Structural Biology of the TNFα Antagonists Used in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
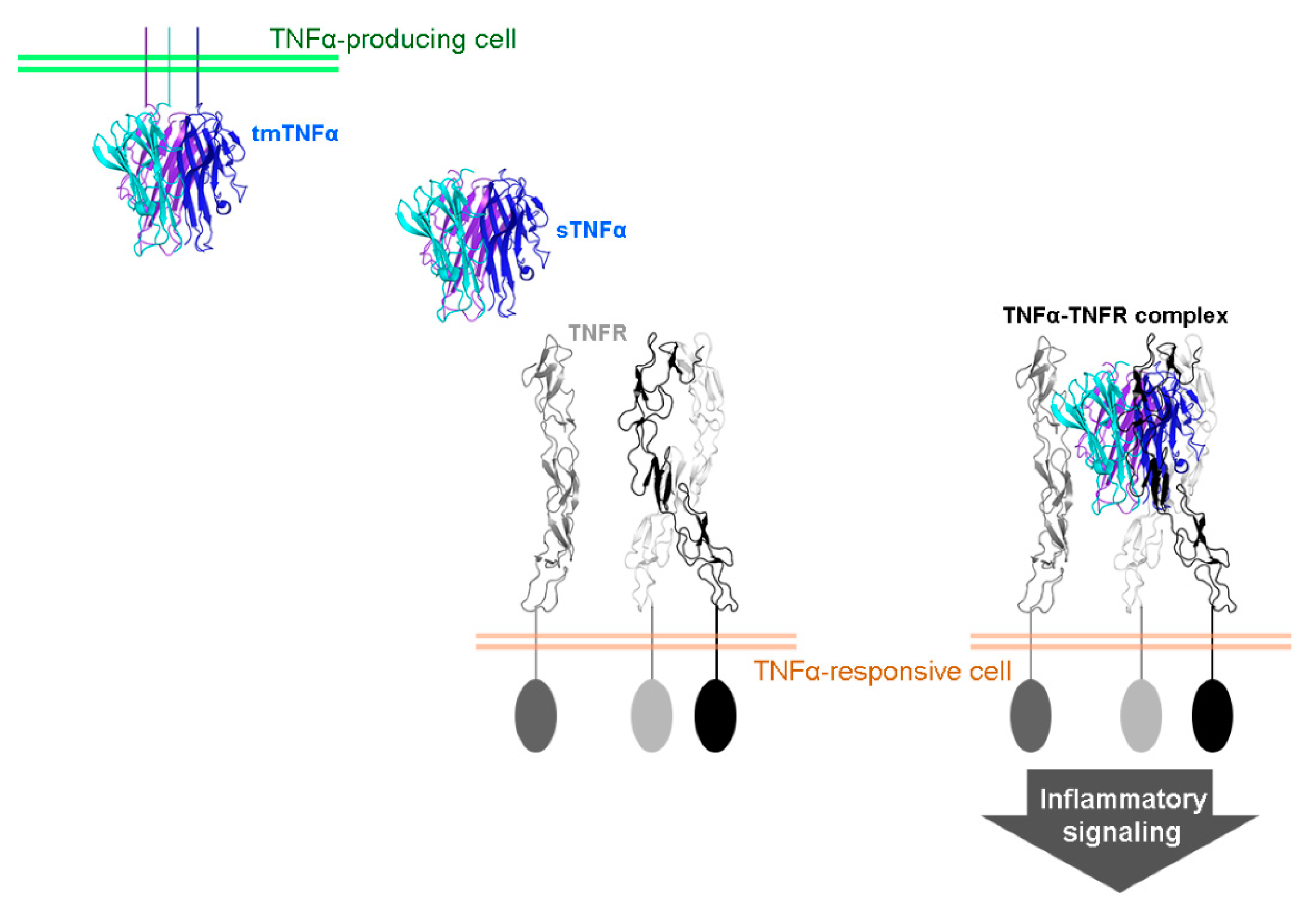
2. TNFα Antagonists for the Treatment of Inflammatory Autoimmune Diseases
3. Interactions between TNFα and FDA-Approved TNFα Antagonists
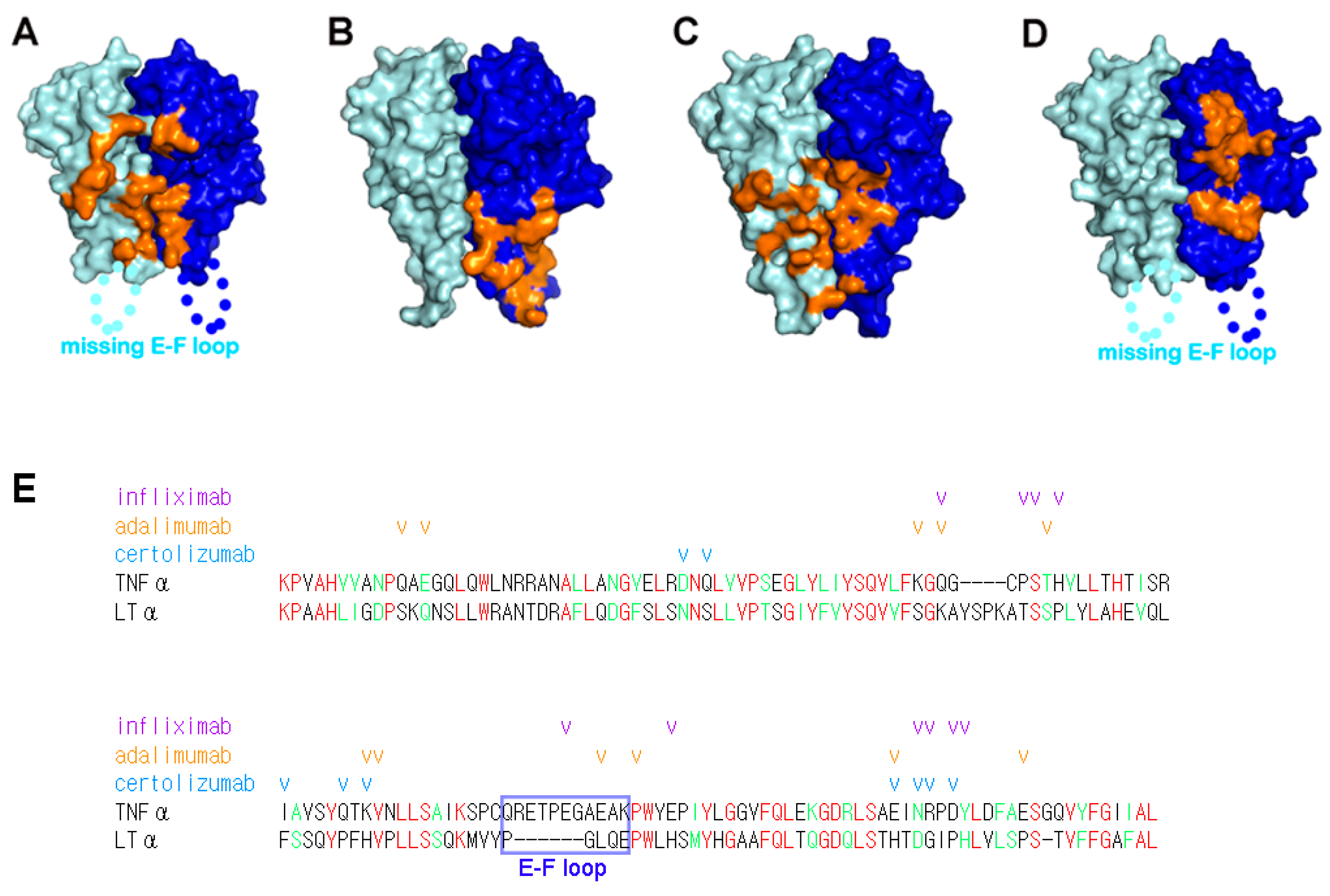
4. Selectivity of TNFα Antagonists against Lymphotoxin α
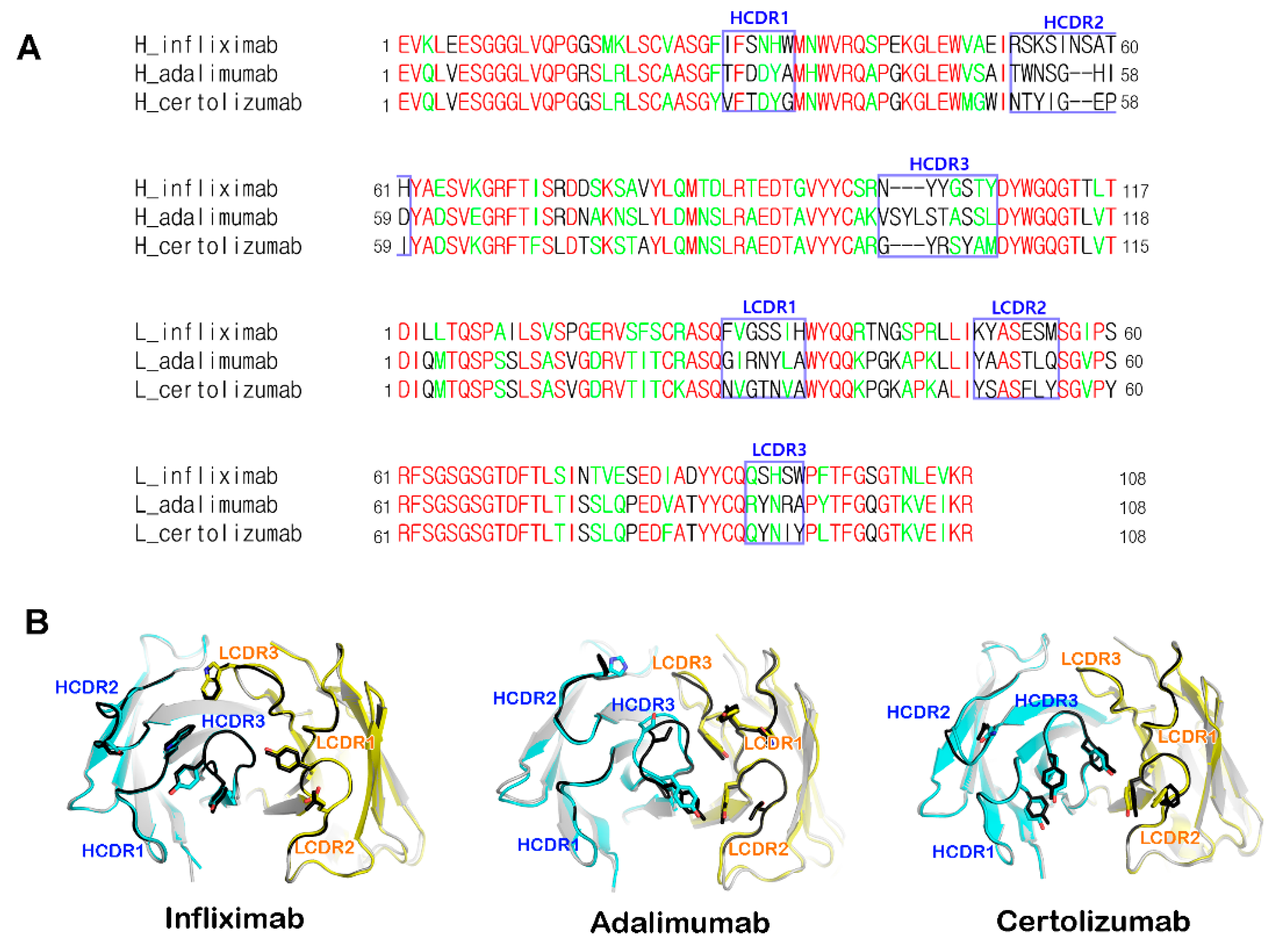
5. Structural Rigidity of the CDR Loops within Anti-TNFα Antibodies
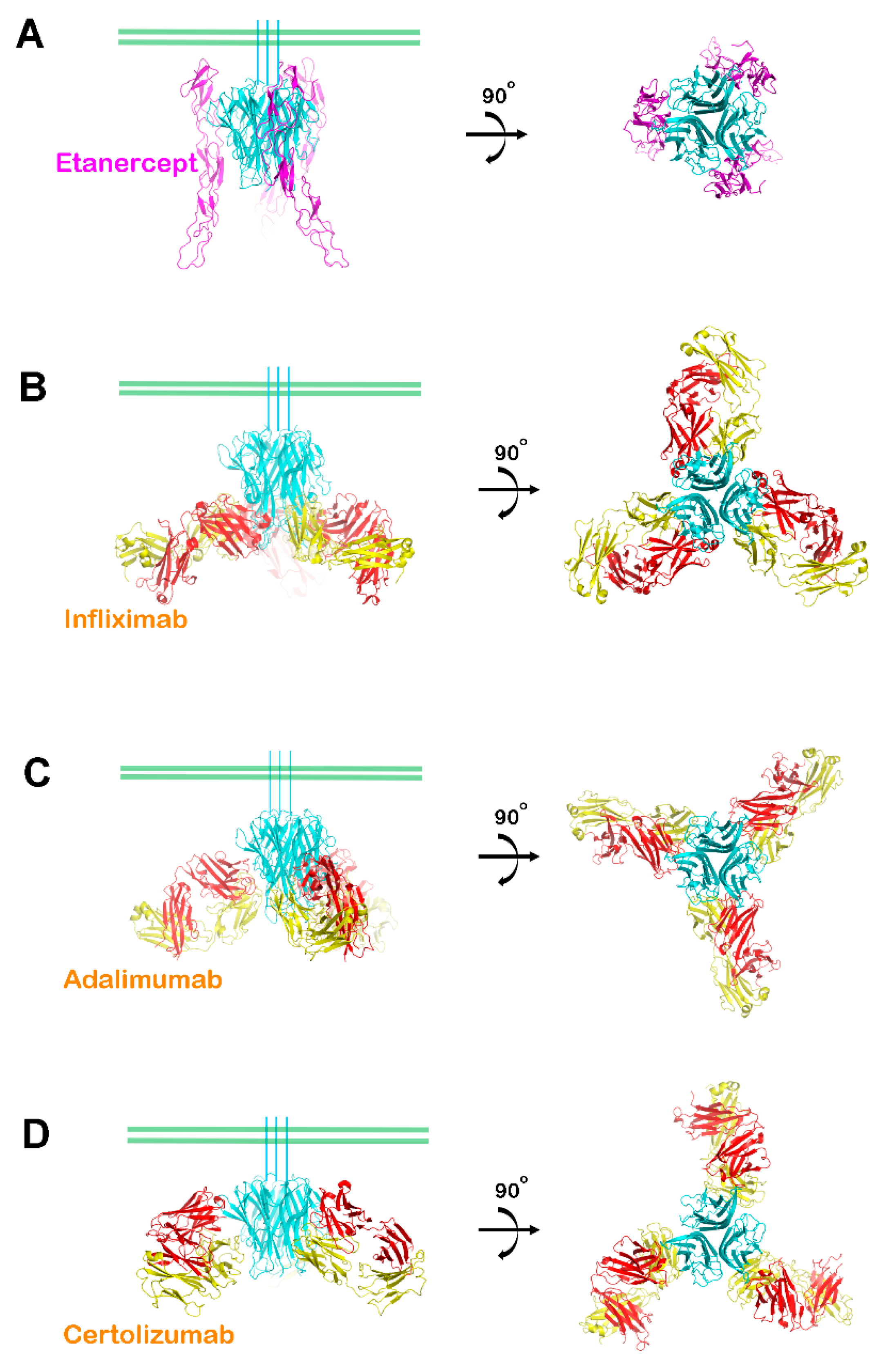
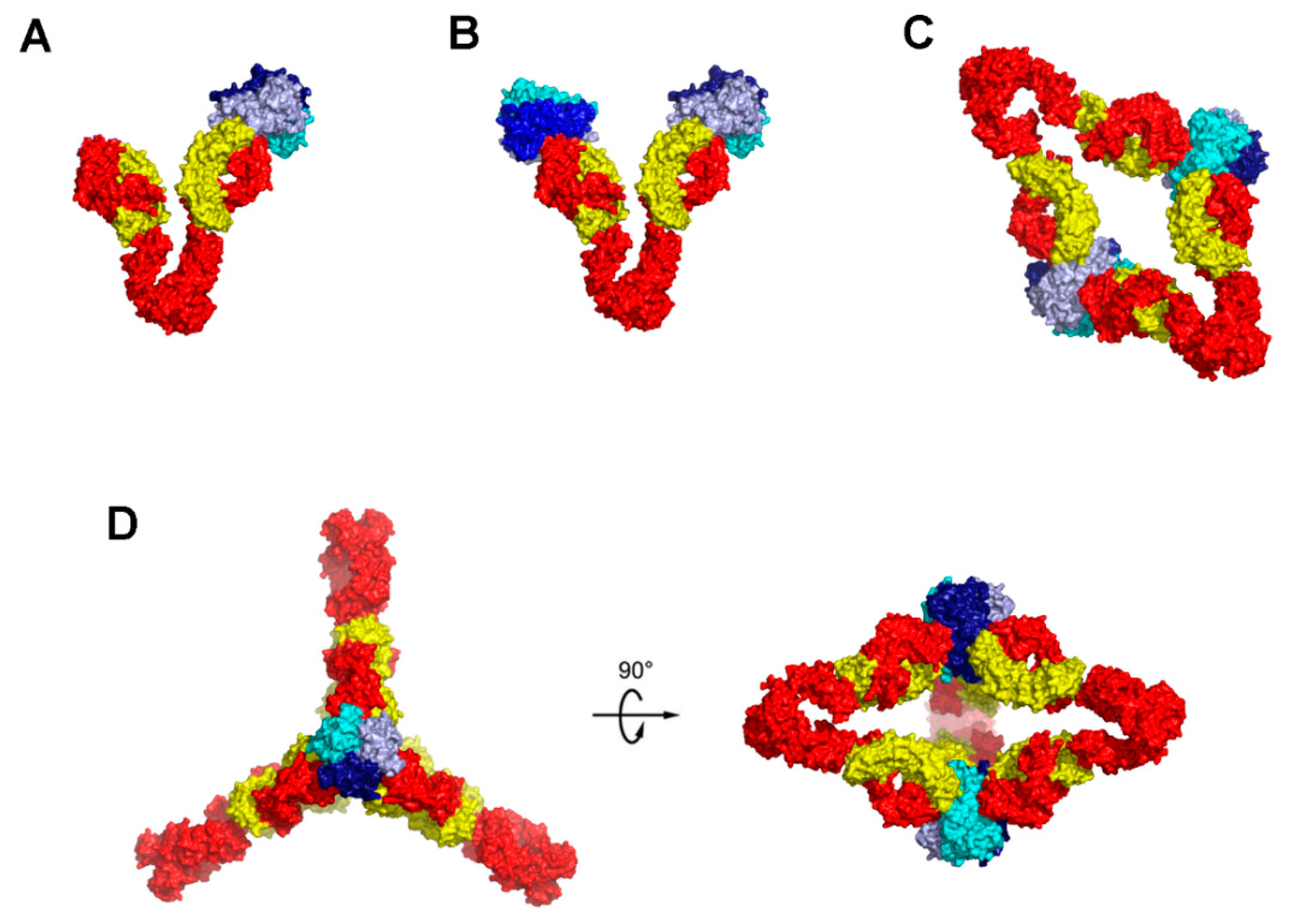
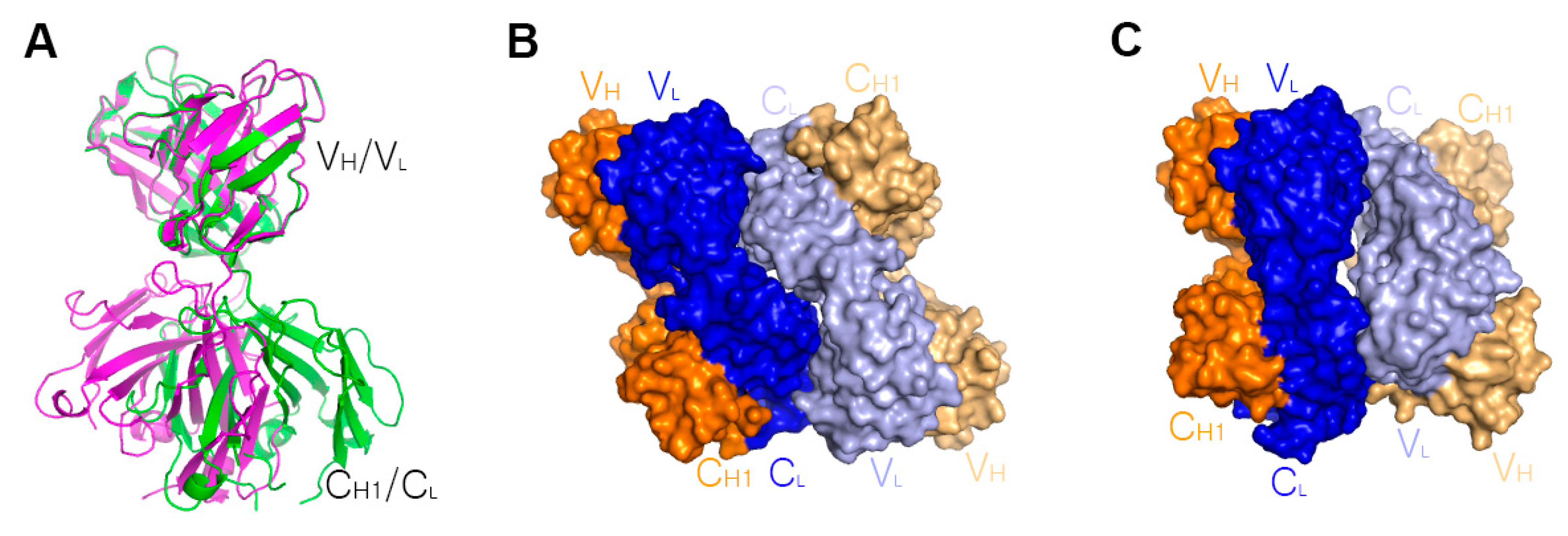
6. Higher Order Structures of Antibody-TNFα Complexes
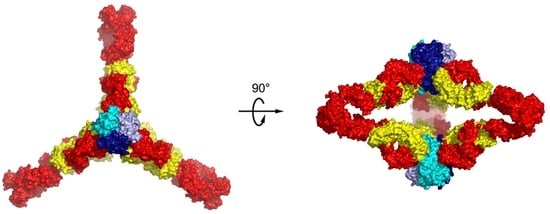
7. The Quinary Structure of Infliximab
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Locksley, R.M.; Killeen, N.; Lenardo, M.J. The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: Integrating mammalian biology. Cell 2001, 104, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiens, G.D.; Glenney, G.W. Origin and evolution of TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1324–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Goeddel, D.V. TNF-R1 signaling: A beautiful pathway. Science 2002, 296, 1634–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennica, D.; Nedwin, G.E.; Hayflick, J.S.; Seeburg, P.H.; Derynck, R.; Palladino, M.A.; Kohr, W.J.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Goeddel, D.V. Human tumor necrosis factor: Precursor structure, cDNA cloning, expression, and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature 1984, 312, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luettiq, B.; Decker, T.; Lohmann-Matthes, M.L. Evidence for the existence of two forms of membrane tumor necrosis factor: An integral protein and a molecule attached to its receptor. J. Immunol. 1989, 143, 4034–4038. [Google Scholar]
- Kriegler, M.; Perez, C.; DeFay, K.; Albert, I.; Lu, S.D. A novel form of TNF/cachectin is a cell surface cytotoxic transmembrane protein: Ramifications for the complex physiology of TNF. Cell 1988, 53, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenabeele, P.; Declercq, W.; Beyaert, R.; Fiers, W. Two tumour necrosis factor receptors: Structure and function. Trends Cell Biol. 1995, 5, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzoni, F.; Beutler, B. The tumor necrosis factor ligand and receptor families. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, R.A.; Rauch, C.T.; Kozlosky, C.J.; Peschon, J.J.; Slack, J.L.; Wolfson, M.F.; Castner, B.J.; Stocking, K.L.; Reddy, P.; Srinivasan, S.; et al. A metalloproteinase disintegrin that releases tumour-necrosis factor-alpha from cells. Nature 1997, 385, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, M.L.; Jin, S.-L.C.; Milla, M.E.; Burkhart, W.; Carter, H.L.; Chen, W.