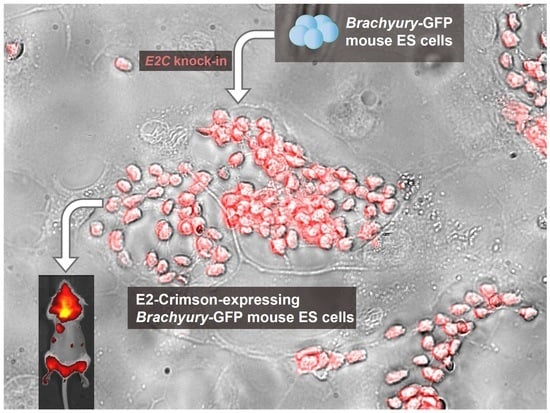
Assessing the Effectiveness of a Far-Red Fluorescent Reporter for Tracking Stem Cells In Vivo
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
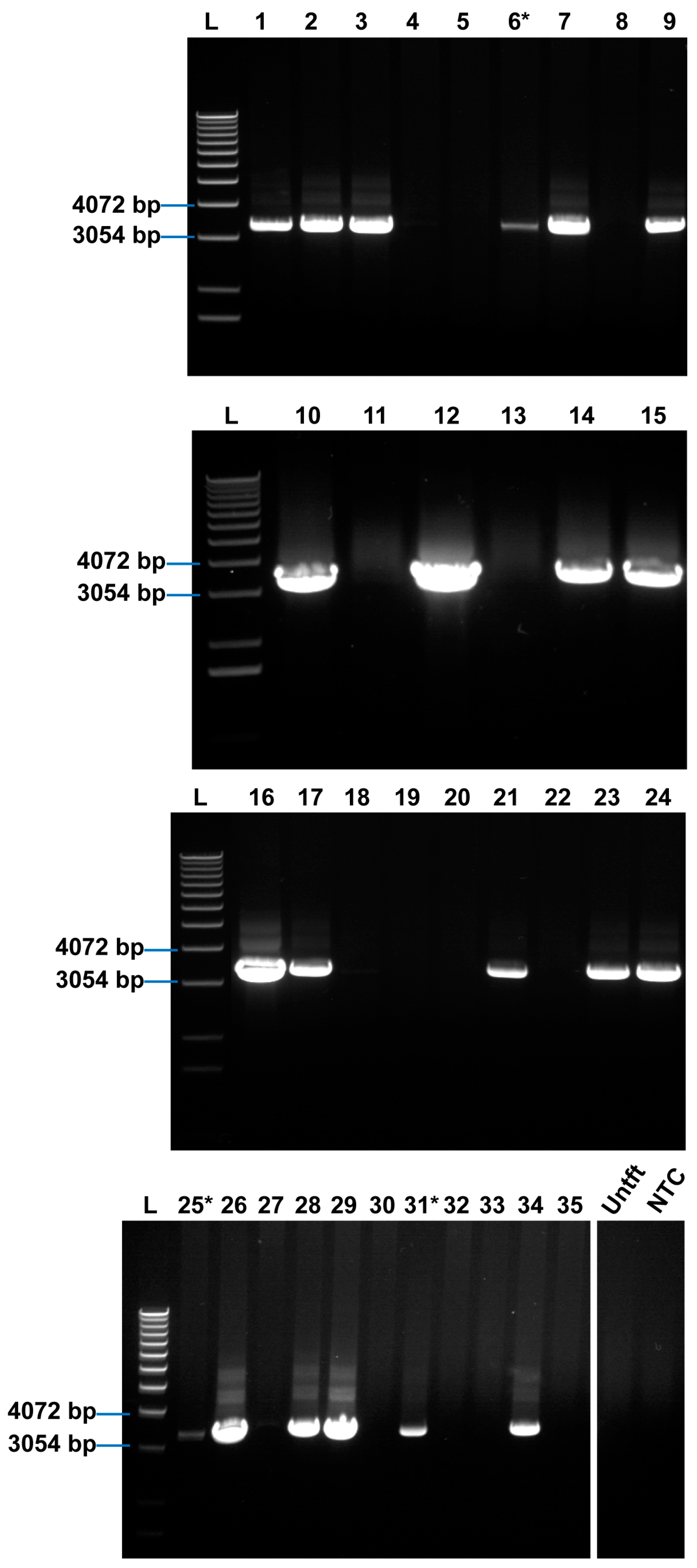
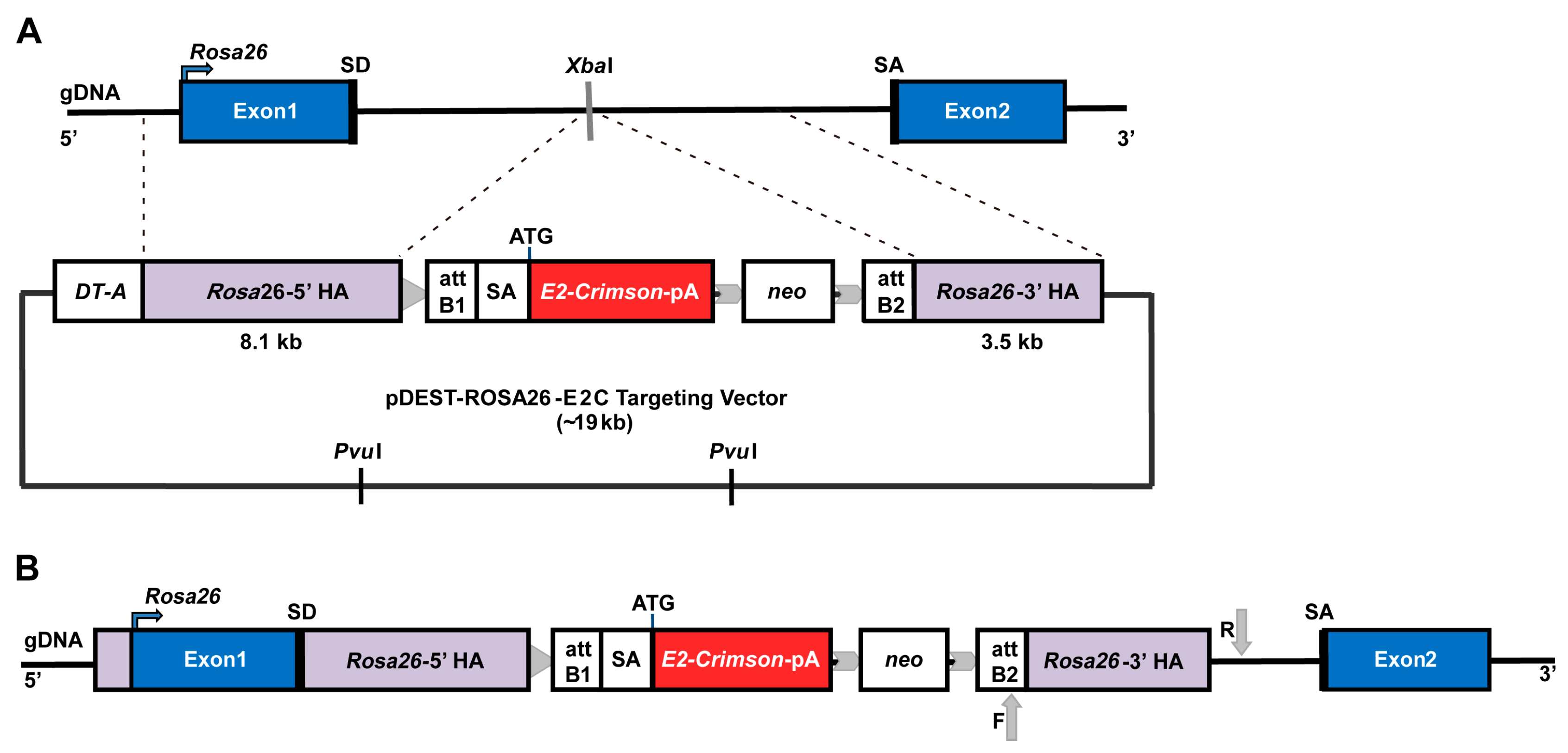
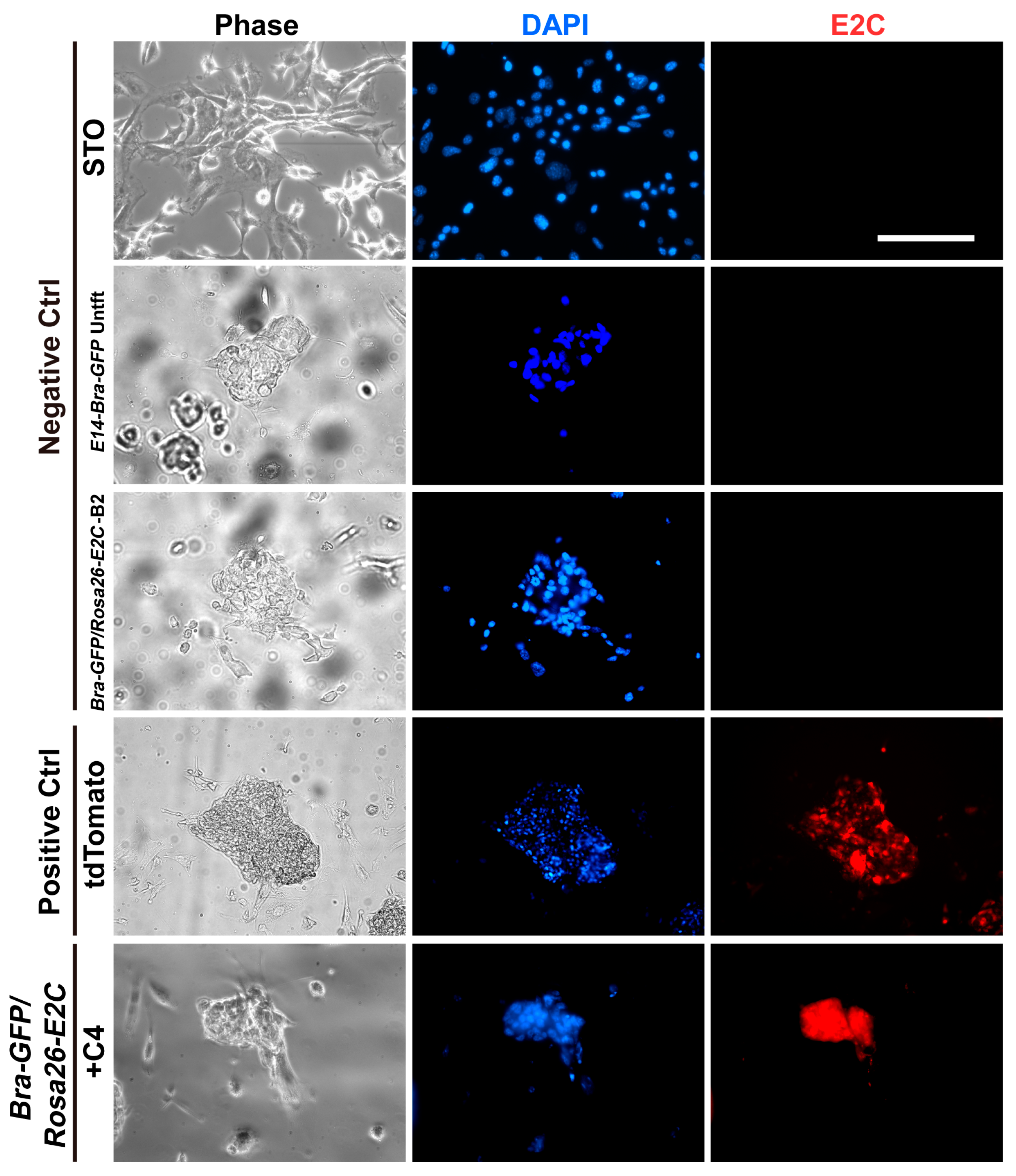
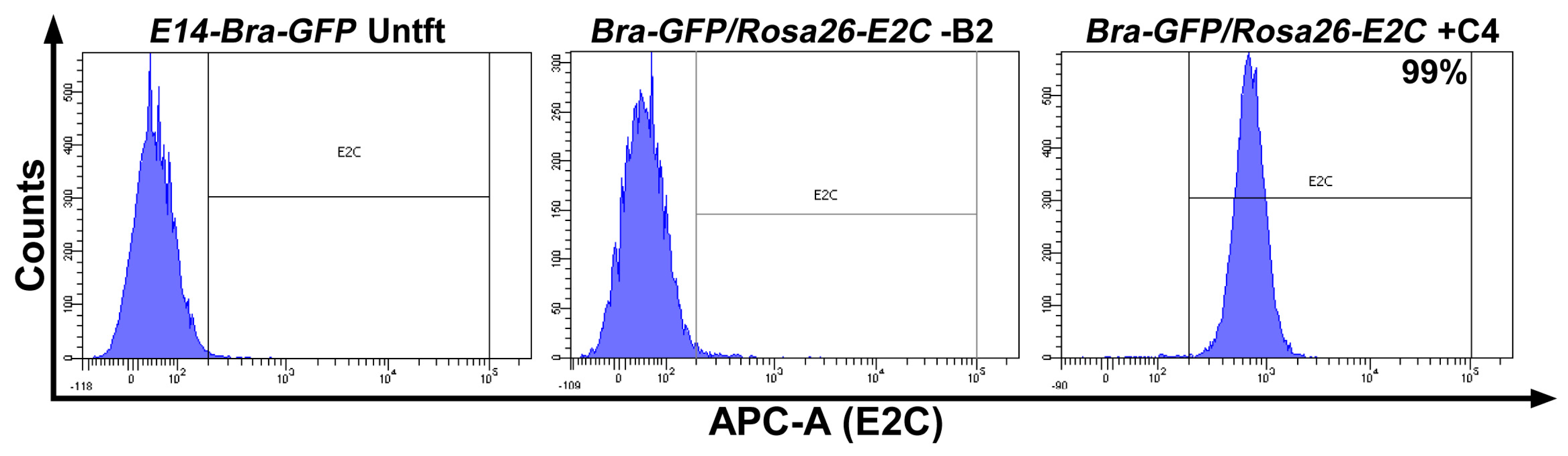
2.1. Rosa26 Knock-in of E2-Crimson Transgene and Analysis of E2C Expression in Screened Positive Clones
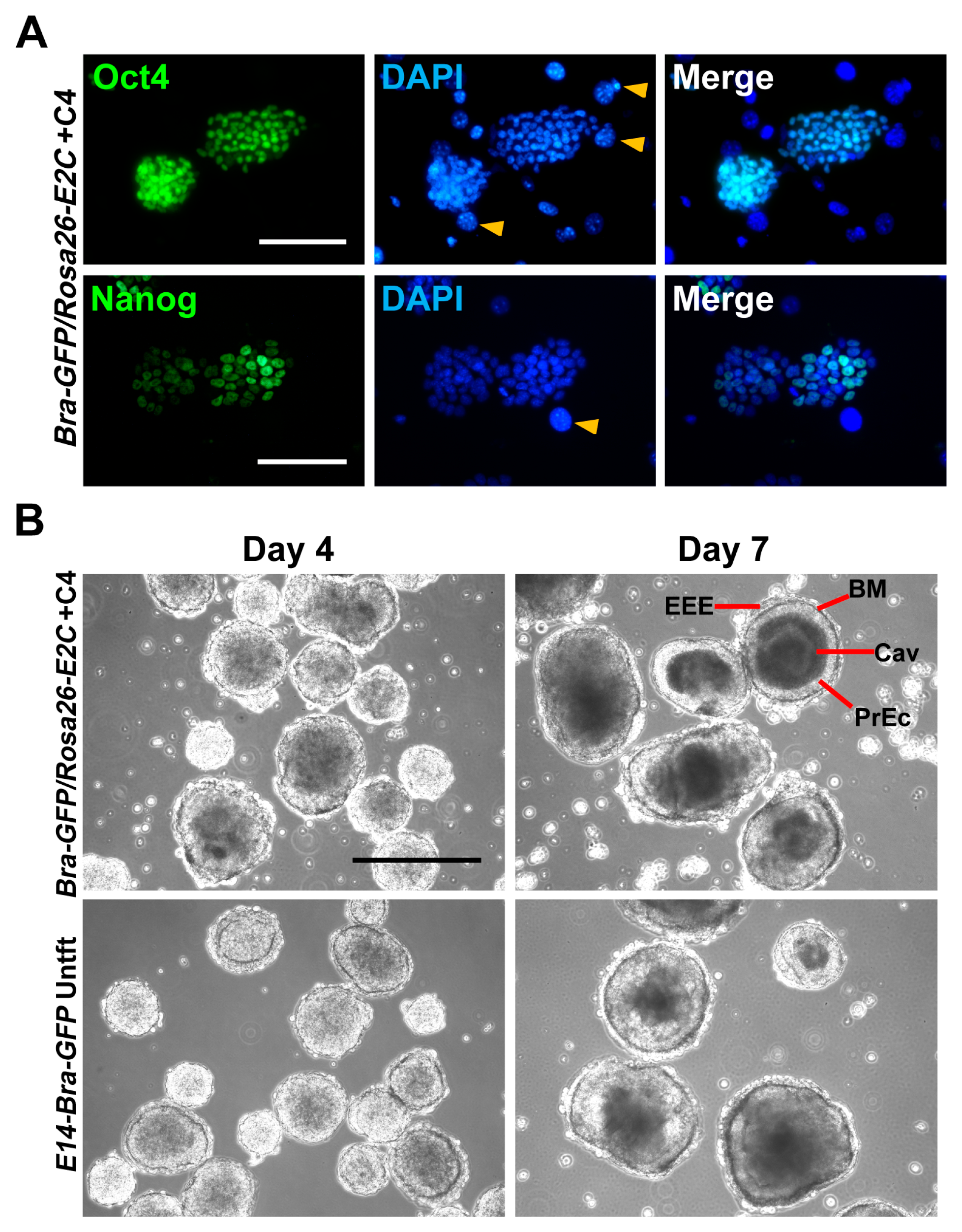
2.2. Stemness and Differentiation Potential of Bra-GFP/Rosa26-E2C mESC Reporter Line
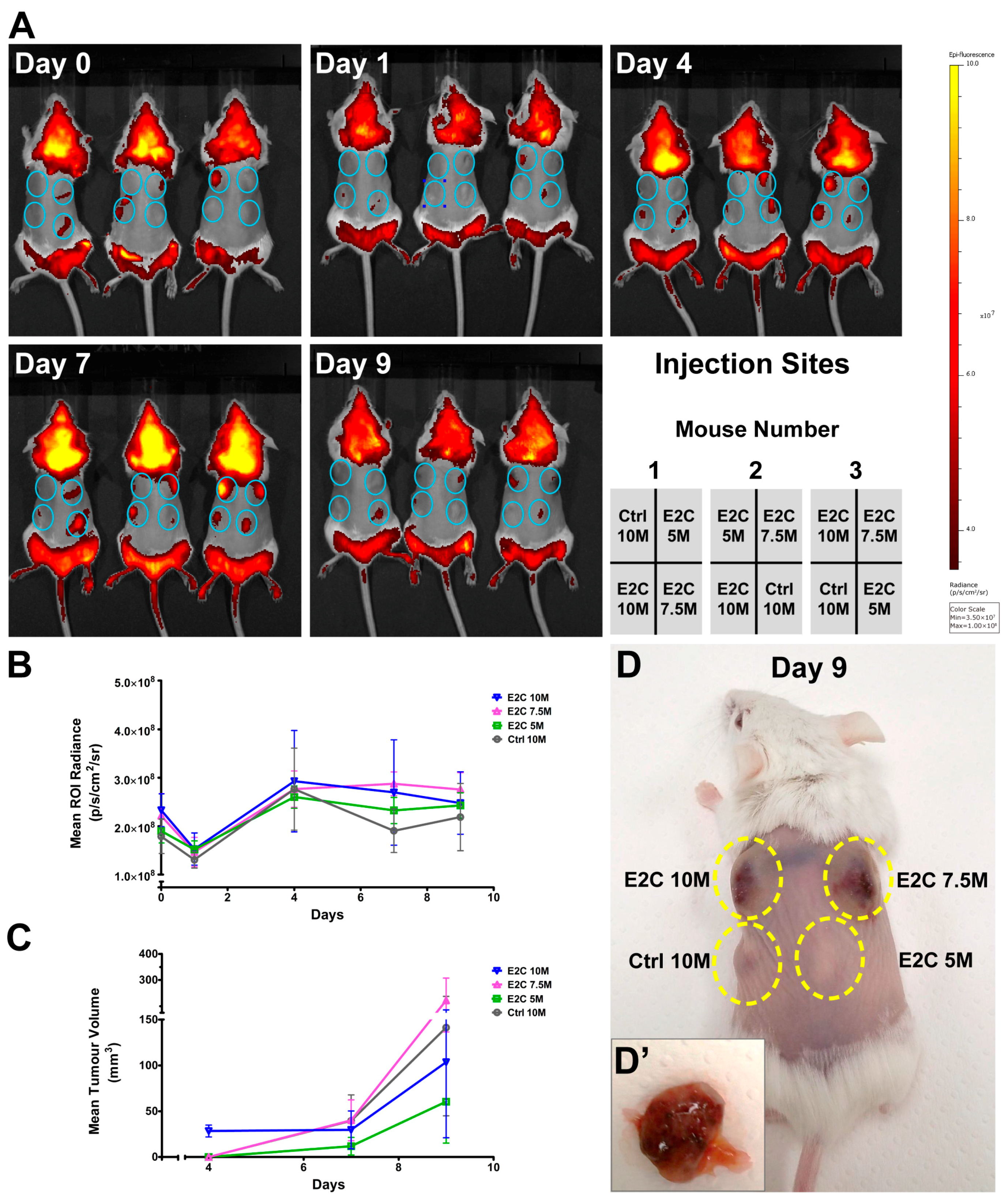
2.3. Quantitative Analysis of E2C Fluorescence Signal In Vivo
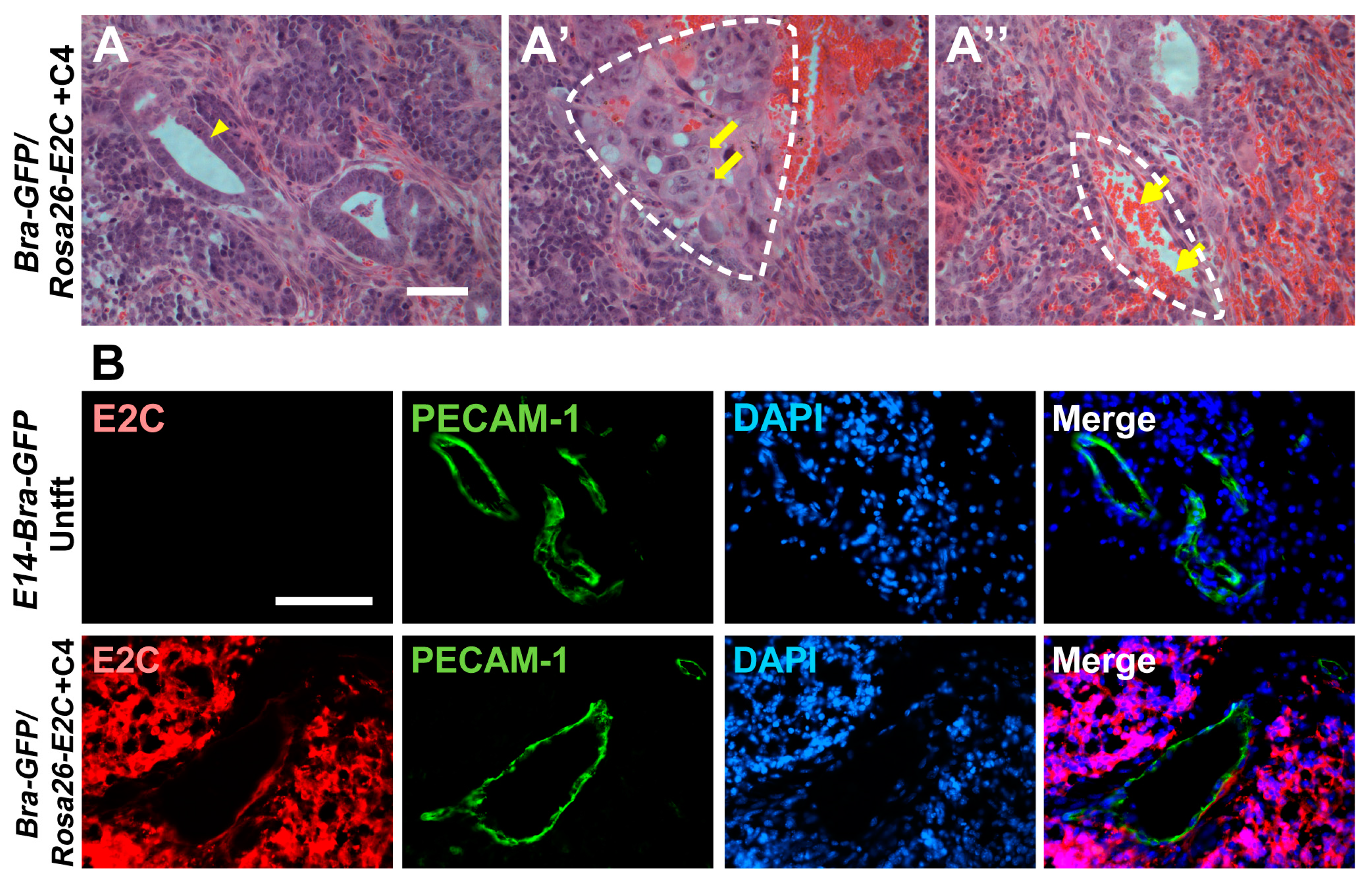
2.4. Histopathology and Immunofluorescence Analyses of Tumours
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sub-Culture of STO and mESCs
4.2. Preparation of Mitomycin-C-Inactivated STO Feeder Cells
4.3. Preparation and Linearisation of Knock-in Construct
4.4. Generation of the Knock-in mESC Reporter Line
4.5. Genomic DNA Extraction of mESCs
4.6. 3′-Homology Arm PCR Analysis
4.7. Analysis of E2C Expression in the PCR Screened Positive Clones with Fluorescence Microscopy
4.8. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.9. Embryoid Body Formation
4.10. Administration and Imaging of Bra-GFP/Rosa26-E2C
4.11. Tumour Volume Measurement
4.12. Tumour Fixation
4.13. Tumour Histopathological Analysis
4.14. Immunofluorescence Staining of Stemness Markers
4.15. Immunofluorescence Staining of Frozen Tumour Sections
4.16. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| DT-A | Diphtheria toxin A |
| E2C | E2-crimson |
| EB | Embryoid body |
| FBS | Foetal bovine serum |
| HA | Homology arm |
| H&E | Haematoxylin and eosin |
| mESC | Mouse embryonic stem cell |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PECAM-1 | Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| ROSA | Reverse orientation splice acceptor |
