Cannabinoid Receptors and the Endocannabinoid System: Signaling and Function in the Central Nervous System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Cannabinoid Receptors
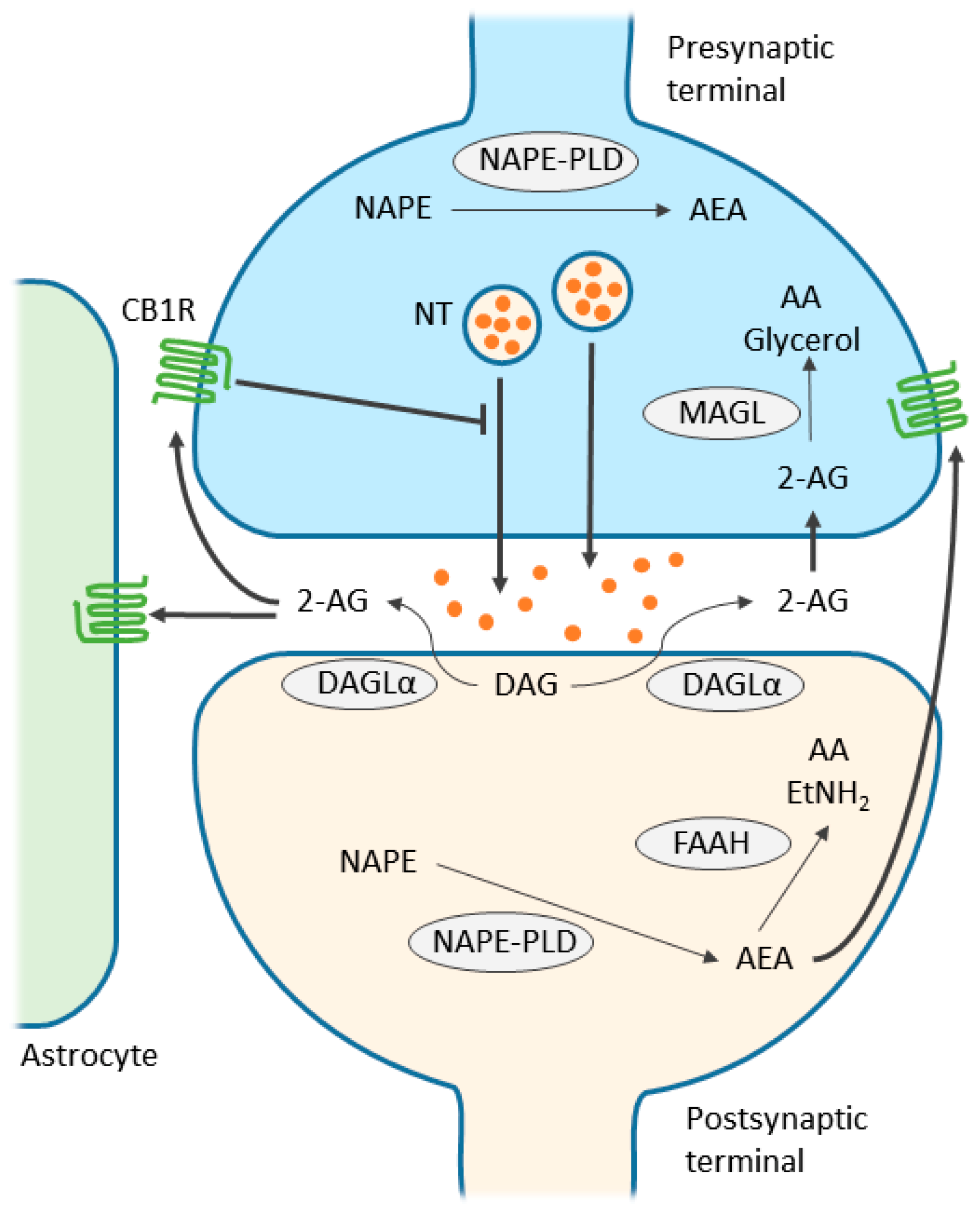
3. Endocannabinoid System
4. Endocannabinoid-Mediated Signaling
5. Distribution of Cannabinoid Receptors
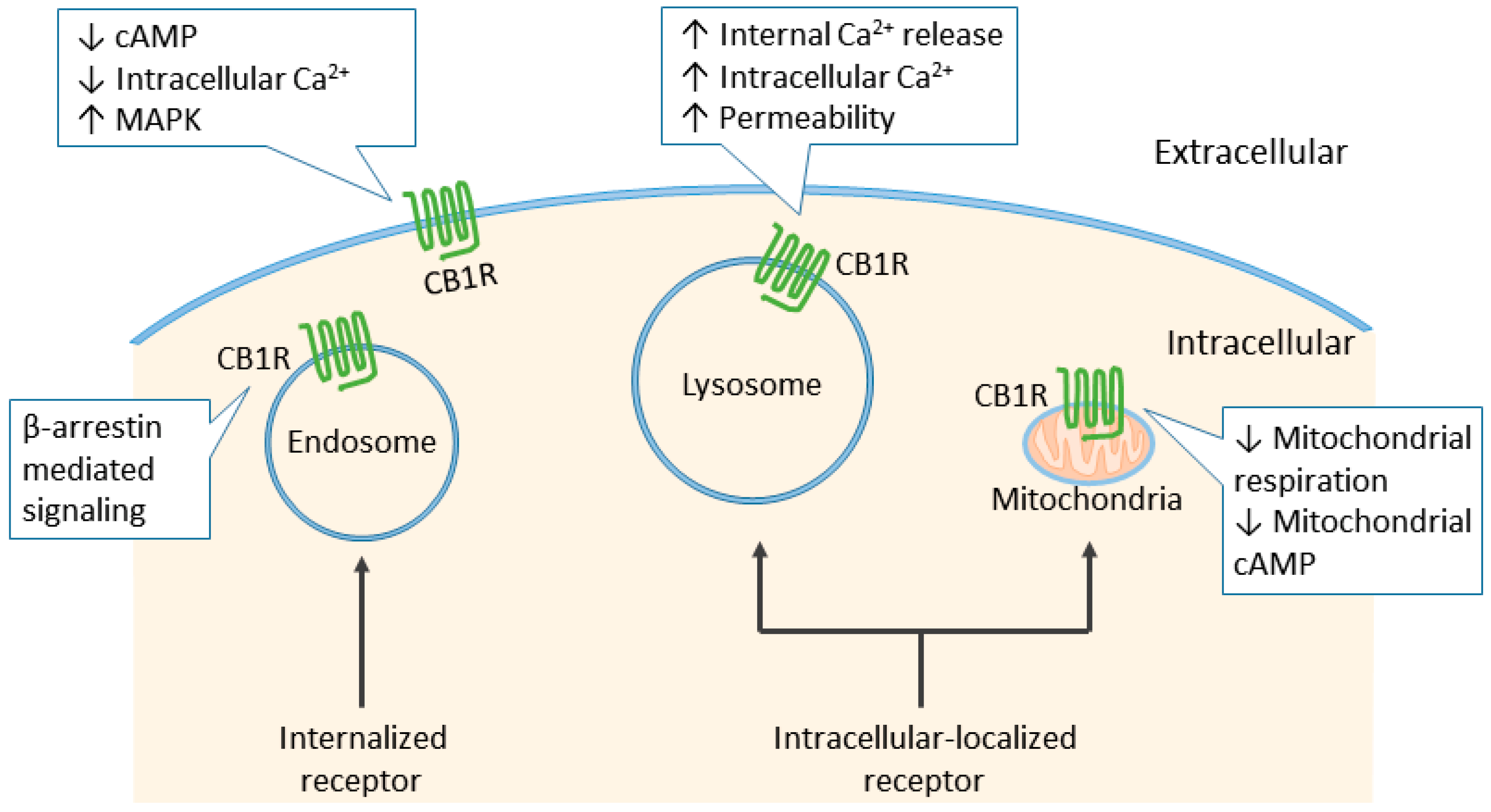
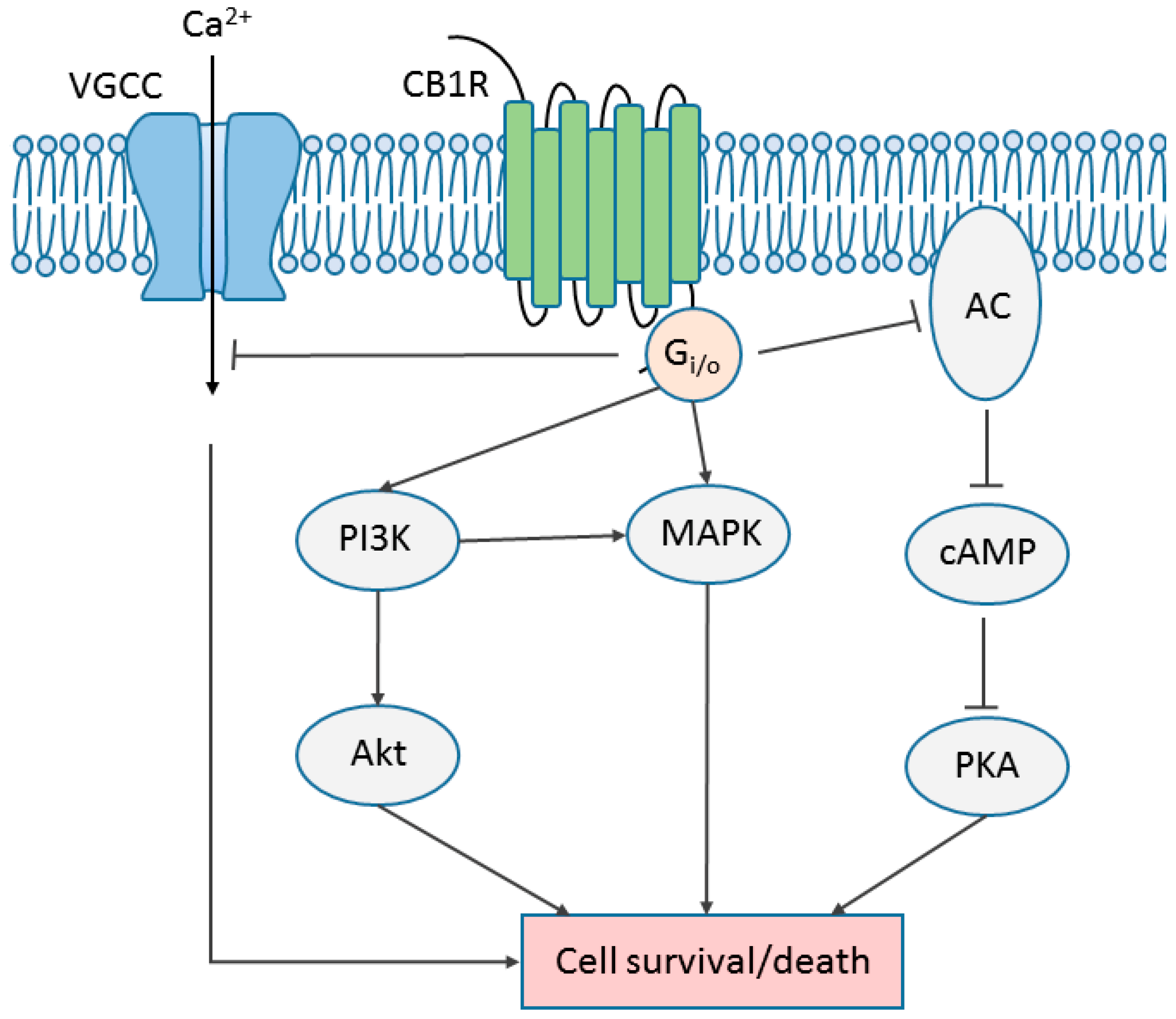
6. Cannabinoid Receptor Signaling
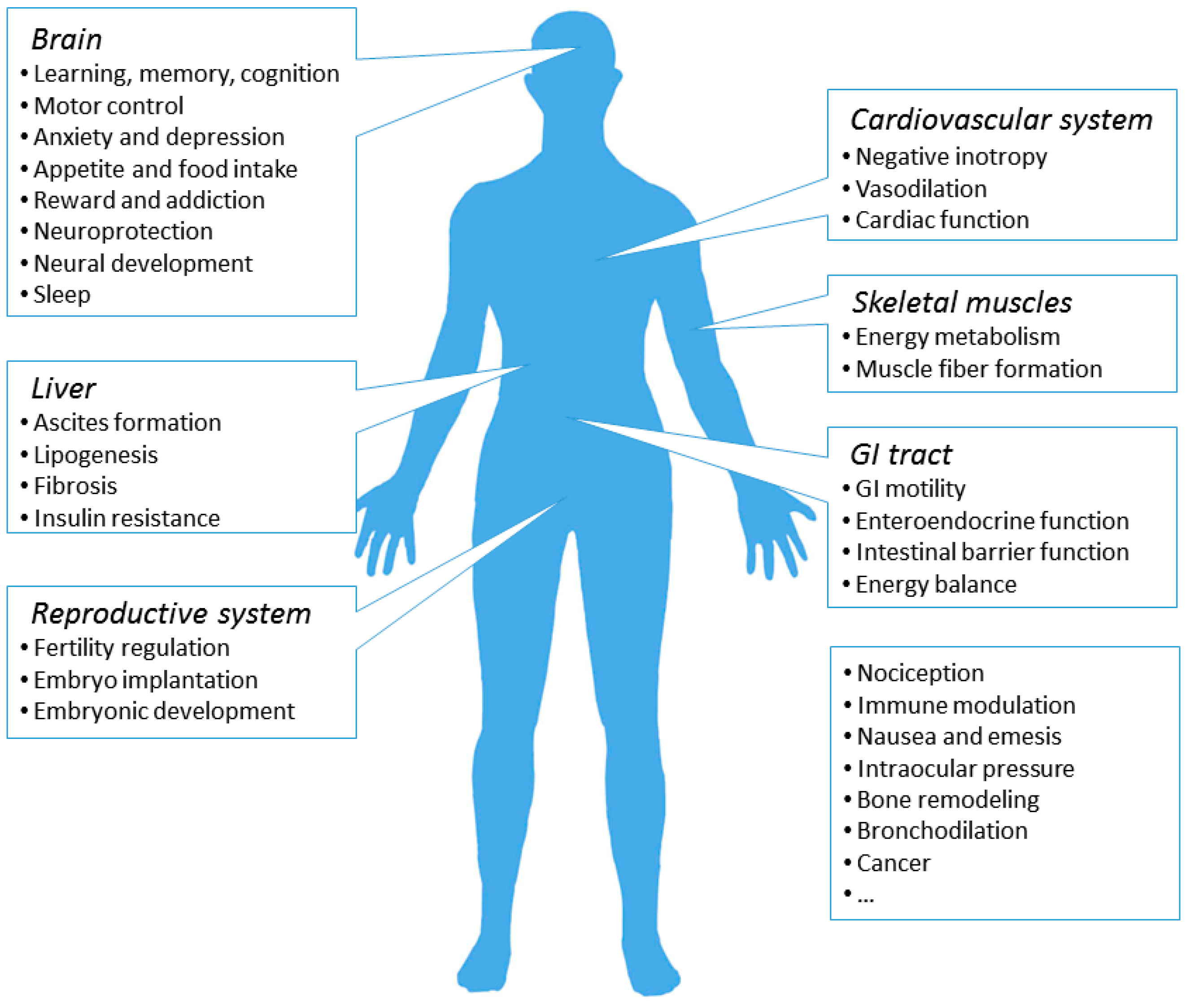
7. Physiological and Pathological Roles of the CB1R
8. Future Directions of Cannabinoid-Based Drug Discovery
9. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| THC | Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol |
| CBR | Cannabinoid receptor |
| AEA | N-arachidonoyl-ethanolamine |
| 2-AG | 2-arachidonoylglycerol |
| CBD | Cannabidiol |
| GPCR | G protein-coupled receptor |
| TRPV1 | Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 |
| NAPE | N-acyl-phosphatidylethanolamine |
| NAPE-PLD | NAPE-specific phospholipase D |
| DAG | Diacylglycerol |
| DAGL | DAG lipase |
| FAAH | Fatty acid amide hydrolase |
| MAGL | Monoacylglycerol lipase |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| DSI | Depolarization-induced suppression of inhibition |
| DSE | Depolarization-induced suppression of excitation |
| LTD | Long-term depression |
| AC | Adenylyl cyclase |
| PNS | Peripheral nervous system |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| PTX | Pertussis toxin |
| WIN | WIN 55,212-2 |
| NMDAR | N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor |
| cDNA | Complementary deoxyribonucleic acid |
| GABA | γ-aminobutyric acid |
| GIRK | G-protein-coupled inwardly rectifying K+ channel |
| ERK1/2 | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinases |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| HD | Huntington’s disease |
| MSN | Medium spiny projection neuron |
| Htt | Huntingtin |
References
- Mechoulam, R. The Pharmacohistory of Cannabis sativa, in Cannabis as Therapeutic Agent; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Iversen, L. The Science of Marijuana; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pacher, P.; Batkai, S.; Kunos, G. The endocannabinoid system as an emerging target of pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 389–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaoni, Y.; Mechoulam, R. Isolation, structure, and partial synthesis of an active constituent of hashish. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964, 86, 1646–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, L.A.; Lolait, S.J.; Brownstein, M.J.; Young, A.C.; Bonner, T.I. Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cdna. Nature 1990, 346, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devane, W.A.; Dysarz, F.A., 3rd; Johnson, M.R.; Melvin, L.S.; Howlett, A.C. Determination and characterization of a cannabinoid receptor in rat brain. Mol. Pharmacol. 1988, 34, 605–613. [Google Scholar]
- Pertwee, R.G.; Howlett, A.C.; Abood, M.E.; Alexander, S.P.; di Marzo, V.; Elphick, M.R.; Greasley, P.J.; Hansen, H.S.; Kunos, G.; Mackie, K.; et al. International union of basic and clinical pharmacology. LXXIX. Cannabinoid receptors and their ligands: Beyond CB1and CB2. Pharmacol. Rev. 2010, 62, 588–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, S.; Thomas, K.L.; Abu-Shaar, M. Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids. Nature 1993, 365, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kano, M.; Ohno-Shosaku, T.; Hashimotodani, Y.; Uchigashima, M.; Watanabe, M. Endocannabinoid-mediated control of synaptic transmission. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 309–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlett, A.C.; Barth, F.; Bonner, T.I.; Cabral, G.; Casellas, P.; Devane, W.A.; Felder, C.C.; Herkenham, M.; Mackie, K.; Martin, B.R.; et al. International union of pharmacology. XXVII. Classification of cannabinoid receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2002, 54, 161–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, T.; Kondo, S.; Sukagawa, A.; Nakane, S.; Shinoda, A.; Itoh, K.; Yamashita, A.; Waku, K. 2-arachidonoylgylcerol—A possible endogenous cannabinoid receptor-ligand in brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 215, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechoulam, R.; Benshabat, S.; Hanus, L.; Ligumsky, M.; Kaminski, N.E.; Schatz, A.R.; Gopher, A.; Almog, S.; Martin, B.R.; Compton, D.R.; et al. Identification of an endogenous 2-monoglyceride, present in canine gut, that binds to cannabinoid receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995, 50, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devane, W.A.; Hanus, L.; Breuer, A.; Pertwee, R.G.; Stevenson, L.A.; Griffin, G.; Gibson, D.; Mandelbaum, A.; Etinger, A.; Mechoulam, R. Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor. Science 1992, 258, 1946–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzo, A.A.; Borrelli, F.; Capasso, R.; di Marzo, V.; Mechoulam, R. Non-psychotropic plant cannabinoids: New therapeutic opportunities from an ancient herb. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, A.J.; Williams, C.M.; Whalley, B.J.; Stephens, G.J. Phytocannabinoids as novel therapeutic agents in cns disorders. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 133, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechoulam, R.; Sumariwalla, P.F.; Feldmann, M.; Gallily, R. Cannabinoids in models of chronic inflammatory conditions. Phytochem. Rev. 2005, 4, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, K.R.; Goyal, S.N.; Sharma, C.; Patil, C.R.; Ojha, S. Phytocannabinoids for cancer therapeutics: Recent updates and future prospects. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 3472–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertwee, R.G. Cannabinoid pharmacology: The first 66 years. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147, S163–S171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schacht, J.P.; Hutchison, K.E.; Filbey, F.M. Associations between cannabinoid receptor-1 (CNR1) variation and hippocampus and amygdala volumes in heavy cannabis users. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 2368–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartman, C.A.; Hopfer, C.J.; Haberstick, B.; Rhee, S.H.; Crowley, T.J.; Corley, R.P.; Hewitt, J.K.; Ehringer, M.A. The association between cannabinoid receptor 1 gene (CNR1) and cannabis dependence symptoms in adolescents and young adults. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2009, 104, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, A.; Lynskey, M.T. Candidate genes for cannabis use disorders: Findings, challenges and directions. Addiction 2009, 104, 518–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, T.; Vemuri, K.; Pu, M.; Qu, L.; Han, G.W.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Shui, W.; Li, S.; Korde, A.; et al. Crystal structure of the human cannabinoid receptor CB1. Cell 2016, 167, 750–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Z.; Yin, J.; Chapman, K.; Grzemska, M.; Clark, L.; Wang, J.; Rosenbaum, D.M. High-resolution crystal structure of the human CB1cannabinoid receptor. Nature 2016, 540, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, T.; Vemuri, K.; Nikas, S.P.; Laprairie, R.B.; Wu, Y.; Qu, L.; Pu, M.; Korde, A.; Jiang, S.; Ho, J.H.; et al. Crystal structures of agonist-bound human cannabinoid receptor CB1. Nature 2017, 547, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryberg, E.; Vu, H.K.; Larsson, N.; Groblewski, T.; Hjorth, S.; Elebring, T.; Sjorgren, S.; Greasley, P.J. Identification and characterisation of a novel splice variant of the human CB1receptor. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shire, D.; Carillon, C.; Kaghad, M.; Calandra, B.; Rinaldicarmona, M.; Lefur, G.; Caput, D.; Ferrara, P. An amino-terminal variant of the central cannabinoid receptor resulting from alternative splicing. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 3726–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Mariscal, I.; Krzysik-Walker, S.M.; Doyle, M.E.; Liu, Q.R.; Cimbro, R.; Calvo, S.S.C.; Ghosh, S.; Ciesla, L.; Moaddel, R.; Carlson, O.D.; et al. Human CB1 receptor isoforms, present in hepatocytes and β-cells, are involved in regulating metabolism. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straiker, A.; Wager-Miller, J.; Hutchens, J.; Mackie, K. Differential signalling in human cannabinoid CB1 receptors and their splice variants in autaptic hippocampal neurones. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 2660–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.C.; Jewell, J.P.; Lin, L.S.; Hagmann, W.K.; Fong, T.M.; Shen, C.P. Similar in vitro pharmacology of human cannabinoid CB1 receptor variants expressed in cho cells. Brain Res. 2008, 1238, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Bi, G.H.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Qu, H.; Zhang, S.J.; Li, C.Y.; Onaivi, E.S.; Gardner, E.L.; Xi, Z.X.; et al. Species differences in cannabinoid receptor 2 and receptor responses to cocaine self-administration in mice and rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 1037–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.R.; Pan, C.H.; Hishimoto, A.; Li, C.Y.; Xi, Z.X.; Llorente-Berzal, A.; Viveros, M.P.; Ishiguro, H.; Arinami, T.; Onaivi, E.S.; et al. Species differences in cannabinoid receptor 2 (CNR2 gene): Identification of novel human and rodent CB2 isoforms, differential tissue expression and regulation by cannabinoid receptor ligands. Genes Brain Behav. 2009, 8, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marzo, V.; de Petrocellis, L. Why do cannabinoid receptors have more than one endogenous ligand? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2012, 367, 3216–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, P.E.; Younts, T.J.; Chavez, A.E.; Hashimotodani, Y. Endocannabinoid signaling and synaptic function. Neuron 2012, 76, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katona, I.; Freund, T.F. Endocannabinoid signaling as a synaptic circuit breaker in neurological disease. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murataeva, N.; Straiker, A.; Mackie, K. Parsing the players: 2-arachidonoylglycerol synthesis and degradation in the CNS. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; McIntosh, A.L.; Martin, G.G.; Landrock, D.; Chung, S.; Landrock, K.K.; Dangott, L.J.; Li, S.R.; Kier, A.B.; Schroeder, F. Fabp1: A novel hepatic endocannabinoid and cannabinoid binding protein. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 5243–5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankman, J.L.; Simon, G.M.; Cravatt, B.F. A comprehensive profile of brain enzymes that hydrolyze the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol. Chem. Biol. 2007, 14, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouzer, C.A.; Marnett, L.J. Endocannabinoid oxygenation by cyclooxygenases, lipoxygenases, and cytochromes p450: Cross-talk between the eicosanoid and endocannabinoid signaling pathways. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5899–5921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maccarrone, M.; Rossi, S.; Bari, M.; de Chiara, V.; Fezza, F.; Musella, A.; Gasperi, V.; Prosperetti, C.; Bernardi, G.; Finazzi-Agro, A.; et al. Anandamide inhibits metabolism and physiological actions of 2-arachidonoylglycerol in the striatum. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno-Shosaku, T.; Kano, M. Endocannabinoid-mediated retrograde modulation of synaptic transmission. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2014, 29, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khlaifia, A.; Farah, H.; Gackiere, F.; Tell, F. Anandamide, cannabinoid type 1 receptor, and nmda receptor activation mediate non-hebbian presynaptically expressed long-term depression at the first central synapse for visceral afferent fibers. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 12627–12637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puente, N.; Cui, Y.H.; Lassalle, O.; Lafourcade, M.; Georges, F.; Venance, L.; Grandes, P.; Manzoni, O.J. Polymodal activation of the endocannabinoid system in the extended amygdala. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 1542–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavez, A.E.; Chiu, C.Q.; Castillo, P.E. Trpv1 activation by endogenous anandamide triggers postsynaptic long-term depression in dentate gyrus. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 1511–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grueter, B.A.; Brasnjo, G.; Malenka, R.C. Postsynaptic trpv1 triggers cell type-specific long-term depression in the nucleus accumbens. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, T.N.; Kreitzer, A.C. Rgs4 is required for dopaminergic control of striatal ltd and susceptibility to parkinsonian motor deficits. Neuron 2012, 73, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlosburg, J.E.; Blankman, J.L.; Long, J.Z.; Nomura, D.K.; Pan, B.; Kinsey, S.G.; Nguyen, P.T.; Ramesh, D.; Booker, L.; Burston, J.J.; et al. Chronic monoacylglycerol lipase blockade causes functional antagonism of the endocannabinoid system. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinelli, S.; Pacioni, S.; Bisogno, T.; di Marzo, V.; Prince, D.A.; Huguenard, J.R.; Bacci, A. The endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol is responsible for the slow self-inhibition in neocortical interneurons. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 13532–13541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, R.; Testa-Silva, G.; Heistek, T.S.; Canto, C.B.; Lodder, J.C.; Bisogno, T.; di Marzo, V.; Brussaard, A.B.; Burnashev, N.; Mansvelder, H.D. Diacylglycerol lipase is not involved in depolarization-induced suppression of inhibition at unitary inhibitory connections in mouse hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 2710–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinelli, S.; Pacioni, S.; Cannich, A.; Marsicano, G.; Bacci, A. Self-modulation of neocortical pyramidal neurons by endocannabinoids. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 1488–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacci, A.; Huguenard, J.R.; Prince, D.A. Long-lasting self-inhibition of neocortical interneurons mediated by endocannabinoids. Nature 2004, 431, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Kesner, P.; Metna-Laurent, M.; Duan, T.T.; Xu, L.; Georges, F.; Koehl, M.; Abrous, D.N.; Mendizabal-Zubiaga, J.; Grandes, P.; et al. Acute cannabinoids impair working memory through astroglial CB1 receptor modulation of hippocampal ltd. Cell 2012, 148, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarrete, M.; Araque, A. Endocannabinoids potentiate synaptic transmission through stimulation of astrocytes. Neuron 2010, 68, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarrete, M.; Araque, A. Endocannabinoids mediate neuron-astrocyte communication. Neuron 2008, 57, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stella, N. Endocannabinoid signaling in microglial cells. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhopeshwarkar, A.; Mackie, K. CB2 cannabinoid receptors as a therapeutic target-what does the future hold? Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 86, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atwood, B.K.; Mackie, K. CB2: A cannabinoid receptor with an identity crisis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.P.; Onaivi, E.S.; Ishiguro, H.; Liu, Q.R.; Tagliaferro, P.A.; Brusco, A.; Uhl, G.R. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors: Immunohistochemical localization in rat brain. Brain Res. 2006, 1071, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den Boon, F.S.; Chameau, P.; Schaafsma-Zhao, Q.; van Aken, W.; Bari, M.; Oddi, S.; Kruse, C.G.; Maccarrone, M.; Wadman, W.J.; Werkman, T.R. Excitability of prefrontal cortical pyramidal neurons is modulated by activation of intracellular type-2 cannabinoid receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3534–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackie, K. Distribution of cannabinoid receptors in the central and peripheral nervous system. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2005, 299–325. [Google Scholar]
- Katona, I.; Sperlagh, B.; Sik, A.; Kafalvi, A.; Vizi, E.S.; Mackie, K.; Freund, T.F. Presynaptically located CB1 cannabinoid receptors regulate GABA release from axon terminals of specific hippocampal interneurons. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 4544–4558. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsou, K.; Brown, S.; Sanudo-Pena, M.C.; Mackie, K.; Walker, J.M. Immunohistochemical distribution of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 1998, 83, 393–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroso, M.; Szabo, G.G.; Kim, H.K.; Alexander, A.; Bui, A.D.; Lee, S.H.; Lutz, B.; Soltesz, I. Cannabinoid control of learning and memory through hcn channels. Neuron 2016, 89, 1059–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maccarrone, M.; Bab, R.; Biro, T.; Cabral, G.A.; Dey, S.K.; di Marzo, V.; Konje, J.C.; Kunos, G.; Mechoulam, R.; Pacher, P.; et al. Endocannabinoid signaling at the periphery: 50 years after thc. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, J.; Trembovler, V.; di Marzo, V.; Petrosino, S.; Leo, G.; Alexandrovich, A.; Regev, E.; Casap, N.; Shteyer, A.; Ledent, C.; et al. The cannabinoid CB1 receptor regulates bone formation by modulating adrenergic signaling. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clapper, J.R.; Moreno-Sanz, G.; Russo, R.; Guijarro, A.; Vacondio, F.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Sanchini, S.; Sciolino, N.R.; Spradley, J.M.; et al. Anandamide suppresses pain initiation through a peripheral endocannabinoid mechanism. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, T.J.; Helesic, G.; Parghi, D.; Hargreaves, K.M.; Flores, C.M. The neuronal distribution of cannabinoid receptor type 1 in the trigeminal ganglion of the rat. Neuroscience 2003, 120, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veress, G.; Meszar, Z.; Muszil, D.; Avelino, A.; Matesz, K.; Mackie, K.; Nagy, I. Characterisation of cannabinoid 1 receptor expression in the perikarya, and peripheral and spinal processes of primary sensory neurons. Brain Struct. Funct. 2013, 218, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzo, A.A.; Sharkey, K.A. Cannabinoids and the gut: New developments and emerging concepts. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 126, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.K.; Devi, L.A. The highs and lows of cannabinoid receptor expression in disease: Mechanisms and their therapeutic implications. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montecucco, F.; di Marzo, V. At the heart of the matter: The endocannabinoid system in cardiovascular function and dysfunction. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozenfeld, R. Type I cannabinoid receptor trafficking: All roads lead to lysosome. Traffic 2011, 12, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leterrier, C.; Bonnard, D.; Carrel, D.; Rossier, J.; Lenkei, Z. Constitutive endocytic cycle of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 36013–36021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimsey, N.L.; Graham, E.S.; Dragunow, M.; Glass, M. Cannabinoid receptor 1 trafficking and the role of the intracellular pool: Implications for therapeutics. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1050–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozenfeld, R.; Devi, L.A. Regulation of CB1 cannabinoid receptor trafficking by the adaptor protein ap-3. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 2311–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brailoiu, G.C.; Oprea, T.I.; Zhao, P.; Abood, M.E.; Brailoiu, E. Intracellular cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) receptors are activated by anandamide. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 29166–29174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, B.R. Cellular effects of cannabinoids. Pharmacol. Rev. 1986, 38, 45–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benard, G.; Massa, F.; Puente, N.; Lourenco, J.; Bellocchio, L.; Soria-Gomez, E.; Matias, I.; Delamarre, A.; Metna-Laurent, M.; Cannich, A.; et al. Mitochondrial CB1 receptors regulate neuronal energy metabolism. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert-Chatelain, E.; Reguero, L.; Puente, N.; Lutz, B.; Chaouloff, F.; Rossignol, R.; Piazza, P.V.; Benard, G.; Grandes, P.; Marsicano, G. Cannabinoid control of brain bioenergetics: Exploring the subcellular localization of the CB1 receptor. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert-Chatelain, E.; Reguero, L.; Puente, N.; Lutz, B.; Chaouloff, F.; Rossignol, R.; Piazza, P.V.; Benard, G.; Grandes, P.; Marsicano, G. Studying mitochondrial CB1 receptors: Yes we can. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morozov, Y.M.; Horvath, T.L.; Rakic, P. A tale of two methods: Identifying neuronal CB1 receptors. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, M.; Varela, L.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, J.D.; Hernandez-Nuno, F.; Simonds, S.E.; Castorena, C.M.; Vianna, C.R.; Elmquist, J.K.; Morozov, Y.M.; et al. Hypothalamic pomc neurons promote cannabinoid-induced feeding. Nature 2015, 519, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Jia, J.; Niu, W.; Jiang, T.; Zhai, Q.; Yang, L.; Bai, F.; Wang, Q.; Xiong, L. Mitochondrial CB1 receptor is involved in acea-induced protective effects on neurons and mitochondrial functions. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert-Chatelain, E.; Desprez, T.; Serrat, R.; Bellocchio, L.; Soria-Gomez, E.; Busquets-Garcia, A.; Pagano Zottola, A.C.; Delamarre, A.; Cannich, A.; Vincent, P.; et al. A cannabinoid link between mitochondria and memory. Nature 2016, 539, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Z.H.; Cai, Q. Mitochondrial transport in neurons: Impact on synaptic homeostasis and neurodegeneration. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattson, M.P.; Gleichmann, M.; Cheng, A. Mitochondria in neuroplasticity and neurological disorders. Neuron 2008, 60, 748–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibault, K.; Carrel, D.; Bonnard, D.; Gallatz, K.; Simon, A.; Biard, M.; Pezet, S.; Palkovits, M.; Lenkei, Z. Activation-dependent subcellular distribution patterns of CB1 cannabinoid receptors in the rat forebrain. Cereb. Cortex 2013, 23, 2581–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brailoiu, G.C.; Deliu, E.; Marcu, J.; Hoffman, N.E.; Console-Bram, L.; Zhao, P.; Madesh, M.; Abood, M.E.; Brailoiu, E. Differential activation of intracellular versus plasmalemmal CB2 cannabinoid receptors. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 4990–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demuth, D.G.; Molleman, A. Cannabinoid signalling. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, M.H.; Bayewitch, M.; Avidor-Reiss, T.; Levy, R.; Vogel, Z. Cannabinoid receptor activation differentially regulates the various adenylyl cyclase isozymes. J. Neurochem. 1998, 71, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maneuf, Y.P.; Brotchie, J.M. Paradoxical action of the cannabinoid win 55,212-2 in stimulated and basal cyclic amp accumulation in rat globus pallidus slices. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 120, 1397–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, M.; Felder, C.C. Concurrent stimulation of cannabinoid CB1 and dopamine d2 receptors augments camp accumulation in striatal neurons: Evidence for a gs linkage to the CB1 receptor. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 5327–5333. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonhaus, D.W.; Chang, L.K.; Kwan, J.; Martin, G.R. Dual activation and inhibition of adenylyl cyclase by cannabinoid receptor agonists: Evidence for agonist-specific trafficking of intracellular responses. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 287, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lauckner, J.E.; Hille, B.; Mackie, K. The cannabinoid agonist win55,212-2 increases intracellular calcium via CB1 receptor coupling to Gq/11 G proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 19144–19149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turu, G.; Hunyady, L. Signal transduction of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 44, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.P.; Safo, P.K.; Regehr, W.G. Endocannabinoids inhibit transmission at granule cell to purkinje cell synapses by modulating three types of presynaptic calcium channels. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 5623–5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twitchell, W.; Brown, S.; Mackie, K. Cannabinoids inhibit N- and P/Q-type calcium channels in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 1997, 78, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackie, K.; Devane, W.A.; Hille, B. Anandamide, an endogenous cannabinoid, inhibits calcium currents as a partial agonist in N18 neuroblastoma-cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 1993, 44, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mackie, K.; Hille, B. Cannabinoids inhibit N-type calcium channels in neuroblastoma glioma-cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 3825–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gergely, G.S.; Nora, L.; Noemi, H.; Tibor, A.; Zoltan, N.; Norbert, H. Presynaptic calcium channel inhibition underlies CB1 cannabinoid receptor-mediated suppression of gaba release. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 7958–7963. [Google Scholar]
