Neuron–Glia Crosstalk and Neuropathic Pain: Involvement in the Modulation of Motor Activity in the Orofacial Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Chronic Orofacial Pain
3. Neuropathic Orofacial Pain
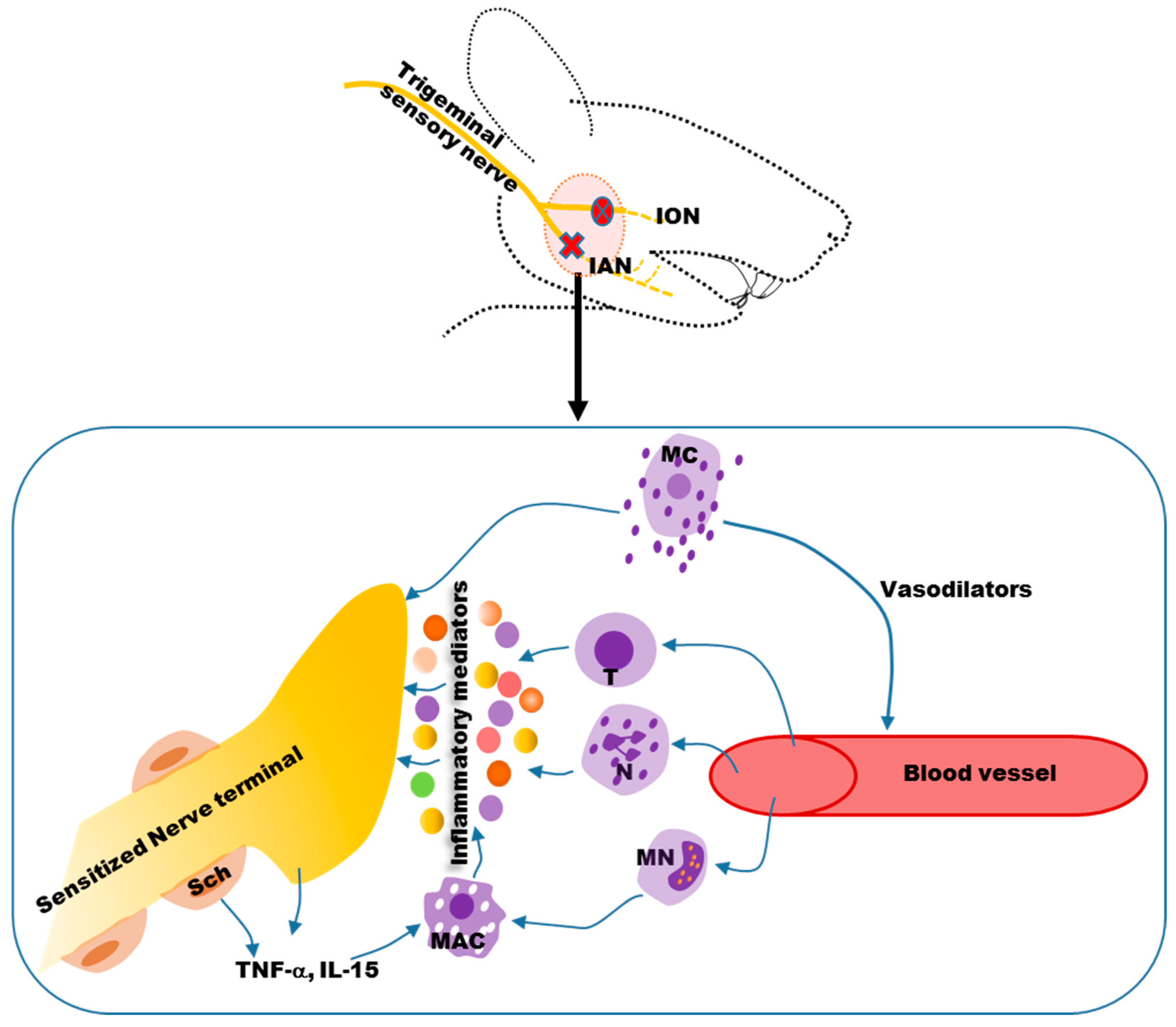
4. Mechanisms of Neuropathic Orofacial Pain: Glial Involvement
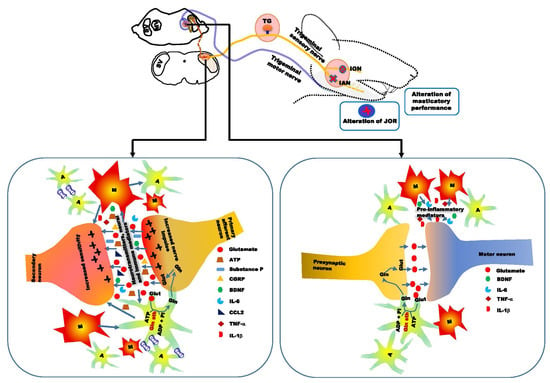
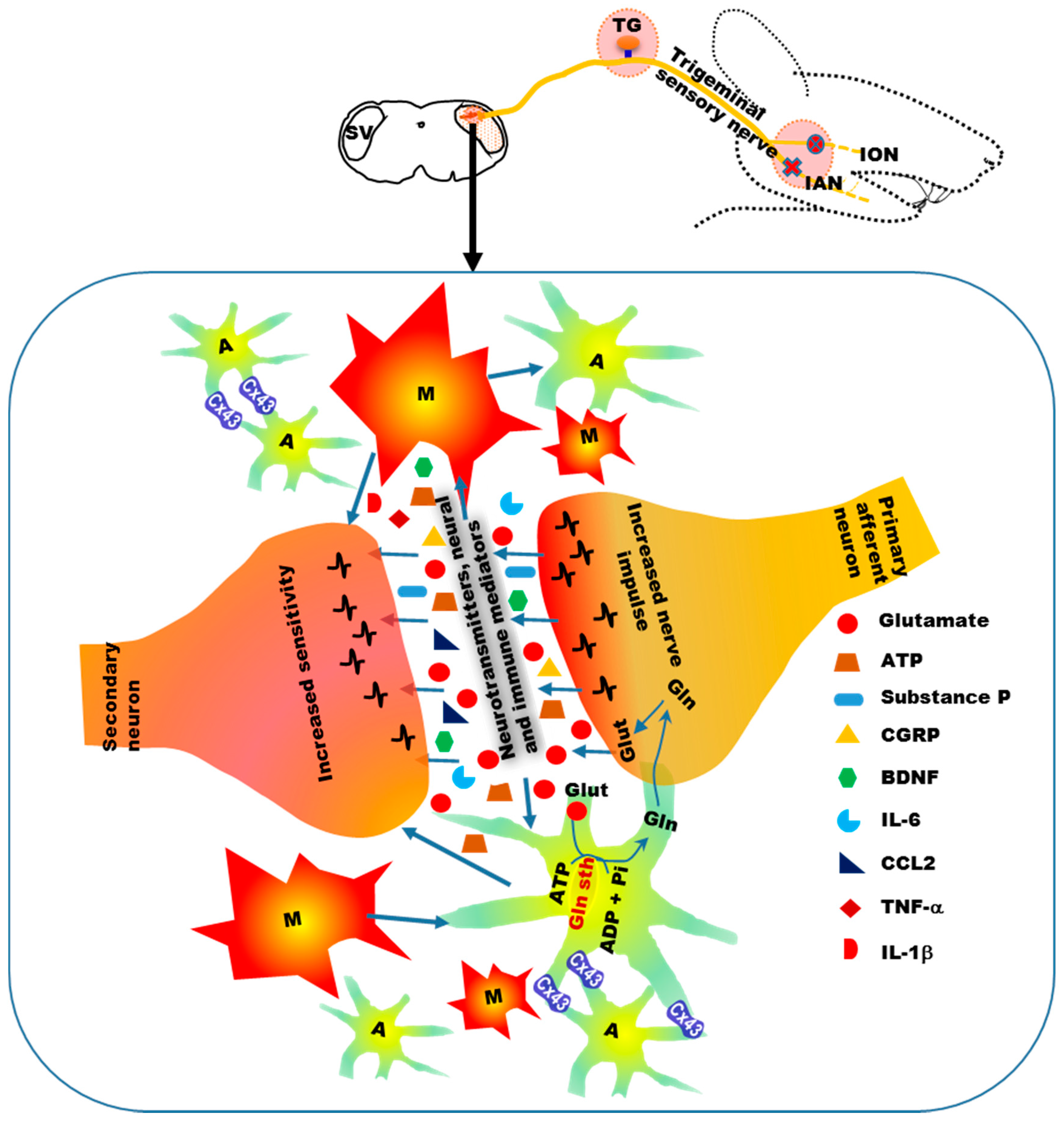
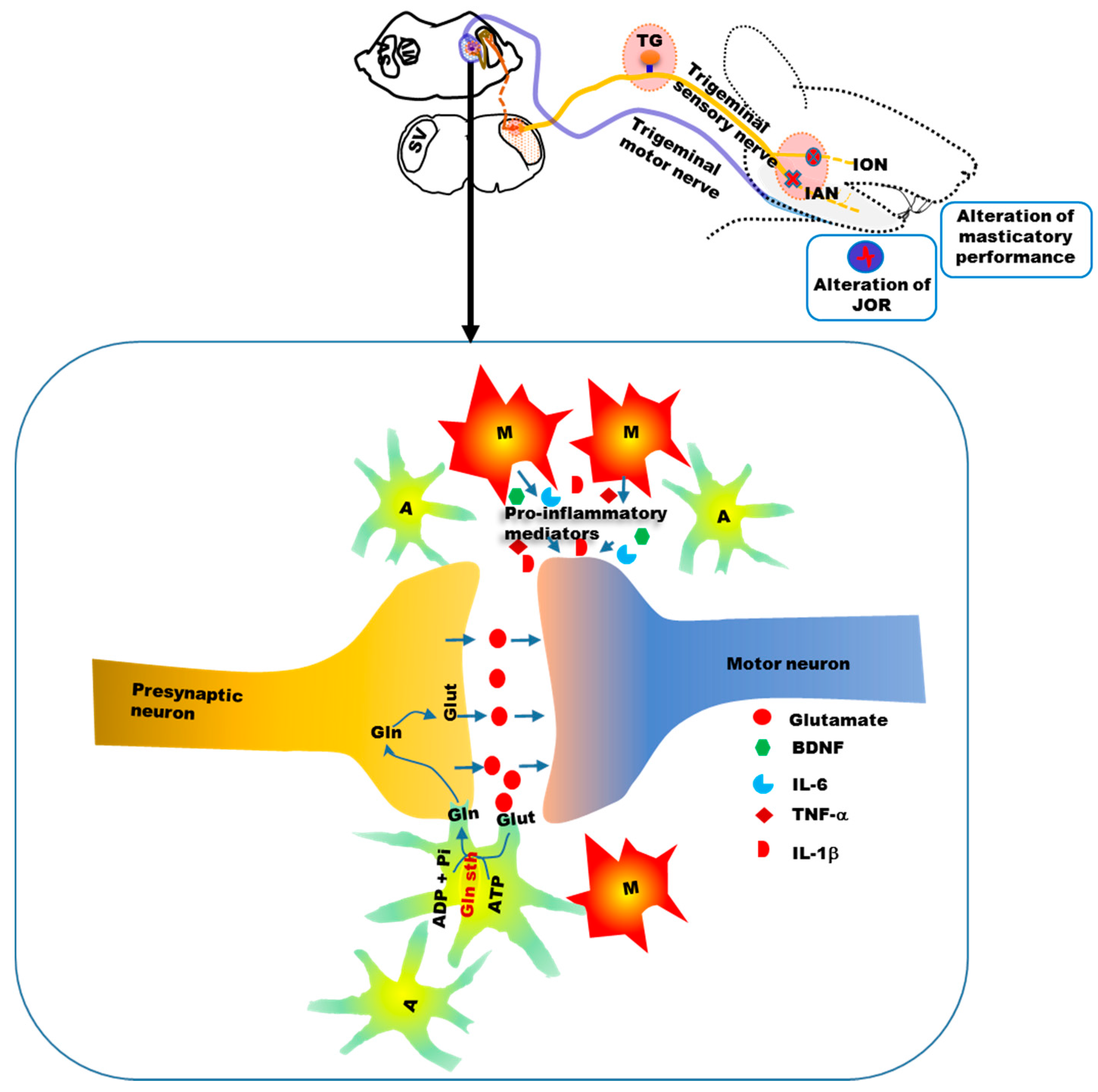
5. Alteration of Orofacial Motor Activity in Neuropathic Pain: Glial Involvement
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duenas, M.; Ojeda, B.; Salazar, A.; Mico, J.A.; Failde, I. A review of chronic pain impact on patients, their social environment and the health care system. J. Pain Res. 2016, 9, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.H.; Cutrer, F.M. Numbness matters: A clinical review of trigeminal neuropathy. Cephalalgia 2011, 31, 1131–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoliel, R.; Sharav, Y. Chronic orofacial pain. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2010, 14, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sessle, B.J. Acute and chronic craniofacial pain: Brainstem mechanisms of nociceptive transmission and neuroplasticity, and their clinical correlates. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2000, 11, 57–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macfarlane, T.V.; Blinkhorn, A.S.; Davies, R.M.; Ryan, P.; Worthington, H.V.; Macfarlane, G.J. Orofacial pain: Just another chronic pain? Results from a population-based survey. Pain 2002, 99, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewska, J.M. Differential diagnosis of facial pain and guidelines for management. Br. J. Anaesth. 2013, 111, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maarbjerg, S.; Di Stefano, G.; Bendtsen, L.; Cruccu, G. Trigeminal neuralgia-diagnosis and treatment. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.N.; Meyer, R.A. Mechanisms of neuropathic pain. Neuron 2006, 52, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakir, H.M.; Mostafeezur, R.M.; Suzuki, A.; Hitomi, S.; Suzuki, I.; Maeda, T.; Seo, K.; Yamada, Y.; Yamamura, K.; Lev, S.; et al. Expression of trpv1 channels after nerve injury provides an essential delivery tool for neuropathic pain attenuation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwata, K.; Imamura, Y.; Honda, K.; Shinoda, M. Physiological mechanisms of neuropathic pain: The orofacial region. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2011, 97, 227–250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sessle, B.J. Peripheral and central mechanisms of orofacial inflammatory pain. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2011, 97, 179–206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, M.; Wu, G.; Wu, L.J. Neuronal and microglial mechanisms of neuropathic pain. Mol. Brain 2011, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoliel, R.; Svensson, P.; Heir, G.M.; Sirois, D.; Zakrzewska, J.; Oke-Nwosu, J.; Torres, S.R.; Greenberg, M.S.; Klasser, G.D.; Katz, J.; et al. Persistent orofacial muscle pain. Oral. Dis. 2011, 17, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoliel, R.; Zadik, Y.; Eliav, E.; Sharav, Y. Peripheral painful traumatic trigeminal neuropathy: Clinical features in 91 cases and proposal of novel diagnostic criteria. J. Orofac. Pain 2012, 26, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murray, H.; Locker, D.; Mock, D.; Tenenbaum, H.C. Pain and the quality of life in patients referred to a craniofacial pain unit. J. Orofac. Pain 1996, 10, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scholz, J.; Woolf, C.J. The neuropathic pain triad: Neurons, immune cells and glia. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, L.; Cahill, C.M. TNF-α and neuropathic pain—A review. J. Neuroinflamm. 2010, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Watanabe, M.; Shimizu, K.; Zou, S.; LaGraize, S.C.; Wei, F.; Dubner, R.; Ren, K. Glial-cytokine-neuronal interactions underlying the mechanisms of persistent pain. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 6006–6018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, K.; Dubner, R. Neuron-glia crosstalk gets serious: Role in pain hypersensitivity. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2008, 21, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarberg, B.H.; Billington, R. Consequences of neuropathic pain: Quality-of-life issues and associated costs. Am. J. Manag. Care 2006, 12, S263–S268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doth, A.H.; Hansson, P.T.; Jensen, M.P.; Taylor, R.S. The burden of neuropathic pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis of health utilities. Pain 2010, 149, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, V.R.; McBeth, J.; Zakrzewska, J.M.; Lunt, M.; Macfarlane, G.J. The epidemiology of chronic syndromes that are frequently unexplained: Do they have common associated factors? Int. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 35, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, D.; Obermann, M.; Yoon, M.S.; Poitz, F.; Hansen, N.; Slomke, M.A.; Dommes, P.; Gizewski, E.; Diener, H.C.; Katsarava, Z. Prevalence of trigeminal neuralgia and persistent idiopathic facial pain: A population-based study. Cephalalgia 2011, 31, 1542–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koopman, J.S.; Dieleman, J.P.; Huygen, F.J.; de Mos, M.; Martin, C.G.; Sturkenboom, M.C. Incidence of facial pain in the general population. Pain 2009, 147, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouhassira, D.; Lanteri-Minet, M.; Attal, N.; Laurent, B.; Touboul, C. Prevalence of chronic pain with neuropathic characteristics in the general population. Pain 2008, 136, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworkin, S.F.; LeResche, L. Research diagnostic criteria for temporomandibular disorders: Review, criteria, examinations and specifications, critique. J. Craniomandib. Disord. 1992, 6, 301–355. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoon, M.S.; Mueller, D.; Hansen, N.; Poitz, F.; Slomke, M.; Dommes, P.; Diener, H.C.; Katsarava, Z.; Obermann, M. Prevalence of facial pain in migraine: A population-based study. Cephalalgia 2010, 30, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, S.; Coakham, H.B. Trigeminal neuralgia: Pathology and pathogenesis. Brain 2001, 124, 2347–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renton, T.; Yilmaz, Z. Profiling of patients presenting with posttraumatic neuropathy of the trigeminal nerve. J. Orofac. Pain 2011, 25, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scala, A.; Checchi, L.; Montevecchi, M.; Marini, I.; Giamberardino, M.A. Update on burning mouth syndrome: Overview and patient management. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2003, 14, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melis, M.; Lobo, S.L.; Ceneviz, C.; Zawawi, K.; Al-Badawi, E.; Maloney, G.; Mehta, N. Atypical odontalgia: A review of the literature. Headache 2003, 43, 1060–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kost, R.G.; Straus, S.E. Postherpetic neuralgia—Pathogenesis, treatment, and prevention. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nixdorf, D.R.; Moana-Filho, E.J.; Law, A.S.; McGuire, L.A.; Hodges, J.S.; John, M.T. Frequency of persistent tooth pain after root canal therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renton, T.; Adey-Viscuso, D.; Meechan, J.G.; Yilmaz, Z. Trigeminal nerve injuries in relation to the local anaesthesia in mandibular injections. Br. Dent. J. 2010, 209, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.G.; Holmin, S.; Mathiesen, T.; Meyerson, B.A.; Linderoth, B. Possible role of inflammatory mediators in tactile hypersensitivity in rat models of mononeuropathy. Pain 2000, 88, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; van Rooijen, N.; Tracey, D.J. Depletion of macrophages reduces axonal degeneration and hyperalgesia following nerve injury. Pain 2000, 86, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.C.; Vakoula, A.; Veinote, R. Inflammatory hypersensitivity in a rat model of trigeminal neuropathic pain. Arch. Oral Biol. 2003, 48, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.C.; Rao, R.D. Interleukin-6 and nerve growth factor levels in peripheral nerve and brainstem after trigeminal nerve injury in the rat. Arch. Oral Biol. 2001, 46, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.K.; Old, E.A.; Malcangio, M. Neuropathic pain and cytokines: Current perspectives. J. Pain Res. 2013, 6, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, G.; MacLean, A.G.; Philipp, M.T. Cytokines and chemokines at the crossroads of neuroinflammation, neurodegeneration, and neuropathic pain. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uceyler, N.; Tscharke, A.; Sommer, C. Early cytokine expression in mouse sciatic nerve after chronic constriction nerve injury depends on calpain. Brain Behav. Immun. 2007, 21, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafers, M.; Sommer, C. Anticytokine therapy in neuropathic pain management. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2007, 7, 1613–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, T.M.; Verri, W.A., Jr.; Fukada, S.Y.; Guerrero, A.T.; Santodomingo-Garzon, T.; Poole, S.; Parada, C.A.; Ferreira, S.H.; Cunha, F.Q. TNF-α and IL-1β mediate inflammatory hypernociception in mice triggered by b1 but not b2 kinin receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 573, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, N.; Kikuchi, S.; Konno, S.; Sekiguchi, M.; Watanabe, K. Anti-TNF-α antibody reduces pain-behavioral changes induced by epidural application of nucleus pulposus in a rat model depending on the timing of administration. Spine 2007, 32, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanella, J.M.; Burright, E.N.; Hildebrand, K.; Hobot, C.; Cox, M.; Christoferson, L.; McKay, W.F. Effect of etanercept, a tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitor, on neuropathic pain in the rat chronic constriction injury model. Spine 2008, 33, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toews, A.D.; Barrett, C.; Morell, P. Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 is responsible for macrophage recruitment following injury to sciatic nerve. J. Neurosci. Res. 1998, 53, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskinen, H.S.; Roytta, M. Increased expression of chemokines (MCP-1, MIP-1α, RANTES) after peripheral nerve transection. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2000, 5, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlikowski, D.; Chazaud, B.; Plonquet, A.; Poron, F.; Sharshar, T.; Maison, P.; Raphael, J.C.; Gherardi, R.K.; Creange, A. Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 and chemokine receptor CCR2 productions in guillain-barre syndrome and experimental autoimmune neuritis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2003, 134, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, L.R.; Maier, S.F. Beyond neurons: Evidence that immune and glial cells contribute to pathological pain states. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 981–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, F.A.; Bhangoo, S.K.; Miller, R.J. Chemokines: Integrators of pain and inflammation. Nat. Rev. 2005, 4, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.H.; Yang, B.; Donnelly, D.F.; Ma, C.; LaMotte, R.H. MCP-1 enhances excitability of nociceptive neurons in chronically compressed dorsal root ganglia. J. Neurophysiol. 2006, 96, 2189–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.B.; Tran, P.B.; Gillard, S.E.; Hurley, R.W.; Hammond, D.L.; Miller, R.J. Chemokines and glycoprotein 120 produce pain hypersensitivity by directly exciting primary nociceptive neurons. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 5027–5035. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abbadie, C.; Lindia, J.A.; Cumiskey, A.M.; Peterson, L.B.; Mudgett, J.S.; Bayne, E.K.; DeMartino, J.A.; MacIntyre, D.E.; Forrest, M.J. Impaired neuropathic pain responses in mice lacking the chemokine receptor CCR2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 7947–7952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, F.A.; Sun, J.; Waters, S.M.; Ma, C.; Ren, D.; Ripsch, M.; Steflik, J.; Cortright, D.N.; Lamotte, R.H.; Miller, R.J. Excitatory monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 signaling is up-regulated in sensory neurons after chronic compression of the dorsal root ganglion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14092–14097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Wan, Y.; Wang, X. CCL2 and CXCL1 trigger calcitonin gene-related peptide release by exciting primary nociceptive neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 82, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.; Miller, R.J. Activation of the nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) mediates upregulation of CCR2 chemokine receptors in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons: A possible mechanism for activity-dependent transcription in DRG neurons in association with neuropathic pain. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2008, 37, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kettenmann, H.; Verkhratsky, A. Neuroglia: The 150 years after. Trends Neurosci. 2008, 31, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jessen, K.R.; Mirsky, R. Glial cells in the enteric nervous system contain glial fibrillary acidic protein. Nature 1980, 286, 736–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volterra, A.; Meldolesi, J. Astrocytes, from brain glue to communication elements: The revolution continues. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.R.; Lopes, A.H.; Talbot, J.; Cecilio, N.T.; Rossato, M.F.; Silva, R.L.; Souza, G.R.; Silva, C.R.; Lucas, G.; Fonseca, B.A.; et al. Neuro-immune-glia interactions in the sensory ganglia account for the development of acute herpetic neuralgia. J. Neurosci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanani, M. Satellite glial cells in sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia: In search of function. Brain Res. Rev. 2010, 64, 304–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherkas, P.S.; Huang, T.Y.; Pannicke, T.; Tal, M.; Reichenbach, A.; Hanani, M. The effects of axotomy on neurons and satellite glial cells in mouse trigeminal ganglion. Pain 2004, 110, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunjigake, K.K.; Goto, T.; Nakao, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Yamaguchi, K. Activation of satellite glial cells in rat trigeminal ganglion after upper molar extraction. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 2009, 42, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaji, K.; Shinoda, M.; Honda, K.; Unno, S.; Shimizu, N.; Iwata, K. Connexin 43 contributes to ectopic orofacial pain following inferior alveolar nerve injury. Mol. Pain 2016, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donegan, M.; Kernisant, M.; Cua, C.; Jasmin, L.; Ohara, P.T. Satellite glial cell proliferation in the trigeminal ganglia after chronic constriction injury of the infraorbital nerve. Glia 2013, 61, 2000–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohara, P.T.; Vit, J.P.; Bhargava, A.; Jasmin, L. Evidence for a role of connexin 43 in trigeminal pain using rna interference in vivo. J. Neurophysiol. 2008, 100, 3064–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capuano, A.; De Corato, A.; Lisi, L.; Tringali, G.; Navarra, P.; Dello Russo, C. Proinflammatory-activated trigeminal satellite cells promote neuronal sensitization: Relevance for migraine pathology. Mol. Pain 2009, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanani, M. Intercellular communication in sensory ganglia by purinergic receptors and gap junctions: Implications for chronic pain. Brain Res. 2012, 1487, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, G.W.; Wang, C.; Huang, L.Y. Neuronal soma-satellite glial cell interactions in sensory ganglia and the participation of purinergic receptors. Neuron Glia Biol. 2010, 6, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suadicani, S.O.; Cherkas, P.S.; Zuckerman, J.; Smith, D.N.; Spray, D.C.; Hanani, M. Bidirectional calcium signaling between satellite glial cells and neurons in cultured mouse trigeminal ganglia. Neuron Glia Boil. 2010, 6, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weick, M.; Cherkas, P.S.; Hartig, W.; Pannicke, T.; Uckermann, O.; Bringmann, A.; Tal, M.; Reichenbach, A.; Hanani, M. P2 receptors in satellite glial cells in trigeminal ganglia of mice. Neuroscience 2003, 120, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, G.; Fumagalli, M.; Verderio, C.; Abbracchio, M.P.; Ceruti, S. Expression and contribution of satellite glial cells purinoceptors to pain transmission in sensory ganglia: An update. Neuron Glia Boil. 2010, 6, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceruti, S.; Fumagalli, M.; Villa, G.; Verderio, C.; Abbracchio, M.P. Purinoceptor-mediated calcium signaling in primary neuron-glia trigeminal cultures. Cell Calcium 2008, 43, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, M.; Takahashi, M.; Matsumoto, S. Contribution of the activation of satellite glia in sensory ganglia to pathological pain. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2009, 33, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katagiri, A.; Shinoda, M.; Honda, K.; Toyofuku, A.; Sessle, B.J.; Iwata, K. Satellite glial cell P2Y12 receptor in the trigeminal ganglion is involved in lingual neuropathic pain mechanisms in rats. Mol. Pain 2012, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, T.; Oh, S.B.; Takeda, M.; Shinoda, M.; Sato, T.; Gunjikake, K.K.; Iwata, K. Recent advances in basic research on the trigeminal ganglion. J. Physiol. Sci. 2016, 66, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Schmidt, T.M.; Perez-Leighton, C.E.; Kofuji, P. Inwardly rectifying potassium channel kir4.1 is responsible for the native inward potassium conductance of satellite glial cells in sensory ganglia. Neuroscience 2016, 166, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellot-Saez, A.; Kekesi, O.; Morley, J.W.; Buskila, Y. Astrocytic modulation of neuronal excitability through K+ spatial buffering. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 77, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vit, J.P.; Ohara, P.T.; Bhargava, A.; Kelley, K.; Jasmin, L. Silencing the kir4.1 potassium channel subunit in satellite glial cells of the rat trigeminal ganglion results in pain-like behavior in the absence of nerve injury. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 4161–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thalakoti, S.; Patil, V.V.; Damodaram, S.; Vause, C.V.; Langford, L.E.; Freeman, S.E.; Durham, P.L. Neuron-glia signaling in trigeminal ganglion: Implications for migraine pathology. Headache 2007, 47, 1008–1023; discussion 1024–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, N.J.; Barres, B.A. Signaling between glia and neurons: Focus on synaptic plasticity. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2005, 15, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Waxman, S.G.; Hains, B.C. Modulation of thalamic nociceptive processing after spinal cord injury through remote activation of thalamic microglia by cysteine cysteine chemokine ligand 21. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 8893–8902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.K.; Han, S.R.; Park, M.K.; Kim, M.J.; Bae, Y.C.; Kim, S.K.; Park, J.S.; Ahn, D.K. Behavioral evidence for the differential regulation of p-p38 MAPK and p-NF-κB in rats with trigeminal neuropathic pain. Mol. Pain 2011, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.; Guo, W.; Zou, S.; Ren, K.; Dubner, R. Supraspinal glial-neuronal interactions contribute to descending pain facilitation. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 10482–10495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.R.; Suter, M.R.; Kawasaki, Y.; Huang, J.; Pertin, M.; Kohno, T.; Berde, C.B.; Decosterd, I.; Ji, R.R. Nerve conduction blockade in the sciatic nerve prevents but does not reverse the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in spinal microglia in the rat spared nerve injury model. Anesthesiology 2007, 107, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Strong, J.A.; Zhang, J.M. Early blockade of injured primary sensory afferents reduces glial cell activation in two rat neuropathic pain models. Neuroscience 2009, 160, 847–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, Y.; Ibuki, T.; Matsumura, K.; Namba, M.; Yamazaki, Y.; Poole, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Kobayashi, S. Interleukin-6 is a candidate molecule that transmits inflammatory information to the CNS. Neuroscience 2007, 145, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; DeLeo, J.A. CNS-infiltrating CD4+ T lymphocytes contribute to murine spinal nerve transection-induced neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costigan, M.; Moss, A.; Latremoliere, A.; Johnston, C.; Verma-Gandhu, M.; Herbert, T.A.; Barrett, L.; Brenner, G.J.; Vardeh, D.; Woolf, C.J.; et al. T-cell infiltration and signaling in the adult dorsal spinal cord is a major contributor to neuropathic pain-like hypersensitivity. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 14415–14422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hathway, G.J.; Vega-Avelaira, D.; Moss, A.; Ingram, R.; Fitzgerald, M. Brief, low frequency stimulation of rat peripheral c-fibres evokes prolonged microglial-induced central sensitization in adults but not in neonates. Pain 2009, 144, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.K.; Yip, P.K.; Malcangio, M. The liberation of fractalkine in the dorsal horn requires microglial cathepsin s. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 6945–6954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milligan, E.D.; Watkins, L.R. Pathological and protective roles of glia in chronic pain. Nat. Rev. 2009, 10, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schobitz, B.; de Kloet, E.R.; Sutanto, W.; Holsboer, F. Cellular localization of interleukin 6 mRNA and interleukin 6 receptor mRNA in rat brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1993, 5, 1426–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallieres, L.; Rivest, S. Regulation of the genes encoding interleukin-6, its receptor, and gp130 in the rat brain in response to the immune activator lipopolysaccharide and the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-1beta. J. Neurochem. 1997, 69, 1668–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, X.Q.; Echeverry, S.; Mogil, J.S.; De Koninck, Y.; Rivest, S. Expression of ccr2 in both resident and bone marrow-derived microglia plays a critical role in neuropathic pain. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 12396–12406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, W.; Mei, X.; Huang, J.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, Y. Crosstalk between spinal astrocytes and neurons in nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain. PLoS ONE 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada-Ogawa, A.; Suzuki, I.; Sessle, B.J.; Chiang, C.Y.; Salter, M.W.; Dostrovsky, J.O.; Tsuboi, Y.; Kondo, M.; Kitagawa, J.; Kobayashi, A.; et al. Astroglia in medullary dorsal horn (trigeminal spinal subnucleus caudalis) are involved in trigeminal neuropathic pain mechanisms. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 11161–11171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, A.; Shinoda, M.; Sessle, B.J.; Honda, K.; Imamura, Y.; Hitomi, S.; Tsuboi, Y.; Okada-Ogawa, A.; Iwata, K. Mechanisms involved in extraterritorial facial pain following cervical spinal nerve injury in rats. Mol. Pain 2011, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trang, T.; Beggs, S.; Wan, X.; Salter, M.W. P2X4-receptor-mediated synthesis and release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in microglia is dependent on calcium and p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 3518–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coull, J.A.; Beggs, S.; Boudreau, D.; Boivin, D.; Tsuda, M.; Inoue, K.; Gravel, C.; Salter, M.W.; De Koninck, Y. BDNF from microglia causes the shift in neuronal anion gradient underlying neuropathic pain. Nature 2005, 438, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Zhang, L.; Oz, H.S.; Mashni, M.; Westlund, K.N. Dysregulated TNF α promotes cytokine proteome profile increases and bilateral orofacial hypersensitivity. Neuroscience 2015, 300, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibuta, K.; Suzuki, I.; Shinoda, M.; Tsuboi, Y.; Honda, K.; Shimizu, N.; Sessle, B.J.; Iwata, K. Organization of hyperactive microglial cells in trigeminal spinal subnucleus caudalis and upper cervical spinal cord associated with orofacial neuropathic pain. Brain Res. 2012, 1451, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, N.B.; Attwell, D. Do astrocytes really exocytose neurotransmitters? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, C.Y.; Wang, J.; Xie, Y.F.; Zhang, S.; Hu, J.W.; Dostrovsky, J.O.; Sessle, B.J. Astroglial glutamate-glutamine shuttle is involved in central sensitization of nociceptive neurons in rat medullary dorsal horn. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 9068–9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, L.L.; Monteiro, M.A.; Alves, P.M.; Carrondo, M.J.; Santos, H. Cultures of rat astrocytes challenged with a steady supply of glutamate: New model to study flux distribution in the glutamate-glutamine cycle. Glia 2005, 51, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, C.Y.; Li, Z.; Dostrovsky, J.O.; Hu, J.W.; Sessle, B.J. Glutamine uptake contributes to central sensitization in the medullary dorsal horn. Neuroreport 2008, 19, 1151–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, B.; Lim, G.; Mao, J. Altered expression and uptake activity of spinal glutamate transporters after nerve injury contribute to the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain in rats. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 2899–2910. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Cao, Y.; Chiang, C.Y.; Dostrovsky, J.O.; Sessle, B.J. The gap junction blocker carbenoxolone attenuates nociceptive behavior and medullary dorsal horn central sensitization induced by partial infraorbital nerve transection in rats. Pain 2014, 155, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, C.Y.; Li, Z.; Dostrovsky, J.O.; Sessle, B.J. Central sensitization in medullary dorsal horn involves gap junctions and hemichannels. Neuroreport 2010, 21, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, K.; Obata, K.; Kondo, T.; Okamura, H.; Noguchi, K. Interleukin-18-mediated microglia/astrocyte interaction in the spinal cord enhances neuropathic pain processing after nerve injury. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 12775–12787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stohler, C.S. Craniofacial pain and motor function: Pathogenesis, clinical correlates, and implications. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 1999, 10, 504–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodges, P.W.; Tucker, K. Moving differently in pain: A new theory to explain the adaptation to pain. Pain 2011, 152, S90–S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, P.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Houe, L. Sensory-motor interactions of human experimental unilateral jaw muscle pain: A quantitative analysis. Pain 1996, 64, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, P.; Graven-Nielsen, T. Craniofacial muscle pain: Review of mechanisms and clinical manifestations. J. Orofac. Pain 2001, 15, 117–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, G.; Lund, J.P. Modification of rhythmical jaw movements by noxious pressure applied to the periosteum of the zygoma in decerebrate rabbits. Pain 1995, 63, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ro, J.Y.; Svensson, P.; Capra, N. Effects of experimental muscle pain on electromyographic activity of masticatory muscles in the rat. Muscle Nerve 2002, 25, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.M.; Sessle, B.J.; Vernon, H.; Hu, J.W. Effects of inflammatory irritant application to the rat temporomandibular joint on jaw and neck muscle activity. Pain 1995, 60, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafeezur, R.M.; Shinoda, M.; Unno, S.; Zakir, H.M.; Takatsuji, H.; Takahashi, K.; Yamada, Y.; Yamamura, K.; Iwata, K.; Kitagawa, J. Involvement of astroglial glutamate-glutamine shuttle in modulation of the jaw-opening reflex following infraorbital nerve injury. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2014, 39, 2050–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafeezur, R.M.; Zakir, H.M.; Yamada, Y.; Yamamura, K.; Iwata, K.; Sessle, B.J.; Kitagawa, J. The effect of minocycline on the masticatory movements following the inferior alveolar nerve transection in freely moving rats. Mol. Pain 2012, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
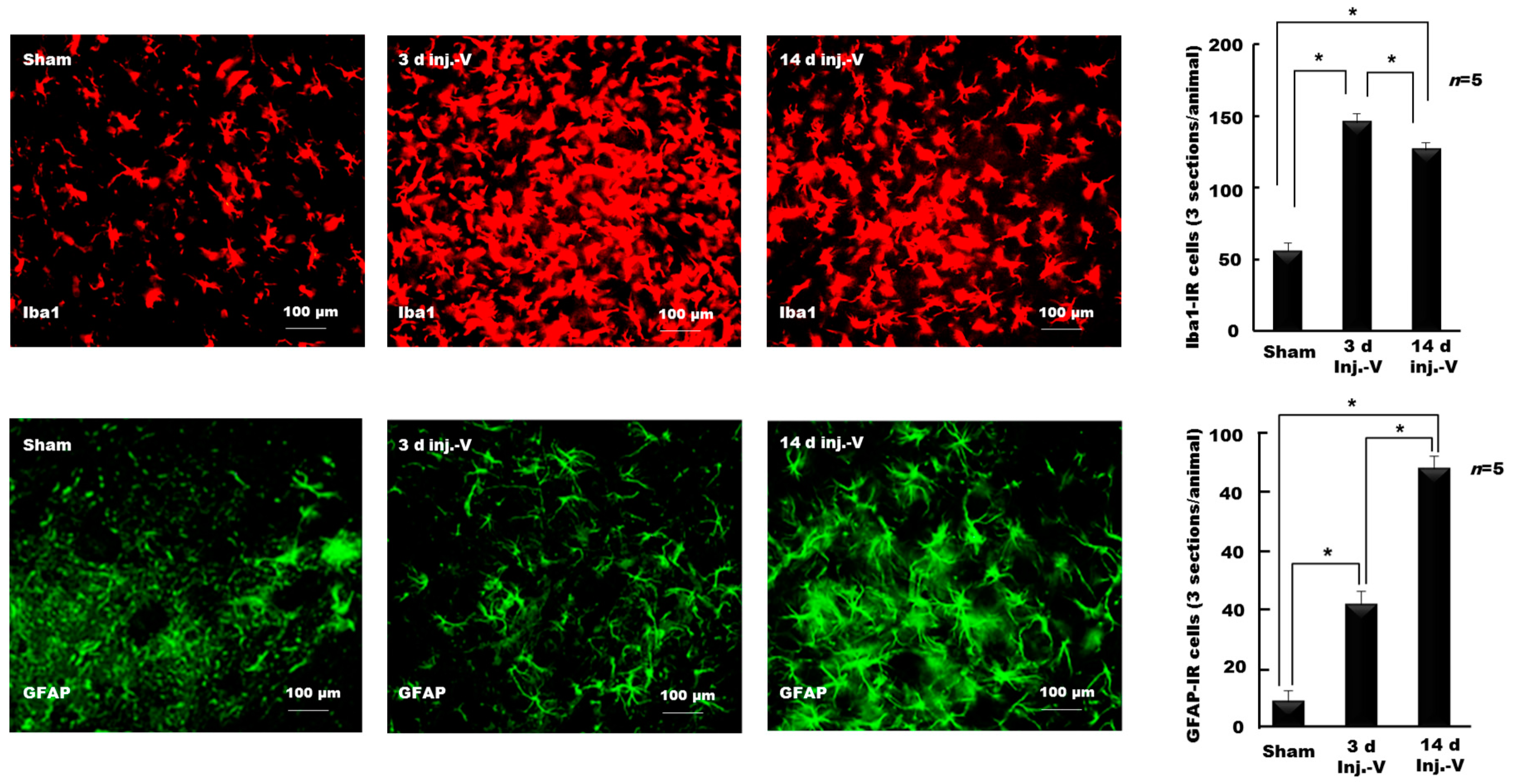
- Hossain, M.Z.; Shinoda, M.; Unno, S.; Ando, H.; Masuda, Y.; Iwata, K.; Kitagawa, J. Involvement of microglia and astroglia in modulation of the orofacial motor functions in rats with neuropathic pain. J. Oral Biosci. 2017, 59, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, Z.G.; Cho, I.H.; Park, C.K.; Hong, J.P.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, S.; Park, K.; Kim, J.S.; Oh, S.B. Activation of glia and microglial p38 MAPK in medullary dorsal horn contributes to tactile hypersensitivity following trigeminal sensory nerve injury. Pain 2006, 121, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledeboer, A.; Sloane, E.M.; Milligan, E.D.; Frank, M.G.; Mahony, J.H.; Maier, S.F.; Watkins, L.R. Minocycline attenuates mechanical allodynia and proinflammatory cytokine expression in rat models of pain facilitation. Pain 2005, 115, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.L.; Yu, A.C.; Lau, L.T.; Lee, C.; Wu, M.L.; Zhu, X.; Tso, M.O.M. Minocycline inhibits LPS-induced retinal microglia activation. Neurochem. Int. 2005, 47, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanjani, T.M.; Sabetkasaei, M.; Mosaffa, N.; Manaheji, H.; Labibi, F.; Farokhi, B. Suppression of interleukin-6 by minocycline in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 538, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owolabi, S.A.; Saab, C.Y. Fractalkine and minocycline alter neuronal activity in the spinal cord dorsal horn. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 4306–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mika, J.; Rojewska, E.; Makuch, W.; Przewlocka, B. Minocycline reduces the injury-induced expression of prodynorphin and pronociceptin in the dorsal root ganglion in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Neuroscience 2010, 165, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikodemova, M.; Duncan, I.D.; Watters, J.J. Minocycline exerts inhibitory effects on multiple mitogen-activated protein kinases and IκBα degradation in a stimulus-specific manner in microglia. J. Neurochem. 2006, 96, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brundula, V.; Rewcastle, N.B.; Metz, L.M.; Bernard, C.C.; Yong, V.W. Targeting leukocyte MMPS and transmigration: Minocycline as a potential therapy for multiple sclerosis. Brain 2002, 125, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovic, N.; Schubart, A.; Goetz, B.D.; Zhang, S.C.; Linington, C.; Duncan, I.D. Inhibition of autoimmune encephalomyelitis by a tetracycline. Ann. Neurol. 2002, 51, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, H.; Zhang, H.; Weng, H.R. Minocycline prevents impaired glial glutamate uptake in the spinal sensory synapses of neuropathic rats. Neuroscience 2010, 170, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Ribeiro-da-Silva, A.; Zhang, J. Distinctive response of CNS glial cells in oro-facial pain associated with injury, infection and inflammation. Mol. Pain 2006, 6, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.F.; Zhang, S.; Chiang, C.Y.; Hu, J.W.; Dostrovsky, J.O.; Sessle, B.J. Involvement of glia in central sensitization in trigeminal subnucleus caudalis (medullary dorsal horn). Brain Behav. Immun. 2007, 21, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Lu, J.; Tay, S.S.; Jiang, H.; He, B.P. Induced NG2 expressing microglia in the facial motor nucleus after facial nerve axotomy. Neuroscience 2010, 166, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, M.; Aldskogius, H. Evidence for activation of the complement cascade in the hypoglossal nucleus following peripheral nerve injury. J. Neuroimmunol. 1992, 40, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiano, M.; Liu, Z.Q.; Kalla, R.; Bohatschek, M.; Koppius, A.; Gschwendtner, A.; Xu, S.; Werner, A.; Kloss, C.U.; Jones, L.L.; et al. Interleukin-6 (IL6) and cellular response to facial nerve injury: Effects on lymphocyte recruitment, early microglial activation and axonal outgrowth in IL6-deficient mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001, 14, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hossain, M.Z.; Unno, S.; Ando, H.; Masuda, Y.; Kitagawa, J. Neuron–Glia Crosstalk and Neuropathic Pain: Involvement in the Modulation of Motor Activity in the Orofacial Region. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102051
Hossain MZ, Unno S, Ando H, Masuda Y, Kitagawa J. Neuron–Glia Crosstalk and Neuropathic Pain: Involvement in the Modulation of Motor Activity in the Orofacial Region. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(10):2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102051
Chicago/Turabian StyleHossain, Mohammad Zakir, Shumpei Unno, Hiroshi Ando, Yuji Masuda, and Junichi Kitagawa. 2017. "Neuron–Glia Crosstalk and Neuropathic Pain: Involvement in the Modulation of Motor Activity in the Orofacial Region" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 10: 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102051
APA StyleHossain, M. Z., Unno, S., Ando, H., Masuda, Y., & Kitagawa, J. (2017). Neuron–Glia Crosstalk and Neuropathic Pain: Involvement in the Modulation of Motor Activity in the Orofacial Region. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(10), 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102051