Comparative Analysis of Volatile Organic Compounds in Different Parts of Ginseng Powder Using Gas Chromatography–Ion Mobility Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
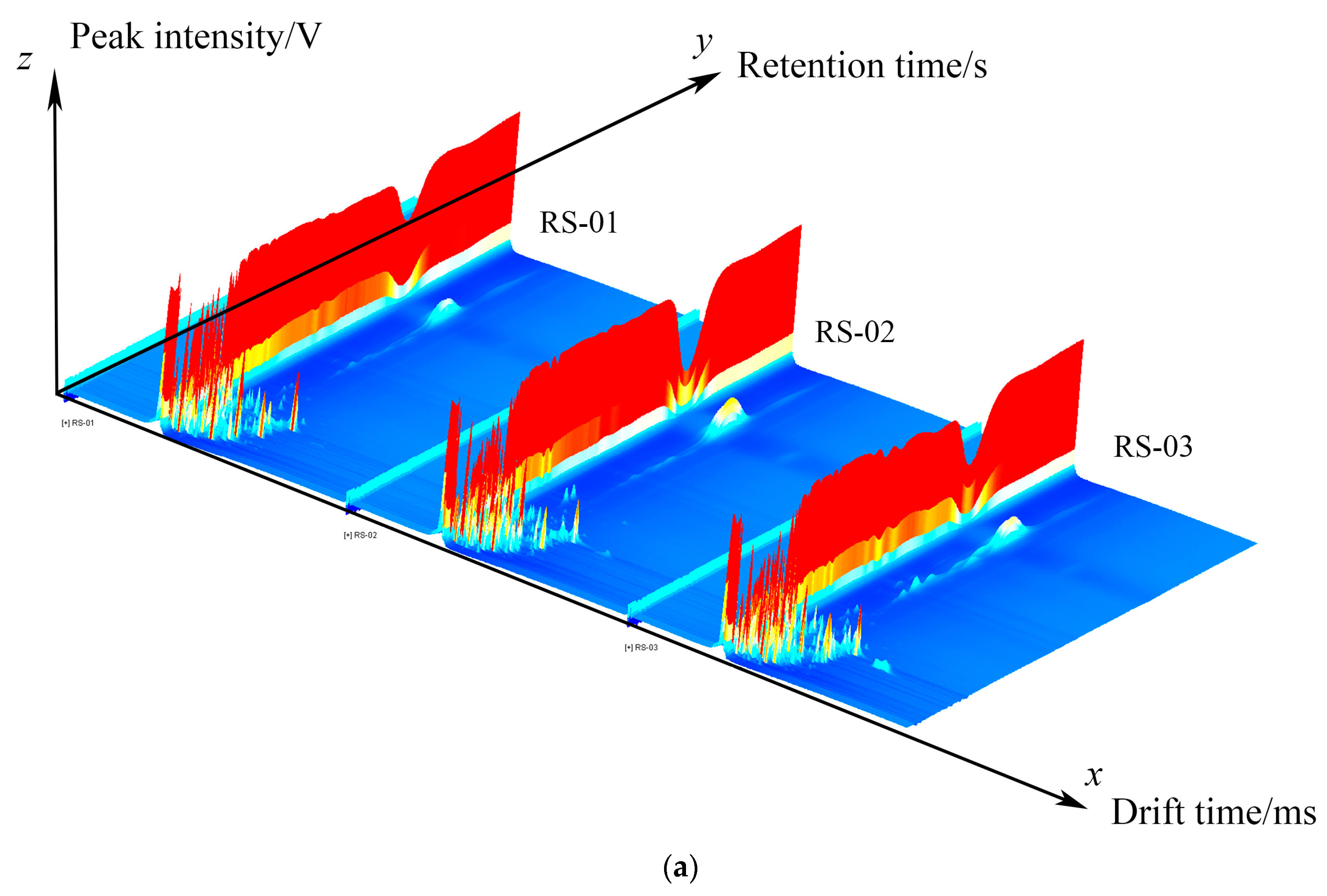
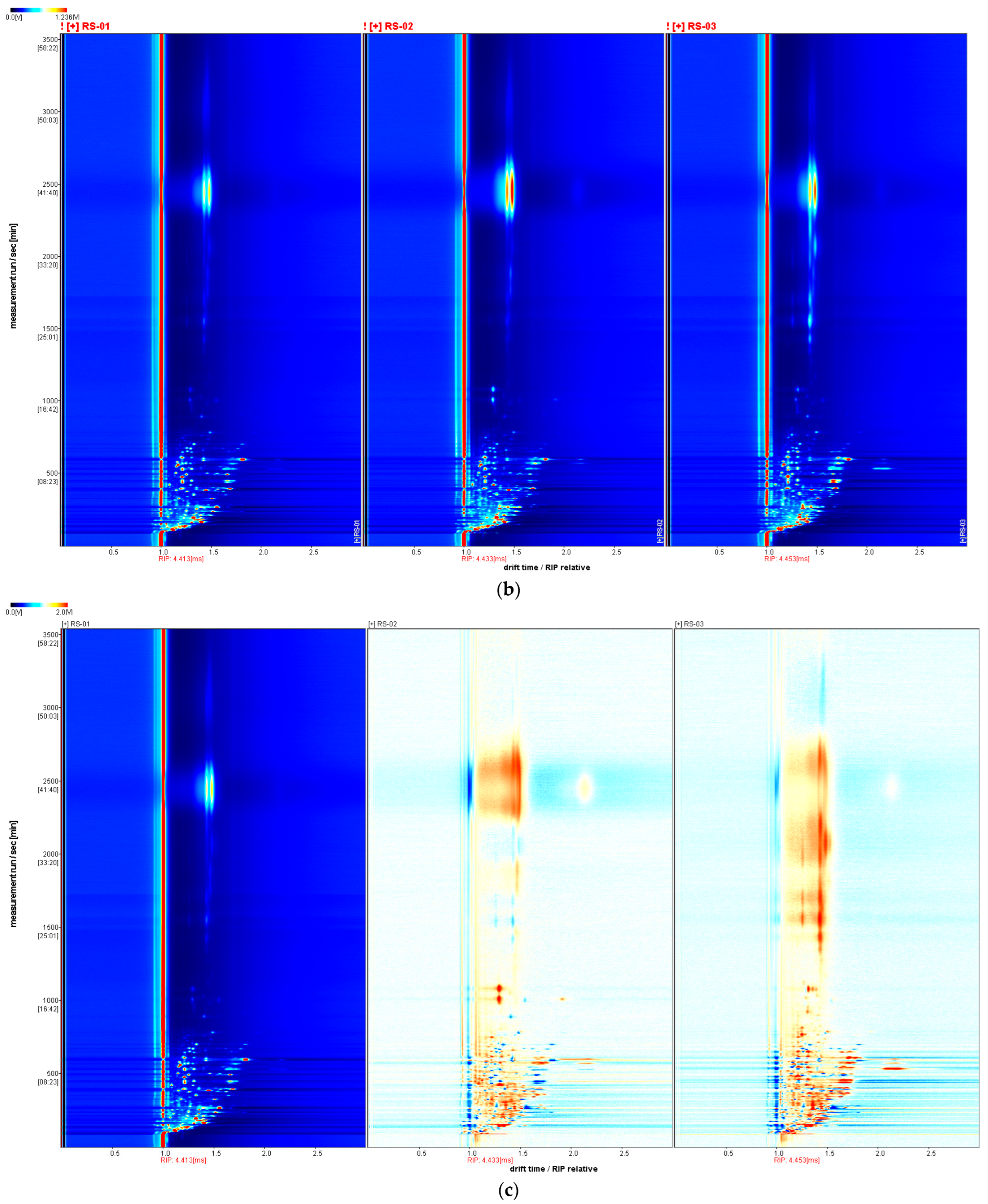
2.1. Qualitative Analysis of VOCs in Different Parts of Ginseng Powder
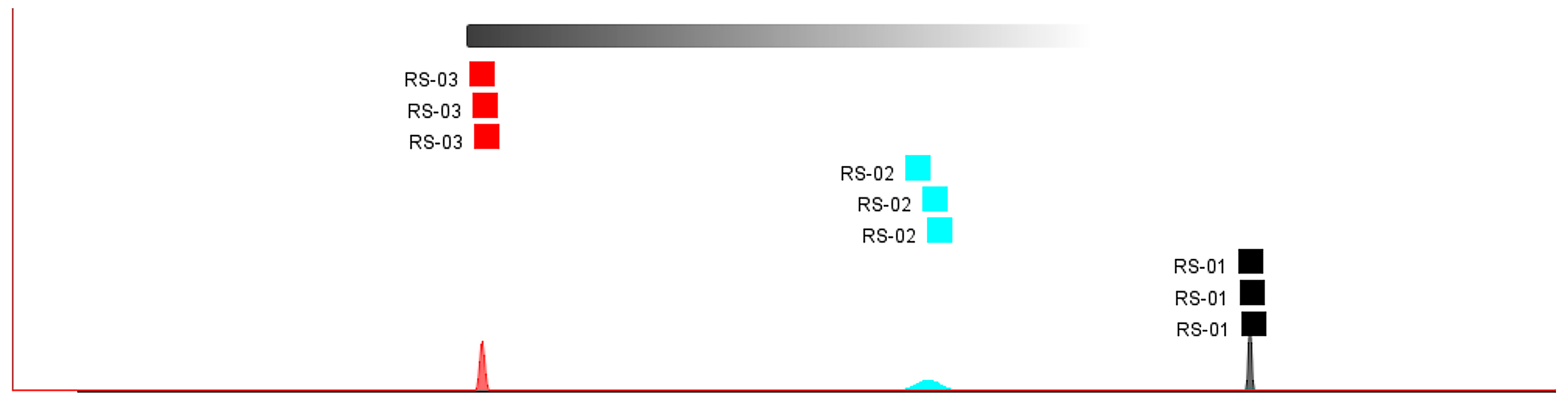
2.2. Differences in Characteristic VOCs Fingerprints
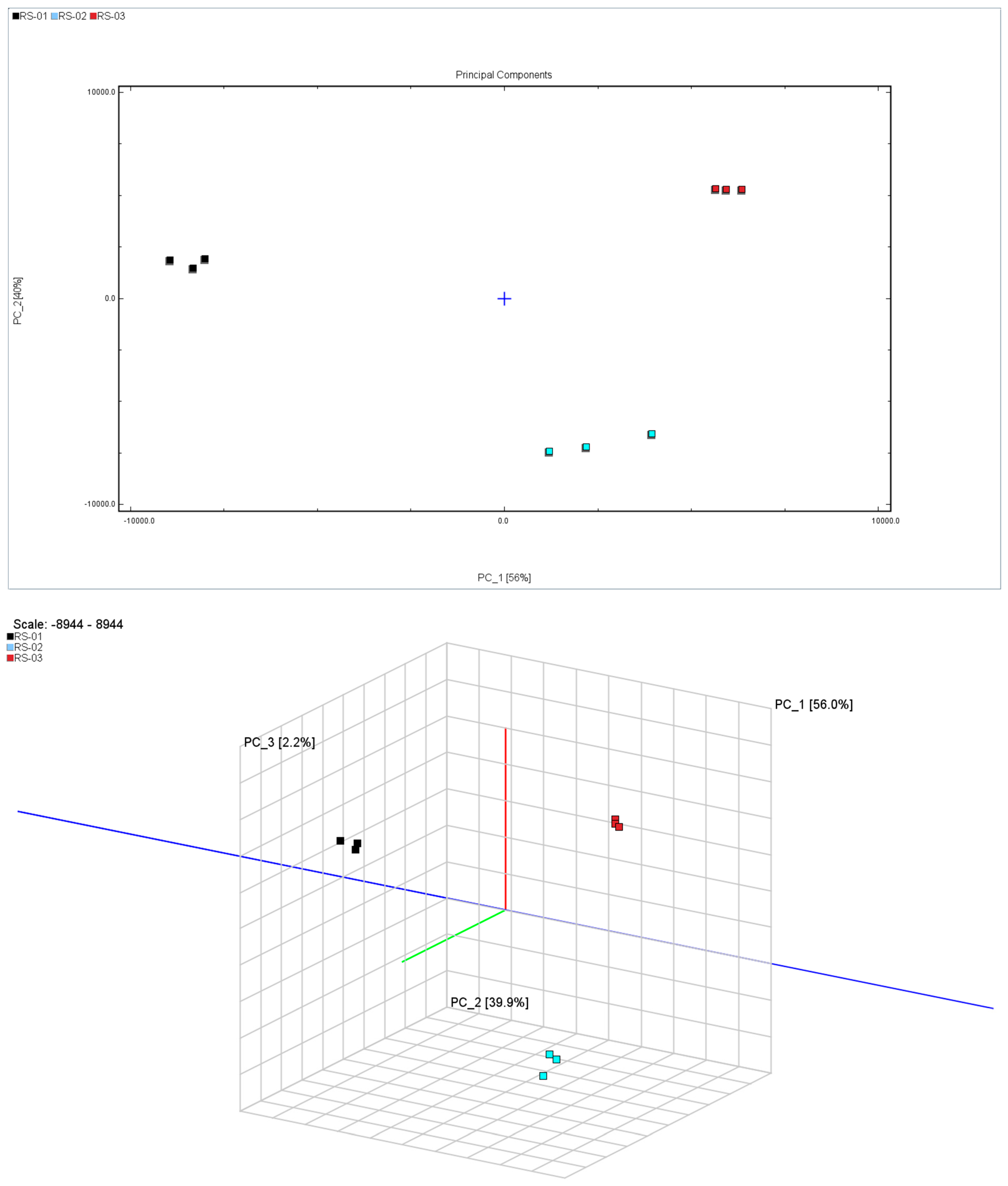
2.3. Chemometric Analysis
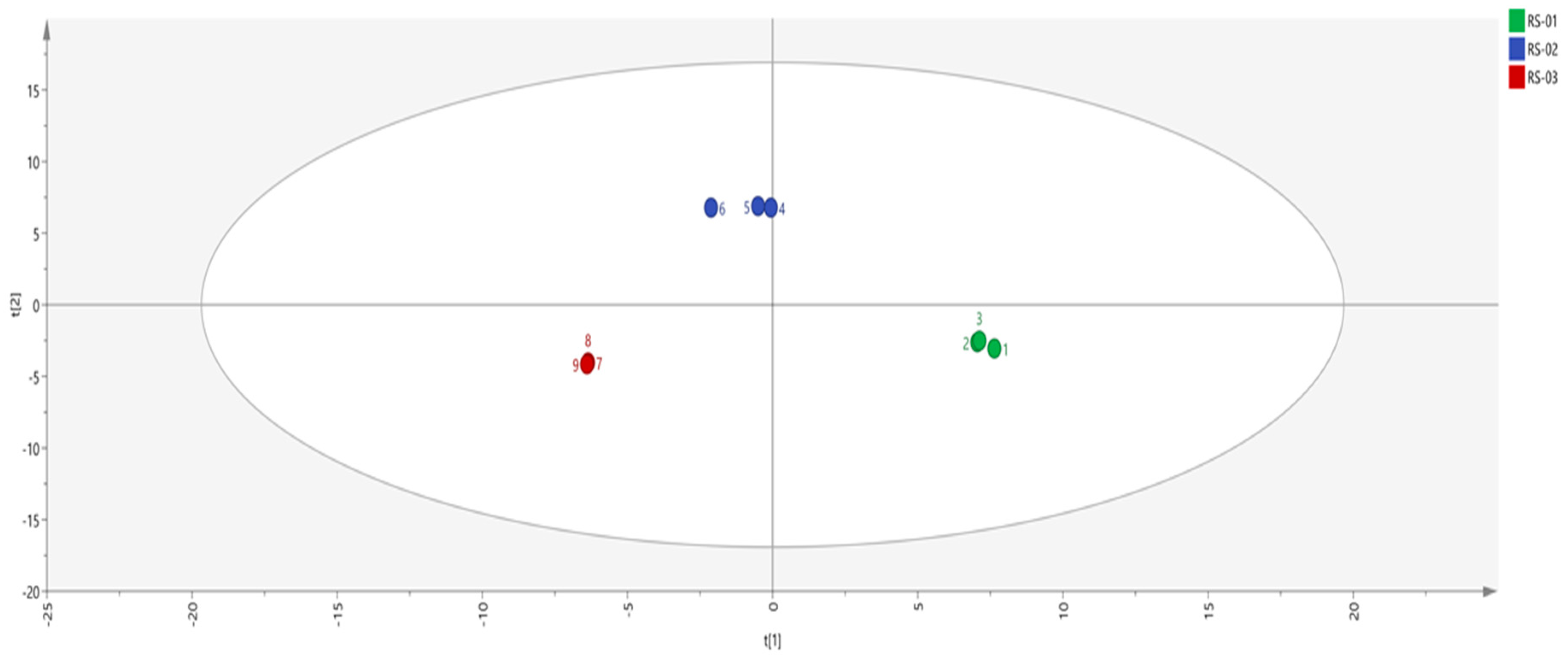
2.3.1. Principal Component Analysis
2.3.2. Euclidean Distance
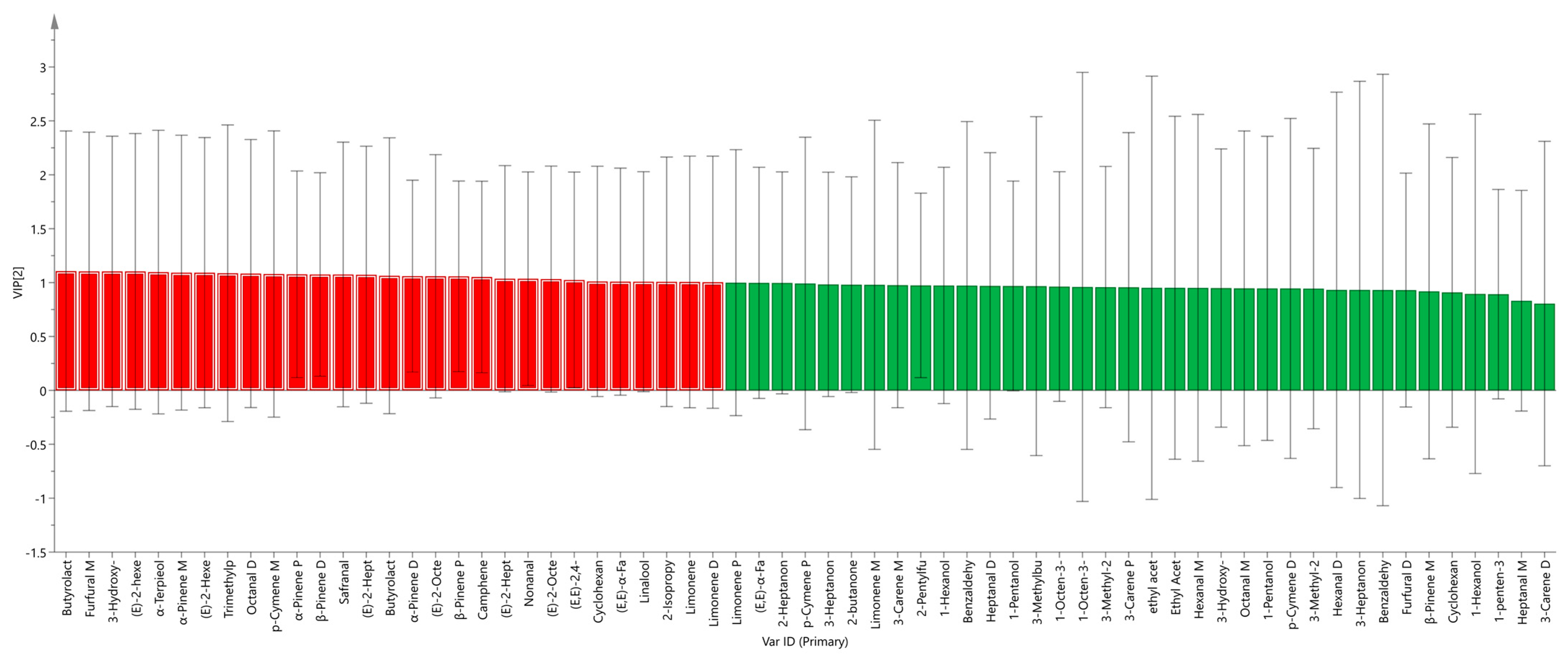
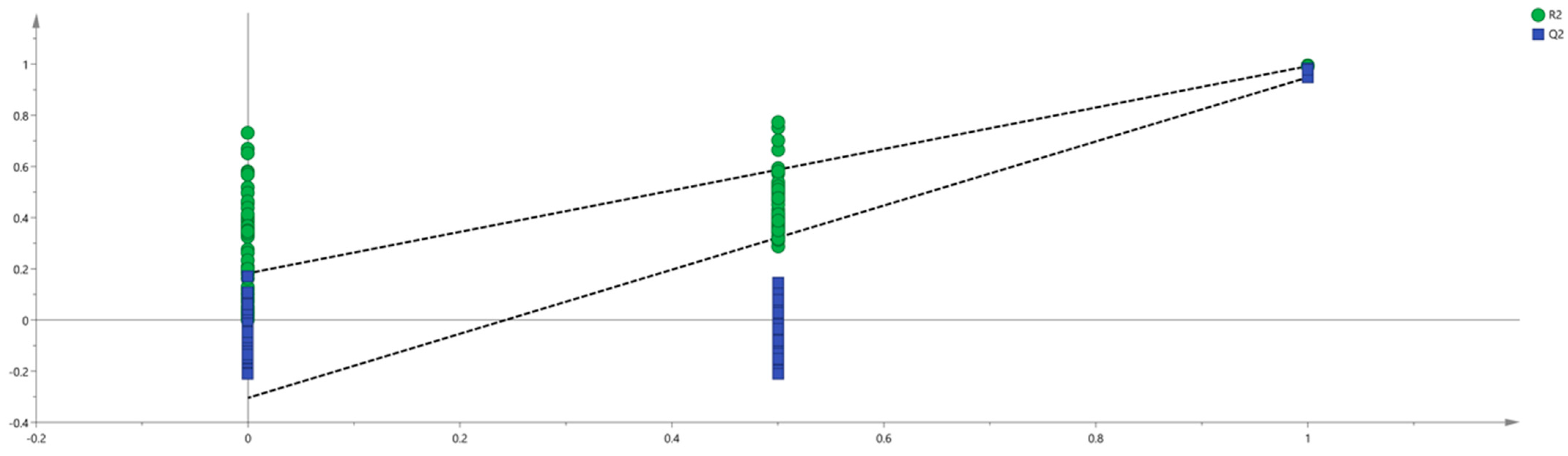
2.3.3. Partial Least-Squares Discriminant Analysis
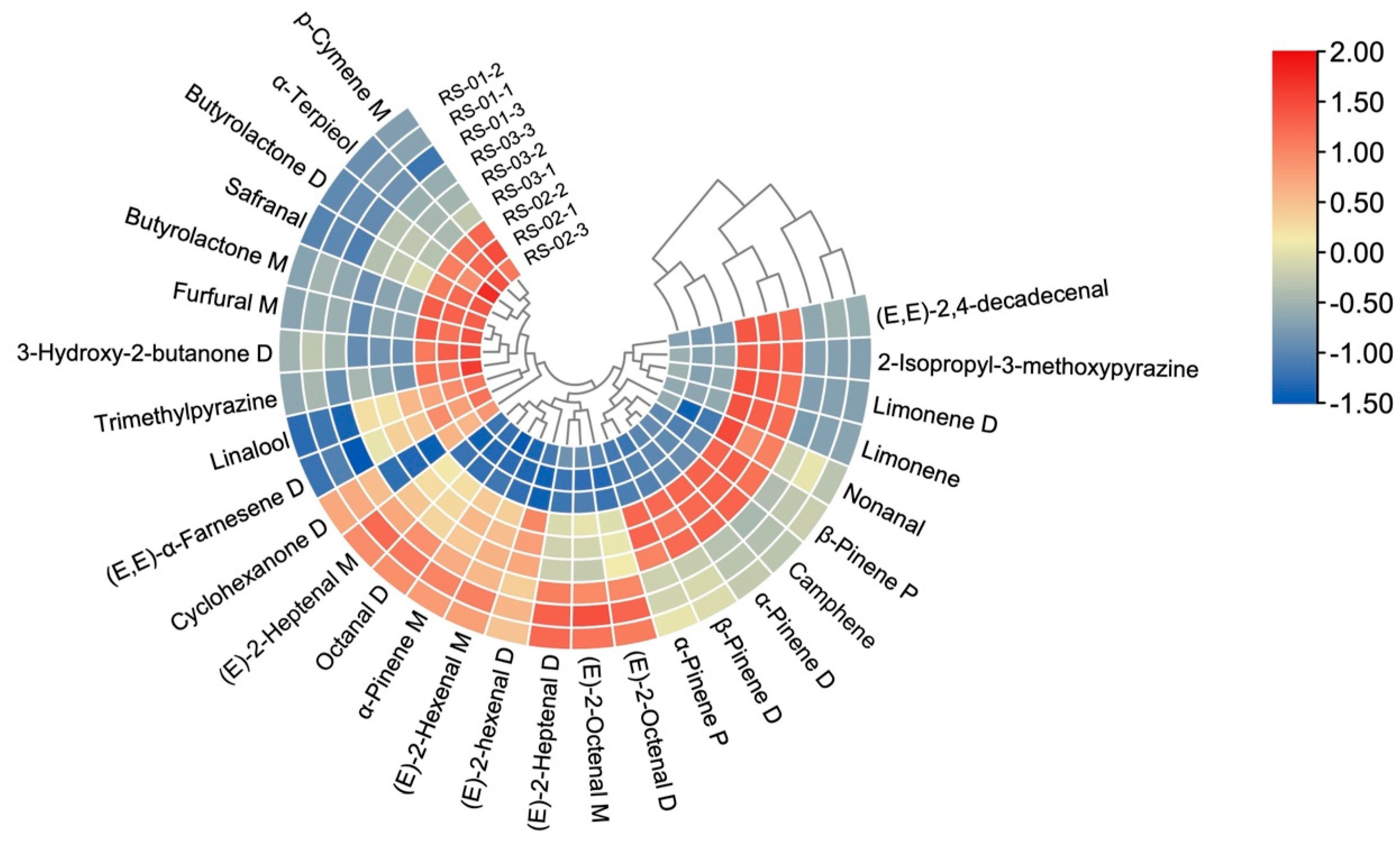
2.3.4. Cluster Analysis (CA)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Instruments and Equipment
4.3. Analysis with GC–IMS
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, M.; Ma, L.; Luo, J.; Ren, T.; Liu, S.; Pan, L.; Bao, Y.; Li, F.; Dai, Y.; Pi, Z.; et al. Low-Medium Polarity Ginsenosides from Wild Ginseng Improves Immunity by Activating the AhR/MAPK Pathway through Tryptophan Metabolism Driven by Gut Microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 26142–26154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Nie, T.; Li, L.; Su, J.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, C.; Huang, Y.; et al. Rg3 regulates myocardial pyruvate metabolism via P300-mediated dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation in TAC-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Chen, J.; Hao, F.; Tian, M. Ginseng Pectin WGPA Alleviates Exercise-Induced Fatigue by Enhancing Gluconeogenesis. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2022, 2022, 7973380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.M.; Yoon, H.; Park, H.M.; Song, B.C.; Yeum, K.J. Implications of red Panax ginseng in oxidative stress associated chronic diseases. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E, M.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, P.; Liu, Q.; Qi, H.; Hou, T.; Su, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. A novel mechanism of major ginsenosides from Panax ginseng against multiple organ aging in middle-aged mice: Phosphatidylcholine-myo-inositol metabolism based on metabolomic analysis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 719, 150027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Wang, Y.; Lv, J.