Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Dehydroabietic Acid-Oxazolidinone Hybrids for Antitumor Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
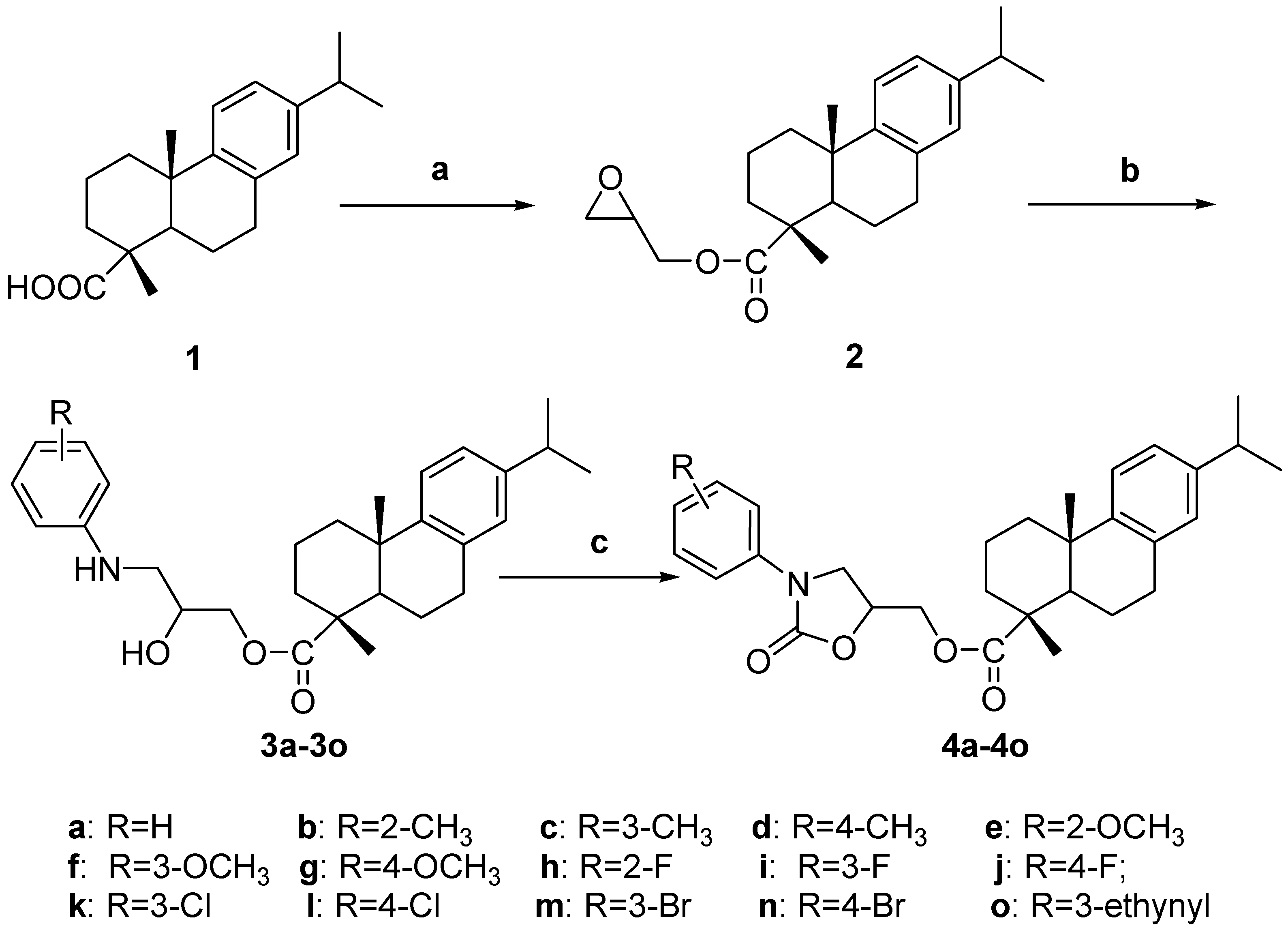
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Assays
2.2.1. Cytotoxicity Measurement
2.2.2. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.2.3. Compound 4j Induces Apoptosis in MGC-803 Cells
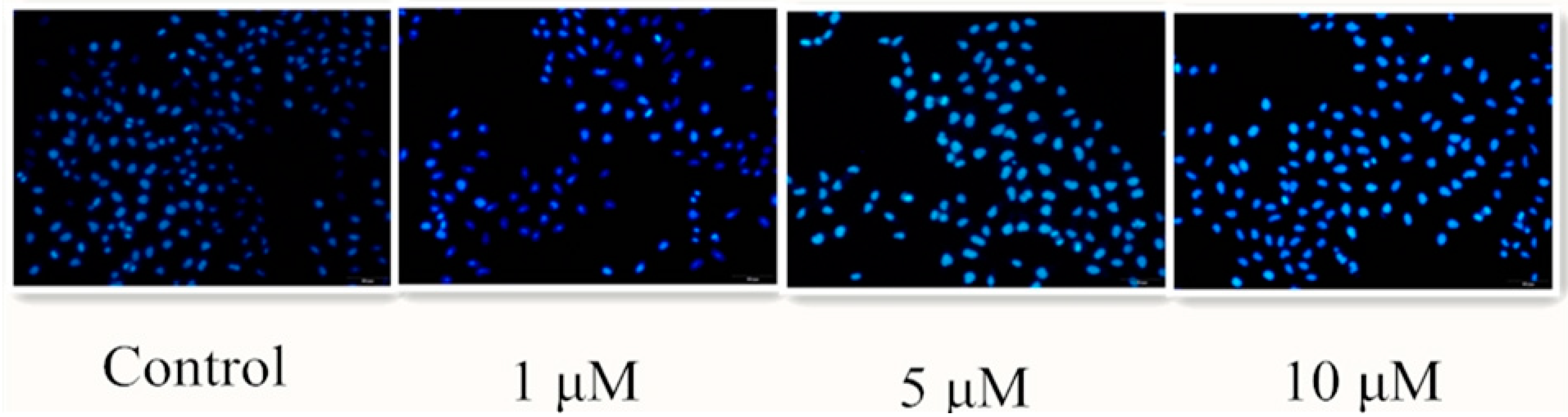
2.2.4. Hoechst 33258 Staining Assay
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Synthesis: General Procedure for Compounds 3a–o
3.2.1. (1R,4aS)-2-Hydroxy-3-(Phenylamino)Propyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4,4a,9,10,10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (3a)
3.2.2. (1R,4aS)-2-Hydroxy-3-(2-Methylphenylamino)Propyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4,4a,9,10, 10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (3b)
3.2.3. (1R,4aS)-2-Hydroxy-3-(3-Methylphenylamino)Propyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4,4a,9,10, 10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (3c)
3.2.4. (1R,4aS)-2-Hydroxy-3-(4-Methylphenylamino)Propyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4,4a,9,10, 10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (3d)
3.2.5. (1R,4aS)-2-Hydroxy-3-(2-Methoxyphenylamino)Propyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4,4a,9, 10,10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (3e)
3.2.6. (1R,4aS)-2-Hydroxy-3-(3-Methoxyphenylamino)Propyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4,4a,9, 10,10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (3f)
3.2.7. (1R,4aS)-2-Hydroxy-3-(4-Methoxyphenylamino)Propyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4,4a,9, 10,10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (3g)
3.2.8. (1R,4aS)-2-Hydroxy-3-(2-Fluorophenylamino)Propyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4,4a,9,10, 10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (3h)
3.2.9. (1R,4aS)-2-Hydroxy-3-(3-Fluorophenylamino)Propyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4,4a,9,10, 10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylatev (3i)
3.2.10. (1R,4aS)-2-Hydroxy-3-(4-Fluorophenylamino)Propyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4,4a,9,10, 10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (3j)
3.2.11. (1R,4aS)-2-Hydroxy-3-(3-Chlorophenylamino)Propyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4,4a,9,10, 10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (3k)
3.2.12. (1R,4aS)-2-Hydroxy-3-(4-Chlorophenylamino)Propyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4,4a,9,10, 10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (3l)
3.2.13. (1R,4aS)-2-Hydroxy-3-(3-Bromophenylamino)Propyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4,4a,9,10, 10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (3m)
3.2.14. (1R,4aS)-2-Hydroxy-3-(4-Bromophenylamino)Propyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4,4a,9,10, 10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (3n)
3.2.15. (1R,4aS)-2-Hydroxy-3-(3-Ethynylphenylamino)Propyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4,4a,9, 10,10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate 3o
3.3. Synthesis: General Procedure for Compounds 4a–o
3.3.1. (1R,4aS)-(2-Oxo-3-Phenyloxazolidin-5-yl)Methyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4,4a,9,10,10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (4a)
