MicroRNA-Based Therapeutic Perspectives in Myotonic Dystrophy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Micro-RNAs and Myotonic Dystrophy
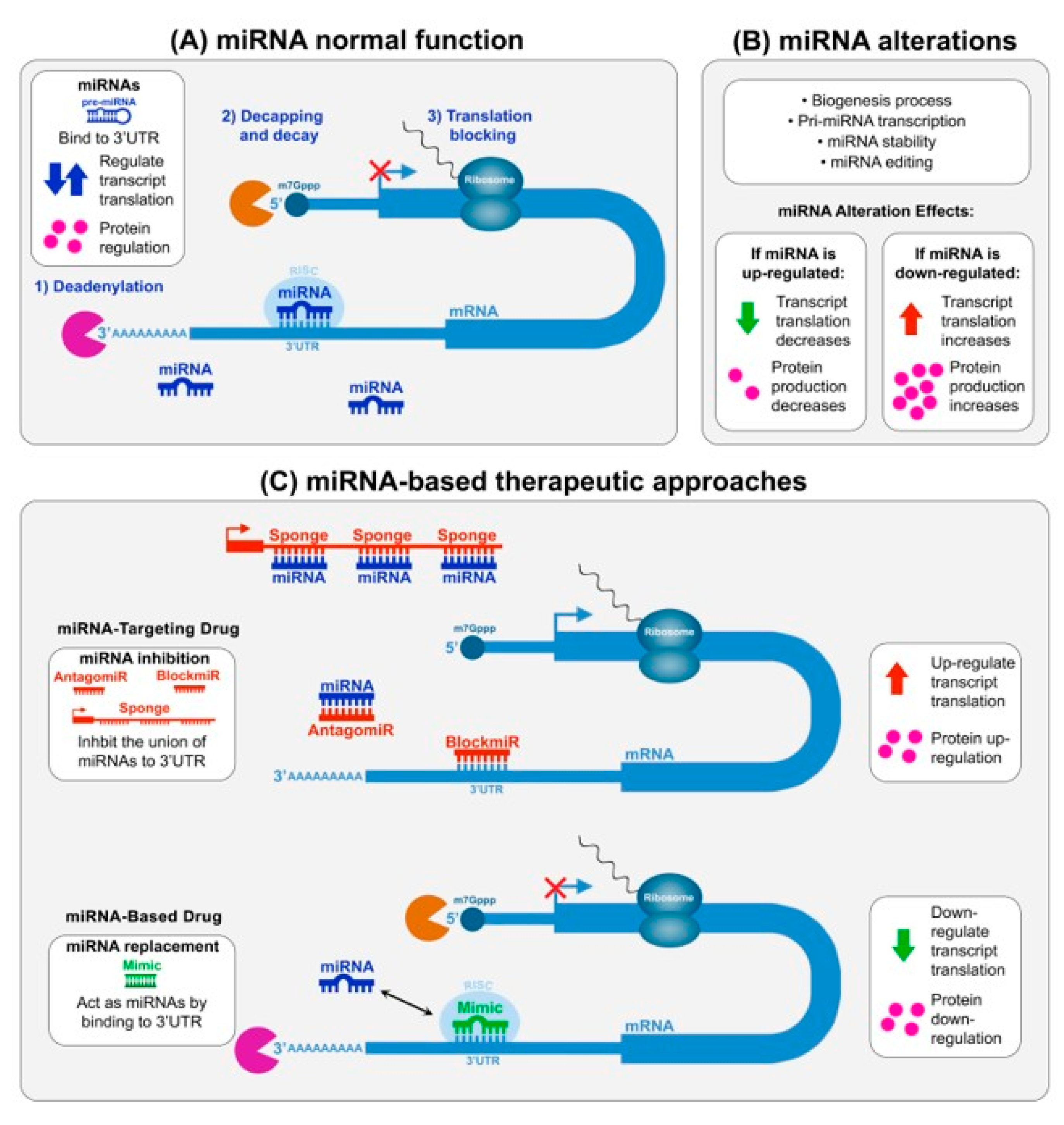
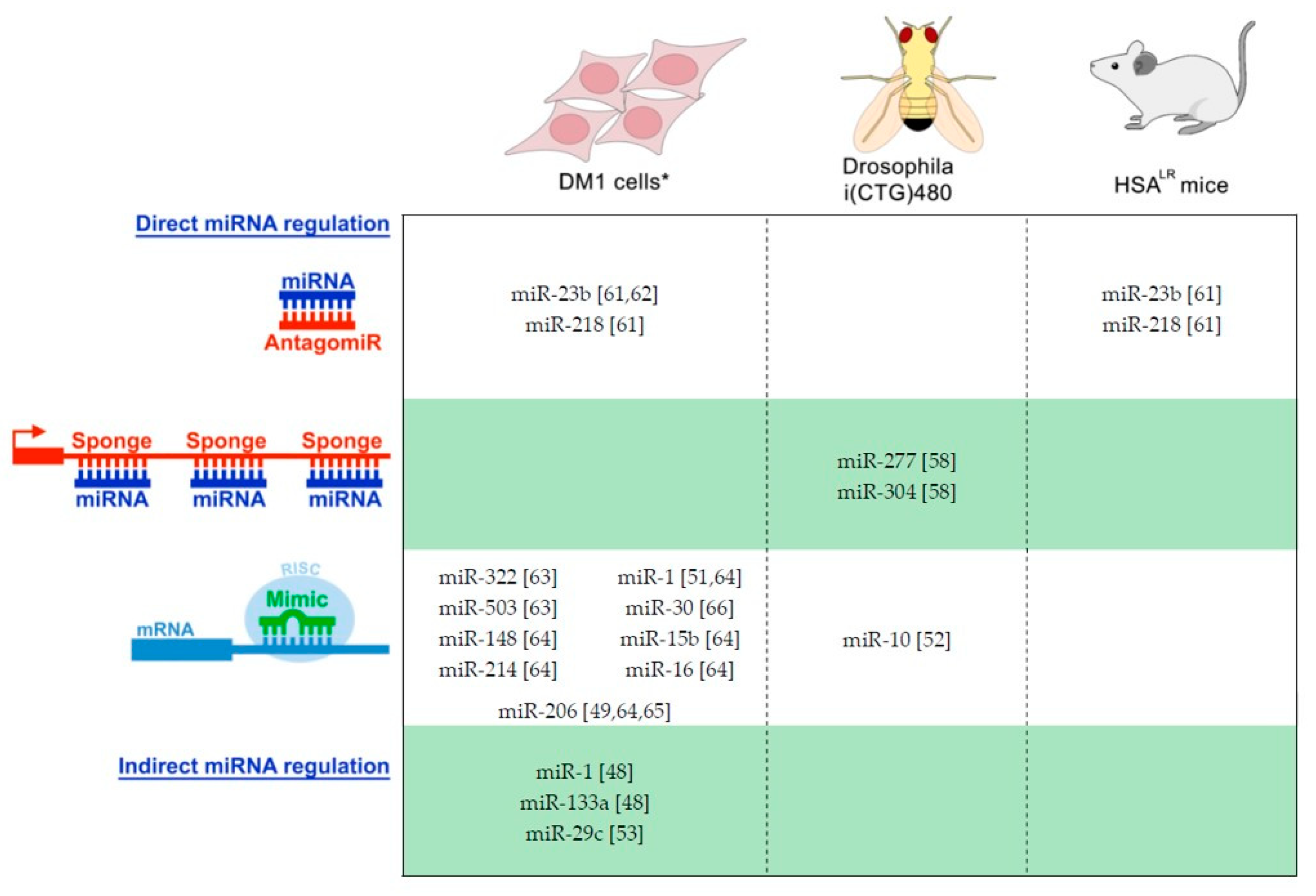
2.1. Therapeutic Intervention of miRNAs in DM
2.2. Picture of miRNAs Dysregulation in DM: Potential as a Disease Biomarker
3. Future Prospects for miRNA-Based Therapeutics in DM
3.1. MiRNA-Based and miRNA-Targeting Drug Development Challenges
3.2. DM Drug Development Opportunities for miRNA-Based and miRNA-Targeting Products
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAV | Adeno-associated virus |
| ASO | Antisense oligonucleotide |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CELF1 | CUGBP Elav-Like Family Member 1 |
| CRISPR | Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat |
| DM | Myotonic dystrophy |
| DM1 | Myotonic dystrophy type1 |
| DM2 | Myotonic dystrophy type 2 |
| DMD | Duchenne muscular dystrophy |
| FXS | Fragile X syndrome |
| GalNac | N-acetyl-D-galactosamine |
| HD | Huntington disease |
| KO | Knockout |
| LNA | Locked nucleic acid |
| MBNL | Muscle blind-like proteins |
| miRNA | MicroRNA |
| 2′-MOE | 2′-O-methoxyethyl |
| mRNA | Messenger RNA |
| nPTB | Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein |
| PLGA | poly(lactide-co-glycolide) |
| PS | Phosphorothioate |
| RISC | RNA-induced silencing complex |
| RNAi | RNA interference |
| SCAs | Spinocerebellar ataxias |
| SCA8 | Spinocerebellar ataxia type 8 |
References
- Thornton, C.A. Myotonic dystrophy. Neurol. Clin. 2014, 32, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenninger, S.; Montagnese, F.; Schoser, B. Core Clinical Phenotypes in Myotonic Dystrophies. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meola, G.; Cardani, R. Myotonic dystrophies: An update on clinical aspects, genetic, pathology, and molecular pathomechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Mandoki, A.; Swanson, M.S.; Moxley, R.T.; Thornton, C.A. Myotonic dystrophy type 1 is associated with nuclear foci of mutant RNA, sequestration of muscleblind proteins and deregulated alternative splicing in neurons. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 3079–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, L.M.; van Cruchten, R.T.P.; Willemse, M.; Wansink, D.G. (CTG)n repeat-mediated dysregulation of MBNL1 and MBNL2 expression during myogenesis in DM1 occurs already at the myoblast stage. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczny, P.; Stepniak-Konieczna, E.; Sobczak, K. MBNL proteins and their target RNAs, interaction and splicing regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 10873–10887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, R.; Manchanda, M.; Swanson, M.S. Global insights into alternative polyadenylation regulation. RNA Biol. 2015, 12, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timchenko, N.A.; Cai, Z.J.; Welm, A.L.; Reddy, S.; Ashizawa, T.; Timchenko, L.T. RNA CUG repeats sequester CUGBP1 and alter protein levels and activity of CUGBP1. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7820–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips, A.V.; Timchenko, L.T.; Cooper, T.A. Disruption of splicing regulated by a CUG-binding protein in myotonic dystrophy. Science 1998, 280, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisbury, E.; Sakai, K.; Schoser, B.; Huichalaf, C.; Schneider-Gold, C.; Nguyen, H.; Wang, G.L.; Albrecht, J.H.; Timchenko, L.T. Ectopic expression of cyclin D3 corrects differentiation of DM1 myoblasts through activation of RNA CUG-binding protein, CUGBP1. Exp. Cell Res. 2008, 314, 2266–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.; Wei, C.; Iakova, P.; Bugiardini, E.; Schneider-Gold, C.; Meola, G.; Woodgett, J.; Killian, J.; Timchenko, N.A.; Timchenko, L.T. GSK3β mediates muscle pathology in myotonic dystrophy. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 4461–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, T.M.; Lueck, J.D.; Swanson, M.S.; Dirksen, R.T.; Thornton, C.A. Correction of ClC-1 splicing eliminates chloride channelopathy and myotonia in mouse models of myotonic dystrophy. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 3952–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savkur, R.S.; Philips, A.V.; Cooper, T.A. Aberrant regulation of insulin receptor alternative splicing is associated with insulin resistance in myotonic dystrophy. Nat. Genet. 2001, 29, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freyermuth, F.; Rau, F.; Kokunai, Y.; Linke, T.; Sellier, C.; Nakamori, M.; Kino, Y.; Arandel, L.; Jollet, A.; Thibault, C.; et al. Splicing misregulation of SCN5A contributes to cardiac-conduction delay and heart arrhythmia in myotonic dystrophy. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.Z.; Yarotskyy, V.; Wei, L.; Sobczak, K.; Nakamori, M.; Eichinger, K.; Moxley, R.T.; Dirksen, R.T.; Thornton, C.A. Muscle weakness in myotonic dystrophy associated with misregulated splicing and altered gating of Ca(V)1.1 calcium channel. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 1312–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugier, C.; Klein, A.F.; Hammer, C.; Vassilopoulos, S.; Ivarsson, Y.; Toussaint, A.; Tosch, V.; Vignaud, A.; Ferry, A.; Messaddeq, N.; et al. Misregulated alternative splicing of BIN1 is associated with T tubule alterations and muscle weakness in myotonic dystrophy. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, F.; Lainé, J.; Ramanoudjame, L.; Ferry, A.; Arandel, L.; Delalande, O.; Jollet, A.; Dingli, F.; Lee, K.Y.; Peccate, C.; et al. Abnormal splicing switch of DMD’s penultimate exon compromises muscle fiber maintenance in myotonic dystrophy. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergeant, N.; Sablonnière, B.; Schraen-Maschke, S.; Ghestem, A.; Maurage, C.A.; Wattez, A.; Vermersch, P.; Delacourte, A. Dysregulation of human brain microtubule-associated tau mRNA maturation in myotonic dystrophy type 1. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001, 10, 2143–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanadia, R.N.; Johnstone, K.A.; Mankodi, A.; Lungu, C.; Thornton, C.A.; Esson, D.; Timmers, A.M.; Hauswirth, W.W.; Swanson, M.S. A muscleblind knockout model for myotonic dystrophy. Science 2003, 302, 1978–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, D.M.; Choi, J.; El-Ghazali, A.; Park, S.Y.; Roos, K.P.; Jordan, M.C.; Fishbein, M.C.; Comai, L.; Reddy, S. Loss of muscleblind-like 1 results in cardiac pathology and persistence of embryonic splice isoforms. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Li, M.; Manchanda, M.; Batra, R.; Charizanis, K.; Mohan, A.; Warren, S.A.; Chamberlain, C.M.; Finn, D.; Hong, H.; et al. Compound loss of muscleblind-like function in myotonic dystrophy. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 1887–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Mandal, M.; Yadava, R.S.; Paillard, L.; Mahadevan, M.S. Evaluating the effects of CELF1 deficiency in a mouse model of RNA toxicity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overby, S.J.; Cerro-Herreros, E.; Llamusi, B.; Artero, R. RNA-mediated therapies in myotonic dystrophy. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 2013–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konieczny, P.; Selma-Soriano, E.; Rapisarda, A.S.; Fernandez-Costa, J.M.; Perez-Alonso, M.; Artero, R. Myotonic dystrophy: Candidate small molecule therapeutics. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1740–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.K.; Wheeler, T.M.; Justice, S.L.; Kim, A.; Younis, H.S.; Gattis, D.; Jauvin, D.; Puymirat, J.; Swayze, E.E.; Freier, S.M. Identification and characterization of modified antisense oligonucleotides targeting DMPK in mice and nonhuman primates for the treatment of myotonic dystrophy type 1. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 355, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassez, G.; Audureau, E.; Hogrel, J.Y.; Arrouasse, R.; Baghdoyan, S.; Bhugaloo, H.; Gourlay-Chu, M.L.; Le Corvoisier, P.; Peschanski, M. Improved mobility with metformin in patients with myotonic dystrophy type 1: A randomized controlled trial. Brain 2018, 141, 2855–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanadia, R.N.; Shin, J.; Yuan, Y.; Beattie, S.G.; Wheeler, T.M.; Thornton, C.A.; Swanson, M.S. Reversal of RNA missplicing and myotonia after muscleblind overexpression in a mouse poly(CUG) model for myotonic dystrophy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11748–11753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Bodycombe, N.E.; Haskell, K.M.; Sun, Y.L.; Wang, E.T.; Morris, C.A.; Jones, L.H.; Wood, L.D.; Pletcher, M.T. A flow cytometry-based screen identifies MBNL1 modulators that rescue splicing defects in myotonic dystrophy type I. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 3056–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Masuda, A.; Konishi, H.; Ohkawara, B.; Ito, M.; Kinoshita, M.; Kiyama, H.; Matsuura, T.; Ohno, K. Phenylbutazone induces expression of MBNL1 and suppresses formation of MBNL1-CUG RNA foci in a mouse model of myotonic dystrophy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenquin, J.R.Y.; Yang, H.; Huigens, R.W., III; Nakamori, M.; Berglund, J.A. Combination Treatment of Erythromycin and Furamidine Provides Additive and Synergistic Rescue of Mis-splicing in Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 Models. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2019, 2, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, C.M.; Ranum, L.P. Mouse model of muscleblind-like 1 overexpression: Skeletal muscle effects and therapeutic promise. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 4645–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Weng, W.C.; Stock, L.; Lindquist, D.; Martinez, A.; Gourdon, G.; Timchenko, N.; Snape, M.; Timchenko, L. Correction of GSK3β in DM1 reduces the mutant RNA and improves postnatal survival of DMSXL mice. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 39, e00155-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, V.N.; Nam, J.W. Genomics of microRNA. Trends Genet. 2006, 22, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirbase. Available online: http://mirbase.org/cgi-bin/mirna_summary.pl?org=hsa (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Wienholds, E.; Plasterk, R.H. MicroRNA function in animal development. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 5911–5922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kowdley, K.V. MicroRNAs in common human diseases. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2012, 10, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupaimoole, R.; Slack, F.J. MicroRNA therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, B.D.; Parsons, C.; Slack, F.J. The tumor-suppressive and potential therapeutic functions of miR-34a in epithelial carcinomas. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 20, 737–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.; Kang, S.; Min, H. MicroRNA-targeting therapeutics for hepatitis C. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2014, 37, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonneau, E.; Neveu, B.; Kostantin, E.; Tsongalis, G.J.; De Guire, V. How close are miRNAs from clinical practice? A perspective on the diagnostic and therapeutic market. EJIFCC 2019, 30, 114–127. [Google Scholar]
