Personalized Antidepressant Selection and Pathway to Novel Treatments: Clinical Utility of Targeting Inflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Need for Personalized Antidepressant Prescription
3. Need for Novel Antidepressants
4. Role of Inflammation in Depression
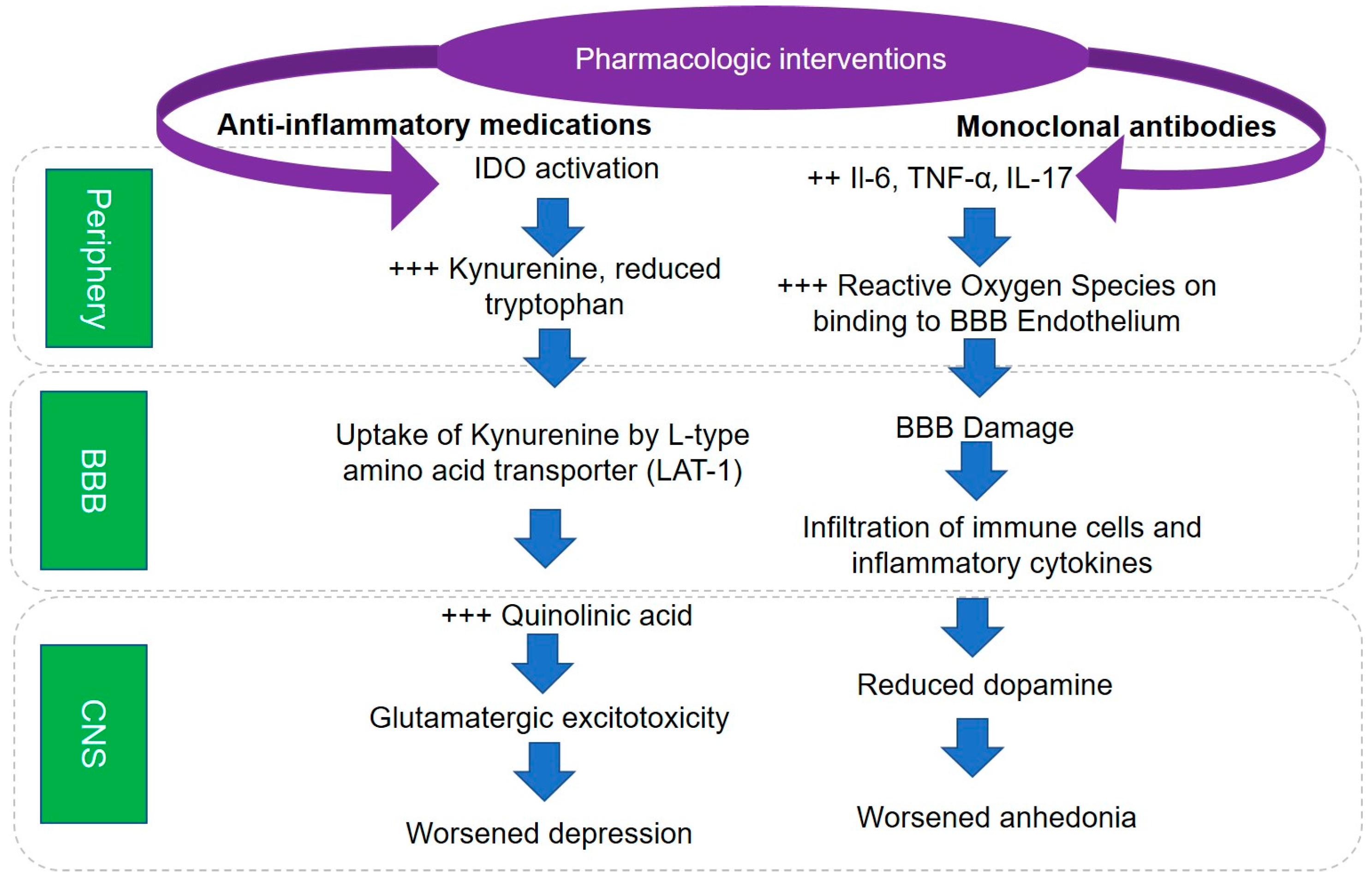
5. Pathophysiological Mechanisms Underlying Role of Inflammation in Depression
6. Effects of Antidepressant Treatments on Inflammation
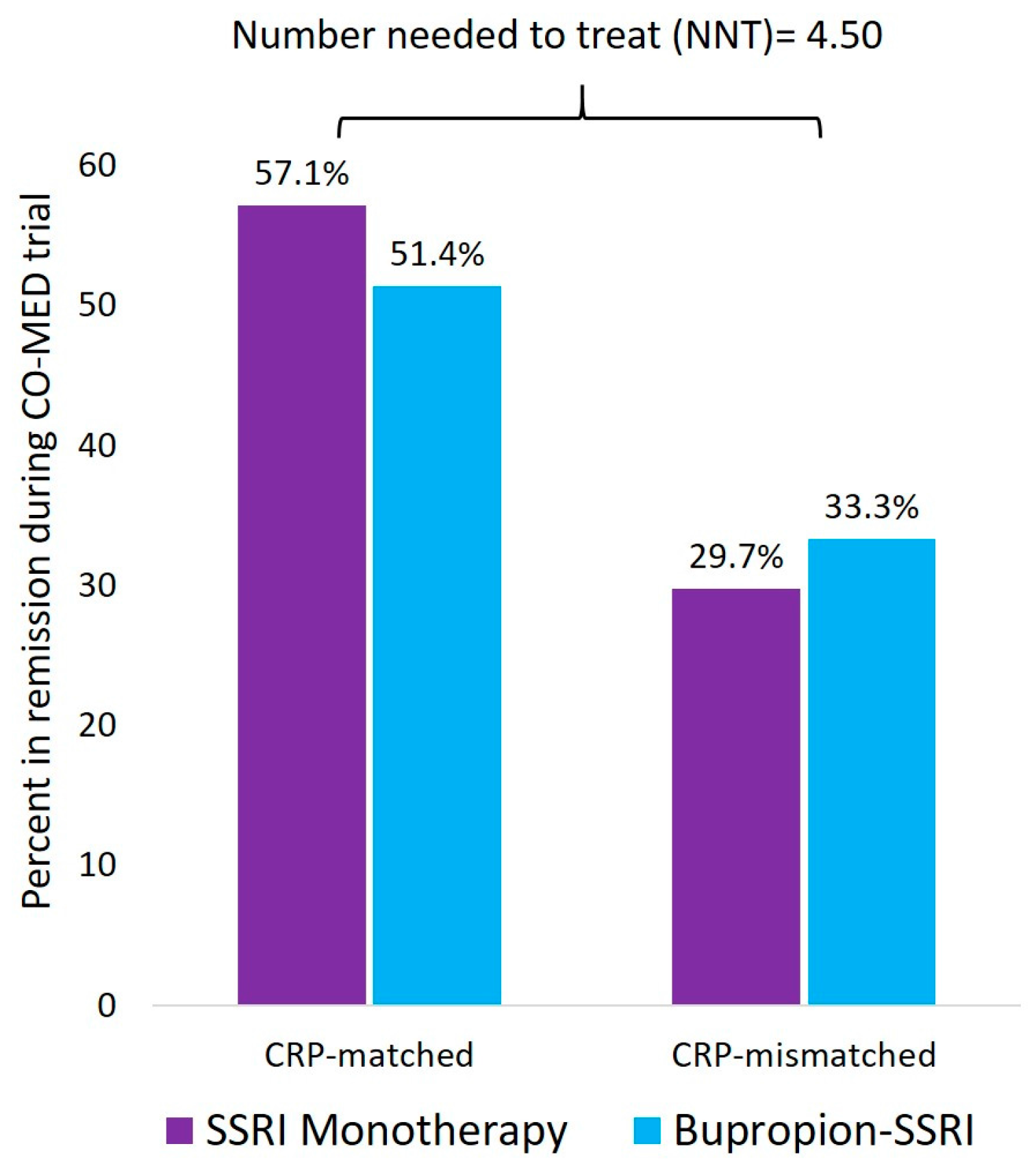
7. Inflammatory Markers to Personalize Antidepressant Prescription
8. Anti-Inflammatory Drugs as Novel Antidepressants
9. Future Directions
10. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDD | Major depressive disorder |
| SSRI | selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor |
| STAR*D | Sequenced Treatment Alternatives to Relieve Depression |
| TRD | Treatment-Resistant Depression |
| RDoC | Research Domain Criteria |
| IFN-α | Interferon Alpha |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| GENDEP | Genome-Based Therapeutics Drugs for Depression |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha |
| IL-17 | Interleukin 17 |
| Th | T-helper |
| RORyT | Retinoid-related Orphan Receptor-yT |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| IDO | Indoleamine Oxygenase |
| LAT-1 | L-type Amino Acid Transporter |
| KMO | Kynurenine 2-Monooxygenase |
| BBB | Blood-Brain Barrier |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| NOS | Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| NSAIDs | Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs |
References
- Hasin, D.S.; Goodwin, R.D.; Stinson, F.S.; Grant, B.F. Epidemiology of major depressive disorder: Results from the national epidemiologic survey on alcoholism and related conditions. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2005, 62, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, R.C.; Berglund, P.; Demler, O.; Jin, R.; Koretz, D.; Merikangas, K.R.; Rush, A.J.; Walters, E.E.; Wang, P.S. The epidemiology of major depressive disorder: Results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication (NCS-R). JAMA 2003, 289, 3095–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judd, L.L.; Akiskal, H.S.; Zeller, P.J.; Paulus, M.; Leon, A.C.; Maser, J.D.; Endicott, J.; Coryell, W.; Kunovac, J.L.; Mueller, T.I.; et al. Psychosocial disability during the long-term course of unipolar major depressive disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2000, 57, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, M.K.; Minhajuddin, A.; Greer, T.L.; Carmody, T.; Rush, A.J.; Trivedi, M.H. Early improvement in work productivity predicts future clinical course in depressed outpatients: Findings from the co-med trial. Am. J. Psychiatry 2016, 173, 1196–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, M.K.; Teer, R.B.; Minhajuddin, A.; Greer, T.L.; Rush, A.J.; Trivedi, M.H. Daily activity level improvement with antidepressant medications predicts long-term clinical outcomes in outpatients with major depressive disorder. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2017, 13, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, M.K.; Minhajuddin, A.; Greer, T.L.; Carmody, T.; Rush, A.J.; Trivedi, M.H. Early improvement in psychosocial function predicts longer-term symptomatic remission in depressed patients. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papakostas, G.I.; Petersen, T.; Mahal, Y.; Mischoulon, D.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Fava, M. Quality of life assessments in major depressive disorder: A review of the literature. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2004, 26, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, T.; Barber, R.M.; Bell, B.; Bertozzi-Villa, A.; Biryukov, S.; Bolliger, I.; Charlson, F.; Davis, A.; Degenhardt, L.; Dicker, D. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013. Lancet 2015, 386, 743–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, P.E.; Fournier, A.A.; Sisitsky, T.; Pike, C.T.; Kessler, R.C. The economic burden of adults with major depressive disorder in the united states (2005 and 2010). J. Clin. Psychiatry 2015, 76, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pence, B.W.; O‘Donnell, J.K.; Gaynes, B.N. The depression treatment cascade in primary care: A public health perspective. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2012, 14, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendler, K.S. What psychiatric genetics has taught us about the nature of psychiatric illness and what is left to learn. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelenberg, A.J.; Freeman, M.P.; Markowitz, J.C.; Rosenbaum, J.F.; Thase, M.E.; Trivedi, M.H.; Van Rhoads, R.S.; Reus, V.I.; Raymond DePaulo, J., Jr.; Fawcett, J.A. Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with major depressive disorder third edition. Am. J. Psychiatry 2010, 167, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, E.S.; Davis, L.L.; Zisook, S.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Trivedi, M.H.; Fava, M.; Rush, A.J. Baseline depression severity as a predictor of single and combination antidepressant treatment outcome: Results from the co-med trial. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012, 22, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, S.C.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Balasubramani, G.K.; Zisook, S.; Kurian, B.; Warden, D.; Trivedi, M.H.; Rush, A.J. Does early-onset chronic or recurrent major depression impact outcomes with antidepressant medications? A co-med trial report. Psychol. Med. 2013, 43, 945–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, S.C.; Haley, C.L.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Fava, M.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Warden, D.; Morris, D.W.; Kurian, B.T.; Trivedi, M.H.; Rush, A.J. The impact of chronic depression on acute and long-term outcomes in a randomized trial comparing selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor monotherapy versus each of 2 different antidepressant medication combinations. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2012, 73, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, S.C.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Luther, J.F.; Trivedi, M.H.; Rush, A.J. Pre-treatment insomnia as a predictor of single and combination antidepressant outcomes: A co-med report. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 174, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnow, B.A.; Blasey, C.; Williams, L.M.; Palmer, D.M.; Rekshan, W.; Schatzberg, A.F.; Etkin, A.; Kulkarni, J.; Luther, J.F.; Rush, A.J. Depression subtypes in predicting antidepressant response: A report from the ispot-d trial. Am. J. Psychiatry 2015, 172, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobo, W.V.; Chen, H.; Trivedi, M.H.; Stewart, J.W.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Fava, M.; Kurian, B.T.; Warden, D.; Morris, D.W.; Luther, J.F.; et al. Randomized comparison of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (escitalopram) monotherapy and antidepressant combination pharmacotherapy for major depressive disorder with melancholic features: A co-med report. J. Affect. Disord. 2011, 133, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gartlehner, G.; Hansen, R.A.; Morgan, L.C.; Thaler, K.; Lux, L.; Van Noord, M.; Mager, U.; Thieda, P.; Gaynes, B.N.; Wilkins, T.; et al. Comparative benefits and harms of second-generation antidepressants for treating major depressive disorder: An updated meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 772–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rush, A.J.; Trivedi, M.H.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Stewart, J.W.; Warden, D.; Niederehe, G.; Thase, M.E.; Lavori, P.W.; Lebowitz, B.D.; et al. Acute and longer-term outcomes in depressed outpatients requiring one or several treatment steps: A STAR*D report. Am. J. Psychiatry 2006, 163, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rush, A.J.; Trivedi, M.H.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Stewart, J.W.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Thase, M.E.; Ritz, L.; Biggs, M.M.; Warden, D.; Luther, J.F.; et al. Bupropion-sr, sertraline, or venlafaxine-xr after failure of ssris for depression. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, C.; Cochran, A.J.; Cameron, I.M. Restarting antidepressant treatment following early discontinuation—A primary care database study. Fam. Pract. 2015, 32, 520–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warden, D.; Rush, A.J.