Preparation, Digestion, and Storage of Microencapsulated Nervonic Acid-Enriched Structured Phosphatidylcholine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
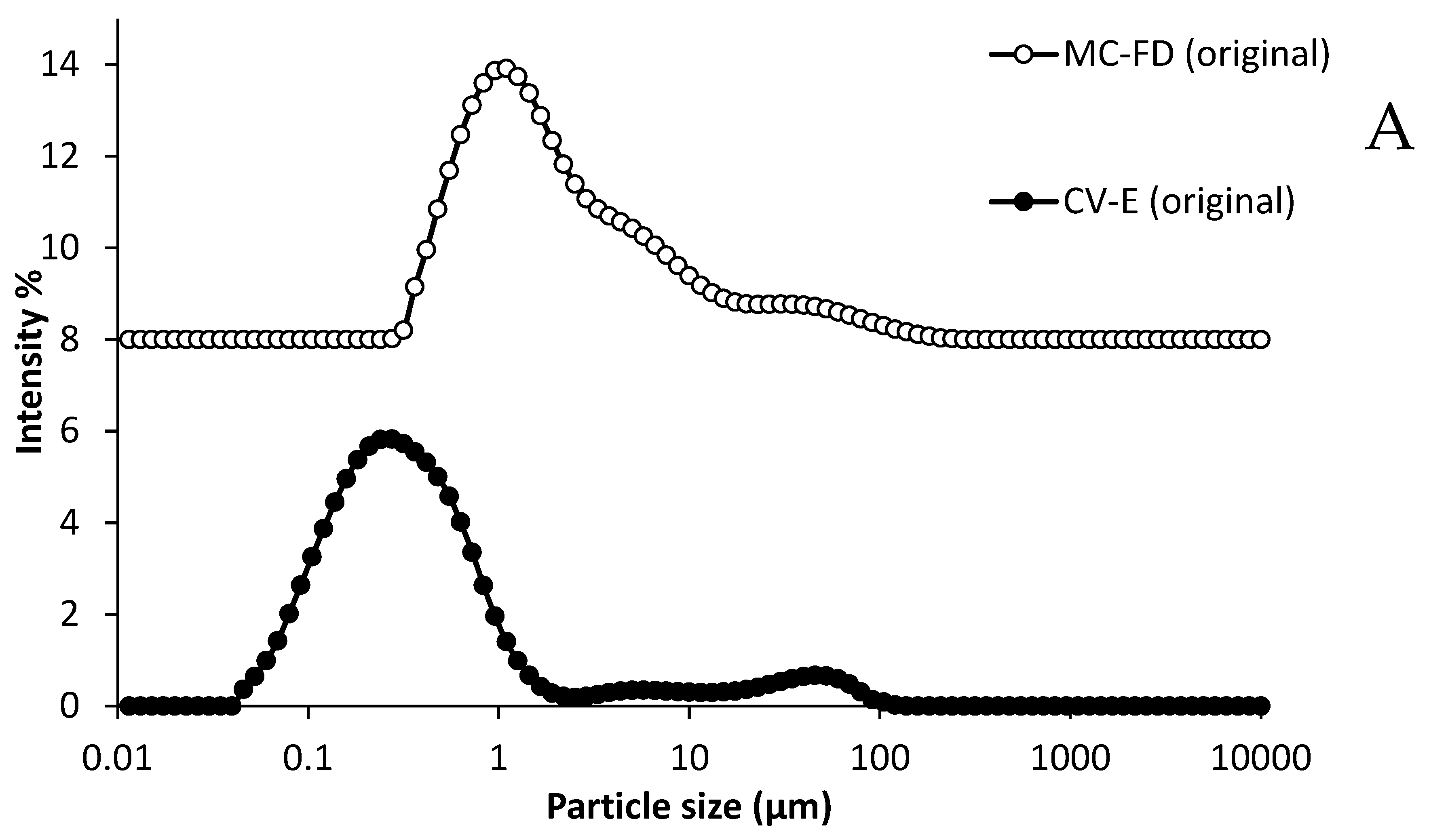
2.1. Characterisation of Conventional Emulsion
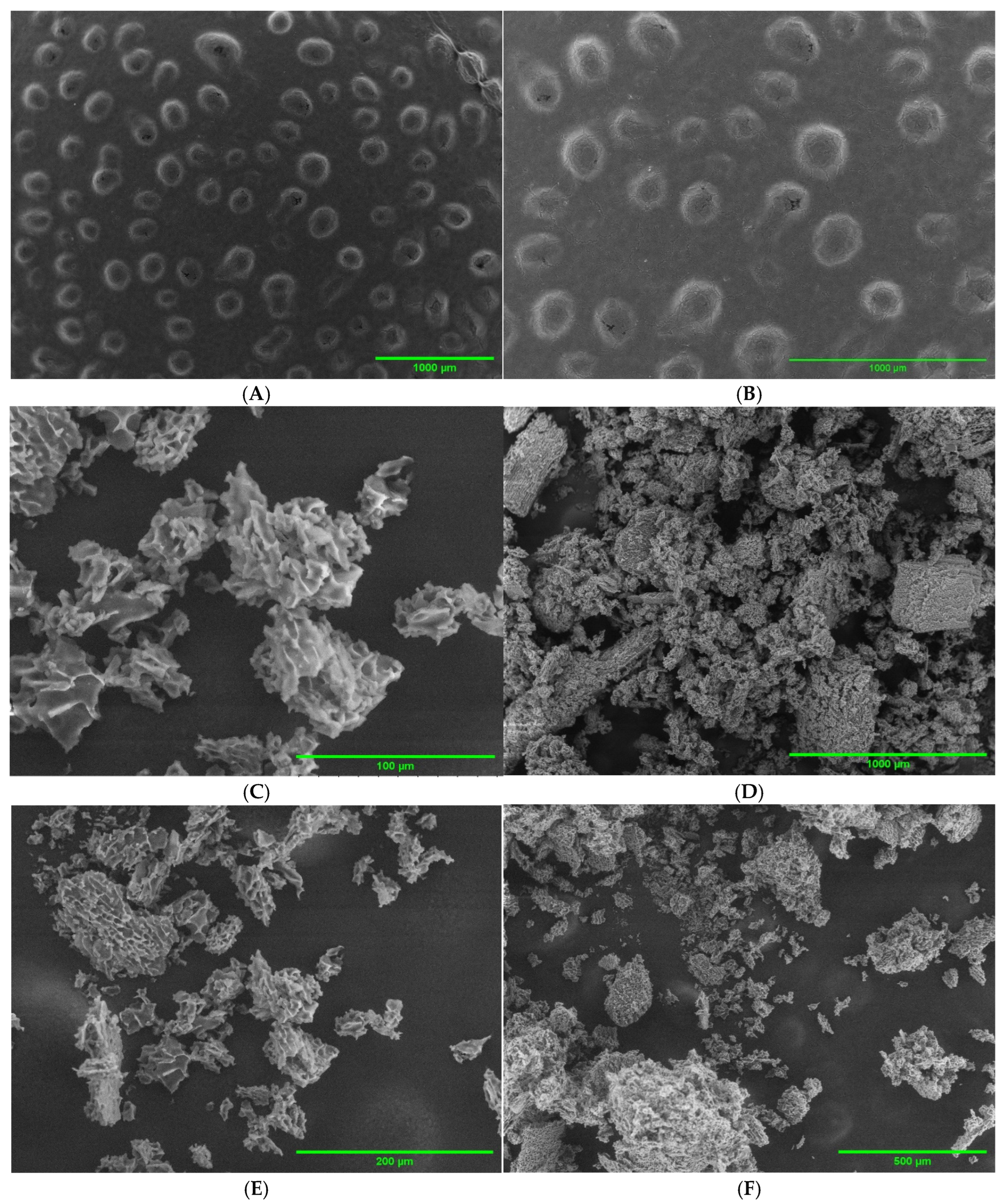
2.2. SEM Imaging
2.3. Thermal Behaviour of CV-E and MC-FD
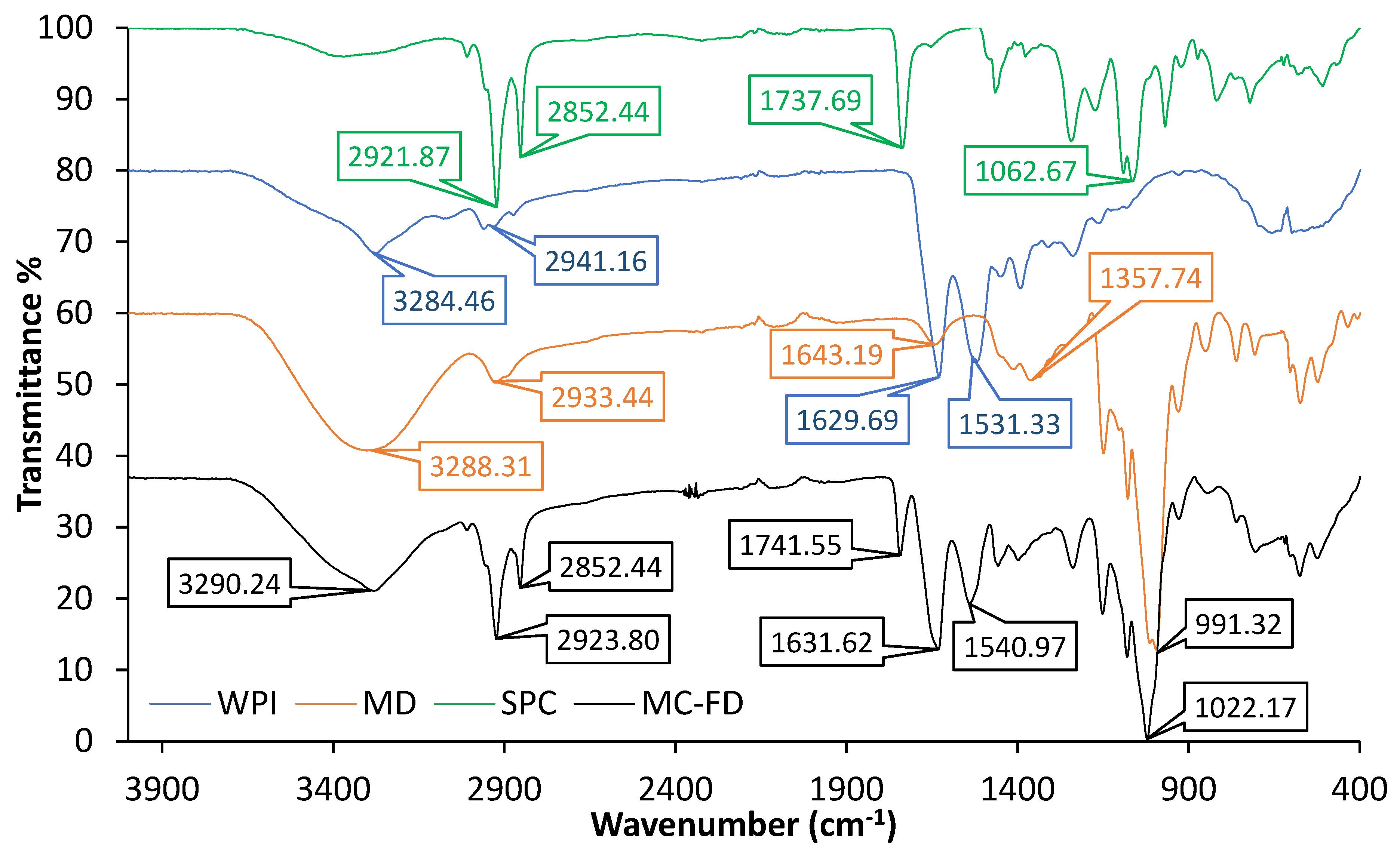
2.4. FTIR of Lipid Particles
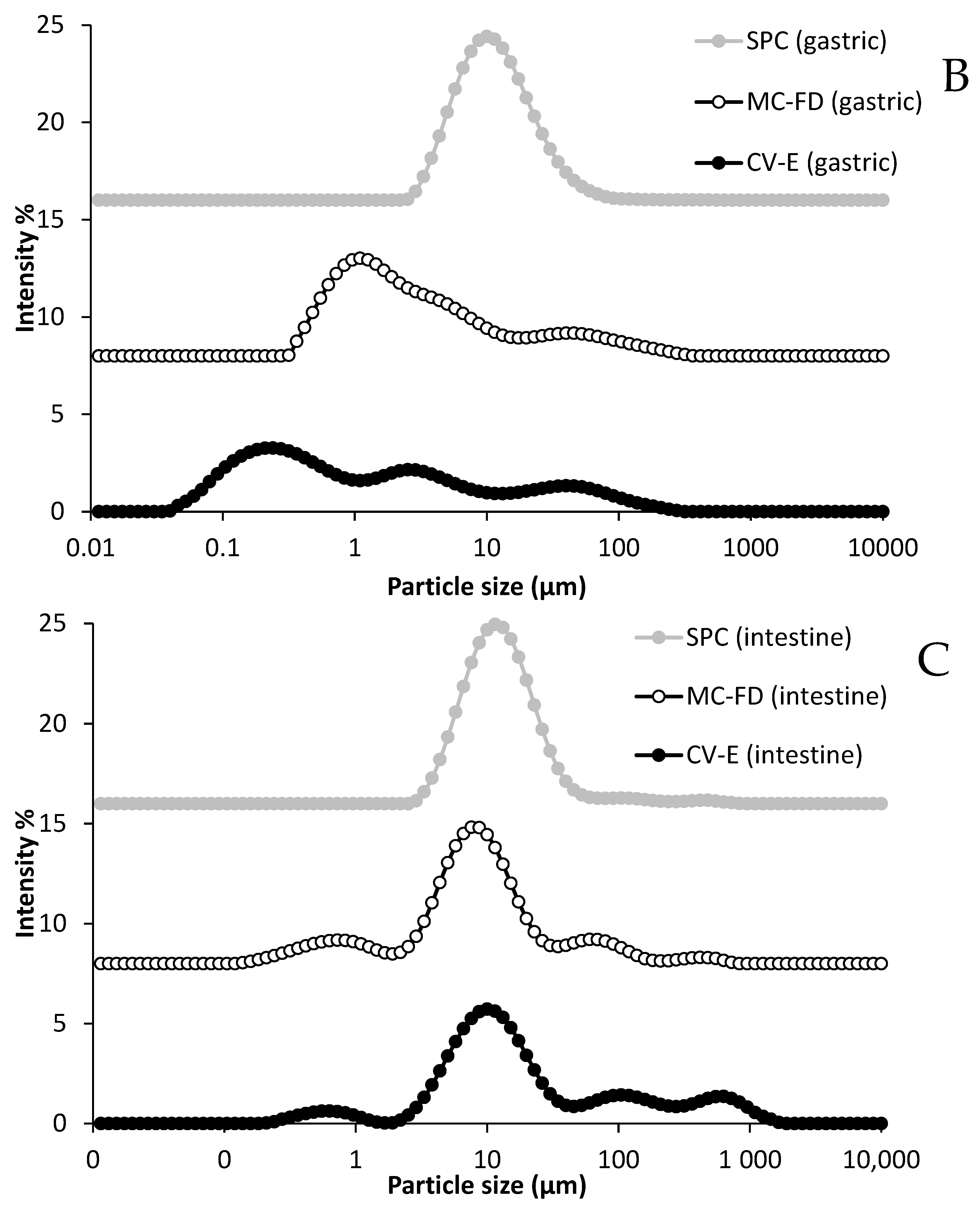
2.5. In Vitro Digestion of Lipids
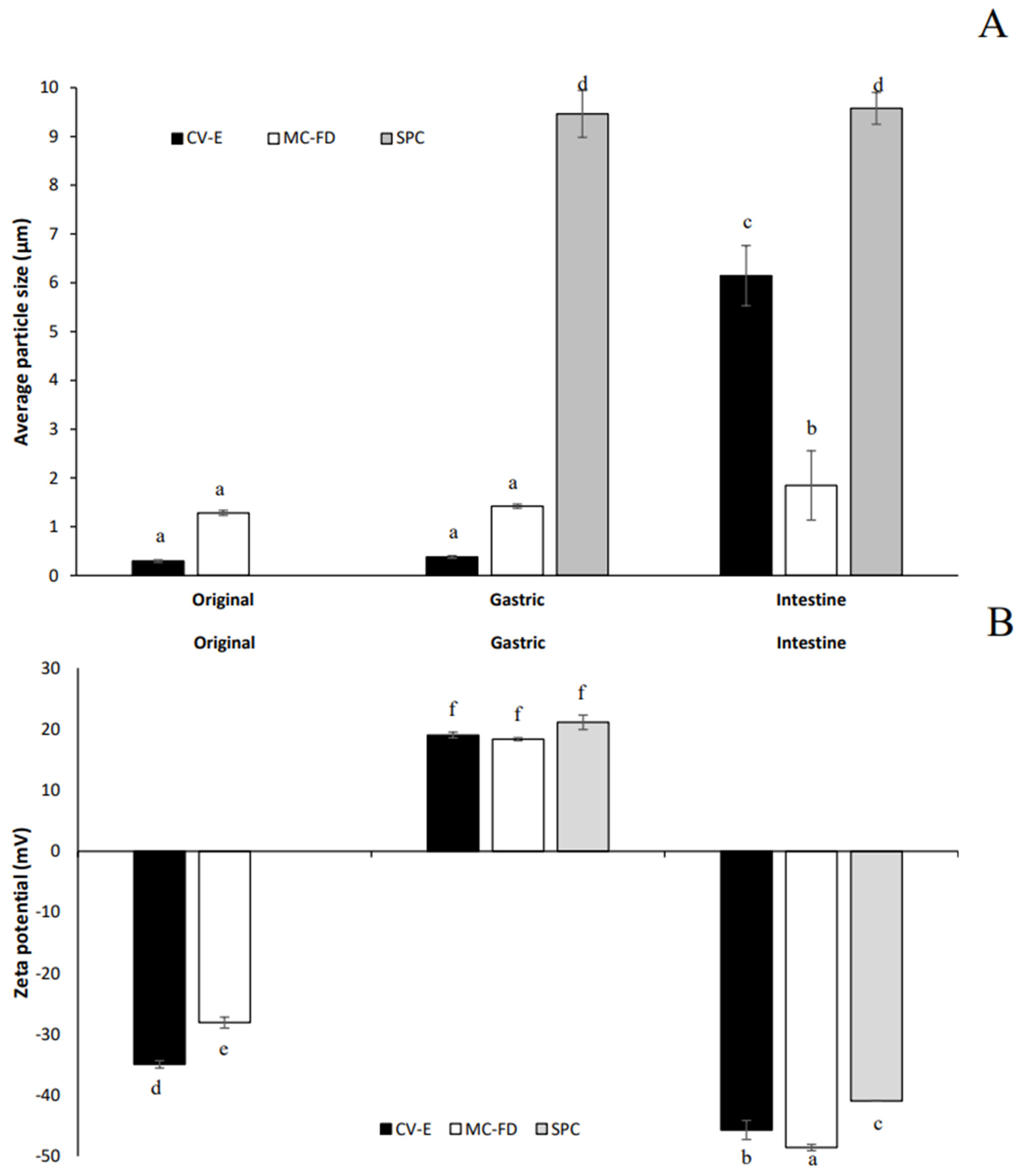
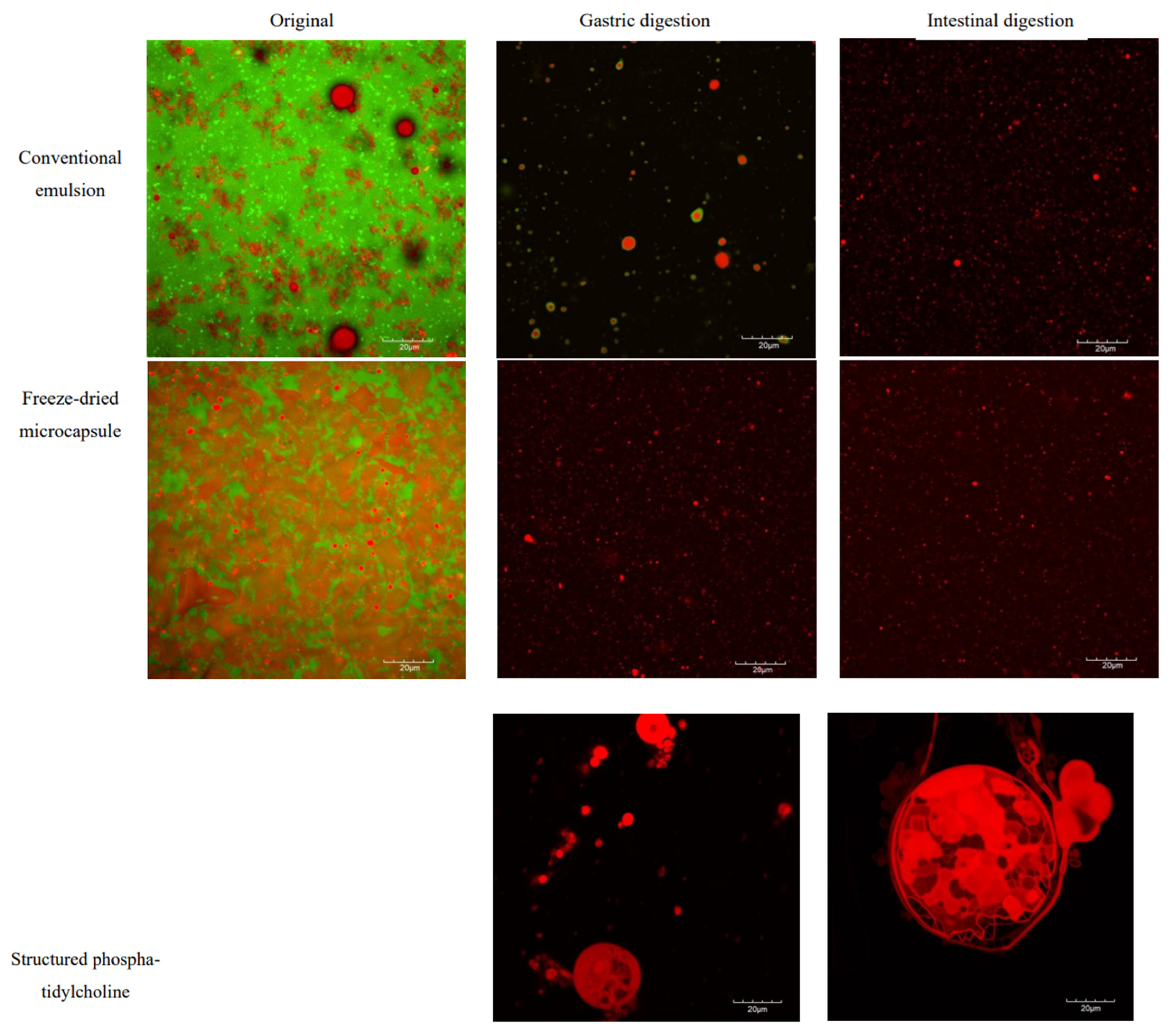
2.6. Microstructure of CV-E and MC-FD During Digestion
2.7. Fatty Acid Composition After Digestion
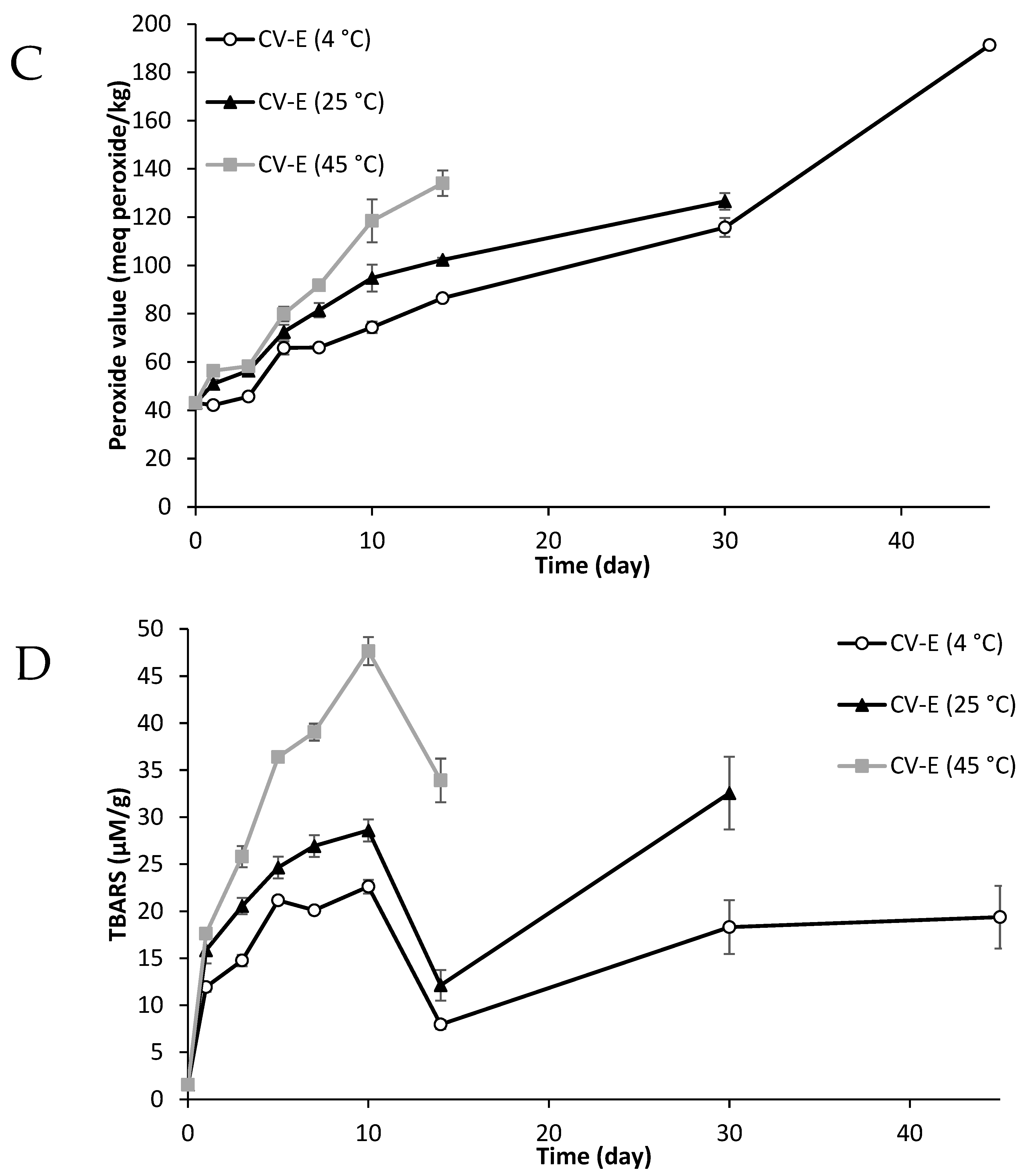
2.8. Primary and Secondary Oxidative Stability of Lipid Particles
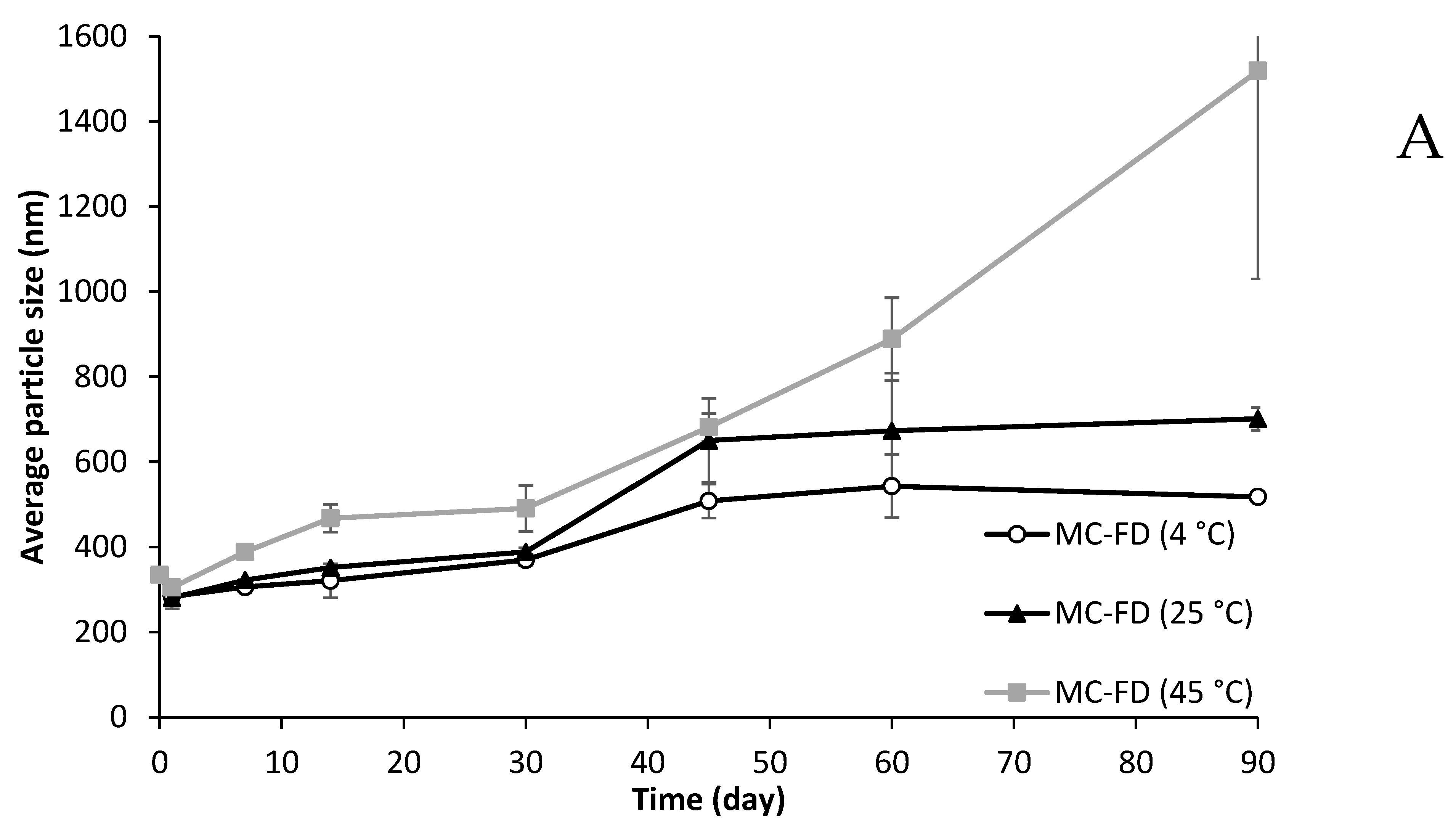
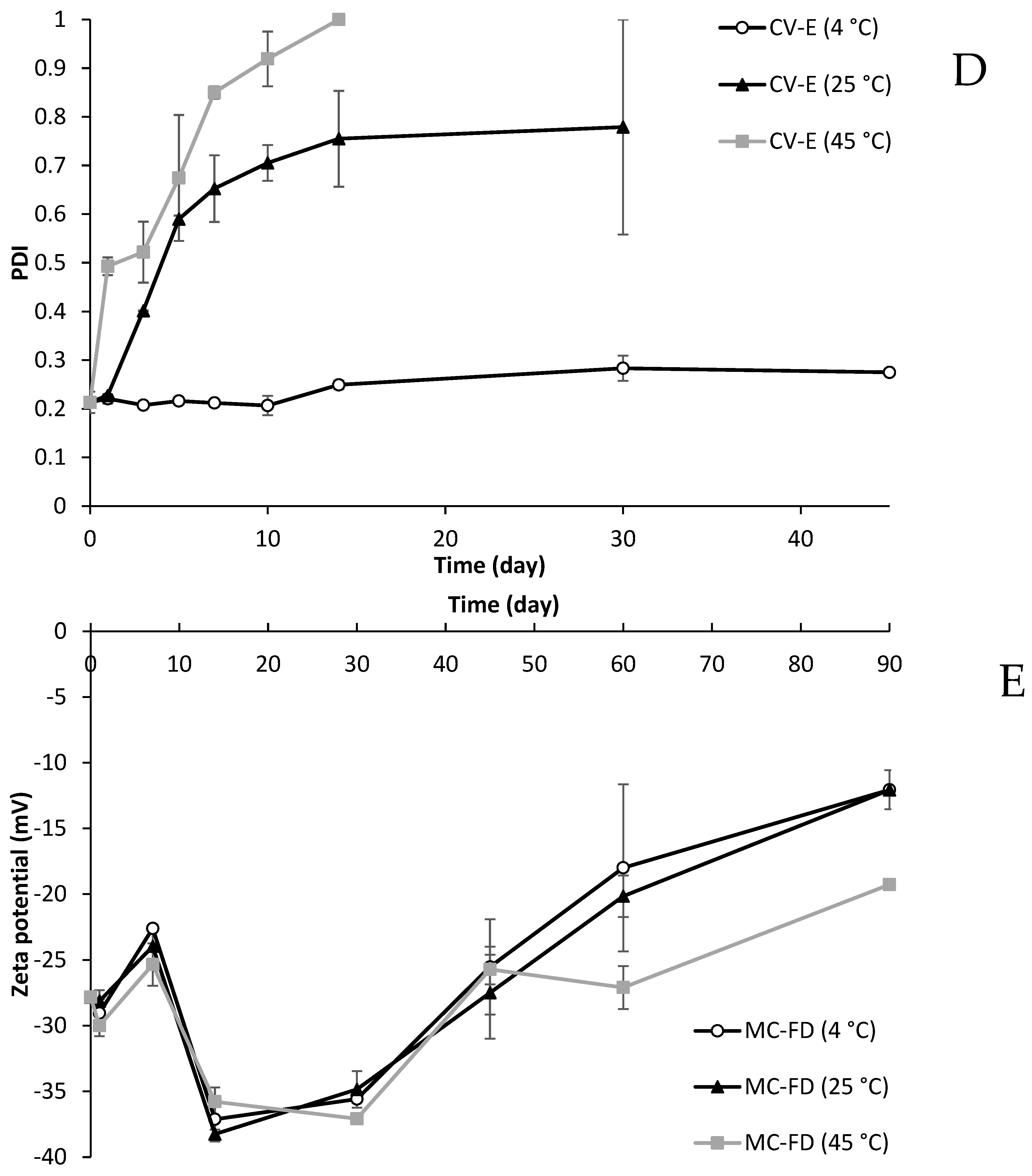
2.9. Particle Size and PDI of Lipid Particles During Storage
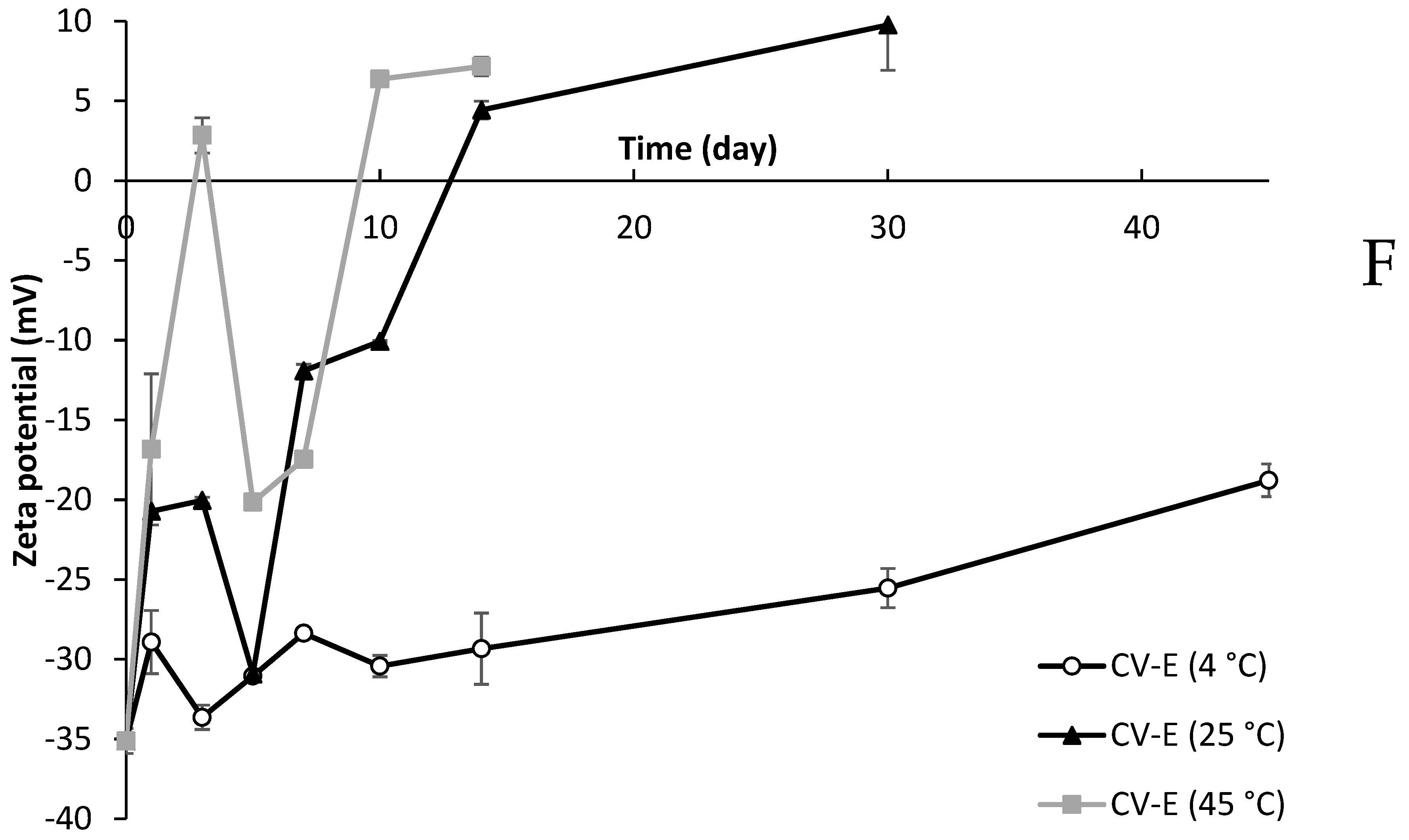
2.10. Zeta Potential of Lipid Particles
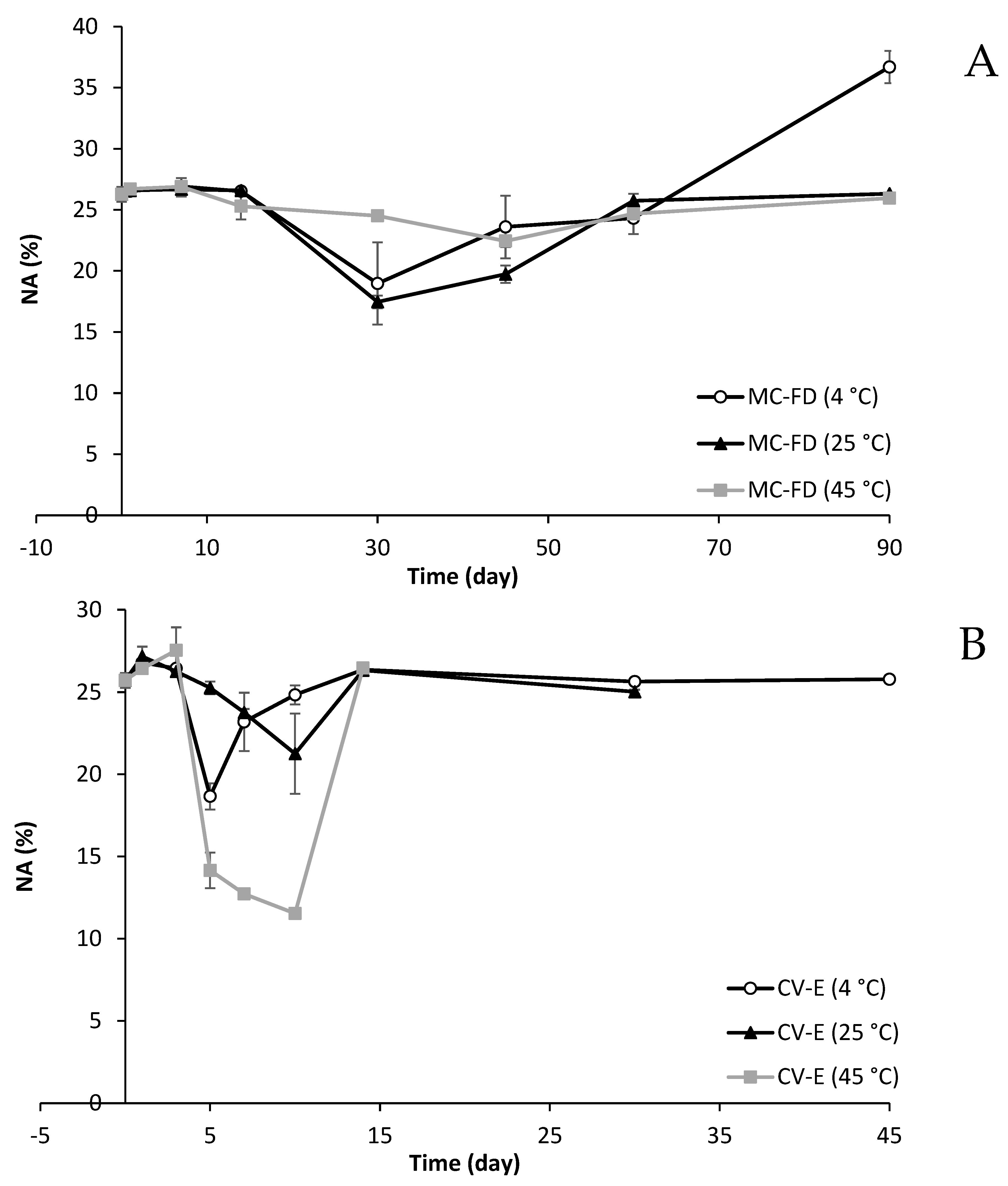
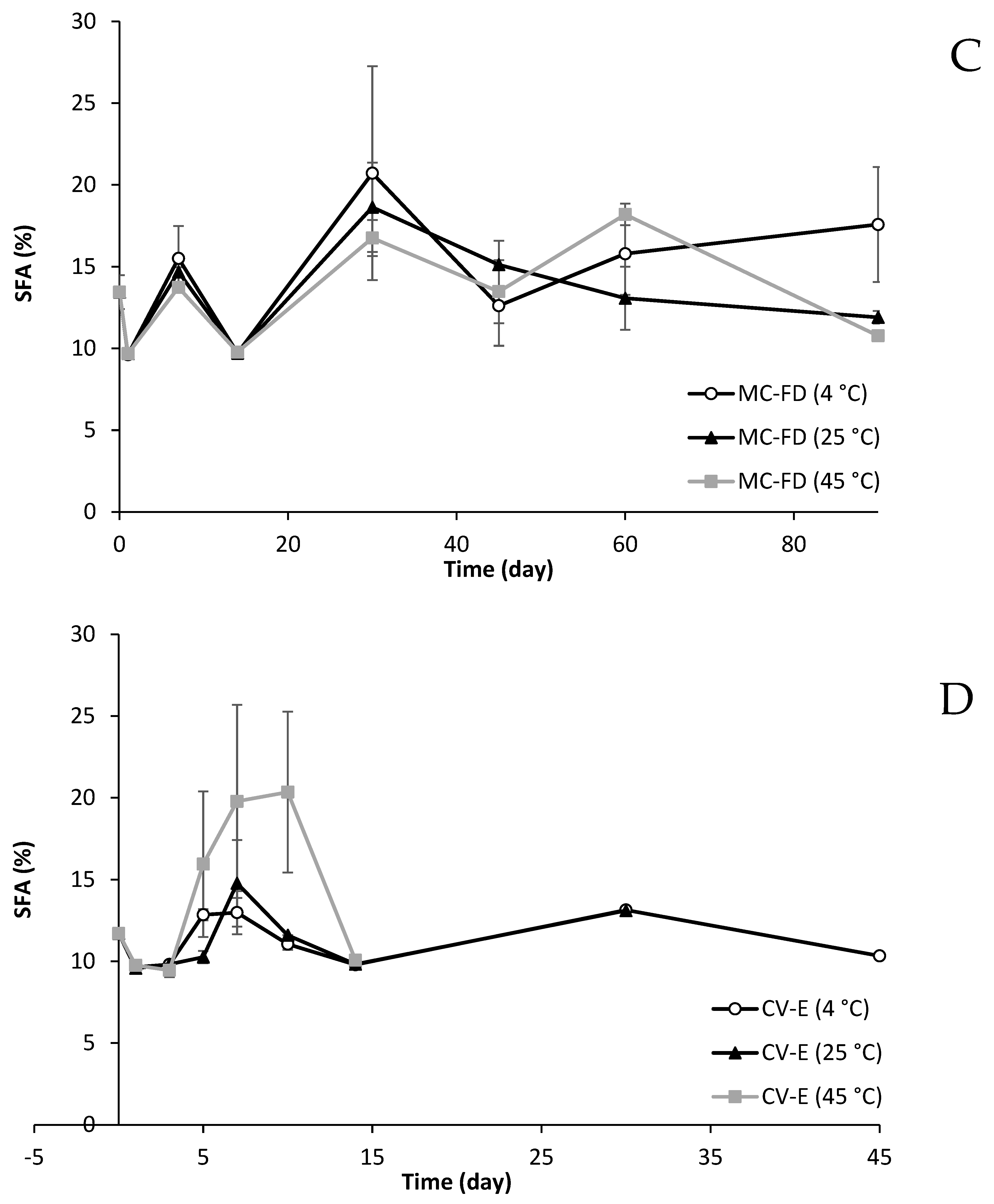
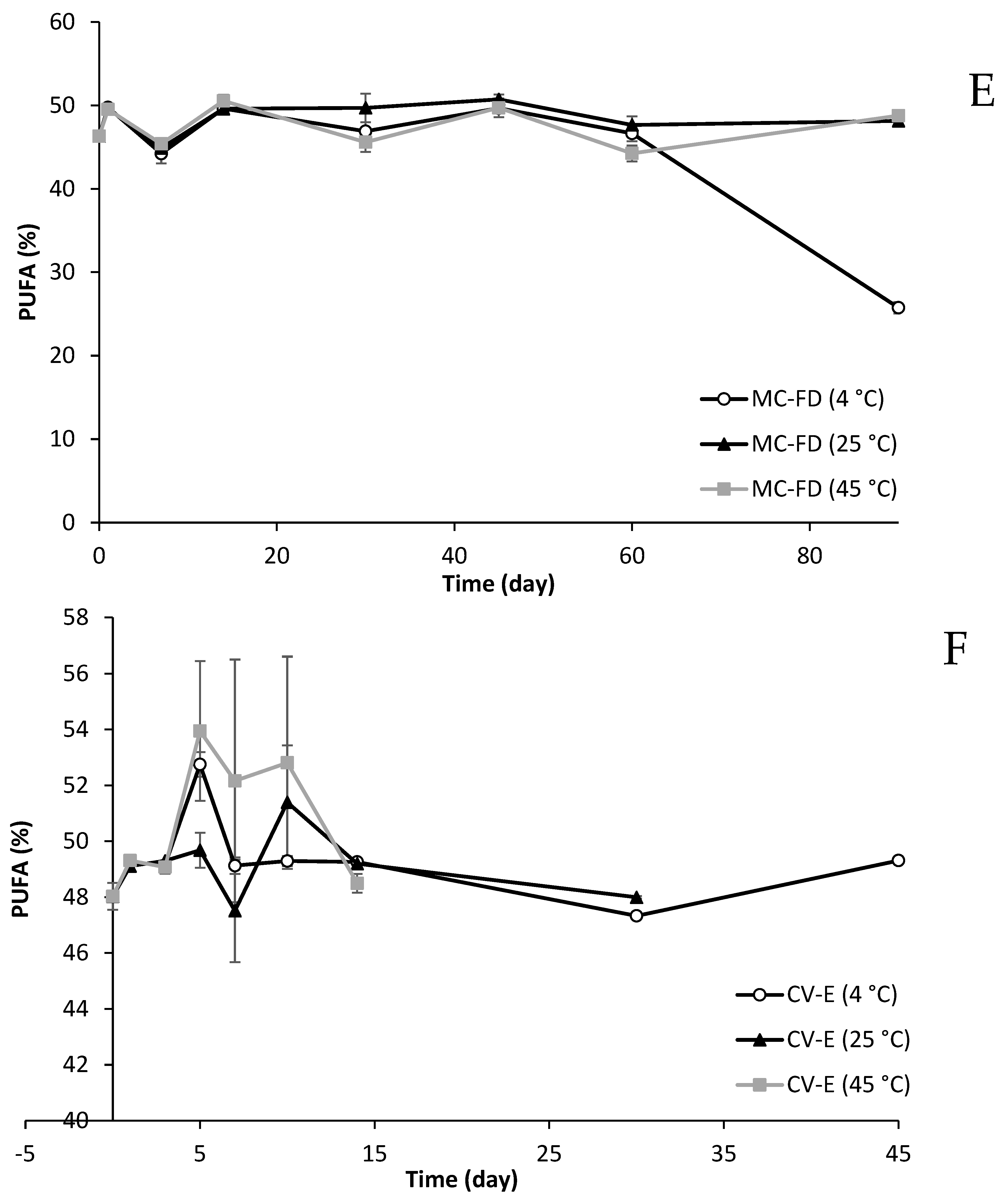
2.11. Fatty Acid Composition Changes of Lipid Particles
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Emulsion and Microcapsule Preparation
3.3. Determination of Particle Size, Polydispersity (PDI), Zeta Potential, and Entrapment Efficiency
3.4. Fatty Acid Composition
3.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.8. In Vitro Digestion
3.9. Confocal Scanning Laser Microscopy (CLSM)
3.10. Storage Stability Tests
3.11. Primary and Secondary Lipid Oxidation Products
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sargent, J.R.; Coupland, K.; Wilson, R. Nervonic acid and demyelinating disease. Med. Hypotheses 1994, 42, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; Xu, X.; Yu, L.L. Interesterified trans-free fats rich in sn-2 nervonic acid prepared using Acer truncatum oil, palm stearin and palm kernel oil, and their physicochemical properties. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 156–163. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Kondo, K.; Maeba, R.; Nishimukai, M.; Nezu, T.; Hara, H. The Proportion of Nervonic Acid in Serum Lipids is Associated with Serum Plasmalogen Levels and Metabolic Syndrome. J. Oleo Sci. 2014, 63, 527–537. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, X.; Chen, H.; Xiang, J.; Wei, F.; Quek, S.Y. Lipase-Catalyzed Preparation and Optimization of Structured Phosphatidylcholine Containing Nervonic Acid. Molecules 2024, 29, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampucci, S.; Tofani, G.; Chetoni, P.; Di Gangi, M.; Mezzetta, A.; Paganini, V.; Burgalassi, S.; Pomelli, C.S.; Monti, D. Sporopollenin Microcapsule: Sunscreen Delivery System with Photoprotective Properties. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakry, A.M.; Abbas, S.; Ali, B.; Majeed, H.; Abouelwafa, M.Y.; Mousa, A.; Liang, L. Microencapsulation of Oils: A Comprehensive Review of Benefits, Techniques, and Applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 143–182. [Google Scholar]
- Soottitantawat, A.; Bigeard, F.; Yoshii, H.; Furuta, T.; Ohkawara, M.; Linko, P. Influence of emulsion and powder size on the stability of encapsulated d-limonene by spray drying. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2005, 6, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Gatlin, L.A.; Nail, S.L. Protein purification process engineering. Freeze drying: A practical overview. Bioprocess Technol. 1994, 18, 317–367. [Google Scholar]
- Gharsallaoui, A.; Roudaut, G.; Chambin, O.; Voilley, A.; Saurel, R. Applications of spray-drying in microencapsulation of food ingredients: An overview. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 1107–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Premi, M.; Sharma, H.K. Effect of different combinations of maltodextrin, gum arabic and whey protein concentrate on the encapsulation behavior and oxidative stability of spray dried drumstick (Moringa oleifera) oil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, L.; Lee, K. Microencapsulation in the food industry. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 1991, 24, 289–297. [Google Scholar]
- Korma, S.A.; Wei, W.; Ali, A.H.; Abed, S.M.; Zheng, L.; Jin, Q.; Wang, X. Spray-dried novel structured lipids enriched with medium-and long-chain triacylglycerols encapsulated with different wall materials: Characterization and stability. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koç, M.; Güngör, Ö.; Zungur, A.; Yalçın, B.; Selek, İ.; Ertekin, F.K.; Ötles, S. Microencapsulation of Extra Virgin Olive Oil by Spray Drying: Effect of Wall Materials Composition, Process Conditions, and Emulsification Method. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2015, 8, 301–318. [Google Scholar]
