Human Macrophages Preferentially Infiltrate the Superficial Adipose Tissue
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Morphology and Paracrine Activity of SAT and DAT
2.2. ASC from SAT Proliferate Faster and Have a Higher Differentiation Potential
2.3. Numbers of ASC Do Not Differ in SAT and DAT
2.4. Numbers of SAT-Homing Macrophages Exceeded Those of DAT
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Tissue Sampling and Isolation of Cells
4.2. Ultrasound and Adipocyte Size Determination
4.3. Immunohistochemistry and Immunoblotting
4.4. Cell Proliferation and In Vitro Differentiation
4.5. RNA Isolation and Quantitative RT-PCR (qPCR)
4.6. Blood
4.7. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.8. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASC | Adipose derived stem cell |
| SAT | Superficial adipose tissue |
| DAT | Deep adipose tissue |
| SCAT | Subcutaneous adipose tissue |
| SVF | Stromal vascular fraction |
References
- McLaughlin, T.; Lamendola, C.; Liu, A.; Abbasi, F. Preferential fat deposition in subcutaneous versus visceral depots is associated with insulin sensitivity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E1756–E1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wronkowitz, N.; Romacho, T.; Sell, H.; Eckel, J. Adipose tissue dysfunction and inflammation in cardiovascular disease. Front. Horm. Res. 2014, 43, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovren, F.; Teoh, H.; Verma, S. Obesity and atherosclerosis: Mechanistic insights. Can. J. Cardiol. 2015, 31, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driskell, R.R.; Jahoda, C.A.; Chuong, C.M.; Watt, F.M.; Horsley, V. Defining dermal adipose tissue. Exp. Dermatol. 2014, 23, 629–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, H.; Imanishi, N.; Minabe, T.; Kishi, K.; Aiso, S. Anatomical study of subcutaneous adipofascial tissue: A concept of the protective adipofascial system (PAFS) and lubricant adipofascial system (LAFS). Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Hand Surg. 2004, 38, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Hijleh, M.F.; Roshier, A.L.; Al-Shboul, Q.; Dharap, A.S.; Harris, P.F. The membranous layer of superficial fascia: Evidence for its widespread distribution in the body. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2006, 28, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, G.E.; Marzullo, P.; Prodam, F.; Bona, G.; Di Blasio, A.M. Obesity modifies expression profiles of metabolic markers in superficial and deep subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue depots. Endocrine 2014, 46, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.S. Body Fat Distribution and the Risk of Incident Metabolic Syndrome: A Longitudinal Cohort Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, A.W.; Humphries, K.H.; Lear, S.A. Longitudinal changes in visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue and metabolic syndrome: Results from the Multicultural Community Health Assessment Trial (M-CHAT). Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2017, 2, S957–S961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lann, D.; Gallagher, E.; Leroith, D. Insulin resistance and the metabolic syndrome. Minerva Med. 2008, 99, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kelley, D.E.; Thaete, F.L.; Troost, F.; Huwe, T.; Goodpaster, B.H. Subdivisions of subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue and insulin resistance. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 278, E941–E948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rosa, V.; Procaccini, C.; Calì, G.; Pirozzi, G.; Fontana, S.; Zappacosta, S.; La Cava, A.; Matarese, G. A key role of leptin in the control of regulatory T cell proliferation. Immunity 2007, 26, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottfried, E.; Kunz-Schughart, L.A.; Weber, A.; Rehli, M.; Peuker, A.; Müller, A.; Kastenberger, M.; Brockhoff, G.; Andreesen, R.; Kreutz, M. Expression of CD68 in non-myeloid cell types. Scand. J. Immunol. 