Molecular Mechanisms of Host Cytoskeletal Rearrangements by Shigella Invasins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Gram (−) Bacteria | Effectors |
|---|---|
| Shigella spp. | IpaA [17,18], IpaC [19,20], IpgB1/IpgB2 [21,22] and IpgD [23,24] |
| Salmonella spp. | SipA [25,26], SipC [13], SopE [27,28], SopB [29,30,31] and SpvB [32,33] |
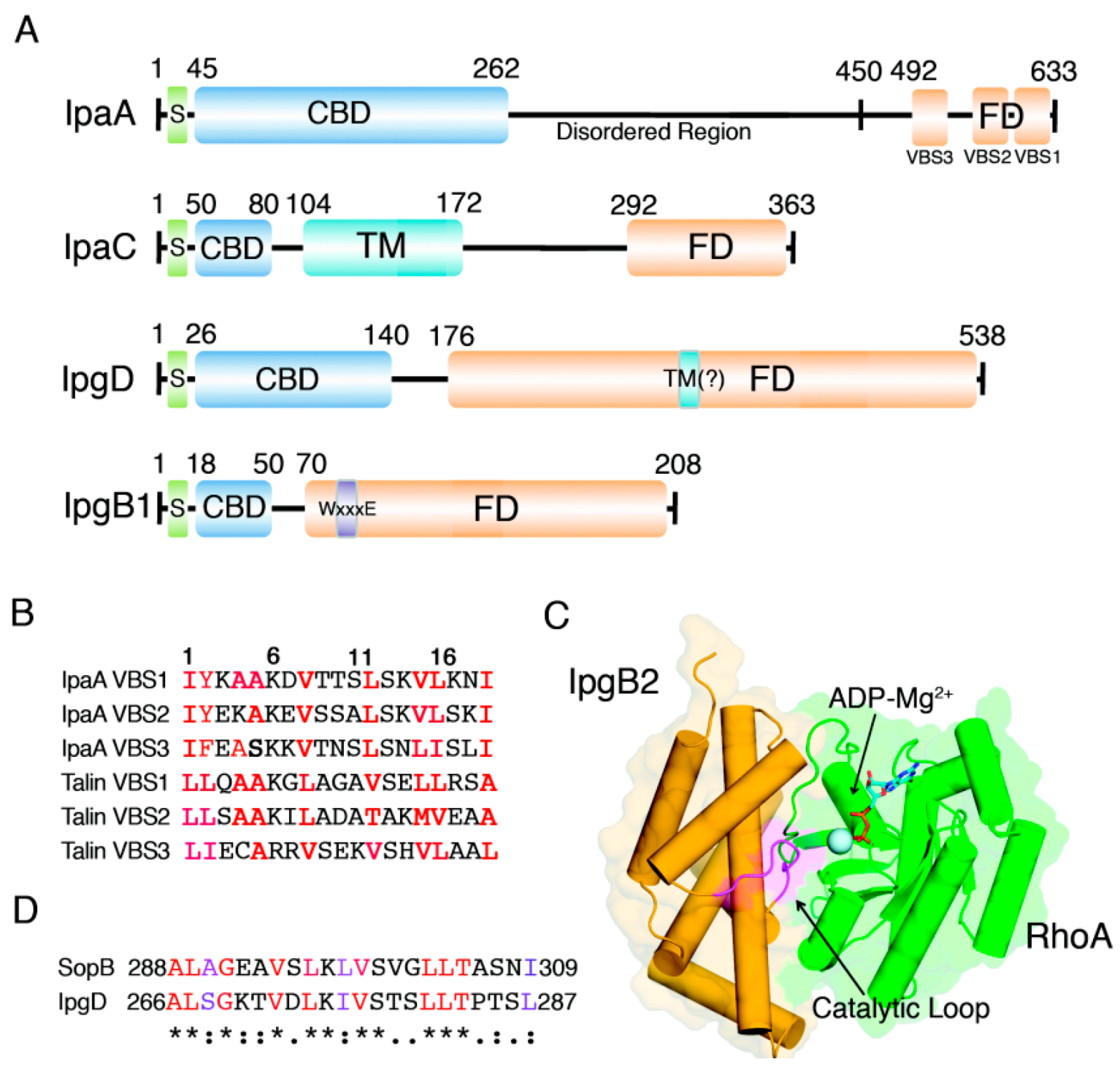
2. IpaA: Mimicry of the Focal Adhesion Protein, Talin
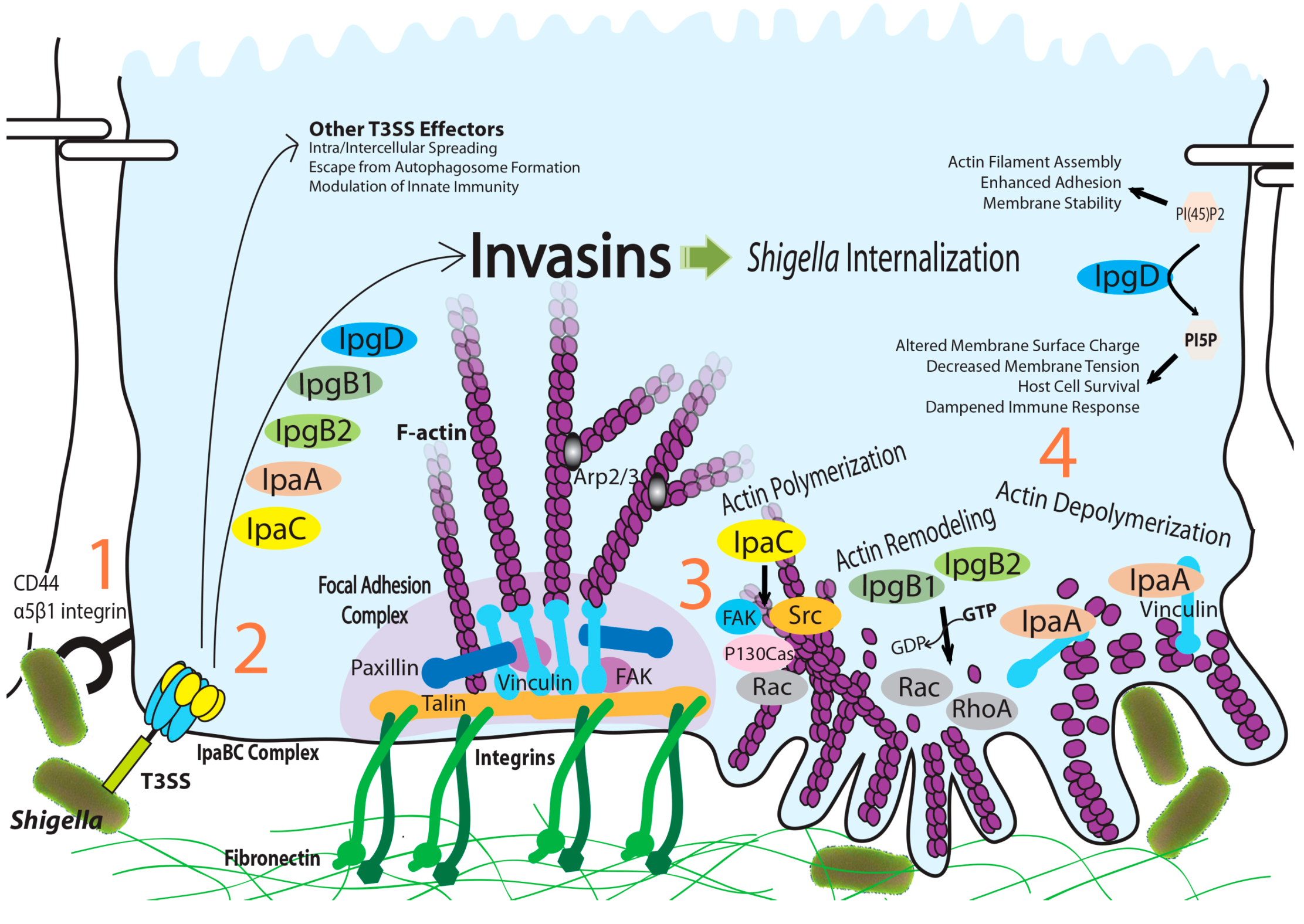
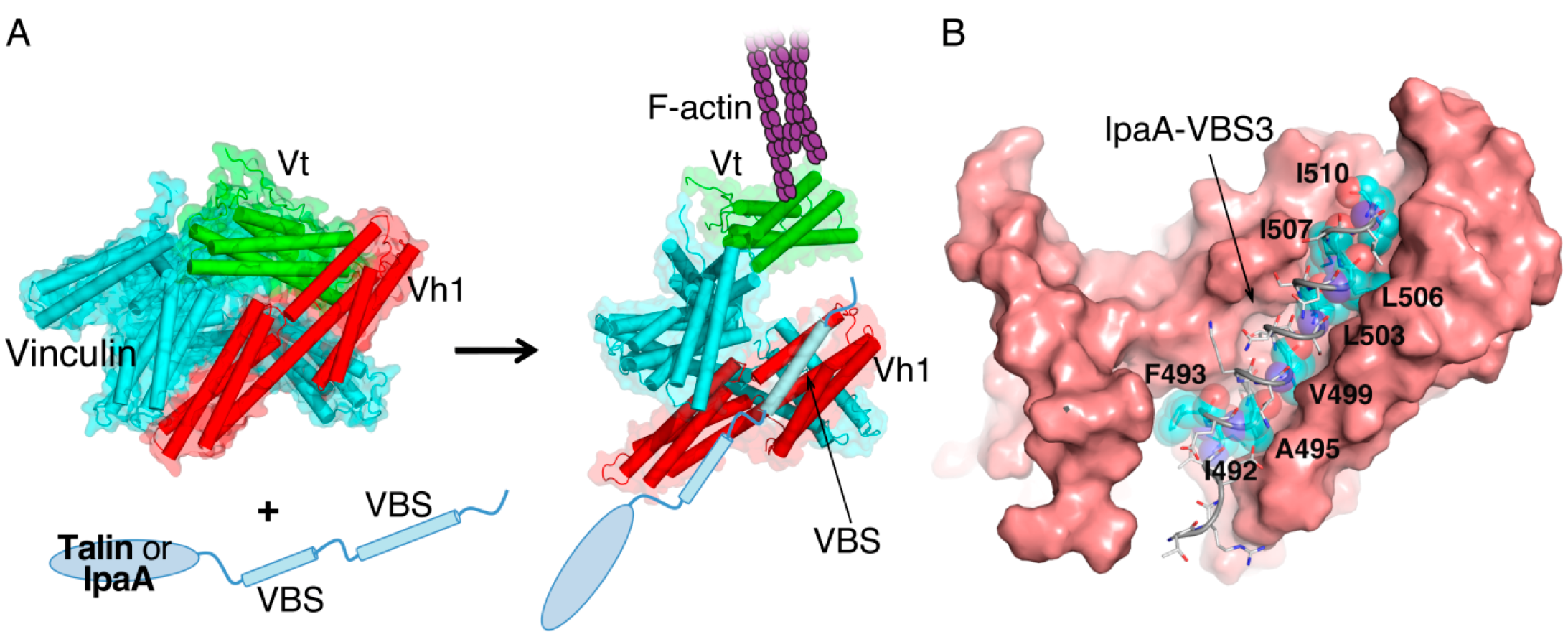
3. IpaC-Dependent Actin Polymerization and Ruffle Formation
4. IpgB1 and IpgB2: Bacterial Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factors
5. IpgD: Phosphoinositide Phosphatase Activity and Beyond
6. Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lecuit, T.; Lenne, P.F. Cell surface mechanics and the control of cell shape, tissue patterns and morphogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 633–644. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, T.S.; Billadeau, D.D. T cell activation and the cytoskeleton: You canʼt have one without the other. Adv. Immunol. 2008, 97, 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Dillon, C.; Goda, Y. The actin cytoskeleton: Integrating form and function at the synapse. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 28, 25–55. [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Roberts, T.H.; Hirschberg, K. Secretory protein trafficking and organelle dynamics in living cells. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2000, 16, 557–589. [Google Scholar]
- Insall, R.H.; Machesky, L.M. Actin dynamics at the leading edge: From simple machinery to complex networks. Dev. Cell 2009, 17, 310–322. [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt, J.K.; Carrizosa, E.; Shaffer, M.H. The actin cytoskeleton in T cell activation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 233–259. [Google Scholar]
- Heng, Y.W.; Koh, C.G. Actin cytoskeleton dynamics and the cell division cycle. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 1622–1633. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Dominguez, R. Regulation of actin cytoskeleton dynamics in cells. Mol. Cells 2010, 29, 311–325. [Google Scholar]
- Sahai, E.; Marshall, C.J. Rho-gtpases and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Aepfelbacher, M.; Zumbihl, R.; Heesemann, J. Modulation of Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton by yopt of yersinia. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 291, 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Carabeo, R.A.; Grieshaber, S.S.; Fischer, E.; Hackstadt, T. Chlamydia trachomatis induces remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton during attachment and entry into HeLa cells. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 3793–3803. [Google Scholar]
- McGhie, E.J.; Hayward, R.D.; Koronakis, V. Cooperation between actin-binding proteins of invasive Salmonella: SipA potentiates SipC nucleation and bundling of actin. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 2131–2139. [Google Scholar]
