The Role of Nrf2 in the Antioxidant Cellular Response to Medical Ozone Exposure
Abstract
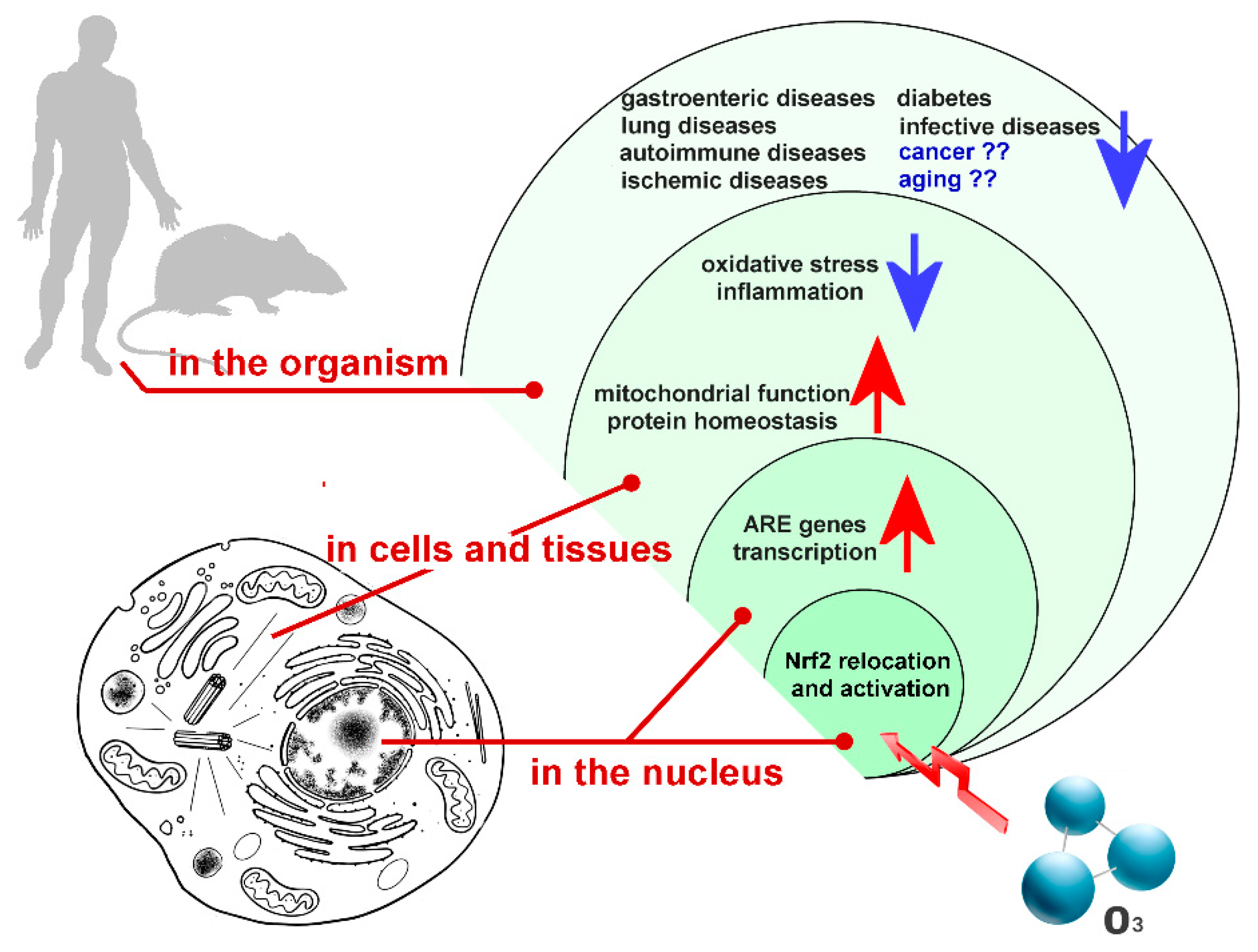
1. Ozone in the Biomedical Field
2. Ozone-Induced Activation of the Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 (Nrf2)
3. Biological Role of Nrf2 and Its Activation by Ozone Treatment
3.1. Nrf2 and Oxidative Stress
3.2. Nrf2 and Proteostasis
3.3. Nrf2 and the Mitochondrial Function
3.4. Nrf2 and Inflammation
3.5. Nrf2 and Adipose Biology
3.6. Nrf2 and Cancer
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Nrf2 | nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| HMOX1 | heme oxygenase 1 |
| CK2 | casein kinase 2 |
| NAD(P)H | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate |
| NQO1 | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate quinone oxidoreductase 1 |
| GST | glutathione-S-transferase |
| HIF-1α | hypoxia inducible factor-1α |
| NFAT | nuclear factor of activated T-cells |
| AP-1 | activated protein-1 |
| CNC | cap‘n’collar basic-region |
| NF-E2 | nuclear factor erythroid 2 |
| Nrf1 | nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 1 |
| Nrf3 | nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 3 |
| BACH1 | BTB domain and CNC homolog 1 |
| BACH2 | BTB domain and CNC homolog 2 |
| Maf | musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma |
| ARE | Antioxidant Responsive Element |
| Keap-1 | Kelch-like ECH associated protein-1 |
| AhR | aryl hydrocarbon receptor |
| C/EBPB | CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein |
| PPARγ | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma |
| RXRA | retinoid X receptor alpha |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| GCL | glutamate cysteine ligase |
| GPX | glutathione peroxidase |
| GSR | glutathione reductase |
| PRDX | peroxiredoxin |
| TXN1 | thioredoxin 1 |
| TXNRD1 | thioredoxin reductase 1 |
| BVR | biliverdin reductase |
| ERCC4 | excision repair cross-complementation group 4 |
| CDKN1A | cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A |
| CTDSP1 | CTD small phosphatase 1 |
| POMP | proteasome maturation protein |
| ATG | autophagy related |
| ULK | unc-51-like autophagy activating kinase |
| SQSTM1 | sequestosome-1 |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| PI3K | phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| Akt | protein-kinase B |
| AMPK | adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase |
| NRF-1 | nuclear respiratory factor-1 |
| TFAM | mitochondrial transcription factor A |
| ALCAR | acetyl-carnitine |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| FGF21 | fibroblast growth factor 21 |
References
- Fuks, K.B.; Woodby, B.; Valacchi, G. Skin damage by tropospheric ozone. Hautarzt 2019, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zu, K.; Shi, L.; Prueitt, R.L.; Liu, X.; Goodman, J.E. Critical review of long-term ozone exposure and asthma development. Inhal. Toxicol. 2018, 30, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snow, S.J.; Henriquez, A.R.; Costa, D.L.; Kodavanti, U.P. Neuroendocrine Regulation of Air Pollution Health Effects: Emerging Insights. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 164, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.J.; Mehta, J.S.; Tong, L. Effects of environment pollution on the ocular surface. Ocul. Surf. 2018, 16, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croze, M.L.; Zimmer, L. Ozone Atmospheric Pollution and Alzheimer’s Disease: From Epidemiological Facts to Molecular Mechanisms. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 62, 503–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leduc, C.; Daneault, C.; Pelletier, É.; Cloutier, J.-N.; Epiney, M.; Lanouette, R. Bleaching efficiency of softwood thermomechanical pulps treated with ozone. Appita. J. 2018, 71, 242–251. [Google Scholar]
- Alresheedi, M.T.; Basu, O.D.; Barbeau, B. Chemical cleaning of ceramic ultrafiltration membranes—Ozone versus conventional cleaning chemicals. Chemosphere 2019, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englezos, V.; Rantsiou, K.; Cravero, F.; Torchio, F.; Giacosa, S.; Río Segade, S.; Gai, G.; Dogliani, E.; Gerbi, V.; Cocolin, L.; et al. Minimizing the environmental impact of cleaning in winemaking industry by using ozone for cleaning-in-place (CIP) of wine bottling machine. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Jin, P.; Wang, X.C.; Zhang, W.; An, W.; Wang, Y. Application of a hybrid gravity-driven membrane filtration and dissolved ozone flotation (MDOF) process for wastewater reclamation and membrane fouling mitigation. J. Environ. Sci.-China 2019, 81, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanacic, E.; Stavrinides, J.; McMartin, D.W. Field-analysis of potable water quality and ozone efficiency in ozone-assisted biological filtration systems for surface water treatment. Water Res. 2016, 104, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, M.; Giovannangeli, F.; Rotunno, S.; Trombetta, C.M.; Montomoli, E. Water and air ozone treatment as an alternative sanitizing technology. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2017, 58, E48–E52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodowska, A.J.; Nowak, A.; Śmigielski, K. Ozone in the food industry: Principles of ozone treatment, mechanisms of action, and applications: An overview. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 2176–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisterna, B.; Boschi, F.; Croce, A.C.; Podda, R.; Zanzoni, S.; Degl’Innocenti, D.; Bernardi, P.; Costanzo, M.; Marzola, P.; Covi, V.; et al. Ozone Treatment of Grapes During Withering for Amarone Wine: A Multimodal Imaging and Spectroscopic Analysis. Microsc. Microanal. 2018, 24, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viebahn-Hansler, R. The Use of Ozone in Medicine, 5th English ed.; ODREI Publishers: Iffezhein, Germany, 2007; pp. 1–170. [Google Scholar]
