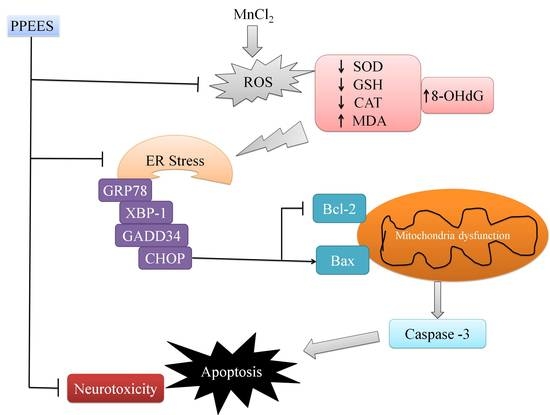
Polyphenolic Extract of Euphorbia supina Attenuates Manganese-Induced Neurotoxicity by Enhancing Antioxidant Activity through Regulation of ER Stress and ER Stress-Mediated Apoptosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Total Phenol and Flavonoid Content
2.2. DPPH Scavenging and RPC of PPEES
2.3. Effect of PPEES on SKNMC Cell Lines
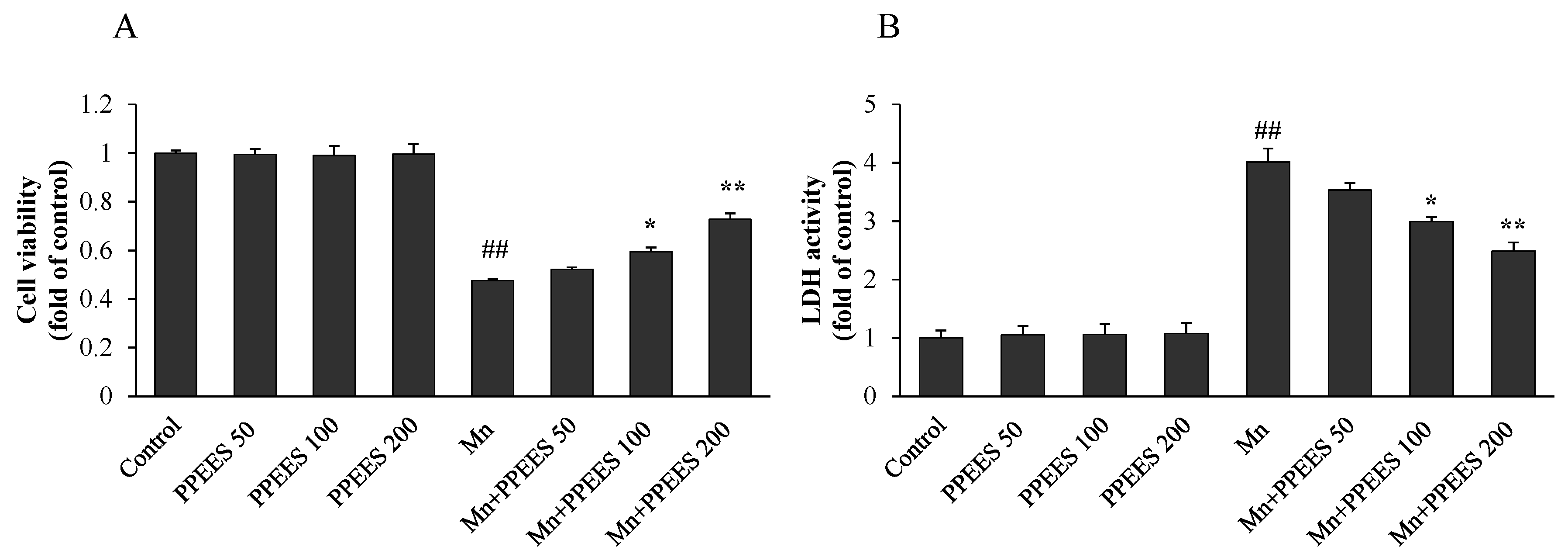
2.4. Protective Effect of PPEES on Mn-Induced Cytotoxicity
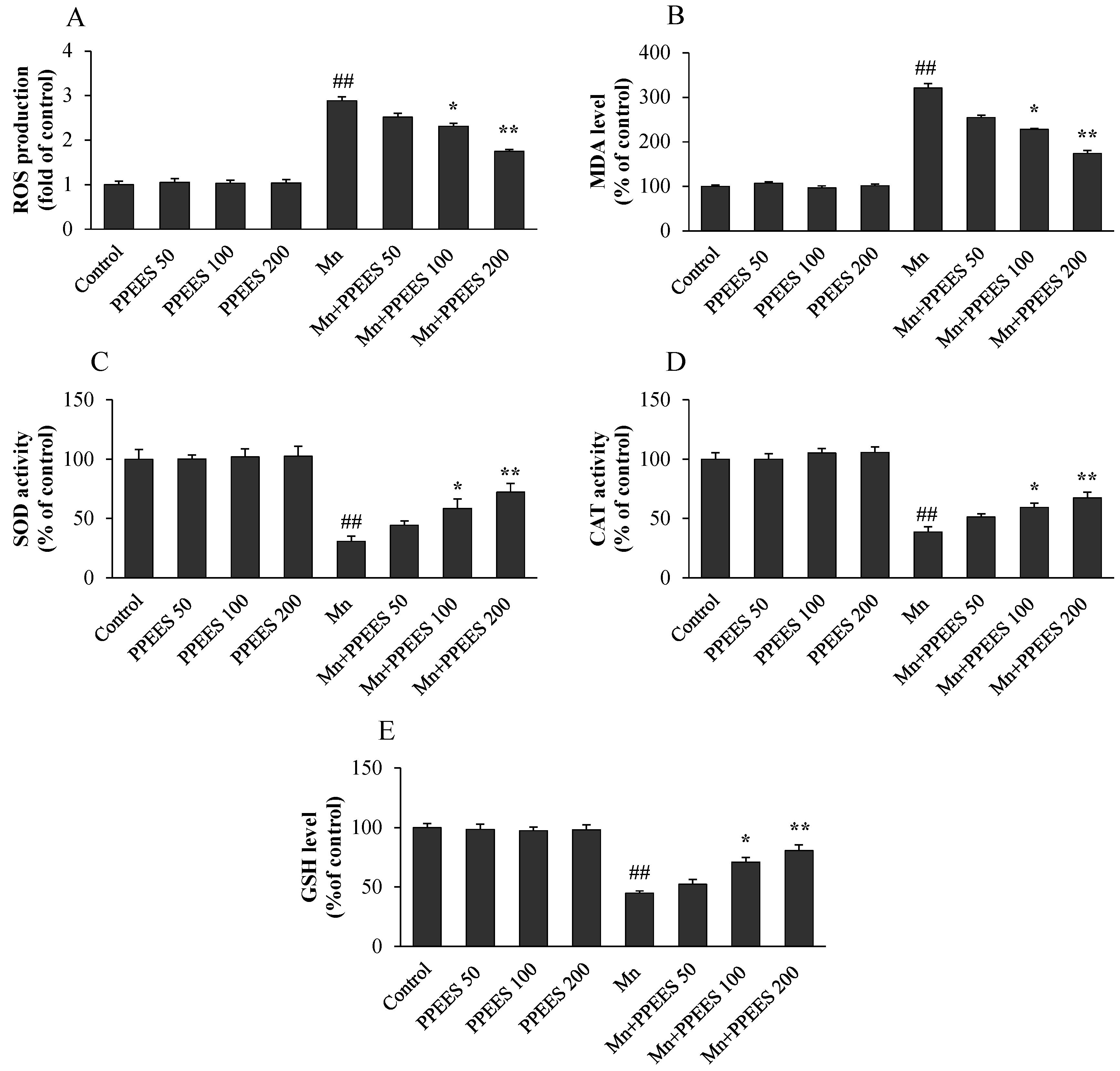
2.5. PPEES Attenuated Mn-Induced Oxidative Stress in SKNMC Cells
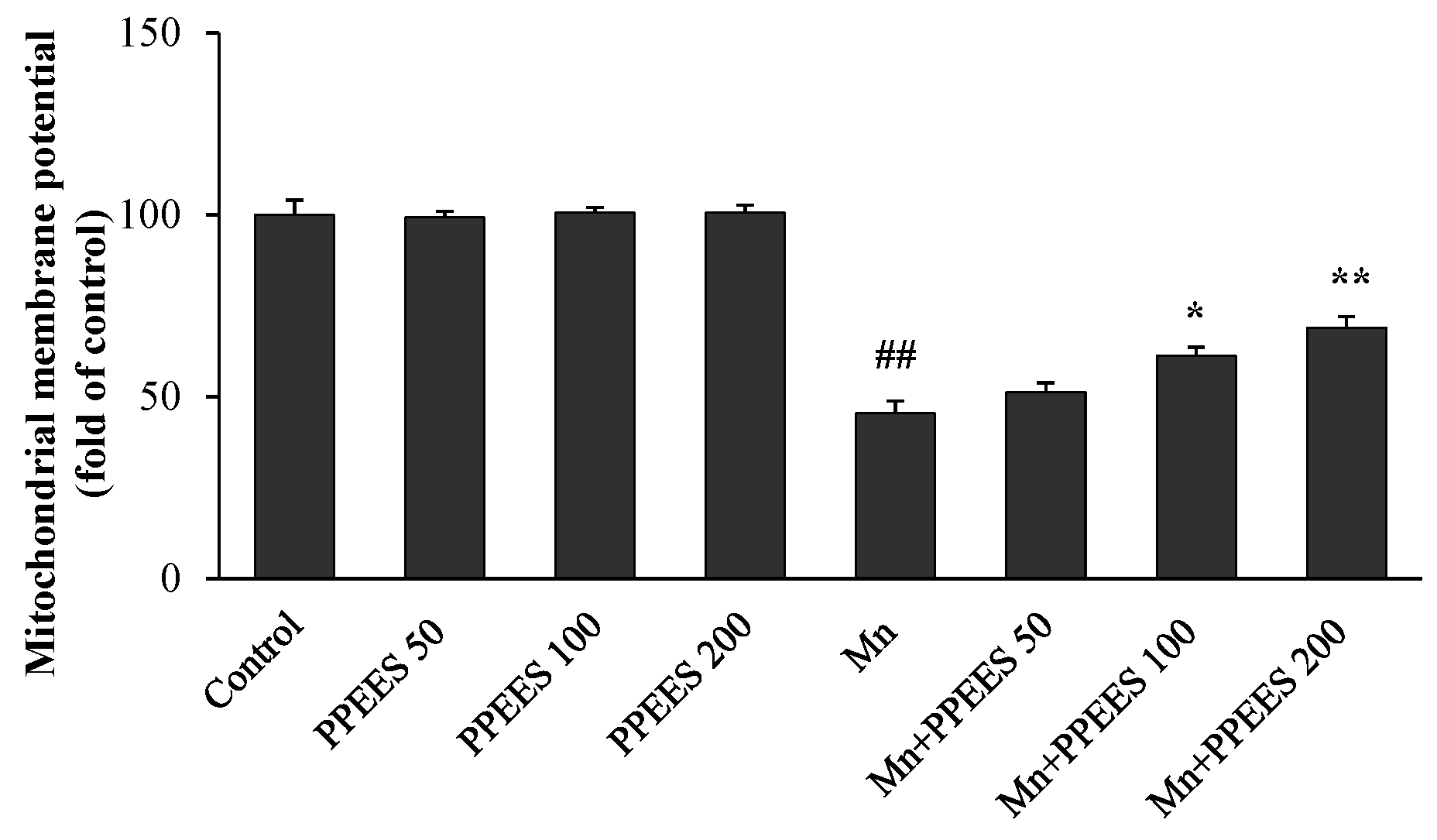
2.6. PPEES Attenuates Mn-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfuction
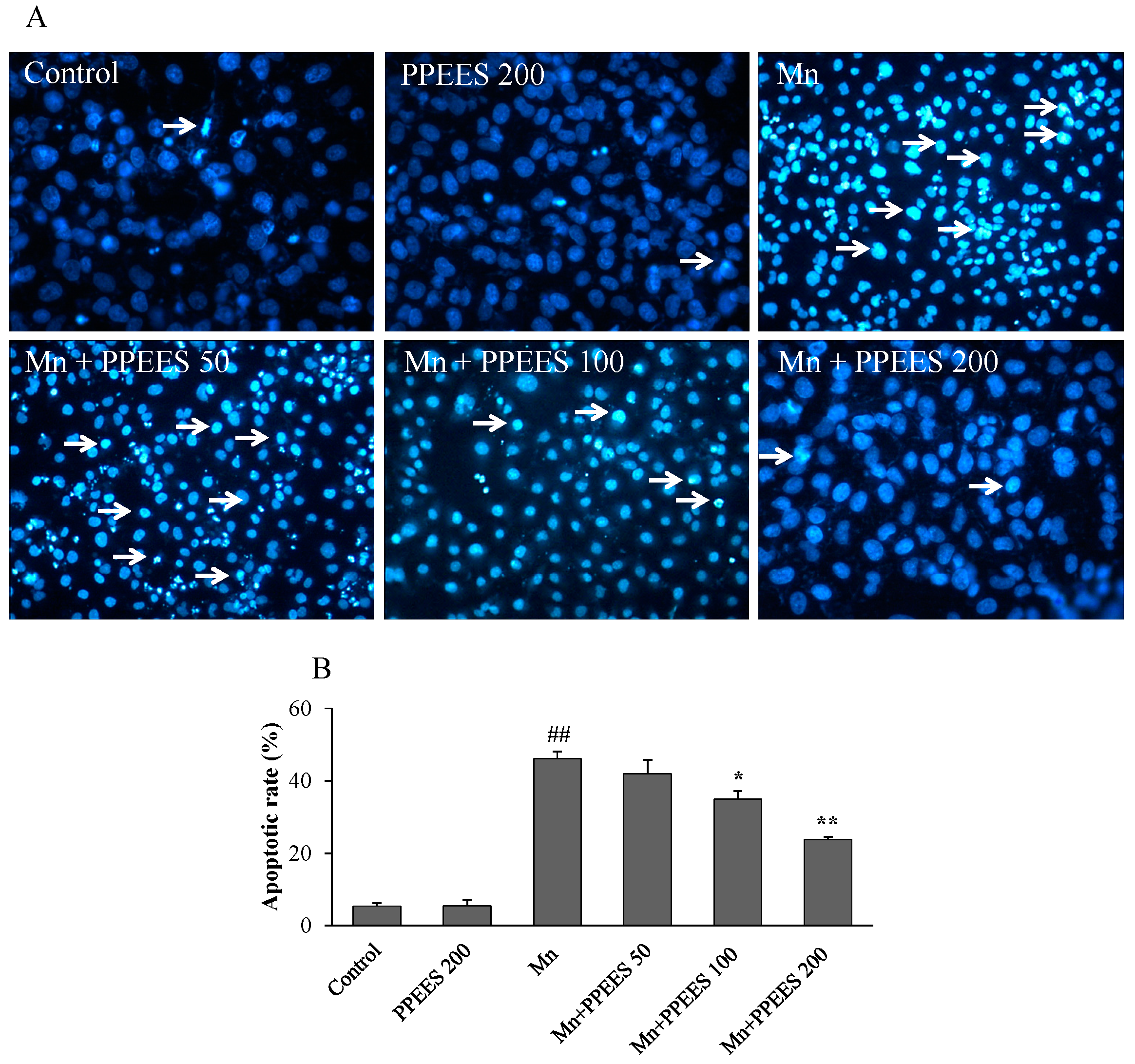
2.7. PPEES Reduced Apoptosis on Manganese-Induced Apoptosis in SKNMC Cells
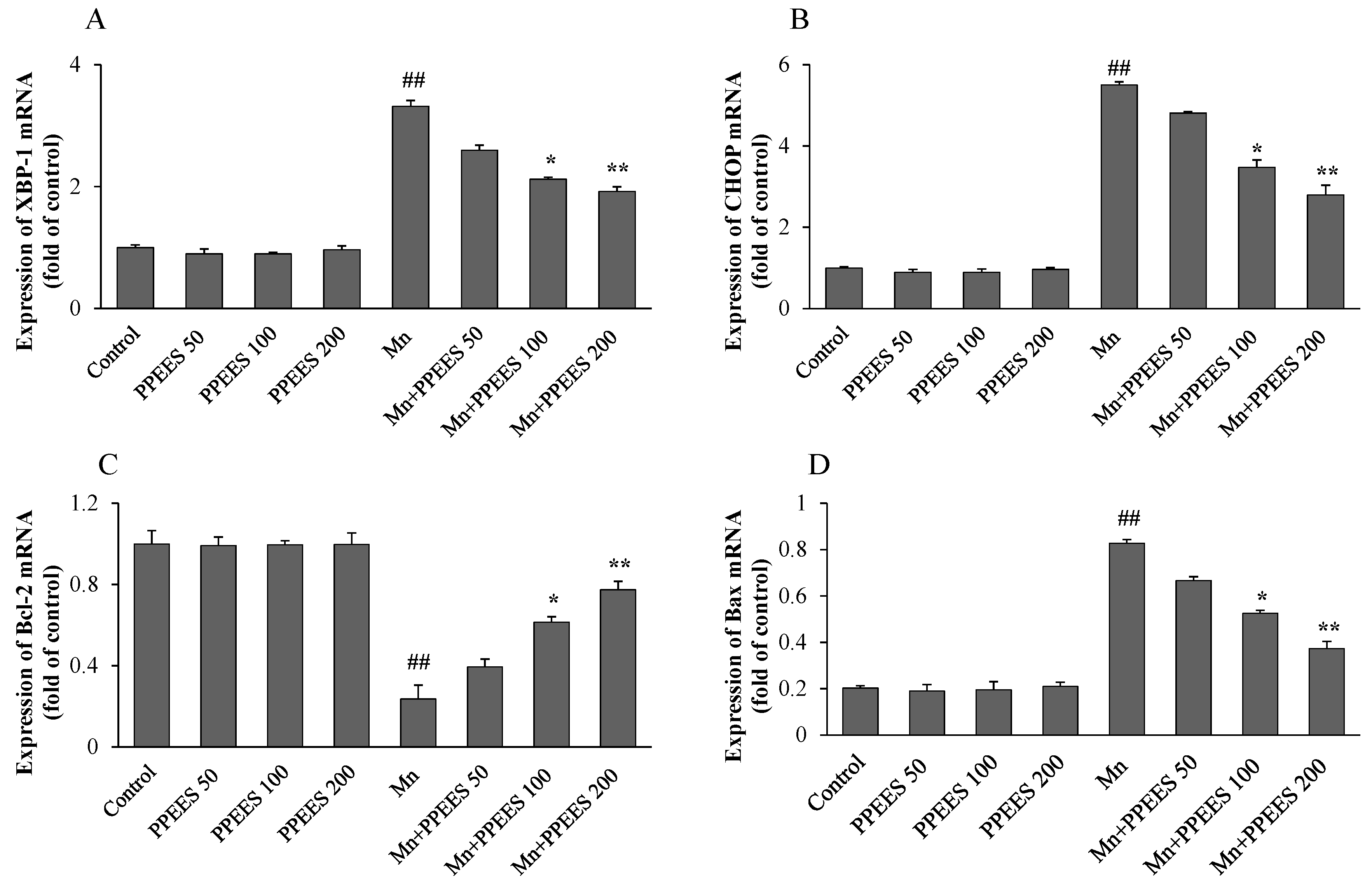
2.8. PPEES Decreased Mn-Induced ER Stress and ER Stress-Mediated Apoptosis
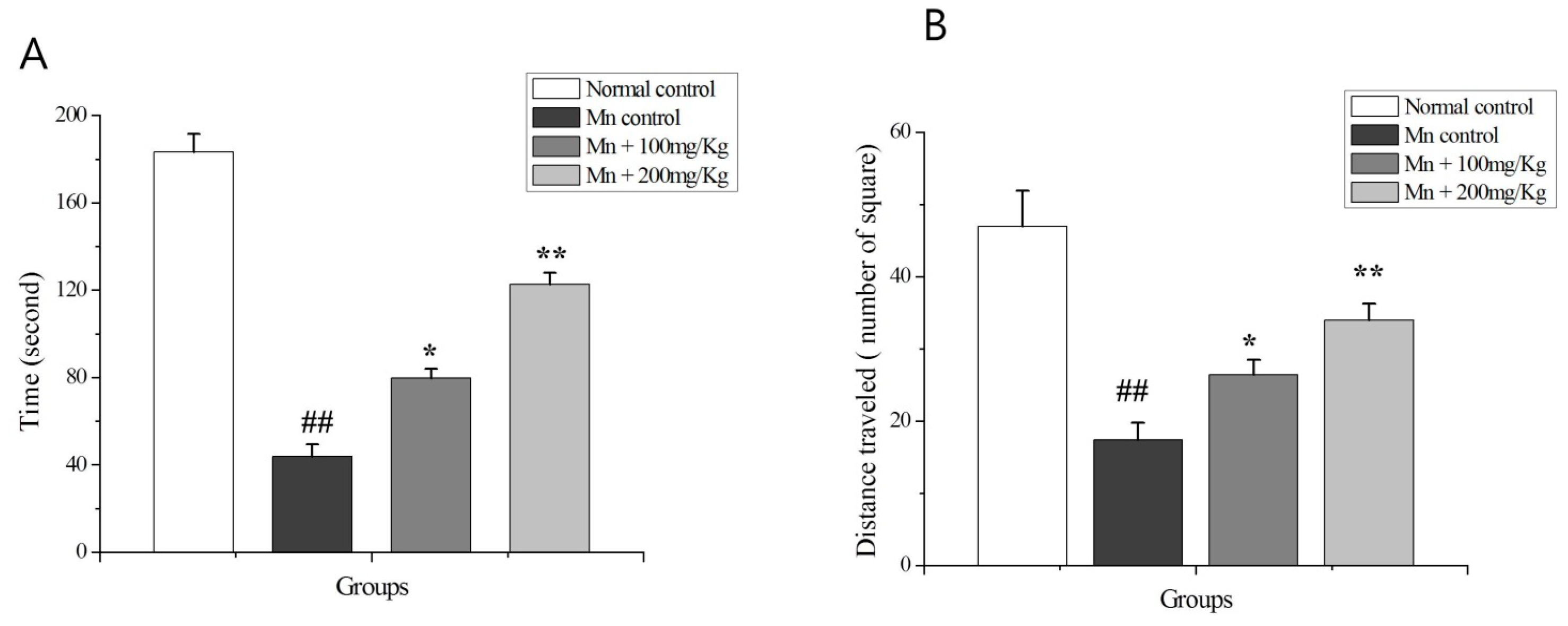
2.9. The OF Test
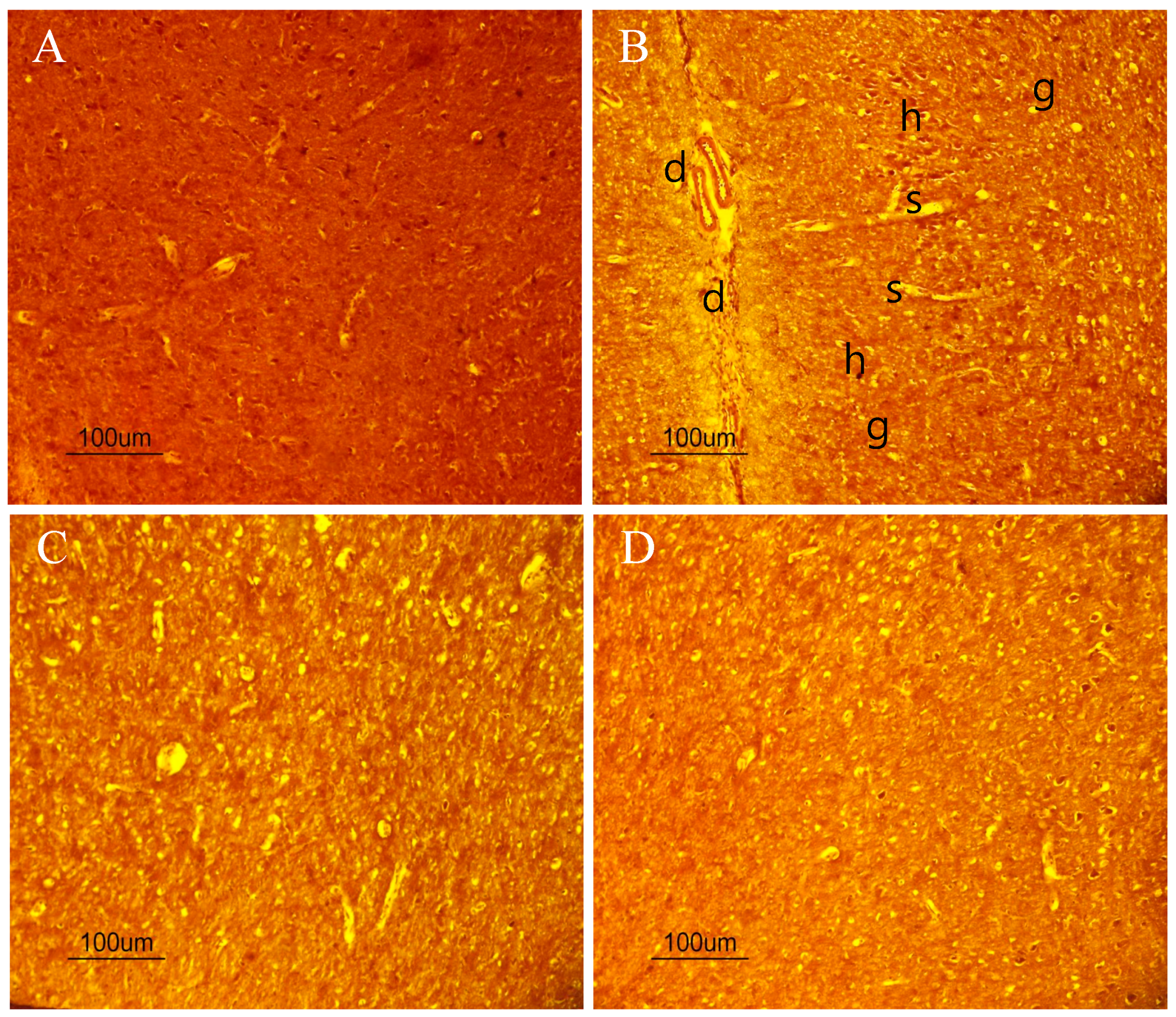
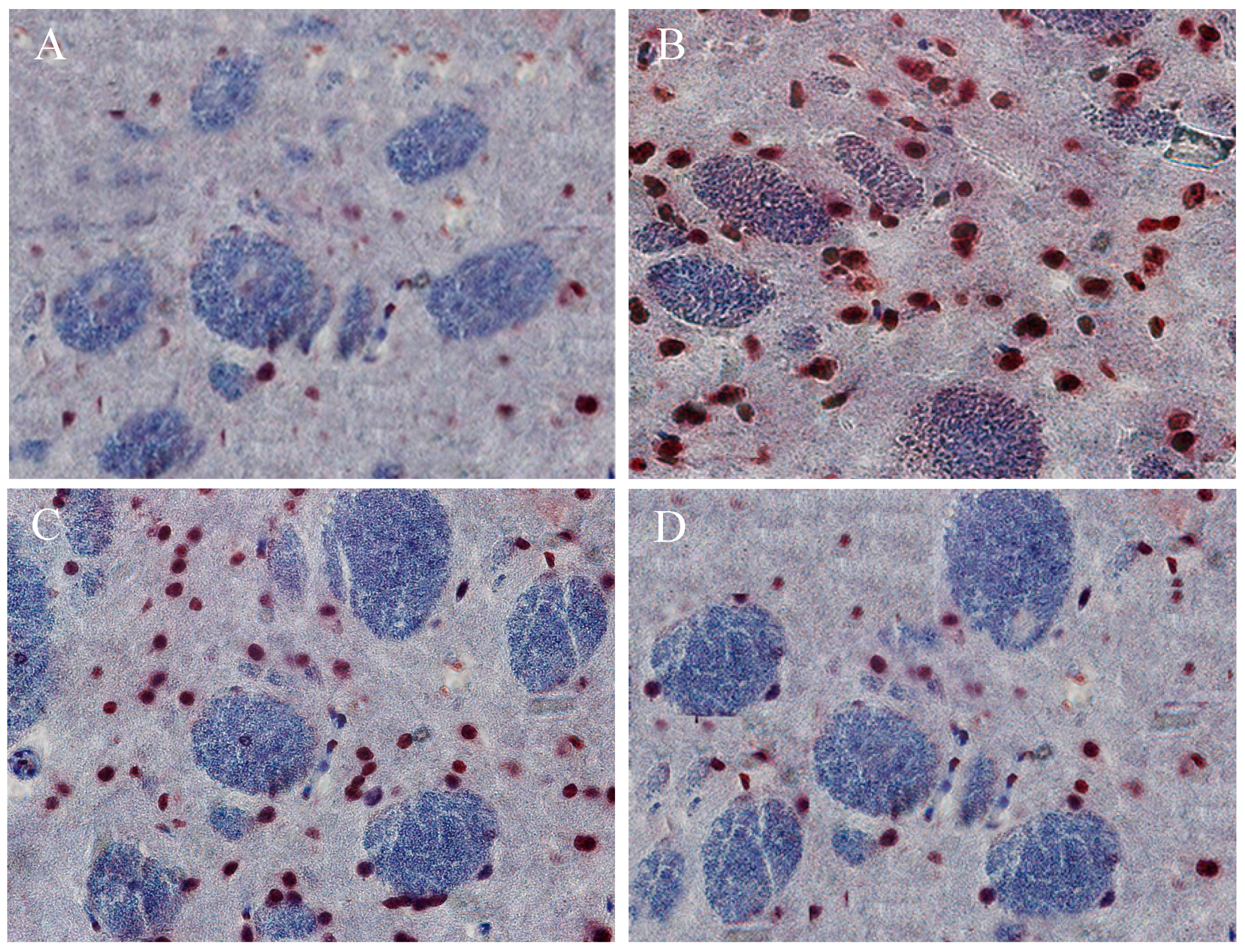
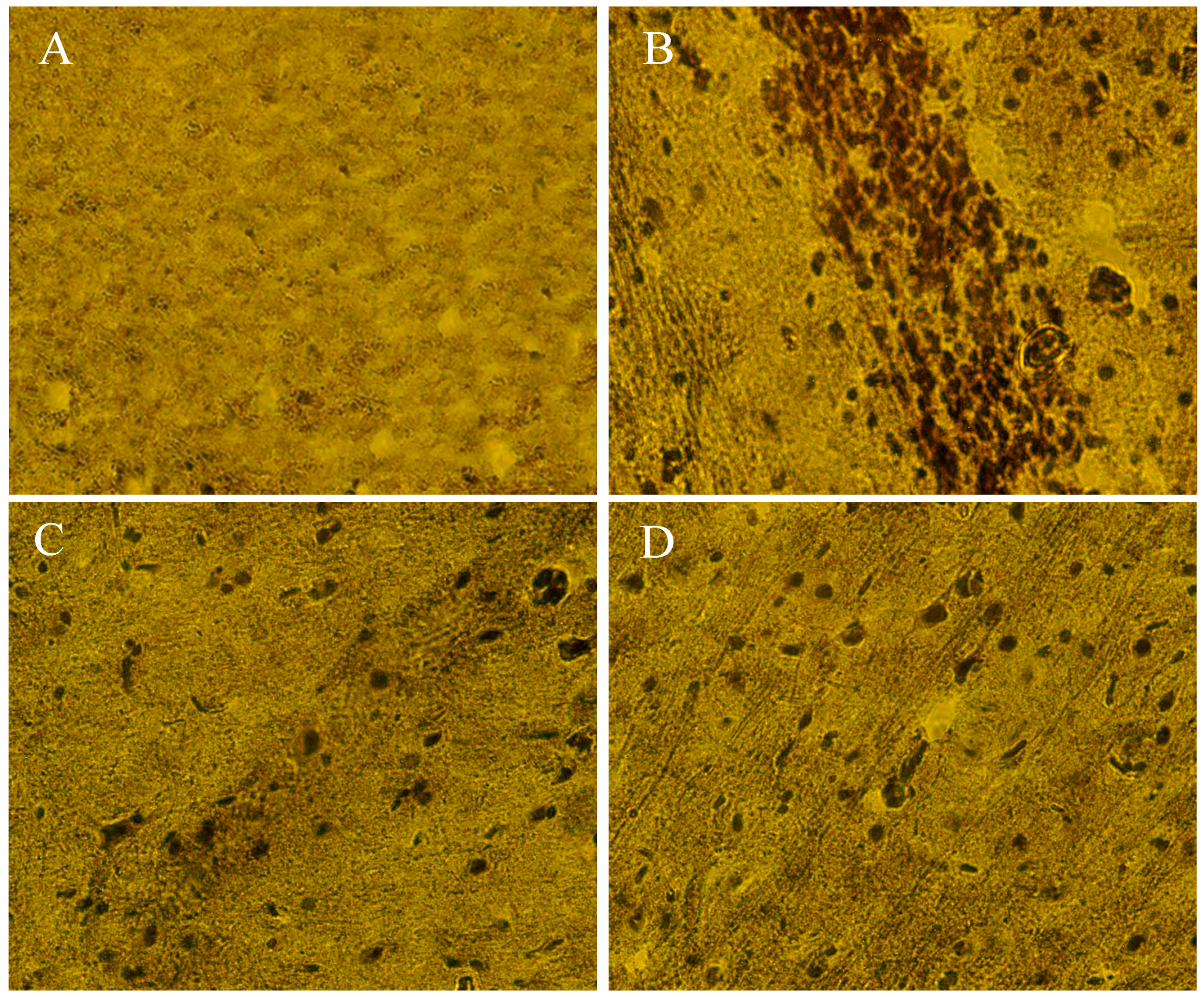
2.10. The Beneficial Effect of PPEES Treatment on Mn-Induced Histopathological and Immunohistochemically Altered Rats Brain
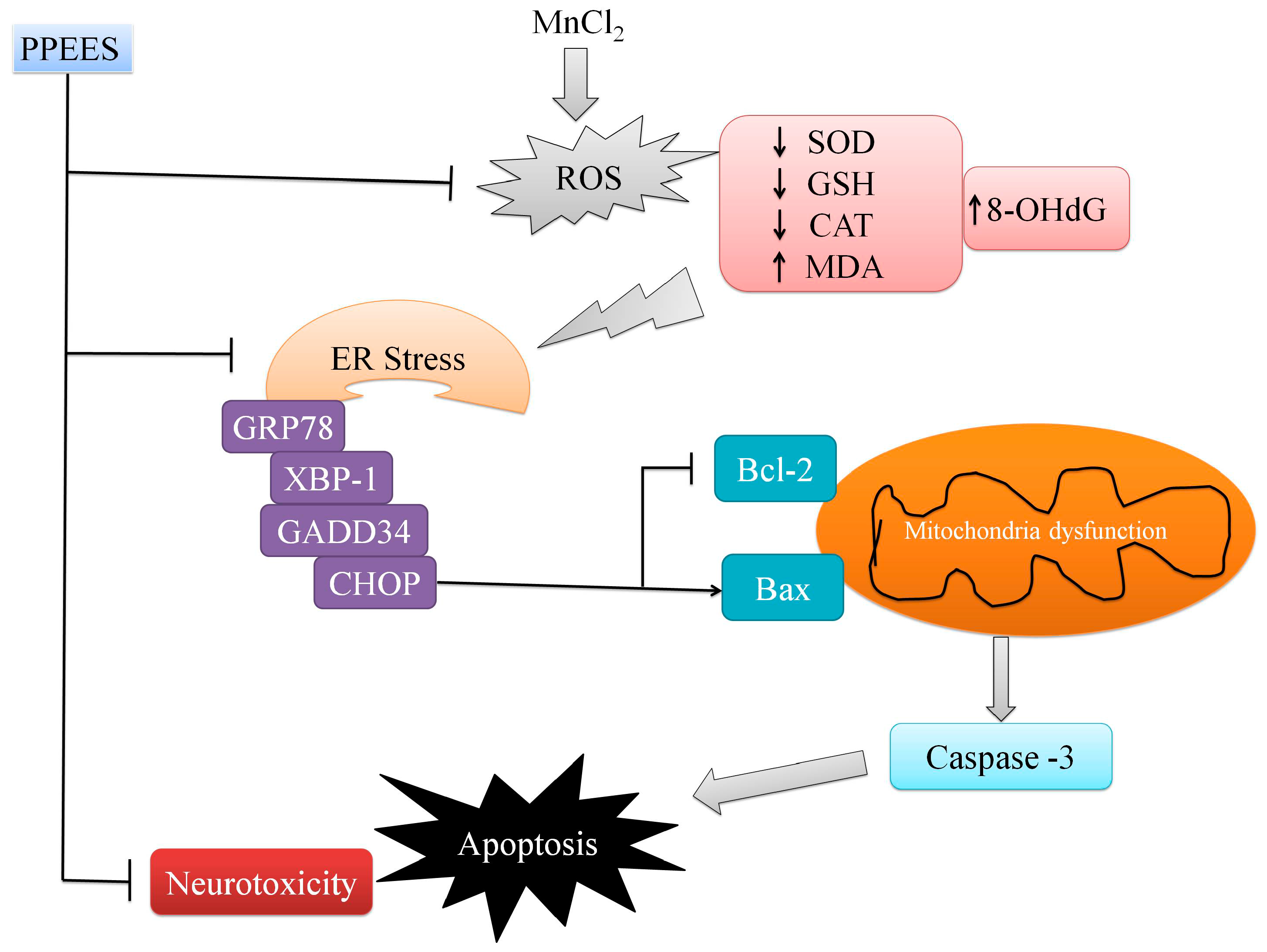
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Extraction of Polyphenol Enriched Extracts of E. supina (PPEES)
4.3. Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
4.4. Total Flavonoid Content (TFC)
4.5. 1,1-Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) Assay
4.6. Reducing Power Capacity (RPC)
4.7. Cell Culture
4.8. Cytotoxicity of PPEES
4.9. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Activity
4.10. Cell Viability
4.11. Measurement of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Level
4.12. Antioxidant Status
4.13. Measurement of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (ΔΨm)
4.14. Apoptosis Assay
4.15. Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.16. Western Blotting
4.17. Experimental Animal and Treatments
4.18. The Open Field (OF) Test
4.19. Collection of Brain
4.20. Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry
