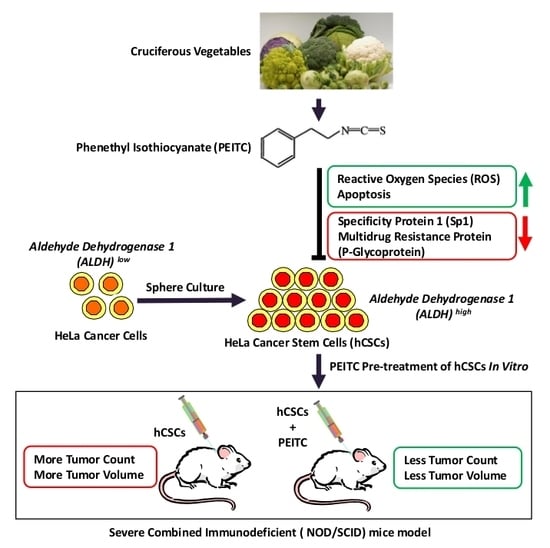
Phenethyl Isothiocyanate Exposure Promotes Oxidative Stress and Suppresses Sp1 Transcription Factor in Cancer Stem Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
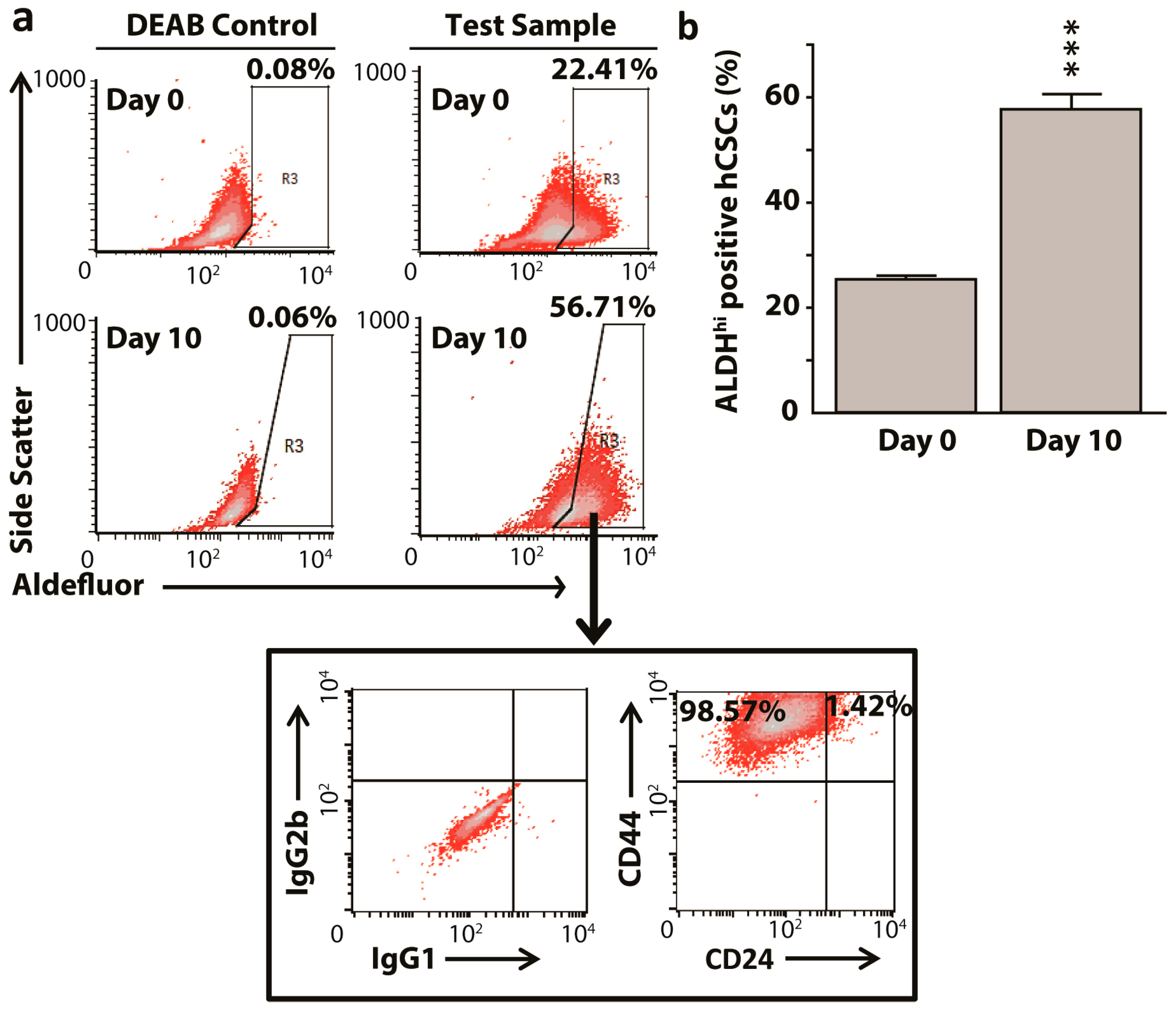
2.1. Enrichment of Aldehyde DehydrogenasehiCD44hi HeLa Cancer Stem Cells
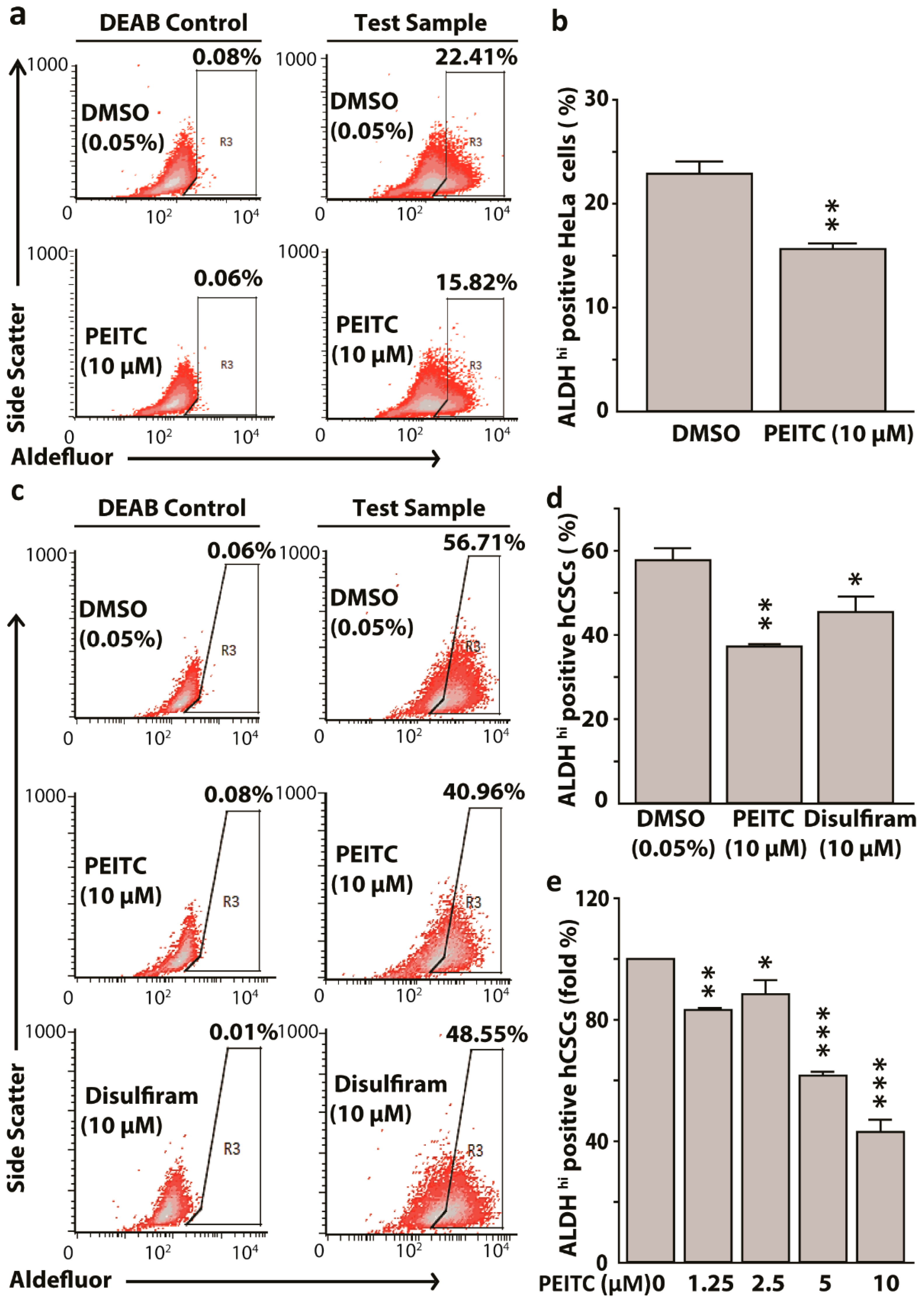
2.2. Phenethyl Isothiocyanate Reduced Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 1 Expressing HeLa Cancer Stem Cells
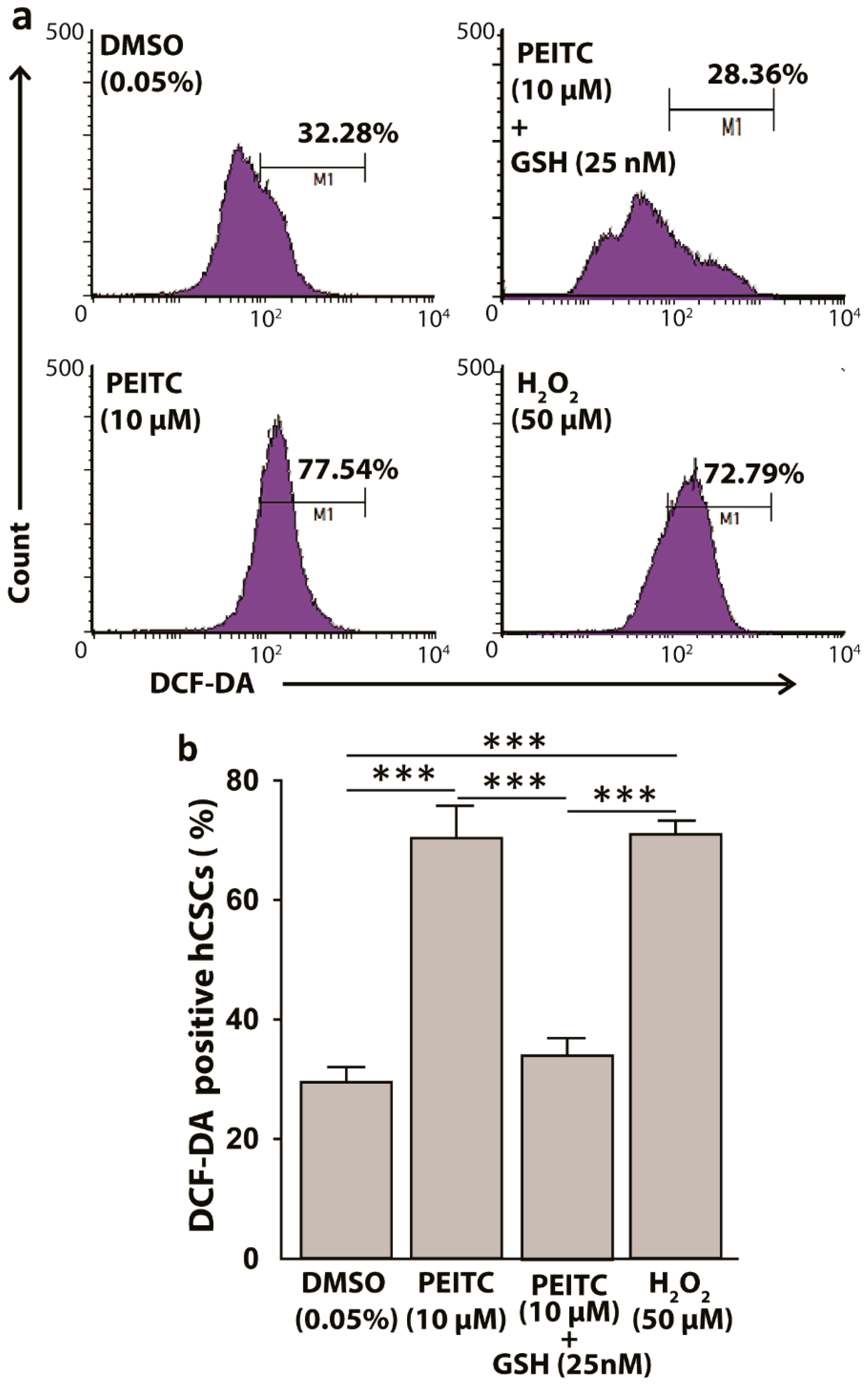
2.3. Reactive Oxygen Species Levels Increased in HeLa Cancer Stem Cells after Phenethyl Isothiocyanate Treatments
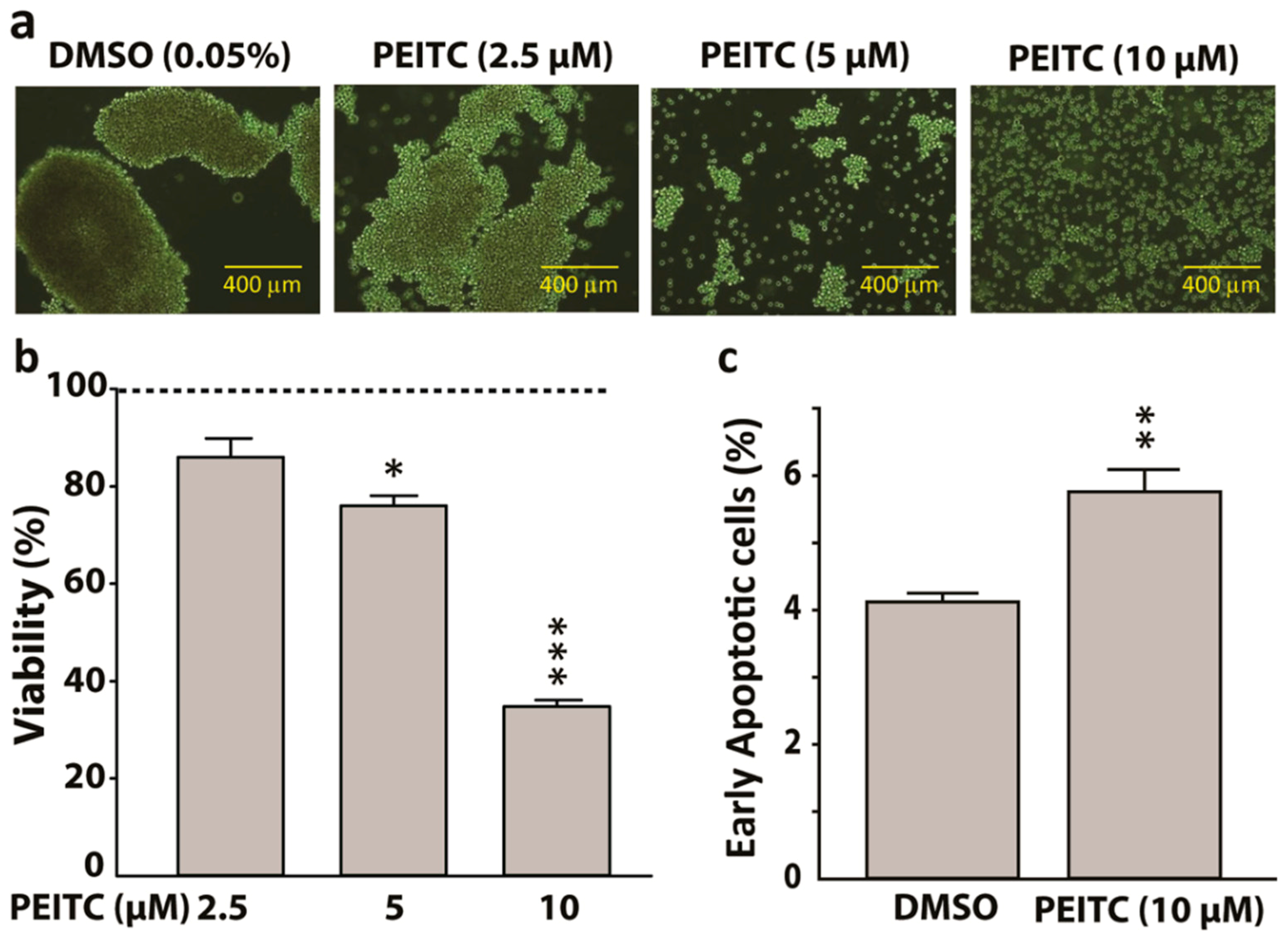
2.4. Phenethyl Isothiocyanate Treatment Suppressed HeLa Cancer Stem Cells Proliferation and Increased Early Apoptosis
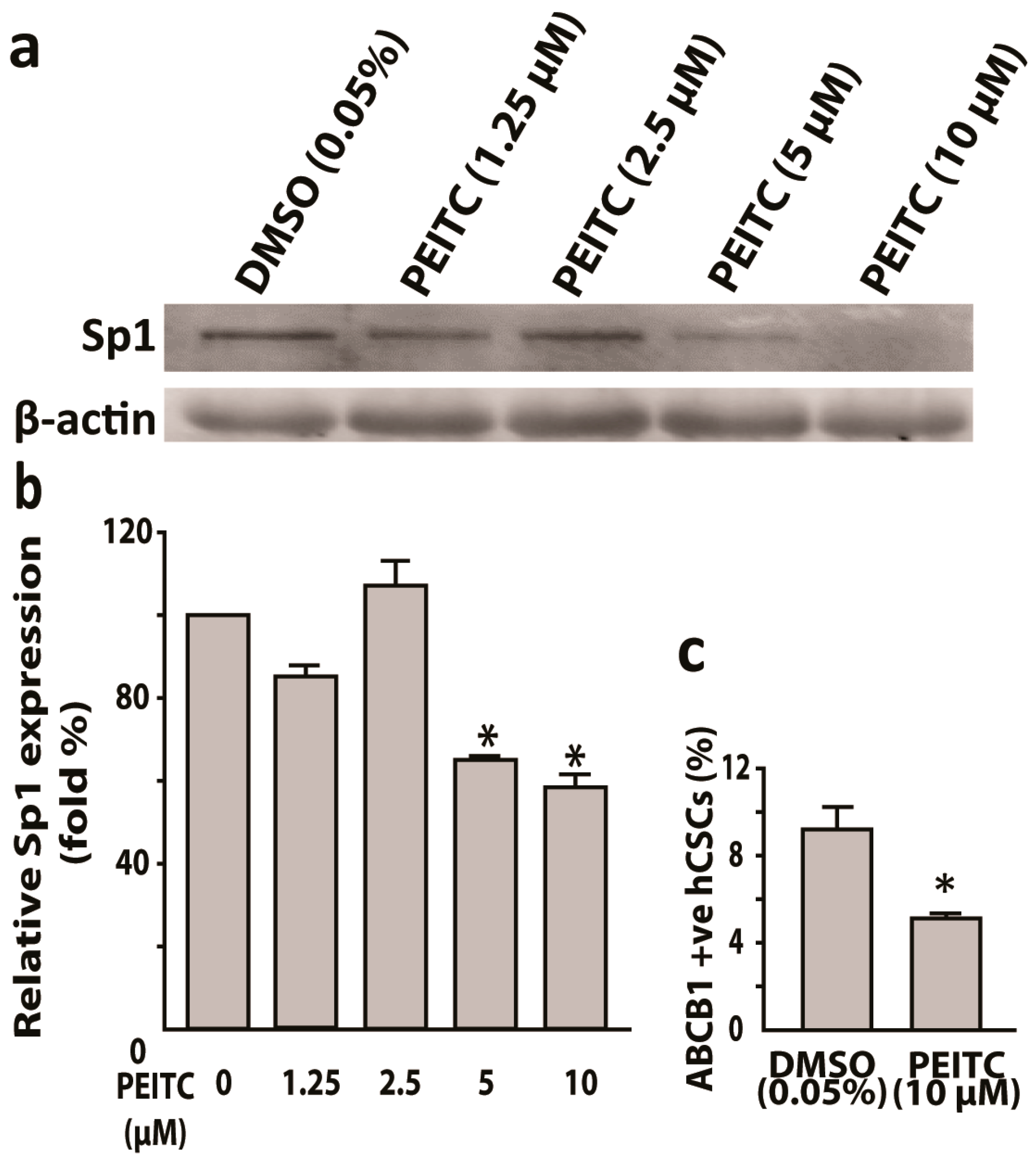
2.5. Phenethyl Isothiocyanate Suppressed the Expression of Sp1 and P-Gp Proteins in HeLa Cancer Stem Cells
2.6. Phenethyl Isothiocyanate Reduced Tumor Initiating Potential of HeLa Cancer Stem Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sphere Cultures of HeLa Cancer Stem Cells
4.2. Aldefluor Assay
4.3. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Assay
4.4. Flow Cytometry
4.5. Sphere-Formation Assay
4.6. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.7. Immunoblotting
4.8. Mice Tumorigenicity Study
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALDH1 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 |
| CSCs | Cancer stem cells |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| hCSCs | HeLa cervical cancer stem cells |
| MDR | Multi-drug resistance |
| NOD/SCID | Non-obese diabetic, severe combined immunodeficient |
| PEITC | Phenethyl isothiocyanate |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
References
