Simultaneous Determination of 32 Polyphenolic Compounds in Berries via HPLC–MS/MS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Optimization of the MS Parameters
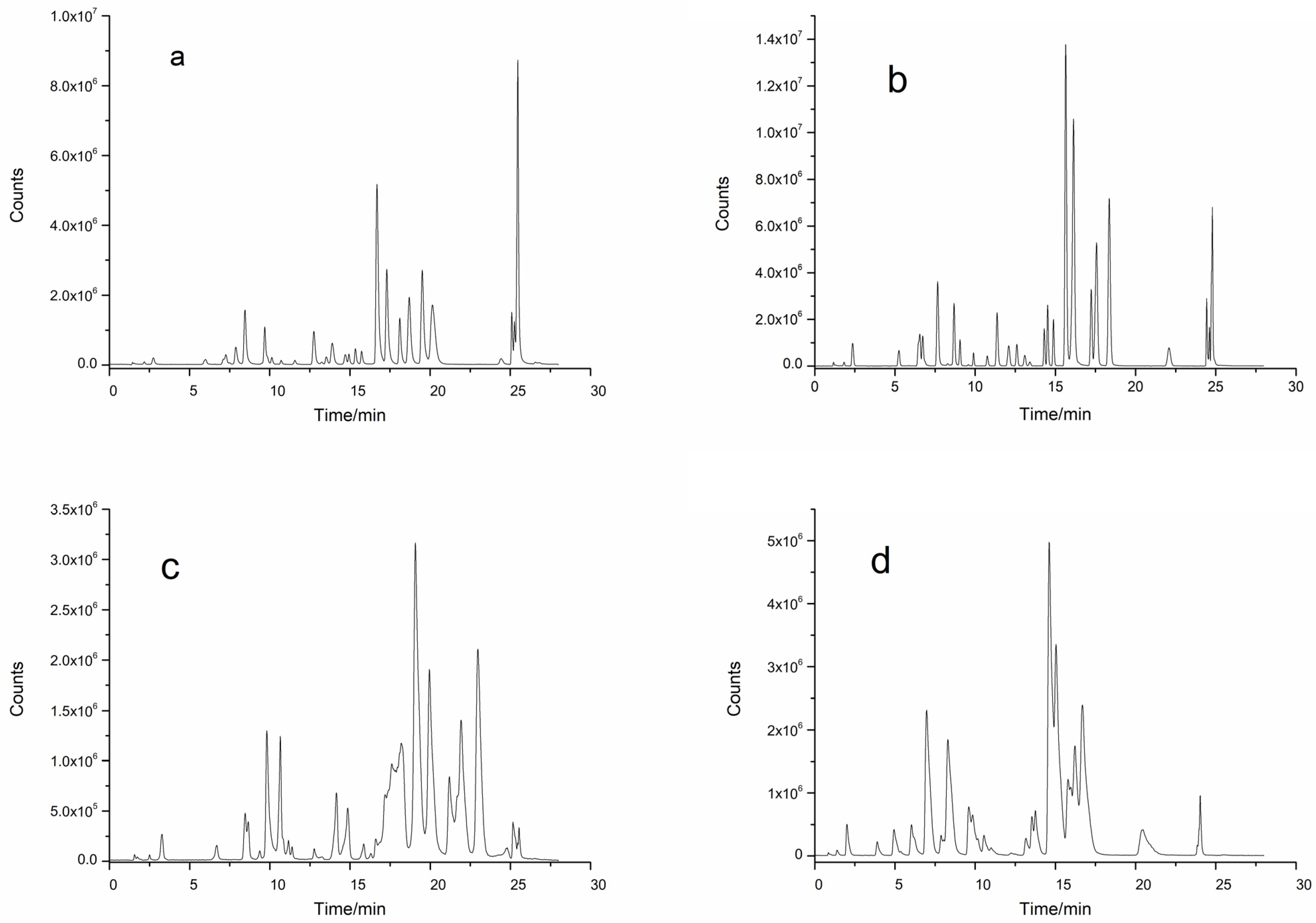
2.2. Effects of Different Chromatographic Columns on Polyphenol Separation
2.3. Effects of Different Mobile Phases on Polyphenol Separation
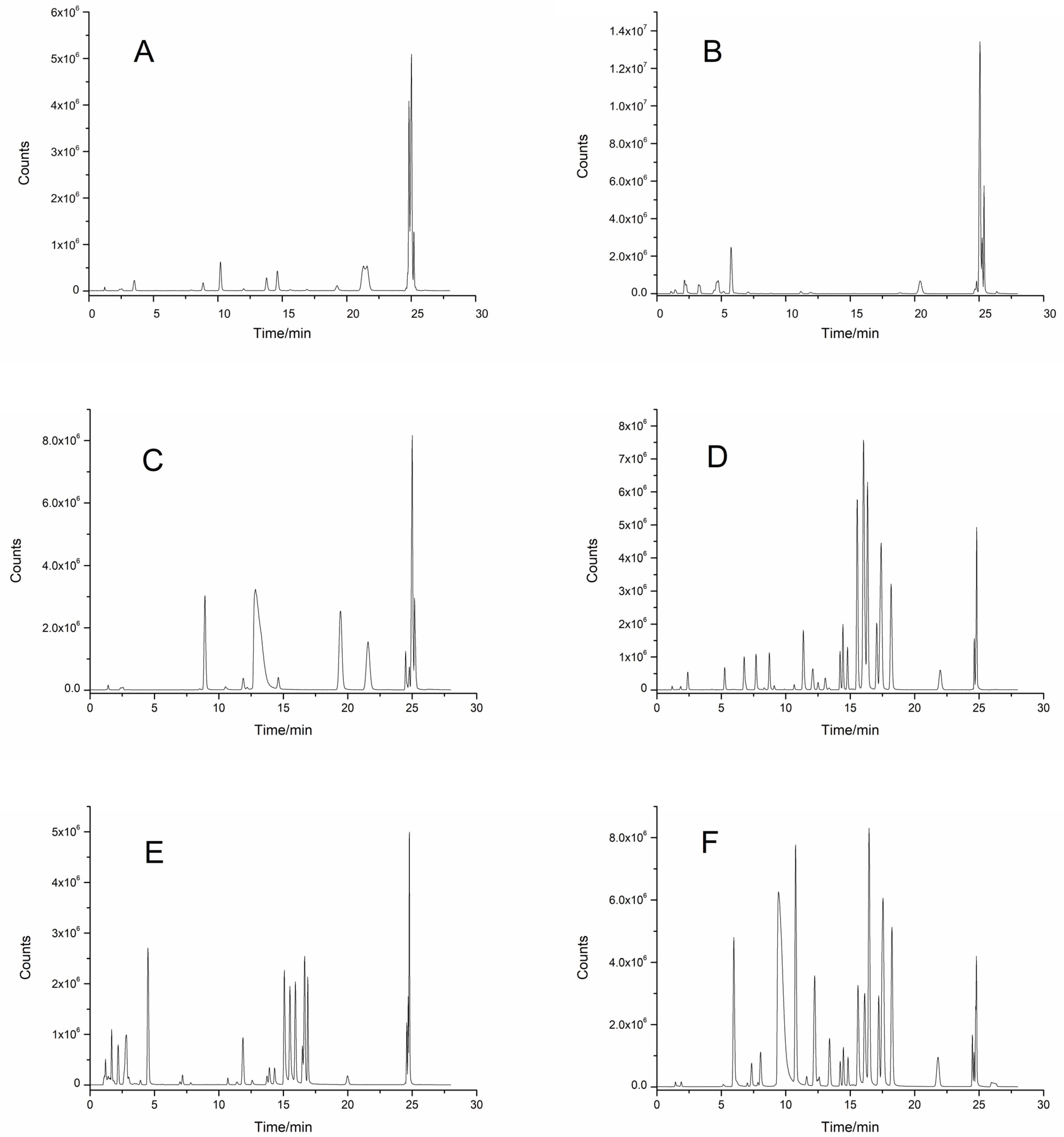
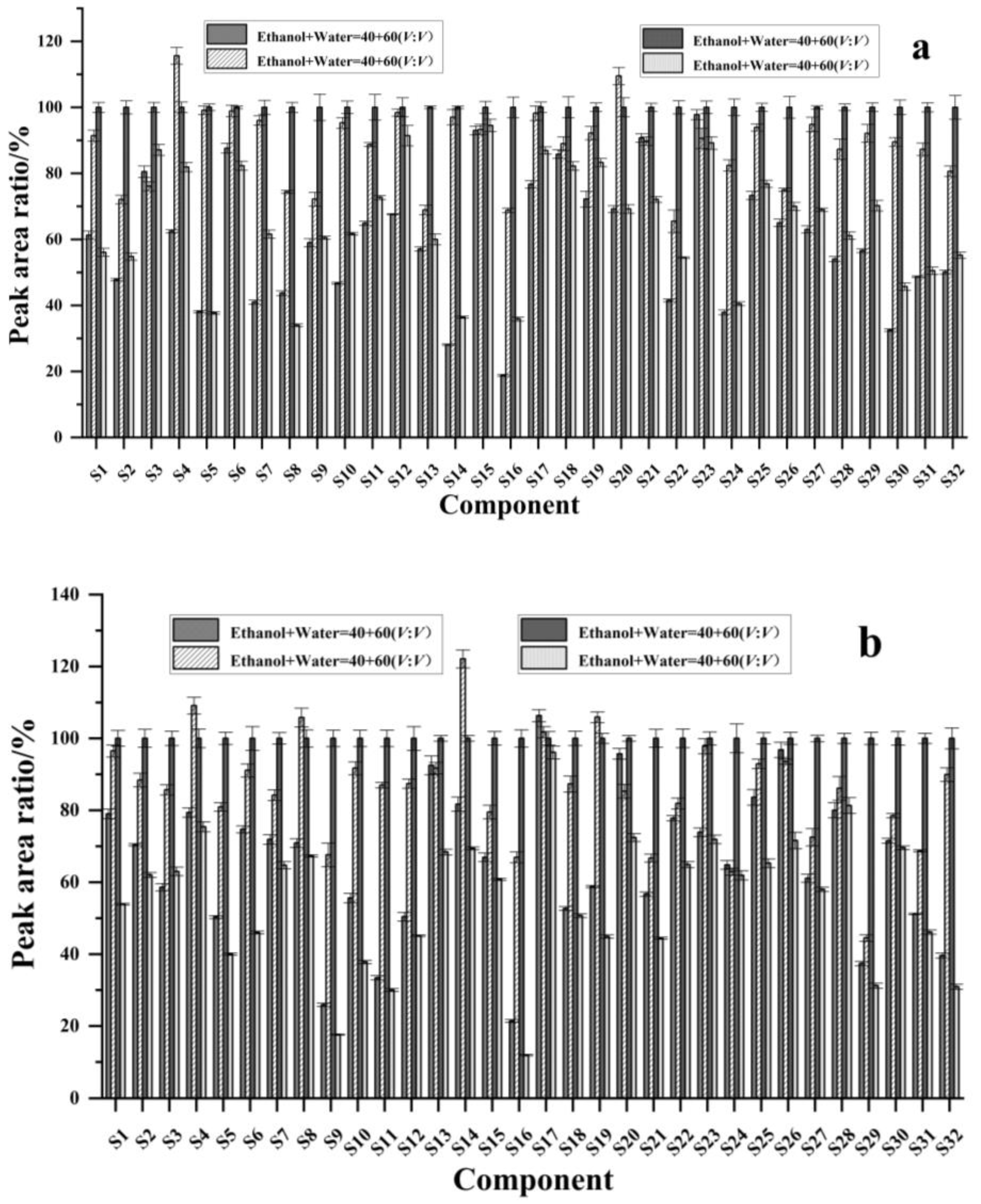
2.4. Effects of Different Solvents on Extraction Efficiency
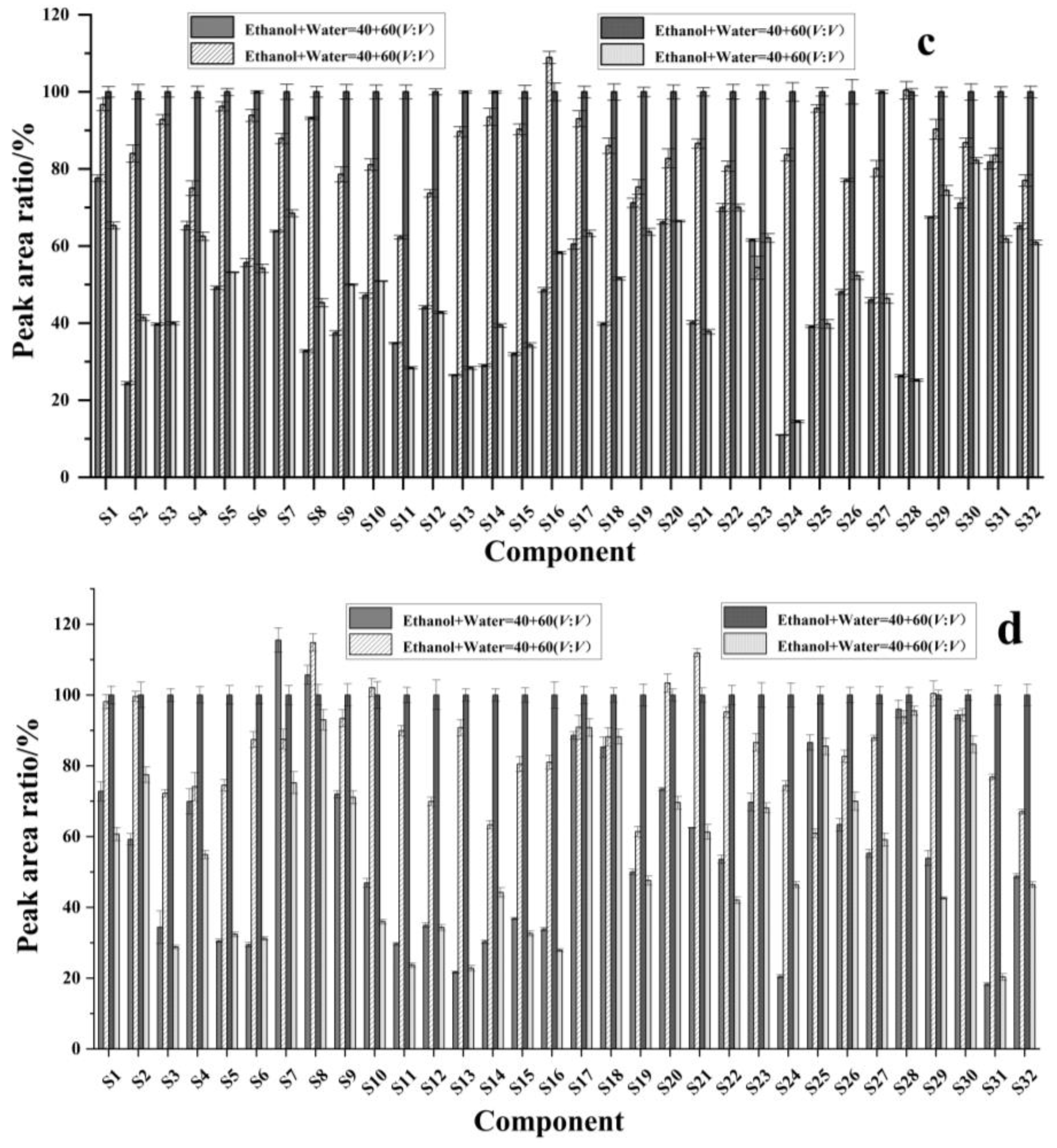
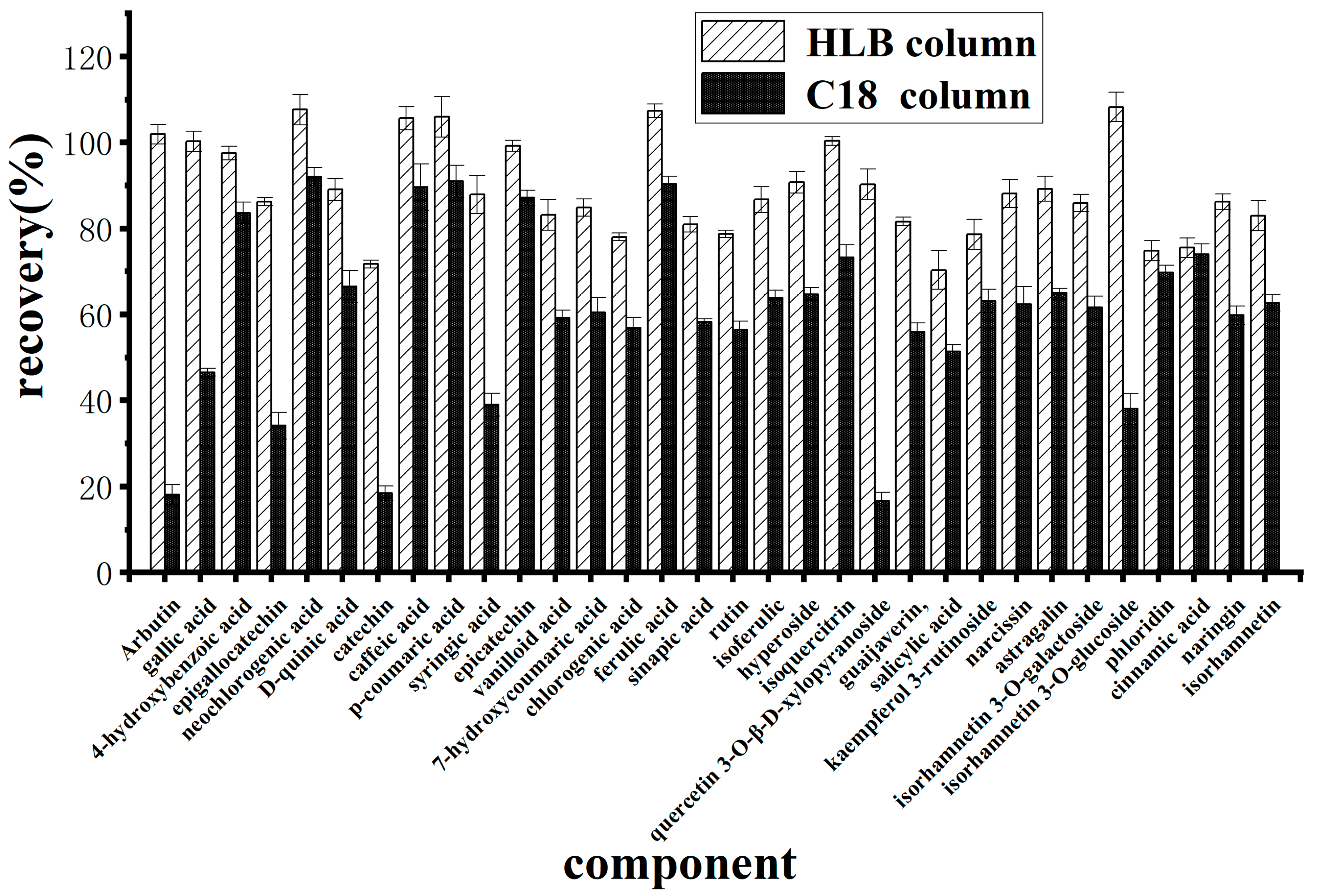
2.5. Effects of Different Solid-Phase Extraction Columns on Purification
2.6. Method Validation
2.6.1. Specificity, Linear Range, Limit of Detection (LOD), and Limit of Quantification (LOQ)
2.6.2. Accuracy and Precision
2.7. Quantitative Analysis of Polyphenolic Compounds in 4 Kinds of Berries Found in Xinjiang
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Materials
4.2. Instruments and Equipment
4.3. Preparation of Standard Solutions
4.4. HPLC-MS/MS Conditions
4.4.1. Chromatographic Conditions
4.4.2. Mass Spectrometry Conditions
4.5. Sample Pretreatment
4.6. Method Validation
4.7. Data Processing
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salo, H.M.; Nguyen, N.; Alakärppä, E.; Klavins, L.; Hykkerud, A.L.; Karppinen, K.; Jaakola, L.; Klavins, M.; Häggman, H. Authentication of berries and berry-based food products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 5197–5225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhang, B.; Chen, G.; Fu, X. The novel contributors of anti-diabetic potential in mulberry polyphenols revealed by UHPLC-HR-ESI-TOF-MS/MS. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zeng, Z.; Hu, N.; Bai, B.; Wang, H.; Suo, Y. Simultaneous optimization of the ultrasound-assisted extraction for phenolic compounds content and antioxidant activity of Lycium ruthenicum Murr. fruit using response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Gong, X.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Li, M. Advanced Research on the Antioxidant Activity and Mechanism of Polyphenols from Hippophae Species—A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manganaris, G.A.; Goulas, V.; Vicente, A.R.; Terry, L.A. Berry antioxidants: Small fruits providing large benefits. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 94, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintus, G.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, L.; Wang, C.; Tang, C.; He, X. Antidiabetic and Antioxidant Effects and Phytochemicals of Mulberry Fruit (Morus alba L.) Polyphenol Enhanced Extract. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71144. [Google Scholar]
- Kubczak, M.; Khassenova, A.B.; Skalski, B.; Michlewska, S.; Wielanek, M.; Skłodowska, M.; Aralbayeva, A.N.; Nabiyeva, Z.S.; Murzakhmetova, M.K.; Zamaraeva, M.; et al. Hippophae rhamnoides L. leaf and twig extracts as rich sources of nutrients and bioactive compounds with antioxidant activity. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Xia, T.; Qiang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, M. Nutrition, Bioactive Components, and Hepatoprotective Activity of Fruit Vinegar Produced from Ningxia Wolfberry. Molecules 2022, 27, 4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebal, L.; Pokajewicz, K.; Djebli, N.; Mostefa, N.; Poliwoda, A.; Wieczorek, P.P. HPLC-DAD profile of phenolic compounds and In vitro antioxidant activity of Ficus carica L. fruits from two Algerian varieties. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokkanen, J.; Mattila, S.; Jaakola, L.; Pirttilä, A.M.; Tolonen, A. Identification of Phenolic Compounds from Lingonberry (Vaccinium vitis-idaea L.), Bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.) and Hybrid Bilberry (Vaccinium x intermedium Ruthe L.) Leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9437–9447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viganó, J.; Sanches, V.L.; de Souza Mesquita, L.M.; de Souza, M.C.; da Silva, L.C.; Chaves, J.O.; Forster-Carneiro, T.; Rostagno, M.A. Comprehensive analysis of phenolic compounds from natural products: Integrating sample preparation and analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1178, 338845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondia-Pons, I.; Savolainen, O.; Törrönen, R.; Martinez, J.A.; Poutanen, K.; Hanhineva, K. Metabolic profiling of Goji berry extracts for discrimination of geographical origin by non-targeted liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Food Res. Int. 2014, 63, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo-Poveda, O.; Zeppa, G.; Ferrocino, I.; Stévigny, C.; Barbosa-Pereira, L. Chemometric Classification of Cocoa Bean Shells Based on Their Polyphenolic Profile Determined by RP-HPLC-PDA Analysis and Spectrophotometric Assays. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.Y.; Liu, D.; Huang, A.G. The efficiency of flavonoids in polar extracts of Lycium chinense Mill fruits as free radical scavenger. Food Chem. 2004, 87, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inbaraj, B.S.; Lu, H.; Kao, T.H.; Chen, B.H. Simultaneous determination of phenolic acids and flavonoids in Lycium barbarum Linnaeus by HPLC–DAD–ESI-MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 51, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltacıoğlu, H.; Baltacıoğlu, C.; Okur, I.; Tanrıvermiş, A.; Yalıç, M. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from tomato: Characterization by FTIR and HPLC and comparison with conventional solvent extraction. Vib. Spectrosc. 2021, 113, 103204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Jubair, A.; Hossain, M.A.; Hossain, M.M.; Azam, M.S.; Biswas, M. Free radical-scavenging capacity and HPLC-DAD screening of phenolic compounds from pulp and seed of Syzygium claviflorum fruit. J. Agric. Food Res. 2021, 6, 100203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoenescu, A.-M.; Trandafir, I.; Cosmulescu, S. Determination of Phenolic Compounds Using HPLC-UV Method in Wild Fruit Species. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakkori, P.; Tağaç, A.A.; Merdivan, M. Fabrication of montmorillonite/ionic liquid composite coated solid-phase microextraction fibers for determination of phenolic compounds in fruit juices by gas chromatography and liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1635, 461741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proestos, C.; Sereli, D.; Komaitis, M. Determination of phenolic compounds in aromatic plants by RP-HPLC and GC-MS. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Fernández, M.A.; Hornedo-Ortega, R.; Cerezo, A.B.; Troncoso, A.M.; García-Parrilla, M.C. Effects of the strawberry (Fragaria ananassa) purée elaboration process on non-anthocyanin phenolic composition and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2014, 164, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medic, A.; Jakopic, J.; Hudina, M.; Solar, A.; Veberic, R. Identification and quantification of the major phenolic constituents in Juglans regia L. peeled kernels and pellicles, using HPLC–MS/MS. Food Chem. 2021, 352, 129404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çarıkçı, S.; Kılıç, T.; Özer, Z.; Dirmenci, T.; Arabacı, T.; Gören, A.C. Quantitative determination of some phenolics in Origanum laevigatum Boiss. extracts via validated LC-MS/MS metod and antioxidant activity. J. Chem. Metrol. 2018, 12, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizzi, L.; Chatzitzika, C.; Gatt, R.; Valdramidis, V. HPLC Analysis of Phenolic Compounds and Flavonoids with Overlapping Peaks. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 58, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritti, F.; Guiochon, G. Repeatability of the efficiency of columns packed with sub-3 μm core–shell particles: Part III. 2.7 μm Poroshell 120 EC-C18 particles in 4.6 mm and 2.1 mm × 100 mm column formats. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1252, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.M.; Angeloni, S.; Abouelenein, D.; Acquaticci, L.; Xiao, J.; Sagratini, G.; Maggi, F.; Vittori, S.; Caprioli, G. A new HPLC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of 36 polyphenols in blueberry, strawberry and their commercial products and determination of antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2022, 367, 130743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstonošić, M.A.; Hogervorst, J.C.; Mikulić, M.; Gojković-Bukarica, L. Development of HPLC method for determination of phenolic compounds on a core shell column by direct injection of wine samples. Acta Chromatogr. 2020, 32, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, S.; Zhou, W.; Meng, J.; Deng, K.; Zhou, H.; Hu, N.; Suo, Y. Rapid qualitative and quantitative analyses of eighteen phenolic compounds from Lycium ruthenicum Murray by UPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS and their antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2018, 269, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yang, B.; Zhu, W.; Li, X.; Tian, J.; Zhang, L. Characterisation of polyphenol constituents of Linderae aggregate leaves using HPLC fingerprint analysis and their antioxidant activities. Food Chem. 2015, 186, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xu, J.; Li, L.; Sun, B. Structural characterization of polymeric polyphenols from different parts of Diospyros kaki L. cv. Mopan persimmons. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 141, 107395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Chang, X.; Guo, X.; Brennan, C.S.; Li, T.; Fu, X.; Liu, R.H. Phenolic compounds, antioxidant activity, antiproliferative activity and bioaccessibility of Sea buckthorn (Hippophaë rhamnoides L.) berries as affected byin vitrodigestion. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 4229–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skendi, A.; Irakli, M.; Chatzopoulou, P. Analysis of phenolic compounds in Greek plants of Lamiaceae family by HPLC. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2017, 6, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mišan, A.; Mimica-Dukić, N.; Mandić, A.; Sakač, M.; Milovanović, I.; Sedej, I. Development of a rapid resolution HPLC method for the separation and determination of 17 phenolic compounds in crude plant extracts. Open Chem. 2011, 9, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaraba, R.; Savych, A.; Marchyshyn, S.; Muzyka, N.; Ilashchuk, P. HPLC-DAD assay of phenols profile in Antennaria dioica (L.) Gaertn. Pharmacia 2022, 69, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno-Herrera, M.; Pérez-Magariño, S. Validation of an extraction method for the quantification of soluble free and insoluble bound phenolic compounds in wheat by HPLC-DAD. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 93, 102984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldana-Mejía, J.A.; Ccana-Ccapatinta, G.V.; Ribeiro, V.P.; Arruda, C.; Veneziani, R.C.S.; Ambrósio, S.R.; Bastos, J.K. A validated HPLC-UV method for the analysis of phenolic compounds in Brazilian red propolis and Dalbergia ecastaphyllum. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 198, 114029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Lima, M.; Silva Dantas, B.; Araújo Carvalho, A.J.d.B.; Pereira, G.E.; Colombo Pimentel, T.; Magnani, M. A novel method for ultra-fast determination of phenolics with performance comparable to UPLC/DAD: Method development and validation on analysis of seedless table grapes. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 134, 106511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbstaite, R.; Raudone, L.; Liaudanskas, M.; Janulis, V. Development, Validation, and Application of the UPLC-DAD Methodology for the Evaluation of the Qualitative and Quantitative Composition of Phenolic Compounds in the Fruit of American Cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon Aiton). Molecules 2022, 27, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cendrowski, A.; Ścibisz, I.; Kieliszek, M.; Kolniak-Ostek, J.; Mitek, M. UPLC-PDA-Q/TOF-MS Profile of Polyphenolic Compounds of Liqueurs from Rose Petals (Rosa rugosa). Molecules 2017, 22, 1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.; Bui, A.D.; Cain, N.; Rose, G.; Downey, M. Analysis of free and bound phenolics in wine and grapes by GC–MS after automated SPE. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 9869–9877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, A.; Ruiz-Montoya, M.; Díaz, M.J.; Giráldez, I.; Morales, E. Optimization of bioactive compounds by ultrasound extraction and gas chromatography—Mass spectrometry in fast-growing leaves. Microchem. J. 2023, 193, 109231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrtsi, E.D.; Koulocheri, S.D.; Iliopoulos, V.; Haroutounian, S.A. High-Throughput Quantification of 32 Bioactive Antioxidant Phenolic Compounds in Grapes, Wines and Vinification Byproducts by LC–MS/MS. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundogdu, M.; Canan, I.; Gecer, M.K.; Kan, T.; Ercisli, S. Phenolic compounds, bioactive content and antioxidant capacity of the fruits of mulberry (Morus spp.) germplasm in Turkey. Folia Hortic. 2017, 29, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoheisel, J.D.; Restivo, A.; Degano, I.; Ribechini, E.; Colombini, M.P. Development and Optimisation of an HPLC-DAD-ESI-Q-ToF Method for the Determination of Phenolic Acids and Derivatives. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88762. [Google Scholar]
- Mulabagal, V.; Keller, W.J.; Calderón, A.I. Quantitative analysis of anthocyanins in Euterpe oleracea (açaí) dietary supplement raw materials and capsules by Q-TOF liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Pharm. Biol. 2012, 50, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.-H.; Shi, Y.-P. Comprehensive analysis of phenolic compounds in four varieties of goji berries at different ripening stages by UPLC–MS/MS. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 106, 104279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Lv, H.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. Characterization of Polyphenols from Lycium ruthenicum Fruit by UPLC-Q-TOF/MSE and Their Antioxidant Activity in Caco-2 Cells. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2016, 64, 2280–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L.; Kang, L.; Liu, H.; Ma, X.; Zhao, D. Comparative Analysis of Polyphenols in Lycium barbarum Fruits Using UPLC-IM-QTOF-MS. Molecules 2023, 28, 4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Component | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Product Ion (m/z) | Fragment (V) | Collision Energy (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| arbutin | 271.0 | 108.0 */160.8 | 115 | 25/7 |
| gallic acid | 169.1 | 125.0 */78.9 | 100 | 10/25 |
| 4-hydroxybenzoic acid | 137.0 | 92.9 */65.0 | 60 | 10/30 |
| epigallocatechin | 305.1 | 125.0 */219.1 | 120 | 20/10 |
| neochlorogenic acid | 353.1 | 191.1 */179.0 | 80 | 10/10 |
| D-quinic acid | 191.2 | 85.1 */93.0 | 125 | 20/20 |
| catechin | 288.9 | 244.9 */202.9 | 130 | 10/15 |
| caffeic acid | 179.1 | 135.1 */106.9 | 100 | 15/25 |
| p-coumaric acid | 163.0 | 119.1 */93.0 | 70 | 15/35 |
| syringic acid | 197.0 | 182.0 */123.3 | 60 | 10/25 |
| epicatechin | 289.0 | 245.0 */203.0 | 125 | 10/15 |
| vanillic acid | 167.0 | 108 */152.1 | 50 | 20/10 |
| 7-hydroxycoumaric acid | 161.1 | 133.1 */105.1 | 100 | 20/25 |
| chlorogenic acid | 366.9 | 135.1 */178.8 | 70 | 30/20 |
| ferulic acid | 193.1 | 134.0 */177.9 | 70 | 15/10 |
| sinapic acid | 223.1 | 208.0 */164.1 | 70 | 10/7 |
| rutin | 609.1 | 299.8 */270.8 | 105 | 40/60 |
| isoferulic acid | 192.9 | 134.2 */178.2 | 90 | 15/10 |
| hyperoside | 463.0 | 299.9 */270.8 | 170 | 30/50 |
| isoquercitrin | 462.9 | 299.8 */270.8 | 150 | 30/45 |
| quercetin 3-O-β-D-xylopyranoside | 433.1 | 299.9 */270.9 | 130 | 25/45 |
| guaijaverin, | 433.0 | 299.8 */270.9 | 120 | 25/45 |
| salicylic acid | 137.1 | 93.0 */65.1 | 80 | 15/35 |
| kaempferol 3-rutinoside | 593.1 | 285.1 */255 | 140 | 30/55 |