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Lesser, I.M.; Kornstein, S.G.; Balasubramani, G.K.; Thase, M.E.; Preskorn, S.H.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Young, E.A.; et al. What predicts attrition in second step medication treatments for depression?: A STAR*D report. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009, 12, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, M.H. Right patient, right treatment, right time: Biosignatures and precision medicine in depression. World Psychiatry 2016, 15, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, M.H.; Rush, A.J.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Warden, D.; Ritz, L.; Norquist, G.; Howland, R.H.; Lebowitz, B.; McGrath, P.J.; et al. Evaluation of outcomes with citalopram for depression using measurement-based care in STAR*D: Implications for clinical practice. Am. J. Psychiatry 2006, 163, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, M.H.; Fava, M.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Thase, M.E.; Quitkin, F.; Warden, D.; Ritz, L.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Lebowitz, B.D.; Biggs, M.M.; et al. Medication augmentation after the failure of ssris for depression. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrazek, D.A.; Hornberger, J.C.; Altar, C.A.; Degtiar, I. A review of the clinical, economic, and societal burden of treatment-resistant depression: 1996–2013. Psychiatr. Serv. 2014, 65, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, S.; Classi, P.; Dennehy, E.B. What happens next?: A claims database study of second-line pharmacotherapy in patients with major depressive disorder (mdd) who initiate selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (ssri) treatment. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2014, 13, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feighner, J.P. Mechanism of action of antidepressant medications. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1999, 60 (Suppl. S4), 4–11, discussion 12–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murrough, J.W.; Charney, D.S. Is there anything really novel on the antidepressant horizon? Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2012, 14, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insel, T.; Cuthbert, B.; Garvey, M.; Heinssen, R.; Pine, D.S.; Quinn, K.; Sanislow, C.; Wang, P. Research domain criteria (rdoc): Toward a new classification framework for research on mental disorders. Am. J. Psychiatry 2010, 167, 748–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantzer, R.; O‘Connor, J.C.; Freund, G.G.; Johnson, R.W.; Kelley, K.W. From inflammation to sickness and depression: When the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.H.; Raison, C.L. The role of inflammation in depression: From evolutionary imperative to modern treatment target. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 16, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raison, C.L.; Borisov, A.S.; Broadwell, S.D.; Capuron, L.; Woolwine, B.J.; Jacobson, I.M.; Nemeroff, C.B.; Miller, A.H. Depression during pegylated interferon-alpha plus ribavirin therapy: Prevalence and prediction. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2005, 66, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNutt, M.D.; Liu, S.; Manatunga, A.; Royster, E.B.; Raison, C.L.; Woolwine, B.J.; Demetrashvili, M.F.; Miller, A.H.; Musselman, D.L. Neurobehavioral effects of interferon-[alpha] in patients with hepatitis-C: Symptom dimensions and responsiveness to paroxetine. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 1444–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raison, C.L.; Broadwell, S.D.; Borisov, A.S.; Manatunga, A.K.; Capuron, L.; Woolwine, B.J.; Jacobson, I.M.; Nemeroff, C.B.; Miller, A.H. Depressive symptoms and viral clearance in patients receiving interferon-α and ribavirin for hepatitis c. Brain Behav. Immun. 2005, 19, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstow, N.J.; Mohamed, Z.; Gomaa, A.I.; Sonderup, M.W.; Cook, N.A.; Waked, I.; Spearman, C.W.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D. Hepatitis C treatment: Where are we now? Int. J. Gen. Med. 2017, 10, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepys, M.B.; Hirschfield, G.M. C-reactive protein: A critical update. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2003, 111, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar]
