Metal–Organic Framework (MOF)-Embedded Magnetic Polysaccharide Hydrogel Beads as Efficient Adsorbents for Malachite Green Removal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
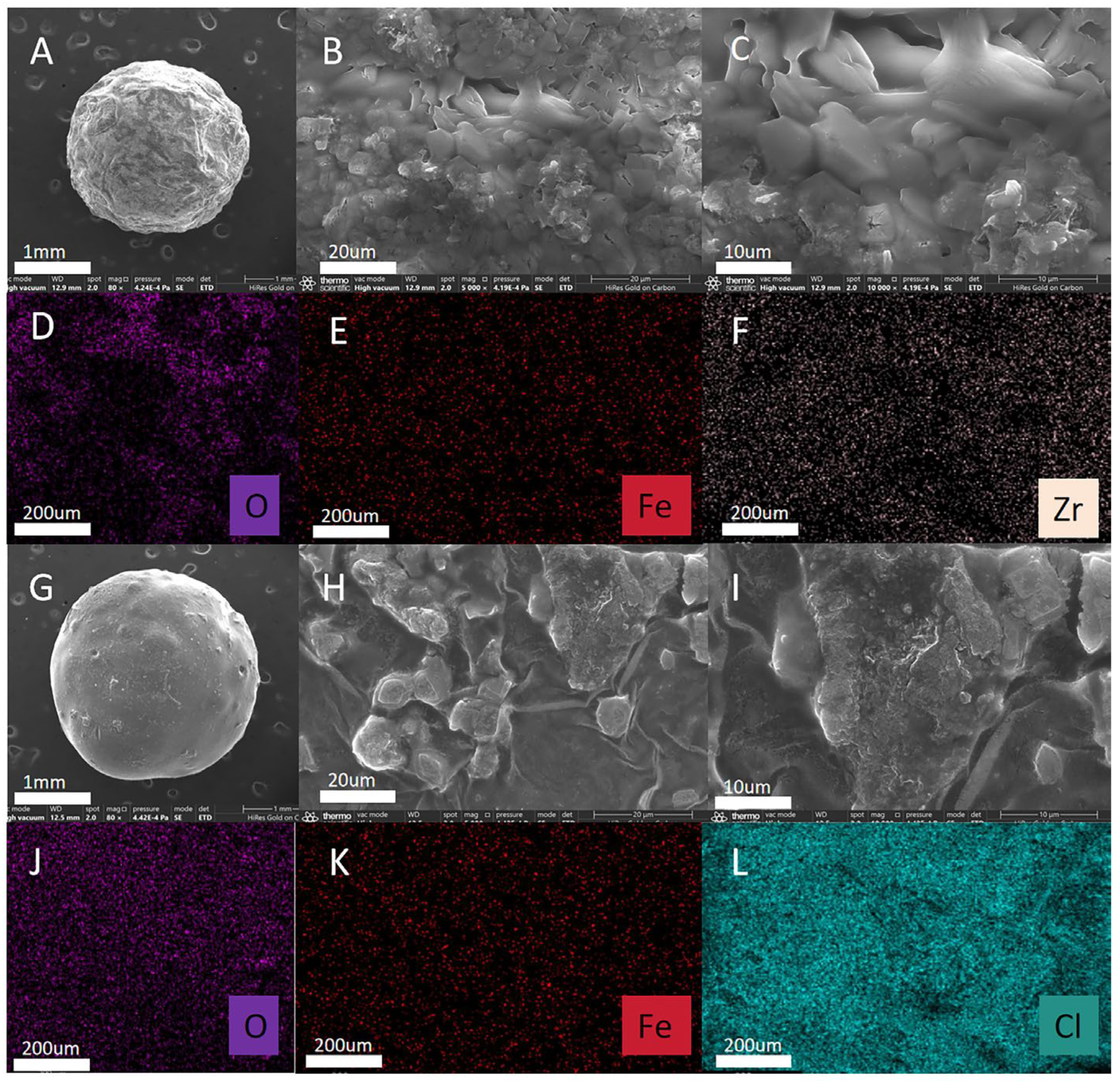
2.1. Characterization of MMOF Hydrogel
2.2. Optimization of Adsorption Conditions
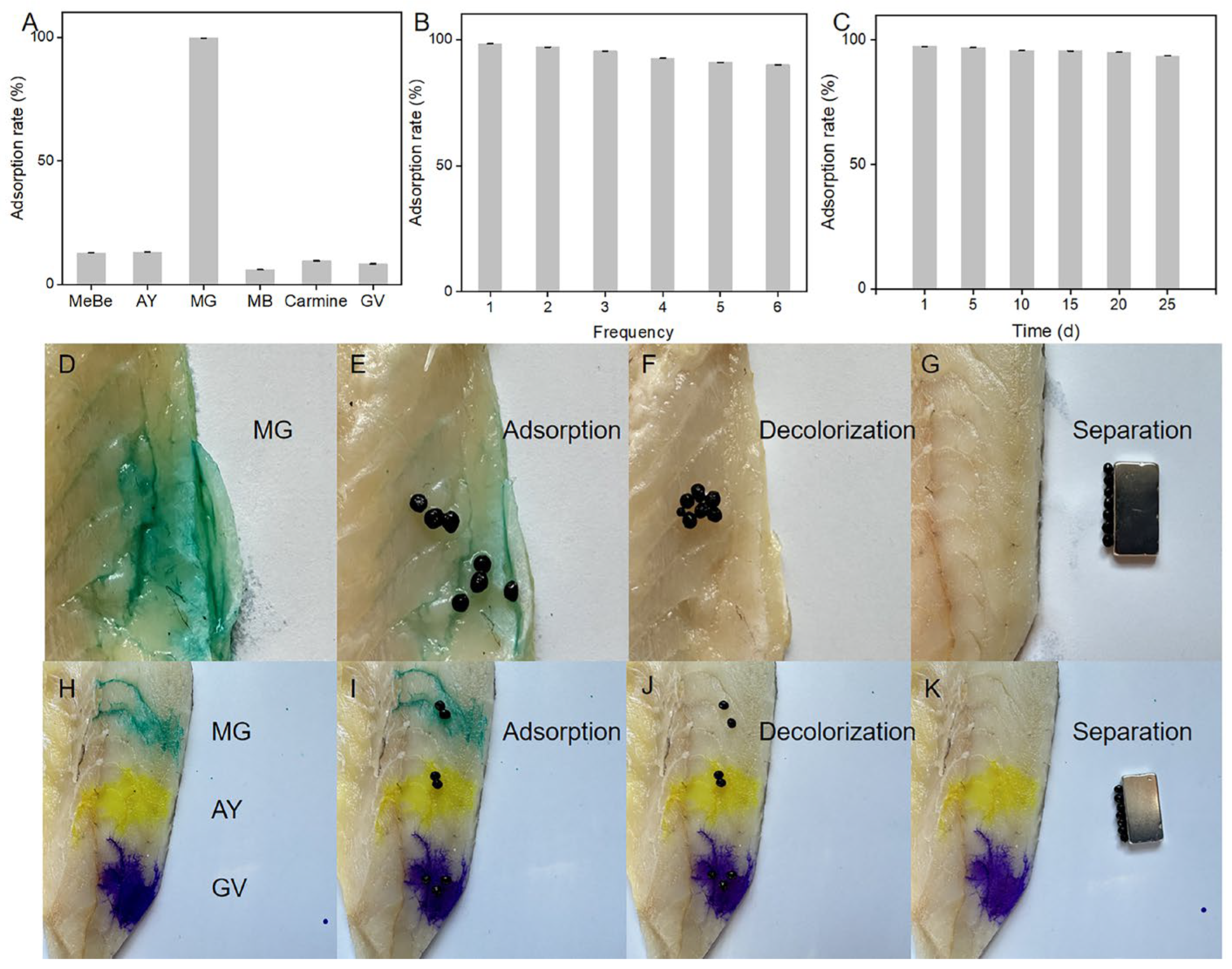
2.2.1. Optimization of Adsorption Materials
2.2.2. Optimization of Adsorption Environment
2.3. Dynamic Adsorption Model
2.4. Application of MMOF Hydrogels to Pigment Removal
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Instruments
3.3. Synthesis
3.3.1. Synthesis of Fe3O4@MOF
3.3.2. Synthesis of the MMOF Hydrogel
3.3.3. Synthesis of the Pure Hydrogel
3.3.4. Synthesis of the Magnetic Hydrogel
3.4. Adsorption of MG by MMOF Hydrogel
3.5. MG Removal Using MMOF Hydrogels
3.6. Supplementary Experimental Conditions
3.7. Data Processing Methods and Software
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, S.; Sengupta, S. Adsorptive removal of Pb (II) by using graphene oxide-impregnated calcium alginate hydrogel beads. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2024, 19, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Wu, J.; Chang, Z.; Yang, F.; Zhang, X.; Hou, K.; Ping, D.; Li, S. Sodium alginate hydrogel loaded with Capparis spinosa L. extract for antimicrobial and antioxidant wound dressing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 289, 138883–138898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfenyuk, E.V.; Dolinina, E.S.; Kraev, A.S. Synthesis and study of organo-modified silica based hydrogels: Rheological properties and drug release kinetics. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2024, 112, 35418–35433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xiao, L.; Cheng, R.; Xiang, B.; Li, X.; Song, J. Chloride sorption kinetics and corrosion-resistant mechanism of MgAl-NO2 LDH. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, 135, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathinejad, H.; Oddi, M. Synthesis and characterisation of hydrogel based on propiolic acid. Mater. Res. Innov. 2025, 29, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Rahul Vaid, V.; Nandal, K.; Sharma, R.K.; Joshi, V.; Saini, P.; Devanshi; Jindal, R.; Kaur, K. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan-tamarind gum-CaO nanoparticle hydrogels for improved adsorption of alizarin red-S dye from aqueous solution: Performance assessment and mechanistic insights. J. Sol.-Gel Sci. Technol. 2024, 358, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Guo, S.; Wang, H.; Gao, X.; Niu, B.; Li, W. pH-sensitive zinc oxide nanoparticle-controlled sodium alginate/silica hydrogel beads: For controlled curcumin release. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1324, 140967–140982. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Hao, L.; Luo, Y.; Gao, J.; Xu, F.; Li, H.; Hao, C.; Lin, C.P.; Yu, H.P.; Zhu, Y.J.; et al. A composite dressing combining ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowire bio-paper and a calcium alginate hydrogel accelerates wound healing. J. Mater. Chem. 2024, 135, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Liang, Z.; Kan, Q.; Kang, G. The influence of water content on the mechanical responses of polyacrylamide hydrogels under stress-controlled cyclic loadings. Int. J. Fatigue 2025, 193, 108766–108781. [Google Scholar]
- Simayi, R.; Jiang, M.; Sawut, A.; Song, H.; Wang, J. UV-initiated preparation and absorption properties of pseudo-polyrotaxane cyclodextrin-based PVA/poly (acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogel. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2023, 35, 6243–6258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Hu, N.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Qu, S.; Kan, Q.; Kang, G. Poroelastic fracture of polyacrylamide hydrogels: Enhanced crack tip swelling driven by chain scission. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2025, 194, 105954–105969. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Sawut, A.; Simayi, R.; Maimaitiyiming, X.; Song, H. Fabrication and enhanced photocatalytic performance of sodium alginate/polyacrylamide hydrogel-supported ZnOVS photocatalysis. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 177623–177638. [Google Scholar]
- Furui, H.; Longzheng, W.; Shujuan, Y.; Wenqi, Q.; Yuhong, F.; Yuanyuan, L.; Yang, Z.; Gaobo, Y.; Jiacheng, L. Highly stretchable and tough alginate-based cyclodextrin/Azo-polyacrylamide interpenetrating network hydrogel with self-healing properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 256, 117595–117612. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.B.H.; Van, H.T.; Dang, V.M.; Tran, T.N.H.; Nguyen, T.T.; Hoang, T.K. Insight into chromium adsorption from contaminated soil using Mg/Al LDH-zeolite. Heliyon 2024, 10, 31084–31098. [Google Scholar]
- Oo, W.; Park, J.H.; Win, M.Z.; Yi, K.B. Dual preservative effects of SnO2-chitosan on Cu+1-doped boehmite composites for stable CO adsorption properties. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 348, 127631–127645. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, B.; Ji, G.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Xia, M.; Tao, Y. Adaptive structural modification of Zr-based MOF-808 via solvent and ligand engineering for enhanced fluoride ion adsorption efficiency. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 348, 127731–127747. [Google Scholar]