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, N.; Lu, C.; Xu, P.; Liu, X. Memory enhancement of fresh ginseng on deficits induced by chronic restraint stress in mice. Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-González, J.A.; Sánchez, M.; Moratilla-Rivera, I.; Iglesias, I.; Gómez-Serranillos, M.P. Immunomodulatory, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Cancer Properties of Ginseng: A Pharmacological Update. Molecules. 2023, 28, 3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.M.; Li, K.Q.; Zhao, D.Q.; Huang, B.T.; Li, J.Q.; Liu, L.; Qi, B. Analysis of ginsenosides in different parts of ginseng by HPLC and chemometry. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2022, 45, 2442–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.L.; Zhao, H.; Song, J.; Yan, M.X.; Luo, J.; Fen, Z.W.; Chen, X.; Dong, X.Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Su, L.M.; et al. Study on the Difference of Volatile Compounds in Underground Parts of Dried Raw Ginseng and Red Ginseng. Spec. Wild Econ. Anim. Plant Res. 2022, 44, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christmann, J.; Rohn, S.; Weller, P. gc-ims-tools-A new Python package for chemometric analysis of GC-IMS data. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitain, C.; Weller, P. Non-Targeted Screening Approaches for Profiling of Volatile Organic Compounds Based on Gas Chromatography-Ion Mobility Spectroscopy (GC-IMS) and Machine Learning. Molecules. 2021, 26, 5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; Yan, W. Differences in Volatile Organic Compounds in Rhizoma gastrodiae(Tian Ma) of Different Origins Determined by HS-GC-IMS. Molecules. 2023, 28, 4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Sun, B. Recent progress in food flavor analysis using gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (GC-IMS). Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhu, D.; Sun, J. Application of GC-IMS coupled with chemometric analysis for the classification and authentication of geographical indication agricultural products and food. