Elevated Levels of Endocannabinoids in Chronic Hepatitis C May Modulate Cellular Immune Response and Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Endocannabinoid (EC) Levels Are Increased in Plasma of Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C (CHC)
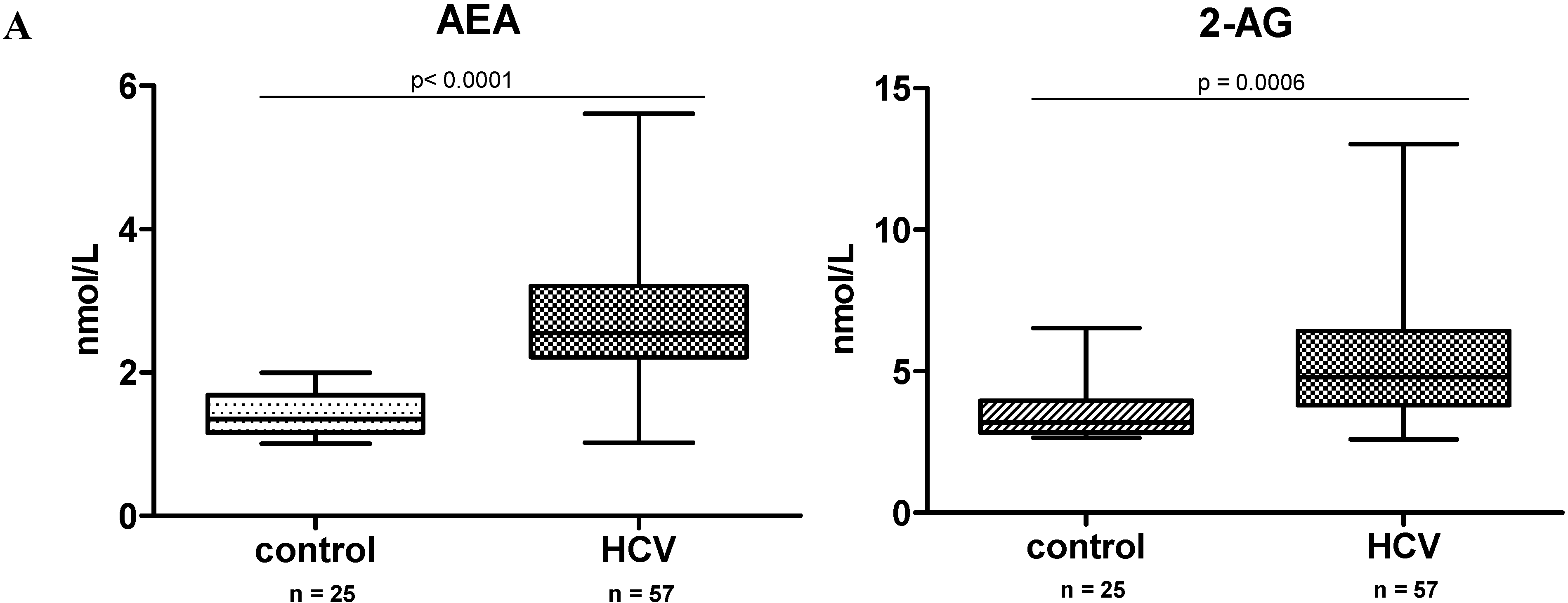
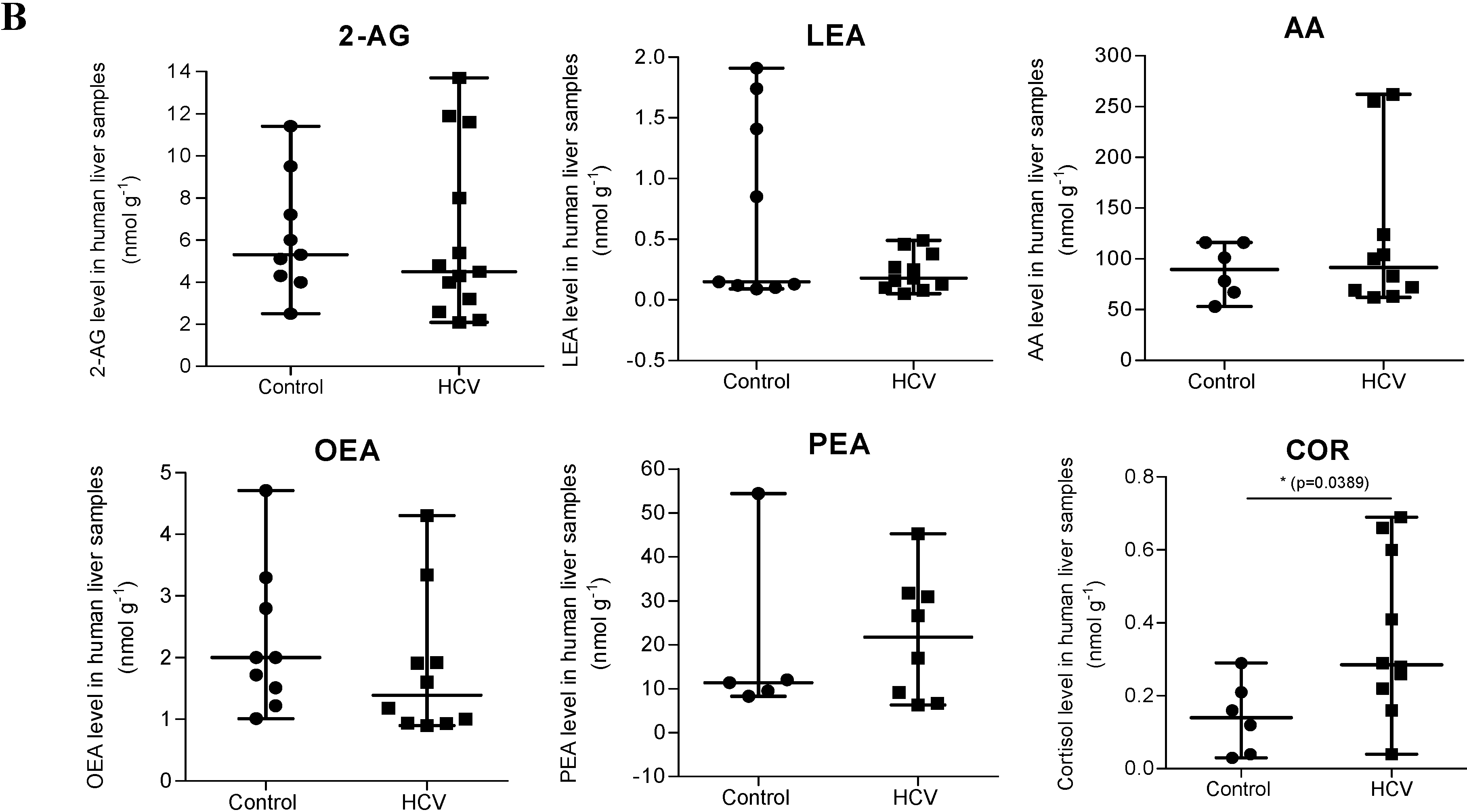
| Anandamide | ||||||
| Parameter | Unadjusted Coefficients | 95% CI | p-Value | Adjusted Coefficients | 95% CI | p-Value |
| Age | −0.00066 | −0.009–0.007 | 0.87 | −0.0036 | 0.013–0.0057 | 0.45 |
| Female | 0.075 | −0.08–0.23 | 0.35 | 0.14 | −0.04–0.33 | 0.13 |
| BMI | 0.011 | −0.009–0.032 | 0.27 | 0.018 | −0.0045–0.041 | 0.12 |
| Diabetes | 0.16 | −0.12–0.43 | 0.26 | 0.14 | −0.16–0.45 | 0.35 |
| Alcohol | 0.046 | −0.18–0.27 | 0.69 | 0.056 | −0.21–0.32 | 0.68 |
| ALT | 0.0006 | −0.0003–0.002 | 0.20 | 0.001 | −0.0005–0.0026 | 0.18 |
| AST | 0.00064 | −0.0007–0.002 | 0.35 | −0.0003 | −0.0025–0.0019 | 0.81 |
| Fibrosis grade (0–2 vs. 3/4) | −0.30 | −0.20–0.24 | 0.73 | −0.09 | −0.28–0.10 | 0.36 |
| Fibrosis grade cont. | −0.0034 | −0.063–0.056 | 0.91 | |||
| Genotype (1 vs. 2–4) | 0.087 | −0.071–0.25 | 0.28 | |||
| Activity grade (1 vs. 2, 1 vs. 3) | 0.082 −0.27 | −0.16–0.33 −0.98–0.43 | 0.51 0.45 | |||
| Steatosis | −0.092 | −0.33–0.14 | 0.44 | |||
| 2-AG | 0.012 | −0.069–0.092 | 0.78 | |||
| 2-AG | ||||||
| Parameter | Unadjusted Coefficients | 95% CI | p-Value | Adjusted Coefficients | 95% CI | p-Value |
| Age | 0.033 | 0.009–0.058 | 0.007 | 0.043 | 0.014–0.072 | 0.004 |
| Female | −0.069 | −0.59–0.45 | 0.80 | −0.14 | −0.72–0.44 | 0.64 |
| BMI | 0.018 | −0.049–0.085 | 0.59 | 0.029 | −0.042–0.10 | 0.42 |
| Diabetes | −0.15 | −1.05–0.75 | 0.75 | −0.54 | −1.49–0.41 | 0.27 |
| Alcohol | −0.33 | −1.06–0.40 | 0.38 | −0.07 | −0.91–0.77 | 0.87 |
| ALT | 0.003 | −0.002–0.007 | 0.23 | −0.00008 | −0.005–0.005 | 0.97 |
| AST | 0.002 | −0.0009–0.005 | 0.17 | 0.0027 | −0.004–0.01 | 0.44 |
| Fibrosis grade (0–2 vs. 3/4) | −0.03 | −0.58–0.51 | 0.90 | −0.25 | −0.85–0.35 | 0.41 |
| Fibrosis grade cont. | 0.009 | −0.18–0.20 | 0.93 | |||
| Genotype (1 vs. 2–4) | 0.087 | −0.071–0.25 | 0.28 | |||
| Activity grade (1 vs. 2, 1 vs. 3) | 0.15 −0.43 | −0.56–0.86 −2.50–1.63 | 0.69 0.68 | |||
| Steatosis | −0.52 | −1.21–0.18 | 0.14 | |||
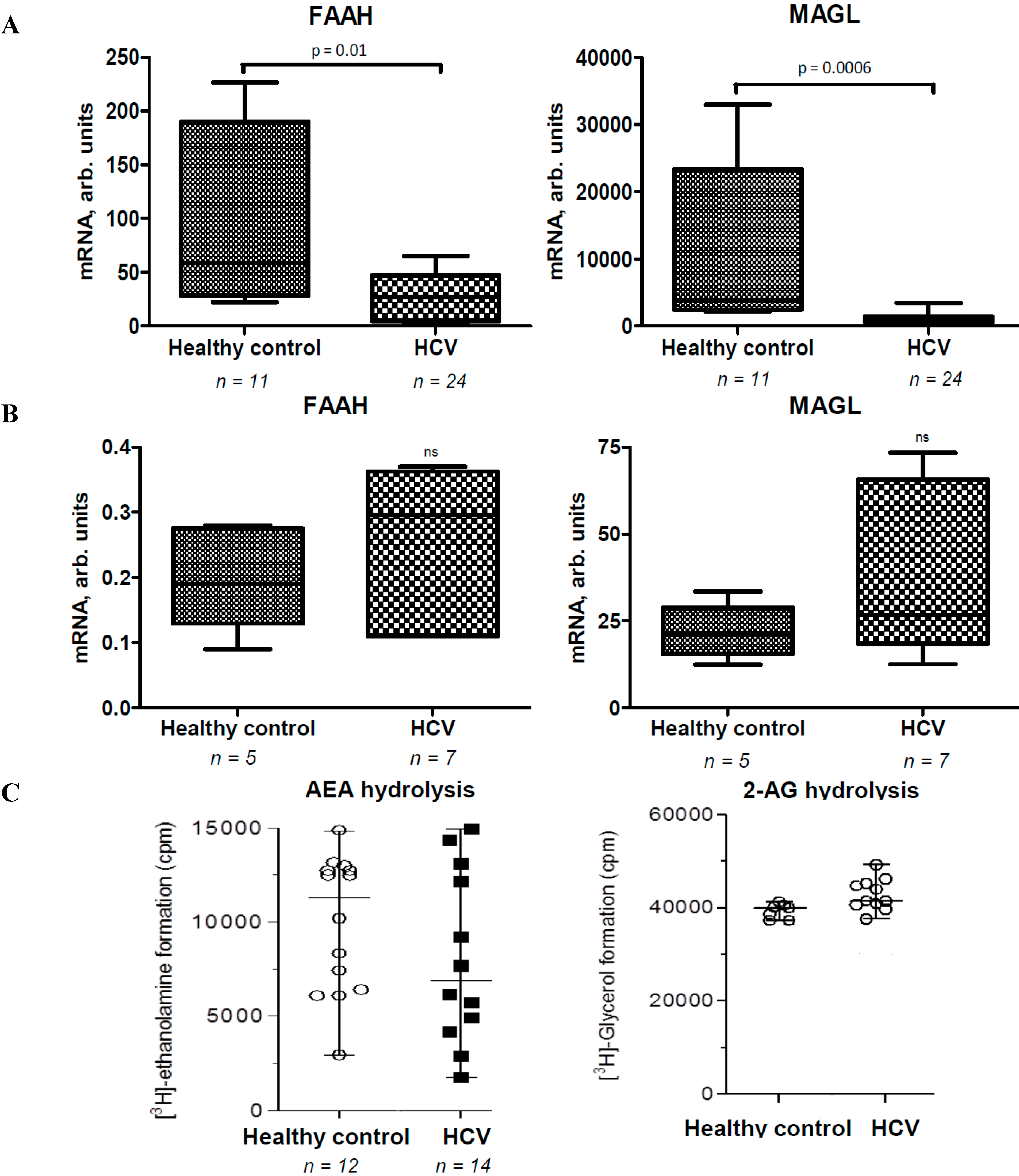
2.2. Activities of EC Degradation Enzymes Are not Affected in CHC Patients
2.3. 2-AG Has a Major Impact on Expression of Components of the EC System in PBMC
