N,N’-alkylated Imidazolium-Derivatives Act as Quorum-Sensing Inhibitors Targeting the Pectobacterium atrosepticum-Induced Symptoms on Potato Tubers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Construction of the Pectobacterium AHL-Biosensor
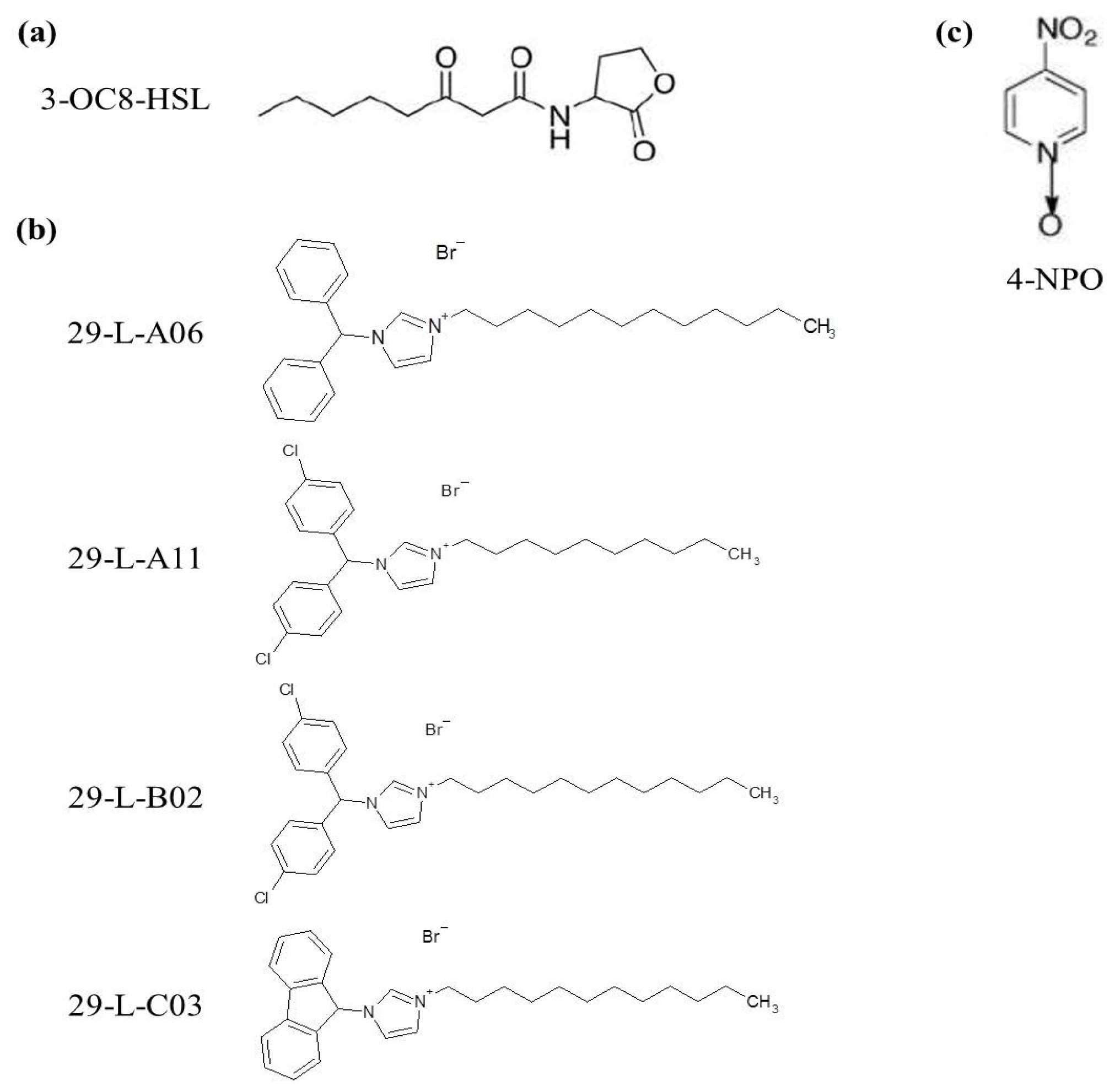
2.2. QSIs Identification
2.3. Biological Effects of the Identified QSIs on Pectobacterium Cells
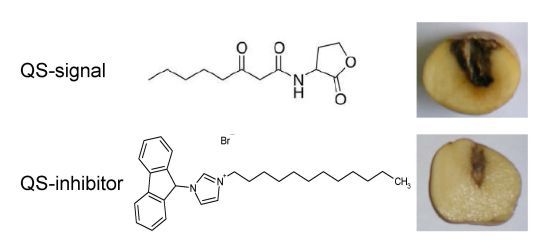
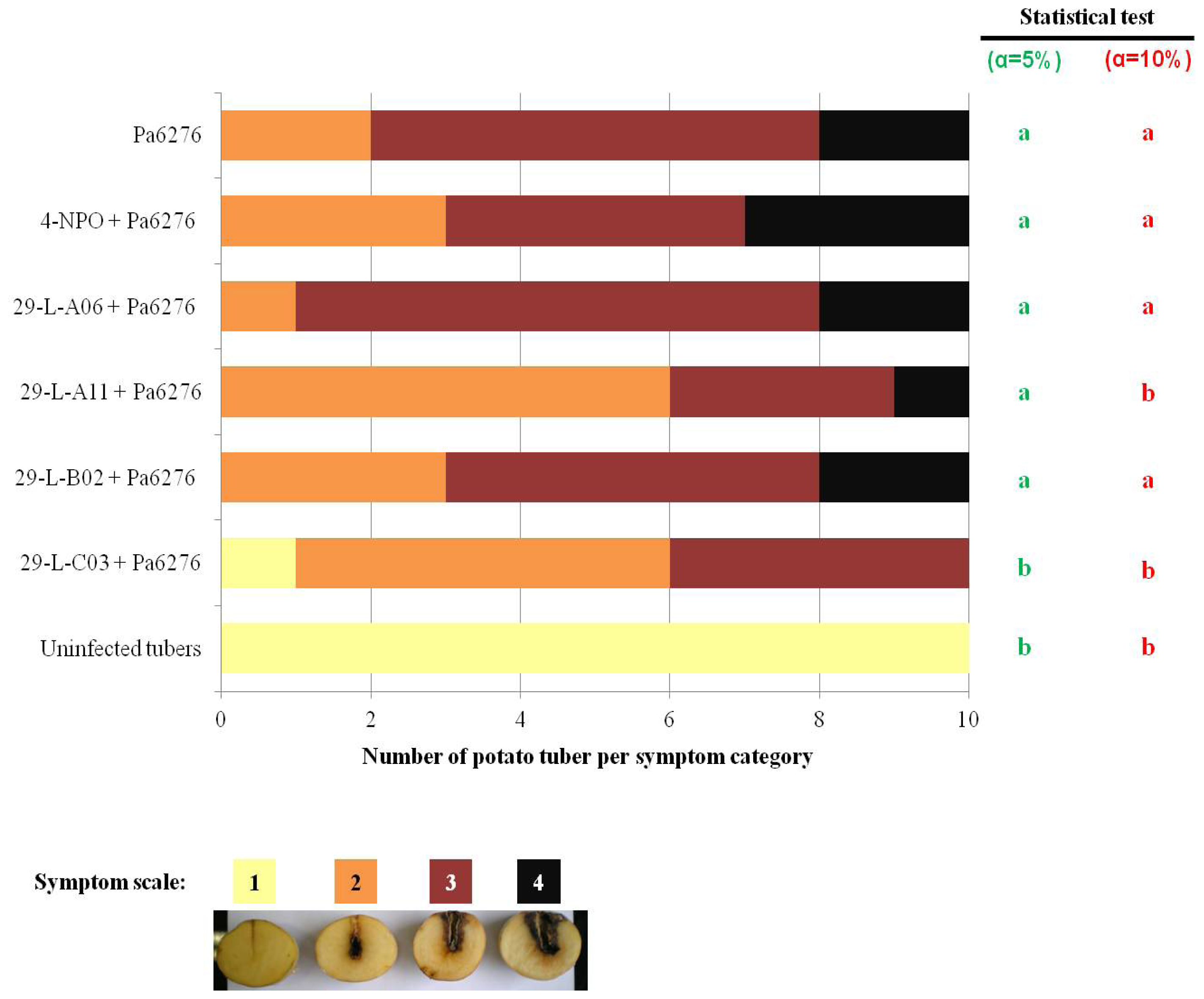
2.4. QSIs Could Moderate the P. atrosepticum-Induced Symptoms in Potato Tubers
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
3.2. Chemical Library
3.3. Screening for QSIs
3.4. Measurement of AC50, GIAC50, MIC and MBC Values of the QSIs
3.5. Virulence Assays on Potato Tubers
4. Conclusions
| Pectobacterium cells | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | AC50a | GIAC50b | MICa | MBCa |
| 4-NPO | >100 (12%) c | 1.00 | 50 | >100 |
| 29-L-A06 | 18 | 0.94 | 25 | 25 |
| 29-L-A11 | 14 | 0.93 | 10 | 25 |
| 29-L-B02 | 16 | 0.99 | <2.5 | 2.5 |
| 29-L-C03 | 20 | 0.93 | 25 | 25 |
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3-OC8-HSL | 3-oxo-octanoyl-l-homoserine lactone |
| 4-NPO | 4-nitropyridine-N-oxide |
| AC50 | half maximal activity concentration |
| AHL | N-acyl homoserine lactone |
| DMSO | dimethylsulfoxide |
| GIAC50 | growth index at the AC50 concentration |
| MBC | minimal bactericidal concentration |
| MIC | minimal inhibitory concentration |
| OD600 | optical density at a wavelength of 600 nm |
| Pa6276 | P. atrosepticum CFBP6276 |
| QS | quorum-sensing |
| QSI | quorum sensing-inhibitor |
References
- Pérombelon, M.C.M. Potato diseases caused by soft rot erwinias: An overview of pathogenesis. Plant Pathol 2002, 51, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Põllumaa, L.; Alamäe, T.; Mäe, A. Quorum sensing and expression of virulence in pectobacteria. Sensors 2012, 12, 3327–3349. [Google Scholar]
- Crépin, A.; Beury-Cirou, A.; Barbey, C.; Farmer, C.; Hélias, V.; Burini, J.F.; Faure, D.; Latour, X. N-Acyl homoserine lactones in diverse Pectobacterium and Dickeya plant pathogens: Diversity, abundance, and involvement in virulence. Sensors 2012, 12, 3484–3497. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Coulthurst, S.J.; Pritchard, L.; Hedley, P.E.; Ravensdale, M.; Humphris, S.; Burr, T.; Takle, G.; Brurberg, M.B.; Birch, P.R.J.; et al. Quorum sensing coordinates brute force and stealth modes of infection in the plant pathogen Pectobacterium atrosepticum. PLoS Pathog 2008, 4, e1000093. [Google Scholar]