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1247695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, H. Ginsenosides: An immunomodulator for the treatment of colorectal cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1408993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Wang, S.; Wu, K.; Li, N.; Fan, W. Ginsenosides and Tumors: A Comprehensive and Visualized Analysis of Research Hotspots and Antitumor Mechanisms. J. Cancer. 2024, 15, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, P.; Liu, J.; Chen, B.; E, M.; Qi, H.; Hou, T.; Huang, Q.; Ding, L.; et al. Ginseng polysaccharide components attenuate obesity and liver lipid accumulation by regulating fecal microbiota and hepatic lysine degradation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 269, 131872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SONG, Q. Research progress on chemical constituents of Panax ginseng and their pharmacological effects. Ginseng Res. 2017, 29, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Choi, J.J.; Ahn, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Oh, K.W.; Kim, S.Y. Effects of red ginseng extract on sleeping behaviors in human volunteers. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 149, 597–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparala, A.; Poudyal, D.; Tashkandi, H.; Witalison, E.E.; Chumanevich, A.A.; Hofseth, J.L.; Nguyen, I.; Hardy, O.; Pittman, D.L.; Wyatt, M.D.; et al. Panaxynol, a bioactive component of American ginseng, targets macrophages and suppresses colitis in mice. Oncotarget. 2020, 11, 2026–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ravipati, A.S.; Koyyalamudi, S.R.; Jeong, S.C.; Reddy, N.; Bartlett, J.; Smith, P.T.; de la Cruz, M.; Monteiro, M.C.; Melguizo, A.; et al. Anti-fungal and anti-bacterial activities of ethanol extracts of selected traditional Chinese medicinal herbs. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2013, 6, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.H. Principal component analysis of hybrid functional and vector data. Stat. Med. 2021, 40, 5152–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.; Zou, M.; Ou, F.; Zhu, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Lei, C. A Comparison of the Impacts of Different Drying Methods on the Volatile Organic Compounds in Ginseng. Molecules. 