The Preparation of Fluorescence-Quenched Probes for Use in the Characterization of Human Factor Xa Substrate Binding Domains
Abstract
:Introduction
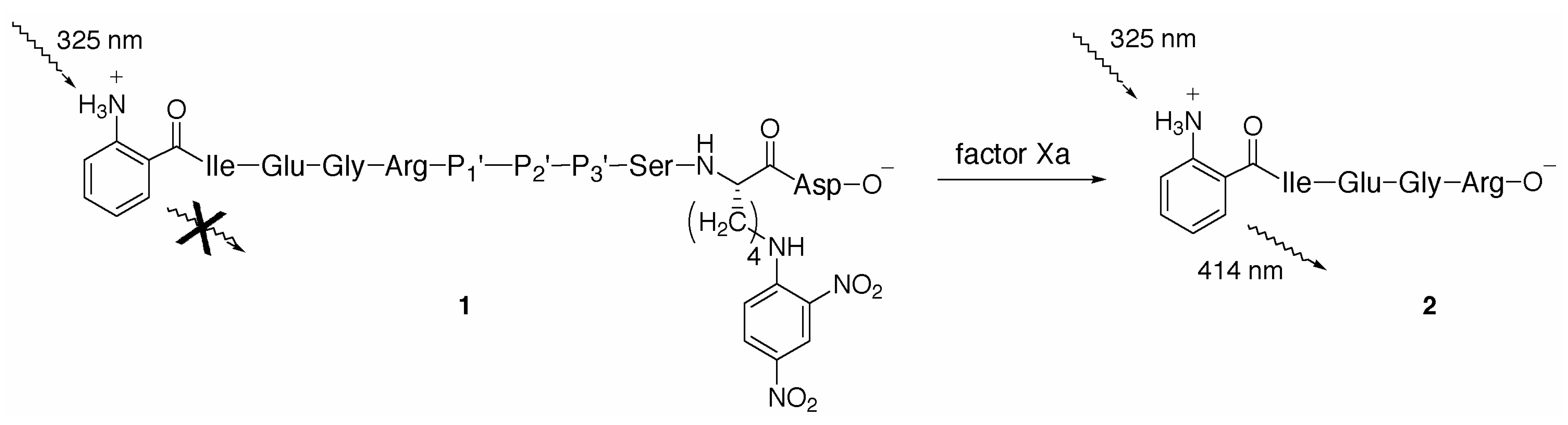
Results and Discussion
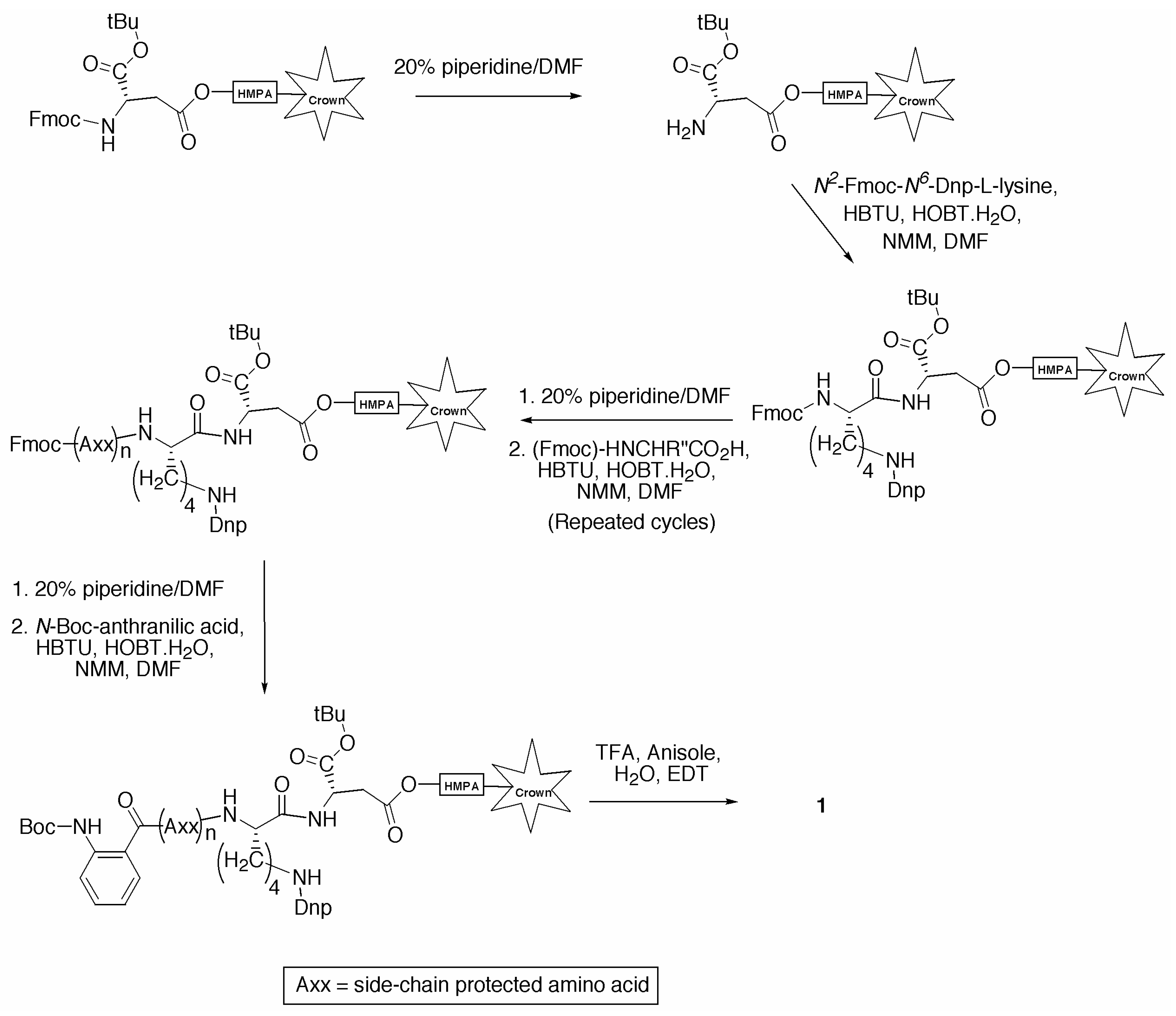
Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Experimental
General
N2-Fmoc-N6-dinitrophenyl-l-lysine
2-Amino(tert-butoxycarbonyl)benzoic acid
General Procedure for the Synthesis of Individual Fluorescence Quenched Peptides
Fmoc Deprotection
Amino Acid and Activation Solutions
Amino Acid Coupling
Side Chain Deprotection and Cleavage
Trituration
| Amino Acid Code | Protecting Group | Mass (mg)A |
|---|---|---|
| Ala | − | 36.0 |
| Arg | Pmc | 76.6 |
| Asn | Trt | 69.0 |
| Asp | OtBu | 47.6 |
| Cys | Trt | 67.7 |
| Gln | Trt | 70.6 |
| Glu | OtBu | 49.2 |
| Gly | − | 34.4 |
| His | Trt | 71.7 |
| Ile | − | 40.9 |
| Leu | − | 40.9 |
| Lys | Boc | 54.2 |
| Met | − | 42.9 |
| Phe | − | 44.8 |
| Pro | − | 39.0 |
| Ser | tBu | 44.3 |
| Thr | tBu | 46.0 |
| Trp | Boc | 60.9 |
| Tyr | tBu | 53.1 |
| Val | − | 39.2 |
| Lys(Dnp) | − | 61.8 |
| Abz B | − | 27.4 |
Synthesis of P1’-P3’ Fluorescence Quenched Substrate Library
| Peptide CodeA | MW | Yield (%)B | Retention Time (min)C | Relative Peak Area (%)D | m/z E | Assignment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KBL1A | 1346.32 | 84 | 9.17 | 100 | 674.0 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL1E | 1360.35 | 76 | 9.08 | >90 | 681.0 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL1F | 1378.41 | 96 | 9.39 | 100 | 690.1 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL1G | 1288.28 | 42F | 11.6G | 100 | 644.9 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL1H | 1368.37 | 49F | 10.70G | 100 | 457.2 | (M+3H+)/3 |
| 685.0 (80 %) | (M+2H+)/2 | |||||
| 568.8 (35 %) | (M-232+2H+)/2 | |||||
| KBL1I | 1344.39 | 72F | 12.2G | 100 | 673.1 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL1K | 1359.40 | 78 | 8.73 | 100 | 454.3 | (M+3H+)/3 |
| 680.6 (45 %) | (M+2H+)/2 | |||||
| 564.5 (20 %) | (M-232+2H+)/2 | |||||
| KBL1L | 1344.39 | 46F | 12.18G | 100 | 673.0 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL1M | 1360.43 | 73 | 9.21 | 100 | 682.3 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL1N | 1345.33 | 78 | 8.84 | >90 | 673.7 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL1P | 1328.35 | 69 | 9.01 | >90 | 665.2 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL1Q | 1359.36 | 55F | 11.64G | >90 | 680.5 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL1R | 1387.42 | 92 | 8.66 | >90 | 463.7 | (M+3H+)/3 |
| 694.6 (60 %) | (M+2H+)/2 | |||||
| 578.6 (40 %) | (M-232+2H+)/2 | |||||