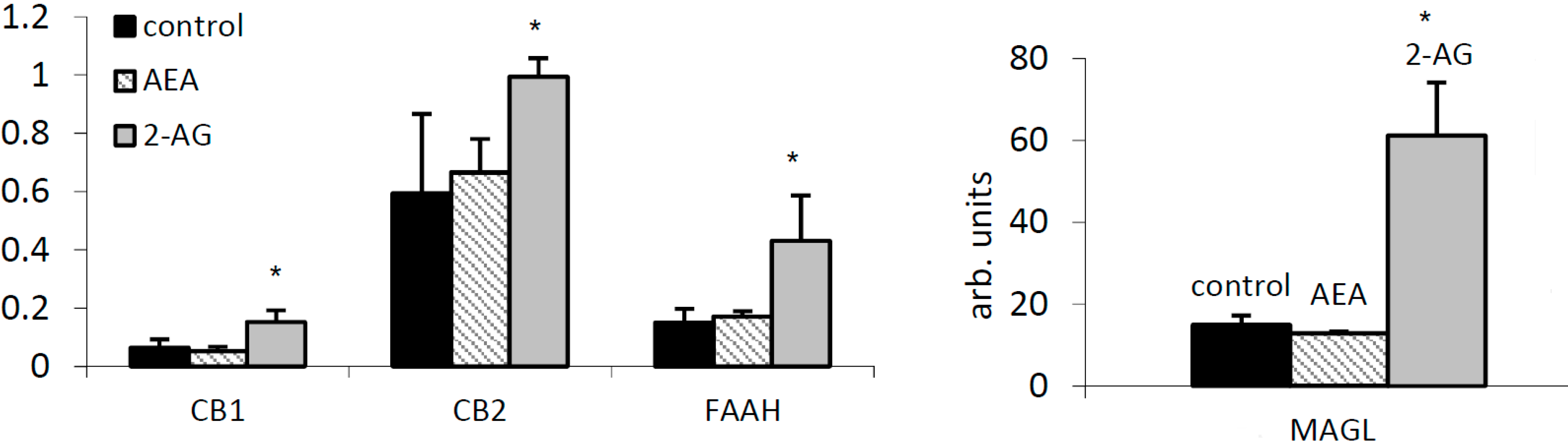
2.4. ECs Suppress Inflammatory Cytokine Production in PBMC
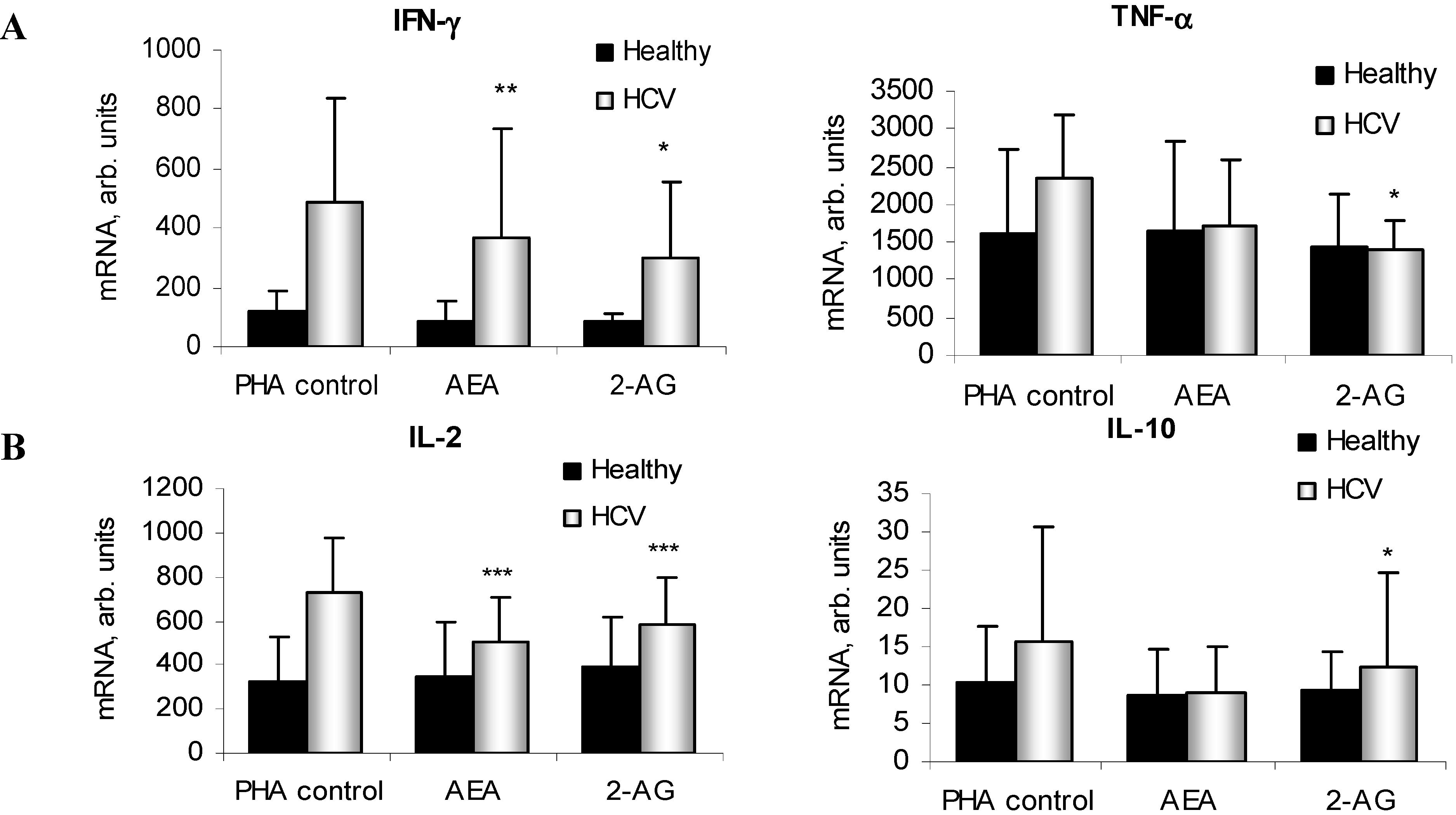
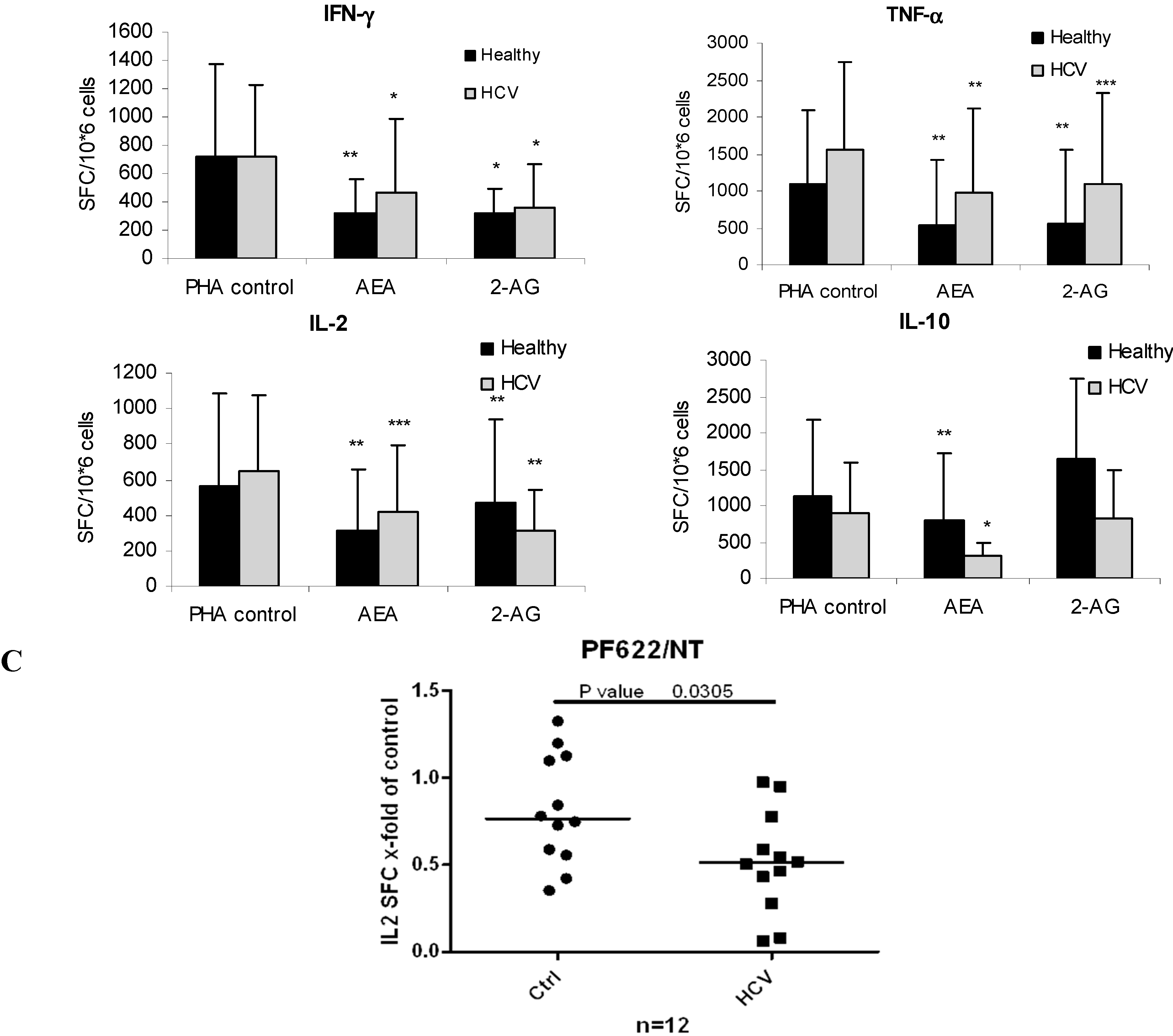
2.5. ECs Reduce Inflammatory Response from HCV-Activated PBMC
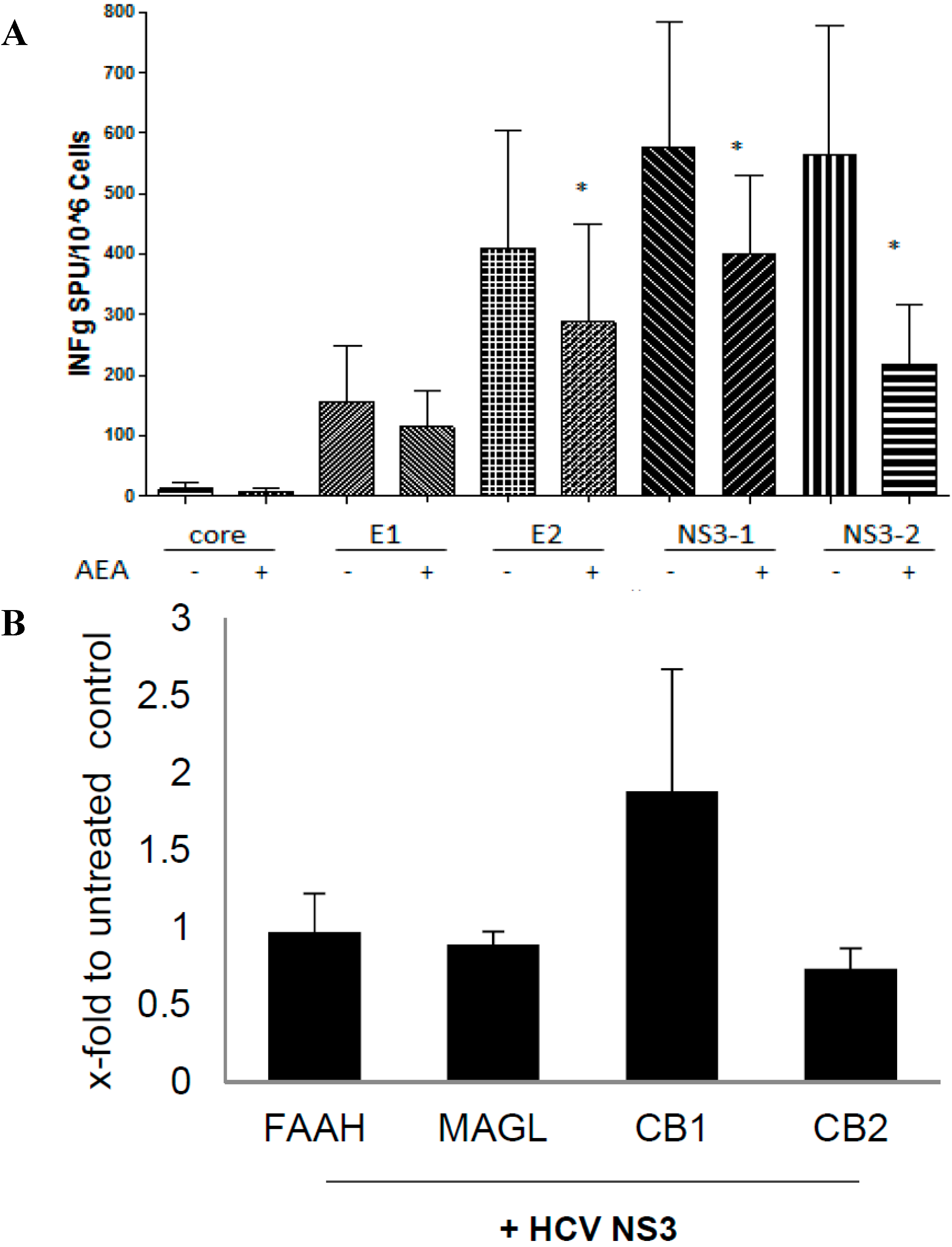
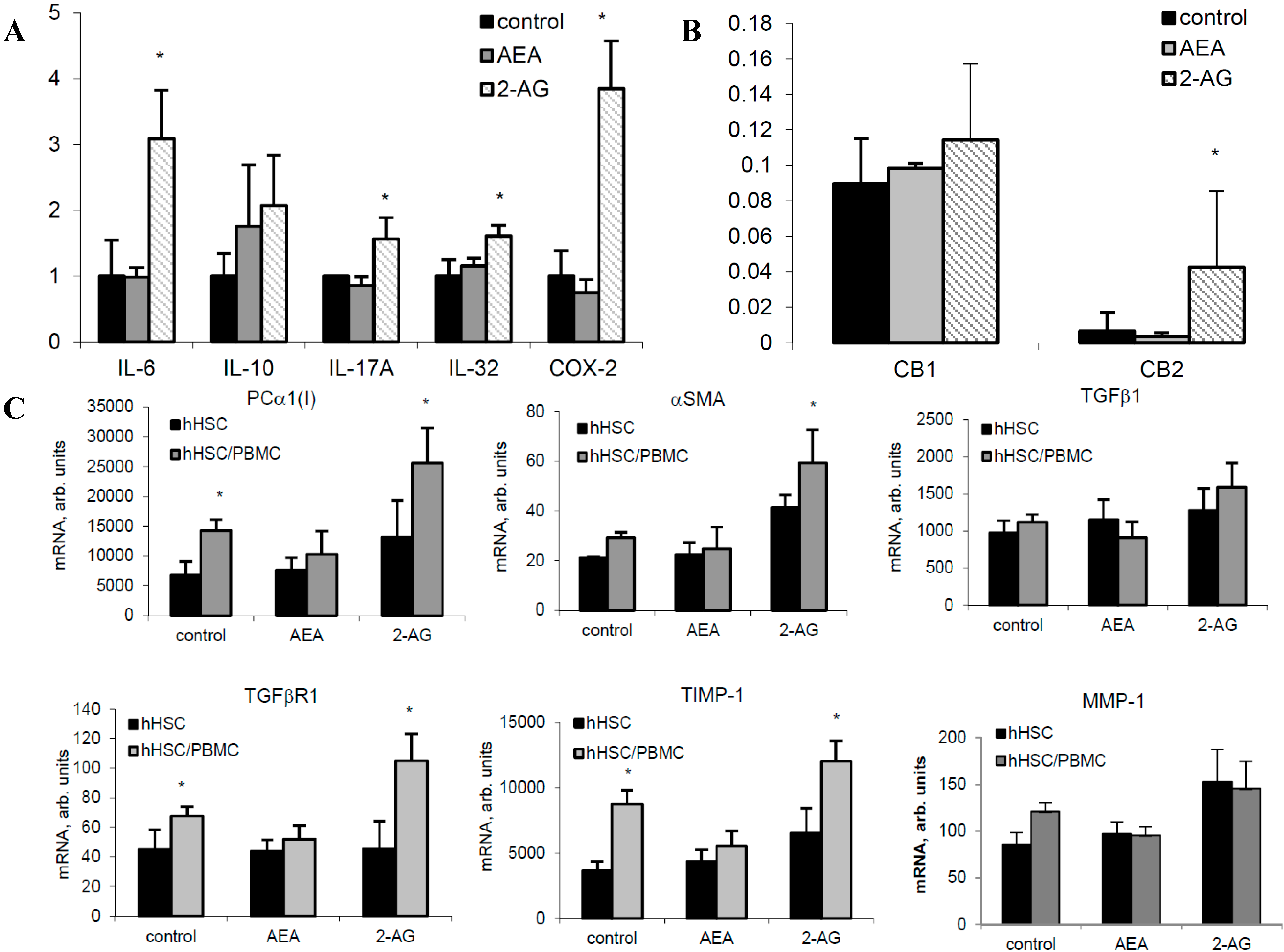
2.6. 2-AG Induces Inflammatory Cytokine Expression in Primary Hepatocytes and Fibrogenic Activation of HSC
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Human Tissues and Patients’ Characteristics
| Control | HCV | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 25 | 57 |
| Female (n, %) | 15 (60) | 22 (38.6) |
| Age (mean, SD) | 44.2 (11.4) | 52.7 (10.0) |
| Diabetes (n, %) | 0 | 5 (8.8) |
| BMI (mean, SD) | NA | 24.7 (3.8) |
| ALT (mean, SD) | NA | 115.8 (84.4) |
| AST (mean, SD) | NA | 91.1 (58.8) |
| INR (mean, SD) | NA | NA |
| Albumin (mean, SD) | NA | NA |
| CHILD | ||
| A | 14 (24.6) | |
| B | 2 (3.5) | |
| C | 0 | |
| Unknown/NA | 25 (100.0) | 41 (71.9) |
| Fibrosis stage | ||
| 0 | 4 (7.0) | |
| 1 | 21 (36.8) | |
| 2 | 11 (19.3) | |
| 3 | 5 (8.8) | |
| 4 | 15 (26.3) | |
| Unknown/NA | 25 (100.0) | 1 (1.8) |
| Activity grade | ||
| 19 (33.3) | ||
| 14 (24.6) | ||
| 1 (1.8) | ||
| Unknown/NA | 25 (100.0) | 23 (40.4) |
| Steatosis | ||
| No | 15 (26.3) | |
| Yes | 16 (28.1) | |
| Unknown | 25 (100.0) | 26 (45.6) |
| Genotype | ||
| 1 | 2 (3.5) | |
| 1A | 11 (19.3) | |
| 1B | 18 (31.6) | |
| 2 | 8 (14.0) | |
| 3 | 14 (24.6) | |
| 4 | 3 (5.3) | |
| Negative | 1 (1.8) | |
| Unknown/NA | 100 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Viral load (mean/SD) Missing | NA | 2,182,222 (2,705,243) 1 (1.8) |
| Control (Bariatric Surgery) | HCV | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 6 | 17 |
| Female (n, %) | 4 (66) | 6 (35.3) |
| Age (mean, SD) | 34 (8.4) | 57.5 (12.7) |
| Diabetes (n, %) | 6 (100) | NA |
| BMI (mean, SD) | 49.5 (7.3) | NA |
| ALT (mean, SD) | NA | NA |
| AST (mean, SD) | NA | NA |
| INR (mean, SD) | NA | NA |
| Albumin (mean, SD) | NA | NA |
| CHILD | ||
| A | 5 (29.4) | |
| B | 0 (0.0) | |
| C | 0 (0.0) | |
| Unknown/NA | ||
| Fibrosis stage | ||
| 0 | 6 (100.0) | 1 (5.9) |
| 1 | 0 (0.0) | |
| 2 | 3 (17.6) | |
| 3 | 8 (47) | |
| 4 | 5 (29.4) | |
| Unknown/NA | ||
| Activity grade | ||
| 1 | 6 (35.3) | |
| 2 | 10 (58.8) | |
| 3 | 1 (5.9) | |
| Unknown/NA | ||
| Steatosis | ||
| No | 6 (100.0) | 5 (29.4) |
| Yes | 12 (70.5) | |