- Hayward, R.D.; Koronakis, V. Direct nucleation and bundling of actin by the SipC protein of invasive Salmonella. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 4926–4934. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, J.D.; Valdivia, R.H. Uncivil engineers: Chlamydia, Salmonella and Shigella alter cytoskeleton architecture to invade epithelial cells. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 1219–1232. [Google Scholar]
- Kalman, D.; Weiner, O.D.; Goosney, D.L.; Sedat, J.W.; Finlay, B.B.; Abo, A.; Bishop, J.M. Enteropathogenic E. coli acts through WASP and Arp2/3 complex to form actin pedestals. Nat Cell Biol. 1999, 1, 389–391. [Google Scholar]
- Gouin, E.; Egile, C.; Dehoux, P.; Villiers, V.; Adams, J.; Gertler, F.; Li, R.; Cossart, P. The RickA protein of Rickettsia conorii activates the Arp2/3 complex. Nature 2004, 427, 457–461. [Google Scholar]
- Bourdet-Sicard, R.; Rudiger, M.; Jockusch, B.M.; Gounon, P.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Nhieu, G.T. Binding of the Shigella protein IpaA to vinculin induces F-actin depolymerization. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 5853–5862. [Google Scholar]
- Izard, T.; van Nhieu, G.T.; Bois, P.R. Shigella applies molecular mimicry to subvert vinculin and invade host cells. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 175, 465–475. [Google Scholar]
- Van Nhieu, G.T.; Caron, E.; Hall, A.; Sansonetti, P.J. IpaC induces actin polymerization and filopodia formation during Shigella entry into epithelial cells. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 3249–3262. [Google Scholar]
- Mounier, J.; Popoff, M.R.; Enninga, J.; Frame, M.C.; Sansonetti, P.J.; van Nhieu, G.T. The IpaC carboxyterminal effector domain mediates Src-dependent actin polymerization during Shigella invasion of epithelial cells. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000271. [Google Scholar]
- Alto, N.M.; Shao, F.; Lazar, C.S.; Brost, R.L.; Chua, G.; Mattoo, S.; McMahon, S.A.; Ghosh, P.; Hughes, T.R.; Boone, C.; et al. Identification of a bacterial type III effector family with G protein mimicry functions. Cell 2006, 124, 133–145. [Google Scholar]
- Hachani, A.; Biskri, L.; Rossi, G.; Marty, A.; Menard, R.; Sansonetti, P.; Parsot, C.; van Nhieu, G.T.; Bernardini, M.L.; Allaoui, A. IpgB1 and IpgB2, two homologous effectors secreted via the Mxi-Spa type III secretion apparatus, cooperate to mediate polarized cell invasion and inflammatory potential of Shigella flexenri. Microbes Infect. 2008, 10, 260–268. [Google Scholar]
- Niebuhr, K.; Giuriato, S.; Pedron, T.; Philpott, D.J.; Gaits, F.; Sable, J.; Sheetz, M.P.; Parsot, C.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Payrastre, B. Conversion of PtdIns(4,5)p(2) into PtdIns(5)p by the S. flexneri effector ipgd reorganizes host cell morphology. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 5069–5078. [Google Scholar]