| SCID | Severe combined immunodeficient |
Appendix A
References
- Weissleder, R. A clearer vision for in vivo imaging. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 316–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.V.; Wu, H.I. Biomedical Optics: Principles and Imaging, 1st ed.; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 1–15. ISBN 9780470177013. [Google Scholar]
- Shcherbo, D.; Merzlyak, E.M.; Chepurnykh, T.V.; Fradkov, A.F.; Ermakova, G.V.; Solovieva, E.A.; Lukyanov, K.A.; Bogdanova, E.A.; Zaraisky, A.G.; Lukyanov, S.; et al. Bright far-red fluorescent protein for whole-body imaging. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strack, R.L.; Hein, B.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Hell, S.W.; Keenan, R.J.; Glick, B.S. A Rapidly maturing far-red derivative of DsRed-Express2 for whole-cell labeling. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 8279–8281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, E.J. Teratocarcinomas and Embryonic Stem Cells: A Practical Approach, 1st ed.; IRL Press: Oxford, UK, 1987; ISBN 9781852210045. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, P.; Edgar, D. The topographical regulation of embryonic stem cell differentiation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2004, 359, 1009–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, J.; Smith, A. Pluripotency in the embryo and in culture. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a008128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, E.; Bradley, A.; Kuehn, M.; Evans, M. Germ-line transmission of genes introduced into cultured pluripotential cells by retroviral vector. Nature 1986, 323, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherry, S.R.; Biniszkiewicz, D.; van Parijs, L.; Baltimore, D.; Jaenisch, R. Retroviral expression in embryonic stem cells and hematopoietic