- Viebahn-Hansler, R.; Leon Fernandez, O.S.; Fahmy, Z. Ozone in medicine: The low dose ozone concept—Guidelines and treatment strategies. Ozone Sci. Engeneering 2012, 34, 408–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, M. Cancer risk of low-level exposure. Science 1996, 271, 1821–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocci, V.A.; Zanardi, I.; Travagli, V. Ozone acting on human blood yields a hormetic dose-response relationship. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocci, V. General mechanism of action of ozone therapy and mechanism in pain treatment. Rev. Soc. Esp. Dolor. 2005, 12, 24–36. [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli, E. Mechanism of action of oxygen ozone therapy in the treatment of disc herniation and low back pain. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2011, 108, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhaes, F.N.; Dotta, L.; Sasse, A.; Teixera, M.J.; Fonoff, E.T. Ozone therapy as a treatment for low back pain secondary to herniated disc: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pain Physician 2012, 15, E115–E129. [Google Scholar]
- Muto, M.; Giurazza, F.; Silva, R.P.; Guarnieri, G. Rational approach, technique and selection criteria treating lumbar disk herniations by oxygen-ozone therapy. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2016, 22, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes de Jesus, C.C.; Dos Santos, F.C.; de Jesus, L.M.O.B.; Monteiro, I.; Sant’Ana, M.S.S.C.; Trevisani, V.F.M. Comparison between intra-articular ozone and placebo in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, S. The role of ozone/oxygen in clindamycin-associated enterocolitis in the Djungarian hamster (Phodopus sungorus sungorus). Lab Anim. 1986, 20, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpendale, M.T.; Freeberg, J.; Griffiss, J.M. Does ozone alleviate AIDS diarrhea? J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 1993, 17, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora Rodríguez, Z.B.; González Alvarez, R.; Guanche, D.; Merino, N.; Hernández Rosales, F.; Menéndez Cepero, S.; Alonso González, Y.; Schulz, S. Antioxidant mechanism is involved in the gastroprotective effects of ozonized sunflower oil in ethanol-induced ulcers in rats. Mediat. Inflamm. 2007, 2007, 65873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altinel, O.; Demirbas, S.; Cakir, E.; Yaman, H.; Ozerhan, I.H.; Duran, E.; Cayci, T.; Akgul, E.O.; Ersoz, N.; Uysal, B.; et al. Comparison of hyperbaric oxygen and medical ozone therapies in a rat model of experimental distal colitis. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 2011, 71, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslaner, A.; Çakır, T.; Tekeli, S.; Avcı, S.; Doğan, U.; Tekeli, F.; Soylu, H.; Akyüz, C.; Koç, S.; Üstünel, İ.; et al. Medical ozone treatment ameliorates the acute distal colitis in rat. Acta Cir. Bras. 2016, 31, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hernández Rosales, F.A.; Calunga Fernández, J.L.; Turrent Figueras, J.; Menéndez Cepero, S.; Montenegro Perdomo, A. Ozone therapy effects on biomarkers and lung function in asthma. Arch. Med. Res. 2005, 36, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaldirim, U.; Uysal, B.; Yuksel, R.; Macit, E.; Eyi, Y.E.; Toygar, M.; Tuncer, S.K.; Ardic, S.; Arziman, I.; Aydin, I.; et al. Ozone therapy ameliorates paraquat-induced lung injury in rats. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2014, 239, 1699–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukgul, A.; Erdogan, S.; Gonenci, R.; Ozan, G. Beneficial effects of nontoxic ozone on H. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 94, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Rodríguez, N.; Llontop, P.; Clavo, B.; Fiuza-Pérez, M.D.; Zerecero, K.; Ayub, A.; Alshehri, K.; Yordi, N.A.; Re, L.; Raad, W.; et al. Ozone Therapy Protects Against Rejection in a Lung Transplantation Model: A New Treatment? Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 104, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Martínez-Sánchez, G.; Al-Dalain, S.M.; Menéndez, S.; Re, L.; Giuliani, A.; Candelario-Jalil, E.; Alvarez, H.; Fernández-Montequín, J.I.; León, O.S. Therapeutic efficacy of ozone in patients with diabetic foot. Eur. J. Pharm. 2005, 523, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpan, A.L.; Toker, H.; Ozer, H. Ozone Therapy Enhances Osseous Healing in Rats With Diabetes With Calvarial Defects: A Morphometric and Immunohistochemical Study. J. Periodontol. 2016, 87, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güçlü, A.; Erken, H.A.; Erken, G.; Dodurga, Y.; Yay, A.; Özçoban, Ö.; Şimşek, H.; Akçılar, A.; Koçak, F.E. The effects of ozone therapy on caspase pathways, TNF-α, and HIF-1α in diabetic nephropathy. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2016, 48, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosul, M.V.; Patskan, B.M. Ozone therapy effectiveness in patients with ulcerous lesions due to diabetes mellitus. Wiad. Lek. 2016, 69, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, T.Y.; Yan, W.; Lou, J.; Chen, X.Y. Effect of ozone on vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and related inflammatory cytokines in rats with diabetic retinopathy. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, M.; Bozorgi, M.; Hosseine, M.S.; Khalili, N.; Jonaidi-Jafari, N. Health-related quality of life in patients with chronic wounds before and after treatment with medical ozone. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018, 97, e12505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, O.S.; Menéndez, S.; Merino, N.; Castillo, R.; Sam, S.; Pérez, L.; Cruz, E.; Bocci, V. Ozone oxidative preconditioning: A protection against cellular damage by free radicals. Mediat. Inflamm. 1998, 7, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajamieh, H.H.; Menéndez, S.; Martínez-Sánchez, G.; Candelario-Jalil, E.; Re, L.; Giuliani, A.; Fernández, O.S. Effects of ozone oxidative preconditioning on nitric oxide generation and cellular redox balance in a rat model of hepatic ischaemia-reperfusion. Liver Int. 2004, 24, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajamieh, H.H.; Berlanga, J.; Merino, N.; Sánchez, G.M.; Carmona, A.M.; Cepero, S.M.; Giuliani, A.; Re, L.; León, O.S. Role of protein synthesis in the protection conferred by ozone-oxidative-preconditioning in hepatic ischaemia/reperfusion. Transpl. Int. 2005, 18, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haj, B.; Sukhotnik, I.; Shaoul, R.; Pollak, Y.; Coran, A.G.; Bitterman, A.; Matter, I. Effect of ozone on intestinal recovery following intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2014, 30, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, A.; Peker, K.; Gursul, C.; Sayar, I.; Firat, D.; Yilmaz, I.; Demiryilmaz, I. The effect of ozone and naringin on intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury in an experimental model. Int. J. Surg. 2015, 21, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancak, E.B.; Turkön, H.; Çukur, S.; Erimsah, S.; Akbas, A.; Gulpinar, M.T.; Toman, H.; Sahin, H.; Uzun, M. Major Ozonated Autohemotherapy Preconditioning Ameliorates Kidney Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Inflammation 2016, 39, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, F.; Kao, M.S.; Lee, S.C.; Hagar, W.L.; Sweet, W.E. Ozone selectively inhibits growth of human cancer cells. Science 1980, 209, 931–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirelli, U.; Cirrito, C.; Pavanello, M.; Del Pup, L.; Lleshi, A.; Berretta, M. Oxygen-ozone therapy as support and palliative therapy in 50 cancer patients with fatigue—A short report. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 22, 8030–8033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luongo, M.; Brigida, A.L.; Mascolo, L.; Gaudino, G. Possible Therapeutic Effects of Ozone Mixture on Hypoxia in Tumor Development. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, K.H.; Latino, J.; Gavalchin, J.; Poiesz, B.J. Inactivation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by ozone in vitro. Blood 1991, 78, 1882–1890. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, W.; Tang, H.; Wu, M.; Liao, Y.; Li, K.; Li, L.; Xu, X. Ozone oil promotes wound healing by increasing the migration of fibroblasts via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Zeng, Q.; Xiang, Y.; Gao, L.; Huang, J.; Wu, K.; Lu, J. The antibacterial effect of topical ozone on the treatment of MRSA skin infection. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 2449–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, L.E. Biological assessment of ozone therapy on experimental oral candidiasis in immunosuppressed rats. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2018, 15, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarpazhooh, A.; Limeback, H. The application of ozone in dentistry: A systematic review of literature. J. Dent. 2008, 36, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.; Mansi, B. Ozone therapy in periodontics. J. Med. Life 2012, 5, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Srikanth, A.; Sathish, M.; Sri Harsha, A.V. Application of ozone in the treatment of periodontal disease. J. Pharm. Bioallied. Sci. 2013, 5, S89–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, I.; Moger, G.; Kumar, N.A. Evaluation of effect of topical ozone therapy on salivary Candidal carriage in oral candidiasis. Indian. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 26, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Omiri, M.K.; Abul Hassan, R.S.; AlZarea, B.K.; Lynch, E. Comparison of dental bleaching effects of ozone and hydrogen peroxide: An ex vivo study. Am. J. Dent. 2016, 29, 251–254. [Google Scholar]
