Long Non Coding RNA H19: A New Player in Hypoxia-Induced Multiple Myeloma Cell Dissemination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
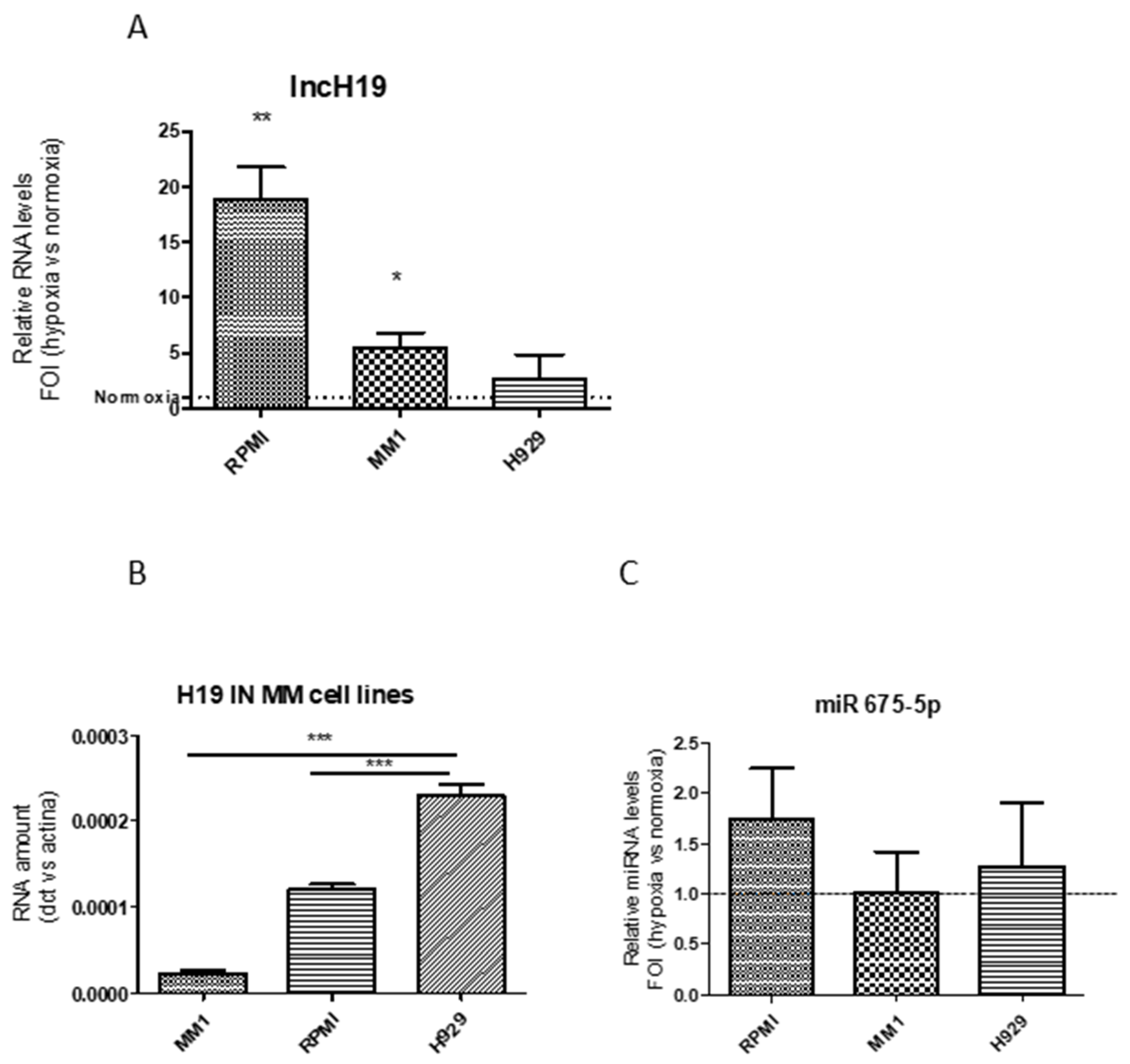
2.1. Hypoxic Stimulation Induced LncH19 Overexpression in MM Cell Models
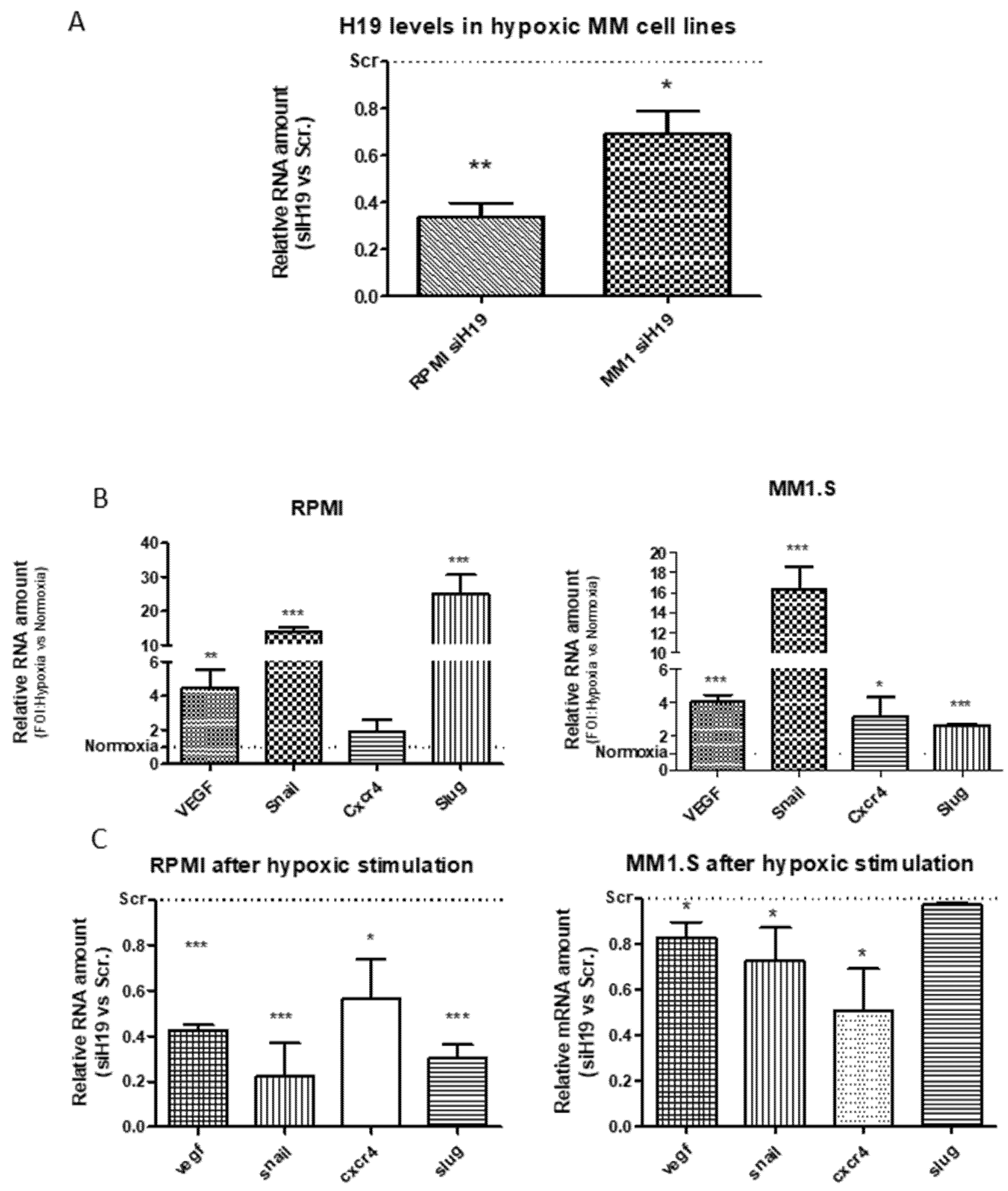
2.2. LncH19 Sustained Hypoxic Response in MM Cell Lines
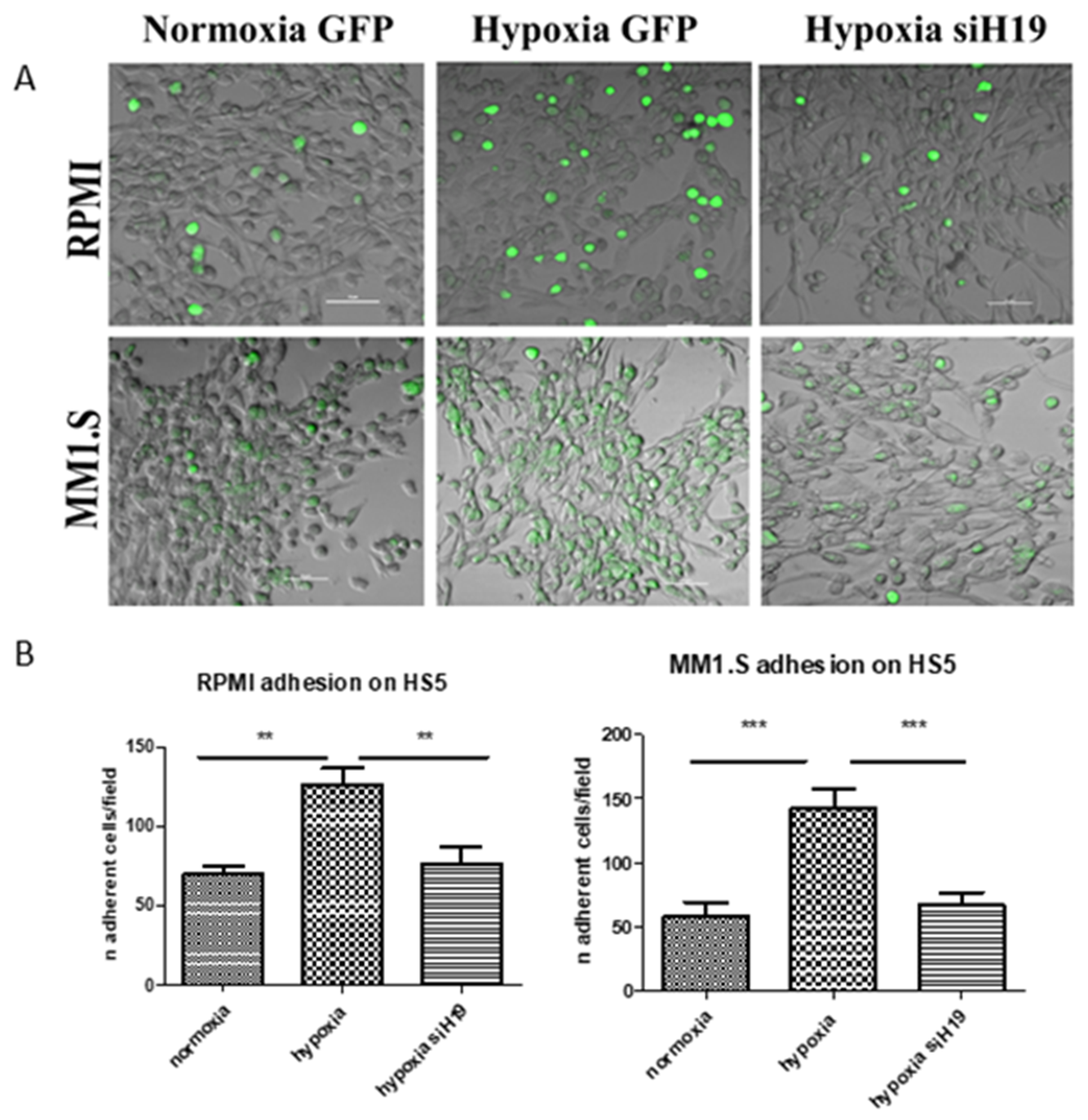
2.3. H19 Silencing Affected the Hypoxia-Induced Adhesion of MM Cells on the Stroma
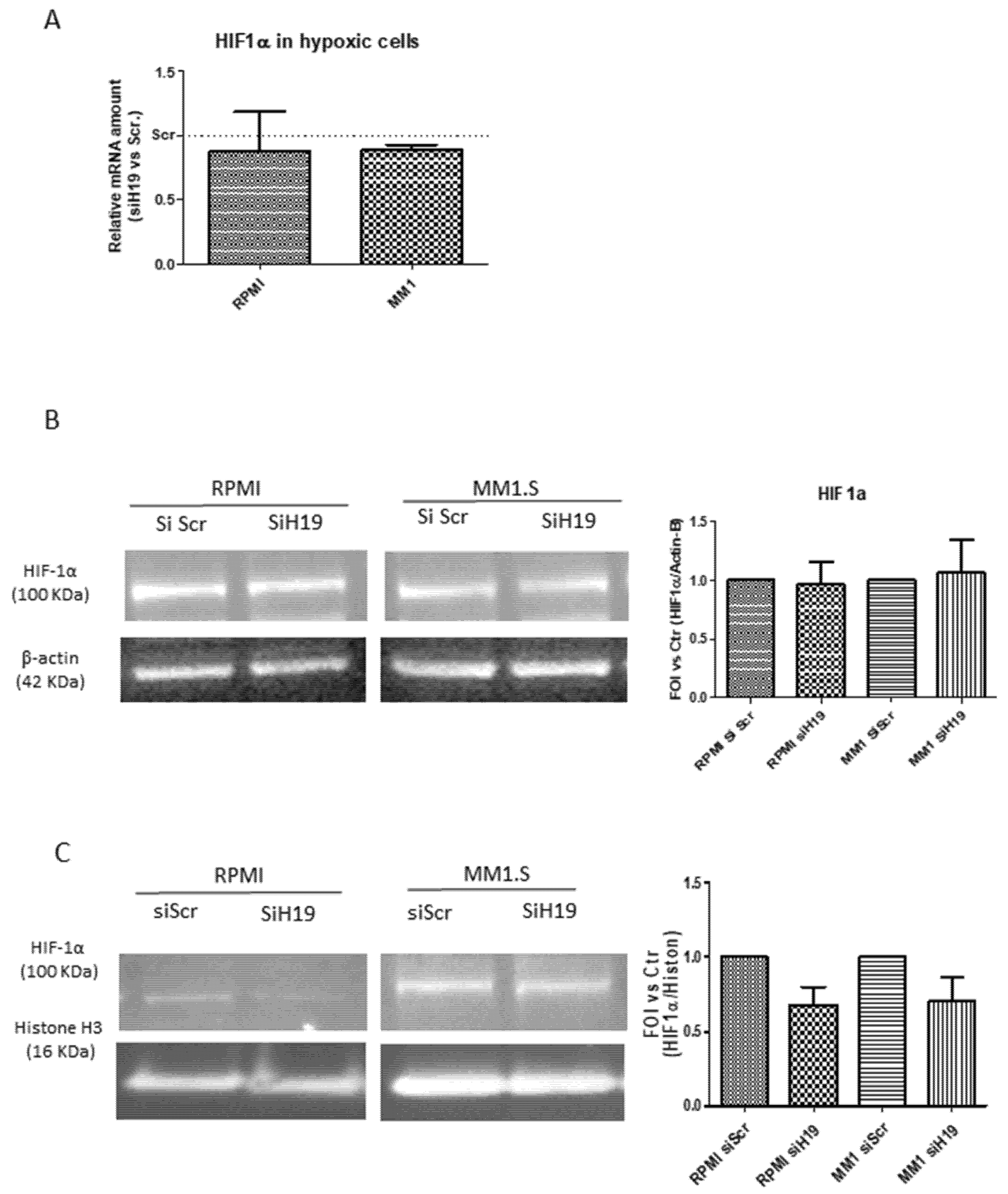
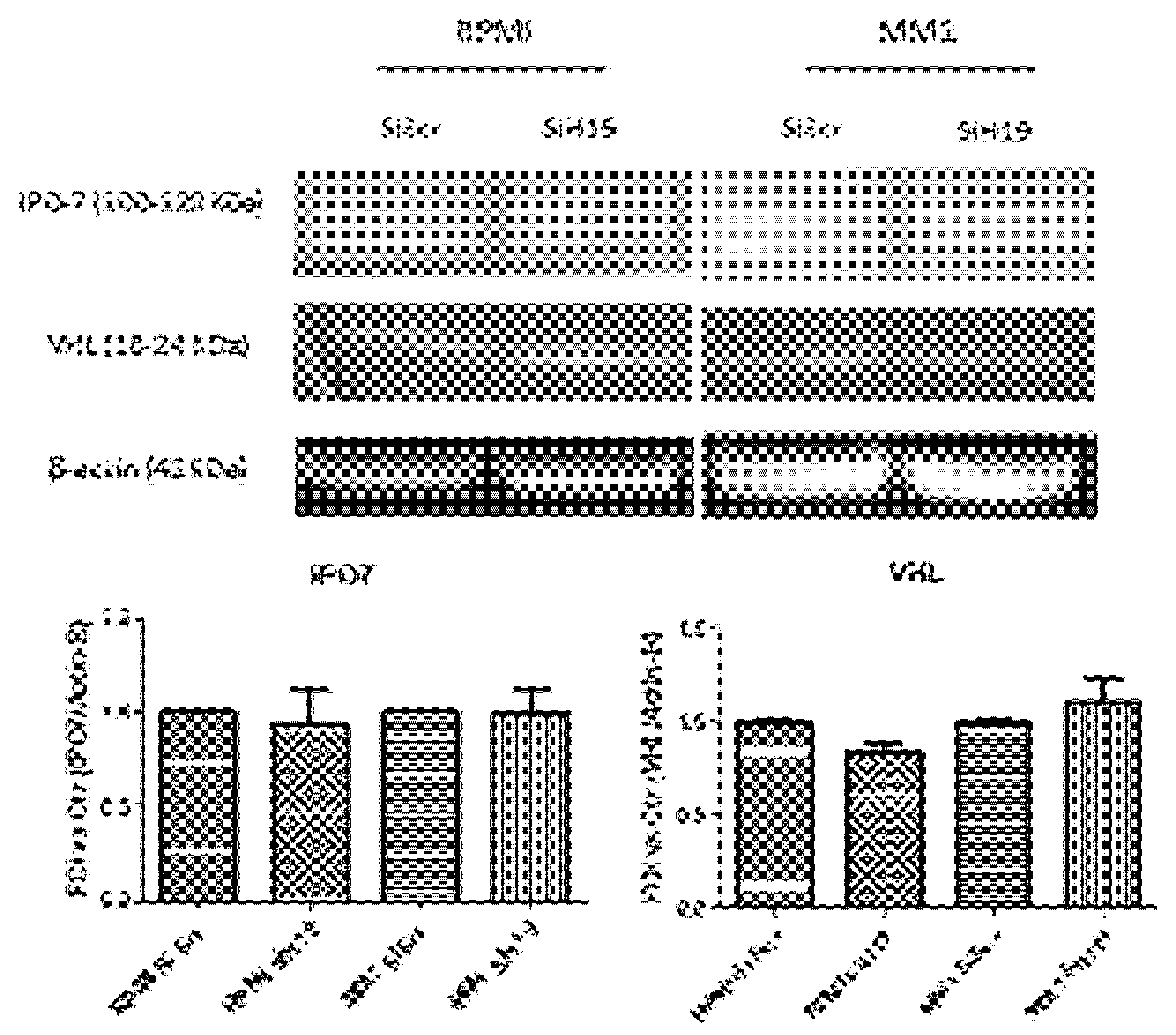
2.4. LncH19 Promoted HIF-1α Activation in Hypoxic MM Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
4.2. Cell Infection
4.3. RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR
4.4. Nuclear Protein Extraction and ELISA
4.5. Adhesion Assay
4.6. Total Protein Extract and Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Diamantopoulos, M.A.; Tsiakanikas, P.; Scorilas, A. Non-coding RNAs: The riddle of the transcriptome and their perspectives in cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Huang, Z.; Sheng, W.; Xu, M.D. Emerging roles of long non-coding RNAs in tumor metabolism. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raveh, E.; Matouk, I.J.; Gilon, M.; Hochberg, A. The H19 Long non-coding RNA in cancer initiation, progression and metastasis—A proposed unifying theory. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, H.; Matsuda, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Kamiya, S.; Ishiwata, T. Expression and role of long non-coding RNA H19 in carcinogenesis. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2018, 23, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, L.; Zhong, T.; Mueller, M.; Men, Y.; Zhang, N.; Xie, J.; Giang, K.; Chung, H.; Sun, X.; et al. H19 lncRNA alters DNA methylation genome wide by regulating S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallen, A.N.; Zhou, X.B.; Xu, J.; Qiao, C.; Ma, J.; Yan, L.; Lu, L.; Liu, C.; Yi, J.S.; Zhang, H.; et al. The imprinted H19 lncRNA antagonizes let-7 microRNAs. Mol. Cell 2013, 52, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keniry, A.; Oxley, D.; Monnier, P.; Kyba, M.; Dandolo, L.; Smits, G.; Reik, W. The H19 lincRNA is a developmental reservoir of miR-675 that suppresses growth and Igf1r. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Xiang, T.; Wu, Q.F.; Wang, W.X. Long Noncoding RNA H19-Derived miR-675 Enhances Proliferation and Invasion via RUNX1 in Gastric Cancer Cells. Oncol. Res. 2016, 23, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Tian, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Z.; Du, C.; Wang, F.; Xie, X.; Gao, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Kornmann, M.; et al. Long noncoding RNA H19 derived miR-675 regulates cell proliferation by down-regulating E2F-1 in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, Y.; She, Q.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Shen, X.; Zhang, W.; Dong, Y.