- Aghdarreh, F.P.; Norouzbeigi, R.; Velayi, E. KOH-activated lightweight expanded clay aggregate (LECA) for malachite green adsorption: Activation mechanism and adsorption process assessment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 456, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Sobhi, H.R.; Yeganeh, M.; Ghambarian, M.; Fallah, S.; Esrafili, A. A new MOF-based modified adsorbent for the efficient removal of Hg(ii) ions from aqueous media: Isotherms and kinetics. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 16617–16623. [Google Scholar]
- Su, M.; Niu, G.; Liu, S.; Hu, J.; Wang, B. Porous alginate hydrogel beads with spatially separated acidic and basic moieties for selective adsorption of dyes. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 451, 141985–141990. [Google Scholar]
- Aboelfetoh, E.F.; Rabea, M.F.; Sheikh, M.Y.E.; Okba, E.A. In situ polymerization of acrylamide on magnetic SnFe2O4/CeO2 nanocomposite: A novel adsorbent for removing various dyes. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1312 Pt. 1, 138566–138585. [Google Scholar]
- Gaur, B.; Mittal, J.; Shah, S.A.A.; Mittal, A.; Baker, R.T. Sequestration of an Azo dye by a potential biosorbent: Characterization of biosorbent, adsorption isotherm and adsorption kinetic studies. Molecules 2024, 29, 2387–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ay, Ç.; Sopaci, Ş.B.; Atakol, O.; Öz, S. Adsorption behavior of reactive red 24 and methylene blue onto brewer’s spent grain: Characterization, kinetics, and isotherms modeling. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 104, 9632–9651. [Google Scholar]
- Majigsuren, E.; Byambasuren, U.; Amgalan, M.B.; Mendsaikhan, E.; Kano, N.; Kim, H.J.; Yunden, G. Adsorption of chromium (III) and chromium (VI) Ions from aqueous solution using chitosan–clay composite materials. Polymers 2024, 16, 1399–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolkun, A.; Muhammad, T.; Gao, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhi, D.; Zhang, S. Batch adsorption kinetic and thermodynamic studies of flavonoids from Dracocephalum moldavia via flow injection online measurement. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 351, 128033–128046. [Google Scholar]
- Aissa, M.A.B.; Khairy, M.; Khalifa, M.E.; Abdelrahman, E.A.; Raza, N.; Masoud, E.M.; Modwi, A. Facile synthesis of TiO2@ZnO nanoparticles for enhanced removal of methyl orange and indigo carmine dyes: Adsorption, kinetics. Heliyon 2024, 10, 31351–31366. [Google Scholar]
- Asghar, H.M.A.; Hussain, S.N.; Brown, N.W.; Roberts, E.P.L. Comparative adsorption-regeneration performance for newly developed carbonaceous adsorbent. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 69, 90–98. [Google Scholar]