- Isler, S.C.; Unsal, B.; Soysal, F.; Ozcan, G.; Peker, E.; Karaca, I.R. The effects of ozone therapy as an adjunct to the surgical treatment of peri-implantitis. J. Periodontal. Implant. Sci. 2018, 48, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.Y.; Song, K.S.; Park, G.H.; Chang, S.H.; Kim, H.W.; Park, J.H.; Jin, H.; Eu, K.J.; Cho, H.S.; Kang, G.; et al. B6C3F1 mice exposed to ozone with 4-(N-methyl-N-nitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone and/or dibutyl phthalate showed toxicities through alterations of NF-kappaB, AP-1, Nrf2, and osteopontin. J. Vet. Sci. 2004, 5, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.Y.; Gladwell, W.; Yamamoto, M.; Kleeberger, S.R. Exacerbated airway toxicity of environmental oxidant ozone in mice deficient in Nrf2. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 254069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegman, C.H.; Li, F.; Clarke, C.J.; Jazrawi, E.; Kirkham, P.; Barnes, P.J.; Adcock, I.M.; Chung, K.F. A comprehensive analysis of oxidative stress in the ozone-induced lung inflammation mouse model. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2014, 126, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, W.O.; Ledbetter, A.D.; Schladweiler, M.C.; Kodavanti, U.P. Lung transcriptional profiling: Insights into the mechanisms of ozone-induced pulmonary injury in Wistar Kyoto rats. Inhal. Toxicol. 2015, 27, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Jin, Y.; An, Z.; Liu, Y.; Samet, J.M.; Wu, W. Inflammatory cell signaling following exposures to particulate matter and ozone. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1860, 2826–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Allen, K.; Rao, X.; Ying, Z.; Braunstein, Z.; Kankanala, S.R.; Xia, C.; Wang, X.; Bramble, L.A.; Wagner, J.G.; et al. Repeated ozone exposure exacerbates insulin resistance and activates innate immune response in genetically susceptible mice. Inhal. Toxicol. 2016, 28, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromberg, P.A. Mechanisms of the acute effects of inhaled ozone in humans. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1860, 2771–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traboulsi, H.; Guerrina, N.; Iu, M.; Maysinger, D.; Ariya, P.; Baglole, C.J. Inhaled Pollutants: The Molecular Scene behind Respiratory and Systemic Diseases Associated with Ultrafine Particulate Matter. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.G.; Lee, P.H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, C.S.; Jang, A.S. Impact of ozone on claudins and tight junctions in the lungs. Environ. Toxicol. 2018, 33, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, V.; Valverde, M.; Rojas, E. Effects of atmospheric pollutants on the Nrf2 survival pathway. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2010, 17, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecorelli, A.; Bocci, V.; Acquaviva, A.; Belmonte, G.; Gardi, C.; Virgili, F.; Ciccoli, L.; Valacchi, G. NRF2 activation is involved in ozonated human serum upregulation of HO-1 in endothelial cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2013, 267, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, L.; Martínez-Sánchez, G.; Bordicchia, M.; Malcangi, G.; Pocognoli, A.; Morales-Segura, M.A.; Rothchild, J.; Rojas, A. Is ozone pre-conditioning effect linked to Nrf2/EpRE activation pathway in vivo? A preliminary result. Eur. J. Pharm. 2014, 742, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valacchi, G.; Sticozzi, C.; Zanardi, I.; Belmonte, G.; Cervellati, F.; Bocci, V.; Travagli, V. Ozone mediators effect on “in vitro” scratch wound closure. Free Radic. Res. 2016, 50, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, T.; Weng, X. Ozone therapy could attenuate tubulointerstitial injury in adenine-induced CKD rats by mediating Nrf2 and NF-κB. Iran. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2016, 19, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado-Roche, L.; Riera-Romo, M.; Mesta, F.; Hernández-Matos, Y.; Barrios, J.M.; Martínez-Sánchez, G.; Al-Dalaien, S.M. Medical ozone promotes Nrf2 phosphorylation reducing oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory cytokines in multiple sclerosis patients. Eur. J. Pharm. 2017, 811, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siniscalco, D.; Trotta, M.C.; Brigida, A.L.; Maisto, R.; Luongo, M.; Ferraraccio, F.; D’Amico, M.; Di Filippo, C. Intraperitoneal Administration of Oxygen/Ozone to Rats Reduces the Pancreatic Damage Induced by Streptozotocin. Biology 2018, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Xu, Y.; Li, D.; Zhu, E.; Deng, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Liu, H. Ozone protects rat heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury: A role for oxidative preconditioning in attenuating mitochondrial injury. Biomed. Pharm. 2017, 88, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, A.; Meng, W.; Wang, T.; Li, D.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H. Ozone protects the rat lung from ischemia-reperfusion injury by attenuating NLRP3-mediated inflammation, enhancing Nrf2 antioxidant activity and inhibiting apoptosis. Eur. J. Pharm. 2018, 835, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braidy, N.; Izadi, M.; Sureda, A.; Jonaidi-Jafari, N.; Banki, A.; Nabavi, S.F.; Nabavi, S.M. Therapeutic relevance of ozone therapy in degenerative diseases: Focus on diabetes and spinal pain. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 2705–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagai, M.; Bocci, V. Mechanisms of Action Involved in Ozone Therapy: Is healing induced via a mild oxidative stress? Med. Gas. Res. 2011, 1, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocci, V. How a calculated oxidative stress can yield multiple therapeutic effects. Free Radic. Res. 2012, 46, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocci, V.; Valacchi, G. Nrf2 activation as target to implement therapeutic treatments. Front. Chem. 2015, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moi, P.; Chan, K.; Asunis, I.; Cao, A.; Kan, Y.W. Isolation of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a NF-E2-like basic leucine zipper transcriptional activator that binds to the tandem NF-E2/AP1 repeat of the beta-globin locus control region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 9926–9930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, K.; Chiba, T.; Takahashi, S.; Ishii, T.; Igarashi, K.; Katoh, Y.; Oyake, T.; Hayashi, N.; Satoh, K.; Hatayama, I.; et al. An Nrf2/small Maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase II detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 236, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushmore, T.H.; Pickett, C.B. Transcriptional regulation of the rat glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit gene. Characterization of a xenobiotic-responsive element controlling inducible expression by phenolic antioxidants. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 14648–14653. [Google Scholar]
- Rushmore, T.H.; Morton, M.R.; Pickett, C.B. The antioxidant responsive element. Activation by oxidative stress and identification of the DNA consensus sequence required for functional activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 11632–11639. [Google Scholar]
- Itoh, K.; Wakabayashi, N.; Katoh, Y.; Ishii, T.; Igarashi, K.; Engel, J.D.; Yamamoto, M. Keap1 represses nuclear activation of antioxidant responsive elements by Nrf2 through binding to the amino-terminal Neh2 domain. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, M.; Xiong, Y. BTB protein Keap1 targets antioxidant transcription factor Nrf2 for ubiquitination by the Cullin 3-Roc1 ligase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiè, M.; Costanzo, M.; Nodari, A.; Boschi, F.; Calderan, L.; Mannucci, S.; Covi, V.; Tabaracci, G.; Malatesta, M. Mild ozonisation activates antioxidant cell response by the Keap1/Nrf2 dependent pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 124, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hybertson, B.M.; Gao, B.; Bose, S.K.; McCord, J.M. Oxidative stress in health and disease: The therapeutic potential of Nrf2 activation. Mol. Aspects Med. 2011, 32, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.D.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T. The Nrf2 regulatory network provides an interface between redox and intermediary metabolism. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, N.; Shin, S.; Slocum, S.L.; Agoston, E.S.; Wakabayashi, J.; Kwak, M.K.; Misra, V.; Biswal, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W. Regulation of notch1 signaling by nrf2: Implications for tissue regeneration. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Wakabayashi, N.; Misra, V.; Biswal, S.; Lee, G.H.; Agoston, E.S.; Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W. NRF2 modulates aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling: Influence on adipogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 7188–7197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Xue, P.; Bai, Y.; Liu, D.; Woods, C.G.; Yarborough, K.; Fu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, G.; Collins, S.; et al. Nuclear factor erythroid-derived factor 2-related factor 2 regulates transcription of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β during adipogenesis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorley, B.N.; Campbell, M.R.; Wang, X.; Karaca, M.; Sambandan, D.; Bangura, F.; Xue, P.; Pi, J.; Kleeberger, S.R.; Bell, D.A. Identification of novel NRF2-regulated genes by ChIP-Seq: Influence on retinoid X receptor alpha. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 7416–7429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulliam, D.A.; Deepa, S.S.; Liu, Y.; Hill, S.; Lin, A.L.; Bhattacharya, A.; Shi, Y.; Sloane, L.; Viscomi, C.; Zeviani, M.; et al. Complex IV-deficient Surf1(-/-) mice initiate mitochondrial stress responses. Biochem. J. 2014, 462, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paupe, V.; Dassa, E.P.; Goncalves, S.; Auchère, F.; Lönn, M.; Holmgren, A.; Rustin, P. Impaired nuclear Nrf2 translocation undermines the oxidative stress response in Friedreich ataxia. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Schoenfeld, R.A.; Hayashi, G.; Napoli, E.; Akiyama, T.; Iodi Carstens, M.; Carstens, E.E.; Pook, M.A.; Cortopassi, G.A. Frataxin deficiency leads to defects in expression of antioxidants and Nrf2 expression in dorsal root ganglia of the Friedreich’s ataxia YG8R mouse model. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2013, 19, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Oria, V.; Petrini, S.; Travaglini, L.; Priori, C.; Piermarini, E.; Petrillo, S.; Carletti, B.; Bertini, E.; Piemonte, F. Frataxin deficiency leads to reduced expression and impaired translocation of NF-E2-related factor (Nrf2) in cultured motor neurons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 7853–7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commoner, B.; Townsend, J.; Pake, G.E. Free radicals in biological materials. Nature 1954, 174, 689–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, J.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y.; Kładna, A.; Bowser, J.E. Oxidative stress in biological systems and its relation with pathophysiological functions: The effect of physical activity on cellular redox homeostasis. Free Radic. Res. 2019, 53, 497–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanito, M.; Agbaga, M.P.; Anderson, R.E. Upregulation of thioredoxin system via Nrf2-antioxidant responsive element pathway in adaptive-retinal neuroprotection in vivo and in vitro. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 42, 1838–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, A.K.; McMahon, M.; Plummer, S.M.; Higgins, L.G.; Penning, T.M.; Igarashi, K.; Hayes, J.D. Characterization of the cancer chemopreventive NRF2-dependent gene battery in human keratinocytes: Demonstration that the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway, and not the BACH1-NRF2 pathway, controls cytoprotection against electrophiles as well as redox-cycling compounds. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyeman, A.S.; Chaerkady, R.; Shaw, P.G.; Davidson, N.E.; Visvanathan, K.; Pandey, A.; Kensler, T.W. Transcriptomic and proteomic profiling of KEAP1 disrupted and sulforaphane-treated human breast epithelial cells reveals common expression profiles. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 132, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scassellati, C.; Costanzo, M.; Cisterna, B.; Nodari, A.; Galiè, M.; Cattaneo, A.; Covi, V.; Tabaracci, G.; Bonvicini, C.; Malatesta, M. Effects of mild ozonisation on gene expression and nuclear domains organization in vitro. Toxicol. Vitr. 2017, 44, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, T.P.; Vendruscolo, M.; Dobson, C.M. The amyloid state and its association with protein misfolding diseases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 15, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, M.K.; Wakabayashi, N.; Greenlaw, J.L.; Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W. Antioxidants enhance mammalian proteasome expression through the Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 8786–8794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapeta, S.; Chondrogianni, N.; Gonos, E.S. Nuclear erythroid factor 2-mediated proteasome activation delays senescence in human fibroblasts. J. Biol Chem 2010, 285, 8171–8184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Wang, Y.; Kim, H.S.; Lalli, M.A.; Kosik, K.S. Nrf2, a regulator of the proteasome, controls self-renewal and pluripotency in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 2616–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajares, M.; Jiménez-Moreno, N.; García-Yagüe, Á.; Escoll, M.; de Ceballos, M.L.; Van Leuven, F.; Rábano, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Rojo, A.I.; Cuadrado, A. Transcription factor NFE2L2/NRF2 is a regulator of macroautophagy genes. Autophagy 2016, 12, 1902–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendavit, G.; Aboulkassim, T.; Hilmi, K.; Shah, S.; Batist, G. Nrf2 Transcription Factor Can Directly Regulate mTOR: Linking Cytoprotective Gene Expression to a Major Metabolic Regulator That Generates Redox Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 25476–25488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Lin, X.; Wang, J.; Xie, J.; Sun, T.; Fu, Z. Ozone induces autophagy in rat chondrocytes stimulated with IL-1β through the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. J. Pain Res. 2018, 11, 3003–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, N.S. Evolution of Mitochondria as Signaling Organelles. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 204–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardamone, M.D.; Tanasa, B.; Cederquist, C.T.; Huang, J.; Mahdaviani, K.; Li, W.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Liesa, M.; Perissi, V. Mitochondrial Retrograde Signaling in Mammals Is Mediated by the Transcriptional Cofactor GPS2 via Direct Mitochondria-to-Nucleus Translocation. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirós, P.M.; Prado, M.A.; Zamboni, N.; D’Amico, D.; Williams, R.W.; Finley, D.; Gygi, S.P.; Auwerx, J. Multi-omics analysis identifies ATF4 as a key regulator of the mitochondrial stress response in mammals. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 2027–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Finkel, T. Mitohormesis. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zid, B.M.; Rogers, A.N.; Katewa, S.D.; Vargas, M.A.; Kolipinski, M.C.; Lu, T.A.; Benzer, S.; Kapahi, P. 4E-BP extends lifespan upon dietary restriction by enhancing mitochondrial activity in Drosophila. Cell 2009, 139, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linford, N.J.; Beyer, R.P.; Gollahon, K.; Krajcik, R.A.; Malloy, V.L.; Demas, V.; Burmer, G.C.; Rabinovitch, P.S. Transcriptional response to aging and caloric restriction in heart and adipose tissue. Aging Cell 2007, 6, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Youle, R.J.; Finkel, T. The Mitochondrial Basis of Aging. Mol. Cell 2016, 61, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, D.C. A mitochondrial bioenergetic etiology of disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piantadosi, C.A.; Carraway, M.S.; Babiker, A.; Suliman, H.B. Heme oxygenase-1 regulates cardiac mitochondrial biogenesis via Nrf2-mediated transcriptional control of nuclear respiratory factor-1. Circ. Res. 2008, 103, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merry, T.L.; Ristow, M. Nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 2 (NFE2L2, Nrf2) mediates exercise-induced mitochondrial biogenesis and the anti-oxidant response in mice. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 5195–5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmström, K.M.; Baird, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hargreaves, I.; Chalasani, A.; Land, J.M.; Stanyer, L.; Yamamoto, M.