The Fascinating Effects of Baicalein on Cancer: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
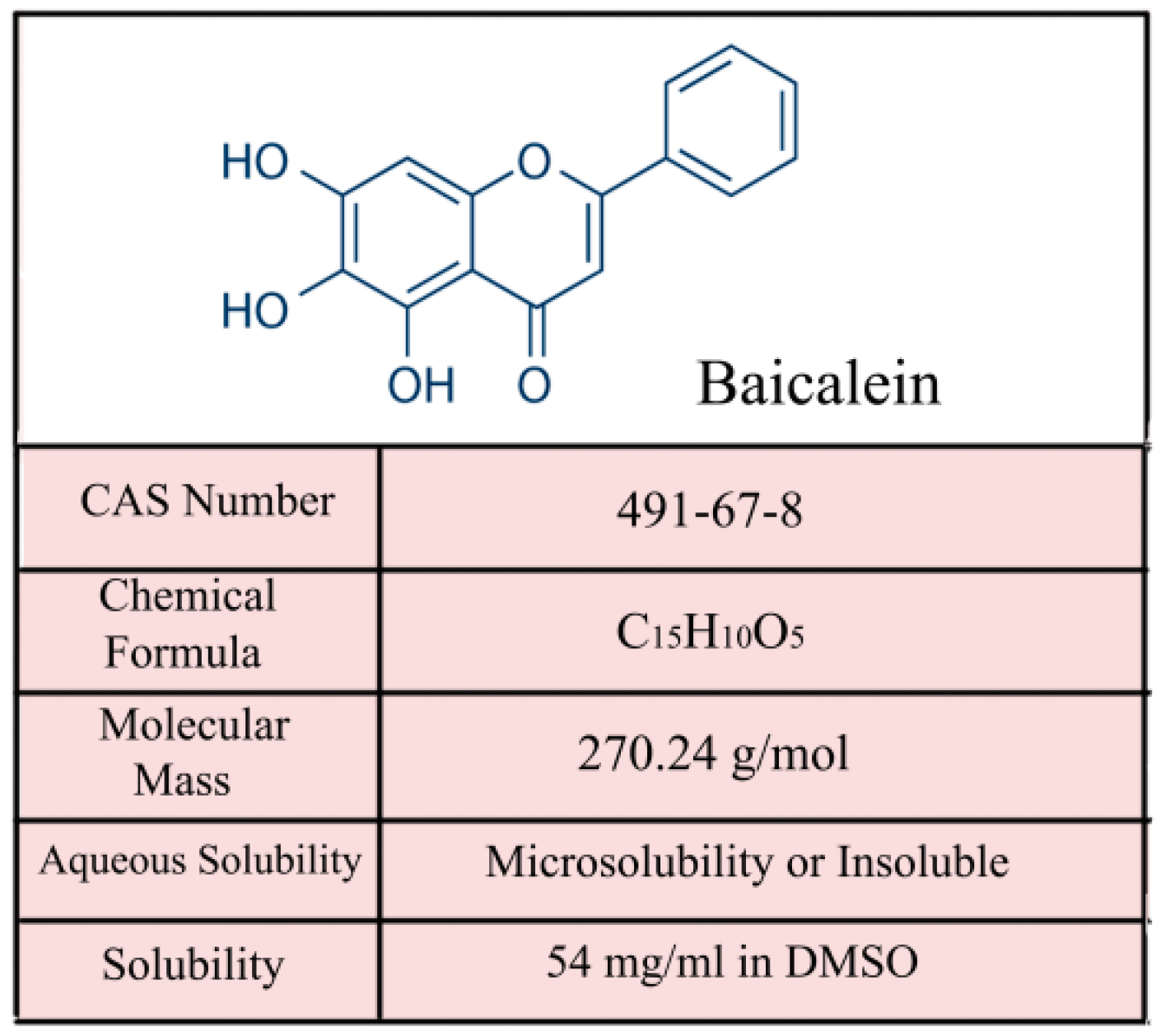
2. The Property and Antitumor Effect of Baicalein
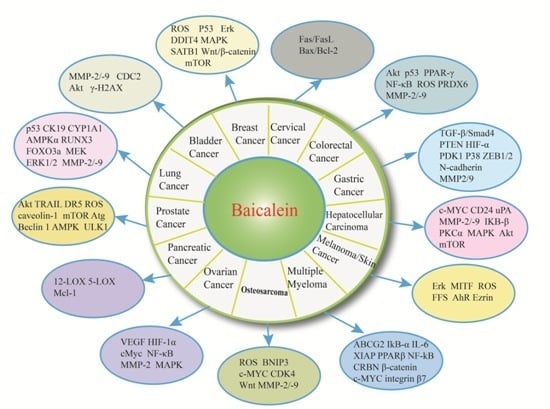
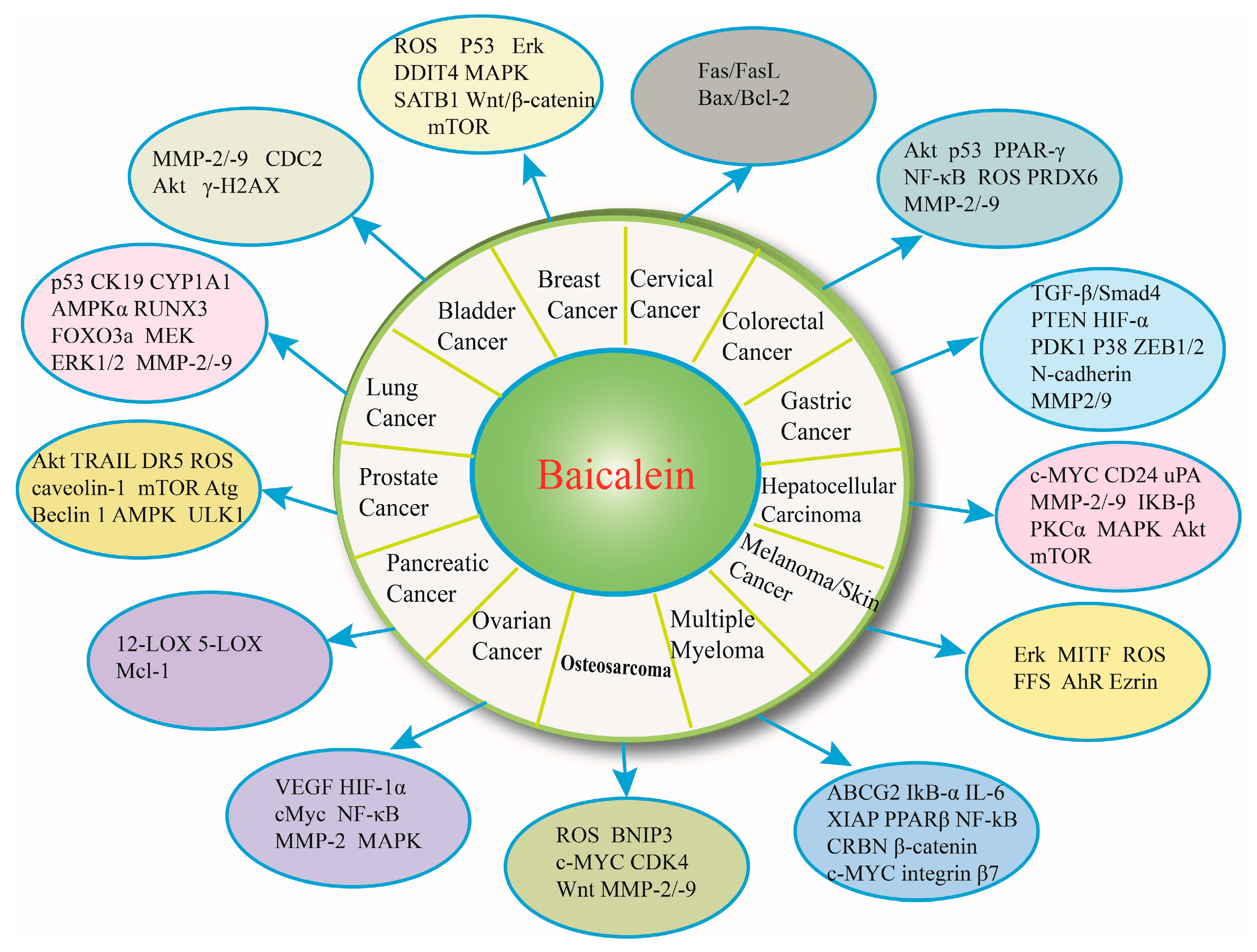
3. Baicalein and Bladder Cancer
4. Baicalein and Breast Cancer
5. Baicalein and Cervical Cancer
6. Baicalein and Colorectal Cancer
7. Baicalein and Gastric Cancer
8. Baicalein and Hepatocelluar Carcinoma
9. Baicalein and Melanoma/Skin Cancer
10. Baicalein and Multiple Myeloma
11. Baicalein and Osteosarcoma
12. Baicalein and Ovarian Cancer
13. Baicalein and Pancreatic Cancer
14. Baicalein and Prostate Cancer
15. Baicalein and Lung Cancer
16. Potential Clinical Implication and Discussion
17. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bandhavkar, S. Cancer stem cells: A metastasizing menace! Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Galindo, C.; Friedrich, P.; Alcasabas, P.; Antillon, F.; Banavali, S.; Castillo, L.; Israels, T.; Jeha, S.; Harif, M.; Sullivan, M.J.; et al. Toward the cure of all children with cancer through collaborative efforts: Pediatric oncology as a global challenge. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3065–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.X.; Chen, G.Q.; Ni, J.H.; Li, X.S.; Xiong, S.M.; Qiu, Q.Y.; Zhu, J.; Tang, W.; Sun, G.L.; Yang, K.Q.; et al. Use of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) II. clinical efficacy and pharmacokinetics in relapsed patients. Blood 1997, 89, 3354–3360. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eckstein-Ludwig, U.; Webb, R.J.; van Goethem, I.D.; East, J.M.; Lee, A.G.; Kimura, M.; O’Neill, P.M.; Bray, P.G.; Ward, S.A.; Krishna, S. Artemisinins target the SERCA of Plasmodium falciparum. Nature 2003, 424, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Rocha, A.B.; Lopes, R.M.; Schwartsmann, G. Natural products in anticancer therapy. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2001, 1, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, B.; Pagano, E.; Montanaro, V.; Fortunato, A.L.; Milic, N.; Borrelli, F. Novel insights into the pharmacology of flavonoids. Phytother. Res. PTR 2013, 27, 1588–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Xu, W.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Z. Dietary flavonoids as cancer prevention agents. J. Environ. Sci. Health C Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 2011, 29, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, M.; Spagnuolo, C.; Tedesco, I.; Russo, G.L. Phytochemicals in cancer prevention and therapy: Truth or dare? Toxins 2010, 2, 517–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.Y.; Tsai, K.W.; Li, Y.Z.; Chang, Y.S.; Lai, Y.C.; Laio, Y.H.; Wu, J.D.; Liu, Y.W. Anti-Bladder-Tumor Effect of Baicalein from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi and Its Application in Vivo. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 579751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Yan, W.; Dai, Z.; Gao, X.; Ma, Y.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, S. Baicalein suppresses metastasis of breast cancer cells by inhibiting EMT via downregulation of SATB1 and Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 1419–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Guo, C.; Yang, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, B.; Li, Q. Baicalein induces apoptosis of human cervical cancer HeLa cells in vitro. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 2129–2134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rui, X.; Yan, X.I.; Zhang, K. Baicalein inhibits the migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells via suppression of the AKT signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.H.; Yin, L.H.; Grahn, T.H.; Ye, A.F.; Zhao, Y.R.; Zhang, Q.Y. Anticancer effects of baicalein on hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1342–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrashekar, N.; Selvamani, A.; Subramanian, R.; Pandi, A.; Thiruvengadam, D. Baicalein inhibits pulmonary carcinogenesis-associated inflammation and interferes with COX-2, MMP-2 and MMP-9 expressions in vivo. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 261, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Hu, X.; Xing, Z.; Xing, R.; Lv, R.; Cheng, X.; Su, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, Z.; Nilsson, S.; et al. Baicalein inhibits prostate cancer cell growth and metastasis via the caveolin-1/AKT/mTOR pathway. Mol. Cell 2015, 406, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li-Weber, M. New therapeutic aspects of flavones: The anticancer properties of Scutellaria and its main active constituents Wogonin, Baicalein and Baicalin. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2009, 35, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Wei, Z.; Zhou, E.; Chen, L.; Kou, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z. Baicalein attenuates inflammatory responses by suppressing TLR4 mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in LPS-induced mastitis in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, C.H.; Ma, K.H.; Liu, P.S.; Kuo, J.K.; Chueh, S.H. Baicalein decreases hydrogen peroxide-induced damage to NG108–15 cells via upregulation of Nrf2. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 1840–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelis, M.; Sithisarn, P.; Cinatl, J., Jr. Effects of flavonoid-induced oxidative stress on anti-H5N1 influenza a virus activity exerted by baicalein and biochanin A. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Tsang, S.Y.; Yao, X.; Chen, Z.Y. Biological Properties of Baicalein in Cardiovascular System. Curr. Drug Targets Cardiovasc. Haematol. Disord. 2005, 5, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorescu, D. Molecular pathogenesis of urothelial bladder cancer. Histol. Histopathol. 2003, 18, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- National Cancer Institute. SEER Data. Available online: http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/ (accessed on 7 July 2016).