- Smadja, B.; Latour, X.; Faure, D.; Chevalier, S.; Dessaux, Y.; Orange, N. Involvement of N-acylhomoserine lactones throughout the plant infection by Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica (Pectobacterium atrosepticum). Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact 2004, 17, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar]
- Fuqua, W.C.; Winans, S.C.; Greenberg, E.P. Quorum sensing in bacteria: The LuxR-LuxI family of cell density-responsive transcriptional regulators. J. Bacteriol 1994, 176, 269–275. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.H.; Wang, L.H.; Xu, J.L.; Zhang, H.B.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, L.H. Quenching quorum-sensing-dependent bacterial infection by an N-acyl homoserinelactonase. Nature 2001, 411, 813–817. [Google Scholar]
- Uroz, S.; D’Angelo-Picard, C.; Carlier, A.; Elasri, M.; Sicot, C.; Petit, A.; Oger, P.; Faure, D.; Dessaux, Y. Novel bacteria degrading N-acylhomoserine lactones and their use as quenchers of quorum-sensing-regulated functions of plant-pathogenic bacteria. Microbiology 2003, 149, 1981–1989. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.H.; Zhang, X.F.; Xu, J.L.; Zhang, L.H. Insecticidal Bacillus thuringi ensis silences Erwinia carotovora virulence by a new form of microbial antagonism, signal interference. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2004, 70, 954–960. [Google Scholar]
- Cirou, A.; Diallo, S.; Kurt, C.; Latour, X.; Faure, D. Growth promotion of quorum-quenching bacteria in the rhizosphere of Solanum tuberosum. Environ. Microbiol 2007, 9, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Manefield, M.; Welch, M.; Givskov, M.; Salmond, G.P.; Kjelleberg, S. Halogenated furanones from the red alga, Delisea pulchra, inhibit carbapenem antibiotic synthesis and exoenzyme virulence factor production in the phytopathogen Erwinia carotovora. FEMS Microbiol. Lett 2001, 205, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, A.G.; Streng, E.; Jewell, K.A.; Blackwell, H.E. Quorum sensing in bacterial species that use degenerate autoinducers can be tuned by using structurally identical non-native ligands. Chembiochem 2011, 12, 138–147. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, A.G.; Streng, E.; Blackwell, H.E. Attenuation of virulence in pathogenic bacteria using synthetic quorum-sensing modulators under native conditions on plant hosts. ACS Chem. Biol 2011, 6, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Kalia, V.C. Quorum sensing inhibitors: An overview. Biotechnol. Adv 2013, 31, 224–245. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, A.M.; Queneau, Y.; Soulère, L.; von Bodman, S.; Doutheau, A. Mechanisms and synthetic modulators of AHL-dependent gene regulation. Chem. Rev 2011, 111, 4–27. [Google Scholar]