-J.; Clay, W.C.; Didsbury, J.R.; Hassler, D.; Hoffman, C.R.; et al. Cloning of a disintegrin metalloproteinase that processes precursor tumour-necrosis factor-alpha. Nature 1997, 385, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, M.J.; Maini, R.N.; Feldmann, M.; Kalden, J.R.; Antoni, C.; Smolen, J.S.; Leeb, B.; Breedveld, F.C.; Macfarlane, J.D.; Bijl, J.A.; et al. Randomised double-blind comparison of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (cA2) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 1994, 344, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinblatt, M.E.; Keystone, E.C.; Furst, D.E.; Moreland, L.W.; Weisman, M.H.; Birbara, C.A.; Teoh, L.A.; Fischkoff, S.A.; Chartash, E.K. Adalimumab, a fully human anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in patients taking concomitant methotrexate: The ARMADA trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanauer, S.B.; Sandborn, W.J.; Rutgeerts, P.; Fedorak, R.N.; Lukas, M.; MacIntosh, D.; Panaccione, R.; Wolf, D.; Pollack, P. Human anti-tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibody (adalimumab) in Crohn’s disease: The CLASSIC-I trial. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdaca, G.; Colombo, B.M.; Cagnati, P.; Gulli, R.; Spanò, F.; Puppo, F. Update upon efficacy and safety of TNF-alpha inhibitors. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2012, 11, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducharme, E.; Weinberg, J.M. Etanercept. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2008, 8, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, P.C. Pharmacology of TNF blockade in rheumatoid arthritis and other chronic inflammatory diseases. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2010, 10, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Simone, C.; Amerio, P.; Amoruso, G.; Bardazzi, F.; Campanati, A.; Conti, A.; Gisondi, P.; Gualdi, G.; Guarneri, C.; Leoni, L.; et al. Immunogenicity of anti-TNFα therapy in psoriasis: A clinical issue? Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2013, 13, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.D.; Keystone, E.C. Intravenous golimumab in rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 10, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeks, E.D. Certolizumab Pegol: A Review in Inflammatory Autoimmune Diseases. BioDrugs 2016, 30, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitoma, H.; Horiuchi, T.; Tsukamoto, H.; Ueda, N. Molecular mechanisms of action of anti-TNF-α agents—Comparison among therapeutic TNF-α antagonists. Cytokine 2018, 101, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiuchi, T.; Mitoma, H.; Harashima, S.; Tsukamoto, H.; Shimoda, T. Transmembrane TNF-alpha: Structure, function and interaction with anti-TNF agents. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2010, 49, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scallon, B.; Cai, A.; Solowski, N.; Rosenberg, A.; Song, X.Y.; Shealy, D.; Wagner, C. Binding and functional comparisons of two types of tumor necrosis factor antagonists. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 301, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringheanu, M.; Daum, F.; Markowitz, J.; Levine, J.; Katz, S.; Lin, X.; Silver, J. Effects of infliximab on apoptosis and reverse signaling of monocytes from healthy individuals and patients with Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2004, 10, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitoma, H.; Horiuchi, T.; Tsukamoto, H.; Tamimoto, Y.; Kimoto, Y.; Uchino, A.; To, K.; Harashima, S.; Hatta, N.; Harada, M. Mechanisms for cytotoxic effects of anti-tumor necrosis factor agents on transmembrane tumor necrosis factor alpha-expressing cells: Comparison among infliximab, etanercept, and adalimumab. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Brande, J.M.; Braat, H.; van den Brink, G.R.; Versteeg, H.H.; Bauer, C.A.; Hoedemaeker, I.; van Montfrans, C.; Hommes, D.W.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; van Deventer, S.J. Infliximab but not etanercept induces apoptosis in lamina propria T-lymphocytes from patients with Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 1774–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, A.; Fossati, G.; Bergin, M.; Stephens, P.; Stephens, S.; Foulkes, R.; Brown, D.; Robinson, M.; Bourne, T. Mechanism of action of certolizumab pegol (CDP870): In vitro comparison with other anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha agents. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2007, 13, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitoma, H.; Horiuchi, T.; Hatta, N.; Tsukamoto, H.; Harashima, S.-I.; Kikuchi, Y.; Otsuka, J.; Okamura, S.; Fujita, S.; Harada, M. Infliximab induces potent anti-inflammatory responses by outside-to-inside signals through transmembrane TNF-alpha. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 376–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaymakcalan, Z.; Sakorafas, P.; Bose, S.; Scesney, S.; Xiong, L.; Hanzatian, D.K.; Salfeld, J.; Sasso, E.H. Comparisons of affinities, avidities, and complement activation of adalimumab, infliximab, and etanercept in binding to soluble and membrane tumor necrosis factor. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 131, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shealy, D.J.; Cai, A.; Staquet, K.; Baker, A.; Lacy, E.R.; Johns, L.; Vafa, O.; Gunn, G.; Tam, S.; Sague, S.; et al. Characterization of golimumab, a human monoclonal antibody specific for human tumor necrosis factor α. MAbs 2010, 2, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, A.C.; Wildenberg, M.E.; Duijvestein, M.; Verhaar, A.P.; van den Brink, G.R.; Hommes, D.W. Anti-tumor necrosis factor-α antibodies induce regulatory macrophages in an Fc region-dependent manner. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtal, K.A.; Rogler, G.; Scharl, M.; Biedermann, L.; Frei, P.; Fried, M.; Weber, A.; Eloranta, J.J.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Vavricka, S.R. Fc gamma receptor CD64 modulates the inhibitory activity of infliximab. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, N.; Tsukamoto, H.; Mitoma, H.; Ayano, M.; Tanaka, A.; Ohta, S.; Inoue, Y.; Arinobu, Y.; Niiro, H.; Akashi, K.; et al. The cytotoxic effects of certolizumab pegol and golimumab mediated by transmembrane tumor necrosis factor α. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derer, S.; Till, A.; Haesler, R.; Sina, C.; Grabe, N.; Jung, S.; Nikolaus, S.; Kuehbacher, T.; Groetzinger, J.; Rose-John, S.; et al. mTNF reverse signalling induced by TNFα antagonists involves a GDF-1 dependent pathway: Implications for Crohn’s disease. Gut 2013, 62, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lubel, J.S.; Testro, A.G.; Angus, P.W. Hepatitis B virus reactivation following immunosuppressive therapy: Guidelines for prevention and management. Intern. Med. J. 2007, 37, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Reino, J.J.; Carmona, L.; Valverde, V.R.; Mola, E.M.; Montero, M.D.; BIOBADASER Group. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors may predispose to significant increase in tuberculosis risk: A multicenter active-surveillance report. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 2122–2127. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, S.L.; Greene, M.H.; Gershon, S.K.; Edwards, E.T.; Braun, M.M. Tumor necrosis factor antagonist therapy and lymphoma development: Twenty-six cases reported to the Food and Drug Administration. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 3151–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banner, D.W.; D’Arcy, A.; Janes, W.; Gentz, R.; Schoenfeld, H.J.; Broger, C.; Loetscher, H.; Lesslauer, W. Crystal structure of the soluble human 55 kd TNF receptor-human TNF beta complex: Implications for TNF receptor activation. Cell 1993, 73, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Yoshikawa, M.; Yoshioka, Y.; Tsunoda, S.; Nakagawa, S.; Yamagata, Y.; Tsutsumi, Y. Solution of the structure of the TNF-TNFR2 complex. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Dai, J.; Hou, S.; Su, L.; Zhang, D.; Guo, H.; Hu, S.; Wang, H.; Rao, Z.; Guo, Y.; et al. Structural basis for treating tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα)-associated diseases with the therapeutic antibody infliximab. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 13799–13807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Liang, S.; Guo, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, W.; Qian, W.; Hou, S.; Wang, H.; et al. Comparison of the inhibition mechanisms of adalimumab and infliximab in treating tumor necrosis factor α-associated diseases from a molecular view. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 27059–27067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.U.; Shin, W.; Son, J.Y.; Yoo, K.Y.; Heo, Y.S. Molecular Basis for the Neutralization of Tumor Necrosis Factor α by Certolizumab Pegol in the Treatment of Inflammatory Autoimmune Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerch, T.F.; Sharpe, P.; Mayclin, S.J.; Edwards, T.E.; Lee, E.; Conlon, H.D.; Polleck, S.; Rouse, J.C.; Luo, Y.; Zou, Q. Infliximab crystal structures reveal insights into self-association. MAbs 2017, 9, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Long, D.S.; Lute, S.C.; Levy, M.J.; Brorson, K.A.; Keire, D.A. Simple NMR methods for evaluating higher order structures of monoclonal antibody therapeutics with quinary structure. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 128, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, B.N.; Chan, S.L.; Ng, C.; Shi, J.; Correia, I.; Radziejewski, C.; Matsudaira, P. Higher order structures of Adalimumab, Infliximab and their complexes with TNFα revealed by electron microscopy. Protein Sci. 2017, 26, 2392–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostini, C.; Sancetta, R.; Cerutti, A.; Semenzato, G. Alveolar macrophages as a cell source of cytokine hyperproduction in HIV-related interstitial lung disease. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1995, 58, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, G.; Delneste, Y.; Aubry, J.P.; Magistrelli, G.; Herbault, N.; Blaecke, A.; Meager, A.; Bonnefoy, J.Y.; Jeannin, P. Human NK cells constitutively express membrane TNF-alpha (mTNFalpha) and present mTNFalpha-dependent cytotoxic activity. Eur. J. Immunol. 1999, 29, 3588–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, M. Cytolytic activities of activated macrophages versus paraformaldehyde-fixed macrophages; soluble versus membrane-associated TNF. Cell Immunol. 1991, 137, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, L.; Thickett, D.R.; Christie, S.J.; Kendall, H.; Millar, A.B. Increased expression of functionally active membrane-associated tumor necrosis factor in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2000, 22, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresse, M.; Latta, M.; Künstle, G.; Riehle, H.M.; van Rooijen, N.; Hentze, H.; Tiegs, G.; Biburger, M.; Lucas, R.; Wendel, A. Kupffer cell-expressed membrane-bound TNF mediates melphalan hepatotoxicity via activation of both TNF receptors. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 4076–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, R.; Brockhaus, M.; Frey, J.R. Cell surface tumor necrosis factor (TNF) accounts for monocyte- and lymphocyte-mediated killing of TNF-resistant target cells. Cell Immunol. 