Structure-Function Relationship of Transporters in the Glutamate–Glutamine Cycle of the Central Nervous System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
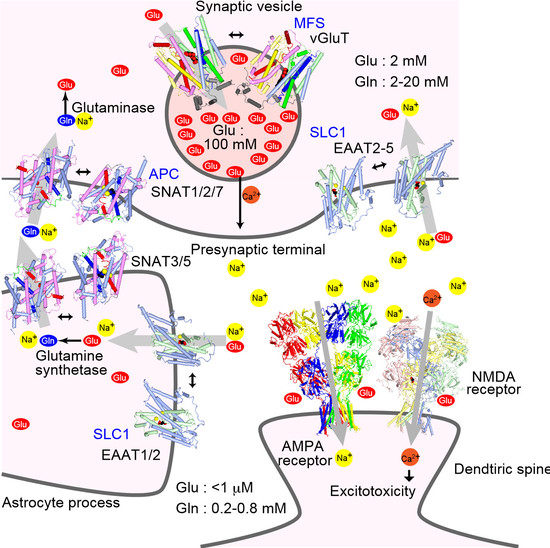
2. Transporter Subtypes and Glutamate–Glutamine Cycle
3. Expression Profile of Plasma Membrane Glutamate Transporter EAATs
4. Plasma Membrane Glutamate Transporter EAAT: Trimeric Transporters
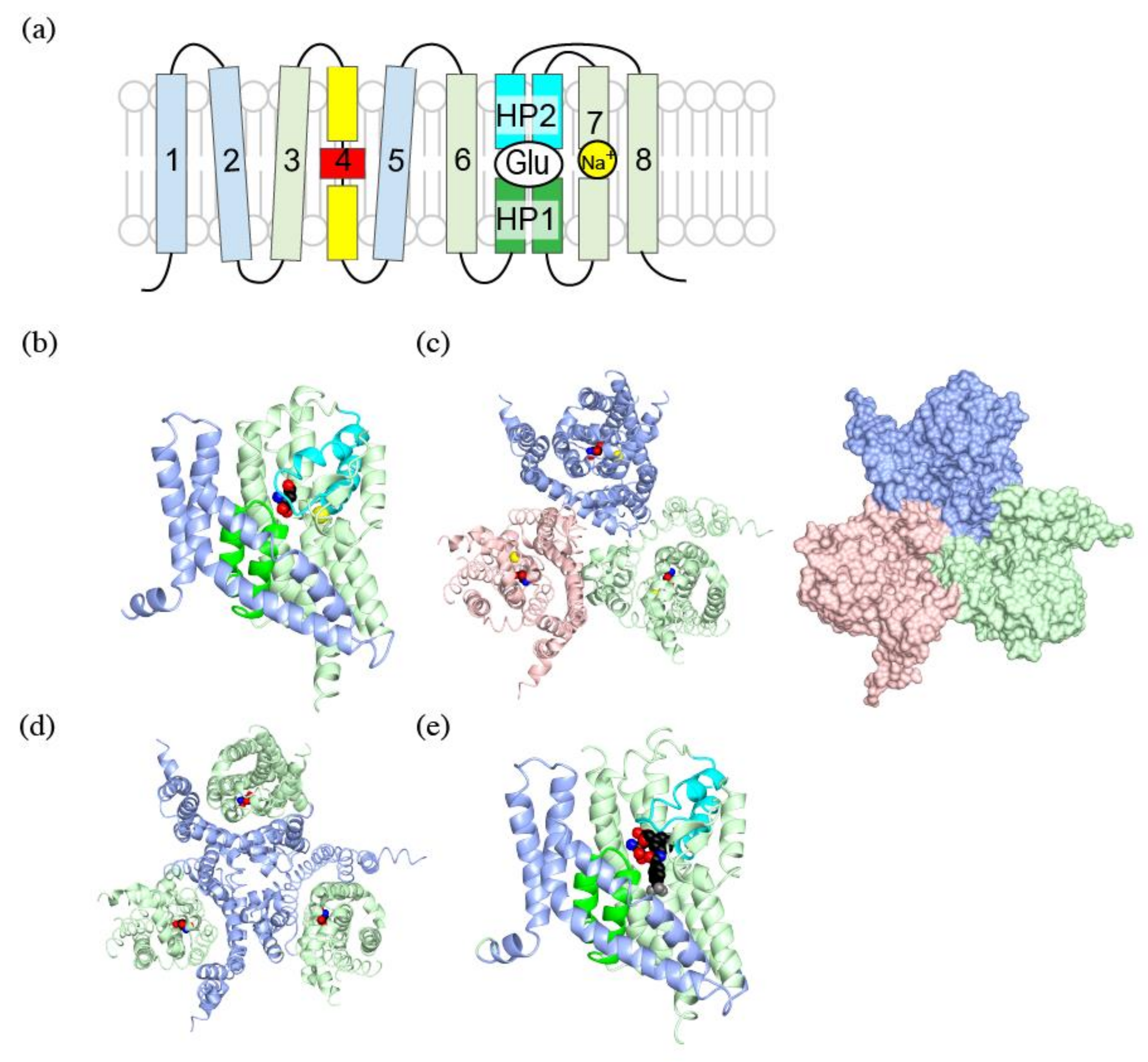
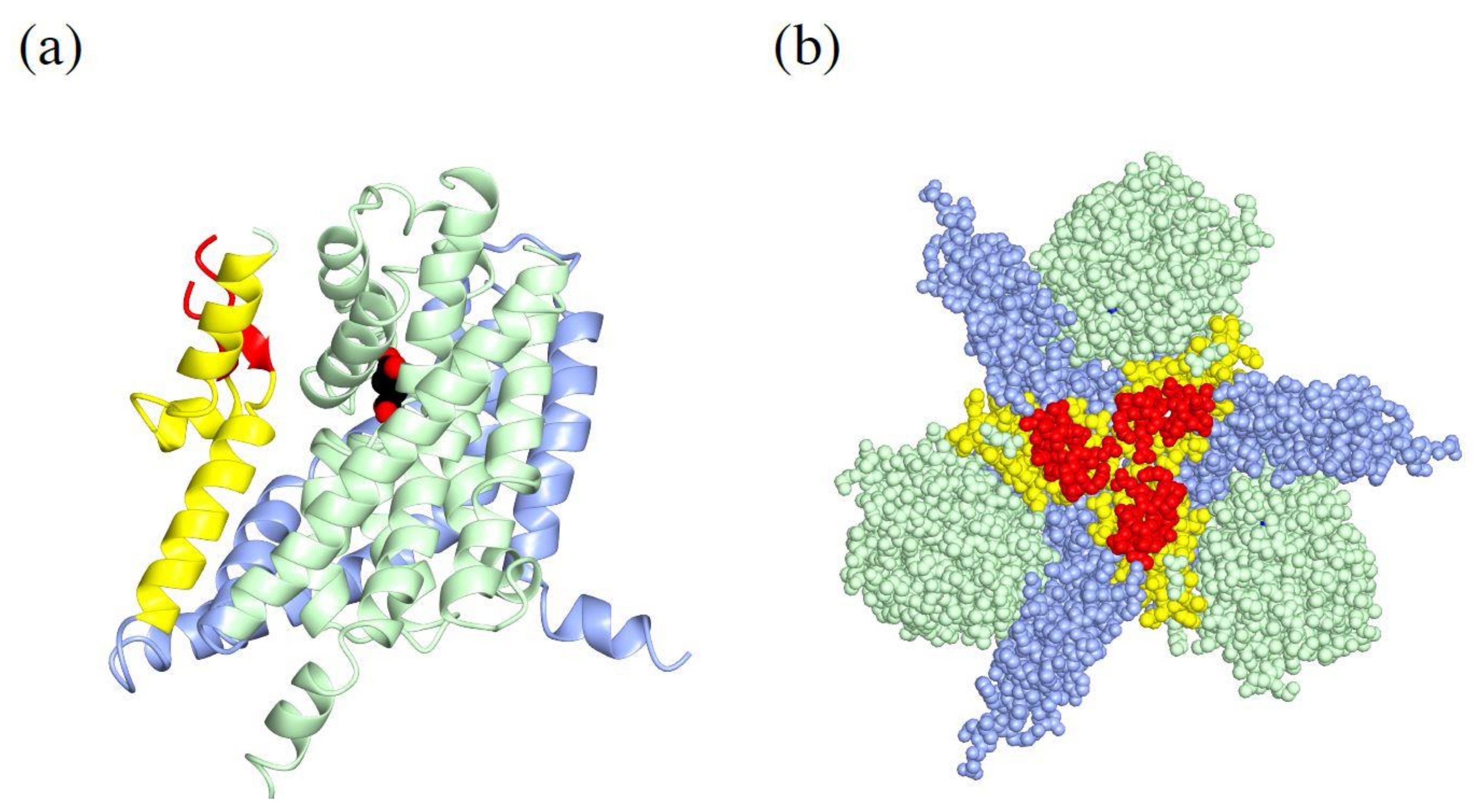
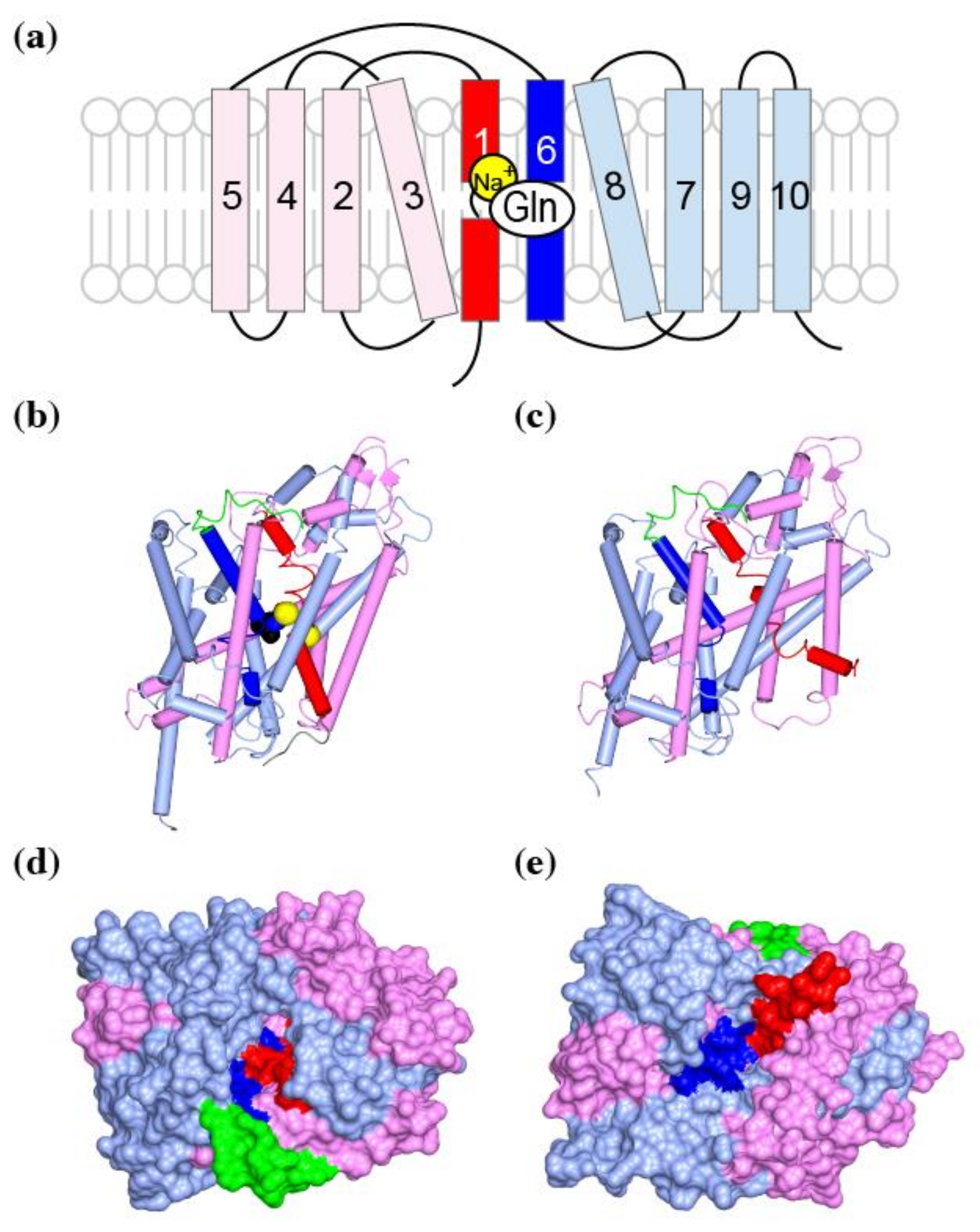
4.1. Trimeric Structure of Glutamate Transporters
4.2. Trimerization Domain and Transport Domain Characterize Trimeric Transporters
4.3. Substrate Binding to the Transport Domain
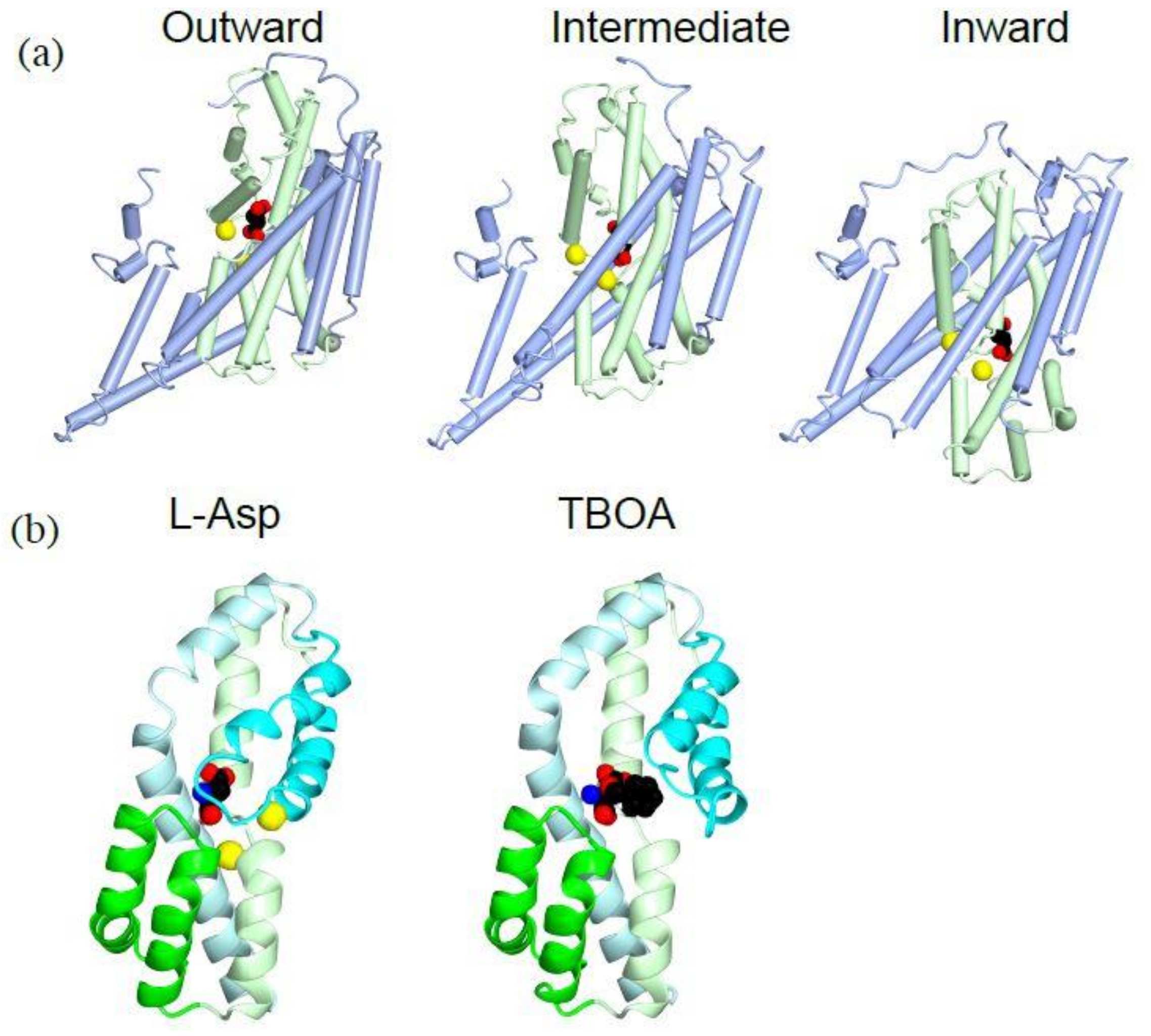
5. Structural Changes During the Substrate Transport
5.1. Transporter Domain Movements During Substrate Transport
5.2. Coordination of Sodium Ions for Co-Transport
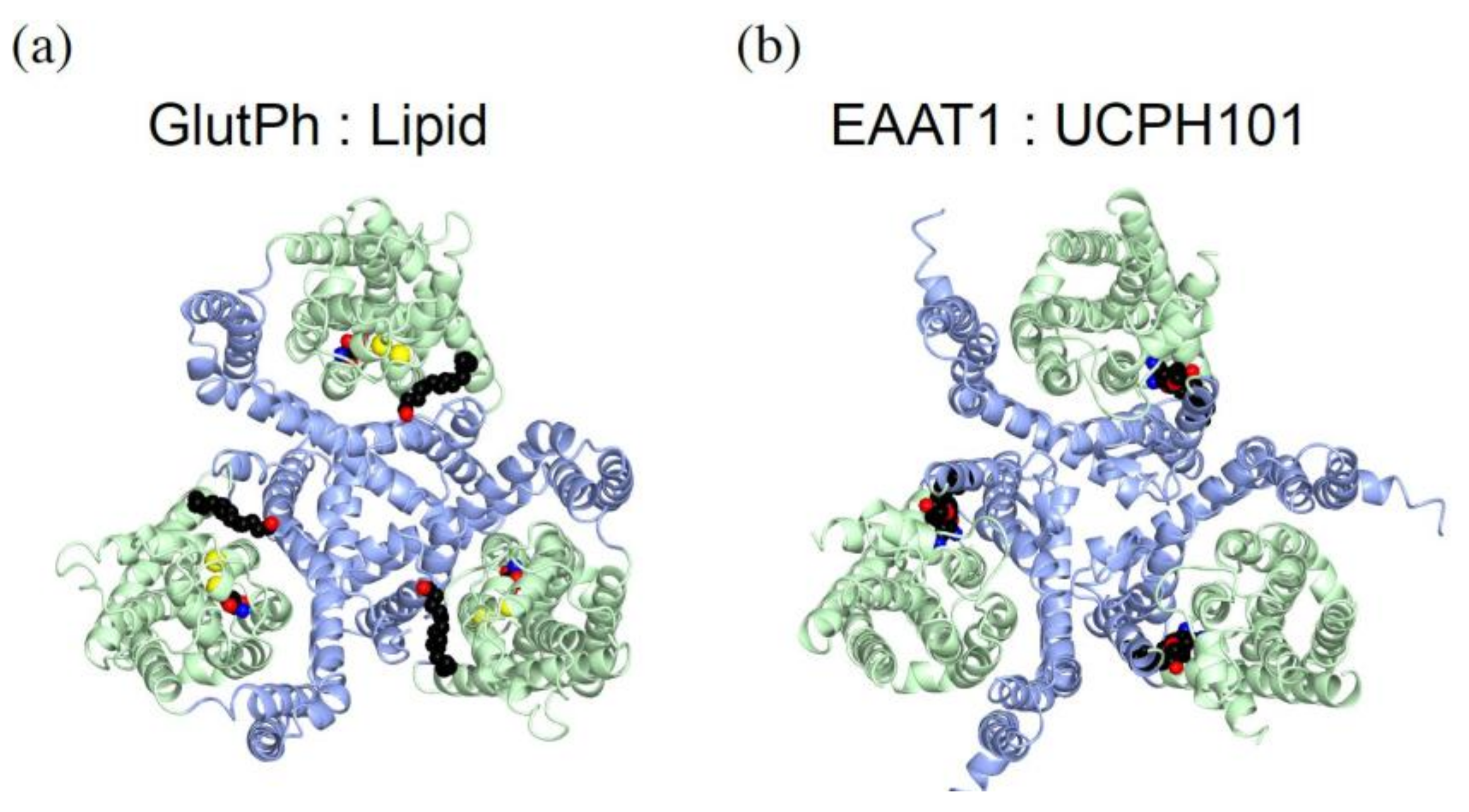
5.3. Interaction with Lipids Affect the Transporter Activity
5.4. Transport Kinetics of Glutamate Transporters
5.5. TM4 of the Trimerization Domain Has an Insertion of an Extracellular Loop
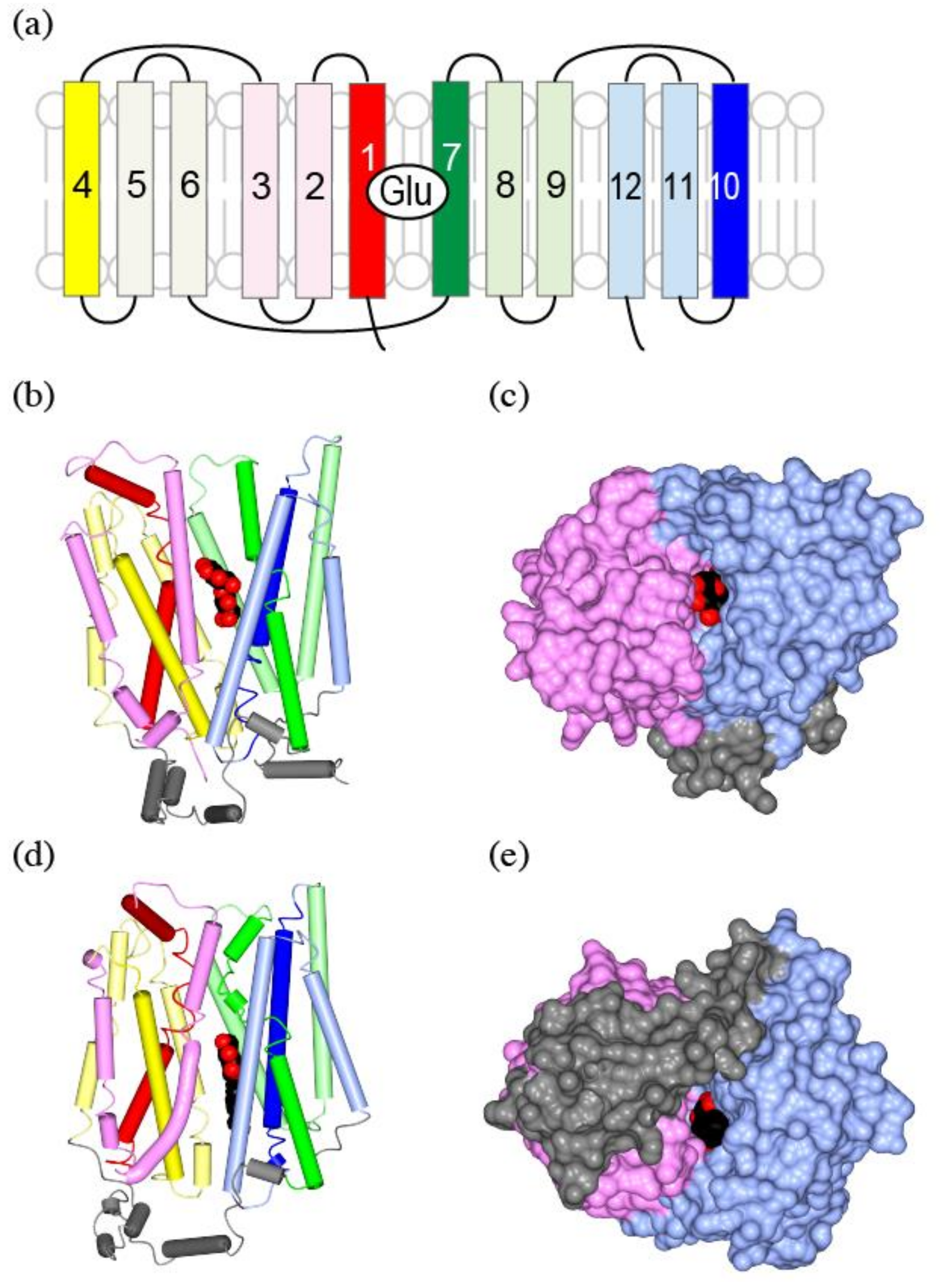
6. Structure of Plasma Membrane Glutamine Transporters: APC Family Transporters
7. Structure of Vesicular Glutamate Transporters: MFS Transporters
8. Regulation of Synaptic Transmission by Glutamate Transporters
8.1. Glutamate Transporters Shape Synaptic Transmission
8.2. Glutamatergic Neurotransmission Affect Glutamate Transporters
8.3. Glutamate Transporters and Astrocyte Morphology
8.4. Transcriptional Regulation of Glutamate Transporters
8.5. Pathophysiology of Glutamate Transporters
9. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EAAT | excitatory amino acid transporter |
| GLAST | glutamate/aspartate-transporter |
| GLT1 | glutamate transporter 1 |
| ASCT | neutral amino acid transporter |
| SLC1 | solute carrier 1 |
| MFS | major facilitator superfamily |
| APC | amino acid-Polyamine-organoCation |
| TBOA | d,l-threo-b-benzyloxyaspartate |
| AMPA | α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid |
| NMDA | N-methyl-d-aspartate |
| SNAT | sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter |
| vGluT | vesicular glutamate transporter |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor-κB |
| KBBP | κB-motif binding phosphoprotein |
References
- Nedergaard, M.; Takano, T.; Hansen, A.J. Beyond the role of glutamate as a neurotransmitter. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerangue, N.; Kavanaugh, M.P. Flux coupling in a neuronal glutamate transporter. Nature 1996, 383, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudker, O.; Verdon, G. Structural perspectives on secondary active transporters. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 31, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danbolt, N.C. Glutamate uptake. Prog. Neurobiol. 2001, 65, 1–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storck, T.; Schulte, S.; Hofmann, K.; Stoffel, W. Structure, expression, and functional analysis of a Na(+)-dependent glutamate/aspartate transporter from rat brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 10955–10959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pines, G.; Danbolt, N.C.; Bjørås, M.; Zhang, Y.; Bendahan, A.; Eide, L.; Koepsell, H.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Seeberg, E.; Kanner, B.I. Cloning and expression of a rat brain L-glutamate transporter. Nature 1992, 360, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriza, J.L.; Kavanaugh, M.P.; Fairman, W.A.; Wu, Y.N.; Murdoch, G.H.; North, R.A.; Amara, S.G. Cloning and expression of a human neutral amino acid transporter with structural similarity to the glutamate transporter gene family. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 15329–15332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shafqat, S.; Tamarappoo, B.K.; Kilberg, M.S.; Puranam, R.S.; McNamara, J.O.; Guadaño-Ferraz, A.; Fremeau, R.T. Cloning and expression of a novel Na+-dependent neutral amino acid transporter structurally related to mammalian Na+/glutamate cotransporters. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 15351–15355. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pingitore, P.; Pochini, L.; Scalise, M.; Galluccio, M.; Hedfalk, K.; Indiveri, C. Large scale production of the active human ASCT2 (SLC1A5) transporter in Pichia pastoris—Functional and kinetic asymmetry revealed in proteoliposomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta -Biomembr. 2013, 1828, 2238–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bröer, A.; Brookes, N.; Ganapathy, V.; Dimmer, K.S.; Wagner, C.A.; Lang, F.; Bröer, S. The astroglial ASCT2 amino acid transporter as a mediator of glutamine efflux. J. Neurochem. 1999, 73, 2184–2194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, H.; Piscitelli, C.L.; Gouaux, E. Unlocking the molecular secrets of sodium-coupled transporters. Nature 2009, 459, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrest, L.R.; Krämer, R.; Ziegler, C. The structural basis of secondary active transport mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenergy 2011, 1807, 167–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deitmer, J.W.; Bröer, A.; Bröer, S. Glutamine efflux from astrocytes is mediated by multiple pathways. J. Neurochem. 2003, 87, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bröer, S. The SLC38 family of sodium-amino acid co-transporters. Pflugers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2014, 466, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laake, J.H.; Slyngstad, T.A.; Haug, F.-M.Š.; Ottersen, O.P. Glutamine from Glial Cells Is Essential for the Maintenance of the Nerve Terminal Pool of Glutamate: Immunogold Evidence from Hippocampal Slice Cultures. J. Neurochem. 1995, 65, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamori, S.; Rhec, J.S.; Rosenmund, C.; Jahn, R. Identification of a vesicular glutamate transporter that defines a glutamatergic phenotype in neurons. Nature 2000, 407, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamori, S.; Rhee, J.S.; Rosenmund, C.; Jahn, R. Identification of Differentiation-Associated Brain-Specific Phosphate Transporter as a Second Vesicular Glutamate Transporter (VGLUT2). J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, RC182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellocchio, E.E.; Reimer, R.J.; Fremeau, J.; Edwards, R.H. Uptake of glutamate into synaptic vesicles by an inorganic phosphate transporter. Science 2000, 289, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fremeau, R.T.; Troyer, M.D.; Pahner, I.; Nygaard, G.O.; Tran, C.H.; Reimer, R.J.; Bellocchio, E.E.; Fortin, D.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Edwards, R.H. The expression of vesicular glutamate transporters defines two classes of excitatory synapse. Neuron 2001, 31, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothstein, J.D.; Martin, L.; Levey, A.I.; Dykes-Hoberg, M.; Jin, L.; Wu, D.; Nash, N.; Kuncl, R.W. Localization of neuronal and glial glutamate transporters. Neuron 1994, 13, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennerick, S.; Dhond, R.P.; Benz, A.; Xu, W.; Rothstein, J.D.; Danbolt, N.C.; Isenberg, K.E.; Zorumski, C.F. Neuronal expression of the glutamate transporter GLT-1 in hippocampal microcultures. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 4490–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieoullon, A.; Canolle, B.; Masmejean, F.; Guillet, B.; Pisano, P.; Lortet, S. The neuronal excitatory amino acid transporter EAAC1/EAAT3: Does it represent a major actor at the brain excitatory synapse? J. Neurochem. 2006, 98, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.I.; Orlov, I.; Ruggiero, A.M.; Dykes-Hoberg, M.; Lee, A.; Jackson, M.; Rothstein, J.D. Modulation of the neuronal glutamate transporter EAAC1 by the interacting protein GTRAP3-18. Nature 2001, 410, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuta, A.; Martin, L.J.; Lin, C.L.; Dykes-Hoberg, M.; Rothstein, J.D. Cellular and synaptic localization of the neuronal glutamate transporters excitatory amino acid transporter 3 and 4. Neuroscience 1997, 81, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Ährlund-Richter, S.; Wang, X.; Deisseroth, K.; Carlén, M.; Sofie, A.; Wang, X.; Deisseroth, K.; Carle, M.; Wang, X.; et al. Prefrontal Parvalbumin Neurons in Control of Attention. Cell 2016, 164, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.; Watanabe, M.; Shibata, T.; Tanaka, K.; Wada, K.; Inoue, Y. EAAT4 is a post-synaptic glutamate transporter at Purkinje cell synapses. Neuroreport 1996, 7, 2013–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehnes, Y.; Chaudhry, F.A.; Ullensvang, K.; Lehre, K.P.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Danbolt, N.C. The glutamate transporter EAAT4 in rat cerebellar Purkinje cells: A glutamate-gated chloride channel concentrated near the synapse in parts of the dendritic membrane facing astroglia. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 3606–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriza, J.L.; Eliasof, S.; Kavanaugh, M.P.; Amara, S.G. Excitatory amino acid transporter 5, a retinal glutamate transporter coupled to a chloride conductance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4155–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pow, D.V.; Barnett, N.L. Developmental expression of excitatory amino acid transporter 5: A photoreceptor and bipolar cell glutamate transporter in rat retina. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 280, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairman, W.A.; Vandenberg, R.J.; Arriza, J.L.; Kavanaugh, M.P.; Amara, S.G. An excitatory amino-acid transporter with properties of a ligand-gated chloride channel. Nature 1995, 375, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Watase, K.; Manabe, T.; Yamada, K.; Watanabe, M.; Takahashi, K.; Iwama, H.; Nishikawa, T.; Ichihara, N.; Kikuchi, T.; et al. Epilepsy and exacerbation of brain injury in mice lacking the glutamate transporter GLT-1. Science 1997, 276, 1699–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petr, G.T.; Sun, Y.; Frederick, N.M.; Zhou, Y.; Dhamne, S.C.; Hameed, M.Q.; Miranda, C.; Bedoya, E.A.; Fischer, K.D.; Armsen, W.; et al. Conditional deletion of the glutamate transporter GLT-1 reveals that astrocytic GLT-1 protects against fatal epilepsy while neuronal GLT-1 contributes significantly to glutamate uptake into synaptosomes. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 5187–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanai, Y.; Hediger, M.A. Primary structure and functional characterization of a high-affinity glutamate transporter. Nature 1992, 360, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yernool, D.; Boudker, O.; Jin, Y.; Gouaux, E. Structure of a glutamate transporter homologue from Pyrococcus horikoshii. Nature 2004, 36, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canul-Tec, J.C.; Assal, R.; Cirri, E.; Legrand, P.; Brier, S.; Chamot-Rooke, J.; Reyes, N. Structure and allosteric inhibition of excitatory amino acid transporter 1. Nature 2016, 544, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, M.; Song, W.; Liu, M.Y.; Jin, L.; Dykes-Hoberg, M.; Lin, C.I.; Bowers, W.J.; Federoff, H.J.; Sternweis, P.C.; Rothstein, J.D. Modulation of the neuronal glutamate transporter EAAT4 by two interacting proteins. Nature 2001, 410, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marie, H.; Billups, D.; Bedford, F.K.; Dumoulin, A.; Goyal, R.K.; Longmore, G.D.; Moss, S.J.; Attwell, D. The amino terminus of the glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 interacts with the LIM protein Ajuba. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2002, 19, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, S.; Pita-Almenar, J.D.; Eskin, A. Regulation of glutamate transporter GLT-1 by MAGI-1. J. Neurochem. 2011, 117, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritter, S.L.; Asay, M.J.; Paquet, M.; Paavola, K.J.; Reiff, R.E.; Yun, C.C.; Hall, R.A. GLAST stability and activity are enhanced by interaction with the PDZ scaffold NHERF-2. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 487, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNicholas, S.; Potterton, E.; Wilson, K.S.; Noble, M.E.M. Presenting your structures: The CCP4mg molecular-graphics software. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2011, 67, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, N.; Ginter, C.; Boudker, O. Transport mechanism of a bacterial homologue of glutamate transporters. Nature 2009, 462, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyuz, N.; Altman, R.B.; Blanchard, S.C.; Boudker, O. Transport dynamics in a glutamate transporter homologue. Nature 2013, 502, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudker, O.; Ryan, R.M.; Yernool, D.; Shimamoto, K.; Gouaux, E. Coupling substrate and ion binding to extracellular gate of a sodium-dependent aspartate transporter. Nature 2007, 445, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdon, G.; Boudker, O. Crystal structure of an asymmetric trimer of a bacterial glutamate transporter homolog. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, C.B.; Hayes, D.; Murphy, A.; Wießner, M.; Rauen, T.; McBean, G.J. Differential modulation of the glutamate transporters GLT1, GLAST and EAAC1 by docosahexaenoic acid. Brain Res. 2005, 1037, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raunser, S.; Haase, W.; Bostina, M.; Parcej, D.N.; Kühlbrandt, W. High-yield expression, reconstitution and structure of the recombinant, fully functional glutamate transporter GLT-1 from Rattus norvegicus. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 351, 598–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Sutherland, M.L. Glutamate transporter cluster formation in astrocytic processes regulates glutamate uptake activity. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6301–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benediktsson, A.M.; Marrs, G.S.; Tu, J.C.; Worley, P.F.; Rothstein, J.D.; Bergles, D.E.; Dailey, M.E. Neuronal activity regulates glutamate transporter dynamics in developing astrocytes. Glia 2012, 60, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, M.K.; Yasui, M. The transmembrane transporter domain of glutamate transporters is a process tip localizer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Hernandez, A.; Bell, K.P.; Norenberg, M.D. Glutamine synthetase: Glial localization in brain. Science 1977, 195, 1356–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, C.F.; Verkhratsky, A.; Parpura, V. Astrocyte glutamine synthetase: Pivotal in health and disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2013, 41, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bröer, S.; Brookes, N. Transfer of glutamine between astrocytes and neurons. J. Neurochem. 2001, 77, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Lozada, Z.; Guillem, A.M.; Flores-Méndez, M.; Hernández-Kelly, L.C.; Vela, C.; Meza, E.; Zepeda, R.C.; Caba, M.; Rodríguez, A.; Ortega, A. GLAST/EAAT1-induced Glutamine release via SNAT3 in Bergmann glial cells: Evidence of a functional and physical coupling. J. Neurochem. 2013, 125, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, F.A.; Schmitz, D.; Reimer, R.J.; Larsson, P.; Gray, A.T.; Nicoll, R.A.; Kavanaugh, M.; Edwards, R.H. Glutamine uptake by neurons: Interaction of protons with system a transporters. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pochini, L.; Scalise, M.; Galluccio, M.; Indiveri, C. Membrane transporters for the special amino acid glutamine: Structure/function relationships and relevance to human health. Front. Chem. 2014, 2, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, A.; Singh, S.K.; Kawate, T.; Jin, Y.; Gouaux, E. Crystal structure of a bacterial homologue of Na+/Cl−-dependent neurotransmitter transporters. Nature 2005, 437, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, H.; Gouaux, E. X-ray structures of LeuT in substrate-free outward-open and apo inward-open states. Nature 2012, 481, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, N. Structural advances for the major facilitator superfamily (MFS) transporters. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2013, 38, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, N. Structural Biology of the Major Facilitator Superfamily Transporters. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2015, 44, 257–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anne, C.; Gasnier, B. Vesicular neurotransmitter transporters: Mechanistic aspects. Curr. Top. Membr. 2014, 73, 149–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perland, E.; Fredriksson, R. Classification Systems of Secondary Active Transporters. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 38, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntire, S.L.; Reimer, R.J.; Schuske, K.; Edwards, R.H.; Jorgensen, E.M. Identification and characterization of the vesicular GABA transporter. Nature 1997, 389, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preobraschenski, J.; Zander, J.F.; Suzuki, T.; Ahnert-Hilger, G.; Jahn, R. Vesicular glutamate transporters use flexible anion and cation binding sites for efficient accumulation of neurotransmitter. Neuron 2014, 84, 1287–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksen, J.; Chang, R.; McGregor, M.; Silm, K.; Suzuki, T.; Edwards, R.H. Protons Regulate Vesicular Glutamate Transporters through an Allosteric Mechanism. Neuron 2015, 90, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, D.; Sun, P.; Yan, C.; Ke, M.; Jiang, X.; Xiong, L.; Ren, W.; Hirata, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Fan, S.; et al. Molecular basis of ligand recognition and transport by glucose transporters. Nature 2015, 526, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, D.; Xu, C.; Sun, P.; Wu, J.; Yan, C.; Hu, M.; Yan, N. Crystal structure of the human glucose transporter GLUT1. Nature 2014, 510, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramson, J.; Smirnova, I.; Kasho, V.; Verner, G.; Kaback, H.R.; Iwata, S. Structure and mechanism of the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Science 2003, 301, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Lemieux, M.J.; Song, J.; Auer, M.; Wang, D.N. Structure and mechanism of the glycerol-3-phosphate transporter from Escherichia coli. Science 2003, 301, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; Scimemi, A.; Rusakov, D.A. Receptor actions of synaptically released glutamate: The role of transporters on the scale from nanometers to microns. Biophys. J. 2008, 95, 4584–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asztely, F.; Erdemli, G.; Kullmann, D.M. Extrasynaptic glutamate spillover in the hippocampus: Dependence on temperature and the role of active glutamate uptake. Neuron 1997, 18, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, H.; Tanaka, K.; Manabe, T. Requirement of appropriate glutamate concentrations in the synaptic cleft for hippocampal LTP induction. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001, 14, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsvetkov, E.; Shin, R.M.; Bolshakov, V.Y. Glutamate Uptake Determines Pathway Specificity of Long-Term Potentiation in the Neural Circuitry of Fear Conditioning. Neuron 2004, 41, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy-Royal, C.; Dupuis, J.P.; Varela, J.A.; Panatier, A.; Pinson, B.; Baufreton, J.; Groc, L.; Oliet, S.H.R. Surface diffusion of astrocytic glutamate transporters shapes synaptic transmission. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armbruster, M.; Hanson, E.; Dulla, C.G. Glutamate Clearance Is Locally Modulated by Presynaptic Neuronal Activity in the Cerebral Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 10404–10415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, R.; Harris, K.M. Three-dimensional relationships between hippocampal synapses and astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 6897–6906. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bernardinelli, Y.; Randall, J.; Janett, E.; Nikonenko, I.; König, S.; Jones, E.V.; Flores, C.E.; Murai, K.K.; Bochet, C.G.; Holtmaat, A.; et al. Activity-dependent structural plasticity of perisynaptic astrocytic domains promotes excitatory synapse stability. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 1679–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannasch, U.; Freche, D.; Dallérac, G.; Ghézali, G.; Escartin, C.; Ezan, P.; Cohen-Salmon, M.; Benchenane, K.; Abudara, V.; Dufour, A.; et al. Connexin 30 sets synaptic strength by controlling astroglial synapse invasion. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakers, K.; Lake, A.M.; Khazanchi, R.; Ouwenga, R.; Vasek, M.J.; Dani, A.; Dougherty, J.D. Astrocytes locally translate transcripts in their peripheral processes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3830–E3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tani, H.; Dulla, C.G.; Farzampour, Z.