- Galloway, W.R.; Hodgkinson, J.T.; Bowden, S.D.; Welch, M.; Spring, D.R. Quorum sensing in gram-negative bacteria: Small-molecule modulation of AHL and AI-2 Quorum sensing pathways. Chem. Rev 2011, 111, 28–67. [Google Scholar]
- Rasch, M.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Andersen, J.B.; Persson, T.; Nielsen, J.; Givskov, M.; Gram, L. Well-known quorum sensing inhibitors do not affect bacterial quorum sensing-regulated bean sprout spoilage. J. Appl. Microbiol 2007, 102, 826–837. [Google Scholar]
- Kwasiborski, A.; Mondy, S.; Beury-Cirou, A.; Faure, D. Genome sequence of the Pectobacterium atrosepticum strain CFBP6276, causing blackleg and soft rot diseases on potato plants and tubers. Genome Announc 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latour, X.; Diallo, S.; Chevalier, S.; Morin, D.; Smadja, B.; Burini, J.F.; Haras, D.; Orange, N. Thermoregulation of N-acyl homoserine lactones-based quorum sensing in the soft rot bacterium Pectobacterium atrosepticum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2007, 73, 4078–4081. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Chatterjee, A.; Hasegawa, H.; Chatterjee, A.K. Erwinia carotovora subspecies produce duplicate variants of ExpR, LuxR homologs that activate rsmA transcription but differ in their interactions with N-acylhomoserine lactone signals. J. Bacteriol 2006, 188, 4715–4726. [Google Scholar]
- Soulère, L.; Sabbah, M.; Fontaine, F.; Queneau, Y.; Doutheau, A. LuxR-dependent quorum sensing: Computer aided discovery of new inhibitors structurally unrelated to N-acylhomoserine lactones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 2010, 20, 4355–4358. [Google Scholar]
- Sabbah, M.; Soulère, L.; Reverchon, S.; Queneau, Y.; Doutheau, A. LuxR dependent quorum sensing inhibition by N,N′-disubstituted imidazolium salts. Bioorg. Med. Chem 2011, 19, 4868–4875. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, T.B.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Skindersoe, M.E.; Hentzer, M.; Kristoffersen, P.; Ko, M.; Nielsen, J.; Eberl, L.; Givskov, M. Screening for Quorum-sensing snhibitors (QSI) by use of a novel genetic system, the QSI selector. J. Bacteriol 2005, 187, 1799–1814. [Google Scholar]