- Pendaries, C.; Tronchere, H.; Arbibe, L.; Mounier, J.; Gozani, O.; Cantley, L.; Fry, M.J.; Gaits-Iacovoni, F.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Payrastre, B. PtdIns5p activates the host cell PI3-kinase/Akt pathway during Shigella flexneri infection. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Mooseker, M.S.; Galan, J.E. Role of the S. typhimurium actin-binding protein SipA in bacterial internalization. Science 1999, 283, 2092–2095. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Mooseker, M.S.; Galan, J.E. An invasion-associated Salmonella protein modulates the actin-bundling activity of plastin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 10176–10181. [Google Scholar]
- Hardt, W.D.; Chen, L.M.; Schuebel, K.E.; Bustelo, X.R.; Galan, J.E.S. Typhimurium encodes an activator of Rho GTPases that induces membrane ruffling and nuclear responses in host cells. Cell 1998, 93, 815–826. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, K.; Parashuraman, S.; Raje, M.; Mukhopadhyay, A. Sope acts as an Rab5-specific nucleotide exchange factor and recruits non-prenylated Rab5 on Salmonella-containing phagosomes to promote fusion with early endosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 23607–23615. [Google Scholar]
- Norris, F.A.; Wilson, M.P.; Wallis, T.S.; Galyov, E.E.; Majerus, P.W. Sopb, a protein required for virulence of Salmonella dublin, is an inositol phosphate phosphatas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14057–14059. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, J.C.; Hueffer, K.; Lam, T.T.; Galan, J.E. Diversification of a Salmonella virulence protein function by ubiquitin-dependent differential localization. Cell 2009, 137, 283–294. [Google Scholar]
- Bakowski, M.A.; Braun, V.; Lam, G.Y.; Yeung, T.; Do Heo, W.; Meyer, T.; Finlay, B.B.; Grinstein, S.; Brumell, J.H. The phosphoinositide phosphatase SopB manipulates membrane surface charge and trafficking of the Salmonella-containing vacuole. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 7, 453–462. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, E.A.; Brittnacher, M.; Haraga, A.; Jeng, R.L.; Welch, M.D.; Miller, S.I. Salmonella effectors translocated across the vacuolar membrane interact with the actin cytoskeleton. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 48, 401–415. [Google Scholar]
- Lesnick, M.L.; Reiner, N.E.; Fierer, J.; Guiney, D.G. The Salmonella spvB virulence gene encodes an enzyme that ADP-ribosylates actin and destabilizes the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 1464–1470. [Google Scholar]