3.3.2. (1R,4aS)-(3-(2-Methylphenyl)-2-Oxooxazolidin-5-yl)Methyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4, 4a,9,10,10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (4b)
3.3.3. (1R,4aS)-(3-(3-Methylphenyl)-2-Oxooxazolidin-5-yl)Methyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4, 4a,9,10,10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (4c)
3.3.4. (1R,4aS)-(3-(4-Methylphenyl)-2-Oxooxazolidin-5-yl)Methyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4, 4a,9,10,10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (4d)
3.3.5. (1R,4aS)-(3-(2-Methoxyphenyl)-2-Oxooxazolidin-5-yl)Methyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4, 4a,9,10,10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (4e)
3.3.6. (1R,4aS)-(3-(3-Methoxyphenyl)-2-Oxooxazolidin-5-yl)Methyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4, 4a,9,10,10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (4f)
3.3.7. (1R,4aS)-(3-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-2-Oxooxazolidin-5-yl)Methyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4, 4a,9,10,10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (4g)
3.3.8. (1R,4aS)-(3-(2-Fluorophenyl)-2-Oxooxazolidin-5-yl)Methyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4,4a, 9,10,10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (4h)
3.3.9. (1R,4aS)-(3-(3-Fluorophenyl)-2-Oxooxazolidin-5-yl)Methyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4,4a, 9,10,10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (4i)
3.3.10. (1R,4aS)-(3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-2-Oxooxazolidin-5-yl)Methyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4, 4a,9,10,10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (4j)
3.3.11. (1R,4aS)-(3-(3-Chlorophenyl)-2-Oxooxazolidin-5-yl)Methyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4, 4a,9,10,10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (4k)
3.3.12. (1R,4aS)-(3-(4-Chlorophenyl)-2-Oxooxazolidin-5-yl)Methyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4, 4a,9,10,10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (4l)
3.3.13. (1R,4aS)-(3-(3-Bromophenyl)-2-Oxooxazolidin-5-yl)Methyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4, 4a,9,10,10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (4m)
3.3.14. (1R,4aS)-(3-(4-Bromophenyl)-2-Oxooxazolidin-5-yl)Methyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4, 4a,9,10,10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate (4n)
3.3.15. (1R,4aS)-(3-(3-Ehynylphenyl)-2-Oxooxazolidin-5-yl)Methyl-7-Isopropyl-1,4a-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4, 4a,9,10,10a-Octahydrophenanthrene-1-Carboxylate 4o
3.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
3.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
3.6. Apoptosis Analysis
3.7. Hoechst 33258 Staining Assay
3.8. Statistics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BTC | bis(trichloromethyl)carbonate |
| DCM | dichloromethane |
| DHAA | dehydroabietic acid |
| DMEM | dulbecco’s modified eagle medium |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| FITC | fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| HR-MS | high resolution mass spectrometr |
| IR | infrared radiation |
| Mp | melting point |
| MRSA | methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus |
| MRSE | methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis |
| MTT | methyl thiazolytetrazolium |