- Dada, A.O.; Inyinbor, A.A.; Tokula, B.E.; Bayode, A.A.; Obayomi, K.S.; Ajanaku, C.O.; Adekola, F.A.; Ajanaku, K.O.; Pal, U. Zinc oxide decorated plantain peel activated carbon for adsorption of cationic malachite green dye: Mechanistic, kinetics and thermodynamics modeling. Environ. Res. 2024, 252 Pt. 3, 119046–119057. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimi, S.M.; Ramavandi, B.; Moslehi, M.H.; Rahiminia, M.; Nasseh, N. Application of CuFe2O4/CuS as a new green magnetic nanocomposite in adsorption of tetracycline from aqueous solutions: Mathematical models of thermodynamics, isotherms, and kinetics. Appl. Water Sci. 2024, 15, 6–21. [Google Scholar]
- Jedynak, K.; Charmas, B. Application of activated carbons obtained from polymer waste for the adsorption of dyes from aqueous solutions. Materials 2024, 17, 748–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Shao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhai, H. Study on preparation of calcium-based modified coal gangue and its adsorption dye characteristics. Molecules 2024, 29, 2183–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Pseudo-First-Order Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | Qe (mg/g) | R2 | K2 | Qe (mg/g) | R2 |
| 1.342 | 2.364 | 0.997 | 0.923 | 2.573 | 0.999 |
| The First Stage | The Second Stage | The Third Stage | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | C1 | R12 | K2 | C2 | R22 | K3 | C3 | R32 |
| 0.676 | 1.134 | 0.951 | 0.201 | 1.94 | 0.817 | 0.032 | 2.308 | 0.999 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, L.; Lu, Y.; Li, P.; Sun, B.; Wu, L. Metal–Organic Framework (MOF)-Embedded Magnetic Polysaccharide Hydrogel Beads as Efficient Adsorbents for Malachite Green Removal. Molecules 2025, 30, 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071560
Cheng L, Lu Y, Li P, Sun B, Wu L. Metal–Organic Framework (MOF)-Embedded Magnetic Polysaccharide Hydrogel Beads as Efficient Adsorbents for Malachite Green Removal. Molecules. 2025; 30(7):1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071560
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Lei, Yunzhu Lu, Peiyi Li, Baoguo Sun, and Lidong Wu. 2025. "Metal–Organic Framework (MOF)-Embedded Magnetic Polysaccharide Hydrogel Beads as Efficient Adsorbents for Malachite Green Removal" Molecules 30, no. 7: 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071560
APA StyleCheng, L., Lu, Y., Li, P., Sun, B., & Wu, L. (2025). Metal–Organic Framework (MOF)-Embedded Magnetic Polysaccharide Hydrogel Beads as Efficient Adsorbents for Malachite Green Removal. Molecules, 30(7), 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071560