- Kaptoge, S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Lowe, G.; Pepys, M.B.; Thompson, S.G.; Collins, R.; Danesh, J. C-reactive protein concentration and risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and mortality: An individual participant meta-analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wium-Andersen, M.; Ørsted, D.; Nielsen, S.; Nordestgaard, B. Elevated c-reactive protein levels, psychological distress, and depression in 73 131 individuals. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cepeda, M.S.; Stang, P.; Makadia, R. Depression is associated with high levels of C-reactive protein and low levels of fractional exhaled nitric oxide: Results from the 2007–2012 national health and nutrition examination surveys. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2016, 77, 1666–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler-Forsberg, O.; Buttenschøn, H.N.; Tansey, K.E.; Maier, W.; Hauser, J.; Dernovsek, M.Z.; Henigsberg, N.; Souery, D.; Farmer, A.; Rietschel, M.; et al. Association between C-reactive protein (crp) with depression symptom severity and specific depressive symptoms in major depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 62, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetter, M.L.; Wadden, T.A.; Vinnard, C.; Moore, R.H.; Khan, Z.; Volger, S.; Sarwer, D.B.; Faulconbridge, L.F. Gender differences in the relationship between symptoms of depression and high-sensitivity crp. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37 (Suppl. S1), S38–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batty, G.; Bell, S.; Stamatakis, E.; Kivimäki, M. Association of systemic inflammation with risk of completed suicide in the general population. JAMA Psychiatry 2016, 73, 993–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haapakoski, R.; Mathieu, J.; Ebmeier, K.P.; Alenius, H.; Kivimaki, M. Cumulative meta-analysis of interleukins 6 and 1beta, tumour necrosis factor alpha and c-reactive protein in patients with major depressive disorder. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 49, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howren, M.B.; Lamkin, D.M.; Suls, J. Associations of depression with c-reactive protein, il-1, and il-6: A meta-analysis. Psychosom. Med. 2009, 71, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, C.A.; Freitas, T.H.; Maes, M.; de Andrade, N.Q.; Liu, C.S.; Fernandes, B.S.; Stubbs, B.; Solmi, M.; Veronese, N.; Herrmann, N.; et al. Peripheral cytokine and chemokine alterations in depression: A meta-analysis of 82 studies. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2017, 135, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowlati, Y.; Herrmann, N.; Swardfager, W.; Liu, H.; Sham, L.; Reim, E.K.; Lanctot, K.L. A meta-analysis of cytokines in major depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, S.; Skoog, I.; Borjesson-Hanson, A.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Ostling, S.; Kern, J.; Gudmundsson, P.; Marlow, T.; Rosengren, L.; et al. Higher csf interleukin-6 and csf interleukin-8 in current depression in older women. Results from a population-based sample. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 41, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindqvist, D.; Janelidze, S.; Hagell, P.; Erhardt, S.; Samuelsson, M.; Minthon, L.; Hansson, O.; Bjorkqvist, M.; Traskman-Bendz, L.; Brundin, L. Interleukin-6 is elevated in the cerebrospinal fluid of suicide attempters and related to symptom severity. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valkanova, V.; Ebmeier, K.P.; Allan, C.L. Crp, il-6 and depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. J. Affect. Disord. 2013, 150, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelton, R.C.; Pencina, M.J.; Barrentine, L.W.; Ruiz, J.A.; Fava, M.; Zajecka, J.M.; Papakostas, G.I. Association of obesity and inflammatory marker levels on treatment outcome: Results from a double-blind, randomized study of adjunctive l-methylfolate calcium in patients with mdd who are inadequate responders to ssris. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2015, 76, 1635–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C. Th17 cells in development: An updated view of their molecular identity and genetic programming. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.; Fanslow, W.C.; Seldin, M.F.; Rousseau, A.M.; Painter, S.L.; Comeau, M.R.; Cohen, J.I.; Spriggs, M.K. Herpesvirus saimiri encodes a new cytokine, il-17, which binds to a novel cytokine receptor. Immunity 1995, 3, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, L.E.; Hatton, R.D.; Mangan, P.R.; Turner, H.; Murphy, T.L.; Murphy, K.M.; Weaver, C.T. Interleukin 17-producing cd4+ effector t cells develop via a lineage distinct from the t helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.O.; Chang, S.H.; Nurieva, R.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.; Hood, L.; Zhu, Z.; Tian, Q.; et al. A distinct lineage of cd4 t cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing interleukin 17. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Dong, C. Il-17 cytokines in immunity and inflammation. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2013, 2, e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beurel, E.; Harrington, L.E.; Jope, R.S. Inflammatory t helper 17 cells promote depression-like behavior in mice. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 73, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, T.; Chen, P.; Ouyang, J.; Xu, G.; Zeng, Z.; Sun, Y. Emerging tendency towards autoimmune process in major depressive patients: A novel insight from th17 cells. Psychiatry Res. 2011, 188, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohleb, E.S.; McKim, D.B.; Sheridan, J.F.; Godbout, J.P. Monocyte trafficking to the brain with stress and inflammation: A novel axis of immune-to-brain communication that influences mood and behavior. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leighton, S.P.; Nerurkar, L.; Krishnadas, R.; Johnman, C.; Graham, G.J.; Cavanagh, J. Chemokines in depression in health and in inflammatory illness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavich, G.M.; Irwin, M.R. From stress to inflammation and major depressive disorder: A social signal transduction theory of depression. Psychol. Bull. 2014, 140, 774–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K.; Derry, H.M.; Fagundes, C.P. Inflammation: Depression fans the flames and feasts on the heat. Am. J. Psychiatry 2015, 172, 1075–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberger, N.I.; Berkman, E.T.; Inagaki, T.K.; Rameson, L.T.; Mashal, N.M.; Irwin, M.R. Inflammation-induced anhedonia: Endotoxin reduces ventral striatum responses to reward. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 68, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remus, J.L.; Dantzer, R. Inflammation models of depression in rodents: Relevance to psychotropic drug discovery. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodes, G.E.; Pfau, M.L.; Leboeuf, M.; Golden, S.A.; Christoffel, D.J.; Bregman, D.; Rebusi, N.; Heshmati, M.; Aleyasin, H.; Warren, B.L.; et al. Individual differences in the peripheral immune system promote resilience versus susceptibility to social stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16136–16141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppert, J.; Closhen, D.; Croxford, A.; White, R.; Kulig, P.; Pietrowski, E.; Bechmann, I.; Becher, B.; Luhmann, H.J.; Waisman, A.; et al. Cellular mechanisms of il-17-induced blood-brain barrier disruption. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kebir, H.; Kreymborg, K.; Ifergan, I.; Dodelet-Devillers, A.; Cayrol, R.; Bernard, M.; Giuliani, F.; Arbour, N.; Becher, B.; Prat, A. Human th17 lymphocytes promote blood-brain barrier disruption and central nervous system inflammation. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1173–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawanokuchi, J.; Shimizu, K.; Nitta, A.; Yamada, K.; Mizuno, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Suzumura, A. Production and functions of il-17 in microglia. J. Neuroimmunol. 