2008, 67, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilling, D.; Fan, T.; Huang, D.; Kaul, B.; Gomer, R.H. Identification of markers that distinguish monocyte-derived fibrocytes from monocytes, macrophages, and fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalbermatten, D.F.; Schaakxs, D.; Kingham, P.J.; Wiberg, M. Neurotrophic activity of human adipose stem cells isolated from deep and superficial layers of abdominal fat. Cell Tissue Res. 2011, 344, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancerotto, L.; Stecco, C.; Macchi, V.; Porzionato, A.; Stecco, A.; De Caro, R. Layers of the abdominal wall: Anatomical investigation of subcutaneous tissue and superficial fascia. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2011, 33, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Gonzalez, G.C.; Shook, B.A.; Andrae, J.; Holtrup, B.; Bollag, K.; Betsholtz, C.; Rodeheffer, M.S.; Horsley, V. Skin Adipocyte Stem Cell Self-Renewal Is Regulated by a PDGFA/AKT-Signaling Axis. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 19, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Festa, E.; Fretz, J.; Berry, R.; Schmidt, B.; Rodeheffer, M.; Horowitz, M.; Horsley, V. Adipocyte lineage cells contribute to the skin stem cell niche to drive hair cycling. Cell 2011, 146, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasza, I.; Suh, Y.; Wollny, D.; Clark, R.J.; Roopra, A.; Colman, R.J.; MacDougald, O.A.; Shedd, T.A.; Nelson, D.W.; Yen, M.I.; et al. Syndecan-1 is required to maintain intradermal fat and prevent cold stress. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.J.; Guerrero-Juarez, C.F.; Hata, T.; Bapat, S.P.; Ramos, R.; Plikus, M.V.; Gallo, R.L. Innate immunity. Dermal adipocytes protect against invasive Staphylococcus aureus skin infection. Science 2015, 347, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morandi, E.M.; Verstappen, R.; Zwierzina, M.E.; Geley, S.; Pierer, G.; Ploner, C. ITGAV and ITGA5 diversely regulate proliferation and adipogenic differentiation of human adipose derived stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basoli, V.; Santaniello, S.; Cruciani, S.; Ginesu, G.C.; Cossu, M.L.; Delitala, A.P.; Serra, P.A.; Ventura, C.; Maioli, M. Melatonin and Vitamin D Interfere with the Adipogenic Fate of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wouters, K.; Gaens, K.; Bijnen, M.; Verboven, K.; Jocken, J.; Wetzels, S.; Wijnands, E.; Hansen, D.; van Greevenbroek, M.; Duijvestijn, A.; et al. Circulating classical monocytes are associated with CD11c(+) macrophages in human visceral adipose tissue. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astori, G.; Vignati, F.; Bardelli, S.; Tubio, M.; Gola, M.; Albertini, V.; Bambi, F.; Scali, G.; Castelli, D.; Rasini, V.; et al. “In vitro” and multicolor phenotypic characterization of cell subpopulations identified in fresh human adipose tissue stromal vascular fraction and in the derived mesenchymal stem cells. J. Transl. Med. 2007, 5, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisberg, S.P.; McCann, D.; Desai, M.; Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Ferrante, A.W., Jr. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancello, R.; Zulian, A.; Gentilini, D.; Maestrini, S.; Della Barba, A.; Invitti, C.; Corà, D.; Caselle, M.; Liuzzi, A.; Di Blasio, A.M. Molecular and morphologic characterization of superficial- and deep-subcutaneous adipose tissue subdivisions in human obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2013, 21, 2562–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khazen, W.; M’bika, J.P.; Tomkiewicz, C.; Benelli, C.; Chany, C.; Achour, A.; Forest, C. Expression of macrophage-selective markers in human and rodent adipocytes. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 5631–5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsuji, T.; Chiang, H.I.; Jiang, S.B.; Nagarajan, H.; Zengler, K.; Gallo, R.L. The microbiome extends to subepidermal compartments of normal skin. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Yang, Q.; Cao, J.; Xie, N.; Liu, K.; Shou, P.; Qian, F.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y. Local proliferation initiates macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue during obesity. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.S.; Tilstam, P.V.; Springenberg-Jung, K.; Boecker, A.H.; Schmitz, C.; Heinrichs, D.; Hwang, S.S.; Stromps, J.P.; Ganse, B.; Kopp, R.; et al. Characterization of adipose tissue macrophages and adipose-derived stem cells in critical wounds. PeerJ 2017, 5, e2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybalko, V.; Hsieh, P.L.; Ricles, L.M.; Chung, E.; Farrar, R.P.; Suggs, L.J. Therapeutic potential of adipose-derived stem cells and macrophages for ischemic skeletal muscle repair. Regen. Med. 2017, 12, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skurk, T.; Ecklebe, S.; Hauner, H. A novel technique to propagate primary human preadipocytes without loss of differentiation capacity. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2007, 15, 2925–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaas, I.; Heinz, K.; Würtinger, P.; Türkcan, A.; Tepeköylü, C.; Grimm, M.; Doppler, C.; Danzl, K.; Messner, B.; Bernhard, D. Vein graft thrombi, a niche for smooth muscle cell colonization—A hypothesis to explain the asymmetry of intimal hyperplasia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banas, M.; Zegar, A.; Kwitniewski, M.; Zabieglo, K.; Marczynska, J.; Kapinska-Mrowiecka, M.; LaJevic, M.; Zabel, B.A.; Cichy, J. The