stem cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 7419–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, T.; Hanazono, Y.; Ueda, Y.; Muramatsu, S.; Kume, A.; Suemori, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Kondo, Y.; Harii, K.; Hasegawa, M.; et al. Highly efficient gene transfer into primate embryonic stem cells with a simian lentivirus vector. Mol. Ther. 2002, 6, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeifer, A.; Ikawa, M.; Dayn, Y.; Verma, I.M. Transgenesis by lentiviral vectors: Lack of gene silencing in mammalian embryonic stem cells and preimplantation embryos. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2140–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith-Arica, J.R.; Thomson, A.J.; Ansell, R.; Chiorini, J.; Davidson, B.; McWhir, J. Infection efficiency of human and mouse embryonic stem cells using adenoviral and adeno-associated viral vectors. Cloning Stem Cells 2003, 5, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmipathy, U.; Pelacho, B.; Sudo, K.; Linehan, J.L.; Coucouvanis, E.; Kaufman, D.S.; Verfaillie, C.M. Efficient transfection of embryonic and adult stem cells. Stem Cells 2014, 22, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohbayashi, F.; Balamotis, M.A.; Kishimoto, A.; Aizawa, E.; Diaz, A.; Hasty, P.; Graham, F.L.; Caskey, C.T.; Mitani, K. Correction of chromosomal mutation and random integration in embryonic stem cells with helper-dependent adenoviral vectors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13628–13633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepperhof, V.; Polchynski, O.; Kruttwig, K.; Brüggemann, C.; Neef, K.; Drey, F.; Zheng, Y.; Ackermann, J.; Choi, Y.; Wunderlich, T.; et al. Bioluminescent imaging of genetically selected induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes after transplantation into infarcted heart of syngeneic recipients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamaguchi, I.; Woods, N.B.; Panagopoulos, I.; Andersson, E.; Mikkola, H.; Fahlman, C.; Zufferey, R.; Carlsson, L.; Trono, D.; Karlsson, S. Lentivirus Vector gene expression during ES cell-derived hematopoietic development in vitro. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 10778–10784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lois, C.; Hong, E.; Pease, S.; Brown, E.; Baltimore, D. Germline transmission and tissue-specific expression of transgenes delivered by lentiviral vectors. Science 2002, 295, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, B.L.; Hirsch, M.L.; Barker, J.C.; Connelly, J.P.; Steininger, R.J., III; Porteus, M.H. A survey of ex vivo/in vitro transduction efficiency of mammalian primary cells and cell lines with nine natural adeno-associated virus (AAV1-9) and one engineered adeno-associated virus serotype. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jähner, D.; Jaenisch, R. Retrovirus-induced de novo methylation of flanking host sequences correlates with gene inactivity. Nature 1985, 315, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaenisch, R.; Schnieke, A.; Harbers, K. Treatment of mice with 5-azacytidine efficiently activates silent retroviral genomes in different tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoder, J.A.; Walsh, C.P.; Bestor, T.H. Cytosine methylation and the ecology of intragenomic parasites. Trends Genet. 1997, 13, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laker, C.; Meyer, J.; Schopen, A.; Friel, J.; Heberlein, C.; Ostertag, W.; Stocking, C. Host cis-mediated extinction of a retrovirus permissive for expression in embryonal stem cells during differentiation. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Capecchi, M.R. The new mouse genetics: Altering the genome by gene targeting. Trends Genet. 