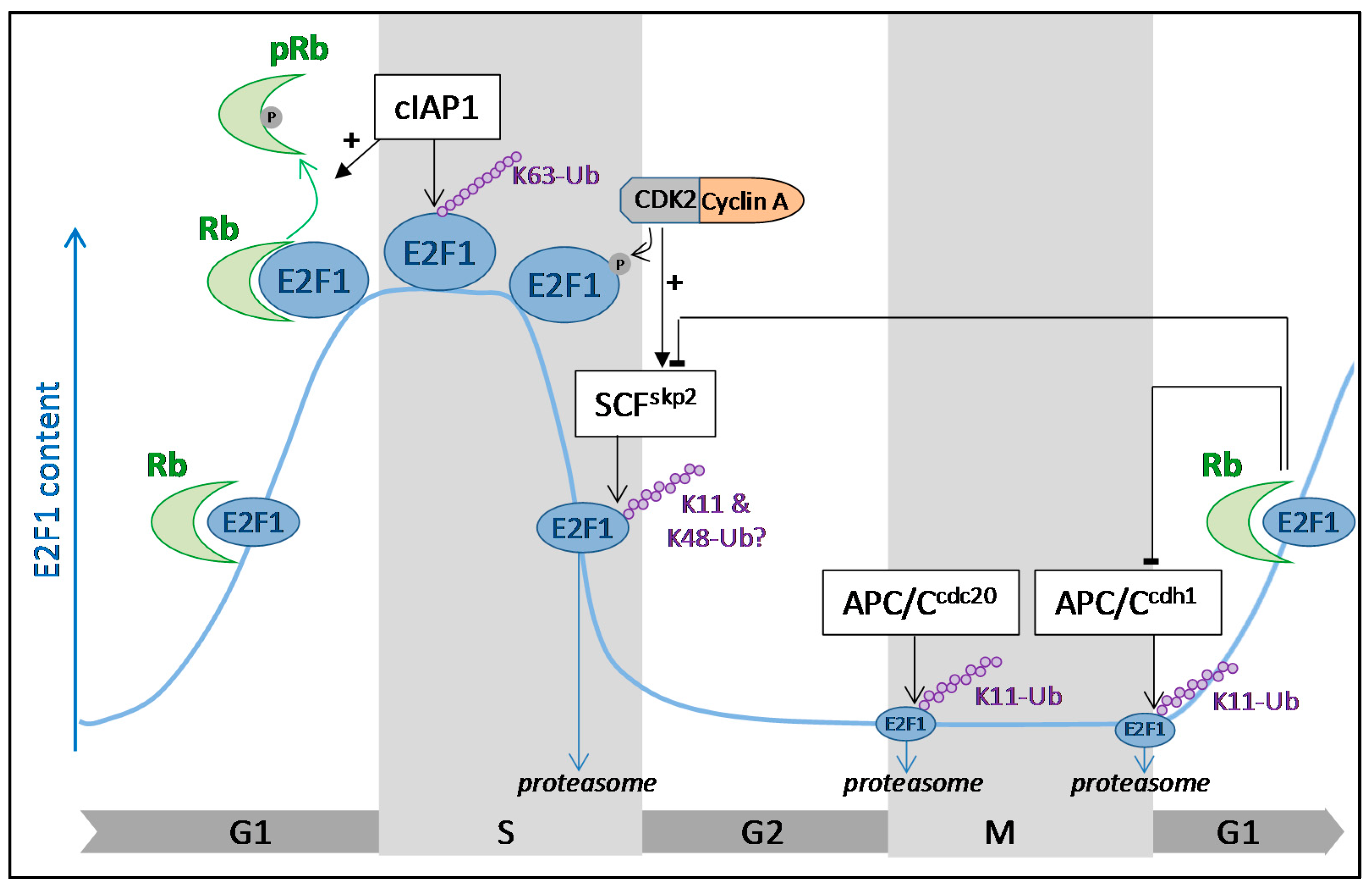
Regulation of E2F1 Transcription Factor by Ubiquitin Conjugation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Ubiquitination
3. Cell Cycle Regulation of E2F1 by Ubiquitination
4. Role of Ubiquitination in the Regulation of E2F1 upon DNA Damage
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APC/C | Anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome |
| ATM | Ataxia telangiectasia mutated |
| ATR | Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related |
| CCNE | Cyclin E gene |
| CCNA | Cyclin A gene |
| CDK2 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 |
| chk2 | Checkpoint kinase 2 |
| cIAP1 | Cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 1 |
| DHRF | Dihydrofolate reductase |
| DBD | DNA binding domain |
| DP1 | Dimerization partner 1 |
| DUBs | Deubiquitylases |
| E2F | E2 promoter binding factor |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MDM2 | Murine double minute 2 |
| PRMT | protein arginine N-methyltransferase |
| PSMD14 | 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 14 |
| Rb | Retinoblastoma |
| Skp | S-phase kinase associated protein |
| SCF | Skp1 (S-phase kinase associated protein 1)-Cullinn1-F-box |
| Ube | ubiquitin conjugating enzyme |
| UBDs | Ubiquitin-binding domains |
| Uch37 | Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase 37 |
| UPS | Ubiquitin-proteasome system |
References
- Kovesdi, I.; Reichel, R.; Nevins, J.R. Role of an adenovirus E2 promoter binding factor in E1A-mediated coordinate gene control. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 2180–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, A.S.; Reichel, R.; Kovesdi, I.; Nevins, J.R. Promoter interaction of the E1A-inducible factor E2F and its potential role in the formation of a multi-component complex. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 2061–2068. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- La Thangue, N.B.; Rigby, P.W. An adenovirus E1A-like transcription factor is regulated during the differentiation of murine embryonal carcinoma stem cells. Cell 1987, 49, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, L.R.; la Thangue, N.B. Adenovirus E1A prevents the retinoblastoma gene product from complexing with a cellular transcription factor. Nature 1991, 351, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagchi, S.; Weinmann, R.; Raychaudhuri, P. The retinoblastoma protein copurifies with E2F-I, an E1A-regulated inhibitor of the transcription factor E2F. Cell 1991, 65, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellappan, S.P.; Hiebert, S.; Mudryj, M.; Horowitz, J.M.; Nevins, J.R. The E2F transcription factor is a cellular target for the rb protein. Cell 1991, 65, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittenden, T.; Livingston, D.M.; Kaelin, W.G. The T/E1A-binding domain of the retinoblastoma product can interact selectively with a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Cell 1991, 65, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Z.; Tsai, S.Y.; Leone, G. Emerging roles of E2Fs in cancer: An exit from cell cycle control. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaal, C.; Pillai, S.; Chellappan, S.P. The Rb-E2F transcriptional regulatory pathway in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Adv. Cancer Res. 2014, 121, 147–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ertosun, M.G.; Hapil, F.Z.; Osman Nidai, O. E2F1 transcription factor and its impact on growth factor and cytokine signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016, 31, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, S.; Carr, S.M.; la Thangue, N.B. Diversity within the pRb pathway: Is there a code of conduct? Oncogene 2012, 31, 4343–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, R.; Rape, M. The increasing complexity of the ubiquitin code. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, D.; Walinda, E.; Sugase, K.; Shirakawa, M. Biological and physicochemical functions of ubiquitylation revealed by synthetic chemistry approaches. Int J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoli, C.; Skotheim, J.M.; de Bruin, R.A. Control of cell cycle transcription during G1 and S phases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krek, W.; Xu, G.; Livingston, D.M. Cyclin A-kinase regulation of E2F-1 DNA binding function underlies suppression of an S phase checkpoint. Cell 1995, 83, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hateboer, G.; Kerkhoven, R.M.; Shvarts, A.; Bernards, R.; Beijersbergen, R.L. Degradation of E2F by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway: Regulation by retinoblastoma family proteins and adenovirus transforming proteins. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 2960–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, F.; Martelli, F.; Livingston, D.M.; Wang, Z. The retinoblastoma gene product protects E2F-1 from degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 2949–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanero, M.R.; Flemington, E.K. Regulation of E2F through ubiquitin-proteasome-dependent degradation: Stabilization by the pRb tumor suppressor protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 2221–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, T.; Xiong, Y. Phosphorylation- and Skp1-independent in vitro ubiquitination of E2F1 by multiple ROC-cullin ligases. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Inuzuka, H.; Korenjak, M.; Tseng, A.; Wu, T.; Wan, L.; Kirschner, M.; Dyson, N.; Wei, W. Cdh1 regulates cell cycle through modulating the claspin/Chk1 and the Rb/E2F1 pathways. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 3305–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budhavarapu, V.N.; White, E.D.; Mahanic, C.S.; Chen, L.; Lin, F.T.; Lin, W.C. Regulation of E2F1 by APC/CCdh1 via K11 linkage-specific ubiquitin chain formation. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 2030–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhang, P. The function of APC/CCdh1 in cell cycle and beyond. Cell Div. 2009, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilberto, S.; Peter, M. Dynamic ubiquitin signaling in cell cycle regulation. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 2259–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peart, M.J.; Poyurovsky, M.V.; Kass, E.M.; Urist, M.; Verschuren, E.W.; Summers, M.K.; Jackson, P.K.; Prives, C. APC/C(Cdc20) targets E2F1 for degradation in prometaphase. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 3956–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Kobayashi, R.; Galaktionov, K.; Beach, D. pl9Skp1 and p45Skp2 are essential elements of the cyclin A-CDK2 S phase kinase. Cell 1995, 82, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, A.; Wirbelauer, C.; Scheffner, M.; Krek, W. Interaction between ubiquitin-protein ligase SCFSKP2 and E2F-1 underlies the regulation of E2F-1 degradation. Nat. Cell Biol. 1999, 1, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, C. F-box protein Skp2: A novel transcriptional target of E2F. Oncogene 2006, 25, 2615–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binné, U.K.; Classon, M.K.; Dick, F.A.; Wei, W.; Rape, M.; Kaelin, W.G.; Näär, A.M.; Dyson, N.J. Retinoblastoma protein and anaphase-promoting complex physically interact and functionally cooperate during cell-cycle exit. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelli, F.; Hamilton, T.; Silver, D.P.; Sharpless, N.E.; Bardeesy, N.; Rokas, M.; DePinho, R.A.; Livingston, D.M.; Grossman, S.R. p19ARF targets certain E2F species for degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4455–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizos, H.; Scurr, L.L.; Irvine, M.; Alling, N.J.; Kefford, R.F. p14ARF regulates E2F-1 ubiquitination and degradation via a p53-dependent mechanism. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; Rayburn, E.R.; Agrawal, S.; Zhang, R. Stabilization of E2F1 protein by MDM2 through the E2F1 ubiquitination pathway. Oncogene 2005, 24, 7238–7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Ma, A.; Zhang, L.; Jin, W.L.; Qian, Y.; Xu, G.; Qiu, B.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xia, Q. Poh1 deubiquitylates and stabilizes E2F1 to promote tumour formation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moniz, S.; Bandarra, D.; Biddlestone, J.; Campbell, K.J.; Komander, D.; Bremm, A.; Rocha, S. Cezanne regulates E2F1-dependent HIF2α expression. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 3082–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahanic, C.S.; Budhavarapu, V.; Graves, J.D.; Li, G.; Lin, W.C. Regulation of E2 promoter binding factor 1 (E2F1) transcriptional activity through a deubiquitinating enzyme, UCH37. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 26508–26522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glorian, V.; Allègre, J.; Berthelet, J.; Dumetier, B.; Boutanquoi, P.M.; Droin, N.; Kayaci, C.; Cartier, J.; Gemble, S.; Marcion, G.; et al. DNA damage and S phase-dependent E2F1 stabilization requires the cIAP1 E3-ubiquitin ligase and is associated with K63-poly-ubiquitination on lysine 161/164 residues. Cell Death Dis 2017, 8, e2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, H.J.; Rape, M. Enhanced protein degradation by branched ubiquitin chains. Cell 2014, 157, 910–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.C.; Lin, F.T.; Nevins, J.R. Selective induction of E2F1 in response to DNA damage, mediated by ATM-dependent phosphorylation. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 1833–1844. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stevens, C.; Smith, L.; la Thangue, N.B. Chk2 activates E2F-1 in response to DNA damage. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontaki, H.; Talianidis, I. Lysine methylation regulates E2F1-induced cell death. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lezina, L.; Aksenova, V.; Ivanova, T.; Purmessur, N.; Antonov, A.V.; Tentler, D.; Fedorova, O.; Garabadgiu, A.V.; Talianidis, I.; Melino, G.; et al. KMTase Set7/9 is a critical regulator of E2F1 activity upon genotoxic stress. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 1889–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Moehlenbrink, J.; Lu, Y.C.; Zalmas, L.P.; Sagum, C.A.; Carr, S.; McGouran, J.F.; Alexander, L.; Fedorov, O.; Munro, S.; et al. Arginine methylation-dependent reader-writer interplay governs growth control by E2F-1. Mol. Cell 2013, 52, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, I.; Higuchi, M.; Gotoh, Y. Neddylation controls the target specificity of E2F1 and apoptosis induction. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3954–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianari, A.; Gallo, R.; Palma, M.; Alesse, E.; Gulino, A. Specific role for p300/CREB-binding protein-associated factor activity in E2F1 stabilization in response to DNA damage. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 30830–30835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galbiati, L.; Mendoza-Maldonado, R.; Gutierrez, M.I.; Giacca, M. Regulation of E2F-1 after DNA damage by p300-mediated acetylation and ubiquitination. Cell Cycle 2005, 4, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, E.C.; Zheng, S.; Munro, S.; Liu, G.; Carr, S.M.; Moehlenbrink, J.; Lu, Y.C.; Stimson, L.; Khan, O.; Konietzny, R.; et al. Arginine methylation controls growth regulation by E2F-1. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 1785–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftus, S.J.; Liu, G.; Carr, S.M.; Munro, S.; La Thangue, N.B. NEDDylation regulates E2F-1-dependent transcription. EMBO Rep. 2012, 13, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Lin, C.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Ohgi, K.A.; Grinstein, J.D.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Rosenfeld, M.G. NcRNA- and Pc2 methylation-dependent gene relocation between nuclear structures mediates gene activation programs. Cell 2011, 147, 773–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagan, R.; Flint, K.J.; Jones, N. Phosphorylation of E2F-1 modulates its interaction with the retinoblastoma gene product and the adenoviral E4 19 kDa protein. Cell 1994, 78, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, I.A.; Nakrieko, K.A.; Dagnino, L. Phosphorylation by p38 MAP kinase is required for E2F1 degradation and keratinocyte differentiation. Oncogene 2009, 28, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Liu, K.; Lin, F.T.; Lin, W.C. A role for 14–3-3 tau in E2F1 stabilization and DNA damage-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 54140–54152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pediconi, N.; Ianari, A.; Costanzo, A.; Belloni, L.; Gallo, R.; Cimino, L.; Porcellini, A.; Screpanti, I.; Balsano, C.; Alesse, E.; et al. Differential regulation of E2F1 apoptotic target genes in response to DNA damage. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartier, J.; Berthelet, J.; Marivin, A.; Gemble, S.; Edmond, V.; Plenchette, S.; Lagrange, B.; Hammann, A.; Dupoux, A.; Delva, L.; et al. Cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein-1 (cIAP1) can regulate E2F1 transcription factor-mediated control of cyclin transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 26406–26417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, I.A.; Vespa, A.; Dagnino, L. A novel mechanism of E2F1 regulation via nucleocytoplasmic shuttling: Determinants of nuclear import and export. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 2186–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dubrez, L. Regulation of E2F1 Transcription Factor by Ubiquitin Conjugation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2188. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102188
Dubrez L. Regulation of E2F1 Transcription Factor by Ubiquitin Conjugation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(10):2188. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102188
Chicago/Turabian StyleDubrez, Laurence. 2017. "Regulation of E2F1 Transcription Factor by Ubiquitin Conjugation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 10: 2188. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102188
APA StyleDubrez, L. (2017). Regulation of E2F1 Transcription Factor by Ubiquitin Conjugation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(10), 2188. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102188