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Abramov, A.Y. Nrf2 impacts cellular bioenergetics by controlling substrate availability for mitochondrial respiration. Biol. Open 2013, 2, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovac, S.; Angelova, P.R.; Holmström, K.M.; Zhang, Y.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Abramov, A.Y. Nrf2 regulates ROS production by mitochondria and NADPH oxidase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, K.; Mimura, J.; Itoh, K.; Satoh, T.; Shimojo, Y.; Kitajima, C.; Maruyama, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Shirasawa, T. Role of Nrf2 and p62/ZIP in the neurite outgrowth by carnosic acid in PC12h cells. J. Biochem. 2010, 147, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibenhener, M.L.; Du, Y.; Diaz-Meco, M.T.; Moscat, J.; Wooten, M.C.; Wooten, M.W. A role for sequestosome 1/p62 in mitochondrial dynamics, import and genome integrity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hota, K.B.; Hota, S.K.; Chaurasia, O.P.; Singh, S.B. Acetyl-L-carnitine-mediated neuroprotection during hypoxia is attributed to ERK1/2-Nrf2-regulated mitochondrial biosynthesis. Hippocampus 2012, 22, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Joe, Y.; Zheng, M.; Kim, H.J.; Yu, J.K.; Cho, G.J.; Chang, K.C.; Kim, H.K.; Han, J.; Ryter, S.W.; et al. Resveratrol induces hepatic mitochondrial biogenesis through the sequential activation of nitric oxide and carbon monoxide production. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 2589–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, M.; Cisterna, B.; Vella, A.; Cestari, T.; Covi, V.; Tabaracci, G.; Malatesta, M. Low ozone concentrations stimulate cytoskeletal organization, mitochondrial activity and nuclear transcription. Eur. J. Histochem. 2015, 59, 2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, S.; You, Y.; Meng, M.; Zheng, Z.; Dong, M.; Lin, J.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, X.; et al. Brown Adipose Tissue Transplantation Reverses Obesity in Ob/Ob Mice. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 2461–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theofilopoulos, A.N.; Kono, D.H.; Baccala, R. The multiple pathways to autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, C.; Campisi, J. Chronic inflammation (inflammaging) and its potential contribution to age-associated diseases. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, S4–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, C.; Garagnani, P.; Morsiani, C.; Conte, M.; Santoro, A.; Grignolio, A.; Monti, D.; Capri, M.; Salvioli, S. The Continuum of Aging and Age-Related Diseases: Common Mechanisms but Different Rates. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2018, 5, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Ametepe, E.S.; Haribabu, N.; Agbayani, G.; Krishnan, L.; Blais, A.; Sad, S. Inhibition of ROS and upregulation of inflammatory cytokines by FoxO3a promotes survival against Salmonella typhimurium. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, E.H.; Suzuki, T.; Funayama, R.; Nagashima, T.; Hayashi, M.; Sekine, H.; Tanaka, N.; Moriguchi, T.; Motohashi, H.; Nakayama, K.; et al. Nrf2 suppresses macrophage inflammatory response by blocking proinflammatory cytokine transcription. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushworth, S.A.; Zaitseva, L.; Murray, M.Y.; Shah, N.M.; Bowles, K.M.; MacEwan, D.J. The high Nrf2 expression in human acute myeloid leukemia is driven by NF-κB and underlies its chemo-resistance. Blood 2012, 120, 5188–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimmulappa, R.K.; Lee, H.; Rangasamy, T.; Reddy, S.P.; Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W.; Biswal, S. Nrf2 is a critical regulator of the innate immune response and survival during experimental sepsis. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, T.L.; Michishita, E.; Adler, A.S.; Damian, M.; Berber, E.; Lin, M.; McCord, R.A.; Ongaigui, K.C.; Boxer, L.D.; Chang, H.Y.; et al. SIRT6 links histone H3 lysine 9 deacetylation to NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression and organismal life span. Cell 2009, 136, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, T.L.; Rapicavoli, N.A.; Wu, A.R.; Qu, K.; Quake, S.R.; Chang, H.Y. Dynamic chromatin localization of Sirt6 shapes stress- and aging-related transcriptional networks. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schug, T.T.; Xu, Q.; Gao, H.; Peres-da-Silva, A.; Draper, D.W.; Fessler, M.B.; Purushotham, A.; Li, X. Myeloid deletion of SIRT1 induces inflammatory signaling in response to environmental stress. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 4712–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, K.S.; Chan, J.Y. Emerging role of Nrf2 in adipocytes and adipose biology. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, S.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y.H.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.G.; Zheng, Y.; Cai, L. The role of the Nrf2/Keap1 pathway in obesity and metabolic syndrome. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2015, 16, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, J.; Leung, L.; Xue, P.; Wang, W.; Hou, Y.; Liu, D.; Yehuda-Shnaidman, E.; Lee, C.; Lau, J.; Kurtz, T.W.; et al. Deficiency in the nuclear factor E2-related factor-2 transcription factor results in impaired adipogenesis and protects against diet-induced obesity. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 9292–9300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vomhof-DeKrey, E.E.; Picklo, M.J. NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 activity reduces hypertrophy in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 53, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vanella, L.; Sanford, C.; Kim, D.H.; Abraham, N.G.; Ebraheim, N. Oxidative stress and heme oxygenase-1 regulated human mesenchymal stem cells differentiation. Int. J. Hypertens. 2012, 2012, 890671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.R.; Lee, G.Y.; Yu, H.; Maeng, H.J.; Oh, T.J.; Kim, K.M.; Moon, J.H.; Lim, S.; Jang, H.C.; Choi, S.H. Suppression of Nrf2 attenuates adipogenesis and decreases FGF21 expression through PPAR gamma in 3T3-L1 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 497, 1149–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, M.; Boschi, F.; Carton, F.; Conti, G.; Covi, V.; Tabaracci, G.; Sbarbati, A.; Malatesta, M. Low ozone concentrations promote adipogenesis in human adipose-derived adult stem cells. Eur. J. Histochem. 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisterna, B.; Costanzo, M.; Boschi, F.; Carton, F.; Covi, V.; Tabaracci, G.; Malatesta, M. Exploring the potential of mild ozonisation in adipose tissue regeneration and differentiation. Eur. J. Histochem. 2019, 63, 9–10. [Google Scholar]
- Rojo de la Vega, M.; Chapman, E.; Zhang, D.D. NRF2 and the Hallmarks of Cancer. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegon, S.; Columbano, A.; Giordano, S. The Dual Roles of NRF2 in Cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 578–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNicola, G.M.; Karreth, F.A.; Humpton, T.J.; Gopinathan, A.; Wei, C.; Frese, K.; Mangal, D.; Yu, K.H.; Yeo, C.J.; Calhoun, E.S.; et al. Oncogene-induced Nrf2 transcription promotes ROS detoxification and tumorigenesis. Nature 2011, 475, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuishi, Y.; Taguchi, K.; Kawatani, Y.; Shibata, T.; Nukiwa, T.; Aburatani, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Motohashi, H. Nrf2 redirects glucose and glutamine into anabolic pathways in metabolic reprogramming. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chio, I.I.; Jafarnejad, S.M.; Ponz-Sarvise, M.; Park, Y.; Rivera, K.; Palm, W.; Wilson, J.; Sangar, V.; Hao, Y.; Öhlund, D.; et al. NRF2 Promotes Tumor Maintenance by Modulating mRNA Translation in Pancreatic Cancer. Cell 2016, 166, 963–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojo, T.; Maishi, N.; Towfik, A.M.; Akiyama, K.; Ohga, N.; Shindoh, M.; Hida, Y.; Minowa, K.; Fujisawa, T.; Hida, K. ROS enhance angiogenic properties via regulation of NRF2 in tumor endothelial cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 45484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kang, K.A.; Hyun, J.W. Oxidative Stress, Nrf2, and Epigenetic Modification Contribute to Anticancer Drug Resistance. Toxicol. Res. 2017, 33, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrucci, M.T.; Gallucci, C.; Agrillo, A.; Mustazza, M.C.; Foà, R. Role of ozone therapy in the treatment of osteonecrosis of the jaws in multiple myeloma patients. Haematologica 2007, 92, 1289–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavo, B.; Santana-Rodriguez, N.; Llontop, P.; Gutierrez, D.; Ceballos, D.; Méndez, C.; Rovira, G.; Suarez, G.; Rey-Baltar, D.; Garcia-Cabrera, L.; et al. Ozone Therapy in the Management of Persistent Radiation-Induced Rectal Bleeding in Prostate Cancer Patients. Evid Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2015, 2015, 480369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motohashi, H.; Yamamoto, M. Nrf2-Keap1 defines a physiologically important stress response mechanism. Trends Mol. Med. 2004, 10, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado, A.; Rojo, A.I.; Wells, G.; Hayes, J.D.; Cousin, S.P.; Rumsey, W.L.; Attucks, O.C.; Franklin, S.; Levonen, A.L.; Kensler, T.W.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of the NRF2 and KEAP1 partnership in chronic diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 295–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado, A.; Manda, G.; Hassan, A.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Barbas, C.; Daiber, A.; Ghezzi, P.; León, R.; López, M.G.; Oliva, B.; et al. Transcription Factor NRF2 as a Therapeutic Target for Chronic Diseases: A Systems Medicine Approach. Pharm. Rev. 2018, 70, 348–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galiè, M.; Covi, V.; Tabaracci, G.; Malatesta, M. The Role of Nrf2 in the Antioxidant Cellular Response to Medical Ozone Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20164009
Galiè M, Covi V, Tabaracci G, Malatesta M. The Role of Nrf2 in the Antioxidant Cellular Response to Medical Ozone Exposure. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(16):4009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20164009
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaliè, Mirco, Viviana Covi, Gabriele Tabaracci, and Manuela Malatesta. 2019. "The Role of Nrf2 in the Antioxidant Cellular Response to Medical Ozone Exposure" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 16: 4009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20164009
APA StyleGaliè, M., Covi, V., Tabaracci, G., & Malatesta, M. (2019). The Role of Nrf2 in the Antioxidant Cellular Response to Medical Ozone Exposure. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(16), 4009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20164009