- Chen, K.; Huang, Y.H.; Chen, J.L. Understanding and targeting cancer stem cells: Therapeutic implications and challenges. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinogradov, S.; Wei, X. Cancer stem cells and drug resistance: The potential of nanomedicine. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 597–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agliano, A.; Calvo, A.; Box, C. The challenge of targeting cancer stem cells to halt metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 44, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.T.; Ryu, C.J. Cancer stem cell surface markers on normal stem cells. BMB Rep. 2017, 50, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douville, J.; Beaulieu, R.; Balicki, D. ALDH1 as a functional marker of cancer stem and progenitor cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2009, 18, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginestier, C.; Hur, M.H.; Charafe-Jauffret, E.; Monville, F.; Dutcher, J.; Brown, M.; Jacquemier, J.; Viens, P.; Kleer, C.G.; Liu, S.; et al. ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell Stem Cell 2007, 1, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clay, M.R.; Tabor, M.; Owen, J.H.; Carey, T.E.; Bradford, C.R.; Wolf, G.T.; Wicha, M.S.; Prince, M.E. Single-marker identification of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cancer stem cells with aldehyde dehydrogenase. Head Neck 2010, 32, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Dallaglio, K.; Chen, Y.; Robinson, W.A.; Robinson, S.E.; McCarter, M.D.; Wang, J.; Gonzalez, R.; Thompson, D.C.; Norris, D.A.; et al. ALDH1A isozymes are markers of human melanoma stem cells and potential therapeutic targets. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 2100–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Chan, K.W.; Lee, T.K.; Tang, K.H.; Wo, J.Y.; Zheng, B.J.; Guan, X.Y. Aldehyde dehydrogenase discriminates the CD133 liver cancer stem cell populations. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008, 6, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.P.; Fleming, J.B.; Wang, H.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Choi, W.; Kopetz, S.; McConkey, D.J.; Evans, D.B.; Gallick, G.E. ALDH activity selectively defines an enhanced tumor-initiating cell population relative to CD133 expression in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, E.H.; Hynes, M.J.; Zhang, T.; Ginestier, C.; Dontu, G.; Appelman, H.; Fields, J.Z.; Wicha, M.S.; Boman, B.M. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 is a marker for normal and malignant human colonic stem cells (SC) and tracks SC overpopulation during colon tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 3382–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Qiu, Q.; Khanna, A.; Todd, N.W.; Deepak, J.; Xing, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Su, Y.; Stass, S.A.; et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 is a tumor stem cell-associated marker in lung cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Hoogen, C.; van der Horst, G.; Cheung, H.; Buijs, J.T.; Lippitt, J.M.; Guzman-Ramirez, N.; Hamdy, F.C.; Eaton, C.L.; Thalmann, G.N.; Cecchini, M.G.; et al. High aldehyde dehydrogenase activity identifies tumor-initiating and metastasis-initiating cells in human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 5163–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Qiu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Leng, Q.; Liu, Z.; Stass, S.A.; Jiang, F. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 A1-positive cell population is enriched in tumor-initiating cells and associated with progression of bladder cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2010, 19, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landen, C.N., Jr.; Goodman, B.; Katre, A.A.; Steg, A.D.; Nick, A.M.; Stone, R.L.; Miller, L.D.; Mejia, P.V.; Jennings, N.B.; Gershenson, D.M.; et al. Targeting aldehyde dehydrogenase cancer stem cells in ovarian cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 3186–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahadiani, N.; Ikeda, J.; Mamat, S.; Matsuzaki, S.; Ueda, Y.; Umehara, R.; Tian, T.; Wang, Y.; Enomoto, T.; Kimura, T.; et al. Expression of aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 (ALDH1) in endometrioid adenocarcinoma and its clinical implications. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.Y.; Zheng, P.S. High aldehyde dehydrogenase activity identifies cancer stem cells in human cervical cancer. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 2462–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, T.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, H.; Lin, Z. The expression of ALDH1 in cervical carcinoma. Med. Sci. Monit. 2011, 17, HY21–HY26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajani, J.A.; Wang, X.; Song, S.; Suzuki, A.; Taketa, T.; Sudo, K.; Wadhwa, R.; Hofstetter, W.L.; Komaki, R.; Maru, D.M.; et al. ALDH-1 expression levels predict response or resistance to preoperative chemoradiation in resectable esophageal cancer patients. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shervington, A.; Lu, C. Expression of multidrug resistance genes in normal and cancer stem cells. Cancer Investig. 2008, 26, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobili, S.; Landini, I.; Giglioni, B.; Mini, E. Pharmacological strategies for overcoming multidrug resistance. Curr. Drug Targets 2006, 7, 861–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornwell, M.M.; Smith, D.E. SP1 activates the MDR1 promoter through one of two distinct G-rich regions that modulate promoter activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 19505–19511. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Waby, J.S.; Chirakkal, H.; Yu, C.; Griffiths, G.J.; Benson, R.S.; Bingle, C.D.; Corfe, B.M. Sp1 acetylation is associated with loss of DNA binding at promoters associated with cell cycle arrest and cell death in a colon cell line. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Shao, L.; Spitz, D.R. Reactive oxygen species in normal and tumor stem cells. Adv. Cancer Res. 2014, 122, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Ai, M.; Wang, Y.; Shen, S.; Gu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Long, Y.; Yu, Q. Selective induction of tumor cell apoptosis by a novel P450-mediated reactive oxygen species (ROS) inducer methyl 3-(4-nitrophenyl) propiolate. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 8826–8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.J.