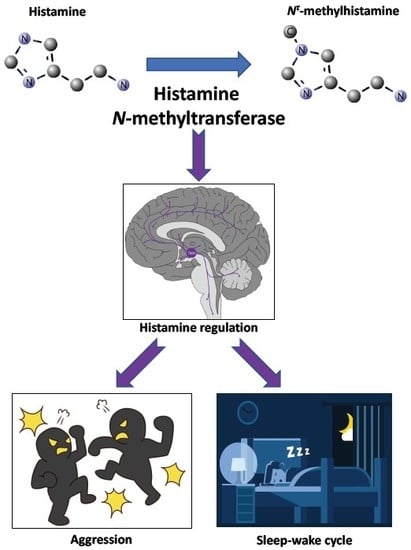
Histamine N-Methyltransferase in the Brain
Abstract
1. Introduction
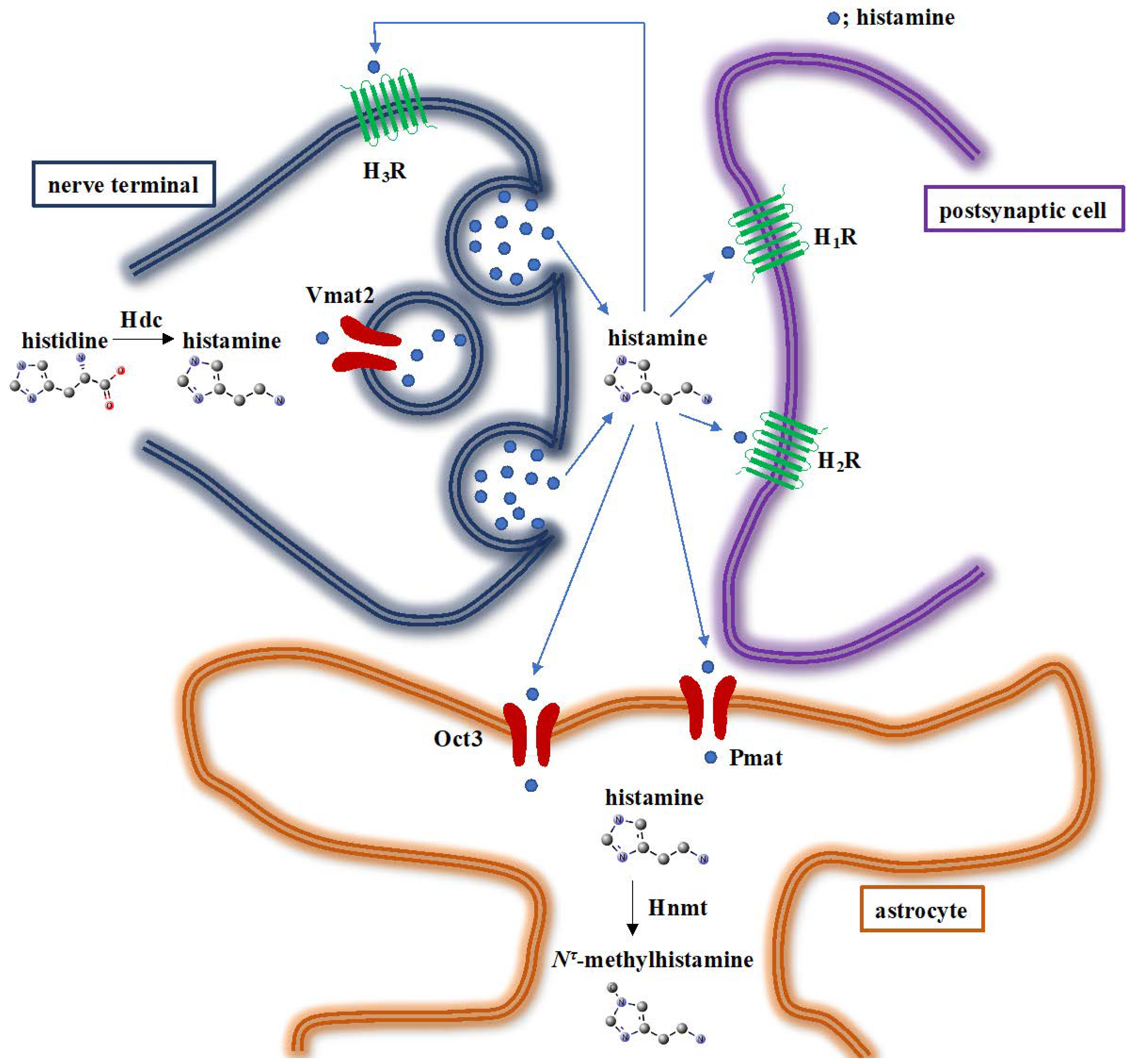
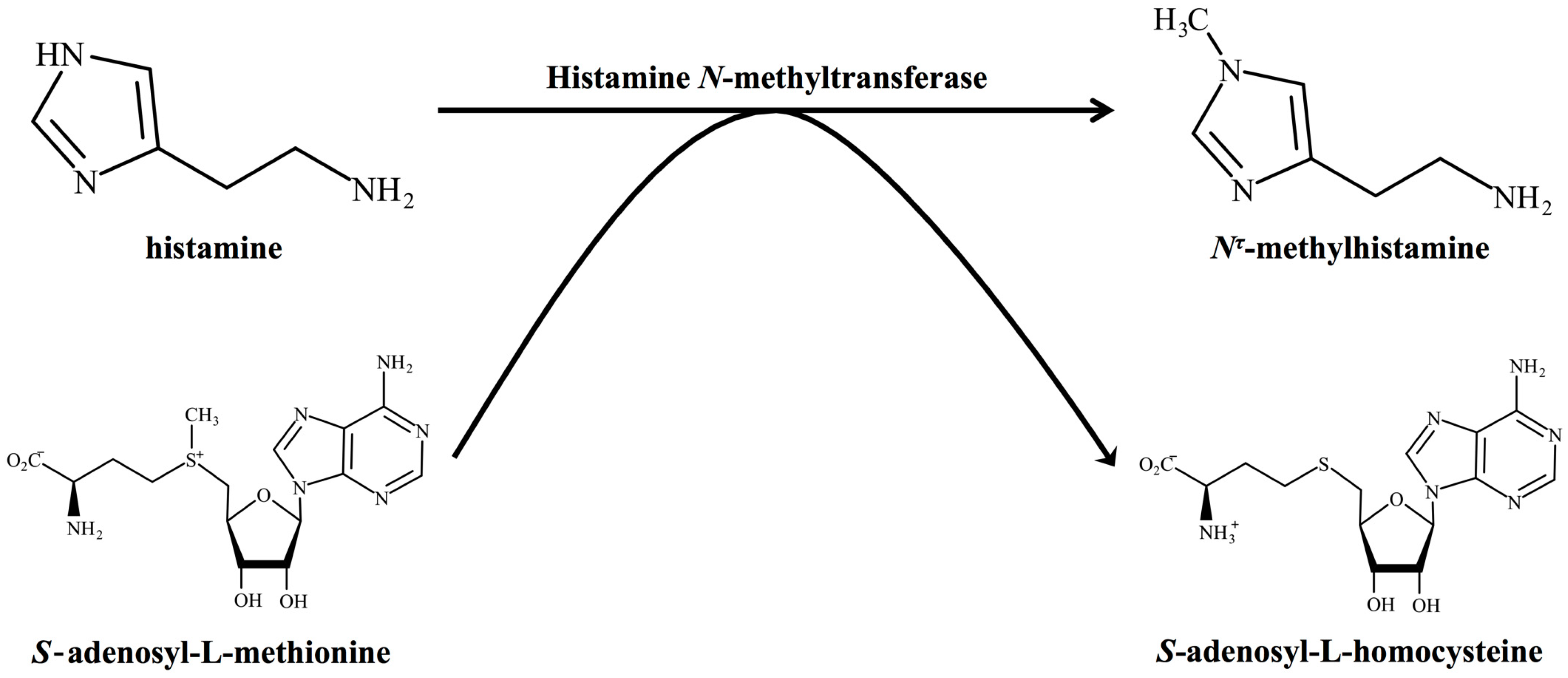
2. Histamine-Metabolising Enzymes
3. HNMT and Human Brain Diseases
4. Pharmacological Analysis Using HNMT Inhibitors
5. Phenotyping of Hnmt-deficient Mice
6. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dale, H.H.; Laidlaw, P.P. The physiological action of beta-iminazolylethylamine. J. Physiol. 1910, 41, 318–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, H.L.; Sergeeva, O.A.; Selbach, O. Histamine in the nervous system. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 1183–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Taguchi, Y.; Shiosaka, S.; Tanaka, J.; Kubota, H.; Terano, Y.; Tohyama, M.; Wada, H. Distribution of the histaminergic neuron system in the central nervous system of rats; a fluorescent immunohistochemical analysis with histidine decarboxylase as a marker. Brain Res. 1984, 295, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldan, L.C.; Williams, K.A.; Gallezot, J.D.; Pogorelov, V.; Rapanelli, M.; Crowley, M.; Anderson, G.M.; Loring, E.; Gorczyca, R.; Billingslea, E.; et al. Histidine decarboxylase deficiency causes tourette syndrome: Parallel findings in humans and mice. Neuron 2014, 81, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlomuzica, A.; Dere, D.; Binder, S.; De Souza Silva, M.A.; Huston, J.P.; Dere, E. Neuronal histamine and cognitive symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology 2016, 106, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazurkiewicz-Kwilecki, I.M.; Nsonwah, S. Changes in the regional brain histamine and histidine levels in postmortem brains of Alzheimer patients. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1989, 67, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panula, P.; Rinne, J.; Kuokkanen, K.; Eriksson, K.S.; Sallmen, T.; Kalimo, H.; Relja, M. Neuronal histamine deficit in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience 1998, 82, 993–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, S.; Sakurai, E.; Nevsimalova, S.; Yoshida, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Yanai, K.; Mignot, E. Decreased CSF histamine in narcolepsy with and without low CSF hypocretin-1 in comparison to healthy controls. Sleep 2009, 32, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanbayashi, T.; Kodama, T.; Kondo, H.; Satoh, S.; Inoue, Y.; Chiba, S.; Shimizu, T.; Nishino, S. CSF histamine contents in narcolepsy, idiopathic hypersomnia and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep 2009, 32, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassetti, C.L.; Baumann, C.R.; Dauvilliers, Y.; Croyal, M.; Robert, P.; Schwartz, J.C. Cerebrospinal fluid histamine levels are decreased in patients with narcolepsy and excessive daytime sleepiness of other origin. J. Sleep Res. 2010, 19, 620–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwabuchi, K.; Ito, C.; Tashiro, M.; Kato, M.; Kano, M.; Itoh, M.; Iwata, R.; Matsuoka, H.; Sato, M.; Yanai, K. Histamine H1 receptors in schizophrenic patients measured by positron emission tomography. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2005, 15, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kano, M.; Fukudo, S.; Tashiro, A.; Utsumi, A.; Tamura, D.; Itoh, M.; Iwata, R.; Tashiro, M.; Mochizuki, H.; Funaki, Y.; et al. Decreased histamine H1 receptor binding in the brain of depressed patients. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 20, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrang, J.M.; Garbarg, M.; Schwartz, J.C. Auto-inhibition of brain histamine release mediated by a novel class (H3) of histamine receptor. Nature 1983, 302, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passani, M.B.; Blandina, P. Histamine receptors in the CNS as targets for therapeutic intervention. Trends Pharmacol. Sci 2011, 32, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leurs, R.; Bakker, R.A.; Timmerman, H.; de Esch, I.J. The histamine H3 receptor: From gene cloning to H3 receptor drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, J.C. The histamine H3 receptor: From discovery to clinical trials with pitolisant. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Y.Y. Pitolisant: First Global Approval. Drugs 2016, 76, 1313–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huszti, Z. Histamine uptake into non-neuronal brain cells. Inflamm. Res. 2003, 52, S3–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Naganuma, F.; Iida, T.; Nakamura, T.; Harada, R.; Mohsen, A.S.; Kasajima, A.; Sasano, H.; Yanai, K. Molecular mechanism of histamine clearance by primary human astrocytes. Glia 2013, 61, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Yanai, K. Histamine Clearance Through Polyspecific Transporters in the Brain. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2017, 241, 173–187. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, K.; Zhou, M.; Wang, J. Identification and characterization of a novel monoamine transporter in the human brain. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 50042–50049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlin, A.; Xia, L.; Kong, W.; Hevner, R.; Wang, J. Expression and immunolocalization of the plasma membrane monoamine transporter in the brain. Neuroscience 2007, 146, 1193–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daws, L.C.; Koek, W.; Mitchell, N.C. Revisiting serotonin reuptake inhibitors and the therapeutic potential of “uptake-2” in psychiatric disorders. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2013, 4, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthaeus, F.; Schloss, P.; Lau, T. Differential Uptake Mechanisms of Fluorescent Substrates into Stem-Cell-Derived Serotonergic Neurons. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 1906–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamsen, D.; Ramaekers, V.; Ho, H.T.; Britschgi, C.; Rufenacht, V.; Meili, D.; Bobrowski, E.; Philippe, P.; Nava, C.; Van Maldergem, L.; et al. Autism spectrum disorder associated with low serotonin in CSF and mutations in the SLC29A4 plasma membrane monoamine transporter (PMAT) gene. Mol. Autism. 2014, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.; Wang, J. Impaired monoamine and organic cation uptake in choroid plexus in mice with targeted disruption of the plasma membrane monoamine transporter (Slc29a4) gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 3535–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Kekuda, R.; Huang, W.; Fei, Y.J.; Leibach, F.H.; Chen, J.; Conway, S.J.; Ganapathy, V. Identity of the organic cation transporter OCT3 as the extraneuronal monoamine transporter (uptake2) and evidence for the expression of the transporter in the brain. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 32776–32786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baganz, N.L.; Horton, R.E.; Calderon, A.S.; Owens, W.A.; Munn, J.L.; Watts, L.T.; Koldzic-Zivanovic, N.; Jeske, N.A.; Koek, W.; Toney, G.M.; et al. Organic cation transporter 3: Keeping the brake on extracellular serotonin in serotonin-transporter-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18976–18981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Aras, R.; Christian, W.V.; Rappold, P.M.; Hatwar, M.; Panza, J.; Jackson-Lewis, V.; Javitch, J.A.; Ballatori, N.; Przedborski, S.; et al. The organic cation transporter-3 is a pivotal modulator of neurodegeneration in the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 8043–8048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Hata, R.; Ogasawara, M.; Cao, F.; Kameda, K.; Yamauchi, K.; Schinkel, A.H.; Maeyama, K.; Sakanaka, M. Targeted disruption of organic cation transporter 3 (Oct3) ameliorates ischemic brain damage through modulating histamine and regulatory T cells. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012, 32, 1897–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganuma, F.; Nakamura, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Iida, T.; Miura, Y.; Karpati, A.; Matsuzawa, T.; Yanai, A.; Mogi, A.; Mochizuki, T.; et al. Histamine N-methyltransferase regulates aggression and the sleep-wake cycle. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naganuma, F.; Yoshikawa, T.; Nakamura, T.; Iida, T.; Harada, R.; Mohsen, A.S.; Miura, Y.; Yanai, K. Predominant role of plasma membrane monoamine transporters in monoamine transport in 1321N1, a human astrocytoma-derived cell line. J. Neurochem. 2014, 129, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishibori, M.; Tahara, A.; Sawada, K.; Sakiyama, J.; Nakaya, N.; Saeki, K. Neuronal and vascular localization of histamine N-methyltransferase in the bovine central nervous system. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, E.; Sakurai, E.; Oreland, L.; Nishiyama, S.; Kato, M.; Watanabe, T.; Yanai, K. Evidence for the presence of histamine uptake into the synaptosomes of rat brain. Pharmacology 2006, 78, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maintz, L.; Novak, N. Histamine and histamine intolerance. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, A.P.; Hilmer, K.M.; Collyer, C.A.; Shepard, E.M.; Elmore, B.O.; Brown, D.E.; Dooley, D.M.; Guss, J.M. Structure and inhibition of human diamine oxidase. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 9810–9822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieganski, T.; Kusche, J.; Lorenz, W.; Hesterberg, R.; Stahlknecht, C.D.; Feussner, K.D. Distribution and properties of human intestinal diamine oxidase and its relevance for the histamine catabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1983, 756, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, B.O.; Bollinger, J.A.; Dooley, D.M. Human kidney diamine oxidase: Heterologous expression, purification, and characterization. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 7, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, B.; Otterness, D.M.; Wood, T.C.; Honchel, R.; Wieben, E.D.; Weinshilboum, R.M. Human histamine N-methyltransferase pharmacogenetics: Cloning and expression of kidney cDNA. Mol. Pharmacol. 1994, 45, 461–468. [Google Scholar]
- Preuss, C.V.; Wood, T.C.; Szumlanski, C.L.; Raftogianis, R.B.; Otterness, D.M.; Girard, B.; Scott, M.C.; Weinshilboum, R.M. Human histamine N-methyltransferase pharmacogenetics: Common genetic polymorphisms that alter activity. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 53, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, J.A.; Schayer, R.W. Metabolism of C14 histamine in man. J. Appl. Physiol. 1956, 9, 481–483. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.D.; Tomchick, R.; Axelrod, J. The distribution and properties of a histamine-methylating enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1959, 234, 2948–2950. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schayer, R.W.; Reilly, M.A. Metabolism of 14C-histamine in brain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1973, 187, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pacifici, G.M.; Donatelli, P.; Giuliani, L. Histamine N-methyl transferase: Inhibition by drugs. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1992, 34, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlen, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallstrom, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, A.; Kampf, C.; Sjostedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lein, E.S.; Hawrylycz, M.J.; Ao, N.; Ayres, M.; Bensinger, A.; Bernard, A.; Boe, A.F.; Boguski, M.S.; Brockway, K.S.; Byrnes, E.J.; et al. Genome-wide atlas of gene expression in the adult mouse brain. Nature 2007, 445, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitanaka, N.; Kitanaka, J.; Oue, T.; Tada, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Takemura, M. Genomic structure of the rat and mouse histamine N-methyltransferase gene. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 88, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, K.; Sekizawa, K.; Suzuki, H.; Nakazawa, H.; Ohkawara, Y.; Katayose, D.; Ohtsu, H.; Tamura, G.; Shibahara, S.; Takemura, M.; et al. Structure and function of human histamine N-methyltransferase: Critical enzyme in histamine metabolism in airway. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 267, L342–L349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yan, L.; McGuire, C.; Kozak, C.A.; Wang, M.; Kim, U.J.; Siciliano, M.; Weinshilboum, R.M. Mouse histamine N-methyltransferase: cDNA cloning, expression, gene cloning and chromosomal localization. Inflamm. Res. 2001, 50, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, M.; Tanaka, T.; Taguchi, Y.; Imamura, I.; Mizuguchi, H.; Kuroda, M.; Fukui, H.; Yamatodani, A.; Wada, H. Histamine N-methyltransferase from rat kidney. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression in Escherichia coli cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 15687–15691. [Google Scholar]
- Kitanaka, J.; Kitanaka, N.; Tsujimura, T.; Kakihana, M.; Terada, N.; Takemura, M. Guinea pig histamine N-methyltransferase: cDNA cloning and mRNA distribution. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 85, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, J.R.; Sawada, K.; Nishibori, M.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, X. Two polymorphic forms of human histamine methyltransferase: Structural, thermal, and kinetic comparisons. Structure 2001, 9, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, K.; Parson, W.W.; Daggett, V. The histamine N-methyltransferase T105I polymorphism affects active site structure and dynamics. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agundez, J.A.; Luengo, A.; Herraez, O.; Martinez, C.; Alonso-Navarro, H.; Jimenez-Jimenez, F.J.; Garcia-Martin, E. Nonsynonymous polymorphisms of histamine-metabolising enzymes in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neuromolecular Med. 2008, 10, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeling, B.H.; Vilarino-Guell, C.; Soto-Ortolaza, A.I.; Ross, O.A.; Uitti, R.J.; Rajput, A.; Wszolek, Z.K.; Farrer, M.J. Histamine N-methyltransferase Thr105Ile is not associated with Parkinson’s disease or essential tremor. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2010, 16, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palada, V.; Terzic, J.; Mazzulli, J.; Bwala, G.; Hagenah, J.; Peterlin, B.; Hung, A.Y.; Klein, C.; Krainc, D. Histamine N-methyltransferase Thr105Ile polymorphism is associated with Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 836 e1–836 e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Han, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y. Association of histamine N-methyltransferase Thr105Ile polymorphism with Parkinson’s disease and schizophrenia in Han Chinese: A case-control study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Jimenez, F.J.; Alonso-Navarro, H.; Garcia-Martin, E.; Agundez, J.A. Thr105Ile (rs11558538) polymorphism in the histamine N-methyltransferase (HNMT) gene and risk for Parkinson disease: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016, 95, e4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, J.; Sonuga-Barke, E.; McCann, D.; Grimshaw, K.; Parker, K.M.; Rose-Zerilli, M.J.; Holloway, J.W.; Warner, J.O. The role of histamine degradation gene polymorphisms in moderating the effects of food additives on children’s ADHD symptoms. Am. J. Psychiatry. 2010, 167, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza-Velazquez, R.; Lopez-Marquez, F.; Espinosa-Padilla, S.; Rivera-Guillen, M.; Avila-Hernandez, J.; Rosales-Gonzalez, M. Association of diamine oxidase and histamine N-methyltransferase polymorphisms with presence of migraine in a group of Mexican mothers of children with allergies. Neurologia 2017, 32, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasovic-Susnjara, I.; Palada, V.; Marinovic-Terzic, I.; Mimica, N.; Marin, J.; Muck-Seler, D.; Mustapic, M.; Presecki, P.; Pivac, N.; Folnegovic-Smalc, V.; et al. No association between histamine N-methyltransferase functional polymorphism Thr105Ile and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 489, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, B.; Ou, R.; Wei, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhao, B.; Wu, Y.; Song, W.; Shang, H.F. Determining the Effect of the HNMT, STK39, and NMD3 Polymorphisms on the Incidence of Parkinson’s Disease, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, and Multiple System Atrophy in Chinese Populations. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 64, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Martin, E.; Martinez, C.; Benito-Leon, J.; Calleja, P.; Diaz-Sanchez, M.; Pisa, D.; Alonso-Navarro, H.; Ayuso-Peralta, L.; Torrecilla, D.; Agundez, J.A.; et al. Histamine-N-methyl transferase polymorphism and risk for multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Jimenez, F.J.; Garcia-Martin, E.; Alonso-Navarro, H.; Martinez, C.; Zurdo, M.; Turpin-Fenoll, L.; Millan-Pascual, J.; Adeva-Bartolome, T.; Cubo, E.; Navacerrada, F.; et al. Thr105Ile (rs11558538) polymorphism in the histamine-1-methyl-transferase (HNMT) gene and risk for restless legs syndrome. J. Neural. Transm. (Vienna) 2017, 124, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuter, M.; Jeste, N.; Klein, T.; Hennig, J.; Goldman, D.; Enoch, M.A.; Oroszi, G. Association of THR105Ile, a functional polymorphism of histamine N-methyltransferase (HNMT), with alcoholism in German Caucasians. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2007, 87, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oroszi, G.; Enoch, M.A.; Chun, J.; Virkkunen, M.; Goldman, D. Thr105Ile, a functional polymorphism of histamine N-methyltransferase, is associated with alcoholism in two independent populations. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2005, 29, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Kang, Y.M.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, B.Y.; Ye, Y.M.; Hur, G.Y.; Park, H.S. Histamine N-methyltransferase 939A>G polymorphism affects mRNA stability in patients with acetylsalicylic acid-intolerant chronic urticaria. Allergy 2009, 64, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellermayer, B.; Polgar, N.; Pal, J.; Banati, M.; Maasz, A.; Kisfali, P.; Hosszu, Z.; Juhasz, A.; Jensen, H.B.; Tordai, A.; et al. Association of myasthenia gravis with polymorphisms in the gene of histamine N-methyltransferase. Hum. Immunol. 2013, 74, 1701–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, A.; Tongsook, C.; Najafipour, R.; Musante, L.; Vasli, N.; Garshasbi, M.; Hu, H.; Mittal, K.; McNaughton, A.J.; Sritharan, K.; et al. Mutations in the histamine N-methyltransferase gene, HNMT, are associated with nonsyndromic autosomal recessive intellectual disability. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 5697–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongsook, C.; Niederhauser, J.; Kronegger, E.; Straganz, G.; Macheroux, P. Leucine 208 in human histamine N-methyltransferase emerges as a hotspot for protein stability rationalizing the role of the L208P variant in intellectual disability. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wamelen, D.J.; Shan, L.; Aziz, N.A.; Anink, J.J.; Bao, A.M.; Roos, R.A.; Swaab, D.F. Functional increase of brain histaminergic signaling in Huntington’s disease. Brain Pathol. 2011, 21, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, L.; Bossers, K.; Luchetti, S.; Balesar, R.; Lethbridge, N.; Chazot, P.L.; Bao, A.M.; Swaab, D.F. Alterations in the histaminergic system in the substantia nigra and striatum of Parkinson’s patients: A postmortem study. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 1488 e1–1488 e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Krapfenbauer, K.; Cheon, M.S.; Fountoulakis, M.; Cairns, N.J.; Lubec, G. Human brain cytosolic histamine-N-methyltransferase is decreased in Down syndrome and increased in Pick’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 321, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Bossers, K.; Unmehopa, U.; Bao, A.M.; Swaab, D.F. Alterations in the histaminergic system in Alzheimer’s disease: A postmortem study. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 2585–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Qi, X.R.; Balesar, R.; Swaab, D.F.; Bao, A.M. Unaltered histaminergic system in depression: A postmortem study. J. Affect. Disord. 