- Morgan, T.M.; Keegan, K.A.; Clark, P.E. Bladder cancer. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2011, 23, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liang, R.R.; Li, J.; An, P.; Wang, Z.M.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.F. Baicalein induces apoptosis via a mitochondrial-dependent caspase activation pathway in T24 bladder cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, J.I.; Su, W.C.; Liu, H.F. Baicalein induces cancer cell death and proliferation retardation by the inhibition of CDC2 kinase and survivin associated with opposite role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and AKT. Mol. Cancer 2007, 6, 3039–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.H.; Su, W.C.; Liu, H.F.; Huang, H.S.; Chao, J.I. Opposite expression of securin and γ-H2AX regulates baicalein-induced cancer cell death. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 111, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikemoto, S.; Sugimura, K.; Kuratukuri, K.; Nakatani, T. Antitumor Effects of Lipoxygenase Inhibitors on Murine Bladder Cancer Cell Line (MBT-2). Anticancer Res. 2004, 24, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Li, Y.C.; Ip, S.W.; Hsu, S.C.; Chang, N.W.; Tang, N.Y.; Yu, C.S.; Chou, S.T.; Lin, S.S.; Lino, C.C. The role of Ca2+ in baicalein-induced apoptosis in human breast MDA-MB-231 cancer cells through mitochondria- and caspase-3-dependent pathway. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 1701–1711. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Po, L.S.; Chen, Z.Y.; Tsang, D.S.; Leung, L.K. Baicalein and genistein display differential actions on estrogen receptor (ER) transactivation and apoptosis in MCF-7 cells. Cancer Lett. 2002, 187, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ren, D.; Deng, S.; Yang, X. Differential effects of baicalein and its sulfated derivatives in inhibiting proliferation of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 221, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Y.Y.; Wang, X.F.; Motoo, Y.; Su, S.B. The combination of baicalin and baicalein enhances apoptosis via the ERK/p38 MAPK pathway in human breast cancer cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2009, 30, 1648–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ling, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.L.; Feng, F.; You, Q.D.; Lu, N.; Guo, Q.L. Flavonoid baicalein suppresses adhesion, migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2010, 297, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.Y.; Xue, X.H.; Ma, Y.N.; Zhang, S.Q. Effect of baicalein on the expression of SATB1 in human breast cancer cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 1665–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Han, E.; Xing, Q.; Yan, J.; Arrington, A.; Wang, C.; Tully, D.; Kowolik, C.M.; Lu, D.M.; Frankel, P.H.; et al. Baicalein upregulates DDIT4 expression which mediates mTOR inhibition and growth inhibition in cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2015, 358, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Li, Q.W.; Li, K.; Zhao, H.W.; Han, Z.S.; Li, F.L.; Sun, M.; Zhang, Y.X. Antitumor activity of baicalein on the mice bearing U14 cervical cancer. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 14169–14176. [Google Scholar]
- Tenesa, A.; Dunlop, M.G. New insights into the aetiology of colorectal cancer from genome-wide association studies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.R.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, S.D.; Choi, C.S.; Nam, J.S.; Jung, J.Y. Antitumor actions of baicalein and wogonin in HT-29 human colorectal cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 6, 1443–1449. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Z.; Zhang, C.F.; Chen, L.; Anderson, S.; Lu, F.; Yuan, C.S. Colon cancer chemopreventive effects of baicalein, an active enteric microbiome metabolite from baicalin. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Hossain, M.A.; Kang, Y.J.; Jang, J.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Im, E.; Yoon, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Chung, H.Y.; Kim, N.D. Baicalein, an active component of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, induces apoptosis in human colon cancer cells and prevents AOM/DSS-induced colon cancer in mice. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 1652–1658. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.S.; Kuo, Y.H.; Chin, C.C.; Wang, J.Y.; Yu, H.R.; Sheen, J.M.; Tung, S.Y.; Shen, C.H.; Chen, T.C.; Sung, M.L.; et al. Proteomic analysis of the effects of baicalein on colorectal cancer cells. Proteomics 2012, 12, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Shin, H.R.; Bray, F.; Forman, D.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2893–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, J.; Liu, T.; Jiang, L.; Wu, X.; Cao, Y.; Li, M.; Dong, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H. The traditional Chinese medicine baicalein potently inhibits gastric cancer cells. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Zhuang, M.; Peng, J.; Wang, X.; Huang, T.; Li, S.; Lin, M.; Lin, H.; Xu, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Baicalein inhibits migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells through suppression of the TGF-β signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 1999–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Rui, X.; Zhang, K. Baicalein inhibits the invasion of gastric cancer cells by suppressing the activity of the p38 signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Zhuang, M.; Zhong, C.; Peng, J.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Y. Baicalein reverses hypoxia-induced 5-FU resistance in gastric cancer AGS cells through suppression of glycolysis and the PTEN/Akt/HIF-1α signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.M.; Tsai, H.C.; Lin, Y.L.; Yang, J.S.; Huang, A.C.; Yang, M.D.; Hsu, S.C.; Chung, M.C.; Gihson Wood, W.; Chung, J.G. Mitochondrial-dependent caspase activation pathway is involved in baicalein-induced apoptosis in human hepatoma J5 cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 35, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Zhu, S.; Han, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, S.; Zheng, R. Baicalein inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cells through suppressing the expression of CD24. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 29, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, N.; Zhang, H.; Wei, L.; Tao, L.; Dai, Q.; Zhao, L.; Lin, B.; Ding, Q.; Guo, Q. HQS-3, a newly synthesized flavonoid, possesses potent anti-tumor effect in vivo and in vitro. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 49, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, Y.W.; Lin, T.H.; Huang, W.S.; Teng, C.Y.; Liou, Y.S.; Kuo, W.H.; Lin, W.L.; Huang, H.I.; Tung, J.N.; Huang, C.Y.; et al. Baicalein inhibits the migration and invasive properties of human hepatoma cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 255, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.F.; Li, T.; Tang, Z.H.; Chang, L.L.; Zhu, H.; Chen, X.P.; Wang, Y.T.; Lu, J.J. Baicalein triggers autophagy and inhibits the protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 Cells. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Chen, W.; Zhang, G.; Luo, D.; Cao, Y.; Wu, J.; Ding, Y.; Liu, B. Baicalein induces apoptosis and autophagy via endoplasmic reticulum stress in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 732516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Huang, T.S.; Wong, C.H.; Hong, C.L.; Tsai, Y.H.; Liang, C.C.; Lu, F.J.; Chang, W.H. Synergistic anti-cancer effect of baicalein and silymarin on human hepatoma HepG2 Cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, C.; Yanez, J.; Vicente, V.; Alcaraz, M.; Benavente-Garcia, O.; Castillo, J.; Lorente, J.; Lozano, J.A. Effects of several polyhydroxylated flavonoids on the growth of B16F10 melanoma and Melan-A melanocyte cell lines: Influence of the sequential oxidation state of the flavonoid skeleton. Melanoma Res. 2003, 13, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Guo, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, J.; Gu, Y.; Li, Y. Baicalein inhibits melanogenesis through activation of the ERK signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 25, 923–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, D.S.; Hsiao, G.; Lai, Y.A.; Tsai, Y.J.; Sheu, J.R. Baicalein induces proliferation inhibition in B16F10 melanoma cells by generating reactive oxygen species via 12-lipoxygenase. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, S.; Baba, K.; Makio, A.; Kumazoe, M.; Huang, Y.; Lin, I.C.; Bae, J.; Murata, M.; Yamada, S.; Tachibana, H. γ-Tocotrienol upregulates aryl hydrocarbon receptor expression and enhances the anticancer effect of baicalein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 473, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.Z.; Liu, C.H.; Wei, B.; Qiao, J.; Lu, T.; Wei, H.C.; Chen, H.D.; He, C.D. Baicalein inhibits DMBA/TPA-induced skin tumorigenesis in mice by modulating proliferation, apoptosis, and inflammation. Inflammation 2013, 36, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Li, J.; Huang, D.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Liao, Y.; Tang, X.; Xie, H.; Tang, F. Baicalein mediates inhibition of migration and invasiveness of skin carcinoma through Ezrin in A431 cells. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallek, M.; Bergsagel, P.L.; Andeson, K.C. Multiple Myeloma: Increasing evidence for a multistep transformation process. Blood 1998, 91, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.G.; Liu, L.P.; Li, C.Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; Qin, J.; Gu, Y.Y.; Li, Z.; Wu, X.L.; Mo, S.L. Scutellaria extract decreases the proportion of side population cells in a myeloma cell line by down-regulating the expression of ABCG2 protein. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 7179–7186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.Y.; Liu, L.P.; Qin, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, Z.; Tang, J.Z.; Mo, S.L. Baicalein decreases side population proportion via inhibition of ABCG2 in multiple myeloma cell line RPMI 8226 in vitro. Fitoterapia 2014, 94, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Otsuyama, K.; Liu, S.; Abroun, S.; Ishikawa, H.; Tsuyama, N.; Obata, M.; Li, F.J.; Zheng, X.; Maki, Y.; et al. Baicalein, a component of Scutellaria radix from Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Tang (HLJDT), leads to suppression of proliferation and induction of apoptosis in human myeloma cells. Blood 2005, 105, 3312–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Ma, Z.; Cai, H.; Li, Q.; Rong, W.; Kawano, M. Inhibitory effect of baicalein on IL-6-mediated signaling cascades in human myeloma cells. Eur. J. Haematol. 2010, 84, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuyama, K.I.; Ma, Z.; Abroun, S.; Amin, J.; Shamsasenjan, K.; Asaoku, H.; Kawano, M.M. PPARβ-mediated growth suppression of baicalein and dexamethasone in human myeloma cells. Leukemia 2007, 21, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielack, S.S.; Kempf-Bielack, B.; Delling, M.; Ulrich Exner, G.; Flege, S.; Helmke, K.; Kotz, R.; Salzer-Kuntschik, M.; Werner, M.; Winfried, W.; et al. Prognostic factors in high-grade osteosarcoma of the extremities or trunk: An analysis of 1702 patients treated on neoadjuvant cooperative osteosarcoma study group protocols. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.B.; He, L.; Huang, Z.; Ma, Z.; Liu, S.Q. Synergistic effect and mechanism of baicalein in combination with lenalidomide-induced apoptosis of myeloma cells. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2013, 34, 546–547. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.P.; Cai, H.L.; He, L.; Ma, Z.; Liu, S.Q. Effect of baicalein on proliferation and migration in multiplemyeloma cell lines RPMI 8226 and U266 cells. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2012, 33, 938–943. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Longhi, A.; Errani, C.; De Paolis, M.; Mercuri, M.; Bacci, G. Primary bone osteosarcoma in the pediatric age: State of the art. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2006, 32, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, F.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zou, Y.; Han, H.; Huang, J. Baicalein induces human osteosarcoma cell line MG-63 apoptosis via ROS-induced BNIP3 expression. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 4731–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, N.; Zhang, Z. Baicalein suppresses the viability of MG-63 osteosarcoma cells through inhibiting c-MYC expression via Wnt signaling pathway. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 405, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, L.; Cai, L.; Wei, R.; Hu, H.; Jin, W. Effects of baicalein on apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; He, S.; Sun, X. HSP70 desensitizes osteosarcoma cells to baicalein and protects cells from undergoing apoptosis. Apoptosis 2014, 19, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, C.J.; Yen, G.C. Chemopreventive effects of dietary phytochemicals against cancer invasion and metastasis: Phenolic acids, monophenol, polyphenol, and their derivatives. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2012, 38, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Li, B.; Rankin, G.O.; Rojanasakul, Y.; Chen, Y.C. Selecting bioactive phenolic compounds as potential agents to inhibit proliferation and VEGF expression in human ovarian cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 9, 1444–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, A.Y.; Ye, X.; Luo, H.; Rankin, G.O.; Chen, Y.C. Inhibitory effect of baicalin and baicalein on ovarian cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 6012–6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Xin, S.; Wang, H.; Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Wei, H. Baicalein inhibits MMP-2 expression in human ovarian cancer cells by suppressing the p38 MAPK-dependent NF-κB signaling pathway. Anticancer Drugs 2015, 26, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donald, G.; Hertzer, K.; Eibl, G. Baicalein—An Intriguing Therapeutic Phytochemical in Pancreatic Cancer. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 13, 1772–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemal, A.; Murray, T.; Samuels, A.; Ghafoor, A.; Ward, E.; Thun, M.J. Cancer Statistics, 2003. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2003, 53, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.Z.; Kuszynski, C.A.; El-Metwally, T.H.; Adrian, T.E. Lipoxygenase Inhibition Induced Apoptosis, Morphological Changes, and Carbonic Anhydrase Expression in Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 266, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, W.G.; Ding, X.Z.; Witt, R.C.; Adrian, T.E. Lipoxygenase Inhibitors Attenuate Growth of Human Pancreatic Cancer Xenografts and Induce Apoptosis through the Mitochondrial Pathway. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2002, 1, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Chen, M.C.; Pham, H.; Angst, E.; King, J.C.; Park, J.; Brovman, E.Y.; Ishiguro, H.; Harris, D.M.; Reber, H.A.; et al. Baicalein, a component of Scutellaria baicalensis, induces apoptosis by Mcl-1 down-regulation in human pancreatic cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miocinovic, R.; McCabe, N.P.; Keck, R.W.; Jankun, J.; Hampton, J.A.; Selman, S.H. In vivo and in vitro effect of baicalein on human prostate cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2005, 26, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pidgeon, G.P.; Kandouz, M.; Meram, A.; Honn, K.V. Mechanisms controlling cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis after 12-Lipoxygenase inhibition in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 2721–2727. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, H.; Yoshida, T.; Horinaka, M.; Yasuda, T.; Goda, A.E.; Konishi, M.; Wakada, M.; Kataoka, K.; Yoshikawa, T.; Sakai, T. Baicalein overcomes tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand resistance via two different cell-specific pathways in cancer cells but not in normal cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8918–8927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovey, J.; Nie, D.; Tovari, J.; Kenessey, I.; Timar, J.; Kandouz, M.; Honn, K.V. Radiosensitivity of human prostate cancer cells can be modulated by inhibition of 12-lipoxygenase. Cancer Lett. 2013, 335, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryal, P.; Kim, K.; Park, P.H.; Ham, S.; Cho, J.; Song, K. Baicalein induces autophagic cell death through AMPK/ULK1 activation and downregulation of mTORC1 complex components in human cancer cells. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 4644–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Morgan, W.A.; Sanchez-Medina, A.; Corcoran, O. The ethanol extract of Scutellaria baicalensis and the active compounds induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis including upregulation of p53 and Bax in human lung cancer cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 254, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Zhao, H.; Hylands, P.J.; Corcoran, O. Secondary metabolite mapping identifies Scutellaria inhibitors of human lung cancer cells. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 53, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, H.W.; Yang, W.H.; Lai, M.Y.; Lin, C.J.; Lee, H.Z. Inhibition of 12-lipoxygenase during baicalein-induced human lung nonsmall carcinoma H460 cell apoptosis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.Z.; Leung, H.W.; Lai, M.Y.; Wu, C.H. Baicalein induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human lung squamous carcinoma CH27 cells. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naveenkumar, C.; Asokkumar, S.; Raghunandhakumar, S.; Jagan, S.; Anandakumar, P.; Augustine, T.A.; Kamaraj, S.; Devaki, T. Potent antitumor and antineoplastic efficacy of baicalein on benzo(a)pyrene-induced experimental pulmonary tumorigenesis. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 26, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveenkumar, C.; Raghunandhakumar, S.; Asokkumar, S.; Devaki, T. Baicalein Abrogates Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-mediated Mitochondrial Dysfunction during Experimental Pulmonary Carcinogenesis in Vivo. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 112, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveenkumar, C.; Raghunandakumar, S.; Asokkumar, S.; Binuclara, J.; Rajan, B.; Premkumar, T.; Devaki, T. Mitigating role of baicalein on lysosomal enzymes and xenobiotic metabolizing enzyme status during lung carcinogenesis of Swiss albino mice induced by benzo(a)pyrene. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 28, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, F.; Wu, J.; Zhao, S.; Luo, Q.; Tang, Q.; Yang, L.; Li, L.; Wu, W.; Hann, S.S. Baicalein increases the expression and reciprocal interplay of RUNX3 and FOXO3a through crosstalk of AMPKα and MEK/ERK1/2 signaling pathways in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 34, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xi, M.; Duan, X.; Wang, Y.; Kong, F. Delivery of baicalein and paclitaxel using self-assembled nanoparticles: Synergistic antitumor effect in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 3737–3750. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.M.; Yuan, G.J.; Deng, J.J.; Guo, H.T.; Xiang, M.; Yang, F. Inhibition of 12-lipoxygenase reduces proliferation and induces apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2012, 11, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.R.; Zhang, S.; Qi, J.A.; Wang, Z.D.; Li, J.; Liu, P.J. Preferential inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma by the flavonoid Baicalein through blocking MEK-ERK signaling. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.J.; Wang, C.J.; Tsai, Y.Y.; Hwang, J.M.; Lin, W.L.; Tseng, T.H.; Chu, C.Y. Inhibitory effect of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-caused tumor promotion in benzo[a]pyrene-initiated CD-1 mouse skin by baicalein. Nutr. Cancer 1999, 34, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonham, M.; Posakony, J.; Coleman, I.; Montgomery, B.; Simon, J.; Nelson, P.S. Characterization of Chemical Constituents in Scutellaria baicalensis with Antiandrogenic and Growth-Inhibitory Activities toward Prostate Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 3905–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cancer | Animal Models | Baicalein Dose | Conclusions | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bladder cancer | MBT-2 cell xenografts in C3H/HeN mice | 0.05 and 0.1 mg/animal, i.h. for 10 days | Baicalein significantly inhibited the tumor growth | [27] |