4.21. Statistical Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Underwood, E.J. Trace metals in human and animal health. J. Hum. Nutr. 1981, 35, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, A.P.; Schneider, J.A.; Nelson, B.C.; Atha, D.H.; Jain, A.; Soliman, K.F.; Aschner, M.; Mazzio, E.; Renee Reams, R. Manganese-induced oxidative DNA damage in neuronal SH-SY5Y cells: Attenuation of thymine base lesions by glutathione and N-acetylcysteine. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 218, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, N.C.; Guilarte, T.R. Manganese neurotoxicity: Lessons learned from longitudinal studies in nonhuman primates. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudnell, H.K. Effects from environmental Mn exposures: A review of the evidence from non-occupational exposure studies. Neurotoxicology 1999, 20, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barbeau, A. Manganese and extrapyramidal disorders (a critical review and tribute to Dr. George C. Cotzias). Neurotoxicology 1984, 5, 13–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mena, I.; Marin, O.; Fuenzalida, S.; Cotzias, G.C. Chronic manganese poisoning. Clinical picture and manganese turnover. Neurology 1967, 17, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iregren, A. Manganese neurotoxicity in industrial exposures: Proof of effects, critical exposure level, and sensitive tests. Neurotoxicology 1999, 20, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Calne, D.B.; Chu, N.S.; Huang, C.C.; Lu, C.S.; Olanow, W. Manganism and idiopathic parkinsonism: Similarities and differences. Neurology 1994, 44, 1583–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olanow, C.W.; Good, P.F.; Shinotoh, H.; Hewitt, K.A.; Vingerhoets, F.; Snow, B.J.; Beal, M.F.; Calne, D.B.; Perl, D.P. Manganese intoxication in the rhesus monkey: A clinical, imaging, pathologic, and biochemical study. Neurology 1996, 46, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, U.; Niehaus, L.; Probst, T.; Benecke, R.; Meyer, B.U.; Dressler, D. Brain parenchyma sonography discriminates Parkinson’s disease and atypical parkinsonian syndromes. Neurology 2003, 60, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Ohno, S.; Okayasu, I.; Okeda, R.; Hatakeyama, S.; Watanabe, H.; Ushio, K.; Tsukagoshi, H. Chronic manganese poisoning: A neuropathological study with determination of manganese distribution in the brain. Acta Neuropathol. 1986, 70, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz, H.B.; Bertolucci, P.H.; Pereira, J.S.; Lima, J.G.; Andrade, L.A. Chronic exposure to the fungicide maneb may produce symptoms and signs of CNS manganese intoxication. Neurology 1988, 38, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brurok, H.; Berg, K.; Sneen, L.; Grant, D.; Karlsson, J.O.; Jynge, P. Cardiac metal contents after infusions of manganese. An experimental evaluation in the isolated rat heart. Investig. Radiol. 