- Salvia-Trujillo, L.; Qian, C.; Martín-Belloso, O.; McClements, D.J. Modulating β-carotene bioaccessibility by controlling oil composition and concentration in edible nanoemulsions. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 878–884. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Influence of lipid type on gastrointestinal fate of oil-in-water emulsions: In vitro digestion study. Food Res. Int. 2015, 75, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A.; Park, Y. Physicochemical and structural aspects of lipid digestion. In Understanding and Controlling the Microstructure of Complex Foods; McClements, D.J., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 483–503. [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani, R.A.; Pinheiro, A.C.; Vicente, A.A.; Cunha, R.L. In vitro digestion of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by whey protein nanofibrils. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 790–798. [Google Scholar]
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu, C.; Carrière, F.; Boutrou, R.; Corredig, M.; Dupont, D.; et al. A standardised static in vitro digestion method suitable for food—An international consensus. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Xiao, H.; Lyu, X.; Chen, H.; Wei, F. Lipid oxidation in food science and nutritional health: A comprehensive review. Oil Crop Sci. 2023, 8, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Q.; Gao, N.; Wang, S.; Sun, Y.; Yang, X. Microencapsulation of brucea javanica oil: Characterization, stability and optimization of spray drying conditions. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 36, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Chaiyasit, W.; McClements, D.J.; Weiss, J.; Decker, E.A. Impact of surface-active compounds on physicochemical and oxidative properties of edible oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 550–556. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Li, F.; Lou, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, F.; Wang, J.; Xu, H. Evaluation of the encapsulation capacity of nervous acid in nanoemulsions obtained with natural and ethoxylated surfactants. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 343, 117632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; McGillivray, D.; Wen, J.; Zhong, F.; Quek, S.Y. Co-encapsulation of fish oil with phytosterol esters and limonene by milk proteins. J. Food Eng. 2013, 117, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Rosenberg, Y.; Rosenberg, M. Microcapsules Consisting of Whey Proteins-Coated Droplets of Lipids Embedded in Wall Matrices of Spray-Dried Microcapsules Consisting Mainly of Non-Fat Milk Solids. Foods 2021, 10, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karrar, E.; Mahdi, A.A.; Sheth, S.; Mohamed Ahmed, I.A.; Manzoor, M.F.; Wei, W.; Wang, X. Effect of maltodextrin combination with gum arabic and whey protein isolate on the microencapsulation of gurum seed oil using a spray-drying method. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 171, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Hydrocolloids as emulsifiers and emulsion stabilizers. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.M.; He, Y.; Bhandari, B. Effectiveness of encapsulating biopolymers to produce sub-micron emulsions by high energy emulsification techniques. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandralekha, A.; Tavanandi, A.H.; Amrutha, N.; Hebbar, H.U.; Raghavarao, K.S.M.S.; Gadre, R. Encapsulation of yeast (Saccharomyces cereviciae) by spray drying for extension of shelf life. Dry. Technol. 2016, 34, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, N.; Bayrak, A.; Tat, T.; Altay, F.; Kiralan, M.; Kurt, A. Microencapsulation of basil essential oil: Utilization of gum arabic/whey protein isolate/maltodextrin combinations for encapsulation efficiency and in vitro release. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 1865–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.-Y.; Liu, Z.-L.; Zou, H.-B.; Zhao, Z.-H.; Wei, X.-C. Effect of surfactant modification on the desulfurization performance of Zn/Ti-PILCs adsorbent. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2011, 39, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Alfaro, D.A.; Muñoz-Correa, M.O.F.; Santos-Luna, D.; Toro-Vazquez, J.F.; Cano-Sarmiento, C.; García-Varela, R.; García, H.S. Encapsulation of an insulin-modified phosphatidylcholine complex in a self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) for oral insulin delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 101622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euston, S.R.; Finnigan, S.R.; Hirst, R.L. Aggregation kinetics of heated whey protein-stabilized emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2000, 14, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazicioglu, B.; Sahin, S.; Sumnu, G. Microencapsulation of wheat germ oil. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 3590–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Krog, N.; Sparsø, F.V.; Friberg, S.E.; Larsson, K.; Sjöblom, J. Food Emulsifiers: Their Chemical and Physical Properties; Marcel Dekker Inc: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Carneiro-da-Cunha, M.G.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Souza, B.W.S.; Teixeira, J.A.; Vicente, A.A. Influence of concentration, ionic strength and pH on zeta potential and mean hydrodynamic diameter of edible polysaccharide solutions envisaged for multinanolayered films production. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 85, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Food Emulsions: Principles, Practices, and Techniques; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tonon, R.V.; Pedro, R.B.; Grosso, C.R.F.; Hubinger, M.D. Microencapsulation of Flaxseed Oil by Spray Drying: Effect of Oil Load and Type of Wall Material. Dry. Technol. 2012, 30, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San, S.M.; Jaturanpinyo, M.; Limwikrant, W. Effects of Wall Material on Medium-Chain Triglyceride (MCT) Oil Microcapsules Prepared by Spray Drying. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolve, R.; Galgano, F.; Condelli, N.; Cela, N.; Lucini, L.; Caruso, M.C. Optimization Model of Phenolics Encapsulation Conditions for Biofortification in Fatty Acids of Animal Food Products. Foods 2021, 10, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böger, B.R.; Georgetti, S.R.; Kurozawa, L.E. Microencapsulation of grape seed oil by spray drying. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 38, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Li, Y. Review of in vitro digestion models for rapid screening of emulsion-based systems. Food Funct. 2010, 1, 32–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eratte, D.; Wang, B.; Dowling, K.; Barrow, C.J.; Adhikari, B.P. Complex coacervation with whey protein isolate and gum arabic for the microencapsulation of omega-3 rich tuna oil. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 2743–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksel, A.; Şahin-Yeşilçubuk, N. Encapsulation of structured lipids containing medium- and long chain fatty acids by complex coacervation of gelatin and gum arabic. J. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41, e12907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, A.R.; Alencar Édo, N.; Xavier Júnior, F.H.; de Oliveira, C.M.; Marcelino, H.R.; Barratt, G.; Fessi, H.; do Egito, E.S.; Elaissari, A. Freeze-drying of emulsified systems: A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 503, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yari, S.; Nasirpour, A.; Fathi, M. Effect of polymer concentration and acidification time on olive oil microcapsules obtained by complex coacervation. Appl. Food Biotechnol. 2016, 3, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Zuanon, L.A.C.; Malacrida, C.R.; Telis, V.R.N. Production of Turmeric Oleoresin Microcapsules by Complex Coacervation with Gelatin–Gum Arabic. J. Food Process Eng. 2013, 36, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanasukarn, P.; Pongsawatmanit, R.; McClements, D.J. Influence of emulsifier type on freeze-thaw stability of hydrogenated palm oil-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Gao, N.; Hu, L.; Li, J.; Sun, Y. Development and evaluation of novel microcapsules containing poppy-seed oil using complex coacervation. J. Food Eng. 2015, 161, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendekal, M.S.; Tegginamat, P.K. Development and characterization of chitosan-polycarbophil interpolyelectrolyte complex-based 5-fluorouracil formulations for buccal, vaginal and rectal application. Daru J. Fac. Pharm. Tehran Univ. Med. Sci. 2012, 20, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutz, J.K.; Borges, C.D.; Zambiazi, R.C.; Crizel-Cardozo, M.M.; Kuck, L.S.; Noreña, C.P.Z. Microencapsulation of palm oil by complex coacervation for application in food systems. Food Chem. 2017, 220, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Campos, J.B.; Prokhorov, E.; Luna-Bárcenas, G.; Fonseca-García, A.; Sanchez, I.C. Dielectric relaxations of chitosan: The effect of water on the α-relaxation and the glass transition temperature. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2009, 47, 2259–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, F.; Mencherini, T.; Picerno, P.; d’Amore, M.; Aquino, R.P.; Lauro, M.R. Maltodextrin/pectin microparticles by spray drying as carrier for nutraceutical extracts. J. Food Eng. 2011, 105, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Camargo, S.; Cruz-Olivares, J.; Barragán-Huerta, B.E.; Dublán-García, O.; Román-Guerrero, A.; Pérez-Alonso, C. Microencapsulation by spray drying of lemon essential oil: Evaluation of mixtures of mesquite gum–nopal mucilage as new wall materials. J. Microencapsul. 2017, 34, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, M.T.; Haughey, S.A.; Elliott, C.T.; Koidis, A. Identification of vegetable oil botanical speciation in refined vegetable oil blends using an innovative combination of chromatographic and spectroscopic techniques. Food Chem. 2015, 189, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, E.A.; Knutson, K. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy investigations of protein structure. Pharm. Biotechnol. 1995, 7, 101–143. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseinnia, M.; Khaledabad, M.A.; Almasi, H. Optimization of Ziziphora clinopodiodes essential oil microencapsulation by whey protein isolate and pectin: A comparative study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, H.; Jiang, H.; Chen, R.; Wang, H. Studies on the interaction between vincamine and human serum albumin: A spectroscopic approach. Luminescence 2014, 29, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, S.C.; Tan, C.P.; Nyam, K.L. Microencapsulation of refined kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) seed oil by spray drying using β-cyclodextrin/gum arabic/sodium caseinate. J. Food Eng. 2018, 237, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Influence of emulsifier type on gastrointestinal fate of oil-in-water emulsions containing anionic dietary fiber (pectin). Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 45, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Ye, A.; Horne, D. Structuring food emulsions in the gastrointestinal tract to modify lipid digestion. Prog. Lipid Res. 2009, 48, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; McClements, D.J. Influence of emulsifier type on the in vitro digestion of fish oil-in-water emulsions in the presence of an anionic marine polysaccharide (fucoidan): Caseinate, whey protein, lecithin, or Tween 80. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelachvili, J.N. Intermolecular and Surface Forces; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wilde, P.J.; Chu, B.S. Interfacial & colloidal aspects of lipid digestion. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 165, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, P.; Holmberg, K.; Watzke, H.; Leser, M.E.; Miller, R. Lipases at interfaces: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 147–148, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Xue, S.J.; Shi, J.; Lim, L.T.; Forney, C.; Xu, G.; Bamba, B.S.B. Effect of In Vitro Digestion on Water-in-Oil-in-Water Emulsions Containing Anthocyanins from Grape Skin Powder. Molecules 2018, 23, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallier, S.; Tate, H.; Singh, H. In Vitro Gastric and Intestinal Digestion of a Walnut Oil Body Dispersion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, A.C.; Lad, M.; Silva, H.D.; Coimbra, M.A.; Boland, M.; Vicente, A.A. Unravelling the behaviour of curcumin nanoemulsions during in vitro digestion: Effect of the surface charge. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 3147–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, S.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Influence of emulsifier type on in vitro digestibility of lipid droplets by pancreatic lipase. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Li, Y.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Role of calcium and calcium-binding agents on the lipase digestibility of emulsified lipids using an in vitro digestion model. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 719–725. [Google Scholar]