| narcissin | 623.0 | 315.0 */299.0 | 140 | 25/50 |
| astragalin | 447.1 | 283.9 */255 | 100 | 25/35 |
| isorhamnetin 3-O-galactoside | 477.0 | 313.8 */271.0 | 140 | 25/45 |
| isorhamnetin 3-O-glucoside | 477.0 | 314.0 */271.1 | 140 | 25/45 |
| phloridin | 435.1 | 272.9 */166.9 | 160 | 10/30 |
| cinnamic acid | 147.0 | 103.1 */77.1 | 70 | 7/25 |
| naringin | 271.1 | 151.0 */119.0 | 80 | 15/20 |
| isorhamnetin | 315.1 | 300.0 */151.0 | 100 | 20/25 |
| Compound | Linear Range (μg/mL) | Linear Equation | R2 a | LOD b (μg/kg) | LOQ c (μg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| arbutin | 2–200 | y = 845.1x + 777.4 | 0.9983 | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| gallic acid | 2–500 | y = 8647.5x + 43,895.1 | 0.9995 | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| 4-hydroxybenzoic acid | 2–500 | y = 9786.5x − 823.5 | 0.9998 | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| epigallocatechin | 2–1000 | y = 788.0x + 5422.5 | 0.9989 | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| neochlorogenic acid | 5–1000 | Y = 30,824.5x + 6201.7 | 0.9977 | 1.0 | 3.0 |
| D-quinic acid | 2–1000 | Y = 1934.8x + 2876.5 | 0.9996 | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| catechin | 2–1000 | Y = 1067.3x + 16,904.7 | 0.9986 | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| caffeic acid | 2–500 | Y = 24,638.5x + 186,859.8 | 0.9973 | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| p-coumaric acid | 5–1000 | Y = 1163.2x − 392.0 | 0.9988 | 1.0 | 3.0 |
| syringic acid | 5–1000 | Y = 1588.9x + 8207.0 | 0.9962 | 1.0 | 3.0 |
| epicatechin | 5–500 | Y = 17,678.2x − 3395.0 | 0.9980 | 1.0 | 3.0 |
| vanillic acid | 5–1000 | Y = 506.7x + 1608.1 | 0.9970 | 1.0 | 3.0 |
| 7-hydroxycoumaric acid | 2–500 | Y = 7133.8x + 24,684.8 | 0.9980 | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| chlorogenic acid | 5–500 | Y = 4547.0x + 6755.4 | 0.9986 | 1.0 | 3.0 |
| ferulic acid | 1–500 | Y = 1397.5x + 10,877.0 | 0.9966 | 0.2 | 0.6 |
| sinapic acid | 2–1000 | Y = 435.4x + 714.7 | 0.9966 | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| rutin | 1–500 | Y = 5789.4x − 1310.0 | 0.9976 | 0.2 | 0.6 |
| isoferulic acid | 1–500 | Y = 254.6x − 153.4 | 0.9977 | 0.2 | 0.6 |
| hyperoside | 5–500 | Y = 11,039.7x − 31,457.0 | 0.9961 | 1.0 | 3.0 |
| isoquercitrin | 2–500 | Y = 8308.4x − 11,066.6 | 0.9968 | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| quercetin 3-O-β-D-xylopyranoside | 2–500 | Y = 112,942.5x + 912,541.6 | 0.9966 | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| guaijaverin, | 2–500 | Y = 57,548.4x + 456,777.7 | 0.9959 | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| salicylic acid | 2–1000 | Y = 71,012.9x + 10,913.0 | 0.9957 | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| kaempferol 3-rutinoside | 5–1000 | Y = 368.9x − 1140.5 | 0.9973 | 1.0 | 3.0 |
| narcissin | 2–1000 | Y = 18,258.5x + 117,031.6 | 0.9994 | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| astragalin | 2–1000 | Y = 8587.7x − 3507.1 | 0.9997 | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| isorhamnetin 3-O-galactoside | 2–1000 | Y = 27,568.0x + 410,150.4 | 0.9967 | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| isorhamnetin 3-O-glucoside | 2–500 | Y = 56,161.1x − 59,046.1 | 0.9994 | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| phloridin | 2–500 | Y = 1522.0x + 29,246.4 | 0.9994 | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| cinnamic acid | 5–500 | Y = 1670.4x − 4455.4 | 0.9974 | 1.0 | 3.0 |