1999, 34, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, D.R.; Haworth, R.A.; Berkoff, H.A. Cellular manganese uptake by the isolated perfused rat heart: A probe for the sarcolemma calcium channel. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1981, 13, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brurok, H.; Schjott, J.; Berg, K.; Karlsson, J.O.; Jynge, P. Manganese and the heart: Acute cardiodepression and myocardial accumulation of manganese. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1997, 159, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brurok, H.; Skoglund, T.; Berg, K.; Skarra, S.; Karlsson, J.O.; Jynge, P. Myocardial manganese elevation and proton relaxivity enhancement with manganese dipyridoxyl diphosphate. Ex vivo assessments in normally perfused and ischemic guinea pig hearts. NMR Biomed. 1999, 12, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jynge, P.; Brurok, H.; Asplund, A.; Towart, R.; Refsum, H.; Karlsson, J.O. Cardiovascular safety of MnDPDP and MnCl2. Acta Radiol. 1997, 38, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goering, P.L. The road to elucidating the mechanism of manganese-bilirubin-induced cholestasis. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 73, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symonds, H.W.; Hall, E.D. Acute manganese toxicity and the absorption and biliary excretion of manganese in cattle. Res. Vet. Sci. 1983, 35, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Treinen, K.A.; Gray, T.J.; Blazak, W.F. Developmental toxicity of mangafodipir trisodium and manganese chloride in Sprague-Dawley rats. Teratology 1995, 52, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, D.J.; Domingo, J.L.; Llobet, J.M.; Keen, C.L. Maternal and developmental toxicity of manganese in the mouse. Toxicol. Lett. 1993, 69, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, G.B.; Leonard, A.; Hantson, P. Carcinogenicity, mutagenicity and teratogenicity of manganese compounds. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2002, 42, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Cai, T.