Effect of Presence and Concentration of Plasticizers, Vegetable Oils, and Surfactants on the Properties of Sodium-Alginate-Based Edible Coatings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
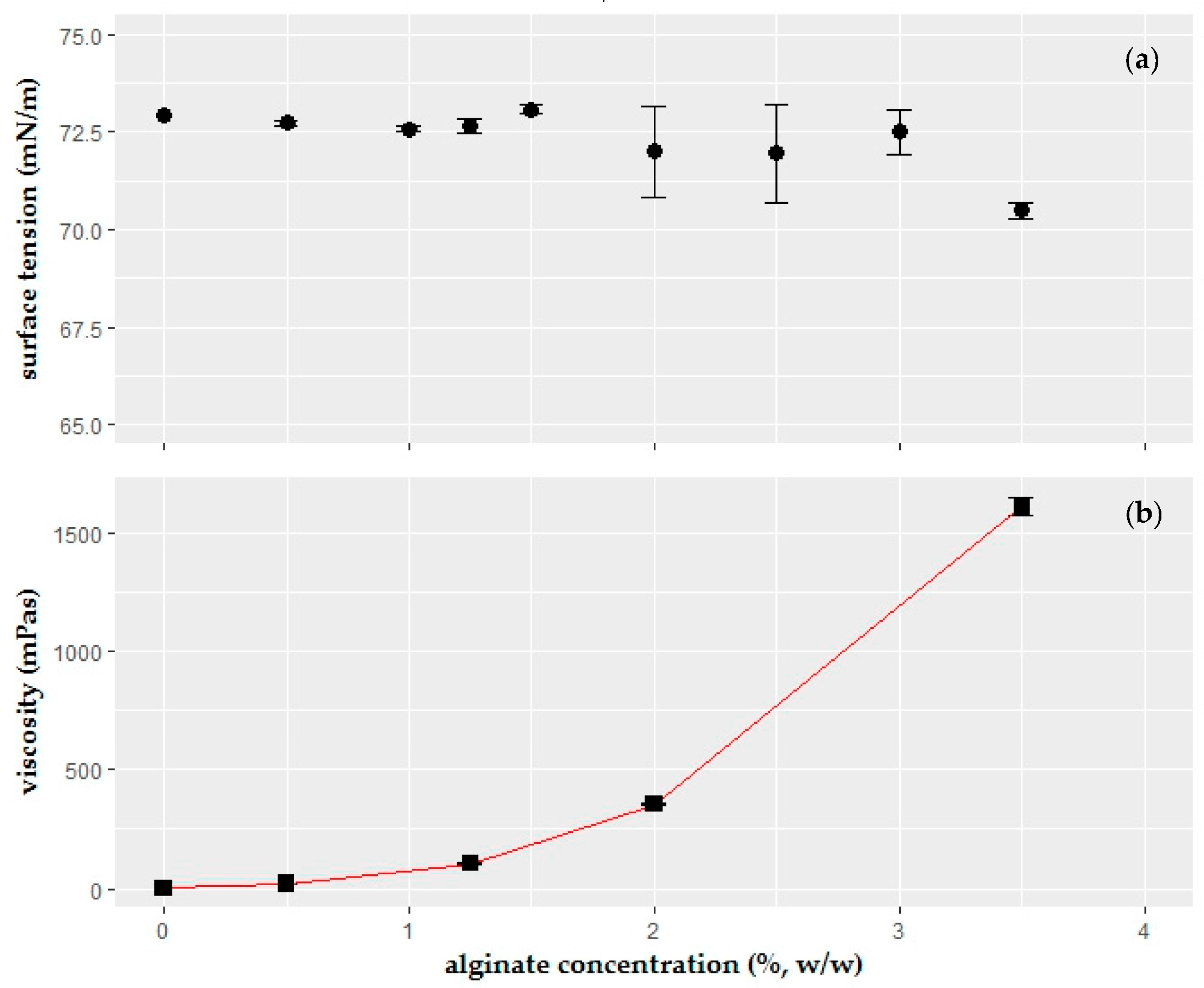
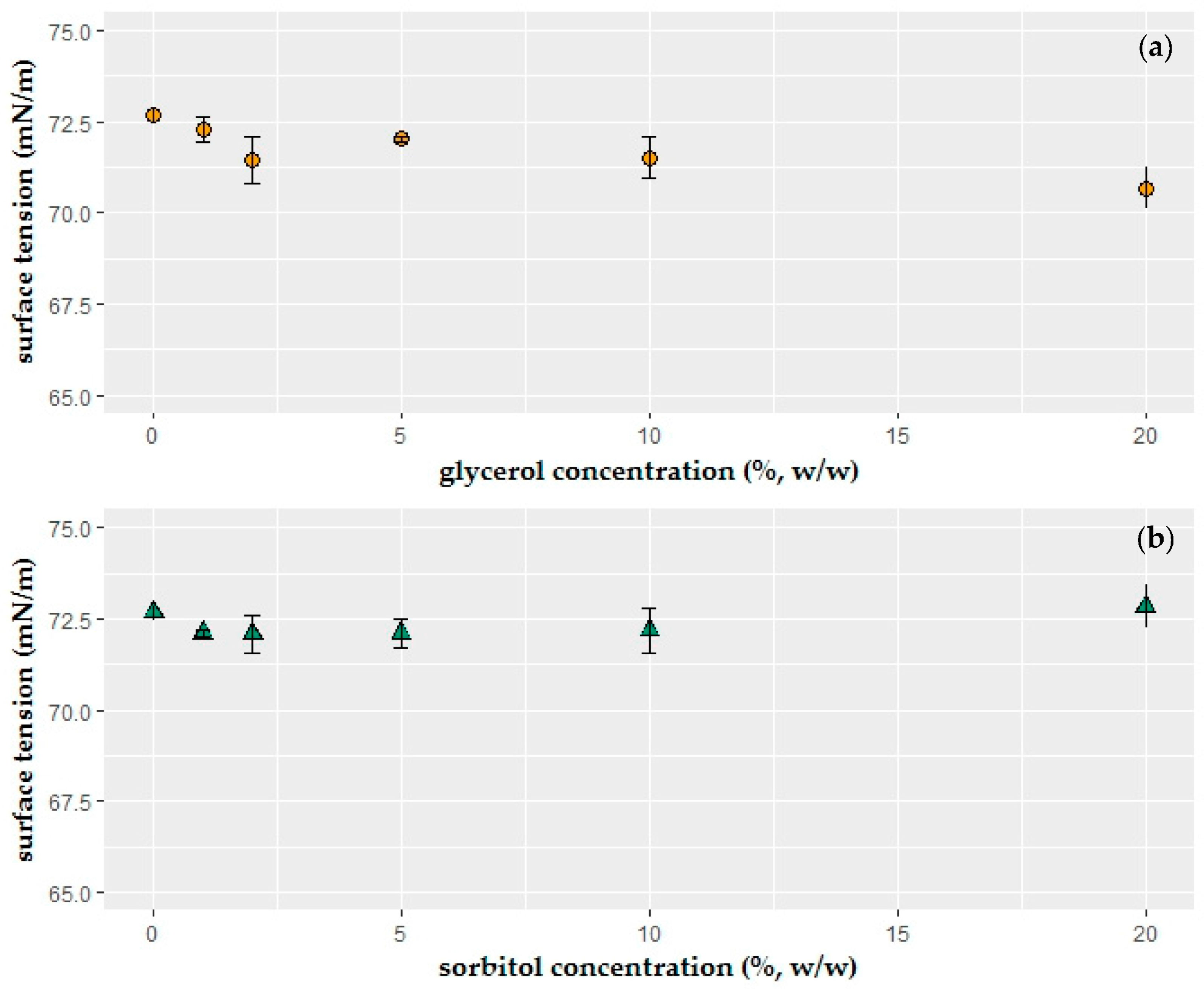
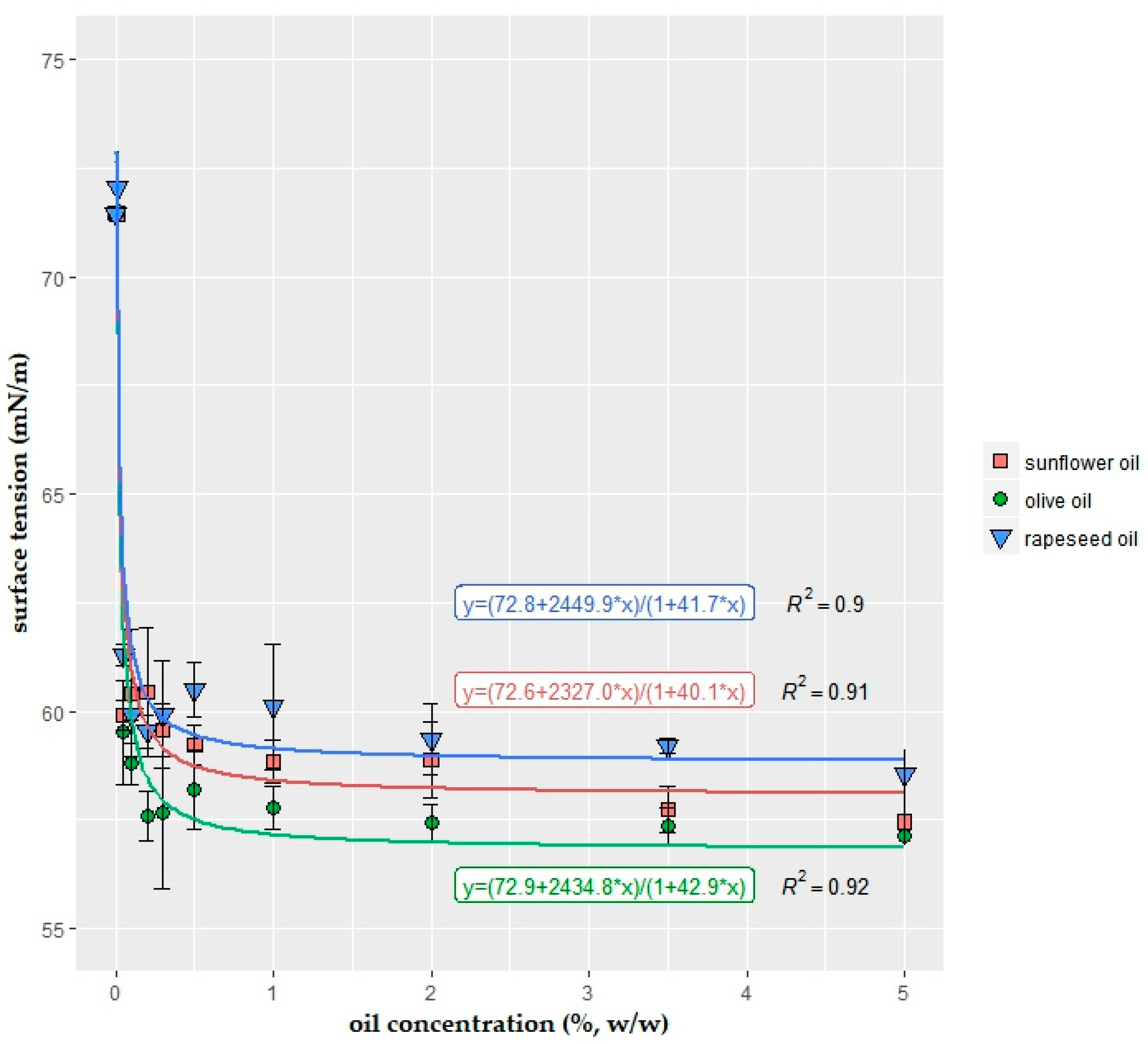
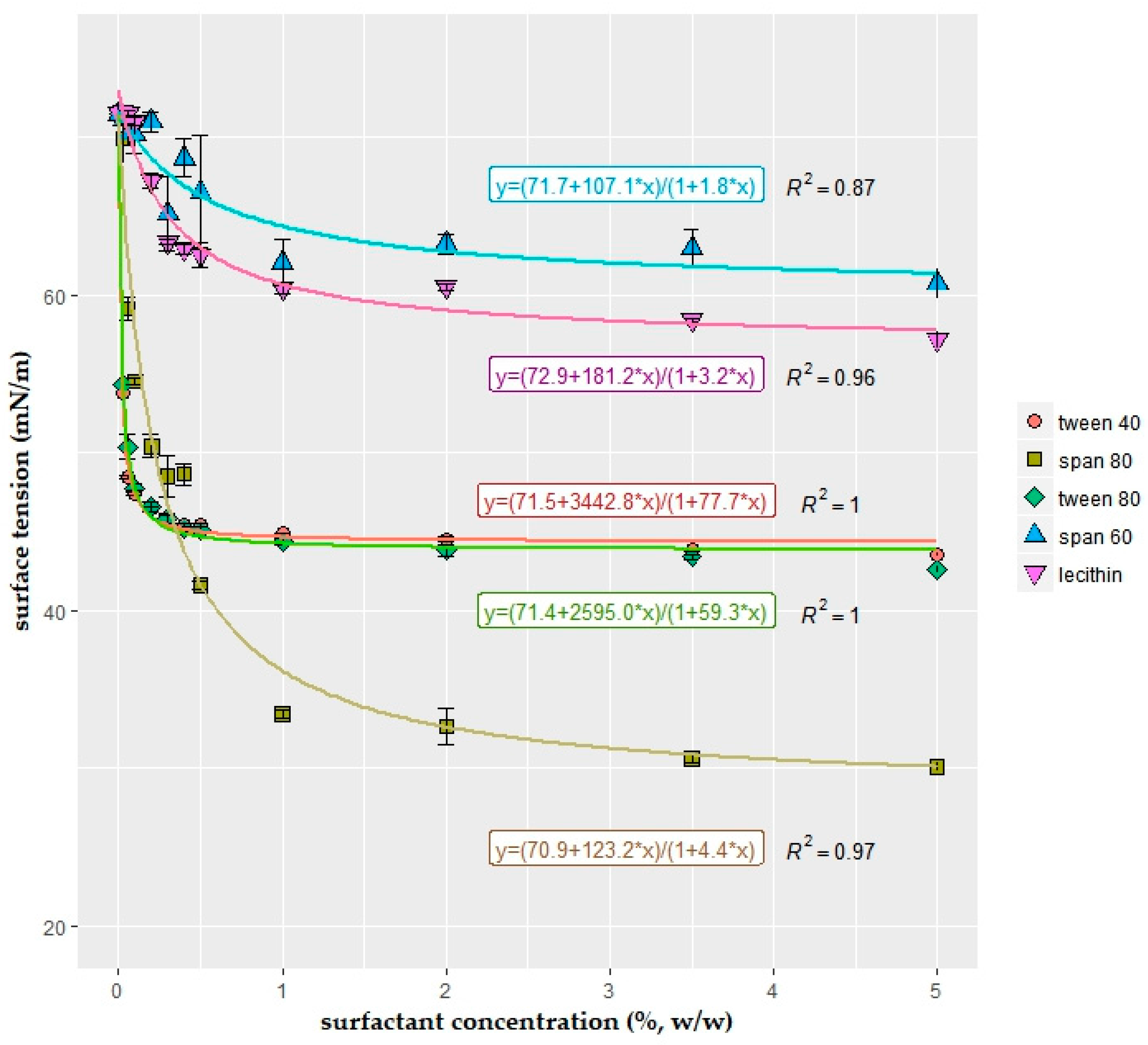
2.1. Surface Tension of the Coating Solutions
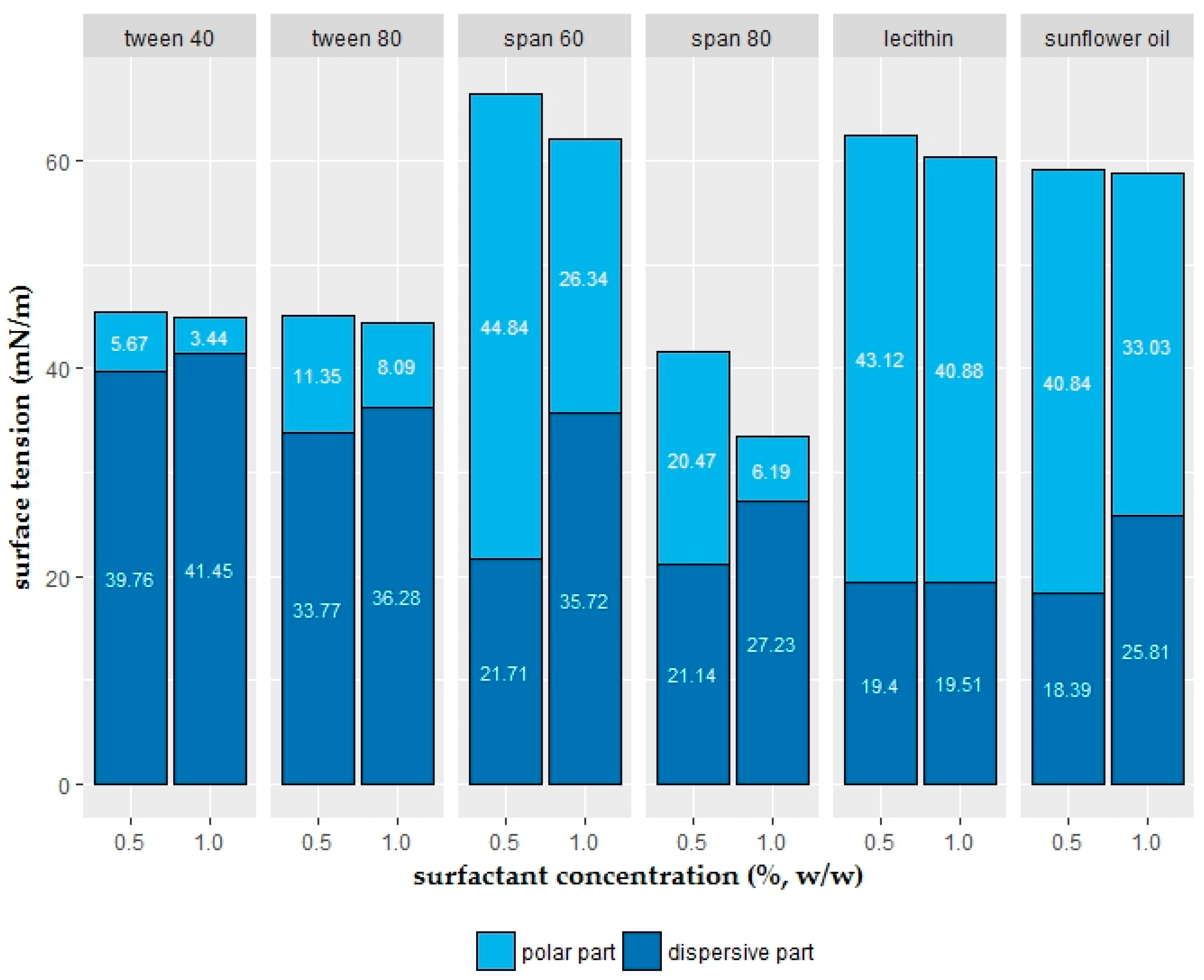
2.2. Polar and Dispersive Components of the Coating Solutions
2.3. Interaction of Surfactants
2.4. Emulsion Stability Measurements
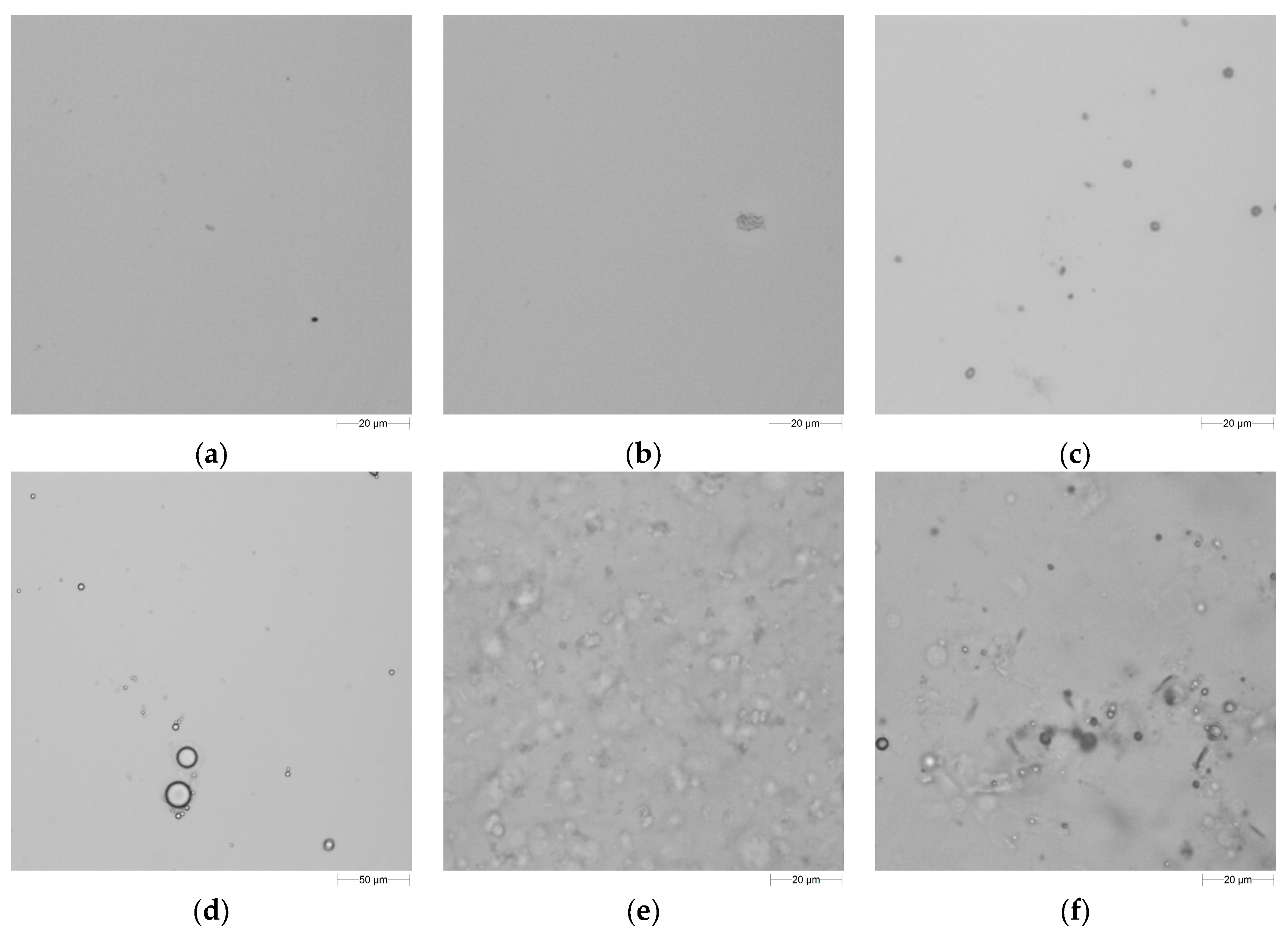
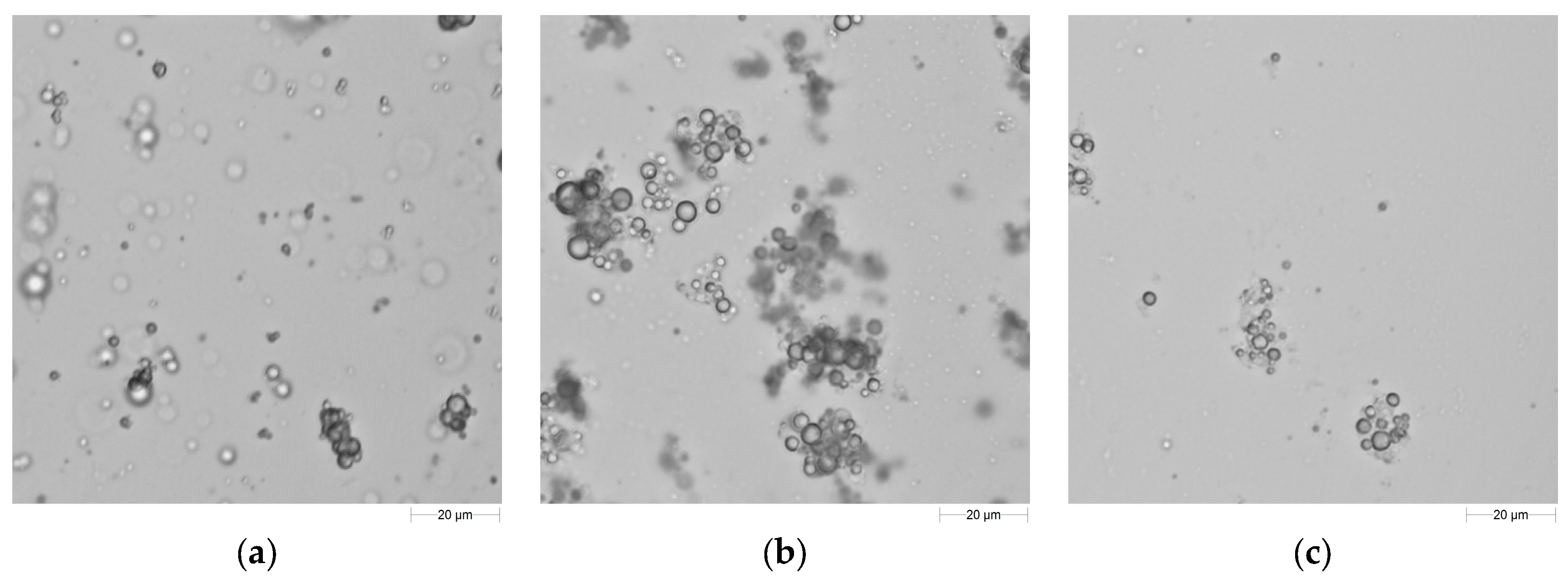
2.4.1. Emulsion Droplet Size Determination and Optical Evaluations
2.4.2. Creaming Index
2.5. Wettability
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Coating Solutions
4.3. Surface Tension Measurements
4.4. Wettability Measurements
