In Vitro Entero-Capillary Barrier Exhibits Altered Inflammatory and Exosomal Communication Pattern after Exposure to Silica Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
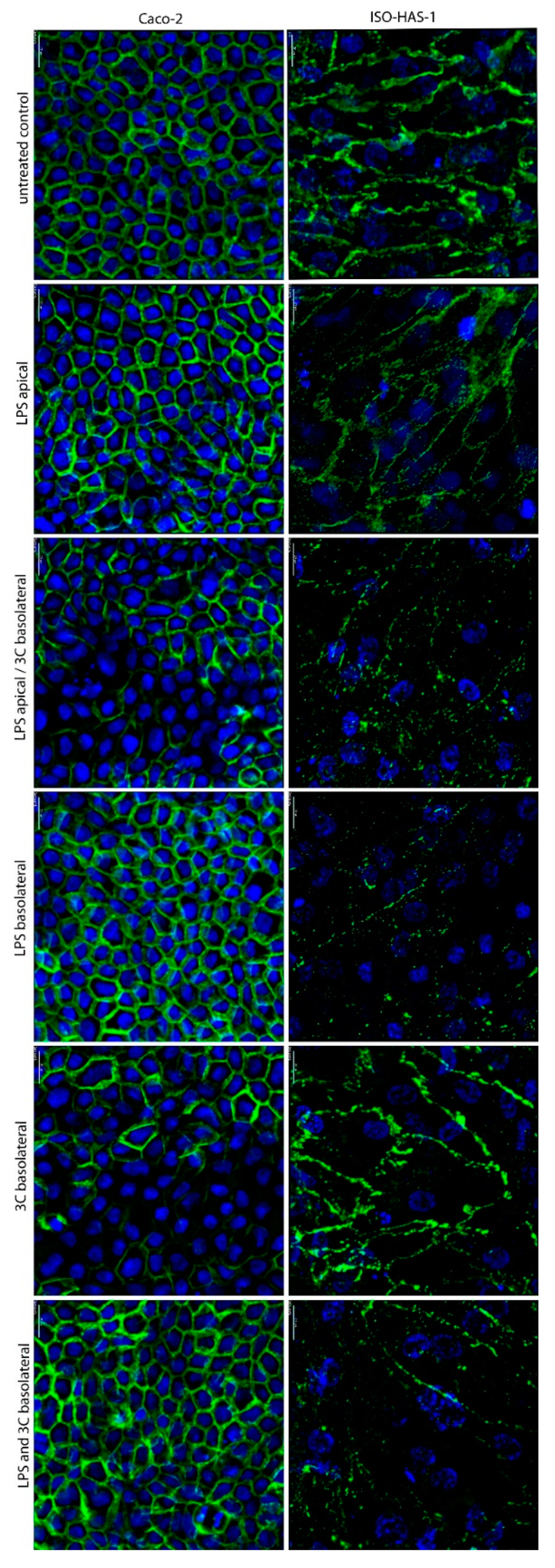
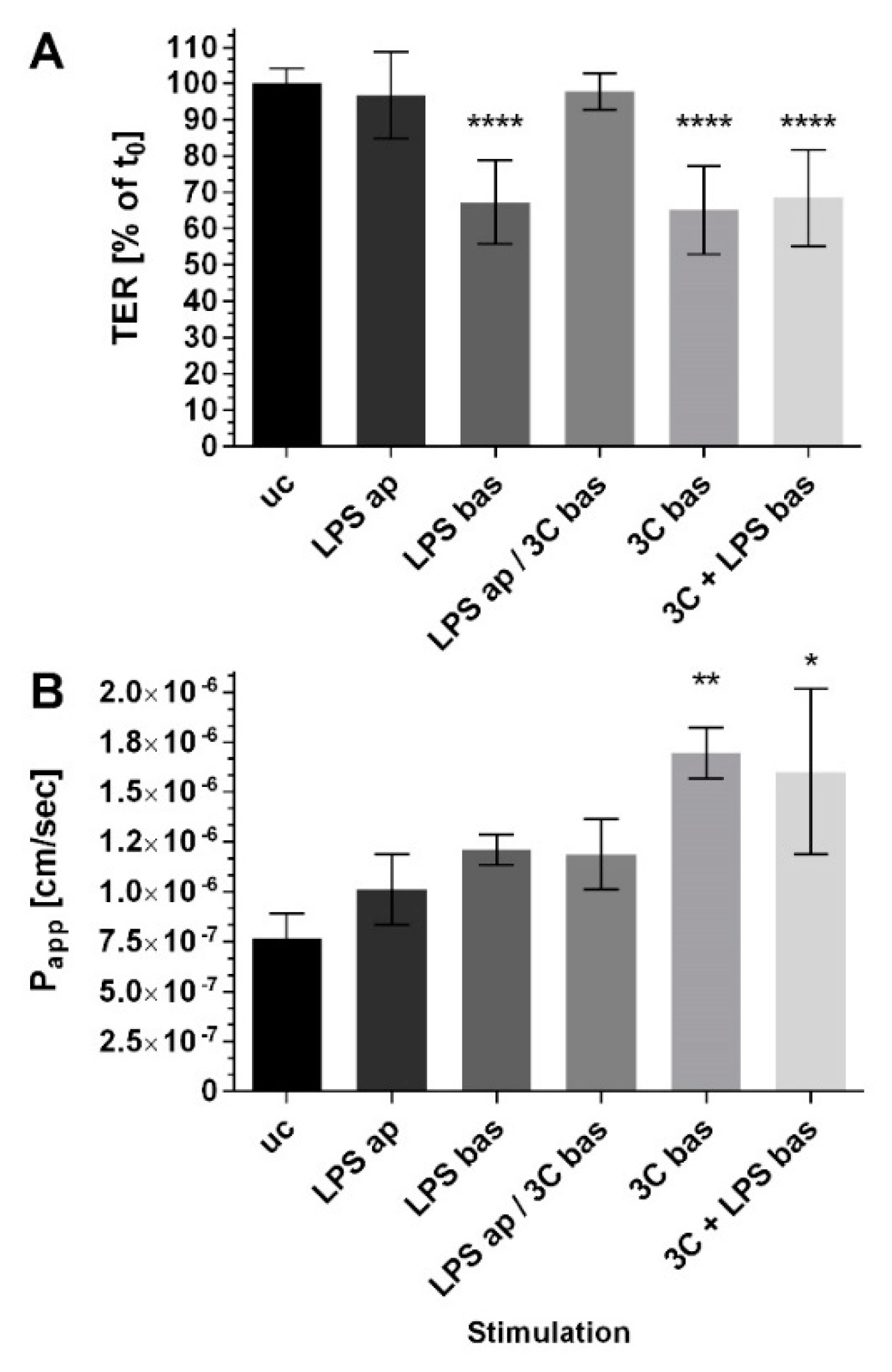
2. Results
3. Discussion
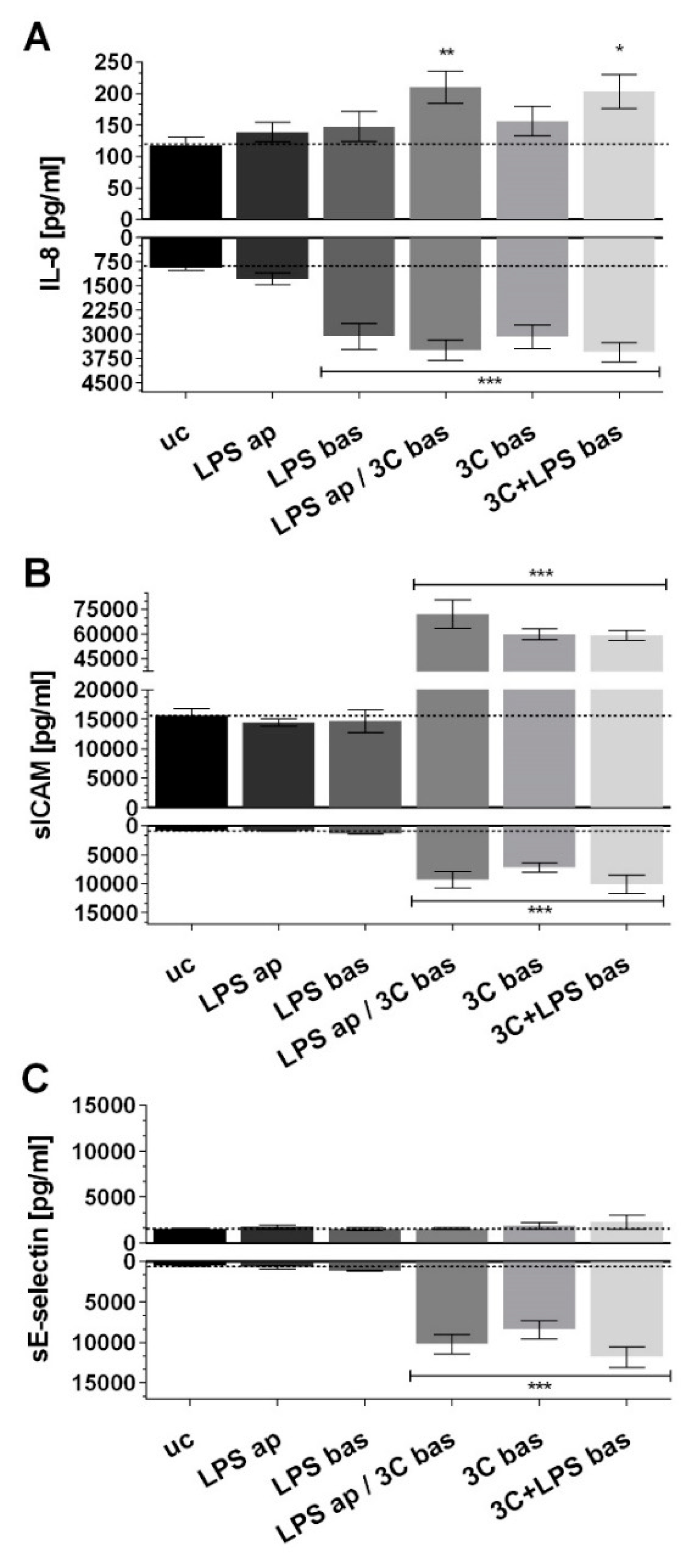
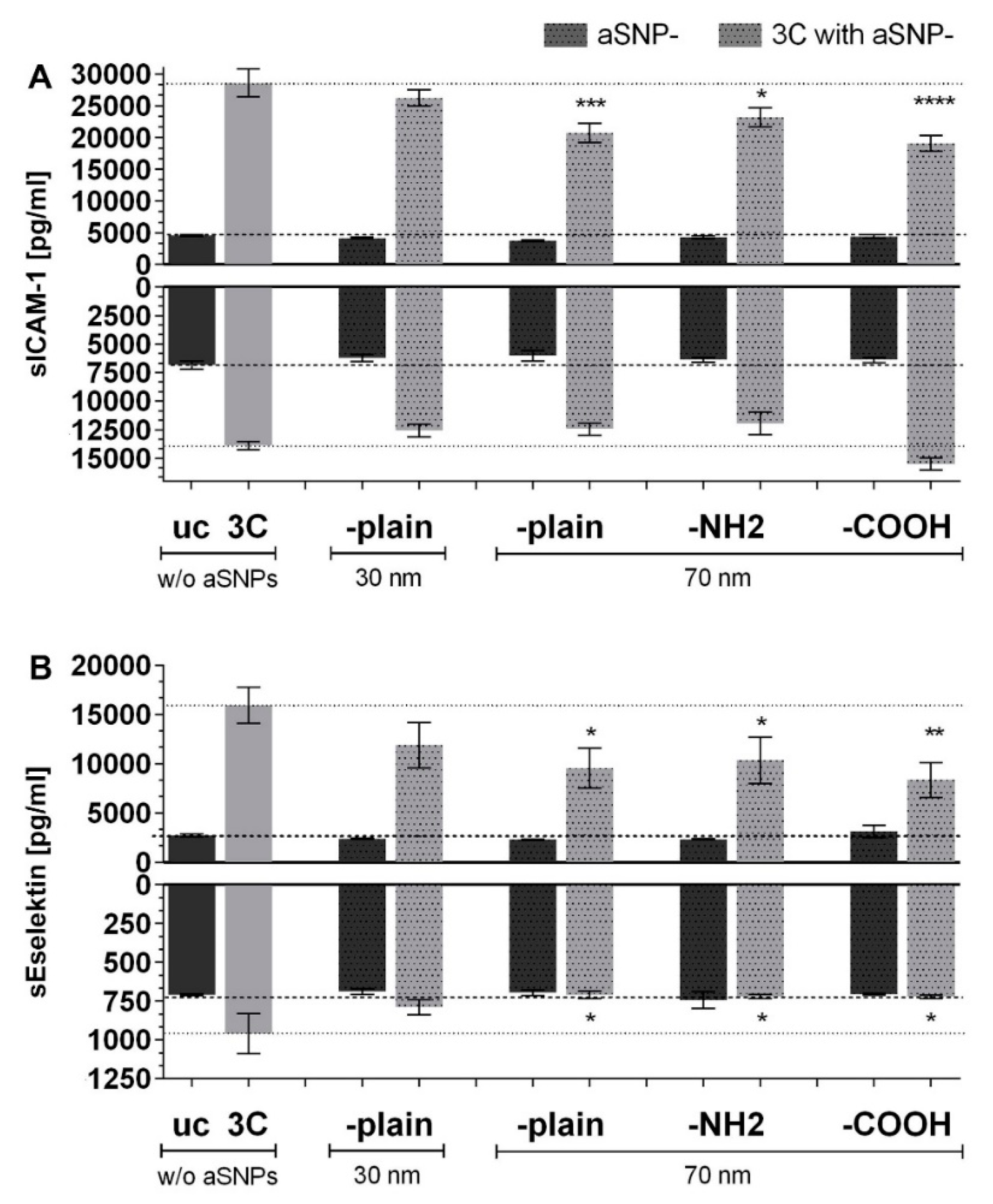
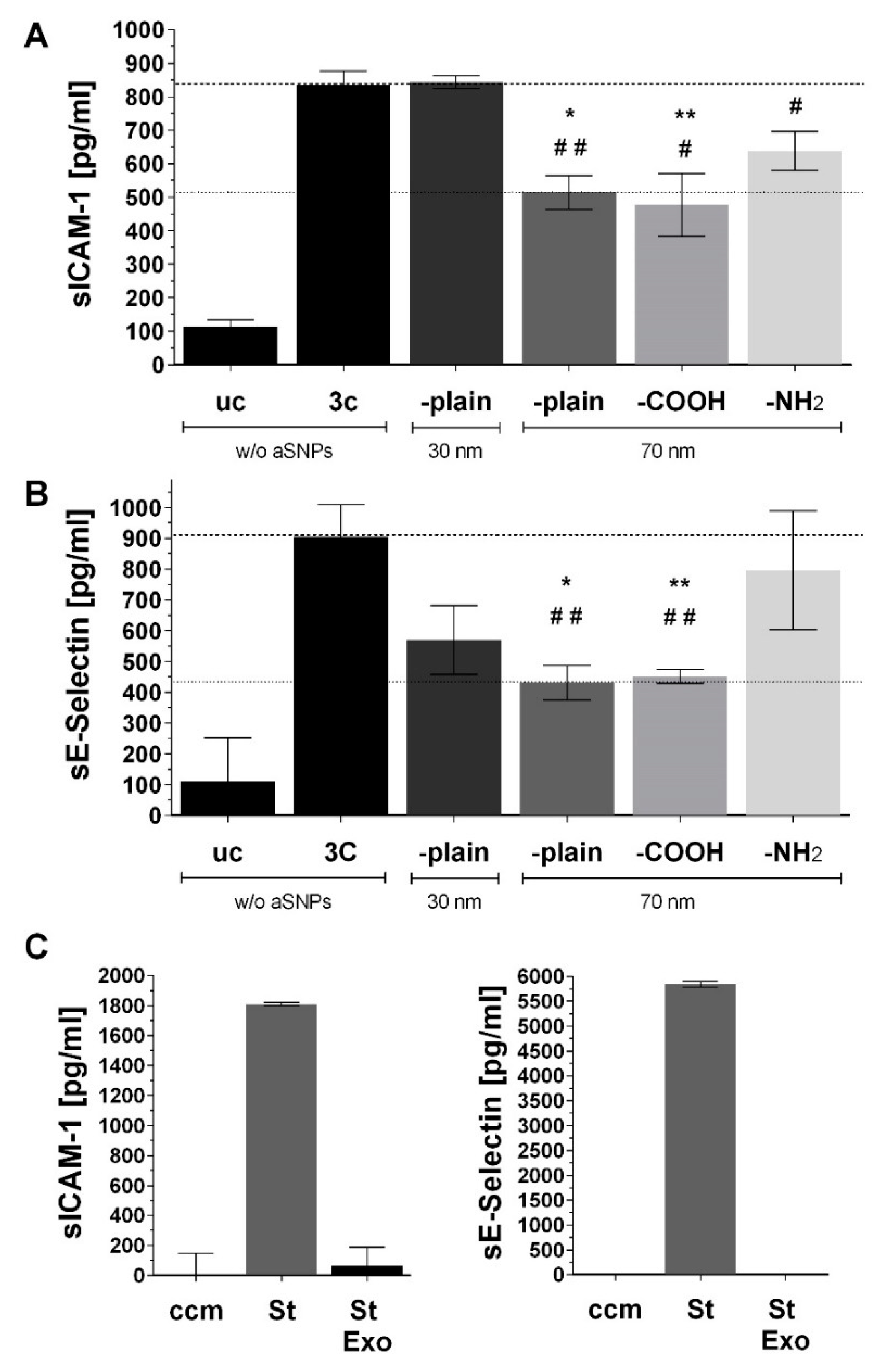
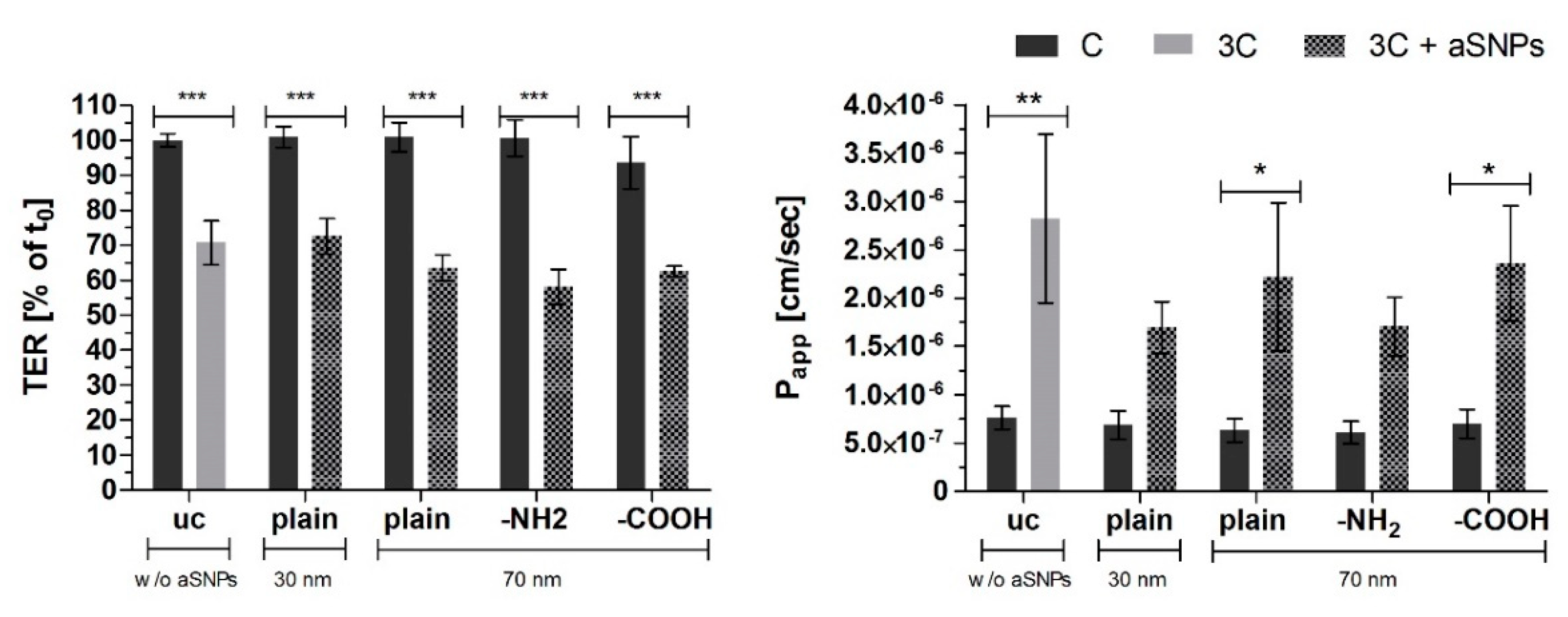
3.1. aSNP Exposure to the Endothelium Decreases sICAM and sE-Selectin Levels on both Sides of the Inflamed Coculture Model
3.2. The Endothelial Release of ICAM and E-Selectin-Bearing Exosomes/Microvesicles Is Increased during Endothelial Inflammation and Reduced during Endothelial aSNP Treatment
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Ethical Standards
Abbreviations
| iMV | intestinal microvasculature |
| IBD | inflammatory bowel disease |
| ICAM-1 | intercellular adhesion molecule 1 |
| TER | transepithelial-electrical resistance |
| Papp | permeability-coefficient |
| aSNP | amorphous silica nanoparticles |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| EMP | endothelial microparticles |
| IMEC | intestinal microvascular endothelial cells |
| NaFlu | Sodium-Fluorescein |
| CC | coculture Caco-2/ISO-HAS-1 |
| CCinv | inverted coculture ISO-HAS-1/Caco-2 |
| 3C | cytokine mixture ((IL-1β, TNF-α, IFN-γ) |
| ap | apical stimulation |
| bas | Basolateral stimulation |
| ccm | cell culture media |
References
- Lissner, D.; Schumann, M.; Batra, A.; Kredel, L.I.; Kuhl, A.A.; Erben, U.; May, C.; Schulzke, J.D.; Siegmund, B. Monocyte and m1 macrophage-induced barrier defect contributes to chronic intestinal inflammation in ibd. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detzel, C.J.; Horgan, A.; Henderson, A.L.; Petschow, B.W.; Warner, C.D.; Maas, K.J.; Weaver, E.M. Bovine immunoglobulin/protein isolate binds pro-inflammatory bacterial compounds and prevents immune activation in an intestinal co-culture model. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalubinski, M.; Wojdan, K.; Gorzelak, P.; Borowiec, M.; Broncel, M. The effect of oxidized cholesterol on barrier functions and il-10 mrna expression in human intestinal epithelium co-cultured with dendritic cells in the transwell system. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 69, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, F.; Collnot, E.M.; Lehr, C.M. A three-dimensional coculture of enterocytes, monocytes and dendritic cells to model inflamed intestinal mucosa in vitro. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 2103–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogoz, A.; Reis, B.S.; Karssemeijer, R.A.; Mucida, D. A 3-D enteroid-based model to study t-cell and epithelial cell interaction. J. Immunol. Methods 2015, 421, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsusaki, M.; Hikimoto, D.; Nishiguchi, A.; Kadowaki, K.; Ohura, K.; Imai, T.; Akashi, M. 3D-fibroblast tissues constructed by a cell-coat technology enhance tight-junction formation of human colon epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 457, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, W.; Sun, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Yang, H. Gdnf is involved in the barrier-inducing effect of enteric glial cells on intestinal epithelial cells under acute ischemia reperfusion stimulation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 50, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheadle, G.A.; Costantini, T.W.; Bansal, V.; Eliceiri, B.P.; Coimbra, R. Cholinergic signaling in the gut: A novel mechanism of barrier protection through activation of enteric glia cells. Surg. Infect. (Larchmt) 2014, 15, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidemann, J.; Domschke, W.; Kucharzik, T.; Maaser, C. Intestinal microvascular endothelium and innate immunity in inflammatory bowel disease: A second line of defense? Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 5425–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatoum, O.A.; Heidemann, J.; Binion, D.G. The intestinal microvasculature as a therapeutic target in inflammatory bowel disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1072, 78–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.T.; Pall, A.A.; Adu, D.; Keighley, M.R. Circulating soluble adhesion molecules in inflammatory bowel disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1995, 7, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dignat-George, F.; Boulanger, C.M. The many faces of endothelial microparticles. Arterioscl. Throm. Vasc. 2011, 31, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansink, M.O.; Patyk, V.; de Groot, H.; Effenberger-Neidnicht, K. Melatonin reduces changes to small intestinal microvasculature during systemic inflammation. J. Surg. Res. 2017, 211, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, S.A.; Pramanik, A.K.; Ganta, V.C.; Jennings, M.; Alexander, J.S. Metabolic-hypoxic modulation of cytokine induction of intestinal endothelial adhesion molecules: Relevance to ischemic injury mediated necrotizing enterocolitis? Pathophysiology 2019, 26, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, J.Y.; Hermanns, M.I.; Cavelius, C.; Kraegeloh, A.; Jung, T.; Danzebrink, R.; Unger, R.E.; Kirkpatrick, C.J. The role of the intestinal microvasculature in inflammatory bowel disease: Studies with a modified caco-2 model including endothelial cells resembling the intestinal barrier in vitro. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 6353–6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietjen, G.T.; Hosgood, S.A.; DiRito, J.; Cui, J.; Deep, D.; Song, E.; Kraehling, J.R.; Piotrowski-Daspit, A.S.; Kirkiles-Smith, N.C.; Al-Lamki, R.; et al. Nanoparticle targeting to the endothelium during normothermic machine perfusion of human kidneys. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaam6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.R. Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol 2009, 9, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, M.C.; Madsen, K.; Doyle, J.; Meddings, J. Reducing small intestinal permeability attenuates colitis in the il10 gene-deficient mouse. Gut 2009, 58, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, L.; Moss, R.L. Necrotizing enterocolitis: An update. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011, 16, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.A.; Doelle, S.M.; Halpern, M.D.; Saunders, T.A.; Holubec, H.; Dvorak, K.; Boitano, S.A.; Dvorak, B. Intestinal barrier failure during experimental necrotizing enterocolitis: Protective effect of egf treatment. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 291, G938–G949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, L.W.; Artis, D. Intestinal epithelial cells: Regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Al-Sadi, R.; Said, H.M.; Ma, T.Y. Lipopolysaccharide causes an increase in intestinal tight junction permeability in vitro and in vivo by inducing enterocyte membrane expression and localization of tlr-4 and cd14. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cush, J.J.; Rothlein, R.; Lindsley, H.B.; Mainolfi, E.A.; Lipsky, P.E. Increased levels of circulating intercellular adhesion molecule 1 in the sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1993, 36, 1098–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littler, A.J.; Buckley, C.D.; Wordsworth, P.; Collins, I.; Martinson, J.; Simmons, D.L. A distinct profile of six soluble adhesion molecules (icam-1, icam-3, vcam-1, e-selectin, l-selectin and p-selectin) in rheumatoid arthritis. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 36, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staunton, D.E.; Dustin, M.L.; Erickson, H.P.; Springer, T.A. The arrangement of the immunoglobulin-like domains of icam-1 and the binding sites for lfa-1 and rhinovirus. Cell 1990, 61, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenisch, C.; Myskiw, D.; Gessl, A.; Graninger, W. Circulating selectins, intercellular adhesion molecule-1, and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in hyperthyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1995, 80, 2122–2126. [Google Scholar]