| MB49 cell xenograft in C57BL/6 mice | 0.8 mg/animal, i.h. for 9 times | Baicalein slightly inhibited tumor growth with some hepatotoxicity | [9] | |
| Breast cancer | MDA-MB-231 cell xenograft in nude mouse | 50 or 100 mg/kg, b.wt., i.g. for 15 days | Baicalein suppresses breast cancer metastasis by inhibition of EMT via downregulation of SATB1 and Wnt/β-catenin pathway | [10] |
| MDA468 cell xenograftin SCID-Bg mice | 20 mg/kg, b.wt., i.p. for 5 days/week | Baicalein suppressed tumor growth of MDA468 cancer cells without toxicity to the host and increased DDIT4 | [34] | |
| Colorectal cancer | AOM/DSS-induced colon cancer | 1, 5, 10 mg/kg, b.wt., orally for 16 weeks | Baicalein significantly decreased the incidence of tumor formation with inflammation | [39] |
| HCT-116 cell xenograft in athymic nude mice | 30 mg/kg, b.wt., i.p. every other day for 4 weeks | Baicalein showed more significant inhibition of tumor growth than those of its parent compound baicalin | [38] | |
| HT-29 cells xenografts in nude mice | 10 mg/kg, b.wt, orally three times every week for 43 days | Baicalein significantly decreased tumor weights and volumes without toxicity | [37] | |
| Gastric cancer | SGC-7901cell xenograft in nude mice | 15 and 50 mg/kg, b.wt, i.g. for 1 week | Baicalein potently inhibited the weight and size of tumors | [42] |
| Hepatocellular cancer | H22 cell xenograft in ICR mice | 50 and 100 mg/kg, i.p. for 13 days | Baicalein significantly inhibited the tumor growth without causing obvious adverse effects on weight or liver and spleen weight | [13] |
| SK-Hep1cell xenograft in athymic BALB/c-nu mice | 5, 10, 20 mg/kg/day; i.p. for 32 days | Baicalein was found to significantly decrease the solid tumor mass and reduced the number of PKCα-positive cells | [50] | |
| DEN-induced rat model | 250 mg/kg, b.wt., i.g. for 2 weeks | Baicalein also reduced neoplastic nodules by inhibition of 12-LOX | [98] | |
| HepG2cell xenograft in nude mice | 20 mg/kg/day, orally | Baicalein suppresses HCC xenograft growth via inhibition of MEK-ERK signaling and by inducing intrinsic apoptosis | [99] | |
| Lung cancer | B(a)P-induced lung cancer | 12 mg/kg, b.wt., orally for 16 weeks | Baicalein abrogates reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction during experimental pulmonary carcinogenesis in vivo | [94] |
| B(a)P-induced lung cancer | 12 mg/kg, b.wt., orally for 16 weeks | Baicalein inhibited pulmonary carcinogenesis-associated inflammation and interfered with COX-2, MMP-2 and MMP-9 expressions in vivo | [14] | |
| B(a)P-induced lung cancer | 12 mg/kg, b.wt., orally for 16 weeks | Baicalein effectively negated B(a)P-induced upregulated expression of CYP1A1 and inhibited lysosomal and microsomal dysfunction. | [95] | |
| B(a)P-induced lung cancer | 12 mg/kg, b.wt., orally for 16 weeks | Baicalein significantly inhibited pulmonary adenoma formation and growth | [93] | |
| Skin cancer | DMBA/TPA-induced skin tumor | 25 mg/kg, b.wt. for 30 weeks | Baicalein inhibited DMBA/TPA-induced skin tumorigenesis in mice by modulating proliferation, apoptosis, and inflammation | [58] |
| B[a]P/TPA-induced skin tumor | 0.08, 0.16, or 0.2 pmol/animal; topical application | Baicalein inhibited the number of TPA-induced tumors per mouse significantly | [100] | |
| Pancreatic cancer | HPAC and AsPC-1 cell xenograft in athymic mice | 250 mg/kg/day b.wt., i.g. for 4 weeks | Baicalein greatly inhibited tumor volume and tumor weight | [81] |
| Prostate cancer | LNCaPcell xenograft in athymic mice | 20 mg/kg/day, b.wt., p.o. for 4 weeks | Baicalein reduced the growth of prostate cancer xenografts in nude mice by 55% at 2 weeks through inhibition of the androgen receptor signaling pathway | [101] |
| DU-145cell xenograft in SCID mice | 10, 20, 40 mg/kg p.o. for 4 weeks | Treatment of mice with baicalein demonstrated a statistically significant tumor volume reduction | [83] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Dong, Y.; Gao, Y.; Du, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, P.; Chen, A.; Huang, H. The Fascinating Effects of Baicalein on Cancer: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101681
Liu H, Dong Y, Gao Y, Du Z, Wang Y, Cheng P, Chen A, Huang H. The Fascinating Effects of Baicalein on Cancer: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(10):1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101681
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hui, Yonghui Dong, Yutong Gao, Zhipeng Du, Yuting Wang, Peng Cheng, Anmin Chen, and Hui Huang. 2016. "The Fascinating Effects of Baicalein on Cancer: A Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 10: 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101681
APA StyleLiu, H., Dong, Y., Gao, Y., Du, Z., Wang, Y., Cheng, P., Chen, A., & Huang, H. (2016). The Fascinating Effects of Baicalein on Cancer: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(10), 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101681