Biopersistence of NiO and TiO2 Nanoparticles Following Intratracheal Instillation and Inhalation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Biopersistence of NiO and TiO2 Nanoparticles in Inhalation and Intratracheal Instillation Studies
2.1.1. Measured Amounts of Nanoparticles in Lung and Calculated Biological Half Time (BHT)
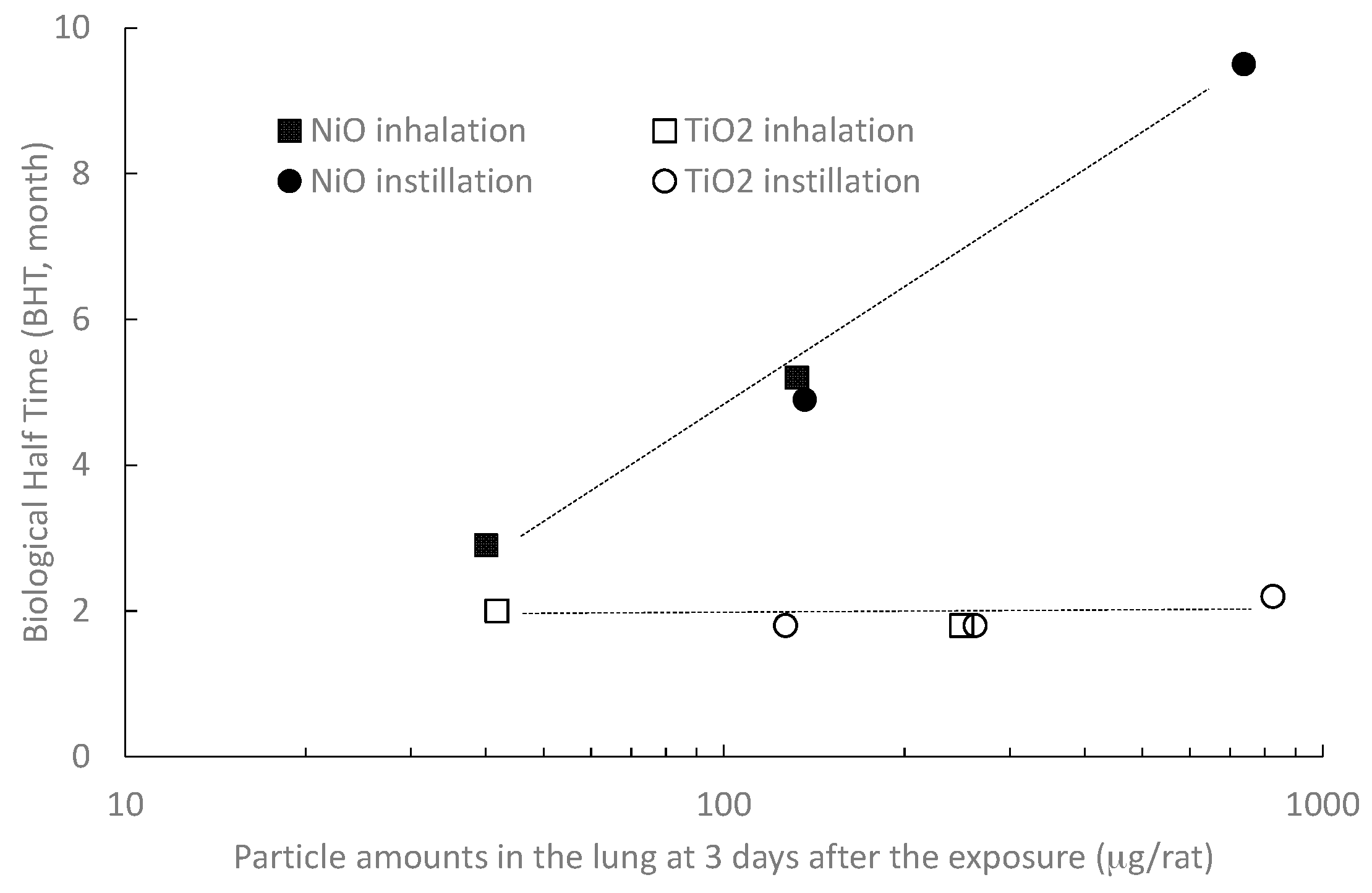
2.1.2. Dose–Response Relationship between Lung Burden and BHT
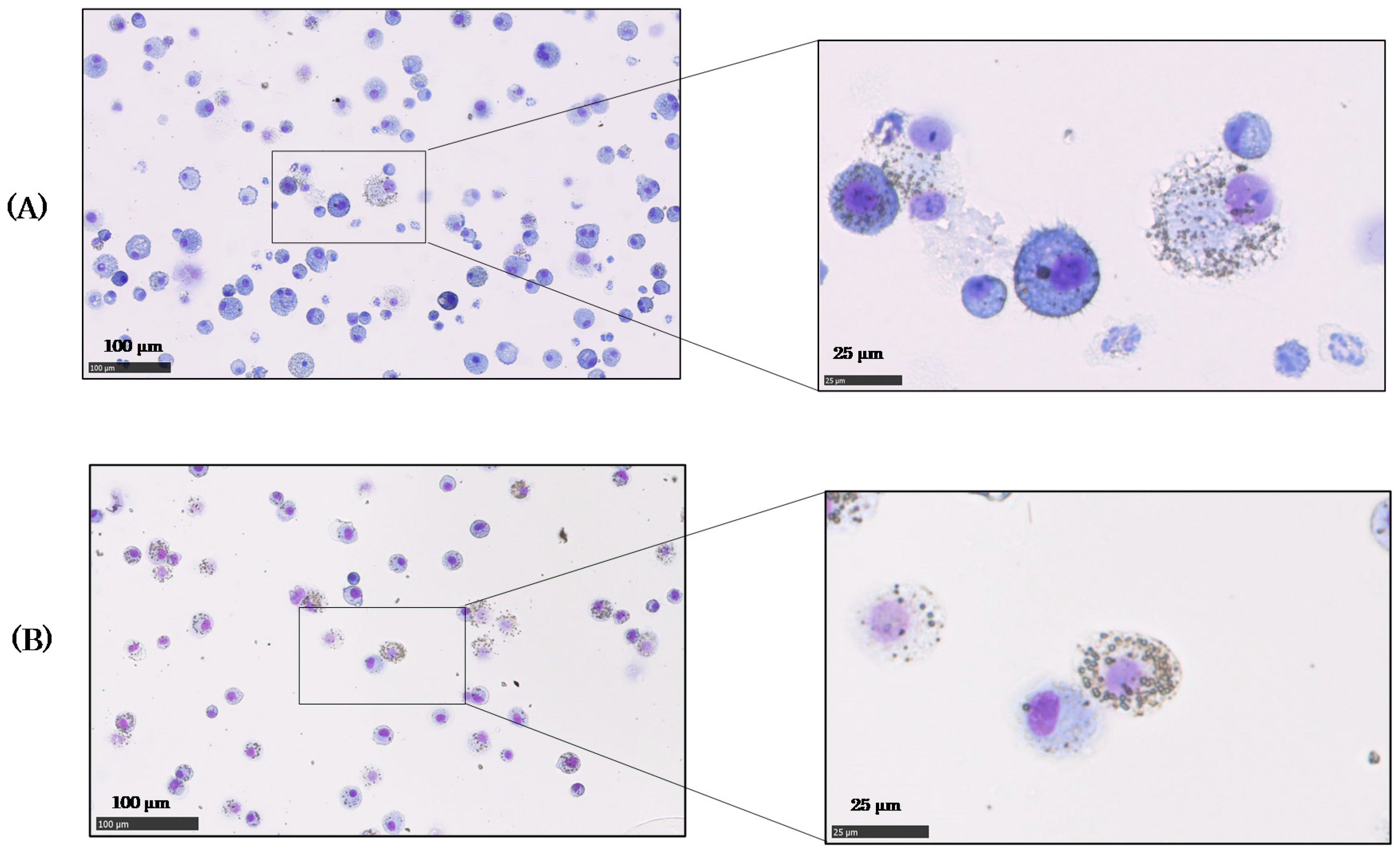
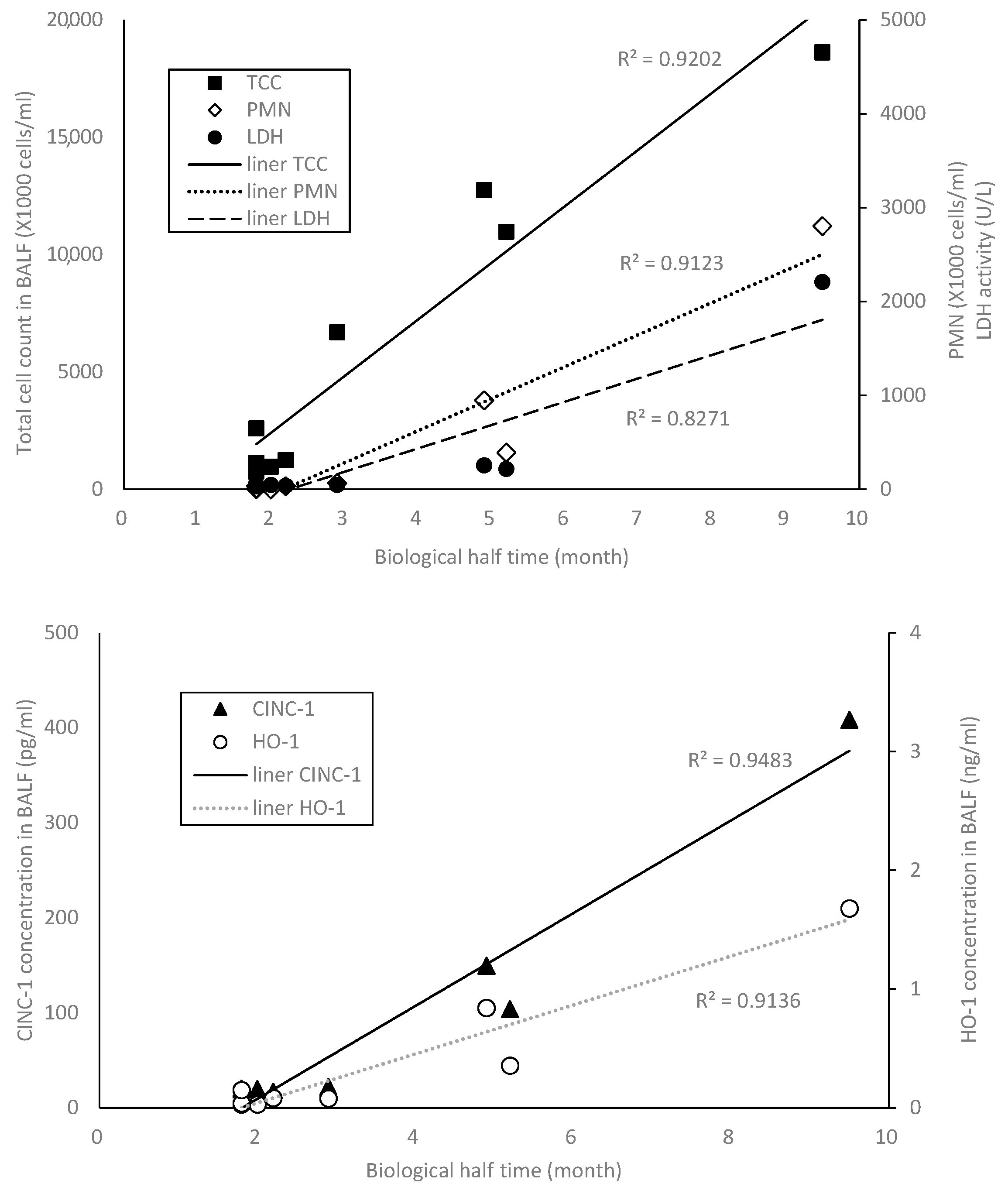
2.2. Cells in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid (BALF) after NiO and TiO2 Inhalation
2.3. Histopathological Finding in the Lungs
2.4. The Relation between BHT and the Other Indicator
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Inhalation and Intratracheal Instillation Studies
4.1.1. NiO and TiO2 Nanoparticles
4.1.2. Animals
4.1.3. Inhalation and Intratracheal Instillation Methods
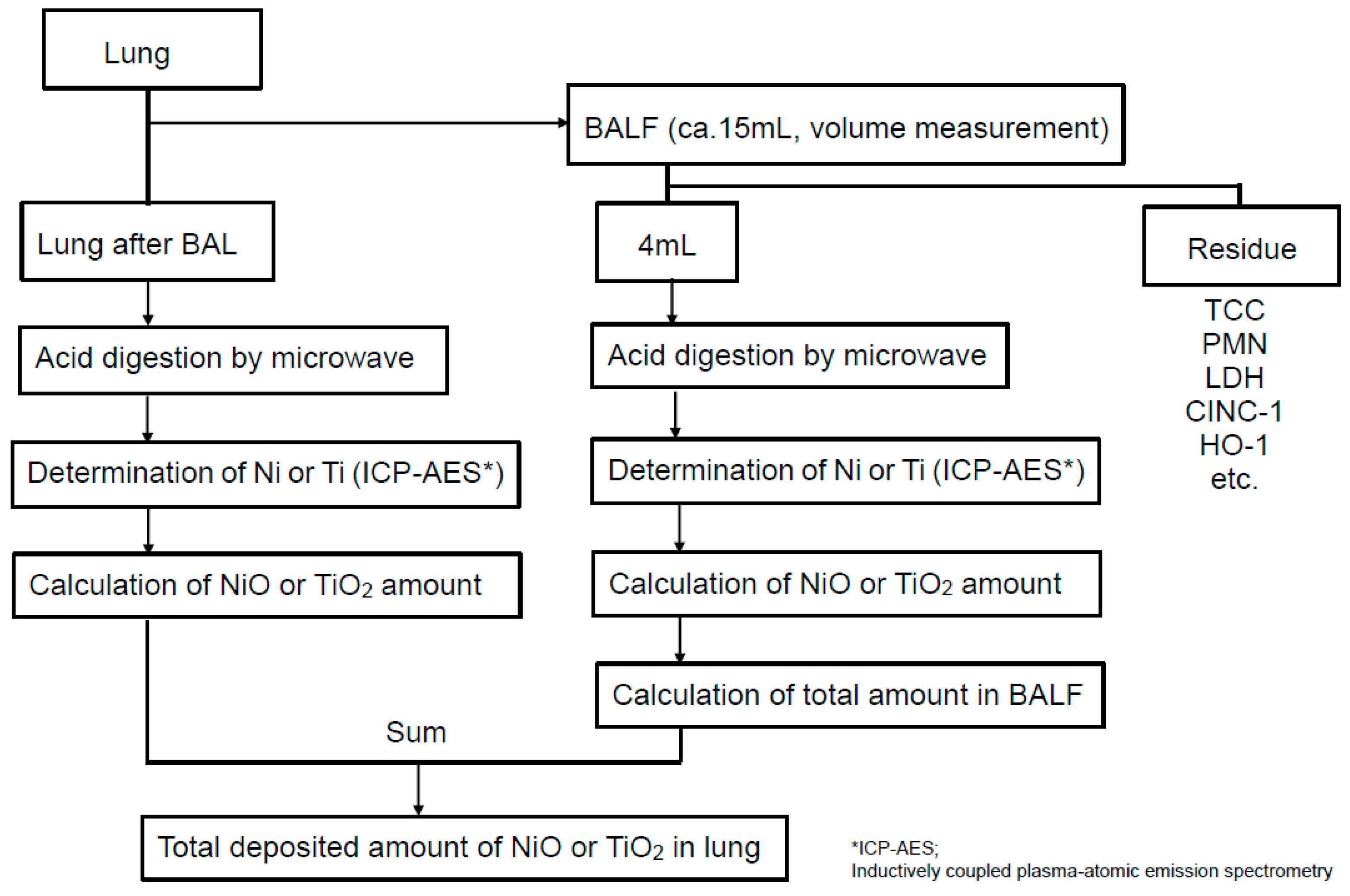
4.2. Measurement Methods of Each Nanoparticle Amounts in Lung
4.3. Observation of Cells in BALF
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferin, J.; Oberdörster, G.; Penney, D.P. Pulmonary retention of ultrafine and fine particles in rats. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1992, 6, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermudez, E.; Mangum, J.B.; Asgharian, B.; Wong, B.A.; Reverdy, E.E.; Janszen, D.B.; Hext, P.M.; Warheit, D.B.; Everitt, J.I. Long-term pulmonary responses of three laboratory rodent species to subchronic inhalation of pigmentary titanium dioxide particles. Toxicol. Sci. 2002, 70, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermudez, E.; Mangum, J.B.; Wong, B.A.; Asgharian, B.; Hext, P.M.; Warheit, D.B.; Everitt, J.I. Pulmonary responses of mice, rats, and hamsters to subchronic inhalation of ultrafine titanium dioxide particles. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 77, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Kusaka, Y.; Zhu, X.; Sato, K.; Mo, Y.; Kluz, T.; Donaldson, K. Comparative toxicity of standard nickel and ultrafine nickel in lung after intratracheal instillation. J. Occup. Health 2003, 45, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberdörster, G.; Sharp, Z.; Atudorei, V.; Elder, A.; Gelein, R.; Kreyling, W.; Cox, C. Translocation of inhaled ultrafine particles to the brain. Inhal. Toxicol. 2004, 16, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elder, A.; Gelein, R.; Silva, V.; Feikert, T.; Opanashuk, L.; Carter, J.; Potter, R.; Maynard, A.; Ito, Y.; Finkelstein, J.; et al. Translocation of inhaled ultrafine manganese oxide particles to the central nervous system. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1172–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warheit, D.B.; Webb, T.R.; Sayes, C.M.; Colvin, V.L.; Reed, K.L. Pulmonary instillation studies with nanoscale TiO2 rods and dots in rats: Toxicity is not dependent upon particle size and surface area. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 91, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, Y.; Izumi, H.; Yoshiura, Y.; Tomonaga, T.; Lee, B.W.; Okada, T.; Oyabu, T.; Myojo, T.; Kawai, K.; Yatera, K.; et al. Comparison of pulmonary inflammatory responses following intratracheal instillation and inhalation of nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsurudome, Y.; Hirano, T.; Yamato, H.; Tanaka, I.; Sagai, M.; Hirano, H.; Nagata, N.; Itoh, H.; Kasai, H. Changes in levels of 8-hydroxyguanine in DNA, its repair and OGG1 mRNA in rat lungs after intratracheal administration of diesel exhaust particles. Carcinogenesis 1999, 20, 1573–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamcakova-Dodd, A.; Stebounova, L.V.; Kim, J.S.; Vorrink, S.U.; Ault, A.P.; O’Shaughnessy, P.T.; Grassian, V.H.; Thorne, P.S. Toxicity assessment of zinc oxide nanoparticles using sub-acute and sub-chronic murine inhalation models. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberdörster, G. Toxicokinetics and effects of fibrous and nonfibrous particles. Inhal. Toxicol. 