- Mrowka, C.; Sieberth, H.G. Circulating adhesion molecules icam-1, vcam-1 and e-selectin in systemic vasculitis: Marked differences between wegener’s granulomatosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Investig. 1994, 72, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blann, A.D.; Steele, C.; McCollum, C.N. The influence of smoking and of oral and transdermal nicotine on blood pressure, and haematology and coagulation indices. Thromb. Haemost. 1997, 78, 1093–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, L.E.; Hennekens, C.H.; Ridker, P.M. Cross-sectional study of soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and cardiovascular risk factors in apparently healthy men. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999, 19, 1595–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, M.; Chapman, P.; Peters, M.; Haskard, D.; Hodgson, H.J. Visualising e-selectin in the detection and evaluation of inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 1998, 43, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, O.H.; Brynskov, J.; Vainer, B. Increased mucosal concentrations of soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sicam-1), se-selectin, and interleukin-8 in active ulcerative colitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1996, 41, 1780–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowska, A.M.; Borawska, M.H. Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sicam-1): An overview. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2004, 15, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Dragovic, R.A.; Gardiner, C.; Brooks, A.S.; Tannetta, D.S.; Ferguson, D.J.; Hole, P.; Carr, B.; Redman, C.W.; Harris, A.L.; Dobson, P.J.; et al. Sizing and phenotyping of cellular vesicles using nanoparticle tracking analysis. Nanomedicine 2011, 7, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, H.; Simpson, R.J.; Ji, H.; Aikawa, E.; Altevogt, P.; Askenase, P.; Bond, V.C.; Borras, F.E.; Breakefield, X.; Budnik, V.; et al. Vesiclepedia: A compendium for extracellular vesicles with continuous community annotation. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanelli, L.; Magini, A.; Buratta, S.; Brozzi, A.; Sagini, K.; Polchi, A.; Tancini, B.; Emiliani, C. Signaling pathways in exosomes biogenesis, secretion and fate. Genes 2013, 4, 152–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, O.G.; van Balkom, B.W.; Gremmels, H.; Verhaar, M.C. Exosomes from hypoxic endothelial cells have increased collagen crosslinking activity through up-regulation of lysyl oxidase-like 2. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, H.L.; Hu, G.W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tu, W.; Lu, Y.M.; Wu, L.; Xu, G.H. Glioma cells promote angiogenesis through the release of exosomes containing long non-coding rna pou3f3. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 959–972. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Li, Q.; Niu, X.; Hu, B.; Chen, S.; Song, W.; Ding, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y. Exosomes secreted from human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent osteonecrosis of the femoral head by promoting angiogenesis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, L.; Sun, X.; Zhao, X.; Sun, X.; Qian, H.; Xu, W.; Zhu, W. Exosomes derived from akt-modified human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improve cardiac regeneration and promote angiogenesis via activating platelet-derived growth factor d. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.Y.; Tran, J.A.; Chang, J.H.; Azar, D.T.; Zieske, J.D. Potential role of corneal epithelial cell-derived exosomes in corneal wound healing and neovascularization. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fevrier, B.; Raposo, G. Exosomes: Endosomal-derived vesicles shipping extracellular messages. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol 2004, 16, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorey, J.S.; Bhatnagar, S. Exosome function: From tumor immunology to pathogen biology. Traffic 2008, 9, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thery, C.; Zitvogel, L.; Amigorena, S. Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.M.; Choi, E.