expression and regulation of chemerin in the epidermis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, N.N.; Gunnarsson, H.I.; Yi, Z.; Gudmundsdottir, S.; Sigurjonsson, O.E.; Agerberth, B.; Gudmundsson, G.H. Glucocorticoid dexamethasone down-regulates basal and vitamin D3 induced cathelicidin expression in human monocytes and bronchial epithelial cell line. Immunobiology 2016, 221, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fjeldborg, K.; Pedersen, S.B.; Møller, H.J.; Christiansen, T.; Bennetzen, M.; Richelsen, B. Human adipose tissue macrophages are enhanced but changed to an anti-inflammatory profile in obesity. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 309548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogarth, M.W.; Houweling, P.J.; Thomas, K.C.; Gordish-Dressman, H.; Bello, L.; Cooperative International Neuromuscular Research Group (CINRG); Pegoraro, E.; Hoffman, E.P.; Head, S.I.; North, K.N. Evidence for ACTN3 as a genetic modifier of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappellano, G.; Ploner, C.; Lobenwein, S.; Sopper, S.; Hoertnagl, P.; Mayerl, C.; Wick, N.; Pierer, G.; Wick, G.; Wolfram, D. Immunophenotypic characterization of human T cells after in vitro exposure to different silicone breast implant surfaces. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
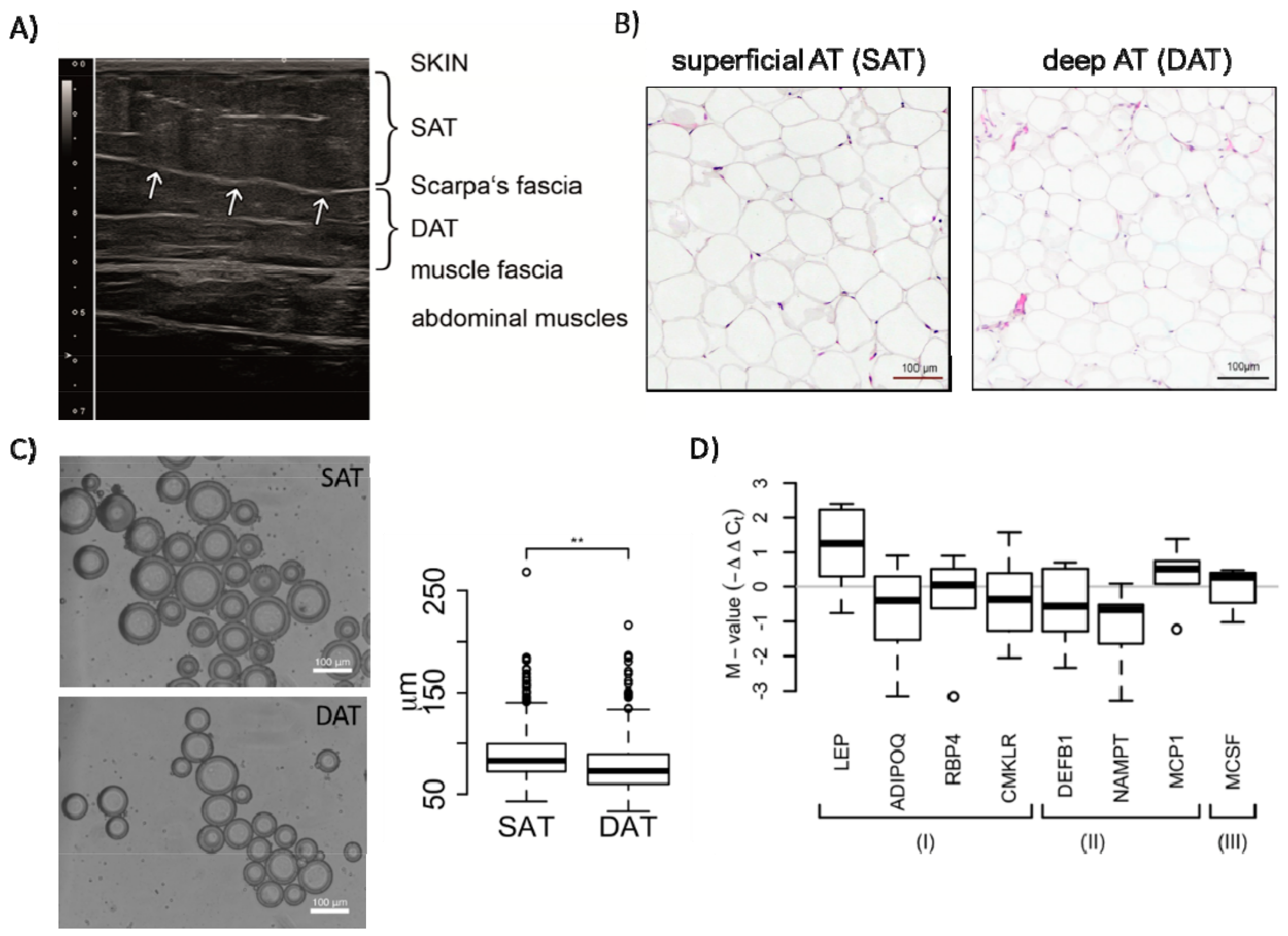

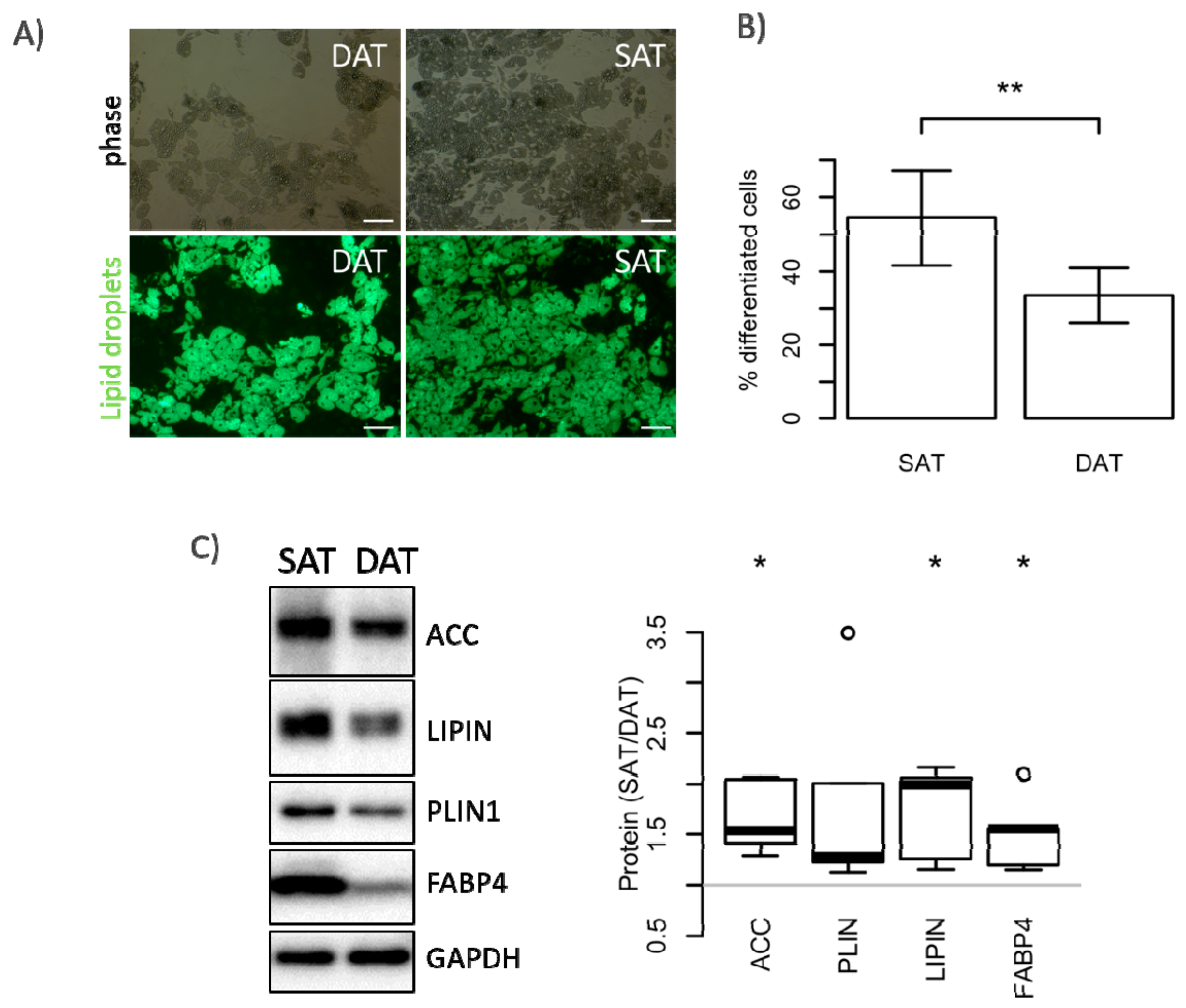

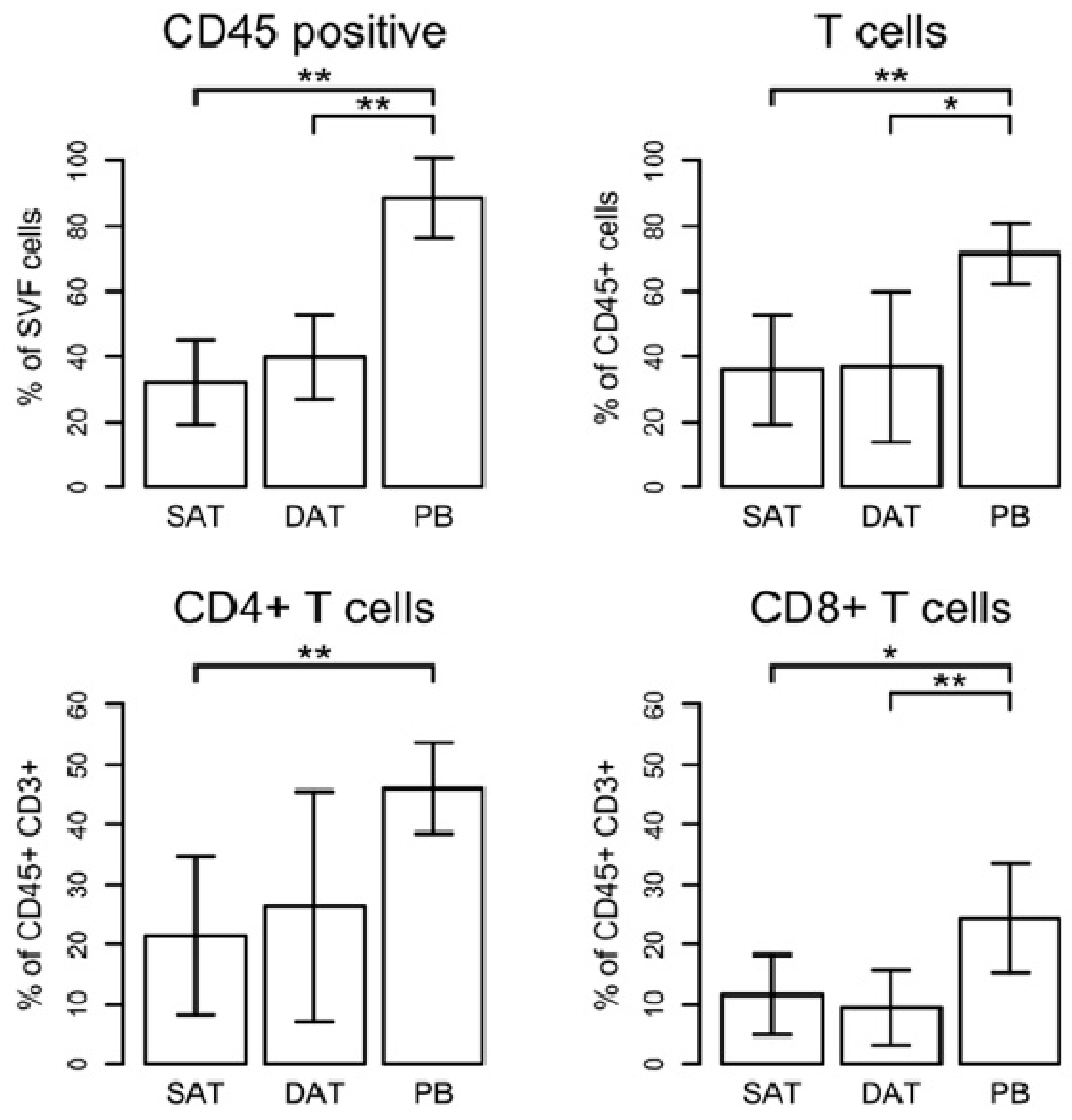
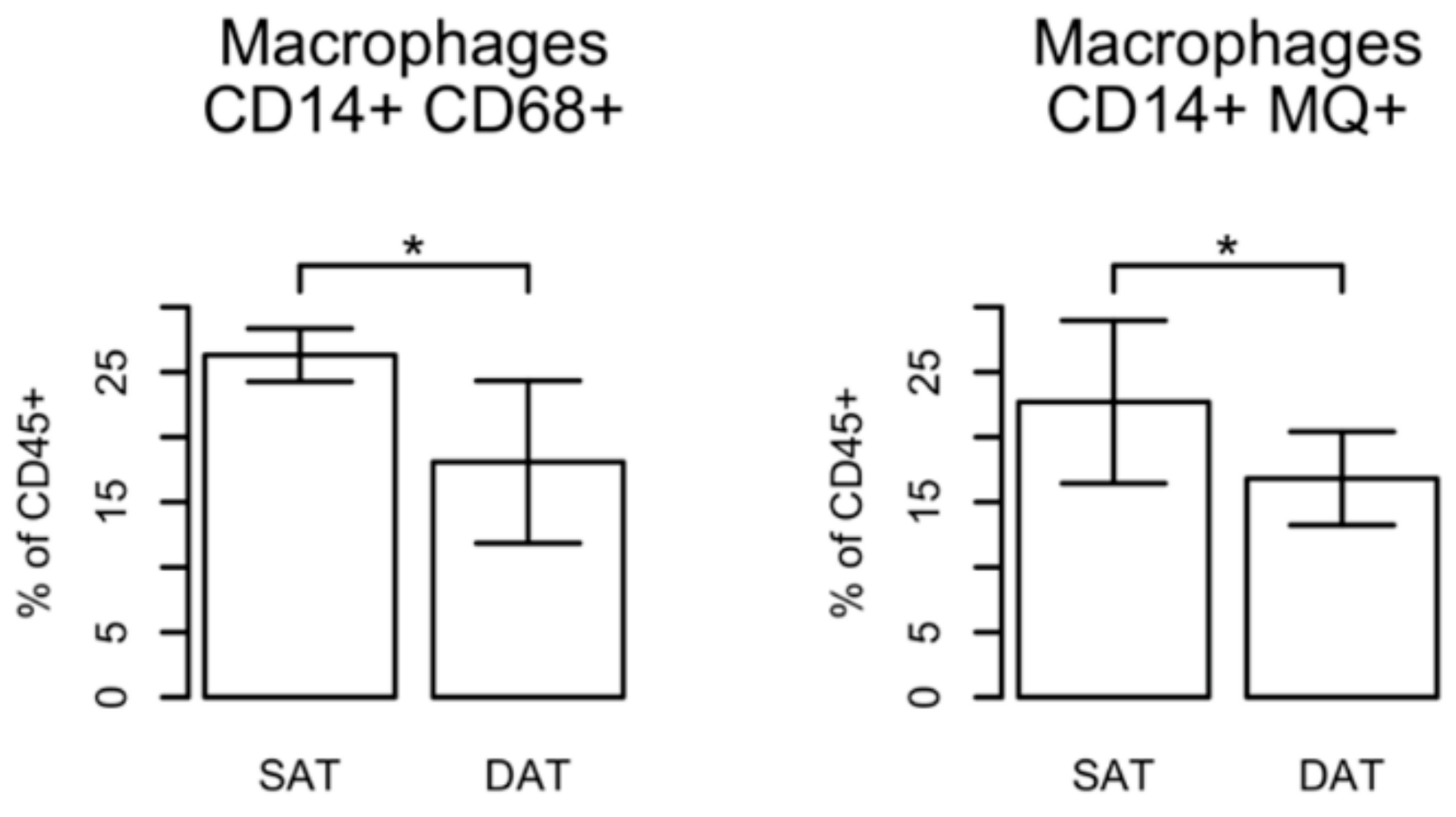
| Gene | Sense Primer | Antisense Primer |
|---|---|---|
| human Leptin | 5′-CACACGCAGTCAGTCTCCTC-3′ | 5′-AGGTTCTCCAGGTCGTTGG-3′ |
| human ADIPOQ | 5′-GATGGCAGAGATGGCACCC-3′ | 5′-GGAATTTACCAGTGGAGCCA-3′ |
| human RBP4 | 5′-TTCGACAAGGCTCGCTTCTC-3′ | 5′-CGATGTTGTCCTGCAGAAAGAG-3′ |
| human CMKLR [34] | 5′-TGGAAGAAACCCGAGTGCAAA-3′ | 5′-AGAACTTGGGTCTCTATGGGG-3′ |