1989, 5, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.J.; van der Weyden, L. Contemporary approaches for modifying the mouse genome. Physiol. Genom. 2008, 34, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambrowicz, B.P.; Imamoto, A.; Fiering, S.; Herzenberg, L.A.; Kerr, W.G.; Soriano, P. Disruption of overlapping transcripts in the ROSA β-geo 26 gene trap strain leads to widespread expression of β-galactosidase in mouse embryos and hematopoietic cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 3789–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefano, C. Mouse models for miRNA expression: The ROSA26 locus. In MicroRNAs and the Immune System: Methods and Protocols, 1st ed.; Monticelli, S., Ed.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 145–150. ISBN 9781607618119. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich, G.; Soriano, P. Promoter traps in embryonic stem cells: A genetic screen to identify and mutate developmental genes in mice. Genes Dev. 1991, 5, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano, P. Generalized lacZ expression with the ROSA26 Cre reporter strain. Nat. Genet. 1999, 21, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohenstein, P.; Slight, J.; Ozdemir, D.D.; Burn, S.F.; Berry, R.; Hastie, N.D. High-efficiency Rosa26 knock-in vector construction for Cre-regulated overexpression and RNAi. Pathogenetics 2008, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, T.; Kiyonari, H.; Shioi, G.; Inoue, K.; Nakao, K.; Aizawa, S.; Fujimori, T. Establishment of conditional reporter mouse lines at ROSA26 locus for live cell imaging. Genesis 2011, 49, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, D.G.; Bhatt, S.; Herrmann, B.G. Expression pattern of the mouse T gene and its role in mesoderm formation. Nature 1990, 343, 657–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, B.G.; Kispert, A. The T genes in embryogenesis. Trends Genet. 