- Sekar, D.; Venugopal, B.; Sekar, P.; Ramalingam, K. Role of microRNA 21 in diabetes and associated/related diseases. Gene 2016, 582, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambardella, S.; Rinaldi, F.; Lepore, S.M.; Viola, A.; Loro, E.; Angelini, C.; Vergani, L.; Novelli, G.; Botta, A. Overexpression of microRNA-206 in the skeletal muscle from myotonic dystrophy type 1 patients. J. Transl. Med. 2010, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perbellini, R.; Greco, S.; Sarra-Ferraris, G.; Cardani, R.; Capogrossi, M.C.; Meola, G.; Martelli, F. Dysregulation and cellular mislocalization of specific miRNAs in myotonic dystrophy type 1. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2011, 21, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritegotto, C.; Ferrati, C.; Pegoraro, V.; Angelini, C. Micro-RNA expression in muscle and fiber morphometry in myotonic dystrophy type 1. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfetti, A.; Greco, S.; Cardani, R.; Fossati, B.; Cuomo, G.; Valaperta, R.; Ambrogi, F.; Cortese, A.; Botta, A.; Mignarri, A.; et al. Validation of plasma microRNAs as biomarkers for myotonic dystrophy type 1. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoulidou, A.; Kyriakides, T.C.; Papadimas, G.K.; Christou, Y.; Kararizou, E.; Papanicolaou, E.Z.; Phylactou, L.A. Elevated Muscle-Specific miRNAs in Serum of Myotonic Dystrophy Patients Relate to Muscle Disease Progress. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoulidou, A.; Photiades, M.; Kyriakides, T.C.; Georgiou, K.; Prokopi, M.; Kapnisis, K.; Lusakowska, A.; Nearchou, M.; Christou, Y.; Papadimas, G.K.; et al. Identification of exosomal muscle-specific miRNAs in serum of myotonic dystrophy patients relating to muscle disease progress. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 3285–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalsotra, A.; Singh, R.K.; Gurha, P.; Ward, A.J.; Creighton, C.J.; Cooper, T.A. The Mef2 transcription network is disrupted in myotonic dystrophy heart tissue, dramatically altering miRNA and mRNA expression. Cell Rep. 2014, 6, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutalianos, D.; Koutsoulidou, A.; Mastroyiannopoulos, N.P.; Furling, D.; Phylactou, L.A. MyoD transcription factor induces myogenesis by inhibiting Twist-1 through miR-206. J. Cell. Sci. 2015, 128, 3631–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, K.K.; Ishak, T.; Lian, L.H.; Goh, K.J.; Wong, K.T.; Ahmad-Annuar, A.; Thong, M.K. Deregulation of microRNAs in blood and skeletal muscles of myotonic dystrophy type 1 patients. Neurol. India 2017, 65, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, F.; Freyermuth, F.; Fugier, C.; Villemin, J.P.; Fischer, M.C.; Jost, B.; Dembele, D.; Gourdon, G.; Nicole, A.; Duboc, D.; et al. Misregulation of miR-1 processing is associated with heart defects in myotonic dystrophy. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Costa, J.M.; Garcia-Lopez, A.; Zuñiga, S.; Fernandez-Pedrosa, V.; Felipo-Benavent, A.; Mata, M.; Jaka, O.; Aiastui, A.; Hernandez-Torres, F.; Aguado, B.; et al. Expanded CTG repeats trigger miRNA alterations in Drosophila that are conserved in myotonic dystrophy type 1 patients. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappella, M.; Perfetti, A.; Cardinali, B.; Garcia-Manteiga, J.M.; Carrara, M.; Provenzano, C.; Fuschi, P.; Cardani, R.; Renna, L.V.; Meola, G.; et al. High-throughput analysis of the RNA-induced silencing complex in myotonic dystrophy type 1 patients identifies the dysregulation of miR-29c and its target ASB2. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perfetti, A.; Greco, S.; Bugiardini, E.; Cardani, R.; Gaia, P.; Gaetano, C.; Meola, G.; Martelli, F. Plasma microRNAs as biomarkers for myotonic dystrophy type 1. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2014, 24, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Greco, S.; Perfetti, A.; Fasanaro, P.; Cardani, R.; Capogrossi, M.C.; Meola, G.; Martelli, F. Deregulated microRNAs in myotonic dystrophy type 2. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiberio, P.; Callari, M.; Angeloni, V.; Daidone, M.G.; Appierto, V. Challenges in Using Circulating miRNAs as Cancer Biomarkers. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 731479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Torrón, R.; García-Puga, M.; Emparanza, J.I.; Maneiro, M.; Cobo, A.M.; Poza, J.J.; Espinal, J.B.; Zulaica, M.; Ruiz, I.; Martorell, L.; et al. Cancer risk in DM1 is sex-related and linked to miRNA-200/141 downregulation. Neurology 2016, 87, 1250–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerro-Herreros, E.; Fernandez-Costa, J.M.; Sabater-Arcis, M.; Llamusi, B.; Artero, R. Derepressing muscleblind expression by miRNA sponges ameliorates myotonic dystrophy-like phenotypes in Drosophila. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Feng, Y.; Coukos, G.; Zhang, L. Therapeutic microRNA strategies in human cancer. AAPS J. 2009, 11, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, M.S.; Neilson, J.R.; Sharp, P.A. MicroRNA sponges: Competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerro-Herreros, E.; Sabater-Arcis, M.; Fernandez-Costa, J.M.; Moreno, N.; Perez-Alonso, M.; Llamusi, B.; Artero, R. miR-23b and miR-218 silencing increase Muscleblind-like expression and alleviate myotonic dystrophy phenotypes in mammalian models. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalsotra, A.; Wang, K.; Li, P.F.; Cooper, T.A. MicroRNAs coordinate an alternative splicing network during mouse postnatal heart development. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Soibam, B.; Benham, A.; Xu, X.; Chopra, M.; Peng, X.; Yu, W.; Bao, W.; Liang, R.; Azares, A.; et al. miR-322/-503 cluster is expressed in the earliest cardiac progenitor cells and drives cardiomyocyte specification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9551–9556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koscianska, E.; Witkos, T.M.; Kozlowska, E.; Wojciechowska, M.; Krzyzosiak, W.J. Cooperation meets competition in microRNA-mediated DMPK transcript regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 9500–9518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, M.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, Q.; Peng, X. Mir-206 partially rescues myogenesis deficiency by inhibiting CUGBP1 accumulation in the cell models of myotonic dystrophy. Neurol. Res. 2019, 41, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.W.; Cai, H.F.; Wei, X.F.; Sun, J.J.; Lan, X.Y.; Lei, C.Z.; Lin, F.P.; Qi, X.L.; Plath, M.; Chen, H. miR-30-5p Regulates Muscle Differentiation and Alternative Splicing of Muscle-Related Genes by Targeting MBNL. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Splawski, I.; Timothy, K.W.; Sharpe, L.M.; Decher, N.; Kumar, P.; Bloise, R.; Napolitano, C.; Schwartz, P.J.; Joseph, R.M.; Condouris, K.; et al. CaV1.2 calcium channel dysfunction causes a multisystem disorder including arrhythmia and autism. Cell 2004, 119, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizon, V.; Iakovenko, A.; van der Ven, P.F.; Kelly, R.; Fatu, C.; Fürst, D.O.; Karsenti, E.; Gautel, M. Transient association of titin and myosin with microtubules in nascent myofibrils directed by the MURF2 RING-finger protein. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 4469–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renna, L.V.; Bosè, F.; Iachettini, S.; Fossati, B.; Saraceno, L.; Milani, V.; Colombo, R.; Meola, G.; Cardani, R. Receptor and post-receptor abnormalities contribute to insulin resistance in myotonic dystrophy type 1 and type 2 skeletal muscle. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, M. Signaling in muscle atrophy and hypertrophy. Physiology 2008, 23, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfiore, A.; Frasca, F.; Pandini, G.; Sciacca, L.; Vigneri, R. Insulin receptor isoforms and insulin receptor/insulin-like growth factor receptor hybrids in physiology and disease. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 586–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duisters, R.F.; Tijsen, A.J.; Schroen, B.; Leenders, J.J.; Lentink, V.; van der Made, I.; Herias, V.; van Leeuwen, R.E.; Schellings, M.W.; Barenbrug, P.; et al. miR-133 and miR-30 regulate connective tissue growth factor: Implications for a role of microRNAs in myocardial matrix remodeling. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thum, T.; Gross, C.; Fiedler, J.; Fischer, T.; Kissler, S.; Bussen, M.; Galuppo, P.; Just, S.; Rottbauer, W.; Frantz, S.; et al. MicroRNA-21 contributes to myocardial disease by stimulating MAP kinase signaling in fibroblasts. Nature 2008, 456, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rooij, E.; Sutherland, L.B.; Thatcher, J.E.; DiMaio, J.M.; Naseem, R.H.; Marshall, W.S.; Hill, J.A.; Olson, E.N. Dysregulation of microRNAs after myocardial infarction reveals a role of miR-29 in cardiac fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13027–13032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, J.R.; Watt, K.I.; Parker, B.L.; Chaudhuri, R.; Ryall, J.G.; Cunningham, L.; Qian, H.; Sartorelli, V.; Sandri, M.; Chamberlain, J.; et al. Integrated expression analysis of muscle hypertrophy identifies Asb2 as a negative regulator of muscle mass. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e85477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murton, A.J.; Constantin, D.; Greenhaff, P.L. The involvement of the ubiquitin proteasome system in human skeletal muscle remodeling and atrophy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1782, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, T.; Nakazato, K.; Song, H.; Ishii, N. TGF-beta1 and TNF-alpha are involved in the transcription of type I collagen alpha 2 gene in soleus muscle atrophied by mechanical unloading. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2008, 104, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tews, D.S. Muscle-fiber apoptosis in neuromuscular diseases. Muscle Nerve. 2005, 32, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.; Peruzzi, P.P.; Lawler, S. MicroRNAs in cancer: Biomarkers, functions and therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Guire, V.; Robitaille, R.; Tetreault, N.; Guerin, R.; Menard, C.; Bambace, N.; Sapieha, P. Circulating miRNAs as sensitive and specific biomarkers for the diagnosis and monitoring of human diseases: Promises and challenges. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 846–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaka, Y.; Kishi, S.; Aoki, Y.; Komaki, H.; Oya, Y.; Takeda, S.; Hashido, K. Three novel serum biomarkers, miR-1, miR-133a, and miR-206 for Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy, and Becker muscular dystrophy. Environ. Health. Prev. Med. 2014, 19, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Costa, J.M.; Llamusi, B.; Bargiela, A.; Zulaica, M.; Alvarez-Abril, M.C.; Perez-Alonso, M.; Lopez de Munain, A.; Lopez-Castel, A.; Artero, R. Six Serum miRNAs Fail to Validate as Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 Biomarkers. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Filippo, E.S.; Mancinelli, R.; Pietrangelo, T.; La Rovere, R.M.L.; Quattrocelli, M.; Sampaolesi, M.; Fulle, S. Myomir dysregulation and reactive oxygen species in aged human satellite cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 473, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberg, I.; Eran, A.; Nishino, I.; Moggio, M.; Lamperti, C.; Amato, A.A.; Lidov, H.G.; Kang, P.B.; North, K.N.; Mitrani-Rosenbaum, S.; et al. Distinctive patterns of microRNA expression in primary muscular disorders. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 17016–17021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magri, F.; Vanoli, F.; Corti, S. MiRNA in spinal muscular atrophy pathogenesis and therapy. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutz, P.L.; Chawla, G.; Stoilov, P.; Black, D.L. MicroRNAs regulate the expression of the alternative splicing factor nPTB during muscle development. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Kong, M.; Ye, Y.; Hong, S.; Cheng, L.; Jiang, L. Serum miR-206 and othe muscle-specific microRNAs as non-invasive biomarkers for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J. Neurochem. 