2024, 29, 5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Lei, C.; Hu, G.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Huang, D. Investigation of 60Co Irradiation on the Volatile Organic Compounds from Finger Citron (Citri Sarcodactylis Fructus) Using GC–IMS. Foods. 2023, 12, 3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Perez, D.; Guan, H.; Madhivanan, P.; Mathee, K.; Narasimhan, G. So you think you can PLS-DA? BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yu, Y.; Zou, B.; Yu, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, F. Evaluation of Dynamic Changes and Regularity of Volatile Flavor Compounds for Different Green Plum (Prunus mume Sieb. et Zucc) Varieties during the Ripening Process by HS-GC–IMS with PLS-DA. Foods. 2023, 12, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Lin, S.; Li, X.; Li, D. Different stages of flavor variations among canned Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba): Based on GC-IMS and PLS-DA. Food Chem. 2024, 459, 140465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Qi, Y.; Lei, M.; Xuan, H.; Li, X.; Lu, W.; Guo, J.; Chen, H. Analysis and discrimination of adhesive species using ATR-FTIR combined with Raman, and HS-GC-IMS together with multivariate statistical analysis. J. Chromatogr. A. 2024, 1736, 465402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Deng, S.Y.; Han, Y.Y.; Mu, W.L.; Ma, D.Z.; Lin, H.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.X. Comparison of volatile components of 7 kinds of commercial smoked fish via headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2023, 14, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, R.Y.; Tian, X. The Active Ingredients and Pharmacological Effects of Eucommia ulmoides and the Application of Its Different Parts in Food Field. Farm. Prod. Process. 2024, 8, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Zhang, S.Y.; Dong, Y. Effect of Preharvest 1-Methylcyclopene Application on Superficial Scald and Antioxidant Capacity of ‘Bartlett’ Pears during Shelf Life. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.L.; Zhang, X.M.; Xu, G.Y.; Zhao, K.J.; Guan, M. Progress of Origin and Clinical Application of Ginseng. Eval. Anal. Drug-Use Hosp. China 2023, 23, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, D.; Ma, C.; Wang, R.; Wang, W. Free Radical Scavenging Effect and Immunomodulatory Activity of Total Saponins Extract of Ginseng Fibrous Roots. Molecules. 2024, 29, 2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, A.Q.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.W.; Li, L.; Cheng, L.Q. Preparation of Ginsenosides 20(S, R)-Rg3 and Rg5 from Ginseng Root Powder Catalyzed by Natural Lemon Juice. Food Res. Dev. 2021, 42, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, B.Y.; Choi, M.J.; Kim, J.S.; Park, E. Comparative Analysis of Ginsenoside Profiles: Antioxidant, Antiproliferative, and Antigenotoxic Activities of Ginseng Extracts of Fine and Main Roots. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 24, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Upadhyay, S.; Erdogan Orhan, I.; Kumar Jugran, A.; LDJayaweera, S.; ADias, D.; Sharopov, F.; Taheri, Y.; Martins, N.; Baghalpour, N.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of α-and β-Pinene: A Miracle Gift of Nature. Biomolecules. 2019, 9, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
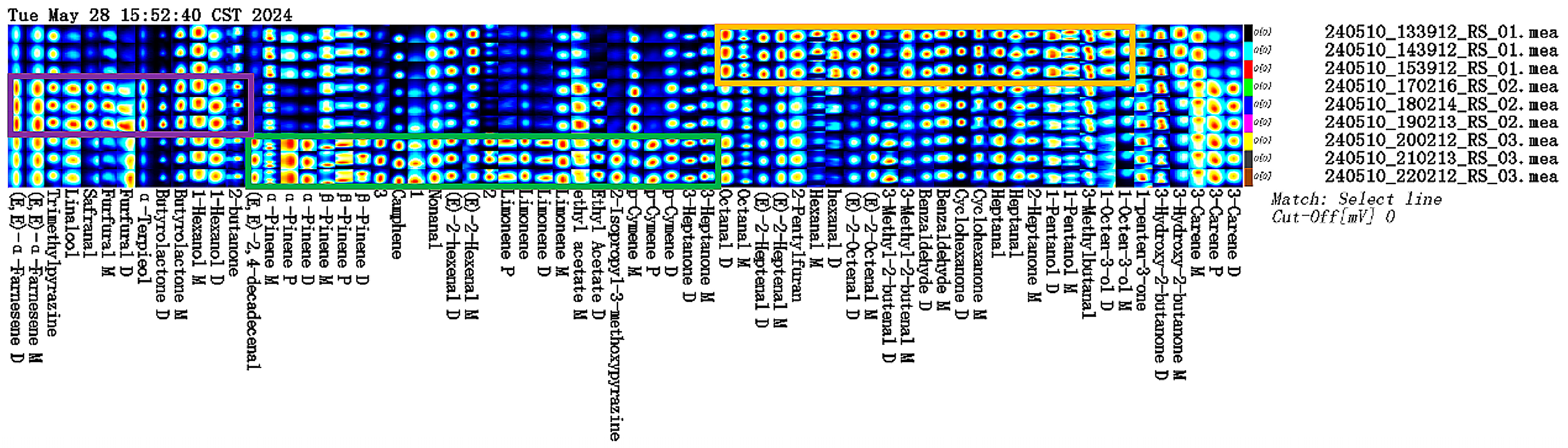
| No | Compounds | CAS# | Formula | RI | Rt/s | Dt/ms | Odor Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (E, E)-α-Farnesene D | C502614 | C15H24 | 1487.1 | 2464.654 | 1.48579 | Citrus, herbal, lavender, bergamot, myrrh, neroli, green |
| 2 | (E, E)-α-Farnesene M | C502614 | C15H24 | 1485.7 | 2454.604 | 1.42258 | Citrus, herbal, lavender, bergamot, myrrh, neroli, green |
| 3 | Safranal | C116267 | C10H14O | 1208.9 | 1077.330 | 1.28714 | herbal, phenolic, tobacco, spicy |
| 4 | α-Terpieol | C10482561 | C10H18O | 1188.8 | 1014.845 | 1.28968 | floral, lilac, terpenic |
| 5 | Nonanal | C124196 | C9H18O | 1104.8 | 790.476 | 1.49418 | rose, citrus, strong oily |
| 6 | 2-Isopropyl-3-methoxypyrazine | C25773404 | C8H12N2O | 1095.1 | 768.110 | 1.25062 | mung, bean |
| 7 | Linalool | C78706 | C10H18O | 1086.2 | 748.099 | 1.21862 | citrus, rose, woody, blueberry |
| 8 | (E)-2-Octenal M | C2548870 | C8H14O | 1065.5 | 703.366 | 1.32707 | fresh cucumber, fatty, green herbal, banana, green leaf |
| 9 | (E)-2-Octenal D | C2548870 | C8H14O | 1065.5 | 703.366 | 1.82308 | fresh cucumber, fatty, green herbal, banana, green leaf |
