Differential Susceptibility of Catheter Biomaterials to Biofilm-Associated Infections and Their Remedy by Drug-Encapsulated Eudragit RL100 Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
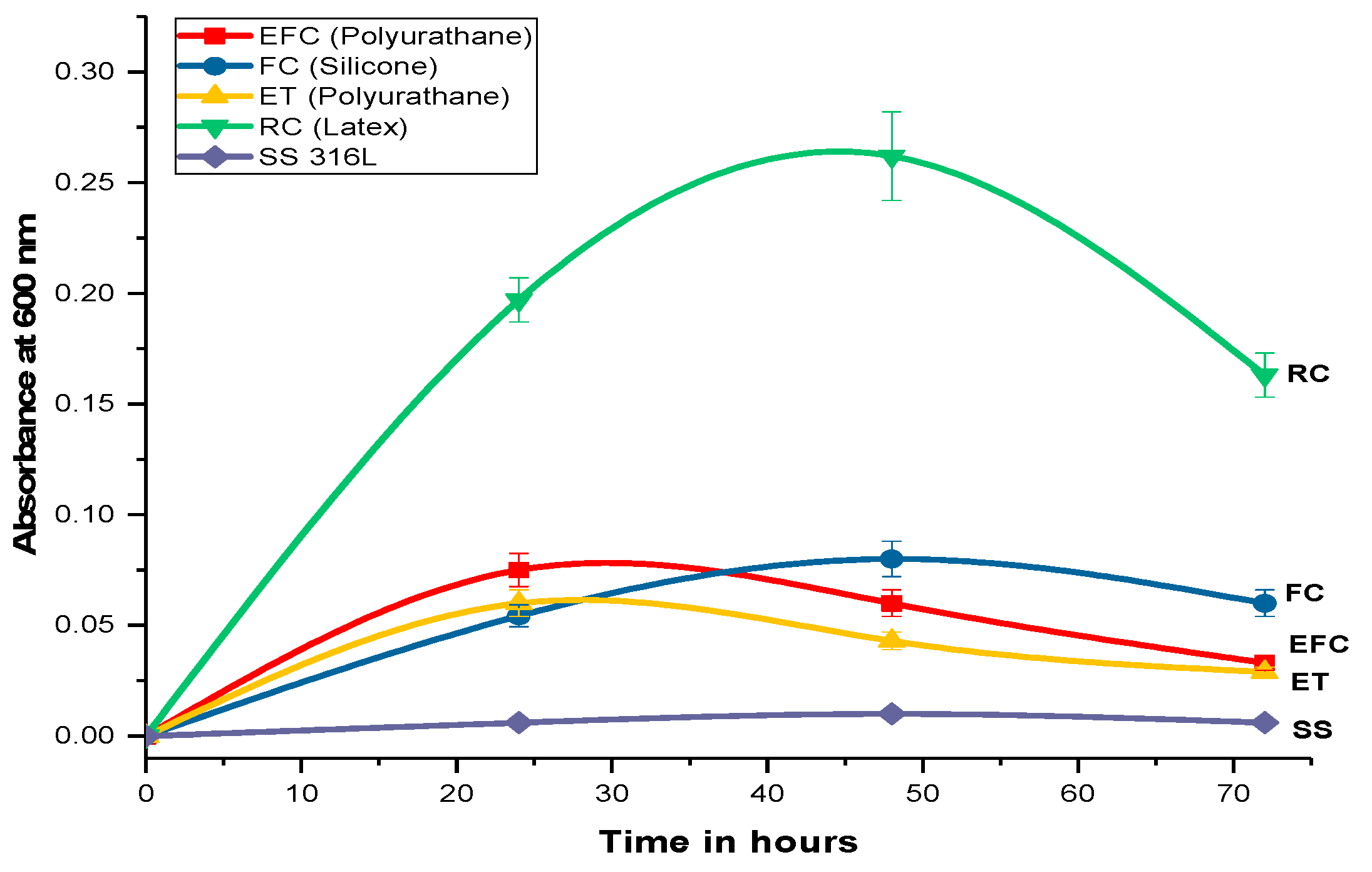
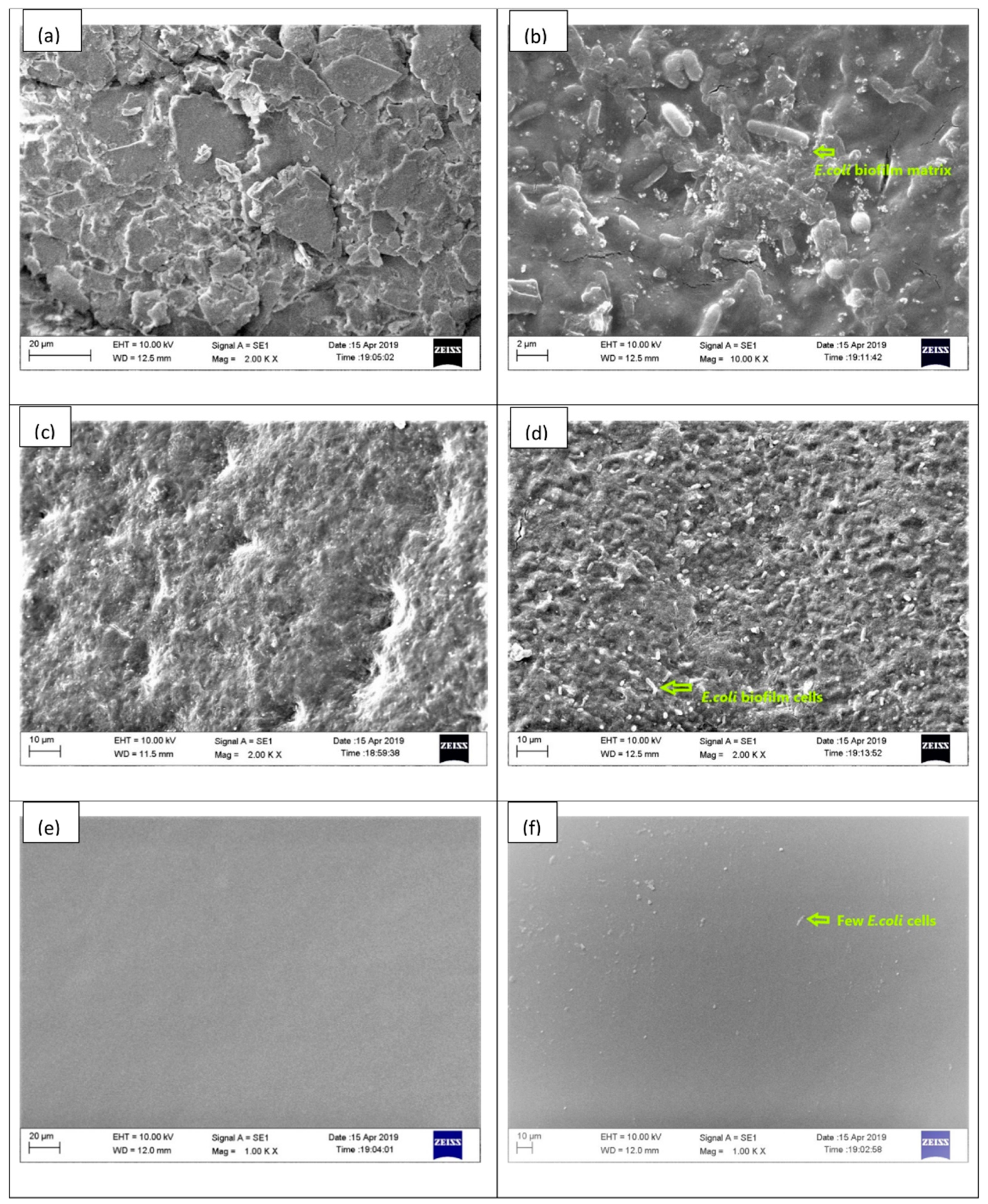
2.1. Biofilm Formation and Quantification
2.2. Physical Characteristic of Indwelling Devices
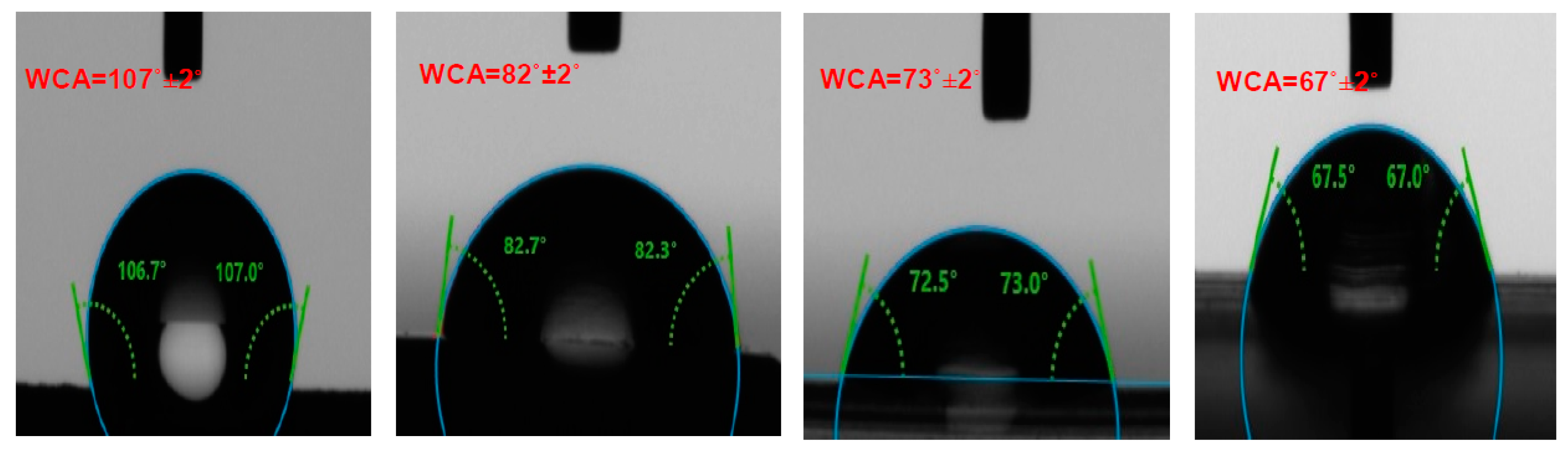
2.3. Contact Angle Measurement
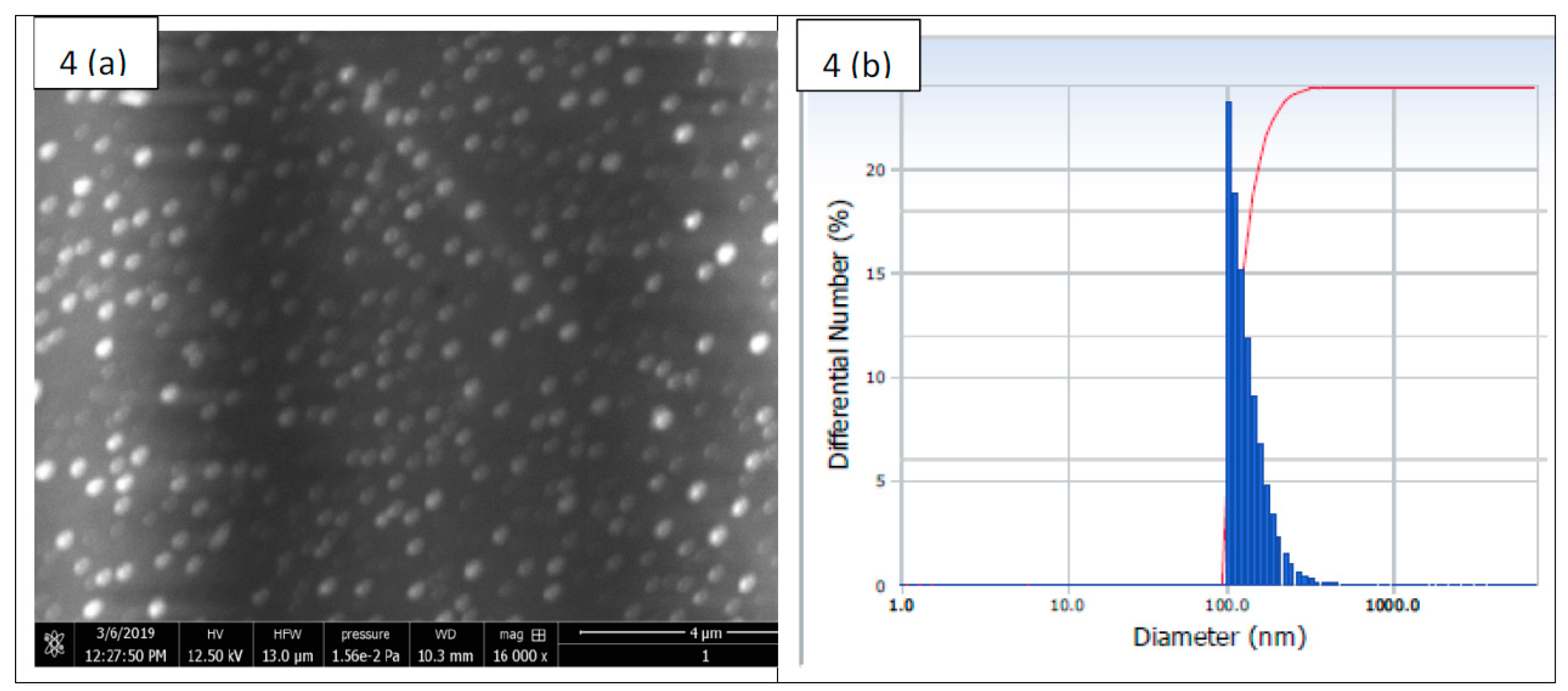
2.4. Physical Characteristic of Nanoparticles
2.5. Drug Entrapment Efficiency
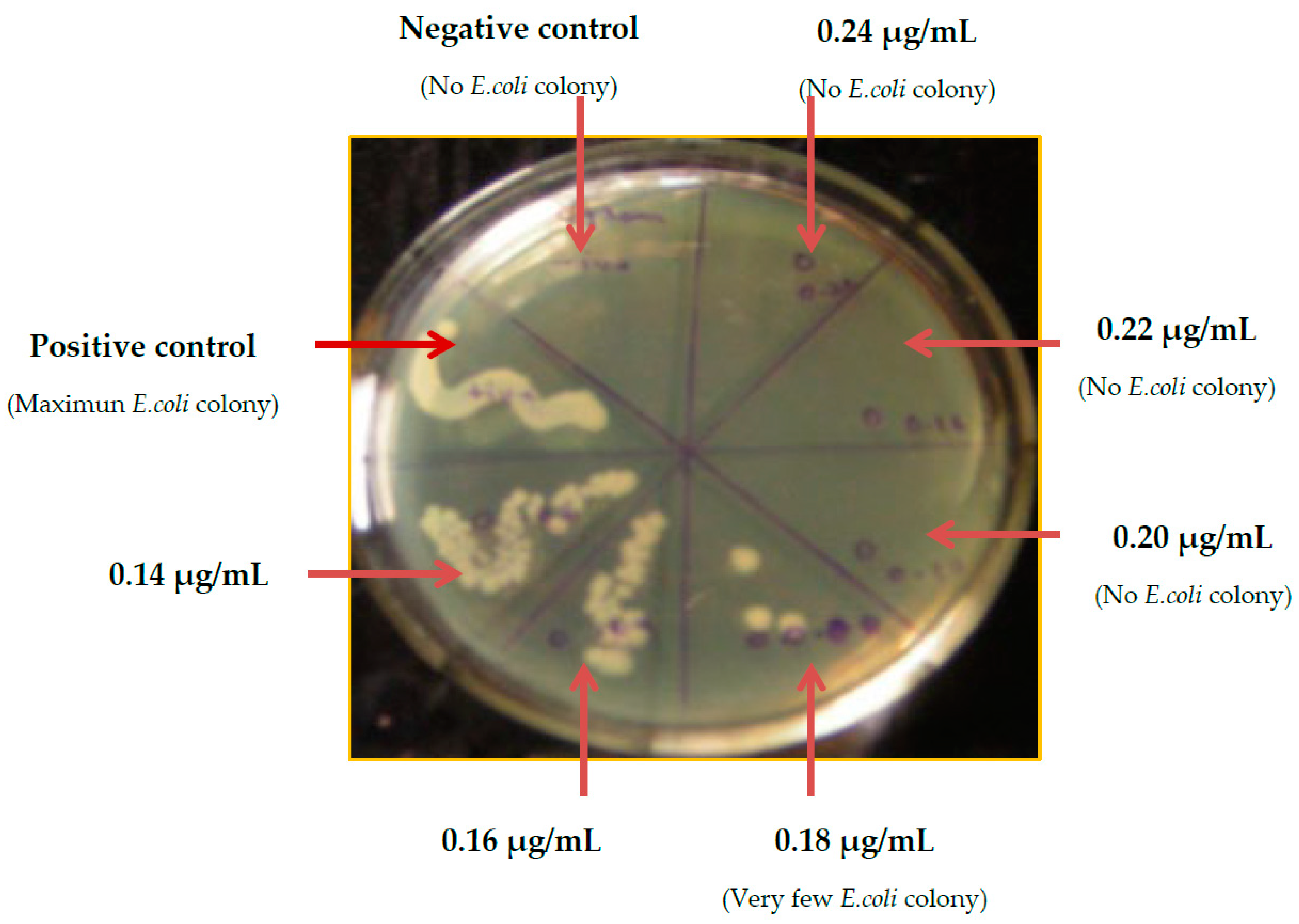
2.6. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Determination of G-S
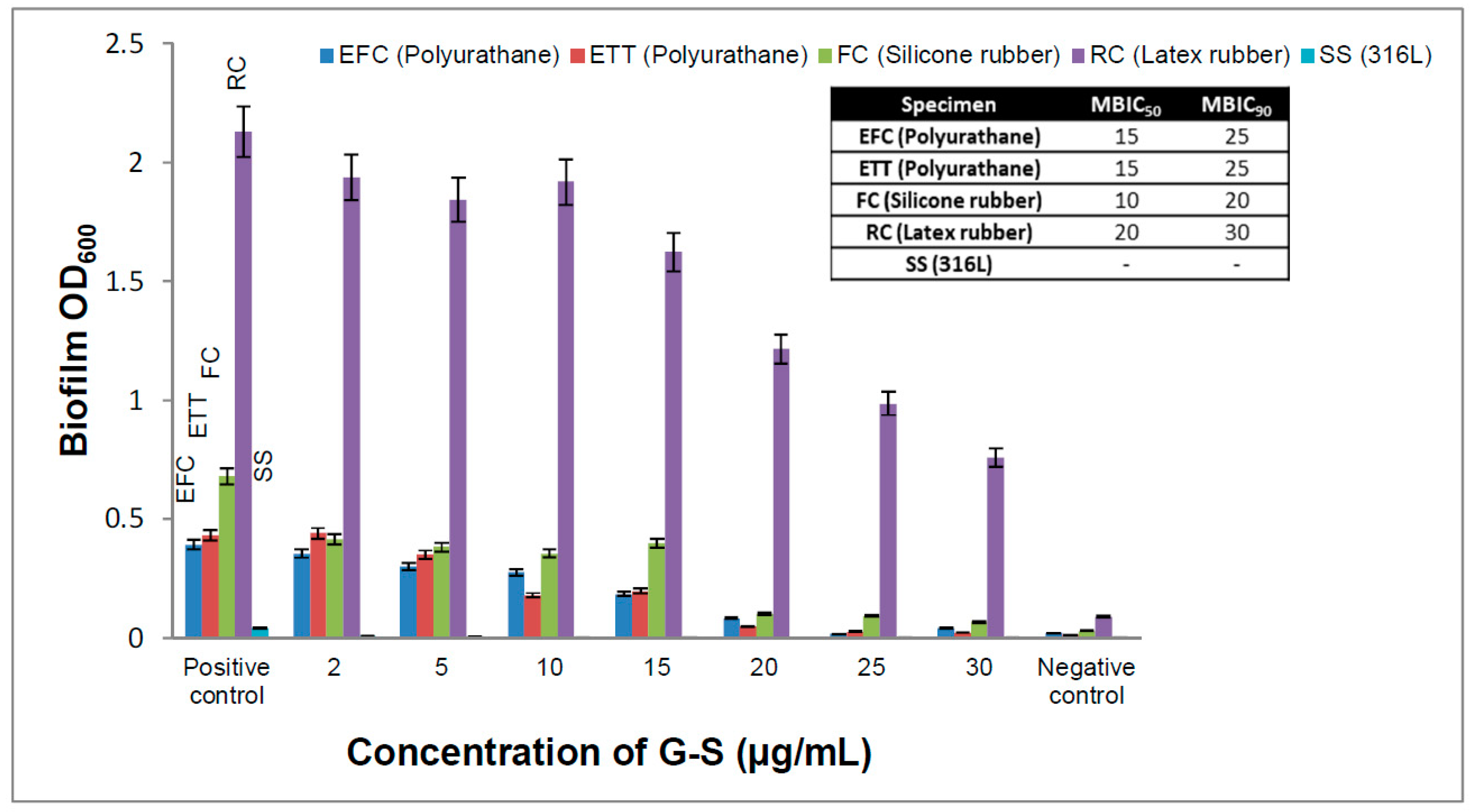
2.7. Minimum Biofilm Inhibitory Concentration (MBIC)
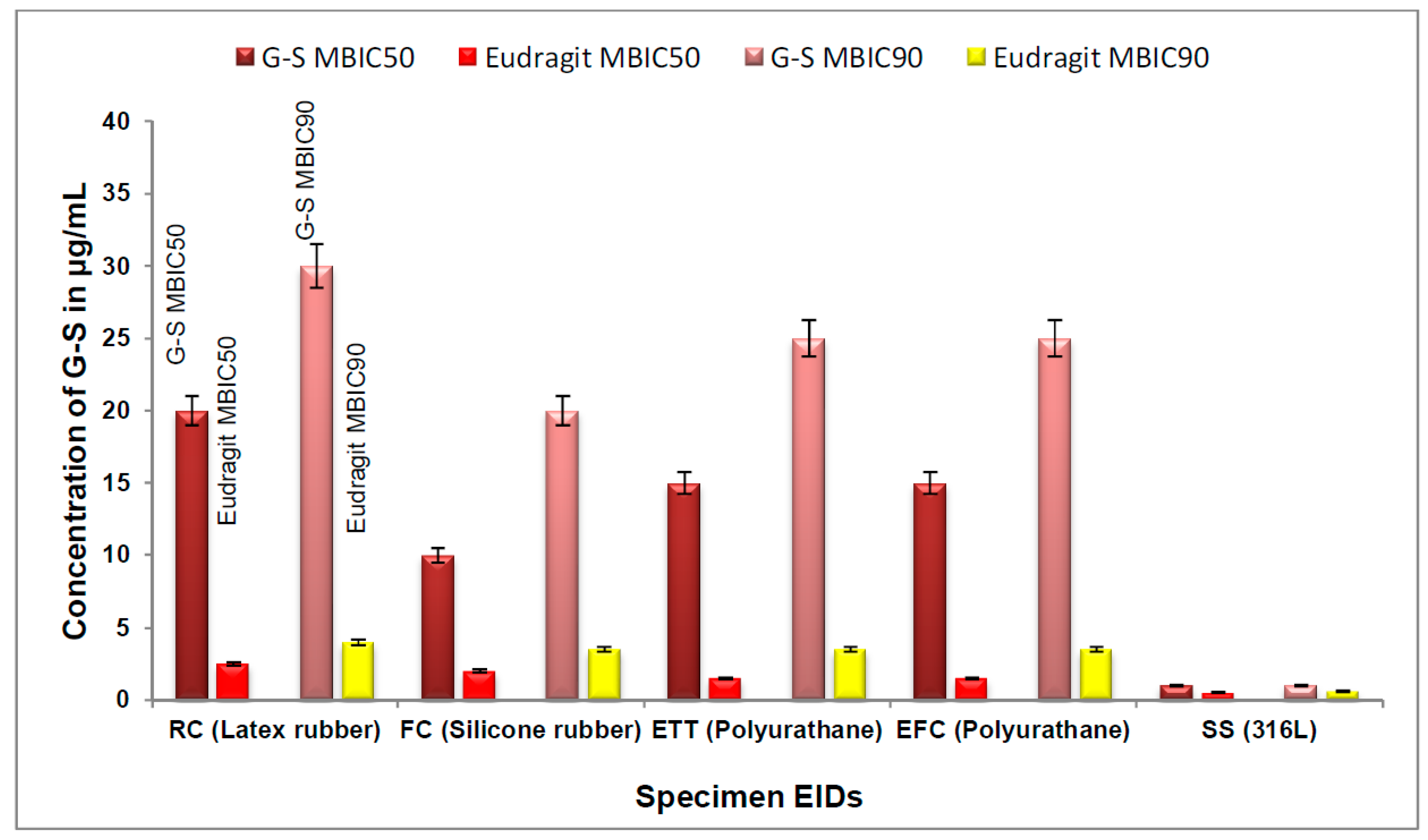
2.8. Determination of MBIC of Eudragit RL100 Nanoparticle-Encapsulated G-S
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. Biofilm Formation and Quantification
4.3. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of G-S
4.4. Determination of Minimum Biofilm Inhibitory Concentration (MBIC) of G-S
4.5. Preparation of Eudragit RL100 Nanoparticle-Encapsulating G-S
4.6. Drug Entrapment Efficiency
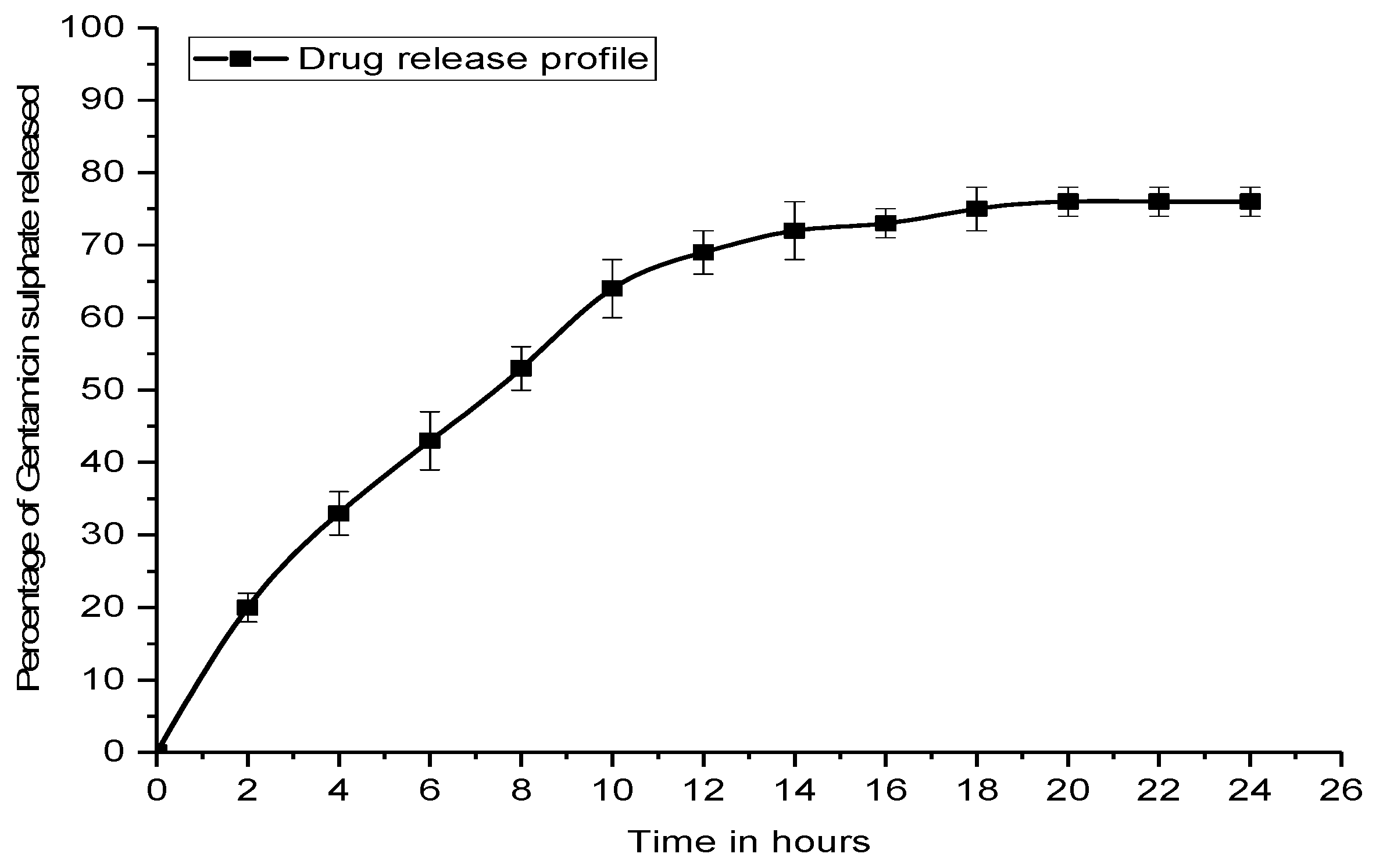
4.7. In Vitro Drug Release Kinetic Study
4.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.9. Contact Angle
4.10. Antimicrobial Assessment
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EIDs | Externally implanted medical devices |
| E-G-S | Eudragit RL100 encapsulated gentamicin sulfate |
| G-S | Gentamicin sulfate |
References