2008, 194, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarma, J.D.; Ciric, B.; Marek, R.; Sadhukhan, S.; Caruso, M.L.; Shafagh, J.; Fitzgerald, D.C.; Shindler, K.S.; Rostami, A. Functional interleukin-17 receptor a is expressed in central nervous system glia and upregulated in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2009, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.H.; Haroon, E.; Felger, J.C. Therapeutic implications of brain-immune interactions: Treatment in translation. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 334–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felger, J.C. The role of dopamine in inflammation-associated depression: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 31, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Felger, J.C.; Treadway, M.T. Inflammation effects on motivation and motor activity: Role of dopamine. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 216–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swardfager, W.; Rosenblat, J.D.; Benlamri, M.; McIntyre, R.S. Mapping inflammation onto mood: Inflammatory mediators of anhedonia. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 64, 148–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedlocha, M.; Marcinowicz, P.; Krupa, R.; Janoska-Jazdzik, M.; Janus, M.; Debowska, W.; Mosiolek, A.; Waszkiewicz, N.; Szulc, A. Effect of antidepressant treatment on peripheral inflammation markers—A meta-analysis. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 80, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, C.A.; Freitas, T.H.; Stubbs, B.; Maes, M.; Solmi, M.; Veronese, N.; de Andrade, N.Q.; Morris, G.; Fernandes, B.S.; Brunoni, A.R.; et al. Peripheral alterations in cytokine and chemokine levels after antidepressant drug treatment for major depressive disorder: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner-Schmidt, J.L.; Vanover, K.E.; Chen, E.Y.; Marshall, J.J.; Greengard, P. Antidepressant effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (ssris) are attenuated by antiinflammatory drugs in mice and humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 9262–9267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenoy, A.R.; Dehmel, T.; Stettner, M.; Kremer, D.; Kieseier, B.C.; Hartung, H.P.; Hofstetter, H.H. Citalopram suppresses thymocyte cytokine production. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 262, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiles, S.A.; Baker, A.L.; de Malmanche, T.; Attia, J. Interleukin-6, c-reactive protein and interleukin-10 after antidepressant treatment in people with depression: A meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2012, 42, 2015–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strawbridge, R.; Arnone, D.; Danese, A.; Papadopoulos, A.; Herane Vives, A.; Cleare, A.J. Inflammation and clinical response to treatment in depression: A meta-analysis. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 25, 1532–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannestad, J.; DellaGioia, N.; Bloch, M. The effect of antidepressant medication treatment on serum levels of inflammatory cytokines: A meta-analysis. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 2452–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadad, B.S.; Jha, M.K.; Grannemann, B.D.; Mayes, T.L.; Trivedi, M.H. Proteomics profiling reveals inflammatory biomarkers of antidepressant treatment response: Findings from the co-med trial. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2017, 94, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, M.; Rocchi, G.; Escelsior, A.; Fornaro, M. Immunomodulation mechanism of antidepressants: Interactions between serotonin/norepinephrine balance and th1/th2 balance. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2012, 10, 97–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brustolim, D.; Ribeiro-dos-Santos, R.; Kast, R.E.; Altschuler, E.L.; Soares, M.B. A new chapter opens in anti-inflammatory treatments: The antidepressant bupropion lowers production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 903–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebbinghaus, M.; Gajda, M.; Boettger, M.K.; Schaible, H.-G.; Bräuer, R. The anti-inflammatory effects of sympathectomy in murine antigen-induced arthritis are associated with a reduction of th1 and th17 responses. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawcett, J.; Rush, A.J.; Vukelich, J.; Diaz, S.H.; Dunklee, L.; Romo, P.; Yarns, B.C.; Escalona, R. Clinical experience with high-dosage pramipexole in patients with treatment-resistant depressive episodes in unipolar and bipolar depression. Am. J. Psychiatry 2016, 173, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieberknecht, V.; Junqueira, S.C.; Cunha, M.P.; Barbosa, T.A.; de Souza, L.F.; Coelho, I.S.; Santos, A.R.; Rodrigues, A.L.; Dafre, A.L.; Dutra, R.C. Pramipexole, a dopamine d2/d3 receptor-preferring agonist, prevents experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis development in mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 54, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, M.H.; Greer, T.L.; Church, T.S.; Carmody, T.J.; Grannemann, B.D.; Galper, D.I.; Dunn, A.L.; Earnest, C.P.; Sunderajan, P.; Henley, S.S.; et al. Exercise as an augmentation treatment for nonremitted major depressive disorder: A randomized, parallel dose comparison. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2011, 72, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rethorst, C.D.; Toups, M.S.; Greer, T.L.; Nakonezny, P.A.; Carmody, T.J.; Grannemann, B.D.; Huebinger, R.M.; Barber, R.C.; Trivedi, M.H. Pro-inflammatory cytokines as predictors of antidepressant effects of exercise in major depressive disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rethorst, C.D.; Greer, T.L.; Toups, M.S.; Bernstein, I.; Carmody, T.J.; Trivedi, M.H. Il-1beta and bdnf are associated with improvement in hypersomnia but not insomnia following exercise in major depressive disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uher, R.; Tansey, K.E.; Dew, T.; Maier, W.; Mors, O.; Hauser, J.; Dernovsek, M.Z.; Henigsberg, N.; Souery, D.; Farmer, A.; et al. An inflammatory biomarker as a differential predictor of outcome of depression treatment with escitalopram and nortriptyline. Am. J. Psychiatry 2014, 171, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, M.K.; Minhajuddin, A.; Gadad, B.S.; Greer, T.; Grannemann, B.; Soyombo, A.; Mayes, T.L.; Rush, A.J.; Trivedi, M.H. Can c-reactive protein inform antidepressant medication selection in depressed outpatients? Findings from the co-med trial. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 78, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennings, J.M.; Uhr, M.; Klengel, T.; Weber, P.; Putz, B.; Touma, C.; Czamara, D.; Ising, M.; Holsboer, F.; Lucae, S. Rna expression profiling in depressed patients suggests retinoid-related orphan receptor alpha as a biomarker for antidepressant response. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, M.K.; Minhajuddin, A.; Gadad, B.S.; Greer, T.L.; Mayes, T.L.; Trivedi, M.H. Interleukin 17 selectively predicts better outcomes with bupropion-ssri combination: Novel T cell biomarker for antidepressant medication selection. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 66, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, M.K.; Minhajuddin, A.; Gadad, B.S.; Trivedi, M.H. Platelet-derived growth factor as an antidepressant treatment selection biomarker: Higher levels selectively predict better outcomes with bupropion-ssri combination. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 20, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, K.S.; Lee, K.J.; Lee, J.S.; Cho, Y.S.; Jung, H.Y. Efficacy of adjunctive celecoxib treatment for patients with major depressive disorder: A meta-analysis. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 48, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raison, C.L.; Rutherford, R.E.; Woolwine, B.J.; Shuo, C.; Schettler, P.; Drake, D.F.; Haroon, E.; Miller, A.H. A randomized controlled trial of the tumor necrosis factor antagonist infliximab for treatment-resistant depression: The role of baseline inflammatory biomarkers. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, M.I.; Strawbridge, R.; Stokes, P.R.; Young, A.H. Anti-inflammatory treatments for mood disorders: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Psychopharmacol. 2017, 31, 1137–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappelmann, N.; Lewis, G.; Dantzer, R.; Jones, P.B.; Khandaker, G.M. Antidepressant activity of anti-cytokine treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials of chronic inflammatory conditions. Mol. Psychiatry 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gossec, L.; Steinberg, G.; Rouanet, S.; Combe, B. Fatigue in rheumatoid arthritis: Quantitative findings on the efficacy of tocilizumab and on factors associated with fatigue. The french multicentre prospective peps study. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Papp, K.A.; Reich, K.; Paul, C.; Blauvelt, A.; Baran, W.; Bolduc, C.; Toth, D.; Langley, R.G.; Cather, J.; Gottlieb, A.B.; et al. A prospective phase iii, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of brodalumab in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 175, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, C.E.M.; Fava, M.; Miller, A.H.; Russell, J.; Ball, S.G.; Xu, W.; Acharya, N.; Rapaport, M.H. Impact of ixekizumab treatment on depressive symptoms and systemic inflammation in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis: An integrated analysis of three phase 3 clinical studies. Psychother. Psychosom. 2017, 86, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, C. Suicidal thoughts end amgen’s blockbuster aspirations for psoriasis drug. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 894–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danesh, M.J.; Kimball, A.B. Brodalumab and suicidal ideation in the context of a recent economic crisis in the united states. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 74, 190–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahnik, B.; Beroukhim, K.; Abrouk, M.; Nakamura, M.; Zhu, T.H.; Singh, R.; Lee, K.; Bhutani, T.; Koo, J. Brodalumab for the treatment of psoriasis: A review of phase iii trials. Dermatol. Ther. 2016, 6, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.H.; Trivedi, M.H.; Jha, M.K. Is C-reactive protein ready for prime time in the selection of antidepressant medications? Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 84, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danesh, J.; Wheeler, J.G.; Hirschfield, G.M.; Eda, S.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Rumley, A.; Lowe, G.D.; Pepys, M.B.; Gudnason, V. C-reactive protein and other circulating markers of inflammation in the prediction of coronary heart disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emberson, J.R.; Whincup, P.H.; Morris, R.W.; Walker, M.; Lowe, G.D.; Rumley, A. Extent of regression dilution for established and novel coronary risk factors: Results from the british regional heart study. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Prev. Rehabil 2004, 11, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, R.; Wu, T.; Wei, X.; Guo, A. Association between point-of-care crp testing and antibiotic prescribing in respiratory tract infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis of primary care studies. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2013, 63, e787–e794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, N.T.T.; Ta, N.T.D.; Tran, N.T.H.; Than, H.M.; Vu, B.T.N.; Hoang, L.B.; van Doorn, H.R.; Vu, D.T.V.; Cals, J.W.L.; Chandna, A.; et al. Point-of-care c-reactive protein testing to reduce inappropriate use of antibiotics for non-severe acute respiratory infections in vietnamese primary health care: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Glob. Health 2016, 4, e633–e641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jha, M.K.; Trivedi, M.H. Personalized Antidepressant Selection and Pathway to Novel Treatments: Clinical Utility of Targeting Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010233
Jha MK, Trivedi MH. Personalized Antidepressant Selection and Pathway to Novel Treatments: Clinical Utility of Targeting Inflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(1):233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010233
Chicago/Turabian StyleJha, Manish K., and Madhukar H. Trivedi. 2018. "Personalized Antidepressant Selection and Pathway to Novel Treatments: Clinical Utility of Targeting Inflammation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 1: 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010233
APA StyleJha, M. K., & Trivedi, M. H. (2018). Personalized Antidepressant Selection and Pathway to Novel Treatments: Clinical Utility of Targeting Inflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(1), 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010233