2002, 14, 29–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesterberg, T.W.; Hart, G.A. Synthetic vitreous fibers: A review of toxicology research and its impact on hazard classification. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2001, 31, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyabu, T.; Ogami, A.; Morimoto, Y.; Myojo, T.; Murakami, M.; Yamato, H.; Tanaka, I. Simple flow-through solubility measurement apparatus and its effectiveness for hazard assessment of particles/fibers. J. Occup. Health 2008, 50, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC Working Group. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; Man-Made Vitreous Fibers; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2002; Volume 81, pp. 241–270. ISBN 92-832-1281-9. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, I.; Oyabu, T.; Ishimatsu, S.; Hori, H.; Higashi, T.; Yamato, H. Pulmonary deposition and clearance of glass fiber in rat lungs after long-term inhalation. Environ. Health Perspect. 1994, 102, 215–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, I.; Yamato, H.; Oyabu, T.; Ogami, A. Biopersistence of man-made fibers by animal inhalation experiments in recent reports. Ind. Health 2001, 39, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, H.; Kasai, T.; Haratake, J.; Ishimatsu, S.; Oyabu, T.; Yamato, H.; Higashi, T.; Tanaka, I. Biological effects of inhaled magnesium sulphate whiskers in rats. Occup. Environ. Med. 1994, 51, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyabu, T.; Yamato, H.; Ogami, A.; Morimoto, Y.; Akiyama, I.; Ishimatsu, S.; Hori, H.; Tanaka, I. The effect of lung burden on biopersistence and pulmonary effects in rats exposed to potassium octatitanate whiskers by inhalation. J. Occup. Health 2004, 46, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyabu, T.; Yamato, H.; Ogami, A.; Morimoto, Y.; Akiyama, I.; Ishimatsu, S.; Hori, H.; Tanaka, I. The effect of lung burden on biopersistence and pulmonary effects in rats exposed to potassium octatitanate whiskers by intratracheal instillation. J. Occup. Health 2006, 48, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Oyabu, T.; Morimoto, Y.; Ogami, A.; Kadoya, C.; Nishi, K.; Todoroki, M.; Myojo, T.; Tanaka, I. Biopersistence of potassium hexatitanate in inhalation and intratracheal instillation studies. Inhal. Toxicol. 