| human DEFB1 [35] | 5′-CCAGTCGCCATGAGAACTTCC-3′ | 5′-GTGAGAAAGTTACCACCTGAGGC-3′ |
| human NAMPT | 5′-GCAGAAGCCGAGTTCAACAT-3′ | 5′-TCTGTCTTCTTTTCACGGCA-3′ |
| human MCP1 [36] | 5′-GTCTTGAAGATCACAGCTTCTTTG-3′ | 5′-AGCCAGATGCAATCAATGCC-3′ |
| human MCSF | 5‘-GCAGCTGCAGGAACTCTCTT-3′ | 5‘-CCAGCAACTGGAGAGGTGTC-3′ |
| human 18sRNA [37] | 5′-GCAATTATTCCCCATGAACG-3′ | 5′-GGCCTCACTAAACCATCCAA-3′ |
| human GUSB | 5′-GGAATTTTGCCGATTTCATGAC-3′ | 5′-TCTCTGCCGAGTGAAGATCCC-3′ |
| human GAPDH | 5′-CAACGAATTTACAGCA-3′ | 5′-TGTGAGGAGGATTCAG-3′ |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cappellano, G.; Morandi, E.M.; Rainer, J.; Grubwieser, P.; Heinz, K.; Wolfram, D.; Bernhard, D.; Lobenwein, S.; Pierer, G.; Ploner, C. Human Macrophages Preferentially Infiltrate the Superficial Adipose Tissue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051404
Cappellano G, Morandi EM, Rainer J, Grubwieser P, Heinz K, Wolfram D, Bernhard D, Lobenwein S, Pierer G, Ploner C. Human Macrophages Preferentially Infiltrate the Superficial Adipose Tissue. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(5):1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051404
Chicago/Turabian StyleCappellano, Giuseppe, Evi M. Morandi, Johannes Rainer, Philipp Grubwieser, Katharina Heinz, Dolores Wolfram, David Bernhard, Susanne Lobenwein, Gerhard Pierer, and Christian Ploner. 2018. "Human Macrophages Preferentially Infiltrate the Superficial Adipose Tissue" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 5: 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051404
APA StyleCappellano, G., Morandi, E. M., Rainer, J., Grubwieser, P., Heinz, K., Wolfram, D., Bernhard, D., Lobenwein, S., Pierer, G., & Ploner, C. (2018). Human Macrophages Preferentially Infiltrate the Superficial Adipose Tissue. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(5), 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051404