| 10 | p-Cymene M | C99876 | C10H14 | 1020.4 | 615.079 | 1.21506 | fresh, citrus, terpene, woody, spice |
| 11 | p-Cymene D | C99876 | C10H14 | 1021.1 | 616.256 | 1.31284 | fresh, citrus, terpene, woody, spice |
| 12 | p-Cymene P | C99876 | C10H14 | 1017.8 | 610.371 | 1.72530 | fresh, citrus, terpene, woody, spice |
| 13 | Octanal D | C124130 | C8H16O | 1013.9 | 603.308 | 1.81241 | aldehyde, waxy, citrus, orange, fruity, fatty |
| 14 | Octanal M | C124130 | C8H16O | 1008.0 | 592.713 | 1.41418 | aldehyde, waxy, citrus, orange, fruity, fatty |
| 15 | Trimethylpyrazine | C14667551 | C7H10N2 | 1000.5 | 579.680 | 1.16306 | roasted potato, peanut, cocoa, chocolate |
| 16 | 1-Octen-3-ol D | C3391864 | C8H16O | 983.8 | 545.935 | 1.59477 | mushroom, lavender, rose, hay |
| 17 | Benzaldehyde M | C100527 | C7H6O | 961.9 | 502.347 | 1.15250 | bitter almond, cherry, nutty |
| 18 | Benzaldehyde D | C100527 | C7H6O | 961.9 | 502.347 | 1.46539 | bitter almond, cherry, nutty |
| 19 | (E)-2-Heptenal D | C18829555 | C7H12O | 959.7 | 498.128 | 1.66210 | spicy, green vegetables, fresh, fatty |
| 20 | (E)-2-Heptenal M | C18829555 | C7H12O | 957.8 | 494.613 | 1.25811 | spicy, green vegetables, fresh, fatty |
| 21 | Heptanal D | C111717 | C7H14O | 899.9 | 396.891 | 1.69906 | fresh, aldehyde, fatty, green herbs, wine, fruity |
| 22 | Heptanal M | C111717 | C7H14O | 902.7 | 401.109 | 1.35053 | fresh, aldehyde, fatty, green herbs, wine, fruity |
| 23 | Cyclohexanone D | C108941 | C6H10O | 893.3 | 387.049 | 1.44426 | strong pungent, earthy |
| 24 | Cyclohexanone M | C108941 | C6H10O | 892.3 | 385.643 | 1.15646 | strong pungent, earthy |
| 25 | 1-Hexanol M | C111273 | C6H14O | 869.7 | 354.709 | 1.32808 | fresh, fruity, wine, sweet, green |
| 26 | 1-Hexanol D | C111273 | C6H14O | 867.2 | 351.447 | 1.64167 | fresh, fruity, wine, sweet, green |
| 27 | (E)-2-Hexenal M | C6728263 | C6H10O | 853.9 | 334.544 | 1.17881 | green, banana, fat |
| 28 | (E)-2-hexenal D | C6728263 | C6H10O | 849.1 | 328.569 | 1.51598 | green, banana, fat |
| 29 | Hexanal D | C66251 | C6H12O | 797.3 | 271.210 | 1.55279 | fresh, green, fat, fruity |
| 30 | Hexanal M | C66251 | C6H12O | 800.8 | 274.795 | 1.26863 | fresh, green, fat, fruity |