| NMR | nuclear magnetic resonance |
| PI | propidium iodide |
| THF | tetrahydrofuran |
| TLC | thin-layer chromatography |
| TMS | tetramethylsilane |
| VRE | vancomycin-resistant enterococcus |
References
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadashpour, S.; Emami, S. Indole in the target-based design of anticancer agents: A versatile scaffold with diverse mechanism. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 150, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidler, J.; Kripke, M.L. Metastasis results from preexisting variant cells within a malignant tumor. Science 1997, 197, 893–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.; Roller, A.; Maulide, N. Synthesis and antimicrobial evaluation of novel analogues of dehydroabietic acid prepared by C–H-Activation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 126, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.-M.; Yang, T.; Pan, X.-Y.; Liu, X.-L.; Lin, H.-X.; Gao, Z.-B.; Yang, G.-G.; Gui, Y.-M. The synthesis and antistaphylococcal activity of dehydroabietic acid derivatives: Modifications at C12 and C7. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 26, 5492–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, T.; Gigante, B.; Marques, M.M.; Gilchristc, T.L.; De Clercq, E. Synthesis and antiviral evaluation of benzimidazoles, quinoxalines and indoles from dehydroabietic acid. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yan, X.-Y.; Gao, Y.-Q.; Rao, X.-P. Synthesis and antifeedant activities of rosin-based esters against armyworm. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2016, 19, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.-Y.; Duan, W.-G.; Lin, G.-S.; Liu, L.-Z.; Zhang, R.; Li, D.-P. Synthesis and antifungal activity of dehydroabietic acid-based 1,3,4-thiadiazole-thiazolidinone compounds. Mol. Divers. 2016, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cu, Y.-M.; Liu, X.-L.; Zhang, W.-M.; Lin, H.-X.; Ohwada, T.; Ido, K.; Sawada, K. The synthesis and BK channel-opening activity of N-acylaminoalkyloxime derivatives of dehydroabietic acid. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertino, M.W.; Vega, C.; Rolón, M.; Coronel, C.; Arias, A.R.; Hirschmann, G.S. Antiprotozoal activity of triazole derivatives of dehydroabietic acid and oleanolic acid. Molecules 2017, 22, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.S.; Hirai, S.; Goto, T.; Kuroyanagi, K.; Lee, J.Y.; Uemura, T.; Ezaki, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Kawada, T. Dehydroabietic acid, a phytochemical, acts as ligand for PPARs in macrophages and adipocytes to regulate inflammation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 369, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.-C.; Huang, R.-Z.; Liao, Z.-X.; Pan, Y.-M.; Gou, S.-H.; Wang, H.-S. Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of dehydroabietic acid thiourea derivatives containing bisphosphonate moiety as an inducer of apoptosis. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 108, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Qu, H.-E.; Huang, X.-C.; Pan, Y.-M.; Liang, D.; Chen, Z.-F.; Wang, H.-S.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel dehydroabietic acid derivatives conjugated with acyl-thiourea peptide moiety as antitumor agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 14571–14593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, G.-J.; Cao, D.-H.; Li, D.; Ruan, H.-Q.; Fang, B.; Ruan, H.