| KBL1S | 1318.31 | 54F | 11.75G | 100 | 660.0 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL1T | 1332.34 | 62F | 11.70G | 100 | 667.1 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL1V | 1330.36 | 64 | 9.16 | 100 | 709.8 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL1W | 1417.44 | 91 | 9.38 | 100 | 709.8 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL1Y | 1394.41 | 79 | 9.27 | >90 | 698.0 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| Peptide CodeA | MW | Yield (%)B | Retention Time (min)C | Relative Peak Area (%)D | m/z E | Assignment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KBL2A | 1302.31 | 92 | 9.28 | >90 | 652.0 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL2D | 1346.32 | Q | 9.16 | >90 | 674.2 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL2E | 1360.35 | 92 | 9.23 | >90 | 681.2 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL2F | 1378.41 | 93 | 9.50 | >90 | 690.2 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL2G | 1288.28 | 62 | 9.30 | >90 | 645.2 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL2H | 1368.37 | 78 | 8.77 | 100 | 457.3 | (M+3H+)/3 |
| 685.2 (55 %) | (M+2H+)/2 | |||||
| 569.0 (20 %) | (M-232+2H+)/2 | |||||
| KBL2I | 1344.39 | 73 | 9.34 | 100 | 673.2 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL2K | 1359.40 | Q | 8.77 | 100 | 453.7 | (M+3H+)/3 |
| 680.7 (95 %) | (M+2H+)/2 | |||||
| 564.6 (25 %) | (M-232+2H+)/2 | |||||
| KBL2L | 1344.39 | 79 | 9.43 | >90 | 673.3 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL2M | 1360.43 | Q | 9.36 | 100 | 681.9 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL2N | 1345.33 | 67 | 9.17 | 100 | 673.7 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL2P | 1328.35 | Q | 9.19 | >90 | 665.2 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL2Q | 1359.36 | 93 | 9.17 | 100 | 680.4 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL2R | 1387.42 | 98 | 8.92 | 100 | 694.6 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| 578.4 (63 %) | (M-232+2H+)/2 | |||||
| KBL2S | 1318.31 | 89F | 9.12 | 100 | 660.0 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL2T | 1332.34 | 87 | 9.16 | >90 | 667.1 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL2V | 1330.36 | 86 | 9.23 | >90 | 665.9 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL2W | 1417.44 | 95F | 9.47 | 100 | 709.7 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL2Y | 1394.41 | 92F | 9.19 | 100 | 698.1 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| Peptide CodeA | MW | Yield (%)B | Retention Time (min)C | Relative Peak Area (%)D | m/z E | Assignment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KBL3D | 1346.32 | 91 | 9.30 | >90 | 674.1 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL3E | 1360.35 | 86 | 9.17 | 100 | 681.0 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL3F | 1378.41 | 86 | 9.47 | 100 | 690.1 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL3G | 1288.28 | 82 | 8.94 | 100 | 654.1 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL3H | 1368.37 | 91 | 8.83 | 100 | 457.3 | (M+3H+)/3 |