- Niyogi, S.K. Shigellosis. J. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 133–143. [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti, P.J. Molecular and cellular biology of Shigella flexneri invasiveness: From cell assay systems to shigellosis. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 1992, 180, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Speelman, P.; Kabir, I.; Islam, M. Distribution and spread of colonic lesions in shigellosis: A colonoscopic study. J. Infect. Dis. 1984, 150, 899–903. [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez-Torres, A.; Fang, F.C. Cellular routes of invasion by enteropathogens. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2000, 3, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Gouin, E.; Welch, M.D.; Cossart, P. Actin-based motility of intracellular pathogens. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2005, 8, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, T.; Arpin, M.; Prevost, M.C.; Gounon, P.; Sansonetti, P.J. Cytoskeletal rearrangements and the functional role of T-plastin during entry of Shigella flexneri into HeLa cells. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 129, 367–381. [Google Scholar]
- Tran van Nhieu, G.; Ben-Ze’ev, A.; Sansonetti, P.J. Modulation of bacterial entry into epithelial cells by association between vinculin and the Shigella ipaa invasion. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 2717–2729. [Google Scholar]
- Niebuhr, K.; Jouihri, N.; Allaoui, A.; Gounon, P.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Parsot, C. IpgD, a protein secreted by the type III secretion machinery of Shigella flexneri, is chaperoned by IpgE and implicated in entry focus formatio. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 8–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ramarao, N.; le Clainche, C.; Izard, T.; Bourdet-Sicard, R.; Ageron, E.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Carlier, M.F.; Tran van Nhieu, G. Capping of actin filaments by vinculin activated by the Shigella ipaa carboxyl-terminal domain. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 853–857. [Google Scholar]
- Blocker, A.; Gounon, P.; Larquet, E.; Niebuhr, K.; Cabiaux, V.; Parsot, C.; Sansonetti, P. The tripartite type III secreton of Shigella flexneri inserts IpaB and IpaC into host membranes. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 147, 683–693. [Google Scholar]
- Bulgin, R.; Raymond, B.; Garnett, J.A.; Frankel, G.; Crepin, V.F.; Berger, C.N.; Arbeloa, A. Bacterial guanine nucleotide exchange factors SopE-like and WxxxE effectors. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar]
- Lock, J.G.; Wehrle-Haller, B.; Stromblad, S. Cell-matrix adhesion complexes: Master control machinery of cell migration. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2008, 18, 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler, W.H.; Liddington, R.C.; Critchley, D.R. The structure and regulation of vinculin. Trends Cell Biol. 2006, 16, 453–460. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.W.; Wulfkuhle, J.D.; Otto, J.J. Vinculin binding site mapped on talin with an anti-idiotypic antibody. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 16355–16358. [Google Scholar]