2011, 23, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishimatsu, S.; Hori, H.; Oyabu, T.; Tanaka, I. Biopersistence of graphite whiskers deposited in rat lungs by 4-week inhalation. Inhal. Toxicol. 2003, 15, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, I.; Ogami, A.; Oyabu, T.; Yamato, H.; Morimoto, Y.; Tanaka, I. Clearance of deposited silicon carbide whisker from rat lungs inhaled during a 4-week exposure. J. Occup. Health 2003, 45, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, I.; Ogami, A.; Oyabu, T.; Yamato, H.; Morimoto, Y.; Tanaka, I. Pulmonary effects and biopersistence of deposited silicon carbide whisker after 1-year inhalation in rats. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuguchi, Y.; Myojo, T.; Oyabu, T.; Hashiba, M.; Lee, B.W.; Yamamoto, M.; Todoroki, M.; Nishi, K.; Kadoya, C.; Ogami, A.; et al. Comparison of dose-response relations between 4-week inhalation and intratracheal instillation of NiO nanoparticles using polimorphonuclear neutrophils in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid as a biomarker of pulmonary inflammation. Inhal. Toxicol. 2013, 25, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyabu, T.; Ogami, A.; Morimoto, Y.; Shimada, M.; Lenggoro, W.; Okuyama, K.; Tanaka, I. Biopersistence of inhaled nickel oxide nanoparticles in rat lung. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19 (Suppl S1), S55–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyabu, T.; Myojo, T.; Morimoto, Y.; Ogami, A.; Hirohashi, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Todoroki, M.; Mizuguchi, Y.; Hashiba, M.; Lee, B.W.; et al. Biopersistence of inhaled MWCNT in rat lungs in a 4-week well-characterized exposure. Inhal. Toxicol. 