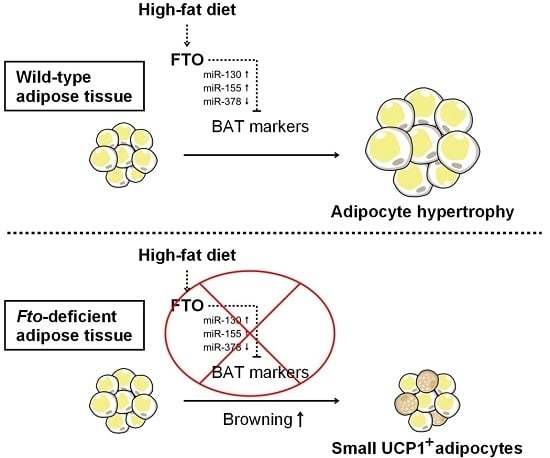
Fto-Deficiency Affects the Gene and MicroRNA Expression Involved in Brown Adipogenesis and Browning of White Adipose Tissue in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
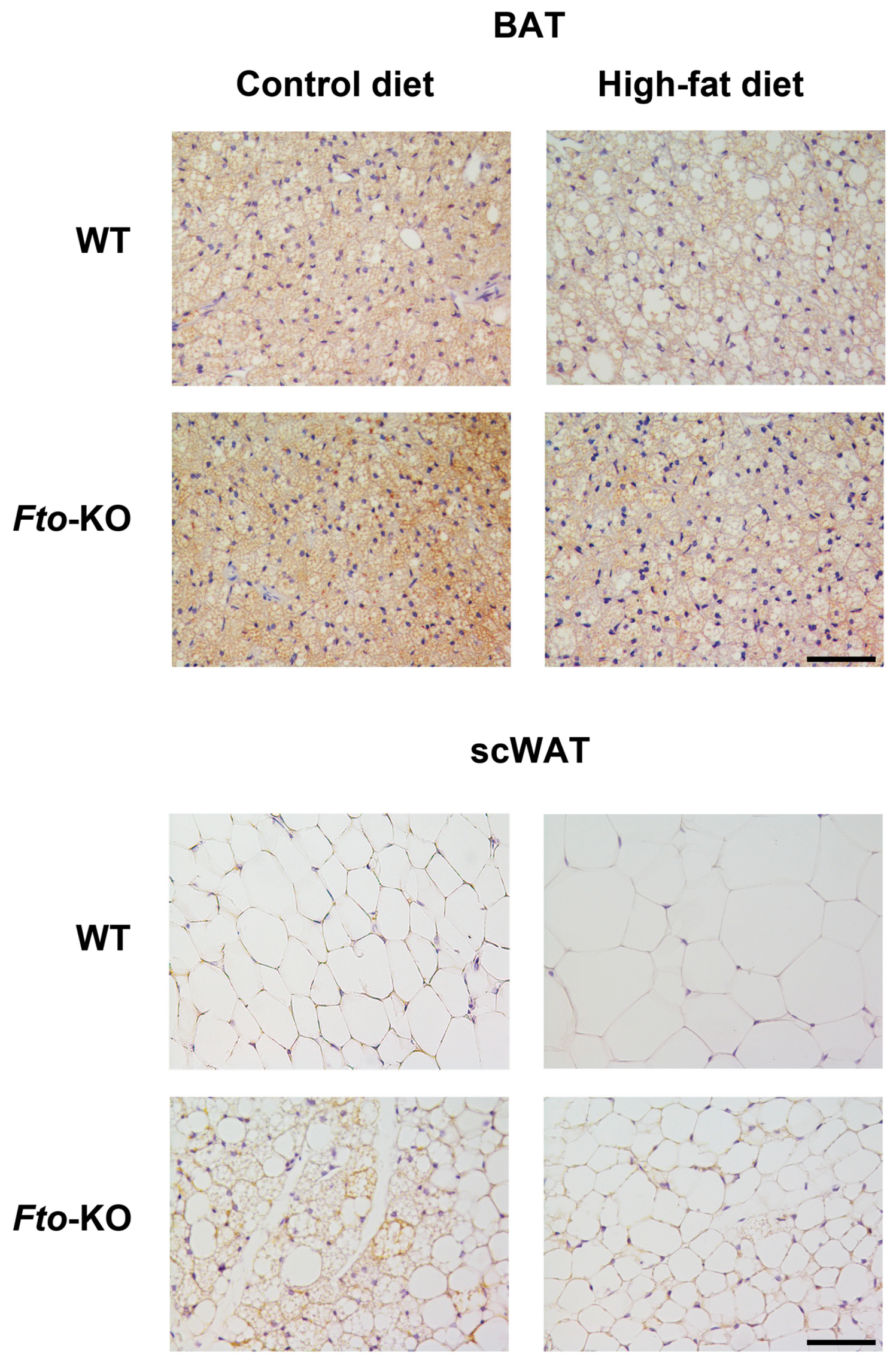
2.1. Phenotype, Adipose Tissue Morphology, and Uncoupling Protein 1 (UCP1) Immunohistochemistry
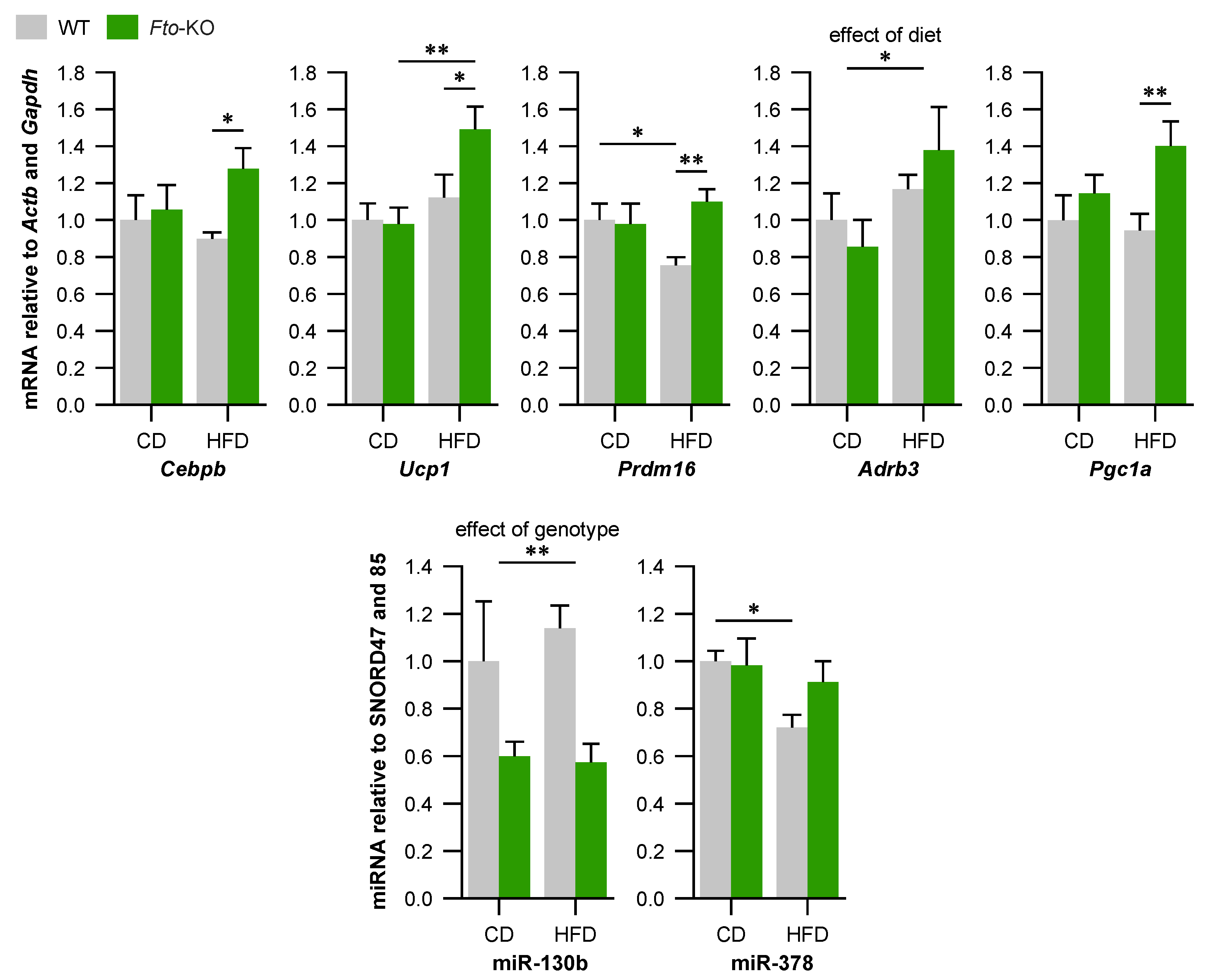
2.2. Expression of Brown Adipocyte Markers Is Altered in Brown Adipose Tissue (BAT) of Fto-Knockout (Fto-KO) Mice
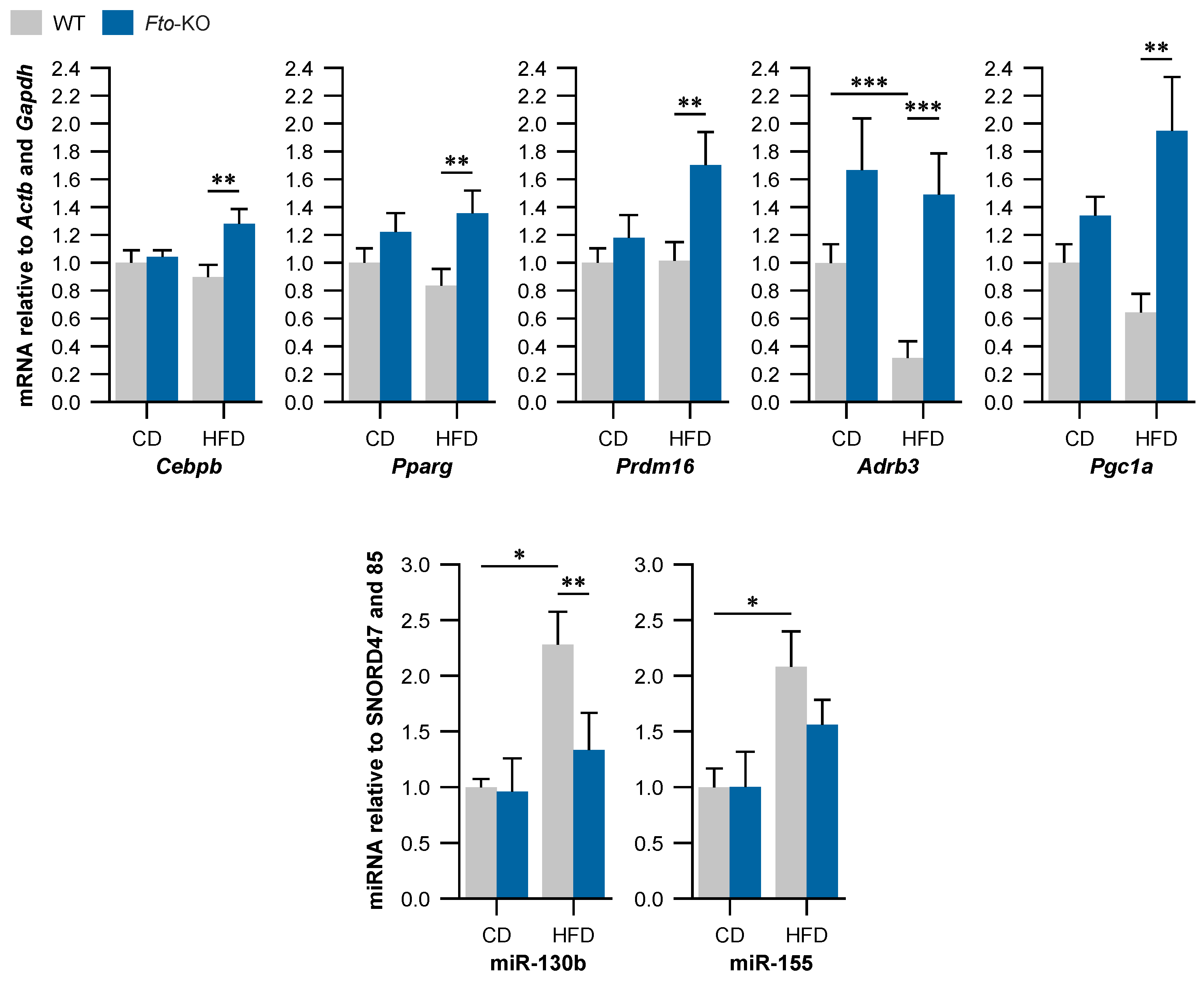
2.3. Beige Adipocyte Markers Are Expressed Higher in Fto-KO Subcutaneous White Adipose Tissue (WAT)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Generation of Fto-KO Mice and Dietary Treatment
4.2. Immunohistochemistry
4.3. Isolation of Total RNA and miRNA-Enriched Fraction and cDNA Synthesis
4.4. Quantitative Real-Time Reverse-Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
4.5. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Actb | β-actin gene |
| Adrb3 | adrenergic receptor β3 gene |
| ALKBH5 | AlkB-homolog 5 |
| BAT | brown adipose tissue |
| BMI | body mass index |
| brite | brown-in-white |
| Cebpb | CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β gene |
| Fto | fat mass- and obesity-associated gene |
| Fto-KO | Fto-knockout |
| Gapdh | glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene |
| m6A | N6-methyladenosine |
| miRNA | microRNA |
| Pgc1a | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α gene |
| Pparg | peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ gene |
| Prdm16 | positive regulatory domain containing 16 gene |
| scWAT | subcutaneous WAT |
| Ucp1 | mitochondrial uncoupling protein 1 gene |
| WAT | white adipose tissue |
References
- Dina, C.; Meyre, D.; Gallina, S.; Durand, E.; Korner, A.; Jacobson, P.; Carlsson, L.M.; Kiess, W.; Vatin, V.; Lecoeur, C.; et al. Variation in FTO Contributes to Childhood Obesity and Severe Adult Obesity. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 724–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frayling, T.M.; Timpson, N.J.; Weedon, M.N.; Zeggini, E.; Freathy, R.M.; Lindgren, C.M.; Perry, J.R.; Elliott, K.S.; Lango, H.; Rayner, N.W.; et al. A Common Variant in the FTO Gene is Associated with Body Mass Index and Predisposes to Childhood and Adult Obesity. Science 2007, 316, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, C.L.; Chiodini, B.D.; Sham, P.; Lewis, C.M.; Abkevich, V.; Adeyemo, A.A.; de Andrade, M.; Arya, R.; Berenson, G.S.; Blangero, J.; et al. Meta-Analysis of Genome-Wide Linkage Studies in BMI and Obesity. Obesity 2007, 15, 2263–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scuteri, A.; Sanna, S.; Chen, W.M.; Uda, M.; Albai, G.; Strait, J.; Najjar, S.; Nagaraja, R.; Orru, M.; Usala, G.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Scan shows Genetic Variants in the FTO Gene are Associated with Obesity-Related Traits. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.; Kang, K.; Zhang, C.; van Dam, R.M.; Kraft, P.; Hunter, D.; Lee, C.H.; Hu, F.B. Fat Mass-and Obesity-Associated (FTO) Gene Variant is Associated with Obesity: Longitudinal Analyses in Two Cohort Studies and Functional Test. Diabetes 2008, 57, 3145–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, A.E.; Kahali, B.; Berndt, S.I.; Justice, A.E.; Pers, T.H.; Day, F.R.; Powell, C.; Vedantam, S.; Buchkovich, M.L.; Yang, J.; et al. Genetic Studies of Body Mass Index Yield New Insights for Obesity Biology. Nature 2015, 518, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llewellyn, C.; Wardle, J. Behavioral Susceptibility to Obesity: Gene-Environment Interplay in the Development of Weight. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 152, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luis, D.A.; Aller, R.; Izaola, O.; de la Fuente, B.; Conde, R.; Sagrado, M.G.; Primo, D. Evaluation of Weight Loss and Adipocytokines Levels After Two Hypocaloric Diets with Different Macronutrient Distribution in Obese Subjects with rs9939609 Gene Variant. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2012, 28, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demerath, E.W.; Choh, A.C.; Johnson, W.; Curran, J.E.; Lee, M.; Bellis, C.; Dyer, T.D.; Czerwinski, S.A.; Blangero, J.; Towne, B. The Positive Association of Obesity Variants with Adulthood Adiposity Strengthens Over an 80-Year Period: A Gene-by-Birth Year Interaction. Hum. Hered. 