- Michalski, M.C. Specific molecular and colloidal structures of milk fat affecting lipolysis, absorption and postprandial lipemia. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2009, 111, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, S.; Decker, E.A.; Park, Y.; Weiss, J.; McClements, D.J. Influence of Interfacial Composition on in Vitro Digestibility of Emulsified Lipids: Potential Mechanism for Chitosan’s Ability to Inhibit Fat Digestion. Food Biophys. 2006, 1, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Monahan, F.J.; McClements, D.J.; German, J.B. Disulfide-mediated Polymerization Reactions and Physical Properties of Heated WPI-stabilized Emulsions. J. Food Sci. 1996, 61, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, A.; Wang, X.; Lin, Q.; Han, J.; Singh, H. Dynamic gastric stability and in vitro lipid digestion of whey-protein-stabilised emulsions: Effect of heat treatment. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126463. [Google Scholar]
- Fathi, M.; Mozafari, M.R.; Mohebbi, M. Nanoencapsulation of food ingredients using lipid based delivery systems. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 23, 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- van Aken, G.A.; Bomhof, E.; Zoet, F.D.; Verbeek, M.; Oosterveld, A. Differences in in vitro gastric behaviour between homogenized milk and emulsions stabilised by Tween 80, whey protein, or whey protein and caseinate. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Decker, E.A.; Xiao, H.; McClements, D.J. Nanoemulsion delivery systems: Influence of carrier oil on β-carotene bioaccessibility. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1440–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, P.; Lozano, M.; Espinosa-Mansilla, A.; González-Gómez, D. In-vitro evaluation of the availability of ϖ-3 and ϖ-6 fatty acids and tocopherols from microencapsulated walnut oil. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.-T.; Nyam, K.-L. Characteristics and controlled release behaviour of microencapsulated kenaf seed oil during in-vitro digestion. J. Food Eng. 2016, 182, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, A.; Cui, J.; Zhu, X.; Singh, H. Effect of calcium on the kinetics of free fatty acid release during in vitro lipid digestion in model emulsions. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tancharoenrat, P. Factors Influencing Fat Digestion in Poultry: A Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Poultry Nutrition at Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand. Ph.D. Thesis, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zangenberg, N.H.; Müllertz, A.; Kristensen, H.G.; Hovgaard, L. A dynamic in vitro lipolysis model: I. Controlling the rate of lipolysis by continuous addition of calcium. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 14, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, C.; Tan, C.-p.; Xie, K.; Liu, Y. A comparative study between freeze-dried and spray-dried goat milk on lipid profiling and digestibility. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Nadeem, M.; Imran, M.; Khan, M.K.; Mushtaq, Z.; Asif, M.; Din, A. Effect of microcapsules of chia oil on Ω-3 fatty acids, antioxidant characteristics and oxidative stability of butter. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadeniz, M.; Sahin, S.; Sumnu, G. Enhancement of storage stability of wheat germ oil by encapsulation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 114, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timilsena, Y.P.; Adhikari, R.; Barrow, C.J.; Adhikari, B. Microencapsulation of chia seed oil using chia seed protein isolate-chia seed gum complex coacervates. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partanen, R.; Yoshii, H.; Kallio, H.; Yang, B.; Forssell, P. Encapsulation of sea buckthorn kernel oil in modified starches. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2002, 79, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghbashlo, M.; Mobli, H.; Madadlou, A.; Rafiee, S. Influence of Wall Material and Inlet Drying Air Temperature on the Microencapsulation of Fish Oil by Spray Drying. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cercaci, L.; Rodriguez-Estrada, M.T.; Lercker, G.; Decker, E.A. Phytosterol oxidation in oil-in-water emulsions and bulk oil. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikbakht Nasrabadi, M.; Goli, S.A.H.; Nasirpour, A. Stability assessment of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) oil-in-water beverage emulsion formulated with acacia and xanthan gums. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A.; Weiss, J. Emulsion-based delivery systems for lipophilic bioactive components. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, R109–R124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partanen, R.; Raula, J.; Seppänen, R.; Buchert, J.; Kauppinen, E.; Forssell, P. Effect of Relative Humidity on Oxidation of Flaxseed Oil in Spray Dried Whey Protein Emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 5717–5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Lipid Oxidation in Oil-in-Water Emulsions: Impact of Molecular Environment on Chemical Reactions in Heterogeneous Food Systems. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 1270–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaich, K.M. Lipid Oxidation: Theoretical Aspects. In Bailey’s Industrial Oil and Fat Products; John Wiley & Sons Inc: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Kalonia, D.S. Removal of peroxides in polyethylene glycols by vacuum drying: Implications in the stability of biotech and pharmaceutical formulations. AAPS PharmSciTech 2006, 7, E47–E53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoen, R.; Jangchud, A.; Jangchud, K.; Harnsilawat, T.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Influence of interfacial composition on oxidative stability of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by biopolymer emulsifiers. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shi, Y.; Han, L. Development and evaluation of microencapsulated peony seed oil prepared by spray drying: Oxidative stability and its release behavior during in-vitro digestion. J. Food Eng. 2018, 231, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judde, A.; Villeneuve, P.; Rossignol-Castera, A.; Le Guillou, A. Antioxidant effect of soy lecithins on vegetable oil stability and their synergism with tocopherols. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2003, 80, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenia, V.; Waraho, T.; Rodriguez-Estrada, M.T.; Julian McClements, D.; Decker, E.A. Antioxidant and Prooxidant Activity Behavior of Phospholipids in Stripped Soybean Oil-in-Water Emulsions. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2011, 88, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmquist, D.L.; Jenkins, T.C. Challenges with fats and fatty acid methods. J. Anim. Sci. 2003, 81, 3250–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salami, M.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A.; Ehsani, M.R.; Yousefi, R.; Haertlé, T.; Chobert, J.M.; Razavi, S.H.; Henrich, R.; Balalaie, S.; Ebadi, S.A.; et al. Improvement of the antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of camel and bovine whey proteins by limited proteolysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3297–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, A.S.; Khadrawy, Y.A.; El-Nekeety, A.A.; Mohamed, S.R.; Hassan, N.S.; Abdel-Wahhab, M.A. Antioxidant activity and hepatoprotective effects of whey protein and Spirulina in rats. Nutrition 2011, 27, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, A.L.; Abdillah, A.A.; Saraswati, Y.R.; Sridhar, K.; Balderamos, C.; Masithah, E.D.; Alamsjah, M.A. Characterization of freeze-dried microencapsulation tuna fish oil with arrowroot starch and maltodextrin. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Shurson, G.C. Evaluation of lipid peroxidation level in corn dried distillers grains with solubles. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 4383–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegg, R.B. Spectrophotometric Measurement of Secondary Lipid Oxidation Products. Curr. Protoc. Food Anal. Chem. 2001, 1, D2.4.1–D2.4.18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, P.; Calvo, M.M.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Gómez-Estaca, J. Microcapsules containing astaxanthin from shrimp waste as potential food coloring and functional ingredient: Characterization, stability, and bioaccessibility. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 70, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Huang, S.; Liu, R.; You, J.; Xiong, S.; Zhang, B.; Rong, J. Storage stability and in-vitro release behavior of microcapsules incorporating fish oil by spray drying. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 628, 127234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.M.; Sasaki, S.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Antioxidant Activity of Whey in a Salmon Oil Emulsion. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 1325–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-P.; Lee, Y.