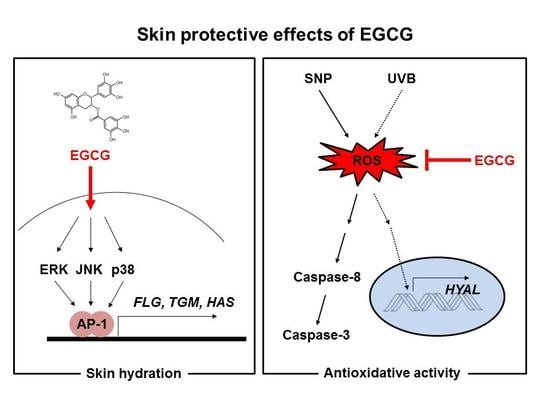
Skin Protective Effect of Epigallocatechin Gallate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
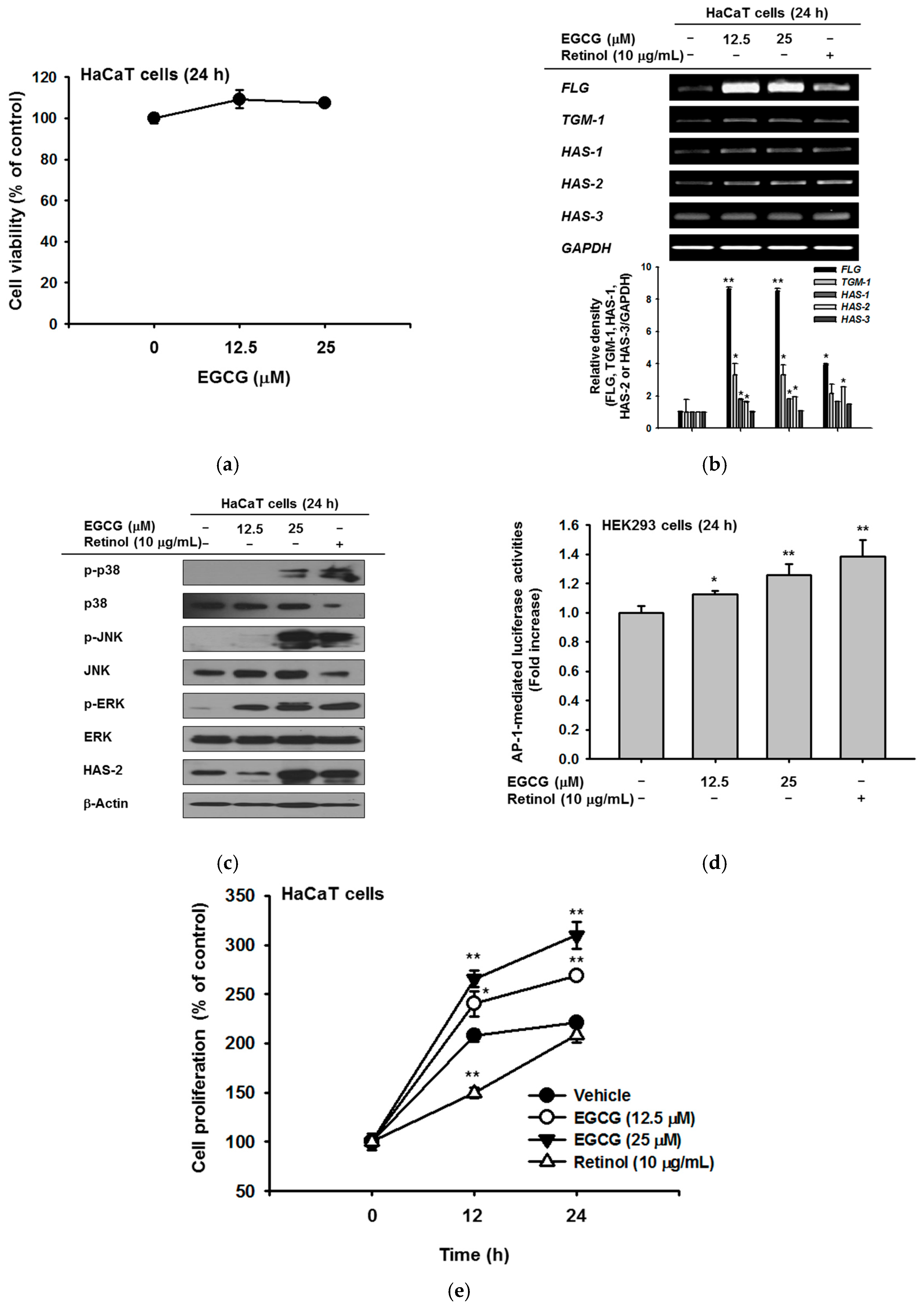
2.1. Effect of EGCG on NMF Synthesis Activity
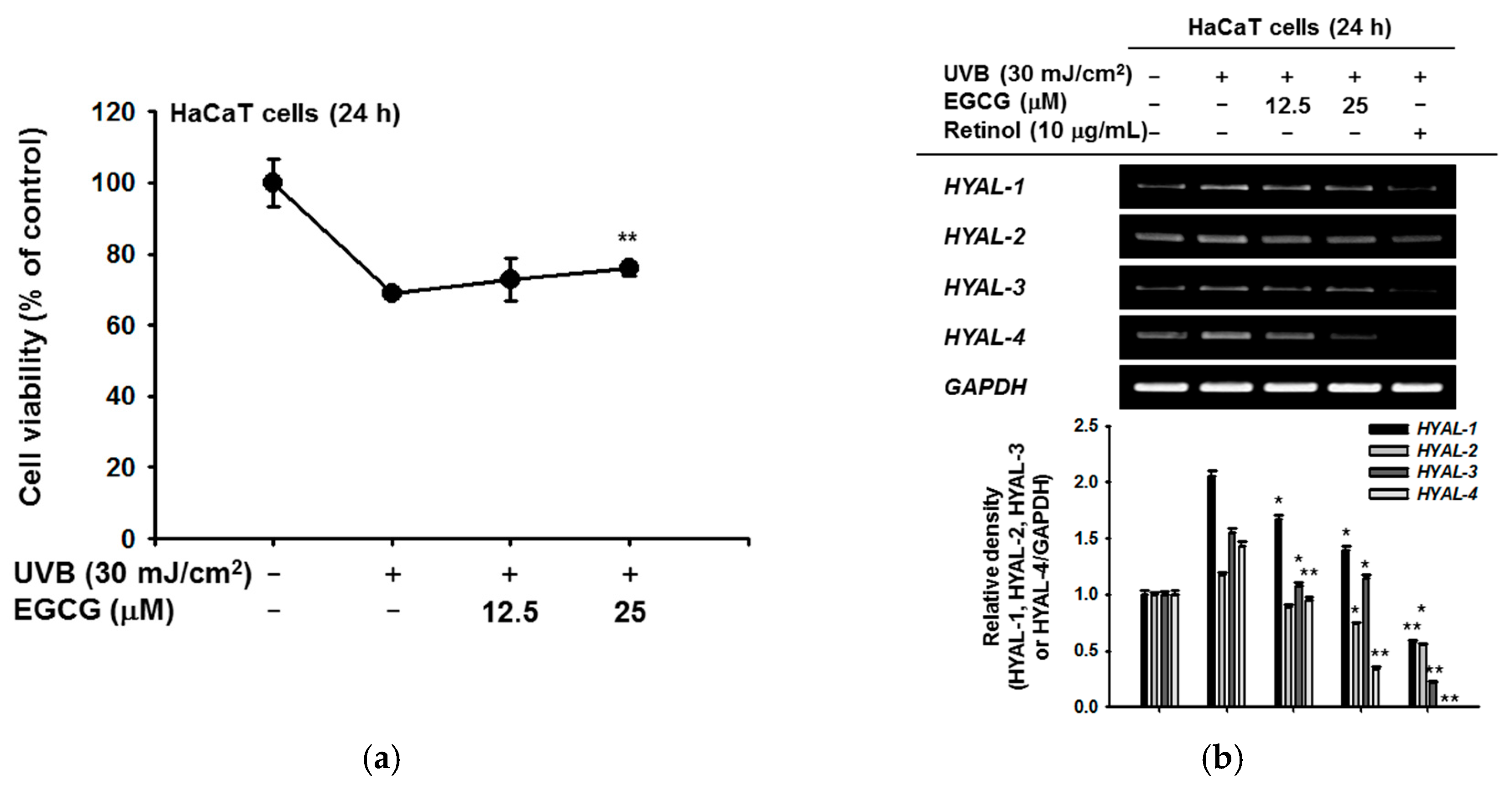
2.2. Effect of EGCG on Skin Moisture Retention Activity
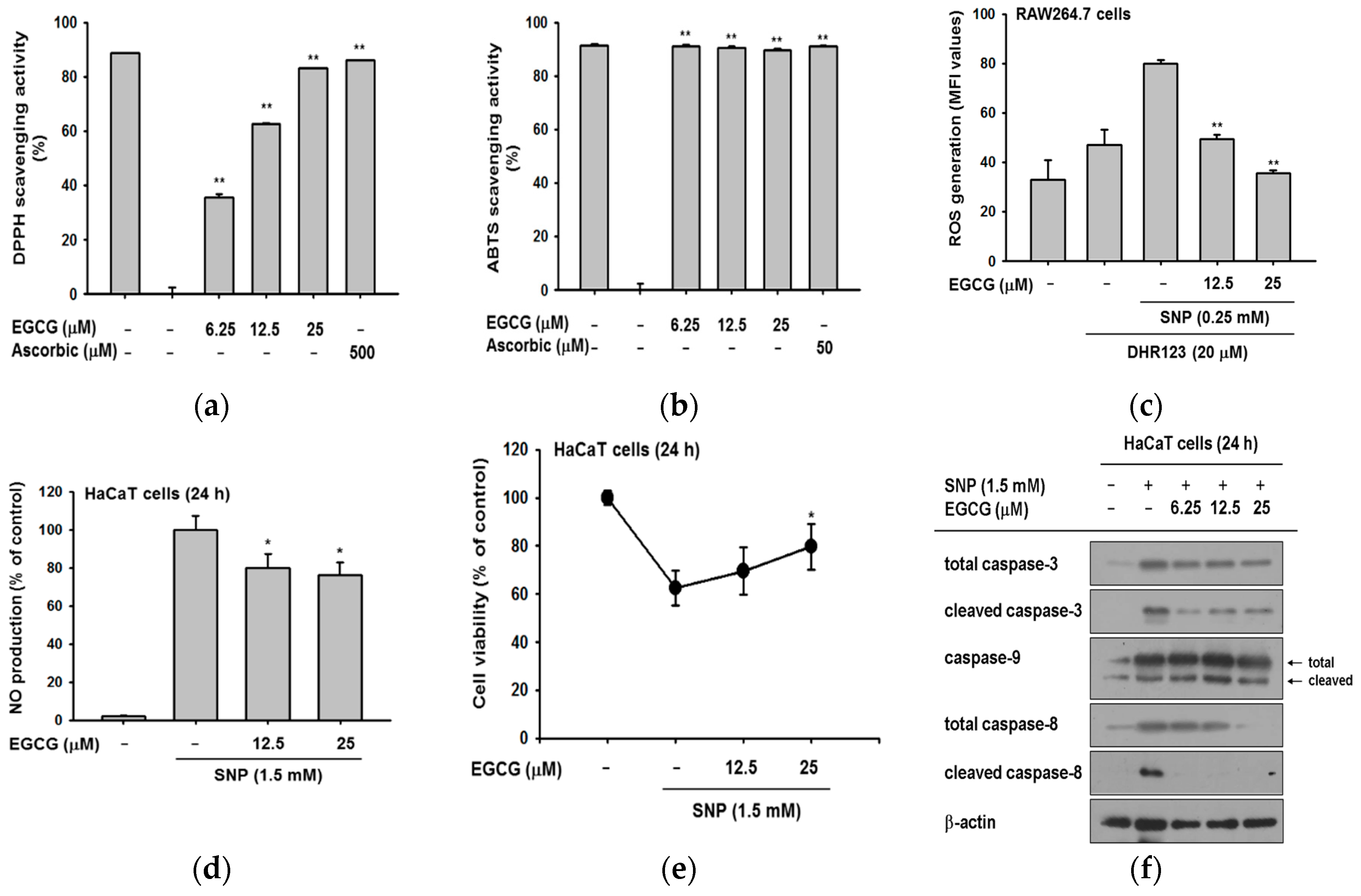
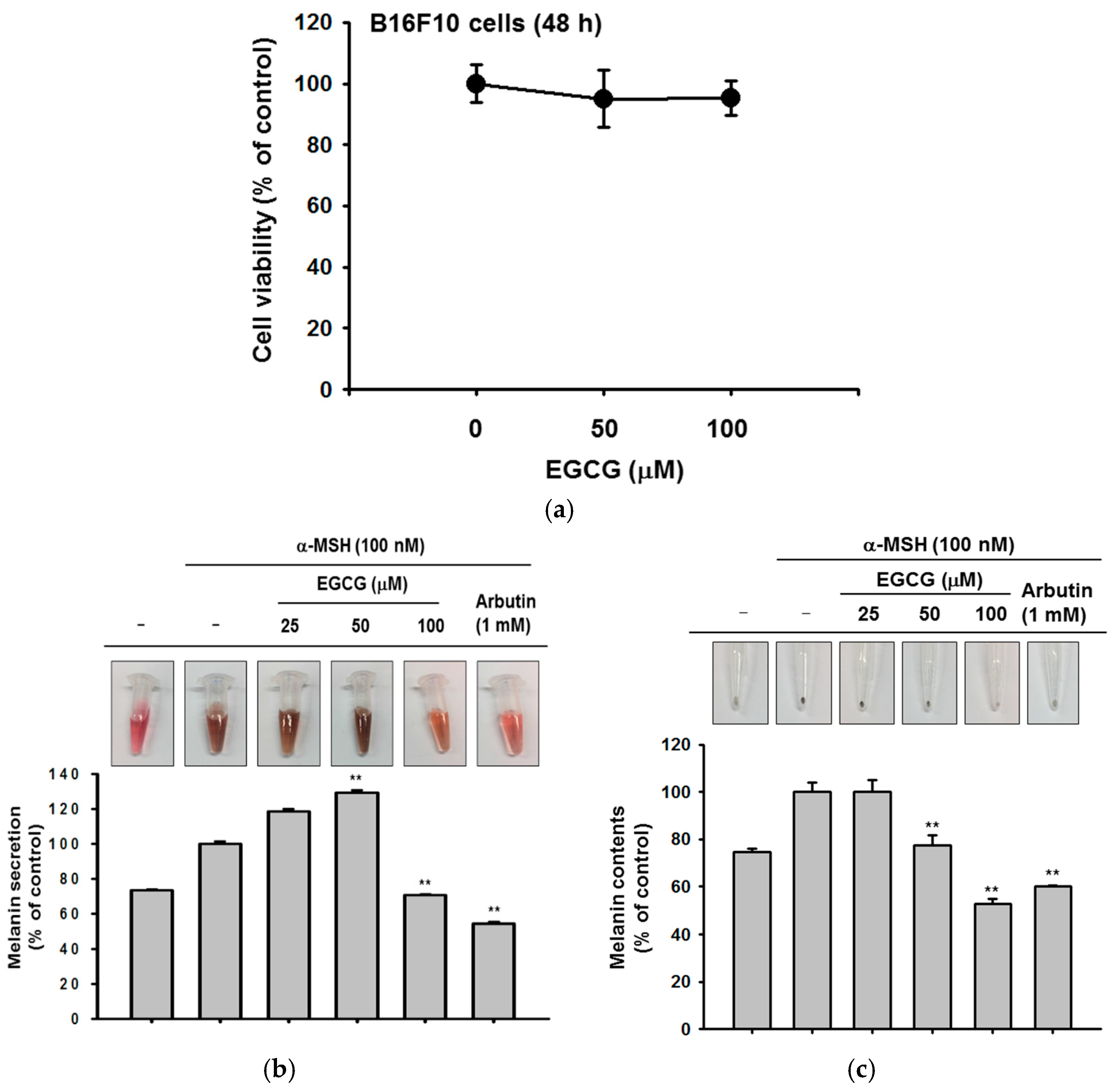
2.3. Antioxidant and Anti-Apoptotic Effect of EGCG
2.4. Antioxidant and Anti-Apoptotic Effect of EGCG
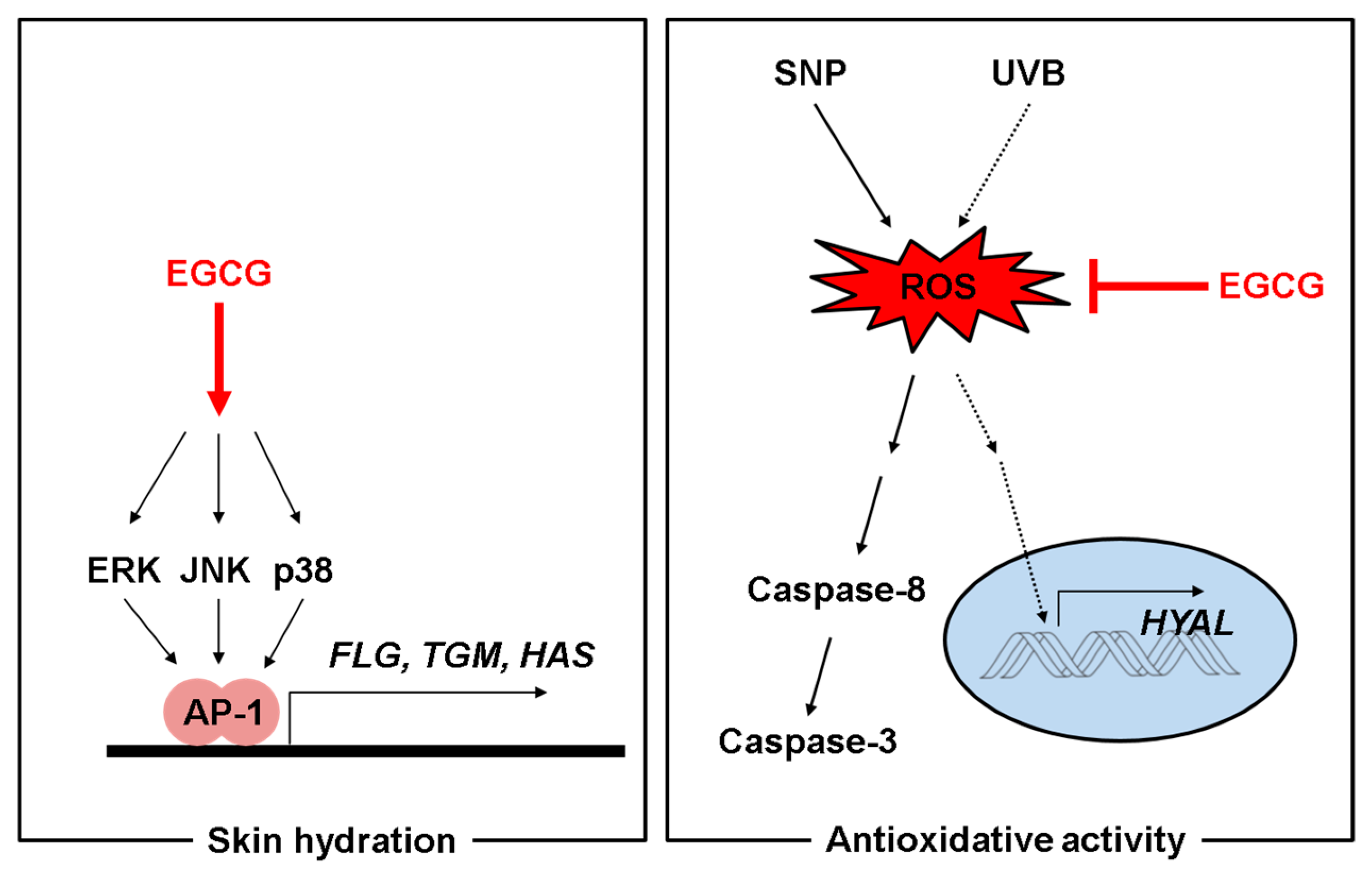
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Viability and Cell Proliferation Assay
4.4. RT-PCR Analysis
4.5. DPPH Assay
4.6. ABTS Assay
4.7. ROS Generation Assay
4.8. Preparation of Cell Lysates and Immunoblotting Analysis
4.9. Luciferase Reporter Gene Assay
4.10. UVB Irradiation
4.11. Measurement of Melanin Secretion and Contents
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jenkins, G. Molecular mechanisms of skin ageing. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2002, 123, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantinou, E.; Roth, M.; Karakiulakis, G. Hyaluronic acid: A key molecule in skin aging. Dermato-Endocrinology 2012, 4, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, J. Understanding the role of natural moisturizing factor in skin hydration. Pract. Dermatol. 2012, 1, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Tammi, R.; Ripellino, J.A.; Margolis, R.U.; Maibach, H.I.; Tammi, M. Hyaluronate accumulation in human epidermis treated with retinoic acid in skin organ culture. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1989, 92, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawlings, A.V.; Harding, C.R. Moisturization and skin barrier function. Dermatol. Ther. 2004, 17, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthusamy, V.; Piva, T.J. The UV response of the skin: A review of the MAPK, NFκB and TNFα signal transduction pathways. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2010, 302, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurdykowski, S.; Mine, S.; Bardey, V.; Danoux, L.; Jeanmaire, C.; Pauly, G.; Brabencova, E.; Wegrowski, Y.; Maquart, F.X. Ultraviolet-B Irradiation Induces Differential Regulations of Hyaluronidase Expression and Activity in Normal Human Keratinocytes. Photochem. Photobiol. 2011, 87, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganceviciene, R.; Liakou, A.I.; Theodoridis, A.; Makrantonaki, E.; Zouboulis, C.C. Skin anti-aging strategies. Dermato-Endocrinology 2012, 4, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birben, E.; Sahiner, U.M.; Sackesen, C.; Erzurum, S.; Kalayci, O. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. World Allergy Organ. J. 2012, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisel, S.H. Antioxidants suppress apoptosis. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 3179S–3180S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Warner, H.R. Apoptosis: A Two-edged Sword in Aging. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 887, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higami, Y.; Shimokawa, I. Apoptosis in the aging process. Cell Tissue Res. 2000, 301, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Chen, H.-D.; Hong-Guang, H.-G. The relationship between apoptosis and aging. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2012, 3, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Brenner, M.; Hearing, V.J. The regulation of skin pigmentation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 27557–27561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Kim, D.; Yoo, S.; Hong, Y.H.; Han, S.Y.; Jeong, S.; Jeong, D.; Kim, J.-H.; Cho, J.Y.; Park, J. The skin protective effects of compound K, a metabolite of ginsenoside Rb1 from Panax ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.