2013, 75, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, J.; Koch, L.; Emmerling, C.; Vierkotten, J.; Peters, T.; Bruning, J.C.; Ruther, U. Inactivation of the Fto Gene Protects from Obesity. Nature 2009, 458, 894–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, C.; Lee, S.; Bagg, E.A.; McTaggart, J.S.; Deacon, R.; Gerken, T.; Lee, A.; Moir, L.; Mecinovic, J.; Quwailid, M.M.; et al. A Mouse Model for the Metabolic Effects of the Human Fat Mass and Obesity Associated FTO Gene. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, F.; Church, C.D.; Larder, R.; Nicholson, G.; Wells, S.; Teboul, L.; Tung, Y.C.; Rimmington, D.; Bosch, F.; Jimenez, V.; et al. Adult Onset Global Loss of the Fto Gene Alters Body Composition and Metabolism in the Mouse. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Shin, Y.H.; Li, M.; Wang, F.; Tong, Q.; Zhang, P. The Fat Mass and Obesity Associated Gene FTO Functions in the Brain to Regulate Postnatal Growth in Mice. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, C.; Moir, L.; McMurray, F.; Girard, C.; Banks, G.T.; Teboul, L.; Wells, S.; Bruning, J.C.; Nolan, P.M.; Ashcroft, F.M.; et al. Overexpression of Fto Leads to Increased Food Intake and Results in Obesity. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerken, T.; Girard, C.A.; Tung, Y.C.; Webby, C.J.; Saudek, V.; Hewitson, K.S.; Yeo, G.S.; McDonough, M.A.; Cunliffe, S.; McNeill, L.A.; et al. The Obesity-Associated FTO Gene Encodes a 2-Oxoglutarate-Dependent Nucleic Acid Demethylase. Science 2007, 318, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratigopoulos, G.; Padilla, S.L.; LeDuc, C.A.; Watson, E.; Hattersley, A.T.; McCarthy, M.I.; Zeltser, L.M.; Chung, W.K.; Leibel, R.L. Regulation of Fto/Ftm Gene Expression in Mice and Humans. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 294, R1185–R1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronkainen, J.; Huusko, T.J.; Soininen, R.; Mondini, E.; Cinti, F.; Makela, K.A.; Kovalainen, M.; Herzig, K.H.; Jarvelin, M.R.; Sebert, S.; et al. Fat Mass- and Obesity-Associated Gene Fto Affects the Dietary Response in Mouse White Adipose Tissue. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tews, D.; Fischer-Posovszky, P.; Fromme, T.; Klingenspor, M.; Fischer, J.; Ruther, U.; Marienfeld, R.; Barth, T.F.; Moller, P.; Debatin, K.M.; et al. FTO Deficiency Induces UCP-1 Expression and Mitochondrial Uncoupling in Adipocytes. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 3141–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peirce, V.; Carobbio, S.; Vidal-Puig, A. The Different Shades of Fat. Nature 2014, 510, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Yoshida, N.; Kishimoto, T.; Akira, S. Defective Adipocyte Differentiation in Mice Lacking the C/EBPβ and/or C/EBPδ Gene. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 7432–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajimura, S.; Seale, P.; Kubota, K.; Lunsford, E.; Frangioni, J.V.; Gygi, S.P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Initiation of Myoblast to Brown Fat Switch by a PRDM16-C/EBP-β Transcriptional Complex. Nature 2009, 460, 1154–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Bostrom, P.; Sparks, L.M.; Ye, L.; Choi, J.H.; Giang, A.H.; Khandekar, M.; Virtanen, K.A.; Nuutila, P.; Schaart, G.; et al. Beige Adipocytes are a Distinct Type of Thermogenic Fat Cell in Mouse and Human. Cell 2012, 150, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, G.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Dai, Q.; Zheng, G.; Yang, Y.; Yi, C.; Lindahl, T.; Pan, T.; Yang, Y.G.; et al. N6-Methyladenosine in Nuclear RNA is a Major Substrate of the Obesity-Associated FTO. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 885–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, K.D.; Saletore, Y.; Zumbo, P.; Elemento, O.; Mason, C.E.; Jaffrey, S.R. Comprehensive Analysis of mRNA Methylation Reveals Enrichment in 3′ UTRs and Near Stop Codons. Cell 2012, 149, 1635–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berulava, T.; Rahmann, S.; Rademacher, K.; Klein-Hitpass, L.; Horsthemke, B. N6-Adenosine Methylation in miRNAs. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagos-Quintana, M.; Rauhut, R.; Lendeckel, W.; Tuschl, T. Identification of Novel Genes Coding for Small Expressed RNAs. Science 2001, 294, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercado, C.; Eades, G.; Zhou, Q. MicroRNAs: A New Class of Master Regulators of Adipogenesis. Hum. Genet. Embryol. 