-M.; Seo, E.-M.; Lee, K.-W.; Kim, H.-S. Optimization of microencapsulation of seed oil by response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, H.C.F.; Tonon, R.V.; Grosso, C.R.F.; Hubinger, M.D. Encapsulation efficiency and oxidative stability of flaxseed oil microencapsulated by spray drying using different combinations of wall materials. J. Food Eng. 2013, 115, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, S.; Ferrando, M.; Aceña-Muñoz, L.; Mestres, M.; De Lamo-Castellví, S.; Güell, C. Influence of Emulsification Technique and Wall Composition on Physicochemical Properties and Oxidative Stability of Fish Oil Microcapsules Produced by Spray Drying. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 1959–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, V.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Hamishehkar, H.; Pezeshki, A.; Ostadrahimi, A. Effects of different stabilizers on colloidal properties and encapsulation efficiency of vitamin D3 loaded nano-niosomes. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 101284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamjidi, F.; Shahedi, M.; Varshosaz, J.; Nasirpour, A. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC): A potential delivery system for bioactive food molecules. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 19, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.Q.; Jiang, S.P.; Du, Y.Z.; Yuan, H.; Ye, Y.Q.; Zeng, S. Preparation and characteristics of monostearin nanostructured lipid carriers. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 314, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, K.; Reineccius, G. Methods to Predict the Physical Stability of Flavor—Cloud Emulsion; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, J.V.L.; Fryer, P.J.; Frith, W.J.; Norton, I.T. The influence of phospholipids and food proteins on the size and stability of model sub-micron emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, J.; Atarés, L.; Vargas, M.; Chiralt, A. Effect of essential oils and homogenization conditions on properties of chitosan-based films. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 26, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misni, N.; Mohamed Nor, Z.; Ahmad, R.; Ithnin, N.R.; Zasmy Unyah, N. Microencapsulation Preservation of the Stability and Efficacy of Citrus Grandis Oil-Based Repellent Formulation against Aedes aegypti during Storage. Molecules 2021, 26, 3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Santos, V.; Braz, B.B.; Silva, A.Á.; Cardoso, L.P.; Ribeiro, A.P.B.; Santana, M.H.A. Nanostructured lipid carriers loaded with free phytosterols for food applications. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 125053. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.-Y.; Guissi, F.; Yang, R.-Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, K.; Chen, D.; Han, Z.-H.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, M.; Gu, Y.-Q. Preparation of Deep Sea Fish Oil-Based Nanostructured Lipid Carriers with Enhanced Cellular Uptake. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 9539–9547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovačević, A.B.; Müller, R.H.; Savić, S.D.; Vuleta, G.M.; Keck, C.M. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) stabilized with polyhydroxy surfactants: Preparation, characterization and physical stability investigation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 444, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, L.; Wen, M.; Du, L.; Gao, X.; Xue, C.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y. Enhanced neuroprotective effect of DHA and EPA-enriched phospholipids against 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) induced oxidative stress in mice brain. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 25, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, S.A.; McNamee, B.F.; O’Riordan, E.D.; O’Sullivan, M. Emulsification and microencapsulation properties of sodium caseinate/carbohydrate blends. Int. Dairy J. 2001, 11, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, F.; Zhao, Q.; Lv, X.; Dong, X.-Y.; Feng, Y.-Q.; Chen, H. Rapid Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction Based on Monodisperse Magnetic Single-Crystal Ferrite Nanoparticles for the Determination of Free Fatty Acid Content in Edible Oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Sanguansri, L.; Augustin, M.A. In vitro lipolysis of fish oil microcapsules containing protein and resistant starch. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar]