1989, 122, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, T.; Morita, C.; Tsukamoto, H.; Mitoma, H.; Sawabe, T.; Harashima, S.; Kashiwagi, Y.; Okamura, S. Increased expression of membrane TNF-alpha on activated peripheral CD8+ T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2006, 17, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grell, M.; Douni, E.; Wajant, H.; Löhden, M.; Clauss, M.; Maxeiner, B.; Georgopoulos, S.; Lesslauer, W.; Kollias, G.; Pfizenmaier, K.; et al. The transmembrane form of tumor necrosis factor is the prime activating ligand of the 80 kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell 1995, 83, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracey, D.; Klareskog, L.; Sasso, E.H.; Salfeld, J.G.; Tak, P.P. Tumor necrosis factor antagonist mechanisms of action: A comprehensive review. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 117, 244–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, D.R.; Choi, Y. Signaing by tumor necrosis factor receptors: pathways, paradigms and targets for therapeutic modulation. Int. Rev. Immunol. 1999, 18, 405–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, F.K.; Chun, H.J.; Zheng, L.; Siegel, R.M.; Bui, K.L.; Lenardo, M.J. A domain in TNF receptors that mediates ligand-independent receptor assembly and signaling. Science 2000, 288, 2351–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacEwan, D.J. TNF ligands and receptors-a matter of life and death. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 135, 855–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eissner, G.; Kolch, W.; Scheurich, P. Ligands working as receptors: Reverse signaling by members of the TNF superfamily enhance the plasticity of the immune system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004, 15, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivkin, A. Certolizumab pegol for the management of Crohn’s disease in adults. Clin. Ther. 2009, 31, 1158–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, T.; Fossati, G.; Nesbitt, A. A PEGylated Fab’ fragment against tumor necrosis factor for the treatment of Crohn disease: Exploring a new mechanism of action. BioDrugs 2008, 22, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasut, G. Pegylation of biological molecules and potential benefits: Pharmacological properties of certolizumab pegol. BioDrugs 2014, 28 (Suppl. 1), S15–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, T.; Padaki, R.; Liu, L.; Hamburger, A.E.; Ellison, A.R.; Stevens, S.R.; Louie, J.S.; Kohno, T. Differences in binding and effector functions between classes of TNF antagonists. Cytokine 2009, 45, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lis, K.; Kuzawińska, O.; Bałkowiec-Iskra, E. Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors—State of knowledge. Arch. Med. Sci. 2014, 10, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narhi, L.O.; Arakawa, T. Dissociation of recombinant tumor necrosis factor-α studied by gel permeation chromatography. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1987, 147, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corti, A.; Fassina, G.; Marcucci, F.; Barbanti, E.; Cassani, G. Oligomeric tumour necrosis factor α slowly converts into inactive forms at bioactive levels. Biochem. J. 1992, 284, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hlodan, R.; Pain, R.H. The folding and assembly pathway of tumour necrosis factor TNFα, a globular trimeric protein. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 231, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Schie, K.A.; Ooijevaar-de Heer, P.; Dijk, L.; Kruithof, S.; Wolbink, G.; Rispens, T. Therapeutic TNF inhibitors can differentially stabilize trimeric TNF by inhibiting monomer exchange. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, J.L.; Miatkowski, K.; Griffiths, D.A.; Bourdon, P.R.; Hession, C.; Ambrose, C.M.; Meier, W. Preparation and characterization of soluble recombinant heterotrimeric complexes of human lymphotoxins alpha and beta. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 8618–8626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calmon-Hamaty, F.; Combe, B.; Hahne, M.; Morel, J. Lymphotoxin α stimulates proliferation and pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Cytokine 2011, 53, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhrmann, C.; Shayan, P.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Shakibaei, M. Evidence that TNF-β (lymphotoxin α) can activate the inflammatory environment in human chondrocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.C. Accessing the Kabat antibody sequence database by computer. Proteins 1996, 25, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, I.A.; Stanfield, R.L. Antibody-antigen interactions: New structures and new conformational changes. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1994, 4, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, T.; Tam, L.T.; Stevens, S.R.; Louie, J.S. Binding characteristics of tumor necrosis factor receptor-Fc fusion proteins vs anti-tumor necrosis factor mAbs. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2007, 12, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santora, L.C.; Kaymakcalan, Z.; Sakorafas, P.; Krull, I.S.; Grant, K. Characterization of noncovalent complexes of recombinant human monoclonal antibody and antigen using cation exchange, size exclusion chromatography, and BIAcore. Anal. Biochem. 