-L.; Su, L.; Xu, H.-T. Click chemistry-based synthesis and anticancer activity evaluation of novel C-14 1,2,3-triazole dehydroabietic acid hybrids. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 138, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.-Z.; Liang, G.-B.; Huang, X.-C.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, M.-M.; Liao, Z.-X.; Wang, H.-S. Discovery of dehydroabietic acid sulfonamide based derivatives as selective matrix metalloproteinases inactivators that inhibit cell migration and proliferation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 138, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, O.A.; D’Silva, R.; Bahta, T.O.; Sharaf, L.H.; Udo, E.E.; Benov, L.; Walters, D.E. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 5-(hydroxamic acid) methyl oxazolidinone derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 106, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaulding, A.; Takrouri, K.; Mahalingam, P.; Cleary, D.C.; Cooper, H.D.; Zucchi, P.; Tear, W.; Koleva, B.; Beuning, P.J.; Hirsch, E.B.; et al. Compound design guidelines for evading the efflux and permeation barriers of Escherichia coli with the oxazolidinone class of antibacterials: Test case for a general approach to improving whole cell Gram-negative activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 5310–5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, A.M.; Sattigeri, J.A.; Javed, K.; Shafi, S.; Shamim, M.; Singhal, S.; Malik, Z.M. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of spiropyrimidinetriones oxazolidinone derivatives as antibacterial agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, K.; Asmat, Y.; Jain, S.; Sharma, S.; Dwivedi, J. An efficient approach to the synthesis of novel oxazolidinones as potential antimicrobial agents. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dow, P.; Bechle, B.; Chou, T.; Clark, D.; Hulin, B.; Stevenson, R. Benzyloxazolidine-2,4-diones as potent hypoglycemic agents. J. Med. Chem. 1991, 5, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kombian, S.B.; Phillips, O.A. Novel actions of oxazolidinones: In vitro screening of a triazolyloxazolidinone for anticonvulsant activity. Med. Princ. Pract. 2013, 22, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbachyne, M.R.; Ford, C.W. Ozaxolidinone structure-activity relationships leading to linezolid. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 2010–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Ha, H.J.; Park, J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, W.K. 3,4-Disubstituted oxazolidin-2-ones as constrained ceramide analogs with anticancer activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6174–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadesse, M.; Svenson, J.; Jaspars, M.; Strom, M.B.; Abdelrahman, M.H.; Andersen, J.H.; Hansen, E.; Kristiansen, P.E.; Stensvåg, K.; Haug, T. A bicyclic member of the synoxazolidinone family with antibacterial and anticancer activities. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 1804–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naresh, A.; Venkateswara, R.M.; Kotapalli, S.S.; Ummanni, R.; Venkateswara, R.B. Oxazolidinone derivatives: Cytoxazone-linezolid hybrids induces apoptosis and senescence in DU145 prostate cancer cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 80, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, J.F.; Pereira, M.C.; de Sena, W.L.B.; de Barros Martins, C.G.; de Oliveira, J.F.; da Cruz Amorim, C.A.; de Melo Rêgo, M.J.B.; da Rocha Pitta, M.G.; de Lima, M.D.C.A.; da Rocha Pitta, M.G.; et al. Synthesis and in vitro anticancer activity of new 2-thioxo-oxazolidin-4-one derivatives. Pharmacol. Rep. 2017, 69, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artico, M.; De Martino, G.; Giuliano, R. Research on compounds with antiblastic activity. XL. Synthesis of 3-p-(2′,5′-dimethoxy-4′-(N,N-bis-(-chloroethyl)-amino)benzylideneamino)phenyl-2-oxazolidinone (GEA 29; BAY a 5850) and its analogues. Farmaco Sci. 1971, 26, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pandit, N.; Singla, R.K.; Shrivastava, B. Current updates on oxazolidinone and its significance. Int. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 2012, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macherla, V.R.R.; Nicholson, B.; Lam, K.S. Anti-Cancer and Anti-Microbial Oxazolidinones. United States Patent Application US 12/124,896, 11 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.-Y.; Wang, X.; Duan, W.-G.; Lin, G.-S. Synthesis and in vitro anticancer activity of novel dehydroabietic acid-based acylhydrazones. Molecules 2017, 22, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.H.; Popov, S.A.; Lee, J.Y.; Shpatov, A.V.; Kukina, T.P.; Kang, S.W.; Pan, C.H.; Um, B.H.; Jung, S.H. Inhibitory effect of ursolic acid derivatives on recombinant human aldose reductase. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2011, 37, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-F.; Jiang, M.-Y.; Zhou, S.-G.; Wu, S.-S.; Zhang, X.-L.; Ma, L.-S.; Zhang, K.; Gong, P. Design, synthesis and structure-activity relationship of oxazolidinone derivatives containing novel S4 ligand as FXa inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 96, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, M.R.; Blake, A.J.; Cadogan, J.I.G.; Doyle, A.A.; Gosney, I.; Hodgson, P.K.G.; Thorburn, P. Asymmetric diels-alder reactions employing modified camphor-derived oxazolidin-2-one chiral auxiliaries. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 4079–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendiran, D.; Kumar, R.S.; Viswanathan, V.; Velmurugan, D.; Rahiman, A.K. In vitro and in vivo anti-proliferative evaluation of bis(4′-(4-tolyl)-2,2′,6′,2″-terpyridine)copper(II) complex against Ehrlich ascites carcinoma tumors. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafez, H.N.; El-Gazzar, A.-R.B.A. Synthesis and evaluation of antitumor activity of new 4-substituted thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidine and thienotriazolopyrimidine derivatives. Acta Pharm. 2017, 67, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Q.-Y.; Wan, D.; Tang, B.; Wang, Y.-J.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Du, F.; He, M.; Liu, Y.-J. Synthesis, characterization and anticancer activity in vitro and in vivo evaluation of an iridium (III) polypyridyl complex. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 145, 338–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Compound | IC50 (μM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MGC-803 | CNE-2 | SK-OV-3 | NCI-H460 | LO2 | |
| 3a | 7.10 ± 1.51 | 27.87 ± 0.25 | 15.08 ± 0.57 | 18.56 ± 0.97 | >100 |
| 3b | 22.56 ± 2.71 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 3c | 12.34 ± 4.87 | 14.61 ± 0.19 | 14.81 ± 4.03 | 20.13 ± 2.95 | 34.67 ± 0.45 |
| 3d | 21.84 ± 2.66 | 44.13 ± 2.89 | 29.95 ± 0.80 | 44.76 ± 5.26 | >100 |