- Kroemker, M.; Rudiger, A.H.; Jockusch, B.M.; Rudiger, M. Intramolecular interactions in vinculin control alpha-actinin binding to the vinculin head. FEBS Lett. 1994, 355, 259–262. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, R.P.; Craig, S.W. F-actin binding site masked by the intramolecular association of vinculin head and tail domains. Nature 1995, 373, 261–264. [Google Scholar]
- Huttelmaier, S.; Illenberger, S.; Grosheva, I.; Rudiger, M.; Singer, R.H.; Jockusch, B.M. Raver1, a dual compartment protein, is a ligand for PTB/hnRNPI and microfilament attachment proteins. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 775–786. [Google Scholar]
- Bakolitsa, C.; Cohen, D.M.; Bankston, L.A.; Bobkov, A.A.; Cadwell, G.W.; Jennings, L.; Critchley, D.R.; Craig, S.W.; Liddington, R.C. Structural basis for vinculin activation at sites of cell adhesion. Nature 2004, 430, 583–586. [Google Scholar]
- Borgon, R.A.; Vonrhein, C.; Bricogne, G.; Bois, P.R.; Izard, T. Crystal structure of human vinculin. Structure 2004, 12, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar]
- Izard, T.; Vonrhein, C. Structural basis for amplifying vinculin activation by talin. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 27667–27678. [Google Scholar]
- Gingras, A.R.; Ziegler, W.H.; Frank, R.; Barsukov, I.L.; Roberts, G.C.; Critchley, D.R.; Emsley, J. Mapping and consensus sequence identification for multiple vinculin binding sites within the talin rod. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 37217–37224. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.; Valencia-Gallardo, C.; Sharff, A.; Tran van Nhieu, G.; Izard, T. Novel vinculin binding site of the IpaA invasin of Shigella. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 23214–23221. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.; Lee, J.H.; Gouin, E.; Cossart, P.; Izard, T. The Rickettsia surface cell antigen 4 applies mimicry to bind to and activate vinculin. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 35096–35103. [Google Scholar]
- Le Clainche, C.; Dwivedi, S.P.; Didry, D.; Carlier, M.F. Vinculin is a dually regulated actin filament barbed end-capping and side-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 23420–23432. [Google Scholar]
- Hanks, S.K.; Ryzhova, L.; Shin, N.Y.; Brabek, J. Focal adhesion kinase signaling activities and their implications in the control of cell survival and motility. Front. Biosci. 2003, 8, d982–d996. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, S.K.; Schlaepfer, D.D. Integrin-regulated FAK-Src signaling in normal and cancer cells. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2006, 18, 516–523. [Google Scholar]
- Watarai, M.; Funato, S.; Sasakawa, C. Interaction of Ipa proteins of Shigella flexneri with alpha5beta1 integrin promotes entry of the bacteria into mammalian cells. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 991–999. [Google Scholar]
- Terry, C.M.; Picking, W.L.; Birket, S.E.; Flentie, K.; Hoffman, B.M.; Barker, J.R.; Picking, W.D. The C-terminus of IpaC is required for effector activities related to Shigella invasion of host cells. Microb. Pathog. 2008, 45, 282–289. [Google Scholar]
