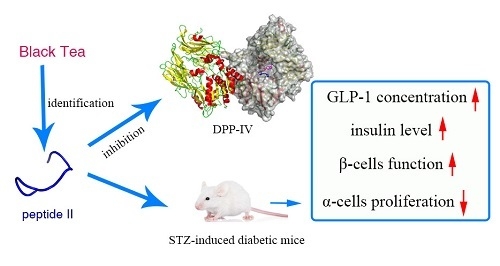
A Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitory Tea Peptide Improves Pancreatic β-Cell Function and Reduces α-Cell Proliferation in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
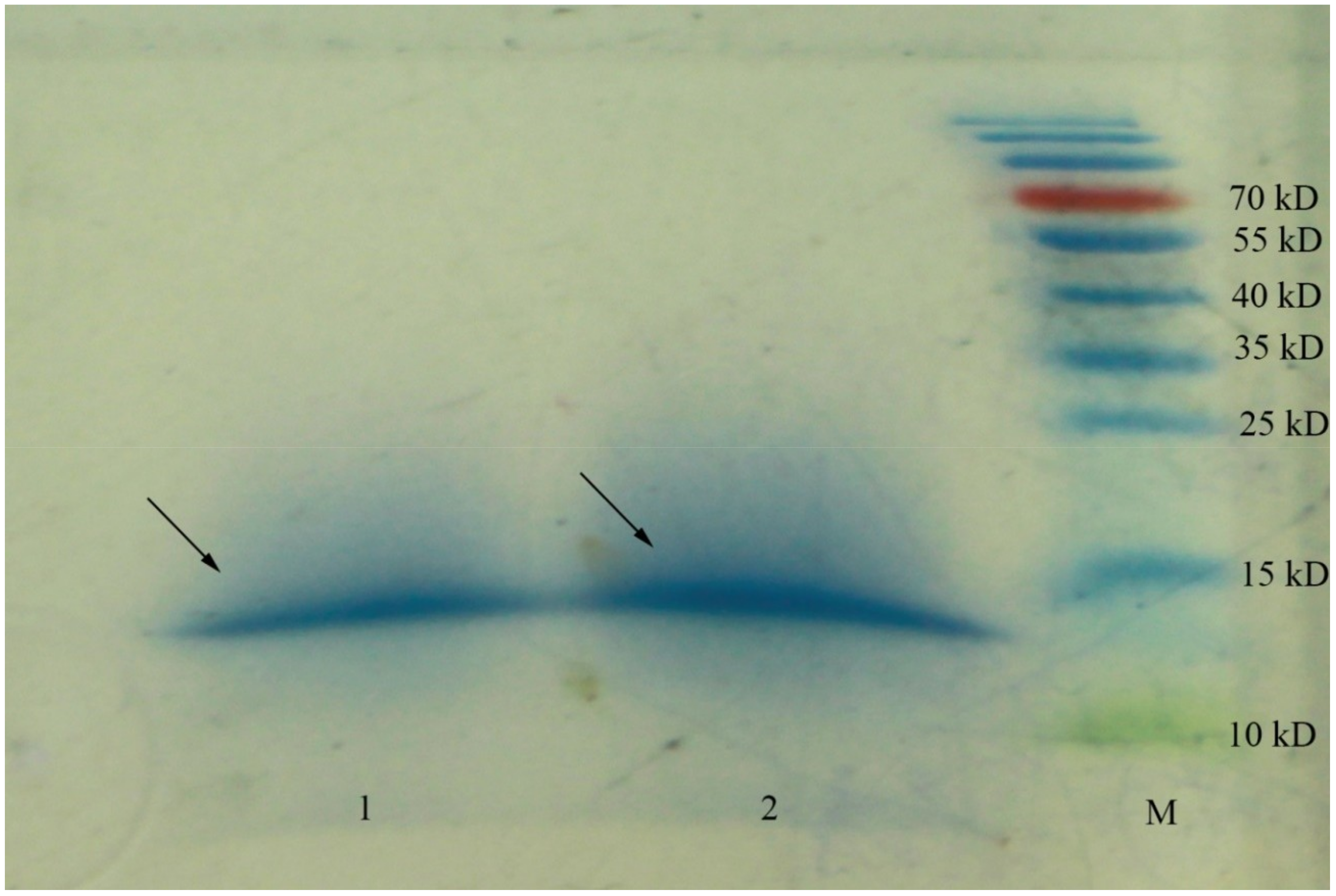
2.1. Peptide Identification
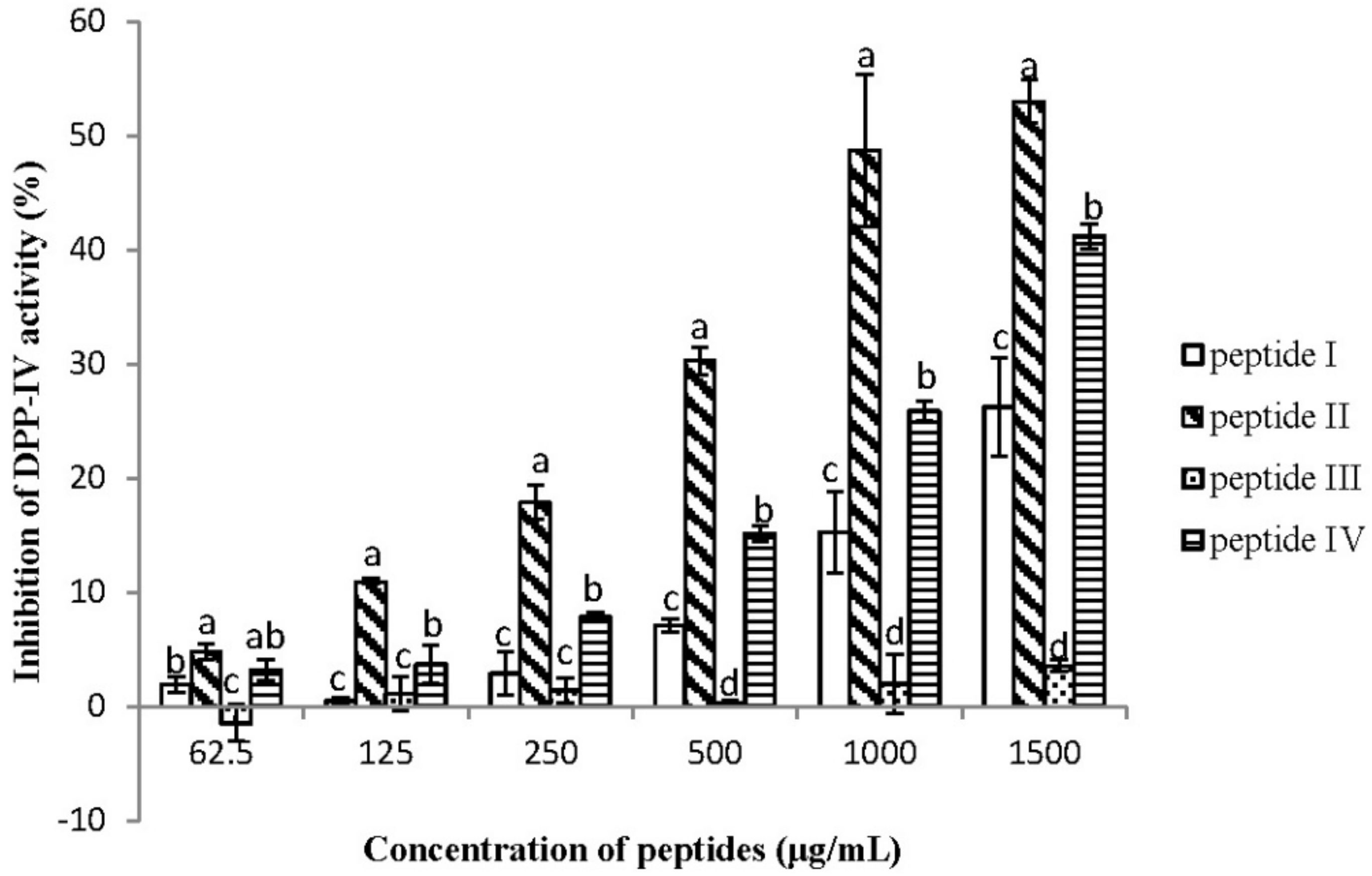
2.2. Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitory Assay
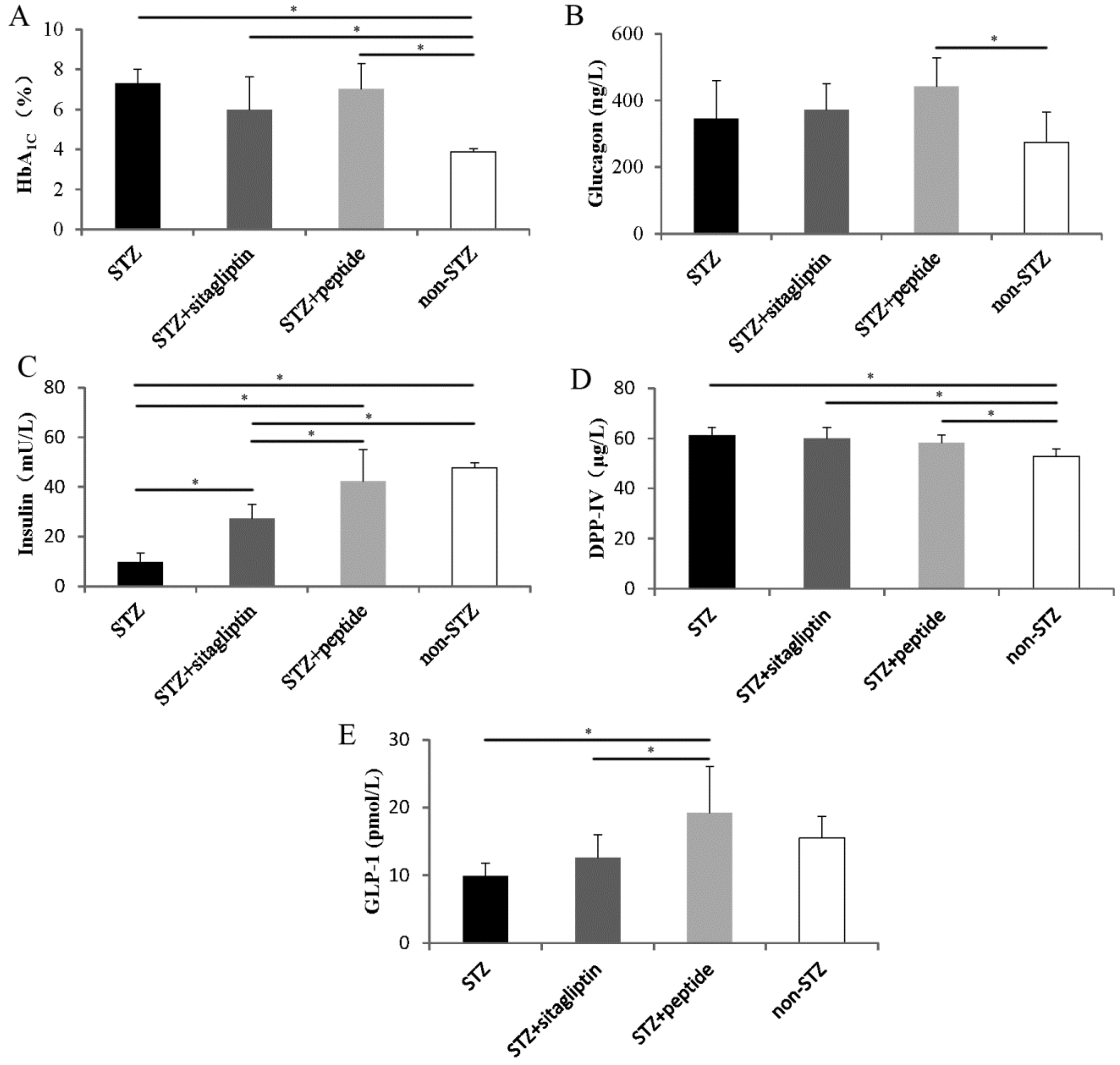
2.3. Effects on Glycated Hemoglobin and Secretion of Glucagon and Insulin
2.4. Effects on Blood Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Concentrations
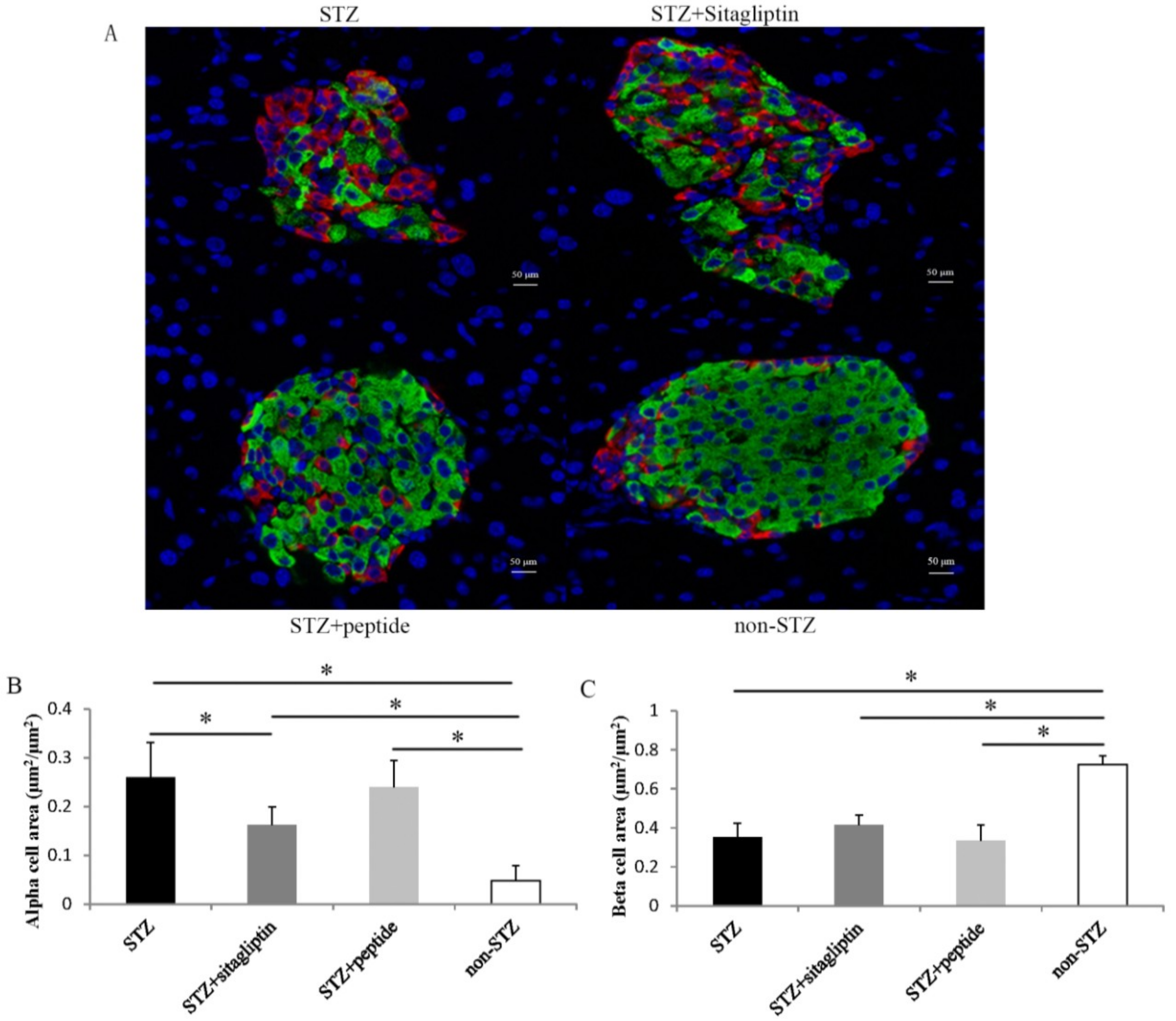
2.5. Effects on Islet Alpha-Cell and Beta-Cell
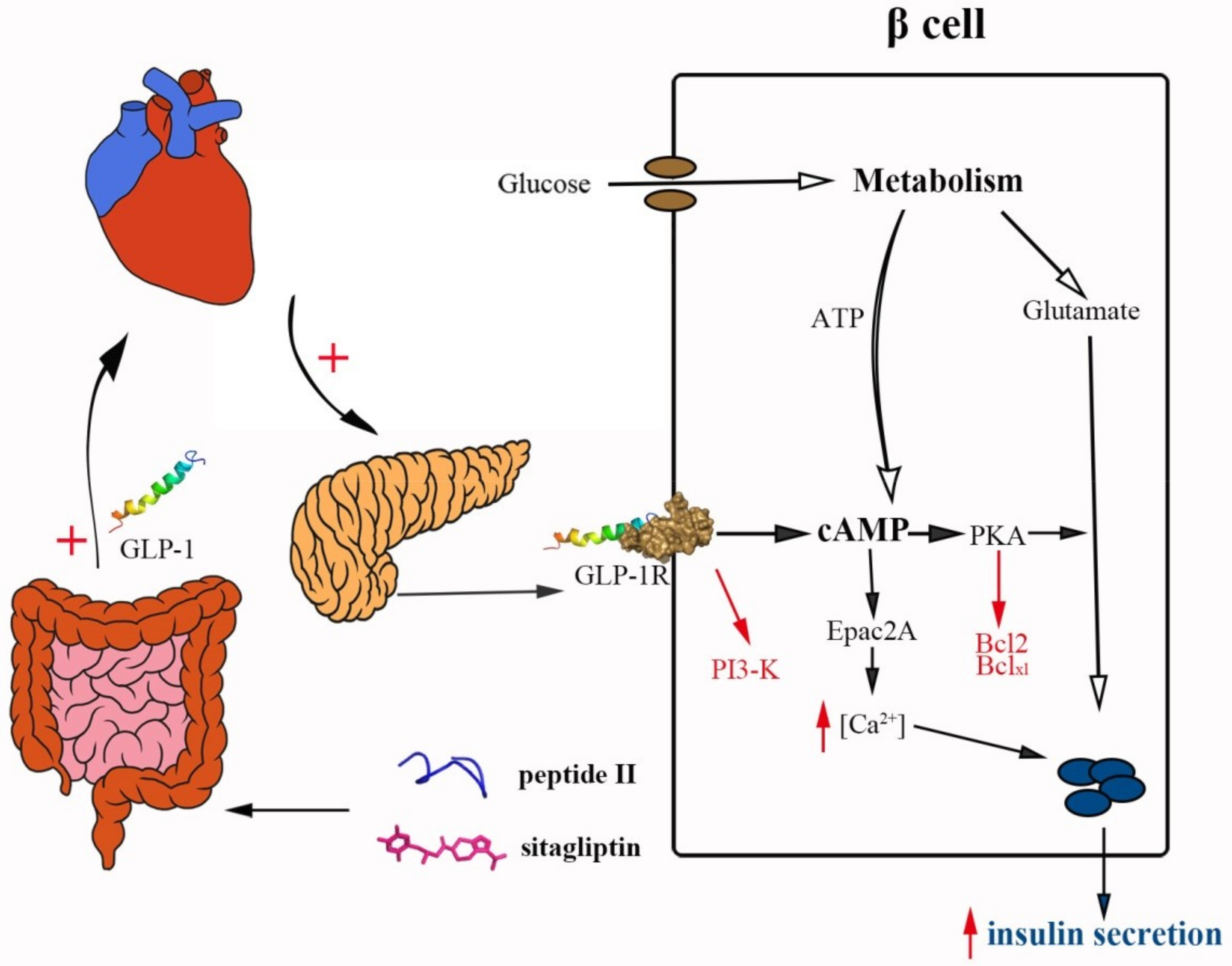
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Materials
4.2. Extraction
4.3. Identification of the Peptide Sequence by LC-MS/MS Analysis
4.4. Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitory Assay and Kinetics Assays
4.5. Docking Analysis of Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV with Peptide II
4.6. Animals
4.7. Research Design and Treatment
4.8. Biochemical Determinations
4.9. Immunohistochemistry and Islet Morphometry
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Longenecker, K.L.; Stewart, K.D.; Madar, D.J.; Jakob, C.G.; Fry, E.H.; Wilk, S.; Lin, C.W.; Ballaron, S.J.; Stashko, M.A.; Lubben, T.H.; et al. Crystal structures of DPP-IV (CD26) from rat kidney exhibit flexible accommodation of peptidase-selective inhibitors. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 7474–7482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Campitelli, J.; Hu, G.; Lin, Y.; Luo, J.; Xue, C. Increase in DPP-IV in the intestine, liver and kidney of the rat treated with high fat diet and streptozotocin. Life Sci. 2007, 81, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilodeau, N.; Fiset, A.; Poirier, G.G.; Fortier, S.; Gingras, M.C.; Lavoie, J.N.; Faure, R.L. Insulin-dependent phosphorylation of DPP IV in liver. Evidence for a role of compartmentalized c-Src. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahren, B.; Landin-Olsson, M.; Jansson, P.A.; Svensson, M.; Holmes, D.; Schweizer, A. Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 reduces glycemia, sustains insulin levels, and reduces glucagon levels in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 2078–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, B.D.; Flatt, P.R.; Bailey, C.J. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP IV) inhibitors: A newly emerging drug class for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2006, 3, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Yan, D.; Sun, J.; Wu, X.; Mulder, H.; Hua, X.; Ma, X. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Stimulates Insulin Secretion via Inhibiting RhoA/ROCK Signaling and Disassembling Glucotoxicity-Induced Stress Fibers. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 4676–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannucci, E.; Ognibene, A.; Cremasco, F.; Bardini, G.; Mencucci, A.; Pierazzuoli, E.; Ciani, S.; Fanelli, A.; Messeri, G.; Rotella, C.M. Glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 and leptin concentrations in obese patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetic Med. 2000, 17, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toft-Nielsen, M.B.; Damholt, M.B.; Madsbad, S.; Hilsted, L.M.; Hughes, T.E.; Michelsen, B.K.; Holst, J.J. Determinants of the impaired secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 in type 2 diabetic patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 3717–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, G.A.; Bergman, A.; Yi, B.; Kipnes, M.; Sitagliptin Study 012 Group. Tolerability and pharmacokinetics of metformin and the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin when co-administered in patients with type 2 diabetes. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2006, 22, 1939–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J.; Nauck, M.A. The incretin system: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2006, 368, 1696–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pospisilik, J.A.; Martin, J.; Doty, T.; Ehses, J.A.; Pamir, N.; Lynn, F.C.; Piteau, S.; Demuth, H.U.; McIntosh, C.H.S.; Pederson, R.A. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor treatment stimulates beta-cell survival and islet neogenesis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes 2003, 52, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, B.; Du, L.; Chen, D.; Wang, C.; Liu, G.; Ran, X. Effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors on beta-cell function and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Fujita, Y.; Honjo, J.; Yanagimachi, T.; Sakagami, H.; Takiyama, Y.; Makino, Y.; Abiko, A.; Kieffer, T.J.; Haneda, M. Reduction of both beta cell death and alpha cell proliferation by dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition in a streptozotocin-induced model of diabetes in mice. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monami, M.; Lamanna, C.; Desideri, C.M.; Mannucci, E. DPP-4 inhibitors and lipids: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Adv. Ther. 2012, 29, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhale, M.; Buse, J.B.; Gray, C.L.; Pate, V.; Marquis, M.A.; Sturmer, T. Dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 inhibitors and pancreatic cancer: A cohort study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.L. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of vildagliptin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2012, 51, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.; Mandal, S.; Tomar, S.K.; Anand, S. Food protein-derived bioactive peptides in management of type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 54, 863–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costante, R.; Stefanucci, A.; Carradori, S.; Novellino, E.; Mollica, A. DPP-4 inhibitors: A patent review (2012–2014). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2015, 25, 209–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jao, C.-L.; Hung, C.-C.; Tung, Y.-S.; Lin, P.-Y.; Chen, M.-C.; Hsu, K.-C. The development of bioactive peptides from dietary proteins as a dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the management of type 2 diabetes. BioMedicine 2015, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Montoya, M.; Hernandez-Ledesma, B.; Mora-Escobedo, R.; Martinez-Villaluenga, C. Bioactive Peptides from Germinated Soybean with Anti-Diabetic Potential by Inhibition of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV, alpha-Amylase, and alpha-Glucosidase Enzymes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wei, X. Sugar compositions, α-glucosidase inhibitory and amylase inhibitory activities of polysaccharides from leaves and flowers of Camellia sinensis obtained by different extraction methods. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Shao, S.; Xu, P.; Chen, H.; Lin-Shiau, S.-Y.; Deng, Y.-T.; Lin, J.-K. Fermentation process enhanced production and bioactivities of oolong tea polysaccharides. Food Res. Int. 2012, 46, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.A.; Polansky, M.M. Tea enhances insulin activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 7182–7186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dembinska-Kiec, A.; Mykkanen, O.; Kiec-Wilk, B.; Mykkanen, H. Antioxidant phytochemicals against type 2 diabetes. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 99 (Suppl. 1), ES109–ES117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Xing, S.; Ho, W.T.; Fu, X.; Zhao, Z.J. Tea contains potent inhibitors of tyrosine phosphatase PTP1B. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 407, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfram, S.; Raederstorff, D.; Preller, M.; Wang, Y.; Teixeira, S.R.; Riegger, C.; Weber, P. Epigallocatechin gallate supplementation alleviates diabetes in rodents. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2512–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Abuin, N.; Martinez-Micaelo, N.; Margalef, M.; Blay, M.; Arola-Arnal, A.; Muguerza, B.; Ardevol, A.; Pinent, M. A grape seed extract increases active glucagon-like peptide-1 levels after an oral glucose load in rats. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 2357–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Abuin, N.; Martinez-Micaelo, N.; Blay, M.; Pujadas, G.; Garcia-Vallve, S.; Pinent, M.; Ardevol, A. Grape Seed-Derived Procyanidins Decrease Dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 Activity and Expression. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9055–9061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraujalyte, V.; Pelvan, E.; Alasalvar, C. Volatile compounds and sensory characteristics of various instant teas produced from black tea. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Li, D.; Luo, X.; Ding, D.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, X. Stepwise Identification of Six Tea (Camellia sinensis (L.)) Categories Based on Catechins, Caffeine, and Theanine Contents Combined with Fisher Discriminant Analysis. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 3242–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, A.M.; Mahanta, P.K. Fermentation characteristics of some Assamica clones and process optimization of black tea manufacturing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 6578–6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafarga, T.; Hayes, M. Bioactive protein hydrolysates in the functional food ingredient industry: Overcoming current challenges. Food Rev. Int. 2017, 33, 217–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, I.M.E.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y. Food-derived dipeptidyl-peptidase IV inhibitors as a potential approach for glycemic regulation—Current knowledge and future research considerations. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 54, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, A.J.; Baxter, N.J.; Khan, M.L.; Moir, A.J.G.; Haslam, E.; Davies, A.P.; Williamson, M.P. Polyphenol/peptide binding and precipitation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 1593–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Liu, F.; Xu, C.; Sun, C.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. Inhibition of the Aggregation of Lactoferrin and (-)-Epigallocatechin Gallate in the Presence of Polyphenols, Oligosaccharides, and Collagen Peptide. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 5035–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joebstl, E.; Fairclough, J.P.A.; Davies, A.P.; Williamson, M.P. Creaming in black tea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 7997–8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Wang, T.Y.; Hung, C.C.; Chen, M.C.; Hsu, K.C. Improvement of glycemic control in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats by Atlantic salmon skin gelatin hydrolysate as the dipeptidyl-peptidase IV inhibitor. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 1887–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uenishi, H.; Kabuki, T.; Seto, Y.; Serizawa, A.; Nakajima, H. Isolation and identification of casein-derived dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (DPP-4)-inhibitory peptide LPQNIPPL from gouda-type cheese and its effect on plasma glucose in rats. Int. Dairy J. 2012, 22, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-L.; Hung, C.-C.; Jao, C.-L.; Tung, Y.-S.; Hsu, K.-C. Porcine skin gelatin hydrolysate as a dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor improves glycemic control in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 11, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, E.S.; Deacon, C.F.; Holst, J.J. Do we know the true mechanism of action of the DPP-4 inhibitors? Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheni, G.; Ogura, M.; Iwasaki, M.; Yokoi, N.; Minami, K.; Nakayama, Y.; Harada, K.; Hastoy, B.; Wu, X.; Takahashi, H.; et al. Glutamate Acts as a Key Signal Linking Glucose Metabolism to Incretin/cAMP Action to Amplify Insulin Secretion. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, J.J. The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 1409–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Nian, C.; Doudet, D.J.; McIntosh, C.H.S. Inhibition of Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV With Sitagliptin (MK0431) Prolongs Islet Graft Survival in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, H.X.; Nourparvar, A.; Zhao, X.N.; Perfetti, R. Glucagon-like peptide-1 inhibits apoptosis of insulin-secreting cells via a cyclic 5′-adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase A- and a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent pathway. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 1444–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrén, B.; Foley, J.E. Improved glucose regulation in type 2 diabetic patients with DPP-4 inhibitors: Focus on alpha and beta cell function and lipid metabolism. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, E.R.; Fu, Z.; Liu, D. Development of a Nongenetic Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiramatsu, H.; Kyono, K.; Higashiyama, Y.; Fukushima, C.; Shima, H.; Sugiyama, S.; Inaka, K.; Yamamoto, A.; Shimizu, R. The structure and function of human dipeptidyl peptidase IV, possessing a unique eight-bladed beta-propeller fold. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 302, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juillerat-Jeanneret, L. Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV and Its Inhibitors: Therapeutics for Type 2 Diabetes and What Else? J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 2197–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajiaghaalipour, F.; Sanusi, J.; Kanthimathi, M.S. Temperature and Time of Steeping Affect the Antioxidant Properties of White, Green, and Black Tea Infusions. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, H246–H254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velarde-Salcedo, A.J.; Barrera-Pacheco, A.; Lara-González, S.; Montero-Morán, G.M.; Díaz-Gois, A.; González de Mejia, E.; Barba de la Rosa, A.P. In vitro inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV by peptides derived from the hydrolysis of amaranth (Amaranthus hypochondriacus L.) proteins. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comeau, S.R.; Gatchell, D.W.; Vajda, S.; Camacho, C.J. ClusPro: An automated docking and discrimination method for the prediction of protein complexes. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comeau, S.R.; Gatchell, D.W.; Vajda, S.; Camacho, C.J. ClusPro: A fully automated algorithm for protein-protein docking. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W96–W99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozakov, D.; Beglov, D.; Bohnuud, T.; Mottarella, S.E.; Xia, B.; Hall, D.R.; Vajda, S. How good is automated protein docking? Proteins-Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2013, 81, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozakov, D.; Brenke, R.; Comeau, S.R.; Vajda, S. PIPER: An FFT-based protein docking program with pairwise potentials. Proteins-Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2006, 65, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Kucukural, A.