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Z.L.; Li, X.B.; Hu, K.S.; Luo, H.Y.; Yang, J.; Huang, P.; Xu, R.H. beta-phenylethyl isothiocyanate reverses platinum resistance by a GSH-dependent mechanism in cancer cells with epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppaka, V.; Thompson, D.C.; Chen, Y.; Ellermann, M.; Nicolaou, K.C.; Juvonen, R.O.; Petersen, D.; Deitrich, R.A.; Hurley, T.D.; Vasiliou, V. Aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibitors: A comprehensive review of the pharmacology, mechanism of action, substrate specificity, and clinical application. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 520–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenwick, G.R.; Heaney, R.K.; Mullin, W.J. Glucosinolates and their breakdown products in food and food plants. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1983, 18, 123–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Wright, S.E.; Kim, S.H.; Srivastava, S.K. Phenethyl isothiocyanate: A comprehensive review of anti-cancer mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1846, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, M.; Kuhn, P.; Ribnicky, D.; Premkumar, V.; Reuhl, K.; Raskin, I. Dietary phenethylisothiocyanate attenuates bowel inflammation in mice. BMC Chem. Biol. 2010, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, M.; Ribnicky, D.; Kurmukov, A.G.; Raskin, I. In vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory activity of a seed preparation containing phenethylisothiocyanate. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 317, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chakravarty, S.; Dey, M. Phenethylisothiocyanate alters site- and promoter-specific histone tail modifications in cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Dey, M. Dietary Phenethyl Isothiocyanate Protects Mice from Colitis Associated Colon Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Upadhyaya, B.; Liu, Y.; Knudsen, D.; Dey, M. Phenethyl isothiocyanate upregulates death receptors 4 and 5 and inhibits proliferation in human cancer stem-like cells. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.H.; Uddin, M.H.; Jo, U.; Kim, B.; Song, J.; Suh, D.H.; Kim, H.S.; Song, Y.S. ROS Accumulation by PEITC Selectively Kills Ovarian Cancer Cells via UPR-Mediated Apoptosis. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trachootham, D.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Demizu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Pelicano, H.; Chiao, P.J.; Achanta, G.; Arlinghaus, R.B.; Liu, J.; et al. Selective killing of oncogenically transformed cells through a ROS-mediated mechanism by beta-phenylethyl isothiocyanate. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, W.; Yeo, E.; McMillan, N.; Yu, C. Silencing oncogene expression in cervical cancer stem-like cells inhibits their cell growth and self-renewal ability. Cancer Gene Ther. 2011, 18, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindros, K.O.; Badger, T.; Ronis, M.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; Koivusalo, M. Phenethyl isothiocyanate, a new dietary liver aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibitor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995, 275, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boesch, M.; Reimer, D.; Rumpold, H.; Zeimet, A.G.; Sopper, S.; Wolf, D. DyeCycle Violet used for side population detection is a substrate of P-glycoprotein. Cytometry A 2012, 81, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Shin, H.R.; Bray, F.; Forman, D.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2893–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huong le, D.; Shim, J.H.; Choi, K.H.; Shin, J.A.; Choi, E.S.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, S.J.; Cho, N.P.; Cho, S.D. Effect of beta-phenylethyl isothiocyanate from cruciferous vegetables on growth inhibition and apoptosis of cervical cancer cells through the induction of death receptors 4 and 5. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 8124–8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jutooru, I.; Guthrie, A.S.; Chadalapaka, G.; Pathi, S.; Kim, K.; Burghardt, R.; Jin, U.H.; Safe, S. Mechanism of action of phenethylisothiocyanate and other reactive oxygen species-inducing anticancer agents. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 2382–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.B.; Onder, T.T.; Jiang, G.; Tao, K.; Kuperwasser, C.; Weinberg, R.A.; Lander, E.S. Identification of selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput screening. Cell 2009, 138, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, J.H.; Kim, K.A.; Yoo, G.; Kim, S.Y.; Shin, J.M.; Kim, J.H.; Jung, S.H.; Kim, J.; Nho, C.W. Phenethyl isothiocyanate suppresses cancer stem cell properties in vitro and in a xenograft model. Phytomedicine 2017, 30, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, Y.C.; Chang, M.Y.; Lee, H.T.; Shen, C.C.; Harnod, T.; Liang, Y.J.; Wu, R.S.; Lai, K.C.; Hsu, F.T.; Chung, J.G. Phenethyl Isothiocyanate Inhibits In Vivo Growth of Xenograft Tumors of Human Glioblastoma Cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L.P.; Silva, P.; Duarte, M.; Rodrigues, L.; Duarte, C.M.; Albuquerque, C.; Serra, A.T. Targeting Colorectal Cancer Proliferation, Stemness and Metastatic Potential Using Brassicaceae Extracts Enriched in Isothiocyanates: A 3D Cell Model-Based Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.L. P-glycoprotein Inhibition for Optimal Drug Delivery. Drug Target Insights 2013, 7, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.; Song, X.; Liu, Y.F.; Wang, W.Y. PEITC reverse multi-drug resistance of human gastric cancer SGC7901/DDP cell line. Cell Biol. Int. 2014, 38, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Z.; Ma, F.; Wu, Y.; Bai, Y.; Gong, W.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, T.; Zhi, F.; et al. Inhibition of the transcription factor Sp1 suppresses colon cancer stem cell growth and induces apoptosis in vitro and in nude mouse xenografts. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 1782–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.G.; Liu, X.M.; Fang, Y.; Dai, W.; Chiao, F.B.; Puccio, G.M.; Feng, J.; Liu, D.; Chiao, J.W. De-repression of the p21 promoter in prostate cancer cells by an isothiocyanate via inhibition of HDACs and c-Myc. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 33, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebes, L.; Conaway, C.C.; Hochster, H.; Mendoza, S.; Hecht, S.S.; Crowell, J.; Chung, F.L. High-performance liquid chromatography-based determination of total isothiocyanate levels in human plasma: Application to studies with 2-phenethyl isothiocyanate. Anal. Biochem. 2001, 291, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyaya, B.P. Impact of Dietary Bioactive Components in Chronic Diseases Using Nutrigenomics, Nutriepigenomics, and Metagenomics Approaches. Ph.D. Thesis, South Dakota State University, Brookings, SD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
| Injection (1 × 106 Cells) | Tumors at Week 2 | Tumors at Week 4 |
|---|---|---|
| hCSCs | 1/8 | 4/8 |
| 10 µM PEITC-treated hCSCs | 0/8 | 1/8 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Upadhyaya, B.; Liu, Y.; Dey, M. Phenethyl Isothiocyanate Exposure Promotes Oxidative Stress and Suppresses Sp1 Transcription Factor in Cancer Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051027
Upadhyaya B, Liu Y, Dey M. Phenethyl Isothiocyanate Exposure Promotes Oxidative Stress and Suppresses Sp1 Transcription Factor in Cancer Stem Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(5):1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051027
Chicago/Turabian StyleUpadhyaya, Bijaya, Yi Liu, and Moul Dey. 2019. "Phenethyl Isothiocyanate Exposure Promotes Oxidative Stress and Suppresses Sp1 Transcription Factor in Cancer Stem Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 5: 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051027
APA StyleUpadhyaya, B., Liu, Y., & Dey, M. (2019). Phenethyl Isothiocyanate Exposure Promotes Oxidative Stress and Suppresses Sp1 Transcription Factor in Cancer Stem Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(5), 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051027