2011, 23, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyabu, T.; Morimoto, Y.; Hirohashi, M.; Horie, M.; Kambara, T.; Lee, B.W.; Hashiba, M.; Mizuguchi, Y.; Myojo, T.; Kuroda, E. Dose-dependent pulmonary response of well-dispersed titanium dioxide nanoparticles following intratracheal instillation. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, M.; Suzuki, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Kasai, T.; Kano, H.; Sanoh, H.; Higashikubo, I.; Araki, A.; Fukushima, S. Improved method for measurement of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in rat lung. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2016, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konduru, N.; Keller, J.; Ma-Hock, L.; Gröters, S.; Landsiedel, R.; Donaghey, T.C.; Brain, J.D.; Wohlleben, W.; Molina, R.M. Biokinetics and effects of barium sulfate nanoparticles. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinohara, N.; Nakazono, T.; Ohkawa, K.; Tamura, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Morimoto, Y.; Oyabu, T.; Myojo, T.; Shimada, M.; Yamamoto, K.; et al. Long-term retention of pristine multi-walled carbon nanotubes in rat lungs after intratracheal instillation. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 36, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gate, L.; Disdier, C.; Cosnier, F.; Gagnaire, G.; Devoy, J.; Saba, W.; Brun, E.; Chalansonnet, M.; Mabondzo, A. Biopersistence and translocation to extrapulmonary organs of titanium dioxide nanoparticles after subacute inhalation exposure to aerosol in adult and elderly rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 265, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semmler, M.; Seitz, J.; Erbe, F.; Mayer, P.; Heyder, J.; Oberdorster, G.; Kreyling, W.G. Long-term clearance kinetics of inhaled ultrafine insoluble iridium particles from the rat lung, including transient translocation into secondary organs. Inhal. Toxicol. 2004, 16, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, P.E. Possible mechanisms to explain dust overloading of the lungs. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1988, 10, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, P.E.; Muhle, H.; Mermelstein, R. Chronic inhalation study findings as a basis for proposing a new occupational dust exposure limit. J. Am. Coll. Toxicol. 1991, 10, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Kim, J.; Seok, S.H.; Cho, W.S. Indium oxide (In2O3) nanoparticles induce progressive lung injury distinct from lung injuries by copper oxide (CuO) and nickel oxide (NiO) nanoparticles. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Duffin, R.; Poland, C.; Daly, P.; Murphy, F.; Drost, E.; MacNee, W.; Stone, V.; Donaldson, K. Efficiency of simple short-term in vitro assays for predicting the potential of metal oxide nanoparticles to cause pulmonary inflammation. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baisch, B.L.; Corson, N.M.; Wade-Mercer, P.; Gelein, R.; Kennell, A.J.; Oberdörster, G.; Elder, A. Equivalent titanium dioxide nanoparticle deposition by intratracheal instillation and whole body inhalation: The effect of dose rate on acute respiratory tract inflammation. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshiura, Y.; Izumi, H.; Oyabu, T.; Hashiba, M.; Kambara, T.; Mizuguchi, Y.; Lee, B.W.; Okada, T.; Tomonaga, T.; Myojo, T.; et al. Pulmonry toxicity of well-dispersed titanium dioxide nanoparticles following intratracheal instillation. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, M.; Nakaoka, A.; Morimoto, K.; Shimada, M.; Horie, M.; Morimoto, Y.; Sasaki, T. Aerosol generation by a spray-drying technique under coulomb explosion and rapid evaporation for the preparation of aerosol particles for inhalation tests. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
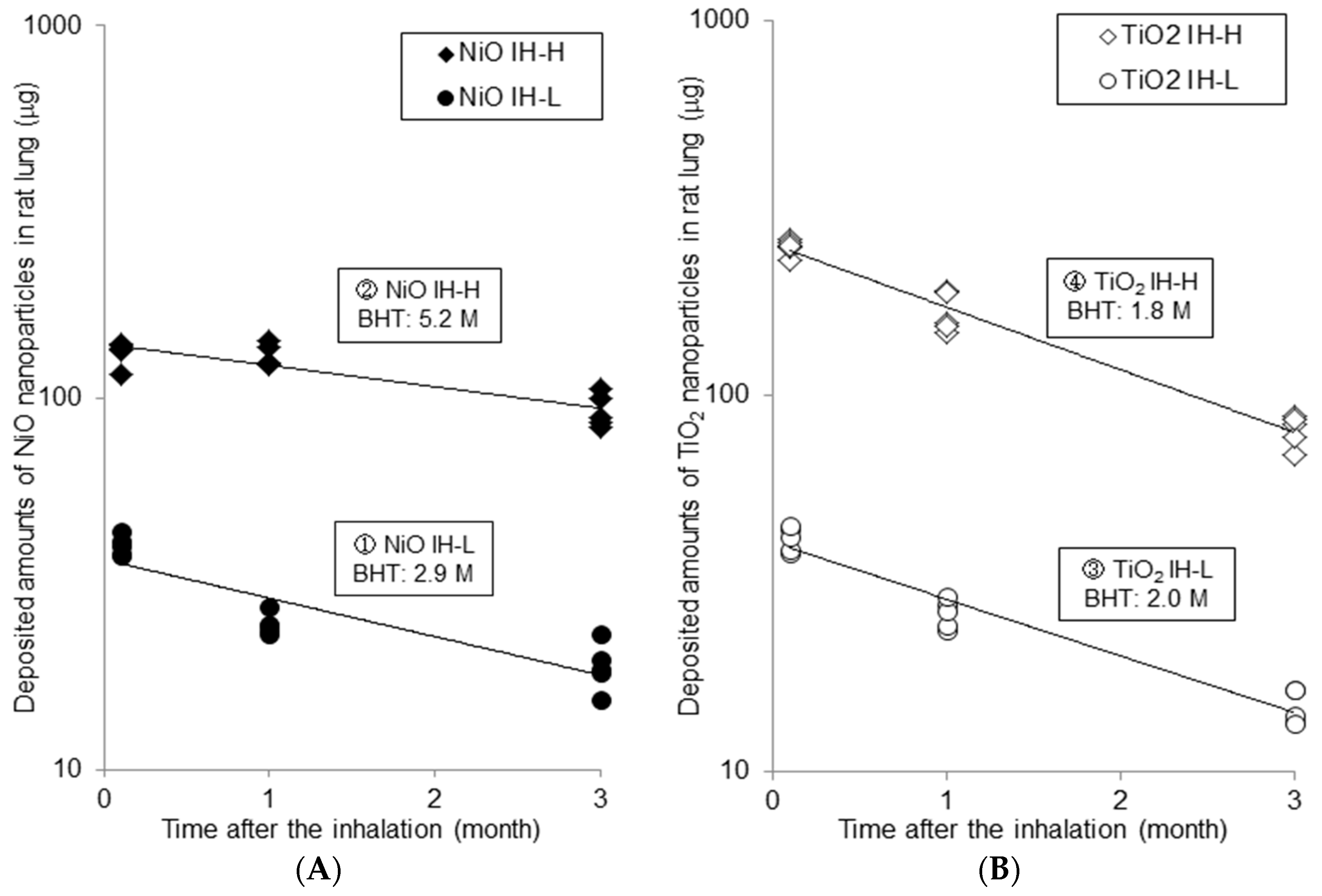
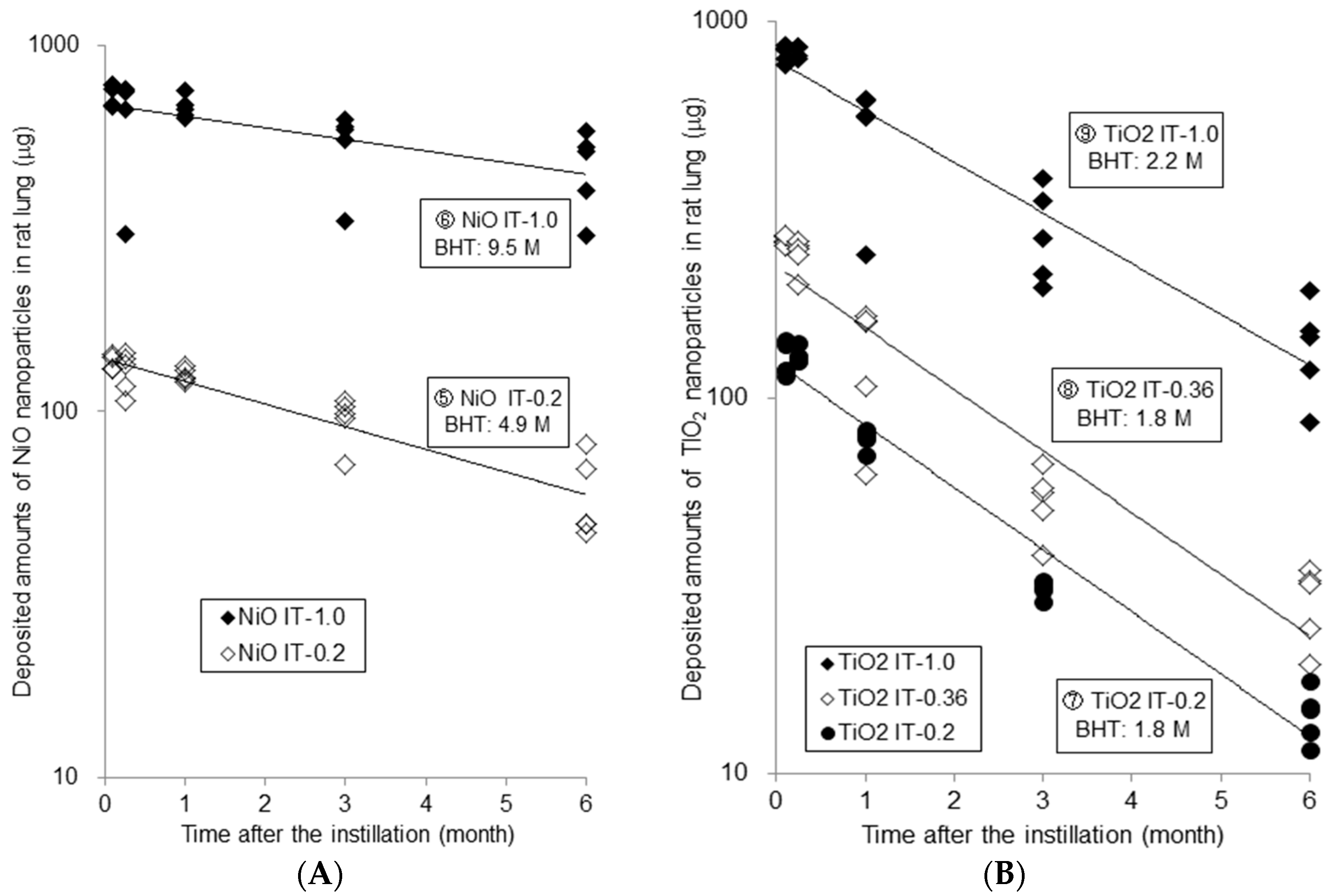
| Time | Measured Amounts of Nanoparticles in Rat Lungs (μg) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiO | TiO2 | ||||||||||||||
| Inhalation | |||||||||||||||
| ① NiO-IH-L | ② NiO-IH-H | ③ TiO2-IH-L | ④ TiO2-IH-H | ||||||||||||
| 3D | 40.0 | ± | 2.4 | 132.5 | ± | 9.9 | 41.8 | ± | 3.2 | 249.3 | ± | 12.4 | |||