| 685.1 (40 %) | (M+2H+)/2 | |||||
| 569.0 (30 %) | (M- 232+2H+)/2 | |||||
| KBL3I | 1344.39 | 68 | 9.36 | 100 | 673.0 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL3K | 1359.40 | 95 | 8.84 | >90 | 454.3 | (M+3H+)/3 |
| 680.7 (55 %) | (M+2H+)/2 | |||||
| 564.6 (40 %) | (M- 232+2H+)/2 | |||||
| KBL3L | 1344.39 | 61 | 9.41 | >90 | 673.0 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL3M | 1360.43 | 61 | 9.34 | 100 | 682.0 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL3N | 1345.33 | 96 | 9.01 | 100 | 673.5 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL3P | 1328.35 | 89 | 9.12 | 100 | 665.2 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL3Q | 1359.36 | 94 | 9.06 | 100 | 680.7 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL3R | 1387.42 | 93 | 8.75 | >90 | 463.7 | (M+3H+)/3 |
| 694.8 (50 %) | (M+2H+)/2 | |||||
| 578.6 (25 %) | (M- 232+2H+)/2 | |||||
| KBL3S | 1318.31 | 59F | 11.55G | 100 | 660.0 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL3T | 1332.34 | 54F | 11.81G | 100 | 667.1 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL3V | 1330.36 | 74 | 9.21 | 100 | 666.2 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL3W | 1417.44 | 89 | 9.39 | 100 | 709.8 | (M+2H+)/2 |
| KBL3Y | 1394.41 | 75 | 9.17 | 100 | 698.2 | (M+2H+)/2 |
References
- Davie, E. W.; Fujikawa, K.; Kisiel, W. The coagulation cascade - initiation, maintenance, and regulation. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 10363–10370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, J.C.; Harper, J.W. Proteinase Inhibitors, 2nd ed.; Barrett, A.J., Salvesen, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, 1986; Vol. 12, p. 55. [Google Scholar]
- Lottenberg, R.; Hall, J.A.; Pautler, E.; Zupan, A.; Christensen, U.; Jackson, C.M. The action of factor Xa on peptide p-nitroanilide substrates: Substrate selectivity and examination of hydrolysis with different reaction conditions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1986, 874, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.; Lynas, J.F. Strategies for the inhibition of serine proteases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 596–624, and references therein. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludeman, J.P.; Pike, R.N.; Bromfield, K.M.; Duggan, P.J.; Cianci, J.; Le Bonniec, B.; Whisstock, J.C.; Bottomley, S.P. Determination of the P’1, P’2 and P’3 subsite-specificity of factor Xa. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2003, 35, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaron, A.; Carmel, A.; Katchalski-Katzir, E. Intramolecularly quenched fluorogenic substrates for hydrolytic enzymes. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bonniec, B.F.; Myles, T.; Johnson, T.; Knight, C.G.; Tapparelli, C.; Stone, S.R. Characterization of the P-2' and P-3' specificities of thrombin using fluorescence-quenched substrates and mapping of the subsites by mutagenesis. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 7114–7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marque, P.-E.; Spuntarelli, R.; Juliano, L.; Aiach, M.; Le Bonniec, B.F. The role of Glu(192) in the allosteric control of the S-2 ' and S-3 ' subsites of thrombin. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasi, A.; Knight, C.G.; Barrett, A.J. Characterization of the bacterial metalloendopeptidase pitrilysin by use of a continuous fluorescence assay. Biochem. J. 1993, 290, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mougenot, P.; Marchand-Brynaert, J. Reactivity assays of surface hydroxyl chain ends of poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) film and membranes using original H-3 and fluorine-labeled derivatization reagents. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 3552–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyman, D.A. Preparation of isatoates from isatoic anhydride. J. Heterocyclic Chem. 1978, 15, 1131–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiron Technologies. Multipin Peptide Synthesis Kit, Software Manual, Chiron Technologies, Pty. Ltd. (now Mimotopes Pty. Ltd.), 1997.
© 2004 by MDPI (http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
Share and Cite
Bromfield, K.M.; Cianci, J.; Duggan, P.J. The Preparation of Fluorescence-Quenched Probes for Use in the Characterization of Human Factor Xa Substrate Binding Domains. Molecules 2004, 9, 427-439. https://doi.org/10.3390/90600427
Bromfield KM, Cianci J, Duggan PJ. The Preparation of Fluorescence-Quenched Probes for Use in the Characterization of Human Factor Xa Substrate Binding Domains. Molecules. 2004; 9(6):427-439. https://doi.org/10.3390/90600427
Chicago/Turabian StyleBromfield, Karen M., Julia Cianci, and Peter J. Duggan. 2004. "The Preparation of Fluorescence-Quenched Probes for Use in the Characterization of Human Factor Xa Substrate Binding Domains" Molecules 9, no. 6: 427-439. https://doi.org/10.3390/90600427
APA StyleBromfield, K. M., Cianci, J., & Duggan, P. J. (2004). The Preparation of Fluorescence-Quenched Probes for Use in the Characterization of Human Factor Xa Substrate Binding Domains. Molecules, 9(6), 427-439. https://doi.org/10.3390/90600427