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA H19/miR-675 Axis Promotes Gastric Cancer via FADD/Caspase 8/Caspase 3 Signaling Pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 2364–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Dico, A.; Costa, V.; Martelli, C.; Diceglie, C.; Rajata, F.; Rizzo, A.; Mancone, C.; Tripodi, M.; Ottobrini, L.; Alessandro, R.; et al. MiR675-5p Acts on HIF-1alpha to Sustain Hypoxic Responses: A New Therapeutic Strategy for Glioma. Theranostics 2016, 6, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, V.; Lo Dico, A.; Rizzo, A.; Rajata, F.; Tripodi, M.; Alessandro, R.; Conigliaro, A. MiR-675-5p supports hypoxia induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in colon cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 24292–24302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Hu, Q.; Nie, E.; Yu, T.; Wu, Y.; Zhi, T.; Jiang, K.; Shen, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Hypoxia induces H19 expression through direct and indirect Hif-1alpha activity, promoting oncogenic effects in glioblastoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muz, B.; de la Puente, P.; Azab, F.; Azab, A.K. The role of hypoxia in cancer progression, angiogenesis, metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Hypoxia (Auckl.) 2015, 3, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irigoyen, M.; Garcia-Ruiz, J.C.; Berra, E. The hypoxia signalling pathway in haematological malignancies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 36832–36844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muz, B.; de la Puente, P.; Azab, F.; Luderer, M.; Azab, A.K. The role of hypoxia and exploitation of the hypoxic environment in hematologic malignancies. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazandjian, D. Multiple myeloma epidemiology and survival: A unique malignancy. Semin. Oncol. 2016, 43, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muz, B.; de la Puente, P.; Azab, F.; Luderer, M.; Azab, A.K. Hypoxia promotes stem cell-like phenotype in multiple myeloma cells. Blood Cancer J. 2014, 4, e262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azab, A.K.; Hu, J.; Quang, P.; Azab, F.; Pitsillides, C.; Awwad, R.; Thompson, B.; Maiso, P.; Sun, J.D.; Hart, C.P.; et al. Hypoxia promotes dissemination of multiple myeloma through acquisition of epithelial to mesenchymal transition-like features. Blood 2012, 119, 5782–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roccaro, A.M.; Mishima, Y.; Sacco, A.; Moschetta, M.; Tai, Y.T.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Reagan, M.R.; Huynh, D.; Kawano, Y.; et al. CXCR4 Regulates Extra-Medullary Myeloma through Epithelial-Mesenchymal-Transition-like Transcriptional Activation. Cell Rep. 2015, 12, 622–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Pan, J.; Zhang, N.; Wei, W.; Yu, S.; Ai, L. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA H19 inhibits multiple myeloma cell growth via NF-kappaB pathway. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 18079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Chen, H.; Shen, X.; Wang, X.; Ju, S.; Lu, M.; Cong, H. Serum level of long noncoding RNA H19 as a diagnostic biomarker of multiple myeloma. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 480, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghobrial, I.M. Myeloma as a model for the process of metastasis: Implications for therapy. Blood 2012, 120, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chachami, G.; Paraskeva, E.; Mingot, J.M.; Braliou, G.G.; Görlich, D.; Simos, G. Transport of hypoxia-inducible factor HIF-1alpha into the nucleus involves importins 4 and 7. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 390, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskar, A.; Tiwary, B.N. Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha and multiple myeloma. Int. J. Adv. Res. (Indore) 2016, 4, 706–715. [Google Scholar]
- Karpova, D.; Bonig, H. Concise Review: CXCR4/CXCL12 Signaling in Immature Hematopoiesis—Lessons From Pharmacological and Genetic Models. Stem Cells 2015, 33, 2391–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsayed, Y.; Ngo, H.; Runnels, J.; Leleu, X.; Singha, U.K.; Pitsillides, C.M.; Spencer, J.A.; Kimlinger, T.; Ghobrial, J.M.; Jia, X.; et al. Mechanisms of regulation of CXCR4/SDF-1 (CXCL12)-dependent migration and homing in multiple myeloma. Blood 2007, 109, 2708–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliani, N.; Storti, P.; Bolzoni, M.; Palma, B.D.; Bonomini, S. Angiogenesis and multiple myeloma. Cancer Microenviron. 