| Unknown | ||
| Genotype | 6 (100.0) | |
| 1 | ||
| 1A | 12 (70.5) | |
| 1B | NA | |
| 2 | NA | |
| 3 | 1 (5.9) | |
| 4 | 2 (11.7) | |
| Negative Unknown/NA | 6 (100.0) | 2 (11.7) |
| Viral load (mean/SD) | NA | 2,530,938 (3,483,784) |
4.2. Materials
4.3. Analysis of ECs in Human Plasma Samples and Liver Biopsies
4.3.1. FAAH and MAGL Activity Assay
4.3.2. In Vitro Experiments
4.3.3. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.3.4. ELISpot
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Abbreviations
| AEA | anandamide |
| 2-AG | 2-arachidonoyl glycerol |
| CHC | chronic hepatitis C |
| FAAH | fatty acid amid hydrolase |
| MAGL | monoacylglycerol lipase |
| hHep | human hepatocytes |
| hHSC | human hepatic stellate cells |
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nagarkatti, P.; Pandey, R.; Rieder, S.A.; Hegde, V.L.; Nagarkatti, M. Cannabinoids as novel anti-inflammatory drugs. Future Med. Chem. 2009, 1, 1333–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julien, B.; Grenard, P.; Teixeira-Clerc, F.; van Nhieu, J.T.; Li, L.; Karsak, M.; Zimmer, A.; Mallat, A.; Lotersztajn, S. Antifibrogenic role of the cannabinoid receptor CB2 in the liver. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 742–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacher, P.; Gao, B. Endocannabinoids and liver disease. III. Endocannabinoid effects on immune cells: Implications for inflammatory liver diseases. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G850–G854. [Google Scholar]
- Guillot, A.; Hamdaoui, N.; Bizy, A.; Zoltani, K.; Souktani, R.; Zafrani, E.S.; Mallat, A.; Lotersztajn, S.; Lafdil, F. Cannabinoid receptor 2 counteracts interleukin-17-induced immune and fibrogenic responses in mouse liver. Hepatology 2014, 59, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira-Clerc, F.; Julien, B.; Grenard, P.; Tran Van Nhieu, J.; Deveaux, V.; Li, L.; Serriere-Lanneau, V.; Ledent, C.; Mallat, A.; Lotersztajn, S. CB1 cannabinoid receptor antagonism: A new strategy for the treatment of liver fibrosis. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallat, A.; Teixeira-Clerc, F.; Deveaux, V.; Manin, S.; Lotersztajn, S. The endocannabinoid system as a key mediator during liver diseases: New insights and therapeutic openings. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraceni, P.; Viola, A.; Piscitelli, F.; Giannone, F.; Berzigotti, A.; Cescon, M.; Domenicali, M.; Petrosino, S.; Giampalma, E.; Riili, A.; et al. Circulating and hepatic endocannabinoids and endocannabinoid-related molecules in patients with cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2009, 30, 816–825. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, K.K.; Sarker, K.P.; Abeyama, K.; Kawahara, K.; Iino, S.; Otsubo, Y.; Saigo, K.; Izumi, H.; Hashiguchi, T.; Yamakuchi, M.; et al. Membrane cholesterol but not putative receptors mediates anandamide-induced hepatocyte apoptosis. Hepatology 2003, 38, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Osei-Hyiaman, D.; DePetrillo, M.; Pacher, P.; Liu, J.; Radaeva, S.; Batkai, S.; Harvey-White, J.; Mackie, K.; Offertaler, L.; Wang, L.; et al. Endocannabinoid activation at hepatic cb1 receptors stimulates fatty acid synthesis and contributes to diet-induced obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar]
- Siegmund, S.V.; Seki, E.; Osawa, Y.; Uchinami, H.; Cravatt, B.F.; Schwabe, R.F. Fatty acid amide hydrolase determines anandamide-induced cell death in the liver. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 10431–10438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldassarre, M.; Giannone, F.A.; Napoli, L.; Tovoli, A.; Ricci, C.S.; Tufoni, M.; Caraceni, P. The endocannabinoid system in advanced liver cirrhosis: Pathophysiological implication and future perspectives. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 1298–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cencioni, M.T.; Chiurchiu, V.; Catanzaro, G.; Borsellino, G.; Bernardi, G.; Battistini, L.; Maccarrone, M. Anandamide suppresses proliferation and cytokine release from primary human t-lymphocytes mainly via CB2 receptors. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, R.; Hegde, V.L.; Singh, N.P.; Hofseth, L.; Singh, U.; Ray, S.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Use of cannabinoids as a novel therapeutic modality against autoimmune hepatitis. Vitam. Horm. 2009, 81, 487–504. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hegde, V.L.; Hegde, S.; Cravatt, B.F.; Hofseth, L.J.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Attenuation of experimental autoimmune hepatitis by exogenous and endogenous cannabinoids: Involvement of regulatory t cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 74, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, T.W.; Newton, C.; Larsen, K.; Chou, J.; Perkins, I.; Lu, L.; Nong, L.; Friedman, H. Cannabinoid receptors and T helper cells. J. Neuroimmunol. 