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, S.; Wang, Y.; Ye, L. alpha-Synuclein overexpression during manganese-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Brain Res. Bull. 2010, 81, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, H.R.; Chae, H.J. Apoptosis Induced by Manganese on Neuronal SK-N-MC Cell Line: Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Stress and Mitochondria Dysfunction. Environ. Health Toxicol. 2011, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, H.R.; Chae, H.J. The effects of 3, 4 or 5 amino salicylic acids on manganese-induced neuronal death: ER stress and mitochondrial complexes. Toxicol. In Vitro 2011, 25, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Fu, J. Effect of manganese chloride exposure on liver and brain mitochondria function in rats. Environ. Res. 2003, 93, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Fu, J.; Zhou, Z. Changes in the brain mitochondrial proteome of male Sprague-Dawley rats treated with manganese chloride. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 202, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neal, S.L.; Lee, J.W.; Zheng, W.; Cannon, J.R. Subacute manganese exposure in rats is a neurochemical model of early manganese toxicity. Neurotoxicology 2014, 44, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorhees, C.V.; Graham, D.L.; Amos-Kroohs, R.M.; Braun, A.A.; Grace, C.E.; Schaefer, T.L.; Skelton, M.R.; Erikson, K.M.; Aschner, M.; Williams, M.T. Effects of developmental manganese, stress, and the combination of both on monoamines, growth, and corticosterone. Toxicol. Rep. 2014, 1, 1046–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moberly, A.H.; Czarnecki, L.A.; Pottackal, J.; Rubinstein, T.; Turkel, D.J.; Kass, M.D.; McGann, J.P. Intranasal exposure to manganese disrupts neurotransmitter release from glutamatergic synapses in the central nervous system in vivo. Neurotoxicology 2012, 33, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Zhao, J.; Yang, L.; Nie, X.; Han, J.; Ma, X.; Wan, C.; Jiang, J. KHSRP participates in manganese-induced neurotoxicity in rat striatum and PC12 cells. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 55, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaimo, A.; Gorojod, R.M.; Beauquis, J.; Munoz, M.J.; Saravia, F.; Kotler, M.L. Deregulation of mitochondria-shaping proteins Opa-1 and Drp-1 in manganese-induced apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Li, X.; Yang, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, P.; Fu, J.; Yao, B.; Zhou, Z. ER stress and ER