- Treter, J.; Macedo, a.J. Catheters: A suitable surface for biofilm formation. Sci. Against Microb. Pathog. Commun. Curr. Res. Technol. Adv. 2011, 835–842. [Google Scholar]
- Khatoon, Z.; McTiernan, C.D.; Suuronen, E.J.; Mah, T.F.; Alarcon, E.I. Bacterial biofilm formation on implantable devices and approaches to its treatment and prevention. Heliyon 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanEpps, J.S.; Younger, J.G. Implantable Device-Related Infection. Shock 2016, 46, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pavithra, D.; Doble, M. Biofilm formation, bacterial adhesion and host response on polymeric implants—Issues and prevention. Biomed. Mater. 2008, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, S.L.; Suleman, L.; Vuotto, C.; Donelli, G. Healthcare-Associated infections, medical devices and biofilms: Risk, tolerance and control. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Larsen, L.H.; Lorenzen, J.; Hall-Stoodley, L.; Kikhney, J.; Moter, A.; Thomsen, T.R. Microbiological diagnosis of device-related biofilm infections. APMIS 2017, 125, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wi, Y.M.; Patel, R. Understanding Biofilms and Novel Approaches to the Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment of Medical Device-Associated Infections. Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 2018, 32, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, C.; Henriques, M.; Oliveira, R. Mini-review: Antimicrobial central venous catheters - recent advances and strategies. Biofouling 2011, 27, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Hu, W.; Tian, Z.; Yuan, D.; Yi, G.