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER: A unified platform for automated protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yan, R.; Roy, A.; Xu, D.; Poisson, J.; Zhang, Y. The I-TASSER Suite: Protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Methods 2014, 12, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server for protein 3D structure prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, A.C.; Laskowski, R.A.; Thornton, J.M. LIGPLOT—A program to generate schematic diagrams of protein ligand interactions. Protein Eng. 1995, 8, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Membrane (kDa) | Total Phenols (μg/mL) | Inhibition of DPP-IV Activity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 50 | 49.2 ± 0.83 a | 75.5 ± 0.47 a |
| 10 | 42.8 ± 0.59 b | 73.8 ± 0.54 a |
| 5 | 42.5 ± 0.42 b | 75.7 ± 1.00 a |
| 1 | 30.7 ± 0.82 c | 72.7 ± 2.57 a |
| No. | Peptide Sequence | pI/MW a |
|---|---|---|
| I | QTDEYGNPPR | 4.37/1176.21 |
| II | AGFAGDDAPR | 4.21/976.01 |
| III | IDESLR | 4.37/731.80 |
| IV | IQDKEGIPPDQQR | 4.56/1523.67 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Lu, P.; Wang, Y.; Fang, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, X. A Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitory Tea Peptide Improves Pancreatic β-Cell Function and Reduces α-Cell Proliferation in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020322
Lu Y, Lu P, Wang Y, Fang X, Wu J, Wang X. A Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitory Tea Peptide Improves Pancreatic β-Cell Function and Reduces α-Cell Proliferation in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(2):322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020322
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yating, Peng Lu, Yu Wang, Xiaodong Fang, Jianming Wu, and Xiaochang Wang. 2019. "A Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitory Tea Peptide Improves Pancreatic β-Cell Function and Reduces α-Cell Proliferation in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 2: 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020322
APA StyleLu, Y., Lu, P., Wang, Y., Fang, X., Wu, J., & Wang, X. (2019). A Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitory Tea Peptide Improves Pancreatic β-Cell Function and Reduces α-Cell Proliferation in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(2), 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020322