2004, 147, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, T.W.; Newton, C.; Larsen, K.; Lu, L.; Perkins, I.; Nong, L.; Friedman, H. The cannabinoid system and immune modulation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2003, 74, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockwell, C.E.; Snider, N.T.; Thompson, J.T.; Vanden Heuvel, J.P.; Kaminski, N.E. Interleukin-2 suppression by 2-arachidonyl glycerol is mediated through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ independently of cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 70, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Louvet, A.; Teixeira-Clerc, F.; Chobert, M.N.; Deveaux, V.; Pavoine, C.; Zimmer, A.; Pecker, F.; Mallat, A.; Lotersztajn, S. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors protect against alcoholic liver disease by regulating kupffer cell polarization in mice. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Ding, L.; Yin, P.; Lu, X.; Wang, X.; Niu, J.; Gao, P.; Xu, G. Serum metabolic profiling study of hepatocellular carcinoma infected with hepatitis B or hepatitis C virus by using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 5433–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallat, A.; Teixeira-Clerc, F.; Lotersztajn, S. Cannabinoid signaling and liver therapeutics. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, J.H.; Peters, M.G.; Jin, C.; Louie, K.; Tan, V.; Bacchetti, P.; Terrault, N.A. Influence of cannabis use on severity of hepatitis c disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 6, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hezode, C.; Roudot-Thoraval, F.; Nguyen, S.; Grenard, P.; Julien, B.; Zafrani, E.S.; Pawlotsky, J.M.; Dhumeaux, D.; Lotersztajn, S.; Mallat, A. Daily cannabis smoking as a risk factor for progression of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis c. Hepatology 2005, 42, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hezode, C.; Zafrani, E.S.; Roudot-Thoraval, F.; Costentin, C.; Hessami, A.; Bouvier-Alias, M.; Medkour, F.; Pawlostky, J.M.; Lotersztajn, S.; Mallat, A. Daily cannabis use: A novel risk factor of steatosis severity in patients with chronic hepatitis c. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Poorten, D.; Shahidi, M.; Tay, E.; Sesha, J.; Tran, K.; McLeod, D.; Milliken, J.S.; Ho, V.; Hebbard, L.W.; Douglas, M.W.; et al. Hepatitis C virus induces the cannabinoid receptor 1. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12841. [Google Scholar]