2011, 4, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Kortuem, K.M.; Stewart, A.K. Molecular mechanism of action of immune-modulatory drugs thalidomide, lenalidomide and pomalidomide in multiple myeloma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2013, 54, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccaro, A.M.; Hideshima, T.; Raje, N.; Kumar, S.; Ishitsuka, K.; Yasui, H.; Shiraishi, N.; Ribatti, D.; Nico, B.; Vacca, A.; et al. Bortezomib mediates antiangiogenesis in multiple myeloma via direct and indirect effects on endothelial cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Highsmith, K.N.; Chen, S.E.; Horowitz, S. Carfilzomib and pomalidomide: Recent advances in the treatment of multiple myeloma. Pharmacotherapy 2014, 34, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, L.; de Veirman, K.; Giannico, D.; Saltarella, I.; Desantis, V.; Frassanito, M.A.; Solimando, A.G.; Ribatti, D.; Prete, M.; Harstrick, A.; et al. Targeting angiogenesis in multiple myeloma by the VEGF and HGF blocking DARPin((R)) protein MP0250: A preclinical study. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 13366–13381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteleone, F.; Taverna, S.; Alessandro, R.; Fontana, S. SWATH-MS based quantitative proteomics analysis reveals that curcumin alters the metabolic enzyme profile of CML cells by affecting the activity of miR-22/IPO7/HIF-1alpha axis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Primer forward | Primer Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| LncH19 | GCACCTTGGACATCTGGAGT | TTCTTTCCAGCCCTAGCTCA |
| HIF-1α | TGATTGCATCTCCATCTCCTACC | GACTCAAAGCGACAGATAACACG |