- Fisyunov, A.; Tsintsadze, V.; Min, R.; Burnashev, N.; Lozovaya, N. Cannabinoids modulate the P-type high-voltage-activated calcium currents in purkinje neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2006, 96, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackie, K.; Lai, Y.; Westenbroek, R.; Mitchell, R. Cannabinoids activate an inwardly rectifying potassium conductance and inhibit Q-type calcium currents in att20 cells transfected with rat-brain cannabinoid receptor. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 6552–6561. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Ikeda, S.R. Endocannabinoids modulate N-type calcium channels and G-protein-coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channels via CB1 cannabinoid receptors heterologously expressed in mammalian neurons. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 65, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbe, D.; Alonso, G.; Duchamp, F.; Bockaert, J.; Manzoni, O.J. Localization and mechanisms of action of cannabinoid receptors at the glutamatergic synapses of the mouse nucleus accumbens. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Howlett, A.C.; Blume, L.C.; Dalton, G.D. CB1 cannabinoid receptors and their associated proteins. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 1382–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galve-Roperh, I.; Rueda, D.; del Pulgar, T.G.; Velasco, G.; Guzman, M. Mechanism of extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation by the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 62, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Otero, J.; Ahn, K.H.; Delgado-Peraza, F.; Mackie, K.; Kendall, D.A.; Yudowski, G.A. Ligand-specific endocytic dwell times control functional selectivity of the cannabinoid receptor 1. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouaboula, M.; Poinotchazel, C.; Bourrie, B.; Canat, X.; Calandra, B.; Rinaldicarmona, M.; Lefur, G.; Casellas, P. Activation of mitogen-activated protein-kinases by stimulation of the central cannabinoid receptor CB1. Biochem. J. 1995, 312, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derkinderen, P.; Ledent, C.; Parmentier, M.; Girault, J.A. Cannabinoids activate p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases through CB1 receptors in hippocampus. J. Neurochem. 2001, 77, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rueda, D.; Galve-Roperh, I.; Haro, A.; Guzman, M. The CB1 cannabinoid receptor is coupled to the activation of c-jun N-terminal kinase. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 58, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Gao, B.; Mirshahi, F.; Sanyal, A.J.; Khanolkar, A.D.; Makriyannis, A.; Kunos, G. Functional CB1 cannabinoid receptors in human vascular endothelial cells. Biochem. J. 2000, 346, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.C.J.; Gomes, I.; Nguyen, T.; Jayaram, G.; Ram, P.T.; Devi, L.A.; Iyengar, R. The Gαo/i-coupled cannabinoid receptor-mediated neurite outgrowth involves rap regulation of src and stat3. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 33426–33434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCudden, C.R.; Hains, M.D.; Kimple, R.J.; Siderovski, D.P.; Willard, F.S. G-protein signaling: Back to the future. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 551–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouznetsova, M.; Kelley, B.; Shen, M.X.; Thayer, S.A. Desensitization of cannabinoid-mediated presynaptic inhibition of neurotransmission between rat hippocampal neurons in culture. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 61, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.Z.; Brown, S.; Roche, J.P.; Hsieh, C.; Celver, J.P.; Kovoor, A.; Chavkin, C.; Mackie, K. Distinct domains of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor mediate desensitization and internalization. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 3773–3780. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Daigle, T.L.; Kearn, C.S.; Mackie, K. Rapid CB1 cannabinoid receptor desensitization defines the time course of erk1/2 map kinase signaling. Neuropharmacology 2008, 54, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.T.; Schmid, C.L.; Raehal, K.M.; Selley, D.E.; Bohn, L.M.; Sim-Selley, L.J. Beta-arrestin2 regulates cannabinoid CB1 receptor signaling and adaptation in a central nervous system region-dependent manner. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 71, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breivogel, C.S.; Lambert, J.M.; Gerfin, S.; Huffman, J.W.; Razdan, R.K. Sensitivity to delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol is selectively enhanced in beta-arrestin2−/− mice. Behav. Pharmacol. 2008, 19, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, K.H.; Mahmoud, M.M.; Shim, J.Y.; Kendall, D.A. Distinct roles of beta-arrestin 1 and beta-arrestin 2 in org27569-induced biased signaling and internalization of the cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1). J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 9790–9800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez del Pulgar, T.; Velasco, G.; Guzman, M. The CB1 cannabinoid receptor is coupled to the activation of protein kinase B/Akt. Biochem. J. 2000, 347, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, O.; Sanchez-Rodriguez, A.; Le, M.Q.U.; Sanchez-Caro, C.; Molina-Holgado, F.; Molina-Holgado, E. Cannabinoid receptor agonists modulate oligodendrocyte differentiation by activating pi3k/akt and the mammalian target of rapamycin (mtor) pathways. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 1520–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Holgado, E.; Vela, J.M.; Arevalo-Martin, A.; Almazan, G.; Molina-Holgado, F.; Borrell, J.; Guaza, C. Cannabinoids promote oligodendrocyte progenitor survival: Involvement of cannabinoid receptors and phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/akt signaling. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 9742–9753. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Molina-Holgado, F.; Pinteaux, E.; Heenan, L.; Moore, J.D.; Rothwell, N.J.; Gibson, R.M. Neuroprotective effects of the synthetic cannabinoid hu-210 in primary cortical neurons are mediated by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/akt signaling. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2005, 28, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaita, A.; Puighermanal, E.; Maldonado, R. Regulation of pi3k/akt/gsk-3 pathway by cannabinoids in the brain. J. Neurochem. 2007, 102, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazquez, C.; Chiarlone, A.; Bellocchio, L.; Resel, E.; Pruunsild, P.; Garcia-Rincon, D.; Sendtner, M.; Timmusk, T.; Lutz, B.; Galve-Roperh, I.; et al. The CB1 cannabinoid receptor signals striatal neuroprotection via a pi3k/akt/mtorc1/bdnf pathway. Cell. Death Differ. 