-H.; Chiang, Y.-C.; Tsai, M.-H.; Liang, C.-J.; Hsu, L.-F.; Li, S.-Y.; Wang, M.-C.; Yen, F.-L.; Lee, C.-W. Eupafolin, a skin whitening flavonoid isolated from Phyla nodiflora, downregulated melanogenesis: Role of MAPK and Akt pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 151, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.-H.; Shin, H.-J. Anti-melanogenesis effect of quercetin. Cosmetics 2016, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagle, D.G.; Ferreira, D.; Zhou, Y.-D. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): Chemical and biomedical perspectives. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.N.; Shankar, S.; Srivastava, R.K. Green tea catechin, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): Mechanisms, perspectives and clinical applications. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 1807–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Eckert, R.L. Keratinocyte proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis—differential mechanisms of regulation by curcumin, EGCG and apigenin. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 224, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katiyar, S.K.; Afaq, F.; Azizuddin, K.; Mukhtar, H. Inhibition of UVB-induced oxidative stress-mediated phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in cultured human epidermal keratinocytes by green tea polyphenol (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2001, 176, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, Y.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Ahn, J.-S.; Nam, S.-H.; Oh, D.-K.; Park, D.-H.; Chung, H.-J.; Kang, S.; Day, D.F.; Kim, D. Synthesis, structure analyses, and characterization of novel epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) glycosides using the glucansucrase from Leuconostoc mesenteroides B-1299CB. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y. Preparation of Epigallocatechin Gallate Esters and Evaluation of their Antioxidant, Antiviral, Anti-Inflammatory and Anticancer Effects. Ph.D. Thesis, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St. John’s, NL, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Macedo, J.; Battestin, V.; Ribeiro, M.; Macedo, G. Increasing the antioxidant power of tea extracts by biotransformation of polyphenols. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.-S.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-B.; Kim, Y.-C. Quantitative analysis of major constituents in green tea with different plucking periods and their antioxidant activity. Molecules 2014, 19, 9173–9186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehshahri, S.; Wink, M.; Afsharypuor, S.; Asghari, G.; Mohagheghzadeh, A. Antioxidant activity of methanolic leaf extract of Moringa peregrina (Forssk.) Fiori. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 7, 111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.J.; Kim, C.S.; Lee, K.Y.; Yang, S.Y. Antioxidant activity of Rubus coreanus fruit extract: In comparison to green tea extract. Chonnam Med. J. 2010, 46, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matés, J.M.; Sánchez-Jiménez, F.M. Role of reactive oxygen species in apoptosis: Implications for cancer therapy. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2000, 32, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimbo, K.; Hsu, G.W.; Nguyen, H.; Mahrus, S.; Trinidad, J.C.; Burlingame, A.L.; Wells, J.A. Quantitative profiling of caspase-cleaved substrates reveals different drug-induced and cell-type patterns in apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12432–12437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, A.G.; Jänicke, R.U. Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 1999, 6, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tait, S.W.; Green, D.R. Mitochondria and cell death: Outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averbeck, M.; Gebhardt, C.A.; Voigt, S.; Beilharz, S.; Anderegg, U.; Termeer, C.C.; Sleeman, J.P.; Simon, J.C. Differential regulation of hyaluronan metabolism in the epidermal and dermal compartments of human skin by UVB irradiation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellemere, G.; Stamatas, G.; Bruere, V.; Bertin, C.; Issachar, N.; Oddos, T. Antiaging action of retinol: From molecular to clinical. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2009, 22, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R453–R462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, S.; Pasparakis, M. Epithelial Cell Death and Inflammation in Skin, Apoptotic and Non-apoptotic Cell Death; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 77–93. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, L.K.; Su, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.-Y. Theaflavins in black tea and catechins in green tea are equally effective antioxidants. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 2248–2251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Valcic, S.; Muders, A.; Jacobsen, N.E.; Liebler, D.C.; Timmermann, B.N. Antioxidant chemistry of green tea catechins. Identification of products of the reaction of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate with peroxyl radicals. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1999, 12, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thawonsuwan, J.; Kiron, V.; Satoh, S.; Panigrahi, A.; Verlhac, V. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) affects the antioxidant and immune defense of the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 36, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Burillo, S.; Tan, D.X.; Mayo, J.C.; Sainz, R.M.; Manchester, L.C.