2014, 129, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, H.L.; Kauppinen, S.; Hodges, M.R. HCV infection and miravirsen. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallant-Behm, C.L.; Piper, J.; Lynch, J.M.; Seto, A.G.; Hong, S.J.; Mustoe, T.A.; Maari, C.; Pestano, L.A.; Dalby, C.M.; Jackson, A.L.; et al. A MicroRNA-29 Mimic (Remlarsen) Represses Extracellular Matrix Expression and Fibroplasia in the Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Yang, B.; Lin, H.; Lu, Y.; Luo, X.; Wang, Z. Novel approaches for gene-specific interference via manipulating actions of microRNAs: Examination on the pacemaker channel genes HCN2 and HCN4. J. Cell Physiol. 2007, 212, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, P.; Medina, P.P.; Wiggins, J.F.; Ruffino, L.; Kelnar, K.; Omotola, M.; Homer, R.; Brown, D.; Bader, A.G.; Weidhaas, J.B.; et al. Regression of murine lung tumors by the let-7 microRNA. Oncogene 2010, 29, 1580–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, J.; Chivukula, R.R.; O’Donnell, K.A.; Wentzel, E.A.; Montgomery, C.L.; Hwang, H.W.; Chang, T.C.; Vivekanandan, P.; Torbenson, M.; Clark, K.R.; et al. Therapeutic microRNA delivery suppresses tumorigenesis in a murine liver cancer model. Cell 2009, 137, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Qian, C.; Sun, Y.; Barajas, M.A.; Prieto, J. Transduction of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) using recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV): In vitro and in vivo effects of genotoxic agents. J. Hepatol. 2000, 32, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakasa, T.; Ishikawa, M.; Shi, M.; Shibuya, H.; Adachi, N.; Ochi, M. Acceleration of muscle regeneration by local injection of muscle-specific microRNAs in rat skeletal muscle injury model. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 2495–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seow, Y.; Sibley, C.R.; Wood, M.J. Artificial mirtron-mediated gene knockdown: Functional DMPK silencing in mammalian cells. RNA 2012, 18, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumireddy, K.; Young, D.D.; Xiong, X.; Hogenesch, J.B.; Huang, Q.; Deiters, A. Small-molecule inhibitors of microrna miR-21 function. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2008, 47, 7482–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly, C.M.; Boer, R.E.; Moon, M.H.; Gareiss, P.; Schneekloth, J.S., Jr. Discovery of Inhibitors of MicroRNA-21 Processing Using Small Molecule Microarrays. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, K.; Song, J.; Han, Y.T.; Lee, S.; Kang, S.; Hwang, K.W.; Min, H.; Min, K.H. Identification of aminosulfonylarylisoxazole as microRNA-31 regulators. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daughters, R.S.; Tuttle, D.L.; Gao, W.; Ikeda, Y.; Moseley, M.L.; Ebner, T.J.; Swanson, M.S.; Ranum, L.P. RNA gain-of-function in spinocerebellar ataxia type 8. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Aleff, R.A.; Soragni, E.; Kalari, K.; Nie, J.; Tang, X.; Davila, J.; Kocher, J.P.; Patel, S.V.; Gottesfeld, J.M.; et al. RNA toxicity and missplicing in the common eye disease fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 5979–5990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koscianska, E.; Kozlowska, E.; Jaworska, E.; Krzyzosiak, W.J. MicroRNA deregulation in trinucleotide repeat expansion disorders. In Applied RNAi. From Fundamental Research to Therapeutic Applications; Arbuthnot, P., Weinberg, M.S., Eds.; Caister Academic Press: Poole, UK, 2014; pp. 227–245. [Google Scholar]
| miRNA | Alteration | Mechanism | Target | Disease Role Suggested | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DM1 | |||||
| miR-206 | ↑ (sk) | Muscle atrophy | [42] | ||
| ≠cd (sk) | [43] | ||||
| ↑ (sk) | [44] | ||||
| ↑ (pl) | Muscle strength | [45] | |||
| ↑ (se) | Progressive wasting | [46,47] | |||