4.5. Viscosity Measurements
4.6. Emulsion Stability Measurements
4.6.1. Droplet Size Measurement with Laser Diffraction System
4.6.2. Optical Evaluation
4.6.3. Creaming Index
4.7. Statistical Evaluations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Debeaufort, F.; Quezada-Gallo, J.-A.; Voilley, A. Edible barriers: A solution to control water migration in foods. In Food Packaging: Testing Methods and Applications; Risch, S.J., Ed.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Galus, S.; Kadzińska, J. Food applications of emulsion-based edible films and coatings. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlath, A.E.; Orts, W. Edible films and coatings: Why, what, and how? In Edible Films and Coatings for Food Applications; Huber, K.C., Embuscado, M.E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Guilbert, S.; Gontard, N.; Cuq, B. Technology and applications of edible protective films. Packag. Technol. Sci. 1995, 8, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.E. Structure and function of starch-based edible films and coatings. In Edible Films and Coatings for Food Applications; Huber, K.C., Embuscado, M.E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 113–134. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Ortega, I.; García-Almendárez, B.E.; Santos-López, E.M.; Amaro-Reyes, A.; Barboza-Corona, J.E.; Regalado, C. Antimicrobial edible films and coatings for meat and meat products preservation. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagri, A.; Ustunol, Z.; Ryser, E.T. Antimicrobial edible films and coatings. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 833–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, Z.; San Martín, D.; Villalobos-Carvajal, R.; Tabilo-Munizaga, G.; Osorio, F.; Leiva-Vega, J. Physicochemical characterization of chitosan-based coating-forming emulsions: Effect of homogenization method and carvacrol content. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draget, K.I. Alginates. In Handbook of Hydrocolloids, 2nd ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 807–828. [Google Scholar]
- Skurtys, O.; Acevedo, C.; Pedreschi, F.; Enrione, J.; Osorio, F.; Aguilera, J.M. Food hydrocolloid edible films and coatings. In Food Hydrocolloids Characteristics, Properties and Structures; Hollingworth, C.S., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 41–80. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration. Code for Federal Regulations Title 21 Part 184—Direct Food Substances Affirmed as Generally Recognized as Safe. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=184.1724 (accessed on 8 September 2017).
- Younes, M.; Aggett, P.; Aguilar, F.; Crebelli, R.; Filipič, M.; Frutos, M.J.; Galtier, P.; Gott, D.; Gundert-Remy, U.; Kuhnle, G.G.; et al. Re-evaluation of alginic acid and its sodium, potassium, ammonium and calcium salts (E 400–E 404) as food additives. EFSA J. 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, M.B. Structure and function of polysaccharide gum-based edible films and coatings. In Edible Films and Coatings for Food Applications; Huber, K.C., Embuscado, M.E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 57–112. [Google Scholar]
- Kester, J.J.; Fennema, O. Resistance of lipid films to water vapor transmission. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1989, 66, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenmaier, R.D.; Shaw, P.E. Moisture permeability of edible films made with fatty acid and hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 1799–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, E.; Nisperos-Carriedo, M.; Baker, R. Edible coatings for lightly processed fruits and vegetables. HortScience 1995, 30, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Krochta, J.M.; Baldwin, E.A.; Nisperos-Carriedo, M.O. Edible Coatings and Films to Improve Food Quality; Technomic Publishing Co., Inc.: Lancaster, PA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, M. Properties of cast films made from different ratios of whey protein isolate, hydrolysed whey protein isolate and glycerol. Materials 2013, 6, 3254–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, M.R. Handbook of Surfactants; Blackie: Glasgow, Scotland, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration. Code of Federal Regulations Title 21 Part 175—Indirect Food Additives: Adhesives and Components of Coatings. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfCFR/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=175.320 (accessed on 8 September 2017).