- Kueltzo, L.A.; Osiecki, J.; Barker, J.; Picking, W.L.; Ersoy, B.; Picking, W.D.; Middaugh, C.R. Structure-function analysis of invasion plasmid antigen C (IpaC) from Shigella flexneri. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 2792–2798. [Google Scholar]
- Myeni, S.K.; Zhou, D. The C terminus of SipC binds and bundles F-actin to promote Salmonella invasion. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 13357–13363. [Google Scholar]
- Dvorsky, R.; Ahmadian, M.R. Always look on the bright site of Rho: Structural implications for a conserved intermolecular interface. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Arbeloa, A.; Bulgin, R.R.; MacKenzie, G.; Shaw, R.K.; Pallen, M.J.; Crepin, V.F.; Berger, C.N.; Frankel, G. Subversion of actin dynamics by espm effectors of attaching and effacing bacterial pathogens. Cell. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1429–1441. [Google Scholar]
- Bulgin, R.R.; Arbeloa, A.; Chung, J.C.; Frankel, G. EspT triggers formation of lamellipodia and membrane ruffles through activation of Rac-1 and Cdc42. Cell. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 217–229. [Google Scholar]
- Handa, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Ohya, K.; Iwai, H.; Ishijima, N.; Koleske, A.J.; Fukui, Y.; Sasakawa, C. Shigella IpgB1 promotes bacterial entry through the ELMO-Dock180 machinery. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Sutton, S.E.; Wallenfang, A.J.; Orchard, R.C.; Wu, X.; Feng, Y.; Chai, J.; Alto, N.M. Structural insights into host GTPase isoform selection by a family of bacterial GEF mimics. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 853–860. [Google Scholar]
- Klink, B.U.; Barden, S.; Heidler, T.V.; Borchers, C.; Ladwein, M.; Stradal, T.E.; Rottner, K.; Heinz, D.W. Structure of Shigella IpgB2 in complex with human Rhoa: Implications for the mechanism of bacterial guanine nucleotide exchange factor mimicry. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 17197–17208. [Google Scholar]
- Buchwald, G.; Friebel, A.; Galan, J.E.; Hardt, W.D.; Wittinghofer, A.; Scheffzek, K. Structural basis for the reversible activation of a Rho protein by the bacterial toxin SopE. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 3286–3295. [Google Scholar]
- Ohya, K.; Handa, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Suzuki, M.; Sasakawa, C. IpgB1 is a novel Shigella effector protein involved in bacterial invasion of host cells. Its activity to promote membrane ruffling via Rac1 and Cdc42 activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 24022–24034. [Google Scholar]
- Ehsani, S.; Santos, J.C.; Rodrigues, C.D.; Henriques, R.; Audry, L.; Zimmer, C.; Sansonetti, P.; Tran van Nhieu, G.; Enninga, J. Hierarchies of host factor dynamics at the entry site of Shigella flexneri during host cell invasion. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 2548–2557. [Google Scholar]