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin, xanthurenic acid, resveratrol, EGCG, vitamin C and α-lipoic acid differentially reduce oxidative DNA damage induced by Fenton reagents: A study of their individual and synergistic actions. J. Pineal Res. 2003, 34, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassina, G.; Buffa, A.; Benelli, R.; Varnier, O.E.; Noonan, D.M.; Albini, A. Polyphenolic antioxidant (–)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate from green tea as a candidate anti-HIV agent. AIDS 2002, 16, 939–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Shahidi, F. Lipophilised epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) derivatives and their antioxidant potential in food and biological systems. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gensler, H.L.; Timmermann, B.N.; Valcic, S.; Wachter, G.A.; Dorr, R.; Dvorakova, K.; Alberts, D.S. Prevention of photocarcinogenesis by topical administration of pure epigallocatechin gallate isolated from green tea. Nutr. Cancer 1996, 26, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katiyar, S.K.; Challa, A.; McCormick, T.S.; Cooper, K.D.; Mukhtar, H. Prevention of UVB-induced immunosuppression in mice by the green tea polyphenol (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate may be associated with alterations in IL-10 and IL-12 production. Carcinogenesis 1999, 20, 2117–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Hwang, J.S.; Cho, Y.K.; Han, Y.; Jeon, Y.J.; Yang, K.H. Protective effects of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on UVA- and UVB-induced skin damage. Skin Pharmacol. Appl. Skin Physiol. 2001, 14, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, K.S.; Yi, Y.S.; Son, Y.J.; Jeong, D.; Sung, N.Y.; Aravinthan, A.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, J.Y. Comparison of anticancer activities of Korean Red Ginseng-derived fractions. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Yang, Y.; Kwak, Y.S.; Song, G.G.; Kim, M.Y.; Rhee, M.H.; Cho, J.Y. Ginsenoside Rc from Panax ginseng exerts anti-inflammatory activity by targeting TANK-binding kinase 1/interferon regulatory factor-3 and p38/ATF-2. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossen, M.J.; Hong, Y.D.; Baek, K.-S.; Yoo, S.; Hong, Y.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.-O.; Kim, D.; Park, J.; Cho, J.Y. In vitro antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects of the compound K-rich fraction BIOGF1K, prepared from Panax ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radical Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Yang, W.S.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.G.; Kim, H.G.; Ko, J.; Hong, Y.D.; Rho, H.S.; Shin, S.S.; Sung, G.-H. Lancemaside A from Codonopsis lanceolata modulates the inflammatory responses mediated by monocytes and macrophages. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 405158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, K.S.; Yi, Y.S.; Son, Y.J.; Yoo, S.; Sung, N.Y.; Kim, Y.; Hong, S.; Aravinthan, A.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, J.Y. In vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory activities of Korean Red Ginseng-derived components. J. Ginseng Res. 2016, 40, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.S.; Yi, Y.S.; Kim, D.; Kim, M.H.; Park, J.G.; Kim, E.; Lee, S.Y.; Yoon, K.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.; et al. Nuclear factor kappa-B- and activator protein-1-mediated immunostimulatory activity of compound K in monocytes and macrophages. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.H.; Kim, D.; Hwang, K.; Yoo, S.; Han, S.Y.; Jeong, S.; Kim, E.; Jeong, D.; Yoon, K.; Kim, S. Photoaging protective effects of BIOGF1K, a compound-K-rich fraction prepared from Panax Ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Sequence (5′ to 3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| FLG | F | AGGGAAGATCCAAGAGCCCA |