| VEGF | CGAGGGCCTGGAGTGTGT | CGCATAATCTGCATGGTGATG |
| SNAIL | GCGAGCTGCAGGACTCTAAT | CCCGCAATGGTCCACAAAAC |
| SLUG | CATGCCTGTCATACCACAAC | GGTGTCAGATGGAGGAGGG |
| CXCR4 | TACACCGAGGAAATGGGCTCA | AGATGATGGAGTAGATGGTGG |
| B−A TIN | ATCAAGATCATTGCTCCTCCTGA | CTGCTTGCTGATCCACATCTG |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corrado, C.; Costa, V.; Giavaresi, G.; Calabrese, A.; Conigliaro, A.; Alessandro, R. Long Non Coding RNA H19: A New Player in Hypoxia-Induced Multiple Myeloma Cell Dissemination. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040801
Corrado C, Costa V, Giavaresi G, Calabrese A, Conigliaro A, Alessandro R. Long Non Coding RNA H19: A New Player in Hypoxia-Induced Multiple Myeloma Cell Dissemination. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(4):801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040801
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorrado, Chiara, Viviana Costa, Gianluca Giavaresi, Annalisa Calabrese, Alice Conigliaro, and Riccardo Alessandro. 2019. "Long Non Coding RNA H19: A New Player in Hypoxia-Induced Multiple Myeloma Cell Dissemination" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 4: 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040801
APA StyleCorrado, C., Costa, V., Giavaresi, G., Calabrese, A., Conigliaro, A., & Alessandro, R. (2019). Long Non Coding RNA H19: A New Player in Hypoxia-Induced Multiple Myeloma Cell Dissemination. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(4), 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040801