- Reverchon, S.; Chantegrel, B.; Deshayes, C.; Doutheau, A.; Cotte-Pattat, N. New synthetic analogues of N-acyl homoserine lactones as agonists or antagonists of transcriptional regulators involved in bacterial quorum sensing. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 2002, 12, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Castang, S.; Chantegrel, B.; Deshayes, C.; Dolmazon, R.; Gouet, P.; Haser, R.; Reverchon, S.; Nasser, W.; Hugouvieux-Cotte-Pattat, N.; Doutheau, A. N-sulfonylhomoserine lactones as antagonists of bacterial quorum sensing. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 2004, 14, 5145–5149. [Google Scholar]
- Frezza, M.; Castang, S.; Estephane, J.; Soulère, L.; Deshayes, C.; Chantegrel, B.; Nasser, W.; Queneau, Y.; Reverchon, S.; Doutheau, A. Synthesis and biological evaluation of homoserine lactone derived ureas as antagonists of bacterial quorum sensing. Bioorg. Med. Chem 2006, 14, 4781–4791. [Google Scholar]
- Frezza, M.; Soulère, L.; Reverchon, S.; Guiliani, N.; Jerez, C.; Queneau, Y.; Doutheau, A. Synthetichomoserine lactone-derived sulfonylureas as inhibitors of Vibrio fischeri quorum sensing regulator. Bioorg. Med. Chem 2008, 16, 3550–3556. [Google Scholar]
- Boukraa, M.; Sabbah, M.; Soulère, L.; El Efrit, M.L.; Queneau, Y.; Doutheau, A. AHL-dependent quorum sensing inhibition: Synthesis and biological evaluation of α-(N-alkyl-carboxamide)-γ-butyrolactones and α-(N-alkyl-sulfonamide)-γ-butyrolactones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 2011, 21, 6876–6879. [Google Scholar]
- Sabbah, M.; Fontaine, F.; Grand, L.; Boukraa, M.; Efrit, M.L.; Doutheau, A.; Soulère, L.; Queneau, Y. Synthesis and biological evaluation as LuxR-dependent Quorum-Sensing modulators of new N-acyl-homoserine-lactone analogues based on triazole and tetrazole scaffolds. Bioorg. Med. Chem 2012, 20, 4727–4736. [Google Scholar]
- Estephane, J.; Dauvergne, J.; Soulere, L.; Reverchon, S.; Queneau, Y.; Doutheau, A. N-Acyl-3-amino-5H-furanone derivatives as new inhibitors of LuxR-dependent quorum sensing: Synthesis, biological evaluation and binding mode study. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 2008, 18, 4321–4324. [Google Scholar]
- Sabbah, M.; Bernollin, M.; Doutheau, A.; Soulère, L.; Queneau, Y. A new route towards fimbrolide analogues: Importance of the exomethylene motif in LuxR dependent quorum sensing inhibition. Med. Chem. Comm 2013, 4, 363–366. [Google Scholar]
- Tannières, M.; Beury-Cirou, A.; Vigouroux, A.; Mondy, S.; Pellissier, F.; Dessaux, Y.; Faure, D. A metagenomic study highlights phylogenetic proximity of quorum-quenching and xenobiotic-degrading amidases of the AS-family. PLoS One 2013, 8, e65473. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, E.M.; Miles, T.D.; Wharton, P.S. The use of natural plant volatile compounds for the control of the potato postharvest diseases, black dot, silver scurf and soft rot. Biol. Control 2013, 64, 152–159. [Google Scholar]