2001, 299, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalonia, C.; Toprani, V.; Toth, R.; Wahome, N.; Gabel, I.; Middaugh, C.R.; Volkin, D.B. Effects of Protein Conformation, Apparent Solubility, and Protein-Protein Interactions on the Rates and Mechanisms of Aggregation for an IgG1Monoclonal Antibody. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 7062–7075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Guo, H.; Xu, J.; Qin, T.; Xu, L.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, D.; Qian, W.; Li, B.; et al. Acid-induced aggregation propensity of nivolumab is dependent on the Fc. MAbs 2016, 8, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| TNFα Antagonist | Original Product | Biosimilar Product | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Etanercept | Enbrel® (1998) | Erelzi® (2016) | TNFR2 ectodomain fused to IgG1 Fc |
| Infliximab | Remicade® (1998) | Inflectra® (2016), Ixifi® (2017) | Chimeric murine/human IgG1 |
| Adalimumab | Humira® (2002) | Amjevita® (2016), Cyltezo® (2017) | Fully Human IgG1 |
| Certolizumab-pegol | Cimzia® (2008) | Humanized, PEGylated Fab’ | |
| Golimumab | Simponi® (2009) | Fully Human IgG1 |
| TNFα Antagonist | Protein/Complex | Method | PDB ID | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Etanercept | TNFR2 ectodomain in complex with TNFα | X-ray | 3ALQ | [38] |
| Infliximab | Fab fragment in complex with TNFα | X-ray | 4G3Y | [39] |
| Fab fragment | X-ray | 5VH3 | [42] | |
| Fab fragment | X-ray | 5VH4 | [42] | |
| Fc fragment | X-ray | 5VH5 | [42] | |
| 1:1, 1:2, 2:2, 3:2 complex | Cryo-EM | [44] | ||
| Adalimumab | Fab fragment in complex with TNFα | X-ray | 3WD5 | [40] |
| Fab fragment | X-ray | 4NYL | to be published | |
| 1:1, 1:2, 2:2, 3:2 complex | Cryo-EM | [44] | ||
| Certolizumab-pegol | Fab fragment in complex with TNFα | X-ray | 5WUX | [41] |
| Fab fragment | X-ray | 5WUV | [41] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, H.T.; Lee, J.U.; Son, J.Y.; Shin, W.; Heo, Y.-S. Structural Biology of the TNFα Antagonists Used in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030768
Lim H, Lee SH, Lee HT, Lee JU, Son JY, Shin W, Heo Y-S. Structural Biology of the TNFα Antagonists Used in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(3):768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030768
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Heejin, Sang Hyung Lee, Hyun Tae Lee, Jee Un Lee, Ji Young Son, Woori Shin, and Yong-Seok Heo. 2018. "Structural Biology of the TNFα Antagonists Used in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 3: 768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030768
APA StyleLim, H., Lee, S. H., Lee, H. T., Lee, J. U., Son, J. Y., Shin, W., & Heo, Y.-S. (2018). Structural Biology of the TNFα Antagonists Used in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(3), 768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030768