| 1M | 24.6 | ± | 1.6 | 130.0 | ± | 9.1 | 26.4 | ± | 2.3 | 166.8 | ± | 20.5 | |||
| 3M | 19.0 | ± | 2.8 | 92.4 | ± | 9.5 | 14.8 | ± | 1.6 | 80.9 | ± | 7.5 | |||
| Instillation | |||||||||||||||
| ⑤ NiO-IT-0.2 | ⑥ NiO-IT-1.0 | ⑦ TiO2-IT-0.2 | ⑧ TiO2-IT-0.36 | ⑨ TiO2-IT-1.0 | |||||||||||
| 3D | 136.4 | ± | 6.5 | 738.1 | ± | 49.7 | 126.6 | ± | 12.8 | 262.5 | ± | 6.5 | 825.0 | ± | 40.8 |
| 1W | 128.7 | ± | 15.8 | 645.9 | ± | 194.5 | 130.0 | ± | 6.1 | 240.6 | ± | 24.4 | 835.5 | ± | 29.4 |
| 1M | 126.2 | ± | 5.4 | 676.4 | ± | 46.0 | 78.0 | ± | 4.6 | 130.9 | ± | 44.9 | 521.0 | ± | 159.6 |
| 3M | 95.6 | ± | 13.9 | 539.5 | ± | 119.1 | 31.2 | ± | 1.6 | 53.8 | ± | 10.6 | 278.5 | ± | 80.0 |
| 6M | 59.4 | ± | 15.4 | 465.5 | ± | 112.5 | 14.5 | ± | 2.3 | 28.7 | ± | 6.4 | 138.6 | ± | 39.9 |
| Materials | NiO Nanoparticle | TiO2 Nanoparticle | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3355 (US Research Nanomaterials) | MT-150AW (Tayca Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan) | |||
| Whole body inhalation | ||||
| Exposure period | 4 weeks (6 h/day, 5 days/week) | 4 weeks (6 h/day, 5 days/week) | ||
| Exposure concentration | ① NiO-IH-L | 0.32 ± 0.07 mg/m3 | ③ TiO2-IH-L | 0.50 ± 0.26 mg/m3 |
| ② NiO-IH-H | 1.65 ± 0.20 mg/m3 | ④ TiO2-IH-H | 1.84 ± 0.74 mg/m3 | |
| Sacrificed time | 3 days, 1, 3 months after the inhalation | 3 days, 1, 3 months after the inhalation | ||
| Intratracheal instillation | ||||
| Instilled amount * | ⑤ NiO-IT-0.2 | 0.2 mg | ⑦ TiO2-IT-0.2 | 0.2 mg |
| ⑥ NiO-IT-1.0 | 1 mg | ⑧ TiO2-IT-0.36 | 0.36 mg | |
| ⑨ TiO2-IT-1.0 | 1 mg | |||
| Particle diameter (nm, DLS) | 59.7 nm | 44.9 nm | ||
| Sacrificed time | 3 days, 1 week, 1, 3, 6 months after the instillation | 3 days, 1 week, 1, 3, 6 months after the instillation | ||
| Property | NiO Nanoparticle | TiO2 Nanoparticle |
|---|---|---|
| Shape * | Sphere | Spindle-shaped |
| Primary diameter * | 19 nm | Short: 12 nm, Long: 55 nm |
| Purity * | More than 99.5% | 99.5% |
| Surface area * (BET, m2/g) | 57 | 111 |
| Crystallinity (XRD spectra **) |  | 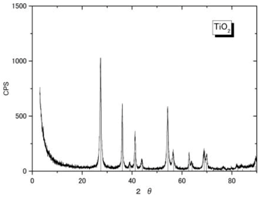 |