- Cirou, A.; Mondy, S.; An, S.; Charrier, A.; Sarrazin, A.; Thoison, O.; DuBow, M.; Faure, D. Efficient biostimulation of the native and introduced quorum-quenching Rhodococcus erythropolis revealed by a combination of analytical chemistry, microbiology and pyrosequencing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2012, 78, 481–492. [Google Scholar]
- Cirou, A.; Raffoux, A.; Diallo, S.; Latour, X.; Dessaux, Y.; Faure, D. Gamma-caprolactone stimulates the growth of quorum-quenching Rhodococcus populations in a large-scale hydroponic system for culturing Solanum tuberosum. Res. Microbiol 2011, 162, 945–950. [Google Scholar]
- Jafra, S.; Przysowa, J.; Czajkowski, R.; Michta, A.; Garbeva, P.; van Der Wolf, J.M. Detection and characterization of N-acyl homoserinelactone-degrading bacteria from the potato rhizosphere. Can. J. Microbiol 2006, 52, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Des Essarts, Y.R.; Sabbah, M.; Comte, A.; Soulère, L.; Queneau, Y.; Dessaux, Y.; Hélias, V.; Faure, D. N,N’-alkylated Imidazolium-Derivatives Act as Quorum-Sensing Inhibitors Targeting the Pectobacterium atrosepticum-Induced Symptoms on Potato Tubers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 19976-19986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141019976
Des Essarts YR, Sabbah M, Comte A, Soulère L, Queneau Y, Dessaux Y, Hélias V, Faure D. N,N’-alkylated Imidazolium-Derivatives Act as Quorum-Sensing Inhibitors Targeting the Pectobacterium atrosepticum-Induced Symptoms on Potato Tubers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(10):19976-19986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141019976
Chicago/Turabian StyleDes Essarts, Yannick Raoul, Mohamad Sabbah, Arnaud Comte, Laurent Soulère, Yves Queneau, Yves Dessaux, Valérie Hélias, and Denis Faure. 2013. "N,N’-alkylated Imidazolium-Derivatives Act as Quorum-Sensing Inhibitors Targeting the Pectobacterium atrosepticum-Induced Symptoms on Potato Tubers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 10: 19976-19986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141019976
APA StyleDes Essarts, Y. R., Sabbah, M., Comte, A., Soulère, L., Queneau, Y., Dessaux, Y., Hélias, V., & Faure, D. (2013). N,N’-alkylated Imidazolium-Derivatives Act as Quorum-Sensing Inhibitors Targeting the Pectobacterium atrosepticum-Induced Symptoms on Potato Tubers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(10), 19976-19986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141019976