| R | ACTCTGGATCCCCTACGCTT | |
| TGM | F | GAAATGCGGCAGATGACGAC |
| R | AACTCCCCAGCGTCTGATTG | |
| HAS-1 | F | CCACCCAGTACAGCGTCAAC |
| R | CATGGTGCTTCTGTCGCTCT | |
| HAS-2 | F | TTCTTTATGTGACTCATCTGTCTCACCGG |
| R | ATTGTTGGCTACCAGTTTATCCAAACG | |
| HAS-3 | F | TATACCGCGCGCTCCAA |
| R | GCCACTCCCGGAAGTAAGACT | |
| HYAL-1 | F | CAGAATGCCAGCCTGATTGC |
| R | CCGGTGTAGTTGGGGCTTAG | |
| HYAL-2 | F | TACACCACAAGCACGGAGAC |
| R | ATGCAGGAAGGTACTGGCAC | |
| HYAL-3 | F | CCAGGATGACCTTGTGCAGT |
| R | CCATCTGTCCTGGATCTCGC | |
| HYAL-4 | F | TGAGCTCTCTTGGCTCTGGA |
| R | AGGCAGCACTTTCTCCTATGG | |
| GAPDH | F | GCACCGTCAAGGCTGAGAAC |
| R | ATGGTGGTGAAGACGCCAGT |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, E.; Hwang, K.; Lee, J.; Han, S.Y.; Kim, E.-M.; Park, J.; Cho, J.Y. Skin Protective Effect of Epigallocatechin Gallate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010173
Kim E, Hwang K, Lee J, Han SY, Kim E-M, Park J, Cho JY. Skin Protective Effect of Epigallocatechin Gallate. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(1):173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010173
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Eunji, Kyeonghwan Hwang, Jongsung Lee, Sang Yun Han, Eun-Mi Kim, Junseong Park, and Jae Youl Cho. 2018. "Skin Protective Effect of Epigallocatechin Gallate" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 1: 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010173
APA StyleKim, E., Hwang, K., Lee, J., Han, S. Y., Kim, E.-M., Park, J., & Cho, J. Y. (2018). Skin Protective Effect of Epigallocatechin Gallate. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(1), 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010173