2013, 146, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duch, D.S.; Bowers, S.W.; Nichol, C.A. Elevation of brain histamine levels by diaminopyrimidine inhibitors of histamine N-methyl transferase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1978, 27, 1507–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duch, D.S.; Edelstein, M.P.; Nichol, C.A. Inhibition of histamine-metabolizing enzymes and elevation of histamine levels in tissues by lipid-soluble anticancer folate antagonists. Mol. Pharmacol. 1980, 18, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Hough, L.B.; Khandelwal, J.K.; Green, J.P. Inhibition of brain histamine metabolism by metoprine. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1986, 35, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmberg-Aiello, P.; Lamberti, C.; Ghelardini, C.; Giotti, A.; Bartolini, A. Role of histamine in rodent antinociception. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 111, 1269–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecklin, A.; Tuomisto, L. Inhibition of histamine catabolism suppresses fat intake but not the intake of carbohydrates and protein. Inflamm. Res. 2002, 51, S53–S54. [Google Scholar]
- Nishibori, M.; Itoh, Y.; Oishi, R.; Saeki, K. Mechanism of the central hyperglycemic action of histamine in mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1987, 241, 582–586. [Google Scholar]
- Malmberg-Aiello, P.; Ipponi, A.; Bartolini, A.; Schunack, W. Antiamnesic effect of metoprine and of selective histamine H(1) receptor agonists in a modified mouse passive avoidance test. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 288, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yawata, I.; Tanaka, K.; Nakagawa, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Murashima, Y.L.; Nakano, K. Role of histaminergic neurons in development of epileptic seizures in EL mice. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2004, 132, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamei, C. Involvement of central histamine in amygdaloid kindled seizures in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2001, 124, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, H.; Onodera, K.; Maeyama, K.; Yanai, K.; Iinuma, K.; Tuomisto, L.; Watanabe, T. Histamine levels and clonic convulsions of electrically-induced seizure in mice: The effects of alpha-fluoromethylhistidine and metoprine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1992, 346, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitanaka, J.; Kitanaka, N.; Hall, F.S.; Uhl, G.R.; Takemura, M. Brain Histamine N-Methyltransferase As a Possible Target of Treatment for Methamphetamine Overdose. Drug Target Insights 2016, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallito, J.C.; Nichol, C.A.; Brenckman, W.D., Jr.; Deangelis, R.L.; Stickney, D.R.; Simmons, W.S.; Sigel, C.W. Lipid-soluble inhibitors of dihydrofolate reductase. I. Kinetics, tissue distribution, and extent of metabolism of pyrimethamine, metoprine, and etoprine in the rat, dog, and man. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1978, 6, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hamrell, M.R. Inhibition of dihydrofolate reductase and cell growth by antifolates in a methotrexate-resistant cell line. Oncology 1984, 41, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaven, M.A.; Shaff, R.E. New inhibitors of histamine-N-methyltransferase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1979, 28, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.S.; Sakai, K.; Jouvet, M. Evidence for histaminergic arousal mechanisms in the hypothalamus of cat. Neuropharmacology 1988, 27, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmberg-Aiello, P.; Lamberti, C.; Ipponi, A.; Hanninen, J.; Ghelardini, C.; Bartolini, A. Effects of two histamine-N-methyltransferase inhibitors, SKF 91488 and BW 301 U, in rodent antinociception. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1997, 355, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorenza, N.G.; Rosa, J.; Izquierdo, I.; Myskiw, J.C. Modulation of the extinction of two different fear-motivated tasks in three distinct brain areas. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 232, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, J.R.; Sawada, K.; Nishibori, M.; Cheng, X. Structural basis for inhibition of histamine N-methyltransferase by diverse drugs. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 353, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachibana, T.; Taniguchi, S.; Imamura, S.; Fujiwara, M.; Hayashi, H. Effects of drugs on the activity of histamine-N-methyltransferase from guinea pig skin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1988, 37, 2872–2876. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cumming, P.; Reiner, P.B.; Vincent, S.R. Inhibition of rat brain histamine-N-methyltransferase by 9-amino-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridine (THA). Biochem. Pharmacol. 1990, 40, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, H.; Mizuta, H.; Norimoto, H.; Masuda, F.; Miura, Y.; Kubo, A.; Kojima, H.; Ashizuka, A.; Matsukawa, N.; Baraki, Z.; et al. Central Histamine Boosts Perirhinal Cortex Activity and Restores Forgotten Object Memories. Biol. Psychiatry 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasahara, I.; Fujimura, N.; Nozawa, Y.; Furuhata, Y.; Sato, H. The effect of histidine on mental fatigue and cognitive performance in subjects with high fatigue and sleep disruption scores. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 147, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmlof, K.; Zaragoza, F.; Golozoubova, V.; Refsgaard, H.H.; Cremers, T.; Raun, K.; Wulff, B.S.; Johansen, P.B.; Westerink, B.; Rimvall, K. Influence of a selective histamine H3 receptor antagonist on hypothalamic neural activity, food intake and body weight. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2005, 29, 1402–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisset, S.; Traiffort, E.; Arrang, J.M.; Schwartz, J.C. Changes in histamine H3 receptor responsiveness in mouse brain. J. Neurochem. 2000, 74, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Martin, E.; Garcia-Menaya, J.; Sanchez, B.; Martinez, C.; Rosendo, R.; Agundez, J.A. Polymorphisms of histamine-metabolizing enzymes and clinical manifestations of asthma and allergic rhinitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2007, 37, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Mann, D.; Singh, T.P.; Ghosh, B. Lack of association of histamine-N-methyltransferase (HNMT) polymorphisms with asthma in the Indian population. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 50, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deindl, P.; Peri-Jerkan, S.; Deichmann, K.; Niggemann, B.; Lau, S.; Sommerfeld, C.; Sengler, C.; Muller, S.; Wahn, U.; Nickel, R.; et al. No association of histamine-N-methyltransferase polymorphism with asthma or bronchial hyperresponsiveness in two German pediatric populations. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2005, 16, 40–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepankiewicz, A.; Breborowicz, A.; Sobkowiak, P.; Popiel, A. Polymorphisms of two histamine-metabolizing enzymes genes and childhood allergic asthma: A case control study. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2010, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Human [39,48] | Mouse [49] | Rat [50] | Guinea pig [51] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cloning year | 1994 | 2001 | 1992 | 2001 | |
| Chromosome | 2q22.1 | 2A3 | 3p13 | N.D. | |
| Amino acid | 292 aa | 295 aa | 292 aa | 295 aa | |
| Homology * | 83% | 83% | 81% | ||
| Km (µM) | Histamine | 13–20 | 5.3 | 7.1 | N.D. |
| SAM | 2.0–6.2 | 5.8 | 6.3 | N.D. | |
| Authors | Year | SNP | Enzymatic Activity | Disease | Association | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jimenez-Jimenez et al. [58] | 2016 | C314T (Thr105Ile) (rs11558538) T allele carrier | Decreased | Parkinson’s disease (PD) | Diagnostic OR 0.61 | Caucasians and Asians |
| Yang et al. [57] | 2015 | C314T (Thr105Ile) (rs11558538) CT hetero allele | Decreased | PD | OR 0.53 | Han Chinese |
| Palada et al. [56] | 2012 | C314T (Thr105Ile) (rs11558538) | Decreased | PD | Thr105 frequency was associated with PD | Caucasians |