| naringin | 5–500 | Y = 9614.4x + 42,844.2 | 0.9956 | 1.0 | 3.0 |
| isorhamnetin | 5–1000 | Y = 4794.5x − 10,609.5 | 0.9983 | 1.0 | 3.0 |
| Compound | Recoveries of Phenolic Compounds in Different Berries ± RSD a (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black Wolfberry | Red Wolfberry | Mulberry | Sea Buckthorn | |
| arbutin | 88.3 ± 0.6 | 96.6 ± 1.5 | 85.6 ± 2.4 | 99.1 ± 2.5 |
| gallic acid | 97.5 ± 2.3 | 93.4 ± 2.3 | 97.3 ± 3.5 | 94.5 ± 3.2 |
| 4-hydroxybenzoic acid | 89.3 ± 3.4 | 102.4 ± 1.8 | 95.5 ± 2.9 | 101.6 ± 3.2 |
| epigallocatechin | 95.1 ± 2.7 | 95.6 ± 2.8 | 85.6 ± 1.5 | 94.9 ± 1.4 |
| neochlorogenic acid | 89.9 ± 3.4 | 91.0 ± 2.6 | 97.1 ± 2.5 | 102.1 ± 2.4 |
| D-quinic acid | 97.5 ± 3.6 | 93.8 ± 3.7 | 90.3 ± 4.2 | 83.7 ± 5.2 |
| catechin | 97.9 ± 0.7 | 92.3 ± 4.2 | 100.2 ± 2.7 | 89.9 ± 3.9 |
| caffeic acid | 100.0 ± 3.1 | 93.2 ± 4.5 | 85.9 ± 2.9 | 85.1 ± 2.3 |
| p-coumaric acid | 93.3 ± 4.2 | 92.4 ± 3.3 | 90.1 ± 3.2 | 94.2 ± 2.8 |
| syringic acid | 100.4 ± 2.6 | 96.2 ± 5.1 | 102.2 ± 1.8 | 97.3 ± 1.4 |
| epicatechin | 88.7 ± 1.4 | 95.2 ± 3.2 | 92.0 ± 2.1 | 96.6 ± 0.4 |
| vanillic acid | 98.6 ± 2.8 | 90.7 ± 2.6 | 87.3 ± 3.1 | 102.4 ± 2.1 |
| 7-hydroxycoumaric acid | 98.2 ± 2.6 | 88.5 ± 1.2 | 88.6 ± 2.9 | 98.1 ± 3.2 |
| chlorogenic acid | 93.6 ± 1.4 | 88.3 ± 2.2 | 89.9 ± 2.7 | 94.4 ± 2.8 |
| ferulic acid | 89.1 ± 4.5 | 91.4 ± 2.4 | 91.5 ± 4.2 | 86.8 ± 0.5 |
| sinapic acid | 92.6 ± 4.8 | 94.4 ± 2.6 | 90.9 ± 4.4 | 97.9 ± 2.9 |
| rutin | 84.9 ± 3.7 | 95.1 ± 2.9 | 96.7 ± 3.6 | 97.6 ± 3.8 |
| isoferulic acid | 89.6 ± 1.6 | 97.0 ± 2.4 | 99.1 ± 4.6 | 87.8 ± 1.2 |
| hyperoside | 84.3 ± 4.4 | 97.8 ± 2.7 | 90.1 ± 4.2 | 90.9 ± 2.7 |
| isoquercitrin | 88.5 ± 2.1 | 89.9 ± 4.2 | 96.4 ± 3.2 | 91.3 ± 4.2 |
| quercetin 3-O-β-D-xylopyrnoside | 100.4 ± 4.9 | 85.6 ± 3.1 | 95.2 ± 4.5 | 98.1 ± 1.9 |
| guaijaverin, | 95.4 ± 3.2 | 95.6 ± 4.5 | 98.9 ± 4.8 | 88.4 ± 4.7 |
| salicylic acid | 101.4 ± 3.0 | 104.8 ± 2.5 | 98.9 ± 1.8 | 89.6 ± 3.1 |
| kaempferol 3-rutinoside | 85.7 ± 4.2 | 96.7 ± 3.9 | 88.2 ± 3.7 | 95.5 ± 2.4 |
| narcissin | 87.0 ± 1.6 | 97.2 ± 2.9 | 101.9 ± 4.4 | 89.5 ± 1.3 |
| astragalin | 94.8 ± 5.2 | 90.1 ± 5.7 | 95.9 ± 5.8 | 96.6 ± 4.3 |
| isorhamnetin 3-O-galactoside | 93.6 ± 3.4 | 92.2 ± 3.4 | 99.8 ± 2.7 | 88.5 ± 4.6 |
| isorhamnetin 3-O-glucoside | 97.3 ± 1.4 | 96.4 ± 4.1 | 85.6 ± 1.7 | 82.8 ± 2.7 |
| phloridin | 97.3 ± 0.7 | 90.9 ± 3.9 | 88.5 ± 4.5 | 95.3 ± 3.2 |
| cinnamic acid | 86.6 ± 3.1 | 92.6 ± 4.1 | 94.2 ± 2.5 | 92.6 ± 1.2 |
| naringin | 104.3 ± 4.1 | 103.1 ± 3.9 | 86.5 ± 4.8 | 90.2 ± 0.5 |
| isorhamnetin | 94.3 ± 2.5 | 90.5 ± 5.5 | 91.2 ± 2.3 | 95.8 ± 2.9 |
| Compound | The Amount of Phenolic Compounds in Different Berries (mg/kg) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black Wolfberry | Red Wolfberry | Mulberry | Sea Buckthorn | |
| gallic acid | 2.11 | ND | 2.01 | 6.25 |
| 4-hydroxybenzoic acid | 13.4 | 4.40 | 2.60 | 1.21 |