2015, 22, 1618–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Cardona, A.P.; Perez-Cerezales, S.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, R.; Laguna-Barraza, R.; Pericuesta, E.; Agirregoitia, N.; Gutierrez-Adan, A.; Agirregoitia, E. CB1 cannabinoid receptor drives oocyte maturation and embryo development via pi3k/akt and mapk pathways. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 3372–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marzo, V.; Stella, N.; Zimmer, A. Endocannabinoid signalling and the deteriorating brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iversen, L. Cannabis and the brain. Brain 2003, 126, 1252–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marzo, V. Targeting the endocannabinoid system: To enhance or reduce? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 438–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdeman, G.; Lovinger, D.M. CB1 cannabinoid receptor inhibits synaptic release of glutamate in rat dorsolateral striatum. J. Neurophysiol. 2001, 85, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarlone, A.; Bellocchio, L.; Blazquez, C.; Resel, E.; Soria-Gomez, E.; Cannich, A.; Ferrero, J.J.; Sagredo, O.; Benito, C.; Romero, J.; et al. A restricted population of CB1 cannabinoid receptors with neuroprotective activity. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8257–8262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsicano, G.; Goodenough, S.; Monory, K.; Hermann, H.; Eder, M.; Cannich, A.; Azad, S.C.; Cascio, M.G.; Gutierrez, S.O.; van der Stelt, M.; et al. CB1 cannabinoid receptors and on-demand defense against excitotoxicity. Science 2003, 302, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoppi, S.; Nievas, B.G.P.; Madrigal, J.L.M.; Manzanares, J.; Leza, J.C.; Garcia-Bueno, B. Regulatory role of cannabinoid receptor 1 in stress-induced excitotoxicity and neuroinflammation. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 805–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazquez, C.; Chiarlone, A.; Sagredo, O.; Aguado, T.; Pazos, M.R.; Resel, E.; Palazuelos, J.; Julien, B.; Salazar, M.; Borner, C.; et al. Loss of striatal type 1 cannabinoid receptors is a key pathogenic factor in huntington’s disease. Brain 2011, 134, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Won, S.J.; Mao, X.O.; Jin, K.; Greenberg, D.A. Molecular mechanisms of cannabinoid protection from neuronal excitotoxicity. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 69, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaspekov, L.G.; Verca, M.S.B.; Frumkina, L.E.; Hermann, H.; Marsicano, G.; Lutz, B. Involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in cannabinoid receptor-dependent protection against excitotoxicity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Blazquez, P.; Rodriguez-Munoz, M.; Vicente-Sanchez, A.; Garzon, J. Cannabinoid receptors couple to nmda receptors to reduce the production of no and the mobilization of zinc induced by glutamate. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1766–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente-Sanchez, A.; Sanchez-Blazquez, P.; Rodriguez-Munoz, M.; Garzon, J. Hint1 protein cooperates with cannabinoid 1 receptor to negatively regulate glutamate nmda receptor activity. Mol. Brain 2013, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brotchie, J.M. CB1 cannabinoid receptor signalling in parkinson’s disease. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2003, 3, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waksman, Y.; Olson, J.M.; Carlisle, S.J.; Cabral, G.A. The central cannabinoid receptor (CB1) mediates inhibition of nitric oxide production by rat microglial cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 288, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Milton, N.G.N. Anandamide and noladin ether prevent neurotoxicity of the human amyloid-beta peptide. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 332, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, C.; Nunez, E.; Tolon, R.M.; Carrier, E.J.; Rabano, A.; Hillard, C.J.; Romero, J. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors and fatty acid amide hydrolase are selectively overexpressed in neuritic plaque-associated glia in alzheimer’s disease brains. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 11136–11141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Romero, J.; Berrendero, F.; Garcia-Gil, L.; de la Cruz, P.; Ramos, J.A.; Fernandez-Ruiz, J.J. Loss of cannabinoid receptor binding and messenger RNA levels and cannabinoid agonist-stimulated [35S]guanylyl-5′-O-(thio)-triphosphate binding in the basal ganglia of aged rats. Neuroscience 1998, 84, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westlake, T.M.; Howlett, A.C.; Bonner, T.I.; Matsuda, L.A.; Herkenham, M. Cannabinoid receptor-binding and messenger-RNA expression in human brain—An in-vitro receptor autoradiography and in-situ hybridization histochemistry study of normal aged and alzheimers brains. Neuroscience 1994, 63, 637–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, B.G.; Blazquez, C.; Gomez del Pulgar, T.; Guzman, M.; de Ceballos, M.L. Prevention of alzheimer’s disease pathology by cannabinoids: Neuroprotection mediated by blockade of microglial activation. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 1904–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghani, M.; Shabani, M.; Javan, M.; Motamedi, F.; Janahmadi, M. CB1 cannabinoid receptor activation rescues amyloid beta-induced alterations in behaviour and intrinsic electrophysiological properties of rat hippocampal ca1 pyramidal neurones. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 29, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aso, E.; Palomer, E.; Juves, S.; Maldonado, R.; Munoz, F.J.; Ferrer, I. CB1 agonist acea protects neurons and reduces the cognitive impairment of AβPP/PS1 mice. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 30, 439–459. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van der Stelt, M.; Mazzola, C.; Esposito, G.; Matias, I.; Petrosino, S.; de Filippis, D.; Micale, V.; Steardo, L.; Drago, F.; Iuvone, T.; et al. Endocannabinoids and beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in vivo: Effect of pharmacological elevation of endocannabinoid levels. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 1410–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, M.; Faull, R.L.M.; Dragunow, M. Loss of cannabinoid receptors in the substantia-nigra in huntingtons-disease. Neuroscience 1993, 56, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, M.; Dragunow, M.; Faull, R.L.M. The pattern of neurodegeneration in huntington’s disease: A comparative study of cannabinoid, dopamine, adenosine and GABAA receptor alterations in the human basal ganglia in huntington’s disease. Neuroscience 2000, 97, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, E.A.; Coy, J.; Swinney, K.; Fung, S.; Cherry, A.E.T.; Marrs, W.R.; Naydenov, A.V.; Lin, Y.H.; Sun, X.C.; Keene, C.D.; et al. Downregulation of cannabinoid receptor 1 from neuropeptide y interneurons in the basal ganglia of patients with huntington’s disease and mouse models. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2013, 37, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, M.; Van Dellen, A.; Blakemore, C.; Hannan, A.J.; Faull, R.L.M. Delayed onset of huntington’s disease in mice in an enriched environment correlates with delayed loss of cannabinoid CB1 receptors. Neuroscience 2004, 123, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mievis, S.; Blum, D.; Ledent, C. Worsening of huntington disease phenotype in CB1 receptor knockout mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 42, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naydenov, A.V.; Sepers, M.D.; Swinney, K.; Raymond, L.A.; Palmiter, R.D.; Stella, N. Genetic rescue of CB1 receptors on medium spiny neurons prevents loss of excitatory striatal synapses but not motor impairment in hd mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 71, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowie, M.J.; Howard, M.L.; Nicholson, L.F.B.; Faull, R.L.M.; Hannan, A.J.; Glass, M. Behavioural and molecular consequences of chronic cannabinoid treatment in huntington’s disease transgenic mice. Neuroscience 2010, 170, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellison, J.M.; Gelwan, E.; Ogletree, J. Complex partial seizure symptoms affected by marijuana abuse. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1990, 51, 439–440. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Consroe, P.F.; Wood, G.C.; Buchsbaum, H. Anticonvulsant nature of marihuana smoking. JAMA 1975, 234, 306–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeler, M.H.; Reifler, C.B. Grand mal convulsions subsequent to marijuana use—Case report. Dis. Nerv. Syst. 1967, 28, 474–475. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clement, A.B.; Hawkins, E.G.; Lichtman, A.H.; Cravatt, B.F. Increased seizure susceptibility and proconvulsant activity of anandamide in mice lacking fatty acid amide hydrolase. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 3916–3923. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wallace, M.J.; Martin, B.R.; DeLorenzo, R.J. Evidence for a physiological role of endocannabinoids in the modulation of seizure threshold and severity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 452, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Neu, A.; Howard, A.L.; Foldy, C.; Echegoyen, J.; Hilgenberg, L.; Smith, M.; Mackie, K.; Soltesz, I. Prevention of plasticity of endocannabinoid signaling inhibits persistent limbic hyperexcitability caused by developmental seizures. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, K.; Ratzliff, A.; Hilgenberg, L.; Gulyas, A.; Freund, T.F.; Smith, M.; Dinh, T.P.; Piomelli, D.; Mackie, K.; Soltesz, I. Long-term plasticity of endocannabinoid signaling induced by developmental febrile seizures. Neuron 2003, 39, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskaran, M.D.; Smith, B.N. Cannabinoid-mediated inhibition of recurrent excitatory circuitry in the dentate gyrus in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falenski, K.W.; Blair, R.E.; Sim-Selley, L.J.; Martin, B.R.; DeLorenzo, R.J. Status epilepticus causes a long-lasting redistribution of hippocampal cannabinoid type 1 receptor expression and function in the rat pilocarpine model of acquired epilepsy. Neuroscience 2007, 146, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wallace, M.J.; Blair, R.E.; Falenski, K.W.; Martin, B.R.; DeLorenzo, R.J. The endogenous cannabinoid system regulates seizure frequency and duration in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 307, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falenski, K.W.; Carter, D.S.; Harrison, A.J.; Martin, B.R.; Blair, R.E.; DeLorenzo, R.J. Temporal characterization of changes in hippocampal cannabinoid CB1 receptor expression following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Brain Res. 2009, 1262, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marzo, V.; Matias, I. Endocannabinoid control of food intake and energy balance. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkham, T.C.; Williams, C.M.; Fezza, F.; di Marzo, V. Endocannabinoid levels in rat limbic forebrain and hypothalamus in relation to fasting, feeding and satiation: Stimulation of eating by 2-arachidonoyl glycerol. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 136, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellocchio, L.; Lafenetre, P.; Cannich, A.; Cota, D.; Puente, N.; Grandes, P.; Chaouloff, F.; Piazza, P.V.; Marsicano, G. Bimodal control of stimulated food intake by the endocannabinoid system. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria-Gomez, E.; Bellocchio, L.; Reguero, L.; Lepousez, G.; Martin, C.; Bendahmane, M.; Ruehle, S.; Remmers, F.; Desprez, T.; Matias, I.; et al. The endocannabinoid system controls food intake via olfactory processes. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, F.A.; Crippa, J.A. The psychiatric side-effects of rimonabant. Rev. Bras. Psiquiatr. 2009, 31, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, M. Cannabinoid receptor signaling in central regulation of feeding behavior: A mini-review. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fine, P.G.; Rosenfeld, M.J. The endocannabinoid system, cannabinoids, and pain. Rambam Maimonides Med. J. 2013, 4, e0022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donvito, G.; Nass, S.R.; Wilkerson, J.L.; Curry, Z.A.; Schurman, L.D.; Kinsey, S.G.; Lichtman, A.H. The endogenous cannabinoid system: A budding source of targets for treating inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 43, 52–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akopian, A.N.; Ruparel, N.B.; Jeske, N.A.; Patwardhan, A.; Hargreaves, K.M. Role of ionotropic cannabinoid receptors in peripheral antinociception and antihyperalgesia. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhaveri, M.D.; Sagar, D.R.; Elmes, S.J.R.; Kendall, D.A.; Chapman, V. Cannabinoid CB2 receptor-mediated anti-nociception in models of acute and chronic pain. Mol. Neurobiol. 2007, 36, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, E.B. Cannabinoids in the management of difficult to treat pain. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2008, 4, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laprairie, R.B.; Bagher, A.M.; Kelly, M.E.; Denovan-Wright, E.M. Cannabidiol is a negative allosteric modulator of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 4790–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, W.; Christie, M.J.; Currow, D. Cannabinoids and cancer: Causation, remediation, and palliation. Lancet Oncol. 2005, 6, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, M. Cannabinoids: Potential anticancer agents. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco, G.; Sanchez, C.; Guzman, M. Towards the use of cannabinoids as antitumour agents. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisanti, S.; Picardi, P.; D’Alessandro, A.; Laezza, C.; Bifulco, M. The endocannabinoid signaling system in cancer. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, C.; de Ceballos, M.L.; del Pulgar, T.G.; Rueda, D.; Corbacho, C.; Velasco, G.; Galve-Roperh, I.; Huffman, J.W.; Cajal, S.R.Y.; Guzman, M. Inhibition of glioma growth in vivo by selective activation of the CB2 cannabinoid receptor. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 5784–5789. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caffarel, M.M.; Sarrio, D.; Palacios, J.; Guzman, M.; Sanchez, C. Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol inhibits cell cycle progression in human breast cancer cells through cdc2 regulation. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 6615–6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, S.; Fischer, O.M.; Ullrich, A. Cannabinoids induce cancer cell proliferation via tumor necrosis factor alpha-converting enzyme (tace/adam17)-mediated transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 1943–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramowicz, M.; Zuccotti, G.; Pflomm, J.M. Cannabis and cannabinoids. JAMA 2016, 316, 2424–2425. [Google Scholar]
- Volkow, N.D.; Swanson, J.M.; Evins, A.E.; DeLisi, L.E.; Meier, M.H.; Gonzalez, R.; Bloomfield, M.A.P.; Curran, H.V.; Baler, R. Effects of cannabis use on human behavior, including cognition, motivation, and psychosis: A review. JAMA Psychiatry 2016, 73, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.; Chicca, A.; Tamborrini, M.; Eisen, D.; Lerner, R.; Lutz, B.; Poetz, O.; Pluschke, G.; Gertsch, J. Identification and quantification of a new family of peptide endocannabinoids (pepcans) showing negative allosteric modulation at CB1 receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 36944–36967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamplona, F.A.; Ferreira, J.; Menezes de Lima, O., Jr.; Duarte, F.S.; Bento, A.F.; Forner, S.; Villarinho, J.G.; Bellocchio, L.; Wotjak, C.T.; Lerner, R.; et al. Anti-inflammatory lipoxin a4 is an endogenous allosteric enhancer of CB1 cannabinoid receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 21134–21139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignatowska-Jankowska, B.M.; Baillie, G.L.; Kinsey, S.; Crowe, M.; Ghosh, S.; Owens, R.A.; Damaj, I.M.; Poklis, J.; Wiley, J.L.; Zanda, M.; et al. A cannabinoid CB1 receptor-positive allosteric modulator reduces neuropathic pain in the mouse with no psychoactive effects. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 2948–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, L.; Mackie, K.; Piomelli, D.; Kendall, D.A. Modulation of CB1 cannabinoid receptor by allosteric ligands: Pharmacology and therapeutic opportunities. Neuropharmacology 2017, 124, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, B.D.; Hebert, T.E.; Kelly, M.E.M. Ligand- and heterodimer-directed signaling of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 77, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, W.; Gomes, I.; Dove, L.S.; Prohaska, D.; McIntyre, G.; Devi, L.A. Molecular characterization of eluxadoline as a potential ligand targeting mu-delta opioid receptor heteromers. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 92, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, G.M. Eluxadoline: A review in diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Drugs 2017, 77, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culler, M.D. Somatostatin-dopamine chimeras: A novel approach to treatment of neuroendocrine tumors. Horm Metab. Res. 2011, 43, 854–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrey, D.A.; Gilmour, B.P.; Thomas, B.F.; Zhang, Y.A. Toward the development of bivalent ligand probes of cannabinoid CB1 and orexin ox1 receptor heterodimers. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, M.; Govindpani, K.; Furkert, D.P.; Hurst, D.P.; Reggio, P.H.; Flanagan, J.U. One for the price of two...Are bivalent ligands targeting cannabinoid receptor dimers capable of simultaneously binding to both receptors? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Esbroeck, A.C.M.; Janssen, A.P.A.; Cognetta, A.B., 3rd; Ogasawara, D.; Shpak, G.; van der Kroeg, M.; Kantae, V.; Baggelaar, M.P.; de Vrij, F.M.S.; Deng, H.; et al. Activity-based protein profiling reveals off-target proteins of the faah inhibitor bia 10-2474. Science 2017, 356, 1084–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, S.; Kumar, U. Cannabinoid Receptors and the Endocannabinoid System: Signaling and Function in the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030833
Zou S, Kumar U. Cannabinoid Receptors and the Endocannabinoid System: Signaling and Function in the Central Nervous System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(3):833. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030833
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Shenglong, and Ujendra Kumar. 2018. "Cannabinoid Receptors and the Endocannabinoid System: Signaling and Function in the Central Nervous System" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 3: 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030833
APA StyleZou, S., & Kumar, U. (2018). Cannabinoid Receptors and the Endocannabinoid System: Signaling and Function in the Central Nervous System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(3), 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030833