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Huguenard, J.R.; Reimer, R.J. A local glutamate-glutamine cycle sustains synaptic excitatory transmitter release. Neuron 2014, 81, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, R.A.; Liu, J.; Miller, J.W.; Rothstein, J.D.; Farrell, K.; Stein, B.A.; Longuemare, M.C. Neuronal regulation of glutamate transporter subtype expression in astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlag, B.D.; Vondrasek, J.R.; Munir, M.; Kalandadze, A.; Zelenaia, O.A.; Rothstein, J.D.; Robinson, M.B. Regulation of the glial Na+-dependent glutamate transporters by cyclic AMP analogs and neurons. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 53, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Gozen, O.; Watkins, A.; Lorenzini, I.; Lepore, A.; Gao, Y.; Vidensky, S.; Brennan, J.; Poulsen, D.; Won Park, J.; et al. Presynaptic Regulation of Astroglial Excitatory Neurotransmitter Transporter GLT1. Neuron 2009, 61, 880–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothstein, J.D.; Patel, S.; Regan, M.R.; Haenggeli, C.; Huang, Y.H.; Bergles, D.E.; Jin, L.; Dykes Hoberg, M.; Vidensky, S.; Chung, D.S.; et al. Beta-lactam antibiotics offer neuroprotection by increasing glutamate transporter expression. Nature 2005, 433, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.G.; Su, Z.Z.; Emdad, L.; Gupta, P.; Sarkar, D.; Borjabad, A.; Volsky, D.J.; Fisher, P.B. Mechanism of ceftriaxone induction of excitatory amino acid transporter-2 expression and glutamate uptake in primary human astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 13116–13123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.L.G.; Bristol, L.A.; Jin, L.; Dykes-Hoberg, M.; Crawford, T.; Clawson, L.; Rothstein, J.D. Aberrant RNA processing in a neurodegenerative disease: The cause for absent EAAT2, a glutamate transporter, in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuron 1998, 20, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, E.; Funicello, M.; Rauen, T.; Gobbi, M.; Mennini, T. Riluzole enhances the activity of glutamate transporters GLAST, GLT1 and EAAC1. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 578, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandya, R.S.; Zhu, H.; Li, W.; Bowser, R.; Friedlander, R.M.; Wang, X. Therapeutic neuroprotective agents for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 4729–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cudkowicz, M.E.; Titus, S.; Kearney, M.; Yu, H.; Sherman, A.; Schoenfeld, D.; Hayden, D.; Shui, A.; Brooks, B.; Conwit, R.; et al. Safety and efficacy of ceftriaxone for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A multi-stage, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, C. Oestrogen as a neuroprotective hormone. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, M.; Yang, Y.; Rothstein, J.D.; Robinson, M.B. Nuclear Factor-κB Contributes to Neuron-Dependent Induction of Glutamate Transporter-1 Expression in Astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 9159–9169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Valla, J.; Sefidvash-Hockley, S.; Rogers, J.; Li, R. Effects of estrogen treatment on glutamate uptake in cultured human astrocytes derived from cortex of Alzheimer’s disease patients. J. Neurochem. 2002, 80, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szatkowski, M.; Barbour, B.; Attwell, D. Non-vesicular release of glutamate from glial cells by reversed electrogenic glutamate uptake. Nature 1990, 348, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, D.J.; Oshima, T.; Attwell, D. Glutamate release in severe brain ischaemia is mainly by reversed uptake. Nature 2000, 403, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubenstein, J.L.R.; Merzenich, M.M. Model of autism: Increased ratio of excitation/inhibition in key neural systems. Genes Brain Behav. 