| D-quinic acid | 82.5 | ND | 44.4 | 4.71 |
| catechin | ND | ND | ND | 4.33 |
| caffeic acid | 1.60 | 1.19 | 0.96 | ND |
| syringic acid | ND | ND | ND | 0.30 |
| epicatechin | 13.5 | 65.9 | 1.64 | 1.98 |
| vanillic acid | ND | ND | 0.11 | 0.16 |
| chlorogenic acid | 55.0 | 3.79 | 25.6 | ND |
| ferulic acid | 3.81 | 7.89 | 0.35 | 0.54 |
| sinapic acid | 1.29 | 1.01 | 0.54 | 9.84 |
| rutin | 84.6 | 130 | 221 | 188 |
| isoferulic acid | 1.54 | 42.0 | ND | 0.18 |
| hyperoside | 1.15 | 0.57 | 95.3 | 169 |
| isoquercitrin | 0.42 | ND | 5.06 | 3.68 |
| salicylic acid | 0.17 | 0.40 | ND | 0.33 |
| kaempferol 3-rutinoside | 58.1 | 40.8 | 106 | 68.3 |
| narcissin | 2.53 | 1.69 | 0.11 | 117 |
| astragalin | 0.11 | ND | 7.15 | 4.69 |
| isorhamnetin 3-O-galactoside | ND | ND | ND | 3.35 |
| isorhamnetin 3-O-glucoside | ND | ND | ND | 41.4 |
| phloridin | 2.14 | ND | 2.59 | 0.26 |
| cinnamic acid | ND | ND | ND | 0.61 |
| naringin | 0.19 | ND | 0.13 | 0.11 |
| isorhamnetin | ND | ND | ND | 8.33 |
| Analytical Method | Species | LOD a | LOQ b | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPLC-MS/MS | 32 | 0.2–1.0 μg/kg | 0.6–3.0 μg/kg | this research |
| HPLC-DAD | 24 | 0.002–0.16 μg/mL | 0.01–0.48 μg/mL | [32] |
| HPLC-DAD | 17 | 0.003–0.063 μg/mL | 0.009–0.211 μg/mL | [33] |
| HPLC-DAD | 16 | 0.03–0.62 mg/L | 0.11–2.08 mg/L | [27] |
| HPLC-DAD | 13 | 0.1–0.3 μg/mL | 0.2–1.0 μg/mL | [34] |
| HPLC-DAD | 10 | 0.016–0.144 μg/mL | 0.051–0.711 μg/mL | [35] |
| HPLC-DAD | 10 | 0.09–0.35 μg/mL | 0.29–0.1.07 μg/mL | [36] |
| UPLC-DAD | 41 | 0.10–0.65 mg/L | 0.23–1.12 mg/L | [37] |
| UPLC-DAD | 9 | 0.18–1.01 μg/mL | 0.54–3.06 μg/mL | [38] |
| UPLC-PDA | 7 | 0.02–0.17 μg/mL | 0.1–0.6 μg/mL | [39] |
| GC-MS | 23 | 2.5–25 ng/mL | 5–50 ng/mL | [40] |
| GC-MS/MS | 8 | 7.9–310 μg/kg | 26–1800 μg/kg | [41] |
| LC-MS/MS | 36 | 0.0004–0.0037 μg/L | 0.0012–0.0111 μg/L | [26] |
| LC-MS/MS | 32 | 7.5–158.3 ng/mL | 22.6–479.8 ng/mL | [42] |
| LC-MS/MS | 8 | 0.003–0.445 mg/L | 0.010–1.483 mg/L | [23] |
| UPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS | 25 | 1.05–4.59 μg/L | 3.59–15.98 μg/L | [43] |
| HPLC-ESI-Q-Tof | 13 | 0.01–0.15 µg/g | 0.02–0.50 µg/g | [44] |
| UPLC- ESI-Q-Tof | 4 | 0.01–0.12 μg/mL | 0.06–0.49 μg/mL | [45] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Xing, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Lu, S. Simultaneous Determination of 32 Polyphenolic Compounds in Berries via HPLC–MS/MS. Molecules 2025, 30, 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30092008
Wang Y, Xing L, Zhang J, Chen Y, Lu S. Simultaneous Determination of 32 Polyphenolic Compounds in Berries via HPLC–MS/MS. Molecules. 2025; 30(9):2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30092008
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yuan, Lijie Xing, Jinlei Zhang, Yongfa Chen, and Shiling Lu. 2025. "Simultaneous Determination of 32 Polyphenolic Compounds in Berries via HPLC–MS/MS" Molecules 30, no. 9: 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30092008
APA StyleWang, Y., Xing, L., Zhang, J., Chen, Y., & Lu, S. (2025). Simultaneous Determination of 32 Polyphenolic Compounds in Berries via HPLC–MS/MS. Molecules, 30(9), 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30092008