2013, 3, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Li, L. MicroRNAs are Key Regulators of Brown Adipogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 1590–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guller, I.; McNaughton, S.; Crowley, T.; Gilsanz, V.; Kajimura, S.; Watt, M.; Russell, A.P. Comparative Analysis of microRNA Expression in Mouse and Human Brown Adipose Tissue. BMC Genom. 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.K.; Lee, M.J.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Kim, W.; Kim, M.M.; Srikantan, S.; Martindale, J.L.; Hutchison, E.R.; Kim, H.H.; Marasa, B.S.; et al. miR-130 Suppresses Adipogenesis by Inhibiting Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ Expression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerin, I.; Bommer, G.T.; McCoin, C.S.; Sousa, K.M.; Krishnan, V.; MacDougald, O.A. Roles for miRNA-378/378* in Adipocyte Gene Expression and Lipogenesis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 299, E198–E206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, T. N6-Methyl-Adenosine Modification in Messenger and Long Non-Coding RNA. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2013, 38, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Siegel, F.; Kipschull, S.; Haas, B.; Frohlich, H.; Meister, G.; Pfeifer, A. miR-155 Regulates Differentiation of Brown and Beige Adipocytes Via a Bistable Circuit. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, Y.; Sun, B.F.; Shi, Y.; Yang, X.; Xiao, W.; Hao, Y.J.; Ping, X.L.; Chen, Y.S.; Wang, W.J.; et al. FTO-Dependent Demethylation of N6-Methyladenosine Regulates mRNA Splicing and is Required for Adipogenesis. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 1403–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.; Mao, C.; Quattrochi, B.; Friedline, R.H.; Zhu, L.J.; Jung, D.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Lewis, B.; Wang, Y.X. MicroRNA-378 Controls Classical Brown Fat Expansion to Counteract Obesity. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frontini, A.; Cinti, S. Distribution and Development of Brown Adipocytes in the Murine and Human Adipose Organ. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.D.; Moore, M.W. The International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium: Past and Future Perspectives on Mouse Phenotyping. Mamm. Genome 2012, 23, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sovio, U.; Mook-Kanamori, D.O.; Warrington, N.M.; Lawrence, R.; Briollais, L.; Palmer, C.N.; Cecil, J.; Sandling, J.K.; Syvanen, A.C.; Kaakinen, M.; et al. Association between Common Variation at the FTO Locus and Changes in Body Mass Index from Infancy to Late Childhood: The Complex Nature of Genetic Association through Growth and Development. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fromme, T.; Klingenspor, M. Uncoupling Protein 1 Expression and High-Fat Diets. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011, 300, R1–R8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldmann, H.M.; Golozoubova, V.; Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J. UCP1 Ablation Induces Obesity and Abolishes Diet-Induced Thermogenesis in Mice Exempt from Thermal Stress by Living at Thermoneutrality. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Lee, H.; Cho, Y.M.; Kwon, O.J.; Kim, W.; Lee, E.K. TNFα-Induced miR-130 Resulted in Adipocyte Dysfunction during Obesity-Related Inflammation. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 3853–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.M.; Janssen, R.C.; Choudhury, M.; Baquero, K.C.; Aikens, R.M.; de la Houssaye, B.A.; Friedman, J.E. CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein β (C/EBPβ) Expression Regulates Dietary-Induced Inflammation in Macrophages and Adipose Tissue in Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 34349–34360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Lim, B.; Lodish, H.F. MicroRNAs Induced during Adipogenesis that Accelerate Fat Cell Development are Downregulated in Obesity. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, F.J.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Pardo, G.; Sabater, M.; Hummel, M.; Ferrer, A.; Rodriguez-Hermosa, J.I.; Ruiz, B.; Ricart, W.; Peral, B.; et al. miRNA Expression Profile of Human Subcutaneous Adipose and during Adipocyte Differentiation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chartoumpekis, D.V.; Zaravinos, A.; Ziros, P.G.; Iskrenova, R.P.; Psyrogiannis, A.I.; Kyriazopoulou, V.E.; Habeos, I.G. Differential Expression of microRNAs in Adipose Tissue After Long-Term High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, M.E.; Hess, S.; Meyer, K.D.; Verhagen, L.A.; Koch, L.; Bronneke, H.S.; Dietrich, M.O.; Jordan, S.D.; Saletore, Y.; Elemento, O.; et al. The Fat Mass and Obesity Associated Gene (Fto) Regulates Activity of the Dopaminergic Midbrain Circuitry. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Dahl, J.A.; Niu, Y.; Fedorcsak, P.; Huang, C.M.; Li, C.J.; Vagbo, C.B.; Shi, Y.; Wang, W.L.; Song, S.H.; et al. ALKBH5 is a Mammalian RNA Demethylase that Impacts RNA Metabolism and Mouse Fertility. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcon, C.R.; Lee, H.; Goodarzi, H.; Halberg, N.; Tavazoie, S.F. N6-Methyladenosine Marks Primary microRNAs for Processing. Nature 2015, 519, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing Real-Time PCR Data by the Comparative CT Method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ronkainen, J.; Mondini, E.; Cinti, F.; Cinti, S.; Sebért, S.; Savolainen, M.J.; Salonurmi, T. Fto-Deficiency Affects the Gene and MicroRNA Expression Involved in Brown Adipogenesis and Browning of White Adipose Tissue in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111851
Ronkainen J, Mondini E, Cinti F, Cinti S, Sebért S, Savolainen MJ, Salonurmi T. Fto-Deficiency Affects the Gene and MicroRNA Expression Involved in Brown Adipogenesis and Browning of White Adipose Tissue in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(11):1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111851
Chicago/Turabian StyleRonkainen, Justiina, Eleonora Mondini, Francesca Cinti, Saverio Cinti, Sylvain Sebért, Markku J. Savolainen, and Tuire Salonurmi. 2016. "Fto-Deficiency Affects the Gene and MicroRNA Expression Involved in Brown Adipogenesis and Browning of White Adipose Tissue in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 11: 1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111851
APA StyleRonkainen, J., Mondini, E., Cinti, F., Cinti, S., Sebért, S., Savolainen, M. J., & Salonurmi, T. (2016). Fto-Deficiency Affects the Gene and MicroRNA Expression Involved in Brown Adipogenesis and Browning of White Adipose Tissue in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(11), 1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111851