stress-mediated apoptosis are involved in manganese-induced neurotoxicity in the rat striatum in vivo. Neurotoxicology 2015, 48, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanalakshmi, C.; Manivasagam, T.; Nataraj, J.; Justin Thenmozhi, A.; Essa, M.M. Neurosupportive Role of Vanillin, a Natural Phenolic Compound, on Rotenone Induced Neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, Y.; Okada, M. Protective effects of plant seed extracts against amyloid beta-induced neurotoxicity in cultured hippocampal neurons. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2013, 5, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obrenovich, M.E.; Nair, N.G.; Beyaz, A.; Aliev, G.; Reddy, V.P. The role of polyphenolic antioxidants in health, disease, and aging. Rejuvenation Res. 2010, 13, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Jeong, S.W.; Lee, W.S.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, G.S.; Lee, S.J.; Jin, J.S.; Kim, C.Y.; Lee, J.E.; et al. Determination of Polyphenol Components of Korean Prostrate Spurge (Euphorbia supina) by Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Overall Contribution to Antioxidant Activity. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, Y.S.; Lee, W.S.; Joo, Y.N.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, G.S.; Jung, J.M.; Ryu, C.H.; Shin, S.C.; Kim, H.J. Polyphenol mixtures of Euphorbia supina the inhibit invasion and metastasis of highly metastatic breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 3035–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumarappan, C.T.; Thilagam, E.; Vijayakumar, M.; Mandal, S.C. Modulatory effect of polyphenolic extracts of Ichnocarpus frutescens on oxidative stress in rats with experimentally induced diabetes. Indian J. Med. Res. 2012, 136, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chun, O.K.; Kim, D.O.; Lee, C.Y. Superoxide radical scavenging activity of the major polyphenols in fresh plums. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 8067–8072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattahi, S.; Zabihi, E.; Abedian, Z.; Pourbagher, R.; Motevalizadeh Ardekani, A.; Mostafazadeh, A.; Akhavan-Niaki, H. Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Contents of Aqueous Extract of Stinging Nettle and In Vitro Antiproliferative Effect on Hela and BT-474 Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Cell. Med. 2014, 3, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sen, S.; De, B.; Devanna, N.; Chakraborty, R. Total phenolic, total flavonoid content, and antioxidant capacity of the leaves of Meyna spinosa Roxb., an Indian medicinal plant. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 11, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar, E.; Siddika, M.; Nath, B.; Yoon, H. Evaluation of In vitro Antioxidant and In vivo Antihyperlipidemic Activities of Methanol Extract of Aerial Part of Crassocephalum crepidioides (Asteraceae) Benth S Moore. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2016, 15, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganie, S.A.; Zargar, B.A.; Masood, A.; Zargar, M.A. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activity of rhizome of Podophyllum hexandrum against carbon tetra chloride induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2013, 26, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zargar, B.A.; Masoodi, M.H.; Ahmed, B.; Ganie, S.A. Antihyperlipidemic and Antioxidant Potential of Paeonia emodi Royle against High-Fat Diet Induced Oxidative Stress. ISRN Pharmacol. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokozawa, T.; Kim, Y.A.; Kim, H.Y.; Okamoto, T.; Sei, Y. Protective effect of the Chinese prescription Kangen-karyu against high glucose-induced oxidative stress in LLC-PK1 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 109, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Li, B.; Zhou, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Xiao, X.; Tang, S. Curcumin attenuates quinocetone induced apoptosis and inflammation via the opposite modulation of Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-kB pathway in human hepatocyte L02 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 95, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Tang, S.; Deng, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Velkov, T.; Li, J.; Xiao, X. Lycopene attenuates colistin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice via activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Tang, S.; Li, D.; Zhao, K.; Xiao, X. Curcumin attenuates quinocetone-induced oxidative stress and genotoxicity in human hepatocyte L02 cells. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2015, 25, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tait, S.W.; Green, D.R. Mitochondria and cell death: Outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravi-Far, R.; Esposti, M.D. Death receptor signals to mitochondria. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2004, 3, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Zheng, Z.M.; Zhang, K.B.; Wang, T.P.; Sribastav, S.S.; Liu, W.S.; Liu, T. Role of death receptor, mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum pathways in different stages of degenerative human lumbar disc. Apoptosis 2011, 16, 990–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wey, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, R.; Lee, A.S. Role of the unfolded protein response regulator GRP78/BiP in development, cancer, and neurological disorders. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 2307–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H.; Matsui, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Okada, T.; Mori, K. XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription factor. Cell 2001, 107, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brush, M.H.; Weiser, D.C.; Shenolikar, S. Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein GADD34 targets protein phosphatase 1 alpha to the endoplasmic reticulum and promotes dephosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 1292–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, H.T.; Chinery, R.; Wu, D.Y.; Kussick, S.J.; Payne, J.M.; Fornace, A.J., Jr.; Tkachuk, D.C. Leukemic HRX fusion proteins inhibit GADD34-induced apoptosis and associate with the GADD34 and hSNF5/INI1 proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 7050–7060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korsmeyer, S.J. BCL-2 gene family and the regulation of programmed cell death. Cancer Res. 1999, 59 (Suppl. 7), 1693s–1700s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, D.T.; Korsmeyer, S.J. BCL-2 family: Regulators of cell death. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 395–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahar, E.; Kim, H.; Yoon, H. ER Stress-Mediated Signaling: Action Potential and Ca(2+) as Key Players. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, T.; Popescu, B.O.; Cedazo-Minguez, A. Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease: Why did antioxidant therapy fail? Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos-Kroohs, R.M.; Bloor, C.P.; Qureshi, M.A.; Vorhees, C.V.; Williams, M.T. Effects of developmental exposure to manganese and/or low iron diet: Changes to metal transporters, sucrose preference, elevated zero-maze, open-field, and locomotion in response to fenfluramine, amphetamine, and MK-801. Toxicol. Rep. 2015, 2, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, L.L.; Li, G.J.; Guo, W.; Liang, W.; Zheng, W. Alteration of serum concentrations of manganese, iron, ferritin, and transferrin receptor following exposure to welding fumes among career welders. Neurotoxicology 2005, 26, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| TPC in PPEES (mg∙GAE/g) | TFC in PPEES (mg∙QE/g) |
|---|---|
| 175.53 ± 5.94 | 98.48 ± 7.73 |
| DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity; IC50 (µg/mL) | Reducing Capacity of PPEES; IC50 (µg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PPEES | Ascorbic acid | PPEES | Ascorbic acid |
| 145.044 ± 6.2 | 14.27 ± 1.06 | 86.0517 ± 3.94 | 10.05 ± 0.64 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bahar, E.; Lee, G.-H.; Bhattarai, K.R.; Lee, H.-Y.; Choi, M.-K.; Rashid, H.-O.; Kim, J.-Y.; Chae, H.-J.; Yoon, H. Polyphenolic Extract of Euphorbia supina Attenuates Manganese-Induced Neurotoxicity by Enhancing Antioxidant Activity through Regulation of ER Stress and ER Stress-Mediated Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020300
Bahar E, Lee G-H, Bhattarai KR, Lee H-Y, Choi M-K, Rashid H-O, Kim J-Y, Chae H-J, Yoon H. Polyphenolic Extract of Euphorbia supina Attenuates Manganese-Induced Neurotoxicity by Enhancing Antioxidant Activity through Regulation of ER Stress and ER Stress-Mediated Apoptosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(2):300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020300
Chicago/Turabian StyleBahar, Entaz, Geum-Hwa Lee, Kashi Raj Bhattarai, Hwa-Young Lee, Min-Kyung Choi, Harun-Or Rashid, Ji-Ye Kim, Han-Jung Chae, and Hyonok Yoon. 2017. "Polyphenolic Extract of Euphorbia supina Attenuates Manganese-Induced Neurotoxicity by Enhancing Antioxidant Activity through Regulation of ER Stress and ER Stress-Mediated Apoptosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 2: 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020300
APA StyleBahar, E., Lee, G.-H., Bhattarai, K. R., Lee, H.-Y., Choi, M.-K., Rashid, H.-O., Kim, J.-Y., Chae, H.-J., & Yoon, H. (2017). Polyphenolic Extract of Euphorbia supina Attenuates Manganese-Induced Neurotoxicity by Enhancing Antioxidant Activity through Regulation of ER Stress and ER Stress-Mediated Apoptosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(2), 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020300