2003, 2, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Hanna, G.L.; Rosenberg, D.R.; Arnold, P.D. The role of glutamate signaling in the pathogenesis and treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 100, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Penzes, P. Common mechanisms of excitatory and inhibitory imbalance in schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorders. Curr. Mol. Med. 2015, 15, 146–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bristol, L.A.; Rothstein, J.D. Glutamate transporter gene expression in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis motor cortex. Ann. Neurol. 1996, 39, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spangaro, M.; Bosia, M.; Zanoletti, A.; Bechi, M.; Cocchi, F.; Pirovano, A.; Lorenzi, C.; Bramanti, P.; Benedetti, F.; Smeraldi, E.; et al. Cognitive dysfunction and glutamate reuptake: Effect of EAAT2 polymorphism in schizophrenia. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 522, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallaspezia, S.; Poletti, S.; Lorenzi, C.; Pirovano, A.; Colombo, C.; Benedetti, F. Influence of an interaction between lithium salts and a functional polymorphism in SLC1A2 on the history of illness in bipolar disorder. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2012, 16, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallolas, J.; Hurtado, O.; Castellanos, M.; Blanco, M.; Sobrino, T.; Serena, J.; Vivancos, J.; Castillo, J.; Lizasoain, I.; Moro, M.A.; Dávalos, A. A polymorphism in the EAAT2 promoter is associated with higher glutamate concentrations and higher frequency of progressing stroke. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, R.M.; Tanaka, K.; Saksida, L.M.; Bussey, T.J.; Heilig, M.; Holmes, A. Assessment of glutamate transporter GLAST (EAAT1)-deficient mice for phenotypes relevant to the negative and executive/cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 1578–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aida, T.; Yoshida, J.; Nomura, M.; Tanimura, A.; Iino, Y.; Soma, M.; Bai, N.; Ito, Y.; Cui, W.; Aizawa, H.; et al. Astroglial glutamate transporter deficiency increases synaptic excitability and leads to pathological repetitive behaviors in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 1569–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hayashi, M.K. Structure-Function Relationship of Transporters in the Glutamate–Glutamine Cycle of the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041177
Hayashi MK. Structure-Function Relationship of Transporters in the Glutamate–Glutamine Cycle of the Central Nervous System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(4):1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041177
Chicago/Turabian StyleHayashi, Mariko Kato. 2018. "Structure-Function Relationship of Transporters in the Glutamate–Glutamine Cycle of the Central Nervous System" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 4: 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041177
APA StyleHayashi, M. K. (2018). Structure-Function Relationship of Transporters in the Glutamate–Glutamine Cycle of the Central Nervous System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(4), 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041177