| ↓ (mh, h) | MEF2 | Arrhythmias/Fibrosis | [48] | ||
| ↓ (sk) | MYOD | ↑ TWIST-1 | Muscle differences | [49] | |
| miR-1 | ↑/≠ cd(sk) | Muscle development | [43] | ||
| ↓ (sk) | ↑ several transcripts | [44] | |||
| ↓ (sk) | [50] | ||||
| ↓ (mh, h) | MBNL1/LIN28 | ↑ GJA1a/↑CACNA1C | Cardiac dysfunction | [51] | |
| ↑ (pl) | Muscle strength | [45] | |||
| ↑ (se) | Progressive wasting | [46,47] | |||
| ↓ (mh, h) | MEF2 | Arrhythmias/Fibrosis | [48] | ||
| ↓ (dm, sk) | Mbl | [52] | |||
| miR-335 | ↑ (sk) | [43] | |||
| miR-29b,c | ↓ (sk) | ↑ several transcripts | Atrophy | [43] | |
| mirR-29c | ↓ (sk) | [50] | |||
| mirR-29b | ↑ (bl) | [50] | |||
| miR-29c | ↓ (sk) | ↑ ASB2 (and others) | Muscle fibrosis/mass | [53] | |
| miR-33 | ↓ (sk) | [43] | |||
| mir-33a | ↑ (bl) | [50] | |||
| miR-133b | ≠ cd (sk) | [43] | |||
| miR-133a/b | ↓ (sk) | [44] | |||
| miR-133a | ↓ (sk)/↑ (bl) | [50] | |||
| miR-133a | ↑ (pl) | [54] | |||
| miR-133a/b | ↑ (pl) | Muscle strength | [45] | ||
| miR-133a/b | ↑ (se) | Progressive wasting | [46,47] | ||
| miR-133a | ↓ (mh, h) | MEF2 | Arrhythmias/Fibrosis | [48] | |
| miR-193b | ↑ (pl) | [54] | |||
| miR-191 | ↑ (pl) | [54] | |||
| miR-140-3p | ↑ (pl) | [54] | |||
| miR-454 | ↑ (pl) | [54] | |||
| miR-574 | ↑ (pl) | [54] | |||
| miR-885-5p | ↑ (pl) | [54] | |||
| miR-886-3p | ↑ (pl) | [54] | |||
| miR-27b | ↓ (pl) | [54] | |||
| miR-23a/b | ↓ (mh, h) | MEF2 | ↑ CELF1 | Arrhythmias/Fibrosis | [48] |
| miR-208a | ↑ (sk) | ↓ several transcripts | Myofiber atrophy and hypertrophy | [55] | |
| miR-381 | ↑ (sk) | ↓ several transcripts | Myofiber atrophy and hypertrophy | [56] | |
| miR-193b-3p | ↓ (sk) | ↑ several transcripts | Myofiber atrophy and hypertrophy | [55] | |
| miR-7 | ↓ (dm, sk) | [52] | |||
| miR-10 | ↓ (dm, sk) | [52] | |||
| miR-15a | ↓ (sk) | ↑↓ several transcripts | [53] | ||
| miR-22 | ↓ (sk) | ERBB3 | [53] | ||
| miR-155 | ↑ (sk) | ↑↓ several transcripts | [53] | ||
| miR-222 | ↑ (sk) | ↑↓ several transcripts | [53] | ||
| miR-381 | ↑ (sk) | ↑↓ several transcripts | [53] | ||
| miR-411 | ↑ (sk) | ↑↓ several transcripts | [53] | ||
| miR-200 | ↓ (bl) | Cancer | [57] | ||
| miR-241 | ↓ (bl) | Cancer | [57] | ||
| DM2 | |||||
| miR-34a-5p; -34b-3p; -34c-5p | ↑ (sk) | ↓ several transcripts | Myofiber atrophy and hypertrophy | [55] | |
| miR-146b-5p | ↑ (sk) | ↓ several transcripts | Myofiber atrophy and hypertrophy | [55] | |
| miR-208a | ↑ (sk) | ↓ several transcripts | Myofiber atrophy and hypertrophy | [55] | |
| miR-221-3p; | ↑ (sk) | ↓ several transcripts | Myofiber atrophy and hypertrophy | [55] | |
| miR-381 | ↑ (sk) | ↓ several transcripts | Myofiber atrophy and hypertrophy | [55] | |
| miR-125-5p | ↓ (sk) | ↑ several transcripts | Myofiber atrophy and hypertrophy | [55] | |
| miR-193a-3p; -193b-3p | ↓ (sk) | ↑ several transcripts | Myofiber atrophy and hypertrophy | [55] | |
| miR-387a-3p | ↓ (sk) | ↑ several transcripts | Myofiber atrophy and hypertrophy | [55] | |
| miR-1 | ↓ (mh, h) | [51] | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López Castel, A.; Overby, S.J.; Artero, R. MicroRNA-Based Therapeutic Perspectives in Myotonic Dystrophy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225600
López Castel A, Overby SJ, Artero R. MicroRNA-Based Therapeutic Perspectives in Myotonic Dystrophy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(22):5600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225600
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez Castel, Arturo, Sarah Joann Overby, and Rubén Artero. 2019. "MicroRNA-Based Therapeutic Perspectives in Myotonic Dystrophy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 22: 5600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225600
APA StyleLópez Castel, A., Overby, S. J., & Artero, R. (2019). MicroRNA-Based Therapeutic Perspectives in Myotonic Dystrophy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(22), 5600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225600