| Yang et al. [57] | 2015 | C314T (Thr105Ile) (rs11558538) CT hetero allele | Decreased | Schizophrenia | OR 0.499 | Han Chinese |
| Stevenson et al. [59] | 2010 | C314T (Thr105Ile) (rs11558538) T allele | Decreased | ADHD | Decreased hyperactivity | Food additives stimulation |
| Stevenson et al. [59] | 2010 | A939G (3′-UTR) (rs1050891) G allele | Increased (mRNA stability) | ADHD | Decreased hyperactivity | Food additives stimulation |
| Meza-Velazquez et al. [60] | 2017 | C314T (Thr105Ile) (rs11558538) CT hetero allele | Decreased | Migraine | OR 37.10 | Migraine-related disability Grade IV |
| Kellermayer et al. [68] | 2017 | A939G (3′-UTR) (rs1050891) G allele | Increased (mRNA stability) | Myasthenia gravis (MG) | OR 0.52 | Anti-Titin positive MG |
| Heidari et al. [69] | 2015 | G179A (Gly60Asp) (rs758252808) | Decreased | Intellectual disability (AR) | Low IQ | Turkish |
| Heidari et al. [69] | 2015 | T632C (Leu208Pro) (rs745756308) | Decreased | Intellectual disability (AR) | Low IQ | Kurdish |
| Marasovic-Susnjara et al. [61] | 2011 | C314T (Thr105Ile) (rs11558538) | Decreased | Alzheimer’s disease | No association | |
| Chen et al. [62] | 2018 | C314 (Thr105Ile) (rs11558538) | Decreased | Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis | No association | |
| Reuter et al. [65] | 2007 | C314T (Thr105Ile) (rs11558538) | Decreased | Alcoholism | No association | German Caucasians |
| Oroszi et al. [66] | 2006 | C314T (Thr105Ile) (rs11558538) | Decreased | Alcoholism | Thr105 frequency was associated with alcoholism. | Finnish Caucasians, Plains Indians |
| Gracia-Martin et al. [63] | 2010 | C314T (Thr105Ile) (rs11558538) | Decreased | Multiple sclerosis | No association | |
| Jimenez-Jimenez et al. [64] | 2016 | C314T (Thr105Ile) (rs11558538) | Decreased | Restless legs syndrome (RLS) | No association (TT allele might be a risk factor for early onset of RLS) |
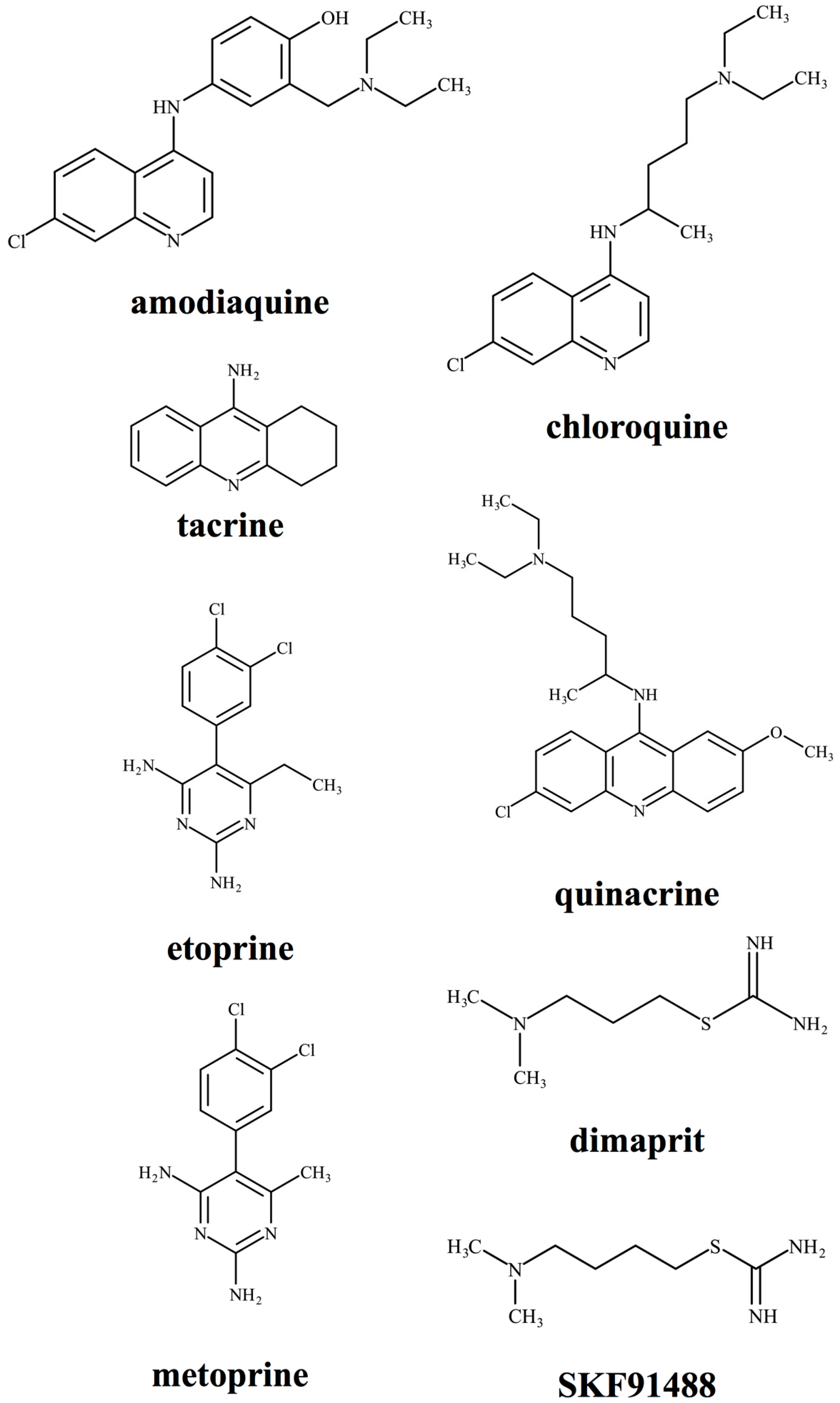
| Inhibitors | M.W. | IC50 or Ki | Inhibition Pattern | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amodiaquine | 355.86 | Ki 18.6 nM (recombinant hHNMT) [93] IC50 400 nM (recombinant hHNMT) [39] | Mixed | An antimalarial drug |
| Chloroquine | 319.88 | IC50 600 nM (guinea pig skin) [94] IC50 12.6, 22.0 19.0 and 21.7 µM (human liver, renal cortex, brain and colon) [44] | Competitive to histamine | An antimalarial drug |
| Dimaprit | 161.27 | Ki 8 µM (rat kidney) [89] Ki 7–9 µM (guinea pig brain) [89] | Noncompetitive to histamine | H2R agonist |
| Etoprine | 283.16 | Ki 760 nM (rat brain) [76] | N.D. | Dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor |
| Metoprine | 269.13 | Ki 100 nM (rat brain) [76] Ki 91 nM (recombinant hHNMT) [93] | Competitive to histamine | Dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor |
| Quinacrine | 399.96 | IC50 160 nM (guinea pig skin) [94] Ki 450 nM (recombinant hHNMT) [52] | Competitive to histamine | An antimalarial drug |
| SKF91488 | 175.29 | Ki 0.9–1.6 µM (rat kidney) [89] Ki 1.85 µM (recombinant rat HNMT) [50] Ki 3 µM (guinea pig brain) [89] | Noncompetitive to histamine | Poor BBB permeability |
| Tacrine | 198.27 | Ki 38.2 nM (recombinant hHNMT) [93] Ki 35 nM (rat kidney) [95] | Competitive to histamine | Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoshikawa, T.; Nakamura, T.; Yanai, K. Histamine N-Methyltransferase in the Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030737
Yoshikawa T, Nakamura T, Yanai K. Histamine N-Methyltransferase in the Brain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(3):737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030737
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoshikawa, Takeo, Tadaho Nakamura, and Kazuhiko Yanai. 2019. "Histamine N-Methyltransferase in the Brain" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 3: 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030737
APA StyleYoshikawa, T., Nakamura, T., & Yanai, K. (2019). Histamine N-Methyltransferase in the Brain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(3), 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030737