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Zhu, J.; Li, M. Developing natural products as potential anti-biofilm agents. Chinese Med. (UK) 2019, 14, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De La Fuente-Núñez, C.; Reffuveille, F.; Mansour, S.C.; Reckseidler-Zenteno, S.L.; Hernández, D.; Brackman, G.; Coenye, T.; Hancock, R.E.W. D-Enantiomeric Peptides that Eradicate Wild-Type and Multidrug-Resistant Biofilms and Protect against Lethal Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. Chem. Biol. 2015, 22, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebreyohannes, G.; Nyerere, A.; Bii, C.; Sbhatu, D.B. Challenges of intervention, treatment, and antibiotic resistance of biofilm-forming microorganisms. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parrino, B.; Schillaci, D.; Carnevale, I.; Giovannetti, E.; Diana, P.; Cirrincione, G.; Cascioferro, S. Synthetic small molecules as anti-biofilm agents in the struggle against antibiotic resistance. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 161, 154–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebeaux, D.; Ghigo, J.-M.; Beloin, C. Biofilm-Related Infections: Bridging the Gap between Clinical Management and Fundamental Aspects of Recalcitrance toward Antibiotics. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 510–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Römling, U.; Balsalobre, C. Biofilm infections, their resilience to therapy and innovative treatment strategies. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 272, 541–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, H.; Allan, R.N.; Howlin, R.P.; Stoodley, P.; Hall-Stoodley, L. Targeting microbial biofilms: Current and prospective therapeutic strategies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 740–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinescu, O.; Sahnazarov, N.; Muţiu, A. Quorum Sensing in Bacteria: the LuxR-LuxI Family of Cell Density-Responsive Transcriptional Regulators. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 269–275. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, T.; Ikeda, T.; Takiguchi, N.; Kuroda, A.; Ohtake, H.; Kato, J. Inhibition of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by N-acyl cyclopentylamides. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3183–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.P.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.P.; Pellechia, P.J.; Benicewicz, B.C.; Decho, A.W. Engineering nanoparticles to silence bacterial communication. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijland, R.; Hall, M.J.; Grant Burgess, J. Dispersal of biofilms by secreted, matrix degrading, Bacterial DNase. PLoS ONE 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Fuente-Núñez, C.; Reffuveille, F.; Fernández, L.; Hancock, R.E.W. Bacterial biofilm development as a multicellular adaptation: Antibiotic resistance and new therapeutic strategies. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das Ghatak, P.; Mathew-Steiner, S.S.; Pandey, P.; Roy, S.; Sen, C.K. A surfactant polymer dressing potentiates antimicrobial efficacy in biofilm disruption. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz De Rienzo, M.A.; Stevenson, P.S.; Marchant, R.; Banat, I.M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm disruption using microbial surfactants. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbois, A.P.; Smith, V.J. Antibacterial free fatty acids: Activities, mechanisms of action and biotechnological potential. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1629–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandenburg, K.S.; Rodriguez, K.J.; McAnulty, J.F.; Murphy, C.J.; Abbott, N.L.; Schurr, M.J.; Czuprynski, C.J. Tryptophan inhibits biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1921–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, W. Indole: a signaling molecule or a mere metabolic byproduct that alters bacterial physiology at a high concentration? J. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banin, E.; Brady, K.M.; Greenberg, E.P. Chelator-induced dispersal and killing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells in a biofilm. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2064–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, F.; Beutler, M.; Enning, D.; Lamprecht-Grandio, M.; Zafra, O.; González-Pastor, J.; De Beer, D. The role of nitric-oxide-synthase-derived nitric oxide in multicellular traits of Bacillus subtilis 3610: Biofilm formation, swarming, and dispersal. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algburi, A.; Comito, N.; Kashtanov, D.; Dicks, L.M.T.; Chikindas, M.L. Control of biofilm formation: Antibiotics and beyond. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattò, C.; Cappitelli, F. Testing Anti-Biofilm Polymeric Surfaces: Where to Start? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carinci; Lauritano; Bignozzi; Pazzi; Candotto; Santos de Oliveira; Scarano A New Strategy Against Peri-Implantitis: Antibacterial Internal Coating. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3897. [CrossRef]
- Querido, M.M.; Aguiar, L.; Neves, P.; Pereira, C.C.; Teixeira, J.P. Self-disinfecting surfaces and infection control. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2019, 178, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; González, B.; Izquierdo-Barba, I. Nanomaterials as Promising Alternative in the Infection Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Suresh, P.K.; Desmukh, R. Design of Eudragit RL 100 nanoparticles by nanoprecipitation method for ocular drug delivery. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neoh, K.G.; Li, M.; Kang, E.T.; Chiong, E.; Tambyah, P.A. Surface modification strategies for combating catheter-related complications: recent advances and challenges. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 2045–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, Y.; Hays, M.P.; Hardwidge, P.R.; Kim, J. Surface characteristics influencing bacterial adhesion to polymeric substrates. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14254–14261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falde, E.J.; Yohe, S.T.; Colson, Y.L.; Grinstaff, M.W. Superhydrophobic materials for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2016, 104, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, J.; Yeap, S.P.; Che, H.X.; Low, S.C. Characterization of magnetic nanoparticle by dynamic light scattering. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Nie, X.; Zou, M.; Shi, Y.; Cheng, G. Recent advances in materials for extended-release antibiotic delivery system. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 2011, 64, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Toole, G.A. Microtiter Dish Biofilm Formation Assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djordjevic, D.; Wiedmann, M.; McLandsborough, L.A. Microtiter plate assay for assessment of Listeria monocytogenes biofilm formation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 2950–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, K.; Jongsthaphongpun, K.L.; Stumpp, N.S.; Winkel, A.; Stiesch, M. Quantifying implant-associated biofilms: Comparison of microscopic, microbiologic and biochemical methods. J. Microbiol. Methods 2016, 130, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiegand, I.; Hilpert, K.; Hancock, R.E.W. Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salama, R.O.; Traini, D.; Chan, H.K.; Young, P.M. Preparation and characterisation of controlled release co-spray dried drug-polymer microparticles for inhalation 2: Evaluation of in vitro release profiling methodologies for controlled release respiratory aerosols. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajmal, G.; Bonde, G.V.; Mittal, P.; Khan, G.; Pandey, V.K.; Bakade, B.V.; Mishra, B. Biomimetic PCL-gelatin based nanofibers loaded with ciprofloxacin hydrochloride and quercetin: A potential antibacterial and anti-oxidant dressing material for accelerated healing of a full thickness wound. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 567, 118480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pandey, V.K.; Srivastava, K.R.; Ajmal, G.; Thakur, V.K.; Gupta, V.K.; Upadhyay, S.N.; Mishra, P.K. Differential Susceptibility of Catheter Biomaterials to Biofilm-Associated Infections and Their Remedy by Drug-Encapsulated Eudragit RL100 Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5110. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205110
Pandey VK, Srivastava KR, Ajmal G, Thakur VK, Gupta VK, Upadhyay SN, Mishra PK. Differential Susceptibility of Catheter Biomaterials to Biofilm-Associated Infections and Their Remedy by Drug-Encapsulated Eudragit RL100 Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(20):5110. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205110
Chicago/Turabian StylePandey, Vivek Kumar, Kumar Rohit Srivastava, Gufran Ajmal, Vijay Kumar Thakur, Vijai Kumar Gupta, Siddh Nath Upadhyay, and Pradeep Kumar Mishra. 2019. "Differential Susceptibility of Catheter Biomaterials to Biofilm-Associated Infections and Their Remedy by Drug-Encapsulated Eudragit RL100 Nanoparticles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 20: 5110. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205110
APA StylePandey, V. K., Srivastava, K. R., Ajmal, G., Thakur, V. K., Gupta, V. K., Upadhyay, S. N., & Mishra, P. K. (2019). Differential Susceptibility of Catheter Biomaterials to Biofilm-Associated Infections and Their Remedy by Drug-Encapsulated Eudragit RL100 Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(20), 5110. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205110






