels and phenotypes of mucopolysaccharidoses. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2018, 6, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, R.; Pellico, A.; Pittalà, A.; Gasperini, S. Neurobehavioral phenotypes of neuronopathic mucopolysaccharidoses. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsten, S.; Voskoboeva, E.; Tishkanina, S.; Pettersson, U.; Krasnopolskaja, X.; Bondeson, M.L. Mutational spectrum of the iduronate-2-sulfatase (IDS.) gene in 36 unrelated Russian MPS II patients. Hum. Genet. 1998, 103, 732–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonuccelli, G.; Di Natale, P.; Corsolini, F.; Villani, G.; Regis, S.; Filocamo, M. The effect of four mutations on the expression of iduronate-2-sulfatase in mucopolysaccharidosis type II. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1537, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gort, L.; Chabás, A.; Coll, M.J. Hunter disease in the Spanish population: Molecular analysis in 31 families. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1998, 21, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopwood, J.J.; Bunge, S.; Morris, C.P.; Wilson, P.J.; Steglich, C.; Beck, M.; Schwinger, E.; Gal, A. Molecular basis of mucopolysaccharidosis type II: Mutations in the iduronate-2-sulphatase gene. Hum. Mutat. 1993, 2, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voznyi, Y.V.; Keulemans, J.L.; van Diggelen, O.P. A fluorimetric enzyme assay for the diagnosis of MPS II (Hunter disease). J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2001, 24, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, V.; Filocamo, M.; Regis, S.; Corsolini, F.; Stroppiano, M.; Duca, M.D.; Gatti, R. Expression studies of two novel in CIS-mutations identified in an intermediate case of Hunter syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2003, 120, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auray-Blais, C.; Bhérer, P.; Gagnon, R.; Young, S.P.; Zhang, H.H.; An, Y.; Clarke, J.T.; Millington, D.S. Efficient analysis of urinary glycosaminoglycans by LC-MS/MS in mucopolysaccharidoses type I., II and VI. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2011, 102, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubaski, F.; Osago, H.; Mason, R.W.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Tsuchiya, M.; Orii, T.; Tomatsu, S. Glycosaminoglycans detection methods: Applications of mass spectrometry. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 120, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.K.; Lin, H.Y.; Wang, T.J.; Tsai, C.C.; Liu, H.L.; Lin, S.P. A modified liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry method for predominant disaccharide units of urinary glycosaminoglycans in patients with mucopolysaccharidoses. Orphanet J. Rare. Dis 2014, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lin, H.Y.; Lo, Y.T.; Wang, T.J.; Huang, S.F.; Tu, R.Y.; Chen, T.L.; Lin, S.P.; Chuang, C.K. Normalization of glycosaminoglycan-derived disaccharides detected by tandem mass spectrometry assay for the diagnosis of mucopolysaccharidosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, E.G.; Escolar, M.L.; Delaney, K.A.; Mitchell, J.J. Assessments of neurocognitive and behavioral function in the mucopolysaccharidoses. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 122S, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).