| 3e | 28.47 ± 1.35 | 27.37 ± 0.51 | 19.48 ± 2.23 | 26.14 ± 1.92 | 32.34 ± 1.56 |
| 3f | 18.37 ± 1.45 | 17.44 ± 4.32 | 18.01 ± 0.09 | 21.87 ± 8.61 | >100 |
| 3g | 51.69 ± 1.85 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 3h | 17.50 ± 3.51 | 45.74 ± 5.80 | >100 | 30.24 ± 3.40 | >100 |
| 3i | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 3j | 14.21 ± 1.70 | 20.73 ± 2.31 | 18.91 ± 1.66 | 15.59 ± 1.45 | 28.69 ± 0.55 |
| 3k | 13.10 ± 2.66 | 18.17 ± 4.06 | 25.07 ± 4.80 | 18.14 ± 2.33 | 35.32 ± 0.57 |
| 3l | 34.48 ± 0.02 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 3m | 16.48 ± 5.20 | 23.17 ± 2.78 | 30.29 ± 0.59 | 19.63 ± 1.12 | >100 |
| 3n | 9.91 ± 7.00 | 17.89 ± 4.47 | 19.03 ± 2.11 | 19.05 ± 5.23 | >100 |
| 3o | 13.38 ± 5.41 | 20.01 ± 1.09 | 23.08 ± 2.23 | 22.30 ± 2.74 | >100 |
| 4a | 11.00 ± 4.41 | 9.69 ± 0.13 | >100 | 4.83 ± 0.77 | >100 |
| 4b | 24.99 ± 5.02 | >100 | >100 | 27.72 ± 5.03 | >100 |
| 4c | 10.50 ± 1.44 | 31.96 ± 0.23 | >100 | 9.13 ± 2.77 | 36.22 ± 2.68 |
| 4d | 5.97 ± 0.87 | 21.14 ± 1.96 | 19.74 ± 1.33 | 2.91 ± 2.38 | 30.55 ± 1.99 |
| 4e | 13.23 ± 1.15 | 20.51 ± 0.97 | >100 | 7.99 ± 6.35 | 40.56 ± 1.96 |
| 4f | 19.71 ± 2.80 | 23.53 ± 1.20 | 42.97 ± 1.05 | 17.25 ± 1.38 | >100 |
| 4g | 6.10 ± 0.35 | 19.76 ± 0.30 | 4.10 ± 2.45 | 14.05 ± 8.04 | 26.36 ± 0.15 |
| 4h | 49.90 ± 1.14 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 4i | 11.48 ± 0.25 | 28.02 ± 3.95 | 9.86 ± 4.30 | 25.09 ± 4.50 | >100 |
| 4j | 3.82 ± 0.18 | 17.76 ± 4.69 | 4.66 ± 2.13 | 8.44 ± 0.36 | >100 |
| 4k | 7.43 ± 1.42 | 31.24 ± 2.50 | 10.33 ± 5.46 | 22.96 ± 2.62 | 37.20 ± 3.14 |
| 4l | 5.82 ± 4.82 | 27.58 ± 1.50 | 15.71 ± 2.32 | 26.55 ± 0.08 | 44.49 ± 2.77 |
| 4m | 9.80 ± 2.37 | >100 | >100 | 25.06 ± 1.39 | 34.16 ± 2.88 |
| 4n | 5.34 ± 3.45 | 42.49 ± 5.68 | >100 | 30.24 ± 2.66 | >100 |
| 4o | 18.22 ± 2.36 | 51.36 ± 5.06 | 23.66 ± 2.02 | 72.36 ± 1.07 | >100 |
| DHA | 29.81 ± 2.06 | 62.59 ± 1.60 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| cisplatin | 14.9 ± 1.78 | 21.02 ± 2.25 | 10.44 ± 0.25 | 24.14 ± 1.74 | 36.37 ± 0.79 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Pang, F.-H.; Huang, L.; Yang, X.-P.; Ma, X.-L.; Jiang, C.-N.; Li, F.-Y.; Lei, F.-H. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Dehydroabietic Acid-Oxazolidinone Hybrids for Antitumor Properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103116
Wang X, Pang F-H, Huang L, Yang X-P, Ma X-L, Jiang C-N, Li F-Y, Lei F-H. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Dehydroabietic Acid-Oxazolidinone Hybrids for Antitumor Properties. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(10):3116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103116
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiu, Fu-Hua Pang, Lin Huang, Xin-Ping Yang, Xian-Li Ma, Cai-Na Jiang, Fang-Yao Li, and Fu-Hou Lei. 2018. "Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Dehydroabietic Acid-Oxazolidinone Hybrids for Antitumor Properties" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 10: 3116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103116
APA StyleWang, X., Pang, F.-H., Huang, L., Yang, X.-P., Ma, X.-L., Jiang, C.-N., Li, F.-Y., & Lei, F.-H. (2018). Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Dehydroabietic Acid-Oxazolidinone Hybrids for Antitumor Properties. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(10), 3116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103116