- Saarikangas, J.; Zhao, H.; Lappalainen, P. Regulation of the actin cytoskeleton-plasma membrane interplay by phosphoinositides. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 259–289. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, H.F.; Clarke, J.H.; Letcher, A.J.; Irvine, R.F.; Hinchliffe, K.A. Effects of lipid kinase expression and cellular stimuli on phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate levels in mammalian cell lines. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 2868–2872. [Google Scholar]
- Lecompte, O.; Poch, O.; Laporte, J. Ptdins5p regulation through evolution: Roles in membrane trafficking? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008, 33, 453–460. [Google Scholar]
- Sbrissa, D.; Ikonomov, O.C.; Strakova, J.; Shisheva, A. Role for a novel signaling intermediate, phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate, in insulin-regulated F-actin stress fiber breakdown and GLUT4 translocation. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 4853–4865. [Google Scholar]
- Downward, J. Pi 3-kinase, Akt and cell survival. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004, 15, 177–182. [Google Scholar]
- Puhar, A.; Tronchere, H.; Payrastre, B.; Nhieu, G.T.; Sansonetti, P.J. A Shigella effector dampens inflammation by regulating epithelial release of danger signal ATP through production of the lipid mediator ptdins5p. Immunity 2013, 39, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Marcus, S.L.; Wenk, M.R.; Steele-Mortimer, O.; Finlay, B.B. A synaptojanin-homologous region of Salmonella typhimurium SigD is essential for inositol phosphatase activity and Akt activation. FEBS Lett. 2001, 494, 201–207. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, W.D.; Inoue, T.; Park, W.S.; Kim, M.L.; Park, B.O.; Wandless, T.J.; Meyer, T. Pi(3,4,5)p3 and pi(4,5)p2 lipids target proteins with polybasic clusters to the plasma membrane. Science 2006, 314, 1458–1461. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.H.; Park, H.; Park, Y.H. Molecular Mechanisms of Host Cytoskeletal Rearrangements by Shigella Invasins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 18253-18266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151018253
Lee JH, Park H, Park YH. Molecular Mechanisms of Host Cytoskeletal Rearrangements by Shigella Invasins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(10):18253-18266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151018253
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jun Hyuck, HaJeung Park, and Yong Ho Park. 2014. "Molecular Mechanisms of Host Cytoskeletal Rearrangements by Shigella Invasins" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 10: 18253-18266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151018253
APA StyleLee, J. H., Park, H., & Park, Y. H. (2014). Molecular Mechanisms of Host Cytoskeletal Rearrangements by Shigella Invasins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(10), 18253-18266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151018253