| 31 | 1-Pentanol D | C71410 | C5H12O | 767.1 | 241.335 | 1.52334 | balsamic |
| 32 | 1-Pentanol M | C71410 | C5H12O | 768.4 | 242.530 | 1.24801 | balsamic |
| 33 | 3-Methylbutanal | C590863 | C5H10O | 668.3 | 164.979 | 1.40801 | chocolate, fat |
| 34 | Ethyl Acetate D | C141786 | C4H8O2 | 628.6 | 144.910 | 1.33439 | fresh, fruity, sweet, grassy |
| 35 | ethyl acetate M | C141786 | C4H8O2 | 633.5 | 147.226 | 1.09980 | fresh, fruity, sweet, grassy |
| 36 | 3-Hydroxy-2-butanone D | C513860 | C4H8O2 | 715.4 | 196.240 | 1.32556 | butter, cream |
| 37 | 3-Hydroxy-2-butanone M | C513860 | C4H8O2 | 722.2 | 201.644 | 1.07231 | butter, cream |
| 38 | Furfural D | C98011 | C5H4O2 | 831.1 | 307.393 | 1.33734 | sweet, woody, almond, bready |
| 39 | Furfural M | C98011 | C5H4O2 | 829.0 | 305.077 | 1.08507 | sweet, woody, almond, bready |
| 40 | Butyrolactone M | C96480 | C4H6O2 | 918.2 | 425.469 | 1.08166 | cream, fat, caramel |
| 41 | β-Pinene M | C127913 | C10H16 | 977.3 | 532.626 | 1.21289 | resin, green |
| 42 | β-Pinene D | C127913 | C10H16 | 976.0 | 529.856 | 1.29733 | resin, green |
| 43 | β-Pinene P | C127913 | C10H16 | 975.0 | 528.009 | 1.63287 | resin, green |
| 44 | Camphene | C79925 | C10H16 | 952.5 | 484.605 | 1.20951 | woody, camphor |
| 45 | α-Pinene M | C80568 | C10H16 | 932.7 | 449.650 | 1.21413 | fresh, camphor, sweet, pine wood |
| 46 | α-Pinene D | C80568 | C10H16 | 934.0 | 451.727 | 1.67103 | fresh, camphor, sweet, pine wood |
| 47 | α-Pinene P | C80568 | C10H16 | 934.3 | 452.246 | 1.72246 | fresh, camphor, sweet, pine wood |
| 48 | 3-Methyl-2-butenal D | C107868 | C5H8O | 786.0 | 260.170 | 1.35635 | fruity |
| 49 | 3-Methyl-2-butenal M | C107868 | C5H8O | 779.3 | 253.422 | 1.08907 | fruity |
| 50 | 1-penten-3-one | C1629589 | C5H8O | 667.2 | 164.389 | 1.30212 | strong pungent odors |
| 51 | 2-butanone | C78933 | C4H8O | 601.2 | 132.494 | 1.23571 | fruity, camphor |
| 52 | 2-Heptanone M | C110430 | C7H14O | 885.6 | 376.157 | 1.26226 | pear, banana, fruity, slight medicinal fragrance |
| 53 | 3-Heptanone D | C106354 | C7H14O | 889.3 | 381.315 | 1.62728 | Fruity, Grass, Oil |
| 54 | Butyrolactone D | C96480 | C4H6O2 | 917.2 | 423.868 | 1.29782 | cream, fat, caramel |
| 55 | Limonene M | C138863 | C10H16 | 1039.9 | 651.878 | 1.21338 | lemon, sweet, orange, pine oil |