1994, 10, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlon, F.L.; Wright, C.V.; Robertson, E.J. Effects of the TWis mutation on notochord formation and mesodermal patterning. Mech. Dev. 1995, 49, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kispert, A.; Koschorz, B.; Herrmann, B.G. The T protein encoded by Brachyury is a tissue-specific transcription factor. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 4763–4772. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- King, T.; Beddington, R.S.P.; Brown, N.A. The role of the brachyury gene in heart development and left–right specification in the mouse. Mech. Dev. 1998, 79, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Showell, C.; Binder, O.; Conlon, F.L. T-box genes in early embryogenesis. Dev. Dyn. 2003, 229, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concepcion, D.; Papaioannou, V.E. Nature and extent of left/right axis defects in TWis/TWis mutant mouse embryos. Dev. Dyn. 2014, 243, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaioannou, V.E. The T-box gene family: Emerging roles in development stem cells and cancer. Development 2014, 141, 3819–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehling, H.J.; Lacaud, G.; Kubo, A.; Kennedy, M.; Robertson, S.; Keller, G.; Kouskoff, V. Tracking mesoderm induction and its specification to the hemangioblast during embryonic stem cell differentiation. Development 2003, 130, 4217–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Nieves, J.L.; Fraser, S.T.; Isern, J.; Douvaras, P.; Papatsenko, D.; D’Souza, S.L.; Lemischka, I.R.; Dyer, M.A.; Baron, M.H. Expression of podocalyxin separates the hematopoietic and vascular potentials of mouse ES cell-derived mesoderm. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Org, T.; Duan, D.; Ferrari, R.; Montel-Hagen, A.; Van Handel, B.; Kerényi, M.A.; Sasidharan, R.; Rubbi, L.; Fujiwara, Y.; Pellegrini, M.; et al. Scl binds to primed enhancers in mesoderm to regulate hematopoietic and cardiac fate divergence. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 759–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsakiridis, A.; Wilson, V. Assessing the bipotency of in vitro-derived neuromesodermal progenitors. F1000Research 2015, 4, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, J.; Vonwil, D.; Shastri, V.P. Non-invasive in vivo imaging and quantification of tumor growth and metastasis in rats using cells expressing far-red fluorescence protein. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Liang, J.; Jiang, H.; Qin, L.J.; Yang, H.T. Promoter-dependent EGFP expression during embryonic stem cell propagation and differentiation. Stem Cells Dev. 2008, 17, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bancroft, G.J.; Sheehan, K.C.F.; Schreiber, R.D.; Unanue, E.R. Tumor necrosis factor is involved in the T cell-independent pathway of macrophage activation in scid mice. J. Immunol. 1989, 143, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leblond, F.; Davis, S.C.; Valdés, P.A.; Pogue, B.W. Pre-clinical whole-body fluorescence imaging: Review of instruments, methods and applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2010, 98, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetherell, D.; Weerakoon, M.; Williams, D.; Beharry, B.K.; Sliwinski, A.; Ow, D.; Manya, K.; Bolton, D.M.; Lawrentschuk, N. Mature and immature teratoma: A review of pathological characteristics and treatment options. Med. Surg. Urol. 2014, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, A.M.; Rezvani, M.; Elsayes, K.M.; Baskin, H.; Mourad, A.; Foster, B.R.; Jarboe, E.A.; Menias, C.O. Ovarian malignant germ cell tumors: Cellular classification and clinical and imaging features. Radiographics 2014, 34, 777–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaBonne, C.; Bronner-Fraser, M. Molecular mechanisms of neural crest formation. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1999, 15, 81–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, L. The development of transplantable teratocarcinomas from intratesticular grafts of pre- and postimplantation mouse embryos. Dev. Biol. 1970, 21, 364–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dethlefsen, L.A.; Prewitt, J.M.S.; Mendelsohn, M.L. Analysis of tumor growth curves. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1968, 40, 389–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomayko, M.M.; Reynolds, C.P. Determination of subcutaneous tumor size in athymic (nude) mice. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1989, 24, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitson, T.D.; Wigg, B.; Becker, G.J. Tissue preparation for histochemistry: Fixation, embedding, and antigen retrieval for light microscopy. In Histology Protocols, 1st ed.; Hewitson, T.D., Darby, I.A., Eds.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 3–18. ISBN 9781603273459. [Google Scholar]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Sharkey, J.; Shukla, R.; Plagge, A.; Murray, P. Assessing the Effectiveness of a Far-Red Fluorescent Reporter for Tracking Stem Cells In Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010019
Zhou J, Sharkey J, Shukla R, Plagge A, Murray P. Assessing the Effectiveness of a Far-Red Fluorescent Reporter for Tracking Stem Cells In Vivo. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jing, Jack Sharkey, Rajeev Shukla, Antonius Plagge, and Patricia Murray. 2018. "Assessing the Effectiveness of a Far-Red Fluorescent Reporter for Tracking Stem Cells In Vivo" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010019
APA StyleZhou, J., Sharkey, J., Shukla, R., Plagge, A., & Murray, P. (2018). Assessing the Effectiveness of a Far-Red Fluorescent Reporter for Tracking Stem Cells In Vivo. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010019