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, T.D.; Kim, Y.K.; Kang, C.; Gho, Y.S. A membranous form of icam-1 on exosomes efficiently blocks leukocyte adhesion to activated endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 397, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, D.M.; Dustin, M.L.; Carron, C.P. Characterization of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 ectodomain (sicam-1) as an inhibitor of lymphocyte function-associated molecule-1 interaction with icam-1. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 3578–3584. [Google Scholar]
- Thery, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (misev2018): A position statement of the international society for extracellular vesicles and update of the misev2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, J.; Hermanns, M.I.; Bantz, C.; Koshkina, O.; Lang, T.; Maskos, M.; Pohl, C.; Unger, R.E.; Kirkpatrick, C.J. Interactions of silica nanoparticles with lung epithelial cells and the association to flotillins. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, J.; Hermanns, M.I.; Bantz, C.; Utech, S.; Koshkina, O.; Maskos, M.; Brochhausen, C.; Pohl, C.; Fuchs, S.; Unger, R.E.; et al. Flotillin-involved uptake of silica nanoparticles and responses of an alveolar-capillary barrier in vitro. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 84, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.H.; Kim, K.; Lim, D.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, S.; Song, J.H.; Moon, B.G.; Choy, H.E.; Park, S.C. Microvasculature remodeling in the mouse lower gut during inflammaging. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.T.; Adriani, G.; Beyer, S.; Nhan, P.T.; Kamm, R.D.; Kah, J.C.Y. A facile method to probe the vascular permeability of nanoparticles in nanomedicine applications. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freese, C.; Schreiner, D.; Anspach, L.; Bantz, C.; Maskos, M.; Unger, R.E.; Kirkpatrick, C.J. In vitro investigation of silica nanoparticle uptake into human endothelial cells under physiological cyclic stretch. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuzawa, M.; Fujimura, T.; Hamada, Y.; Fujita, Y.; Hara, H.; Nishiyama, S.; Katsuoka, K.; Tamauchi, H.; Sakurai, Y. Establishment of a human hemangiosarcoma cell line (iso-has). Int. J. Cancer 1999, 81, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, R.E.; Krump-Konvalinkova, V.; Peters, K.; Kirkpatrick, C.J. In vitro expression of the endothelial phenotype: Comparative study of primary isolated cells and cell lines, including the novel cell line hpmec-st1.6r. Microvasc. Res. 2002, 64, 384–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, J.; Hermanns, M.I.; Bantz, C.; Maskos, M.; Stauber, R.; Pohl, C.; Unger, R.E.; Kirkpatrick, J.C. Inflammatory and cytotoxic responses of an alveolar-capillary coculture model to silica nanoparticles: Comparison with conventional monocultures. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2011, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kasper, J.Y.; Hermanns, M.I.; Kraegeloh, A.; Roth, W.; Kirkpatrick, C.J.; Unger, R.E. In Vitro Entero-Capillary Barrier Exhibits Altered Inflammatory and Exosomal Communication Pattern after Exposure to Silica Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133301
Kasper JY, Hermanns MI, Kraegeloh A, Roth W, Kirkpatrick CJ, Unger RE. In Vitro Entero-Capillary Barrier Exhibits Altered Inflammatory and Exosomal Communication Pattern after Exposure to Silica Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(13):3301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133301
Chicago/Turabian StyleKasper, Jennifer Y., M. Iris Hermanns, Annette Kraegeloh, W. Roth, C. James Kirkpatrick, and Ronald E. Unger. 2019. "In Vitro Entero-Capillary Barrier Exhibits Altered Inflammatory and Exosomal Communication Pattern after Exposure to Silica Nanoparticles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 13: 3301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133301
APA StyleKasper, J. Y., Hermanns, M. I., Kraegeloh, A., Roth, W., Kirkpatrick, C. J., & Unger, R. E. (2019). In Vitro Entero-Capillary Barrier Exhibits Altered Inflammatory and Exosomal Communication Pattern after Exposure to Silica Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(13), 3301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133301