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration. Code of Federal Regulations Title 21 Part 178—Indirect Food Additives: Adjuvants, Production Aids, and Sanitizers. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfCFR/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=178.3400 (accessed on 8 September 2017).
- Croda Europe Ltd. Span and Tween. Available online: Chemagent.ru/prodavtsy/download/849/968/19 (accessed on 15 November 2017).
- Courthaudon, J.L.; Dickinson, E.; Christie, W.W. Competitive adsorption of lecithin and beta-casein in oil in water emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1991, 39, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food Allergy Research and Resource Program, University of Nebraska-Lincoln. Soy Lecithin. Available online: https://farrp.unl.edu/soy-lecithin (accessed on 5 January 2017).
- Park, H.J. Development of advanced edible coatings for fruits. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1999, 10, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, B.W.S.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Teixeira, J.A.; Vicente, A.A. The use of electric fields for edible coatings and films development and production: A review. Food Eng. Rev. 2010, 2, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.; Vicente, A.A.; Teixeira, J.A.; Miranda, C. Optimization of edible coating composition to retard strawberry fruit senescence. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2007, 44, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Springer, J. Determination of interfacial tension from the profile of a pendant drop using computer-aided image processing: 1. Theoretical. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 184, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, B.; Springer, J. Determination of interfacial tension from the profile of a pendant drop using computer-aided image processing: 2. Experimental. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 184, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Owens, D.K.; Wendt, R.C. Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. J. Appl. Polym Sci. 1969, 13, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejda, F.; Solar, P.; Kousal, J. Surface free energy determination by contact angle measurements—A comparison of various approaches. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual Conference of Doctoral Students, Prague, Czech Republic, 1–4 June 2010; WDS’10 Proceedings Contributed Papers. MATFYZPRESS: Sokolovská, Czech Republic, 2010. Part III. pp. 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zenkiewicz, M. Methods for the calculation of surface free energy of solids. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2007, 24, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, M.; Yabe, A. Dispersion and polar force components of surface tension of some polymer films. Text. Res. J. 1983, 53, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oss, C.J.; Chaudhury, M.K.; Good, R.J. Interfacial lifshitz-van der waals and polar interactions in macroscopic systems. Chem. Rev. 1988, 88, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skurtys, O.; Velásquez, P.; Henriquez, O.; Matiacevich, S.; Enrione, J.; Osorio, F. Wetting behavior of chitosan solutions on blueberry epicarp with or without epicuticular waxes. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 1449–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, P.; André, V.; Rieger, J.; Kühnle, A. Nano-emulsion formation by emulsion phase inversion. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2004, 251, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Critical review of techniques and methodologies for characterization of emulsion stability. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 47, 611–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levich, V.G. Physicochemical Hydrodynamics; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Poirier, M.; Fernando Fondeur, F.; Samuel Fink, S. Determination of Liquid Film Thickness Following Draining of Contactors, Vessels, and Pipes in the Mcu Process; No. WSRC-STI-2006-00031; SRS: Aiken, SC, USA, 2006.
- Lee, A.; Zumbe, A.; Storey, D. Breath hydrogen after ingestion of the bulk sweeteners sorbitol, isomalt and sucrose in chocolate. Br. J. Nutr. 1994, 71, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tapia, M.S.; Rojas-Graü, M.A.; Carmona, A.; Rodríguez, F.J.; Soliva-Fortuny, R.; Martin-Belloso, O. Use of alginate- and gellan-based coatings for improving barrier, texture and nutritional properties of fresh-cut papaya. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 1493–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Krochta, J.M. Dependence of coating thickness on viscosity of coating solution applied to fruits and vegetables by dipping method. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.; Osés, J.; Ziani, K.; Maté, J.I. Combined effect of plasticizers and surfactants on the physical properties of starch based edible films. Food Res. Int. 2006, 39, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahraee, S.; Milani, J.M.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Hamishehkar, H. Effect of corn oil on physical, thermal, and antifungal properties of gelatin-based nanocomposite films containing nano chitin. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.S.C.; Lee, P.F.S. CMC of polysorbates. J. Pharm. Sci. 1974, 63, 136–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltonen, L.J.; Yliruusi, J. Surface pressure, hysteresis, interfacial tension, and CMC of four sorbitan monoesters at water–air, water–hexane, and hexane–air interfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 227, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltonen, L.; Hirvonen, J.; Yliruusi, J. The behavior of sorbitan surfactants at the water–oil interface: Straight-chained hydrocarbons from pentane to dodecane as an oil phase. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 240, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rulison, C. Models for Surface Free Energy Calculation. Available online: https://www.kruss.de/fileadmin/user_upload/website/literature/kruss-tn306-en.pdf (accessed on 14 September 2017).