- Kosaraju, S.L.; Weerakkody, R.; Augustin, M.A. In-vitro evaluation of hydrocolloid–based encapsulated fish oil. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornero-Méndez, D.; Pérez-Gálvez, A.; Mínguez-Mosquera, M.I. A rapid spectrophotometric method for the determination of peroxide value in food lipids with high carotenoid content. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2001, 78, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.-J.; Hu, Y.-Q.; Yin, S.-W.; Yang, X.-Q.; Lai, F.-R.; Wang, S.-Q. Fabrication and Characterization of Antioxidant Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Zein/Chitosan Complex Particles (ZCPs). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 2514–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Wall Material | Particle Size (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential | EE% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPI | 193 ± 3 a | 0.259 ± 0.05 ab | −35.2 ± 1.1 a | 99.2 ± 0.9 a | |
| WPI | GA | 191 ± 1 a | 0.331 ± 0.01 b | −23.2 ± 0.9 b | 99.7 ± 0.2 a |
| WPI | MD | 175 ± 6 a | 0.169 ± 0.02 a | −32.2 ± 1.3 a | 99.5 ± 0.1 a |
| WPI | OSA | 228 ± 19 a | 0.308 ± 0.00 ab | −21.3 ± 0.7 b | 99.6 ± 0.1 a |
| Core:Wall | Particle Size (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential | EE% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:1 | 924 ± 64 a | 0.777 ± 0.05 a | −54.8 ± 4.9 a | 95.0 ± 0.2 a |
| 1:2 | 369 ± 9 b | 0.685 ± 0.12 a | −58.9 ± 1.1 a | 97.2 ± 0.1 a |
| 1:3 | 188 ± 11 c | 0.177 ± 0.02 b | −33.0 ± 1.6 b | 99.5 ± 0.3 b |
| 1:4 | 171 ± 7 c | 0.176 ± 0.02 b | −31.5 ± 3 b | 99.5 ± 0.1 b |
| Melting Point (°C) | Enthalpy (J/g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MC-FD | 1st peak | 151.63 | 5.997 |
| 2nd peak | 161.77 | 105.3 | |
| 3rd peak | 268.42 | 24.16 | |
| CV-E | 105.99 | 1622 | |
| Fatty Acid | Before Digestion (CV-E) | After Digestion (CV-E) | Before Digestion (MC-FD) | After Digestion (MC-FD) | Before Digestion (SPC) | After Digestion (SPC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C16:0 | 7.08 ± 0.11 c | 3.8 ± 0.64 ab | 8.13 ± 0.69 c | 6.04 ± 0.07 bc | 1.91 ± 0.23 a | 3.16 ± 0.01 a |
| C18:0 | 2.95 ± 0.09 b | 1.71 ± 0.33 a | 3.58 ± 0.38 b | 2.96 ± 0.03 b | 0.54 ± 0.09 a | 1.34 ± 0.07 a |
| C18:1 | 14.55 ± 0.42 d | 10.59 ± 0.15 c | 13.96 ± 0.08 d | 10.22 ± 0.04 c | 5.03 ± 0.19 b | 4.24 ± 0.03 a |
| C18:2 | 43.47 ± 0.42 b | 32.81 ± 0.81 b | 41.78 ± 0.3 b | 32.73 ± 0.08 b | 34.88 ± 1.39 b | 26.74 ± 0.27 a |
| C18:3 | 4.56 ± 0.06 c | 3.17 ± 0.07 b | 4.54 ± 0.04 c | 3.19 ± 0.01 b | 3.58 ± 0.18 b | 2.61 ± 0.08 a |
| C20:0 | 0.74 ± 0.00 a | 0.99 ± 0.03 b | 0.77 ± 0.02 a | 0.95 ± 0.01 b | 1.21 ± 0.01 c | 1.24 ± 0.03 c |
| C24:0 | 0.94 ± 0.01 a | 1.54 ± 0.00 b | 0.96 ± 0.02 a | 1.53 ± 0.01 b | 2.7 ± 0.23 c | 1.96 ± 0.06 b |
| C24:1 | 25.72 ± 0.45 a | 45.39 ± 0.04 b | 26.28 ± 0.61 a | 42.39 ± 0.04 b | 50.16 ± 1.86 c | 58.72 ± 0.09 d |
| Total SFA | 11.71 | 8.04 | 13.44 | 11.48 | 6.36 | 7.7 |
| Total USFA | 88.3 | 91.96 | 86.56 | 88.53 | 93.65 | 92.31 |
| Total MUFA | 40.27 | 55.98 | 40.24 | 42.61 | 55.19 | 62.96 |
| Total PUFA | 48.03 | 35.98 | 46.32 | 35.92 | 38.46 | 29.35 |
| Samples | CV-E | MC-FD |
|---|---|---|
| Storage conditions | 4 °C/25 °C/45 °C, 75% (relative humidity) | |
| Frequency (days) | 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, 14, 30 | 1, 7, 14, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90 |
| Analysis | Particle size, PDI, zeta potential, PV, TBA test, and fatty acid content | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ang, X.; Chen, H.; Xiang, J.; Wei, F.; Quek, S.Y. Preparation, Digestion, and Storage of Microencapsulated Nervonic Acid-Enriched Structured Phosphatidylcholine. Molecules 2025, 30, 2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30092007
Ang X, Chen H, Xiang J, Wei F, Quek SY. Preparation, Digestion, and Storage of Microencapsulated Nervonic Acid-Enriched Structured Phosphatidylcholine. Molecules. 2025; 30(9):2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30092007
Chicago/Turabian StyleAng, Xun, Hong Chen, Jiqian Xiang, Fang Wei, and Siew Young Quek. 2025. "Preparation, Digestion, and Storage of Microencapsulated Nervonic Acid-Enriched Structured Phosphatidylcholine" Molecules 30, no. 9: 2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30092007
APA StyleAng, X., Chen, H., Xiang, J., Wei, F., & Quek, S. Y. (2025). Preparation, Digestion, and Storage of Microencapsulated Nervonic Acid-Enriched Structured Phosphatidylcholine. Molecules, 30(9), 2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30092007