| Size distribution (DLS) | 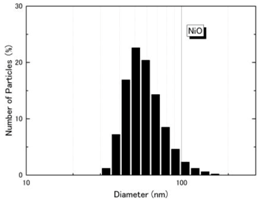 | 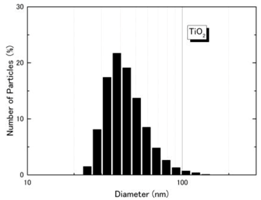 |
| TEM picture | 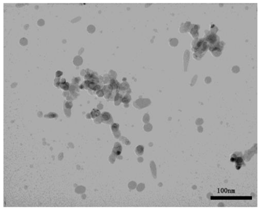 | 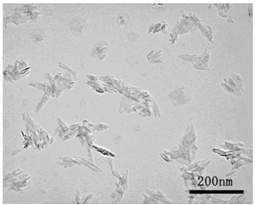 |
| NiO Nanoparticle | |||
| Step | Time (min) | Power (W) * | Temperature (°C) |
| 1 | 2 | 1000 | 50 |
| 2 | 3 | 0 | 30 |
| 3 | 25 | 1000 | 180 |
| 4 | 1 | 0 | 150 |
| 5 | 4 | 1000 | 180 |
| 6 | 10 | 1000 | 180 |
| TiO2 Nanoparticle | |||
| Step | Time (min) | Power (W) * | Temperature (°C) |
| 1 | 10 | 1000 | 240 |
| 2 | 20 | 1000 | 240 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oyabu, T.; Myojo, T.; Lee, B.-W.; Okada, T.; Izumi, H.; Yoshiura, Y.; Tomonaga, T.; Li, Y.-S.; Kawai, K.; Shimada, M.; et al. Biopersistence of NiO and TiO2 Nanoparticles Following Intratracheal Instillation and Inhalation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122757
Oyabu T, Myojo T, Lee B-W, Okada T, Izumi H, Yoshiura Y, Tomonaga T, Li Y-S, Kawai K, Shimada M, et al. Biopersistence of NiO and TiO2 Nanoparticles Following Intratracheal Instillation and Inhalation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(12):2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122757
Chicago/Turabian StyleOyabu, Takako, Toshihiko Myojo, Byeong-Woo Lee, Takami Okada, Hiroto Izumi, Yukiko Yoshiura, Taisuke Tomonaga, Yun-Shan Li, Kazuaki Kawai, Manabu Shimada, and et al. 2017. "Biopersistence of NiO and TiO2 Nanoparticles Following Intratracheal Instillation and Inhalation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 12: 2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122757
APA StyleOyabu, T., Myojo, T., Lee, B.-W., Okada, T., Izumi, H., Yoshiura, Y., Tomonaga, T., Li, Y.-S., Kawai, K., Shimada, M., Kubo, M., Yamamoto, K., Kawaguchi, K., Sasaki, T., & Morimoto, Y. (2017). Biopersistence of NiO and TiO2 Nanoparticles Following Intratracheal Instillation and Inhalation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(12), 2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122757