- Garrett, E.R. Stability of oil-in-water emulsions. J. Pharm. Sci. 1965, 54, 1557–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casariego, A.; Souza, B.W.S.; Vicente, A.A.; Teixeira, J.A.; Cruz, L.; Díaz, R. Chitosan coating surface properties as affected by plasticizer, surfactant and polymer concentrations in relation to the surface properties of tomato and carrot. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos, R.; Chanona, J.; Hernández, P.; Gutiérrez, G.; Chiralt, A. Gloss and transparency of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose films containing surfactants as affected by their microstructure. Food Hydrocoll. 2005, 19, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruss GmbH. Pendant Drop. Available online: https://www.kruss.de/services/education-theory/glossary/pendant-drop/ (accessed on 8 November 2017).
- Senturk Parreidt, T.; Schmid, M.; Hauser, C. Validation of a novel technique and evaluation of the surface free energy of food. Foods 2017, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasband, W.S. Imagej. Available online: https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ (accessed on 23 July 2017).
- Stalder, A. Drop Shape Analysis. Available online: http://bigwww.epfl.ch/demo/dropanalysis/ (accessed on 29 July 2017).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Auguie, B. gridExtra: Miscellaneous Functions for “Grid” Graphics. R Package Version 2.2.1. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=gridExtra (accessed on 1 March 2017).
- Wickham, H. The split-apply-combine strategy for data analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 40, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston Chang. extrafont: Tools for Using Fonts. R package version 0.17. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=extrafont (accessed on 1 March 2017).
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, D. Learning Statistics with R: A Tutorial for Psychology Students and Other Beginners; Version 0.5; University of Adelaide: Adelaide, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, G. _userfriendlyscience: Quantitative Analysis Made Accessible_. R Package Version 0.7.0. Available online: http://userfriendlyscience.com (accessed on 2 January 2018).
- Soetaert, K. rootsolve: Nonlinear Root Finding, Equilibrium and Steady-State Analysis of Ordinary Differential Equations. R-Package Version 1.6. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=rootSolve (accessed on 15 December 2017).
- Soetaert, K.; Herman, P.M.J. A Practical Guide to Ecological Modelling: Using R as a Simulation Platform; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]

| Span 80 (%) | Tween 40 (%) | Tween 80 (%) | γL (mN/m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.06 | 0.03 | - | 55.42 ± 0.66 A |
| 0.06 | - | 0.03 | 54.64 ± 0.14 A |
| 1 | - | 1 | 38.05 ± 0.30 B |
| 1 | 1 | - | 37.75 ± 0.27 B |
| Sunflower Oil | Span 80 (%) | Tween 40 (%) | γL (mN/m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 55.42 ± 0.66 A |
| 1 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 50.10 ± 0.25 B |
| 0.05 | 0.06 | 1 | 43.72 ± 0.42 C |
| 1 | 0.06 | 1 | 43.13 ± 0.05 C |
| 0.05 | 1 | 0.03 | 33.63 ± 0.60 D |
| 1 | 1 | 0.03 | 34.99 ± 0.28 E |
| 0.05 | 1 | 1 | 37.75 ± 0.27 F |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 37.16 ± 0.12 F |
| Component | 0.25% | 0.5% | 0.75% | 1% | 3.5% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunflower oil | 2.31 ± 0.09 a | 2.08 ± 0.21 a | 2.08 ± 0.30 a | 2.06 ± 0.16 a | 2.06 ± 0.43 a |
| Lecithin | - 1 | - 1 | 0.53 ± 0.01 b | 0.44 ± 0.01 c | 0.41 ± 0.01 d |
| Formulation | γL (mN/m) | θ (°) | Wa (mN/m) | Wc (mN/m) | WS (mN/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formula 1 | 31.80 ± 0.09 A | 66.39 ± 5.98 D | 45.83 ± 2.29 F | 63.60 H | −17.77 ± 2.29 L |
| Formula 2 | 36.26 ± 0.51 C | 72.62 ± 5.31 E | 47.05 ± 3.05 FG | 72.52 K | −25.47 ± 3.18 N |
| Formula 3 | 35.41 ± 0.27 B | 65.99 ± 8.28 D | 49.68 ± 4.64 G | 70.82 I | −21.14 ± 4.64 M |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Senturk Parreidt, T.; Schott, M.; Schmid, M.; Müller, K. Effect of Presence and Concentration of Plasticizers, Vegetable Oils, and Surfactants on the Properties of Sodium-Alginate-Based Edible Coatings. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030742
Senturk Parreidt T, Schott M, Schmid M, Müller K. Effect of Presence and Concentration of Plasticizers, Vegetable Oils, and Surfactants on the Properties of Sodium-Alginate-Based Edible Coatings. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(3):742. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030742
Chicago/Turabian StyleSenturk Parreidt, Tugce, Michael Schott, Markus Schmid, and Kajetan Müller. 2018. "Effect of Presence and Concentration of Plasticizers, Vegetable Oils, and Surfactants on the Properties of Sodium-Alginate-Based Edible Coatings" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 3: 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030742
APA StyleSenturk Parreidt, T., Schott, M., Schmid, M., & Müller, K. (2018). Effect of Presence and Concentration of Plasticizers, Vegetable Oils, and Surfactants on the Properties of Sodium-Alginate-Based Edible Coatings. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(3), 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030742