| 56 | Limonene D | C138863 | C10H16 | 1038.1 | 648.350 | 1.29803 | lemon, sweet, orange, pine oil |
| 57 | Limonene | C138863 | C10H16 | 1038.5 | 649.055 | 1.6614 | lemon, sweet, orange, pine oil |
| 58 | Limonene P | C138863 | C10H16 | 1038.5 | 649.055 | 1.72667 | lemon, sweet, orange, pine oil |
| 59 | 2-Pentylfuran | C3777693 | C9H14O | 996.3 | 572.413 | 1.25131 | bean, fruity, earthy, green, vegetable |
| 60 | 3-Carene M | C13466789 | C10H16 | 997.9 | 575.175 | 1.21279 | citrus, lemon, woody |
| 61 | 3-Carene D | C13466789 | C10H16 | 995.3 | 570.204 | 1.30035 | citrus, lemon, woody |
| 62 | 3-Carene P | C13466789 | C10H16 | 995.5 | 570.756 | 1.71712 | citrus, lemon, woody |
| 63 | 1-Octen-3-ol M | C3391864 | C8H16O | 985.8 | 550.111 | 1.15382 | mushroom, lavender, rose, hay |
| 64 | 3-Heptanone M | C106354 | C7H14O | 899.9 | 396.892 | 1.19904 | fruity, grass, oil |
| 65 | (E, E)-2,4-decadecenal | C25152845 | C10H16O | 1331.6 | 1552.147 | 1.42880 | cucumber, melon, citrus, pumpkin, nutty |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, M.; Yu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Ou, F.; Lei, C. Comparative Analysis of Volatile Organic Compounds in Different Parts of Ginseng Powder Using Gas Chromatography–Ion Mobility Spectrometry. Molecules 2025, 30, 1965. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091965
Zou M, Yu X, Liu Y, Zhu L, Ou F, Lei C. Comparative Analysis of Volatile Organic Compounds in Different Parts of Ginseng Powder Using Gas Chromatography–Ion Mobility Spectrometry. Molecules. 2025; 30(9):1965. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091965
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Manshu, Ximing Yu, Yuhuan Liu, Lijun Zhu, Feilin Ou, and Chang Lei. 2025. "Comparative Analysis of Volatile Organic Compounds in Different Parts of Ginseng Powder Using Gas Chromatography–Ion Mobility Spectrometry" Molecules 30, no. 9: 1965. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091965
APA StyleZou, M., Yu, X., Liu, Y., Zhu, L., Ou, F., & Lei, C. (2025). Comparative Analysis of Volatile Organic Compounds in Different Parts of Ginseng Powder Using Gas Chromatography–Ion Mobility Spectrometry. Molecules, 30(9), 1965. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091965