- Parfieniuk, A.; Flisiak, R. Role of cannabinoids in chronic liver diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 6109–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegmund, S.V.; Schwabe, R.F. Endocannabinoids and liver disease. II. Endocannabinoids in the pathogenesis and treatment of liver fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G357–G362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clugston, R.D.; Jiang, H.; Lee, M.X.; Piantedosi, R.; Yuen, J.J.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Lewis, M.J.; Gottesman, M.E.; Huang, L.S.; Goldberg, I.J.; et al. Altered hepatic lipid metabolism in c57bl/6 mice fed alcohol: A targeted lipidomic and gene expression study. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 2021–2031. [Google Scholar]
- Balvers, M.G.; Verhoeckx, K.C.; Meijerink, J.; Bijlsma, S.; Rubingh, C.M.; Wortelboer, H.M.; Witkamp, R.F. Time-dependent effect of in vivo inflammation on eicosanoid and endocannabinoid levels in plasma, liver, ileum and adipose tissue in c57bl/6 mice fed a fish-oil diet. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 13, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marzo, V.; Petrosino, S. Endocannabinoids and the regulation of their levels in health and disease. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2007, 18, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauer, D.; Schelling, G.; Gola, H.; Campolongo, P.; Morath, J.; Roozendaal, B.; Hamuni, G.; Karabatsiakis, A.; Atsak, P.; Vogeser, M.; et al. Plasma concentrations of endocannabinoids and related primary fatty acid amides in patients with post-traumatic stress disorder. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62741. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.J.; Yu, J.W.; Wan, L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Shi, Y.G.; Chen, M.Y. Endocannabinoid system activation contributes to glucose metabolism disorders of hepatocytes and promotes hepatitis C virus replication. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 23, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahidi, M.; Tay, E.S.; Read, S.A.; Ramezani-Moghadam, M.; Chayama, K.; George, J.; Douglas, M.W. Endocannabinoid CB1 antagonists inhibit hepatitis C virus production, providing a novel class of antiviral host targeting agents. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2468–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patsenker, E.; Stoll, M.; Millonig, G.; Agaimy, A.; Wissniowski, T.; Schneider, V.; Mueller, S.; Brenneisen, R.; Seitz, H.K.; Ocker, M.; et al. Cannabinoid receptor type I modulates alcohol-induced liver fibrosis. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, M.; Spangenberg, H.C.; Kersting, N.; Altay, T.; Blum, H.E.; Klenerman, P.; Thimme, R.; Semmo, N. Virus-specific cd4+ T cell responses in chronic hcv infection in blood and liver identified by antigen-specific upregulation of cd154. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glassner, A.; Eisenhardt, M.; Kokordelis, P.; Kramer, B.; Wolter, F.; Nischalke, H.D.; Boesecke, C.; Sauerbruch, T.; Rockstroh, J.K.; Spengler, U.; et al. Impaired CD4+ T cell stimulation of nk cell anti-fibrotic activity may contribute to accelerated liver fibrosis progression in HIV/HCV patients. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe, R.F.; Siegmund, S.V. Potential role of CB2 receptors in cannabis smokers with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2005, 42, 975–976; author reply 976–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marzo, V. Targeting the endocannabinoid system: To enhance or reduce? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 438–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Mulvihill, M.M.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Xu, H.; Erdelyi, K.; Hao, E.; Holovac, E.; Hasko, G.; Cravatt, B.F.; Nomura, D.K.; et al. Monoacylglycerol lipase controls endocannabinoid and eicosanoid signaling and hepatic injury in mice. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 808–817. [Google Scholar]
- Von Schonfels, W.; Patsenker, E.; Fahrner, R.; Itzel, T.; Hinrichsen, H.; Brosch, M.; Erhart, W.; Gruodyte, A.; Vollnberg, B.; Richter, K.; et al. Metabolomic tissue signature in human non-alcoholic fatty liver disease identifies protective candidate metabolites. Liver Int. 2014, 35, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Semmo, N.; Krashias, G.; Willberg, C.; Klenerman, P. Analysis of the relationship between cytokine secretion and proliferative capacity in hepatitis C virus infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2007, 14, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chicca, A.; Marazzi, J.; Nicolussi, S.; Gertsch, J. Evidence for bidirectional endocannabinoid transport across cell membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 34660–34682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patsenker, E.; Popov, Y.; Stickel, F.; Jonczyk, A.; Goodman, S.L.; Schuppan, D. Inhibition of integrin αvβ6 on cholangiocytes blocks transforming growth factor-β activation and retards biliary fibrosis progression. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semmo, N.; Barnes, E.; Taylor, C.; Kurtz, J.; Harcourt, G.; Smith, N.; Klenerman, P. T-cell responses and previous exposure to hepatitis c virus in indeterminate blood donors. Lancet 2005, 365, 327–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semmo, N.; Day, C.L.; Ward, S.M.; Lucas, M.; Harcourt, G.; Loughry, A.; Klenerman, P. Preferential loss of IL-2-secreting CD4+ T helper cells in chronic HCV infection. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patsenker, E.; Sachse, P.; Chicca, A.; Gachet, M.S.; Schneider, V.; Mattsson, J.; Lanz, C.; Worni, M.; De Gottardi, A.; Semmo, M.; et al. Elevated Levels of Endocannabinoids in Chronic Hepatitis C May Modulate Cellular Immune Response and Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 7057-7076. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16047057
Patsenker E, Sachse P, Chicca A, Gachet MS, Schneider V, Mattsson J, Lanz C, Worni M, De Gottardi A, Semmo M, et al. Elevated Levels of Endocannabinoids in Chronic Hepatitis C May Modulate Cellular Immune Response and Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(4):7057-7076. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16047057
Chicago/Turabian StylePatsenker, Eleonora, Philip Sachse, Andrea Chicca, María Salomé Gachet, Vreni Schneider, Johan Mattsson, Christian Lanz, Mathias Worni, Andrea De Gottardi, Mariam Semmo, and et al. 2015. "Elevated Levels of Endocannabinoids in Chronic Hepatitis C May Modulate Cellular Immune Response and Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 4: 7057-7076. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16047057
APA StylePatsenker, E., Sachse, P., Chicca, A., Gachet, M. S., Schneider, V., Mattsson, J., Lanz, C., Worni, M., De Gottardi, A., Semmo, M., Hampe, J., Schafmayer, C., Brenneisen, R., Gertsch, J., Stickel, F., & Semmo, N. (2015). Elevated Levels of Endocannabinoids in Chronic Hepatitis C May Modulate Cellular Immune Response and Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(4), 7057-7076. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16047057





