Centrifugal Partition Chromatography Is a Powerful Tool for the Isolation of Antibiofilm Quantum Carbon Dots Synthesized by Hydrothermal Treatment of Avocado Peels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots (CQD) from Avocado Peels
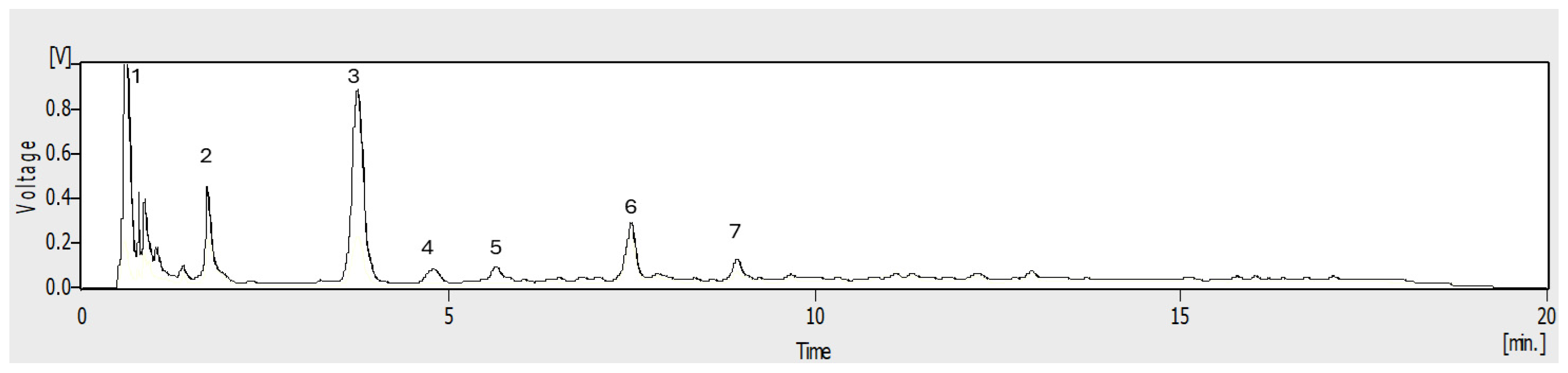
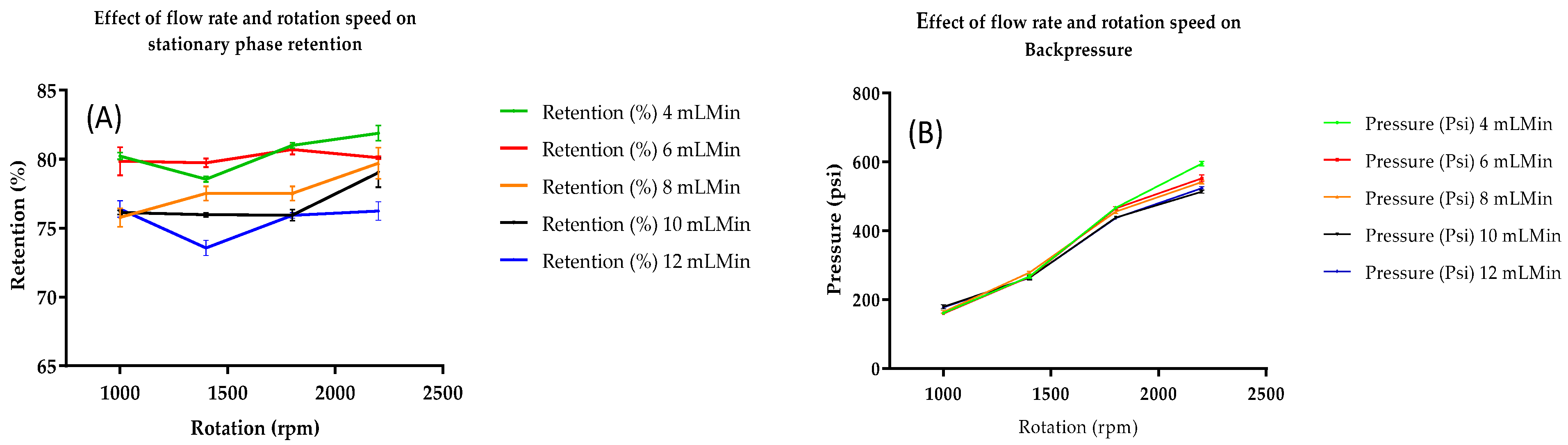
2.2. Fractionation by Preparative Centrifugal Partition Chromatography (CPC)
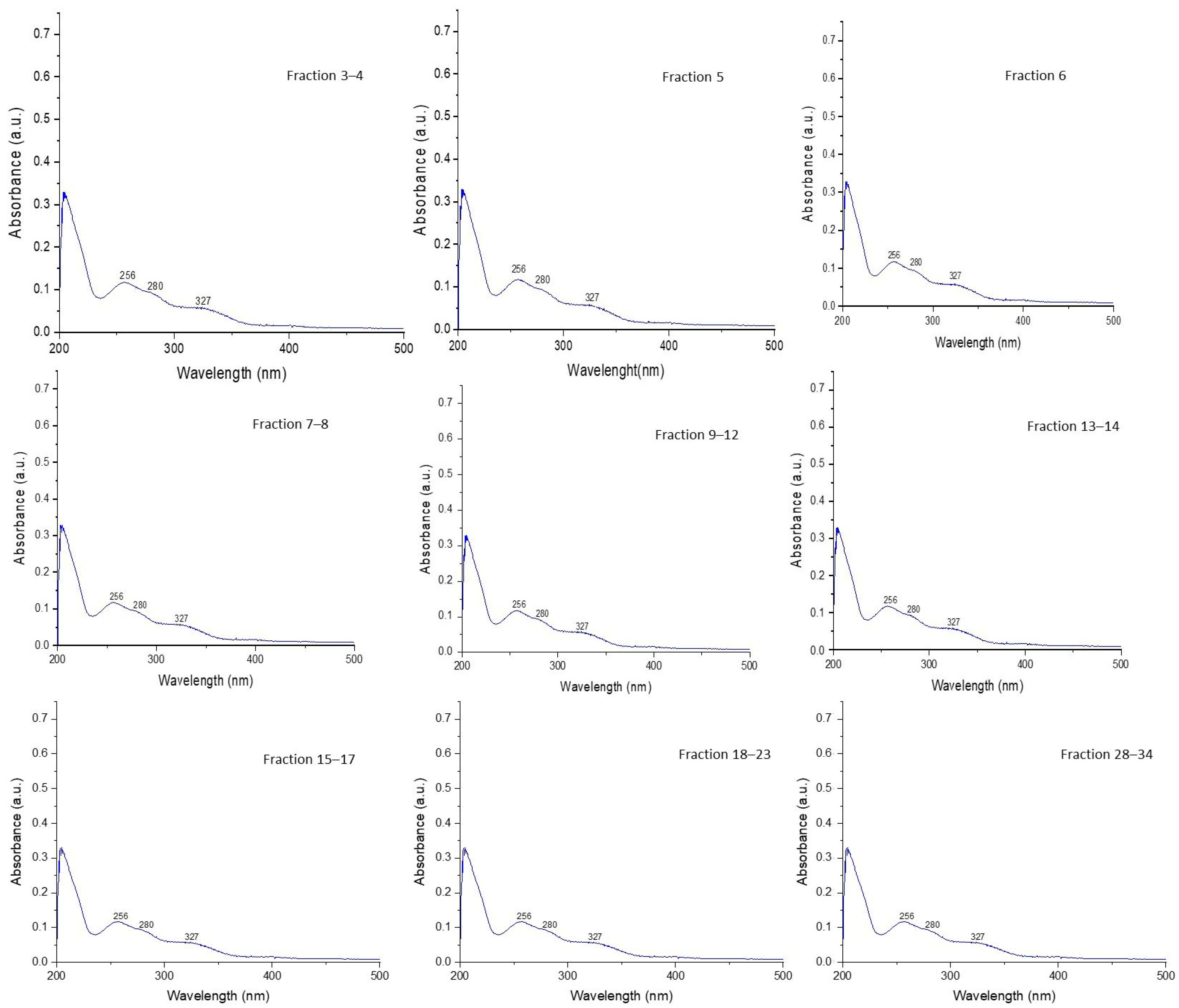
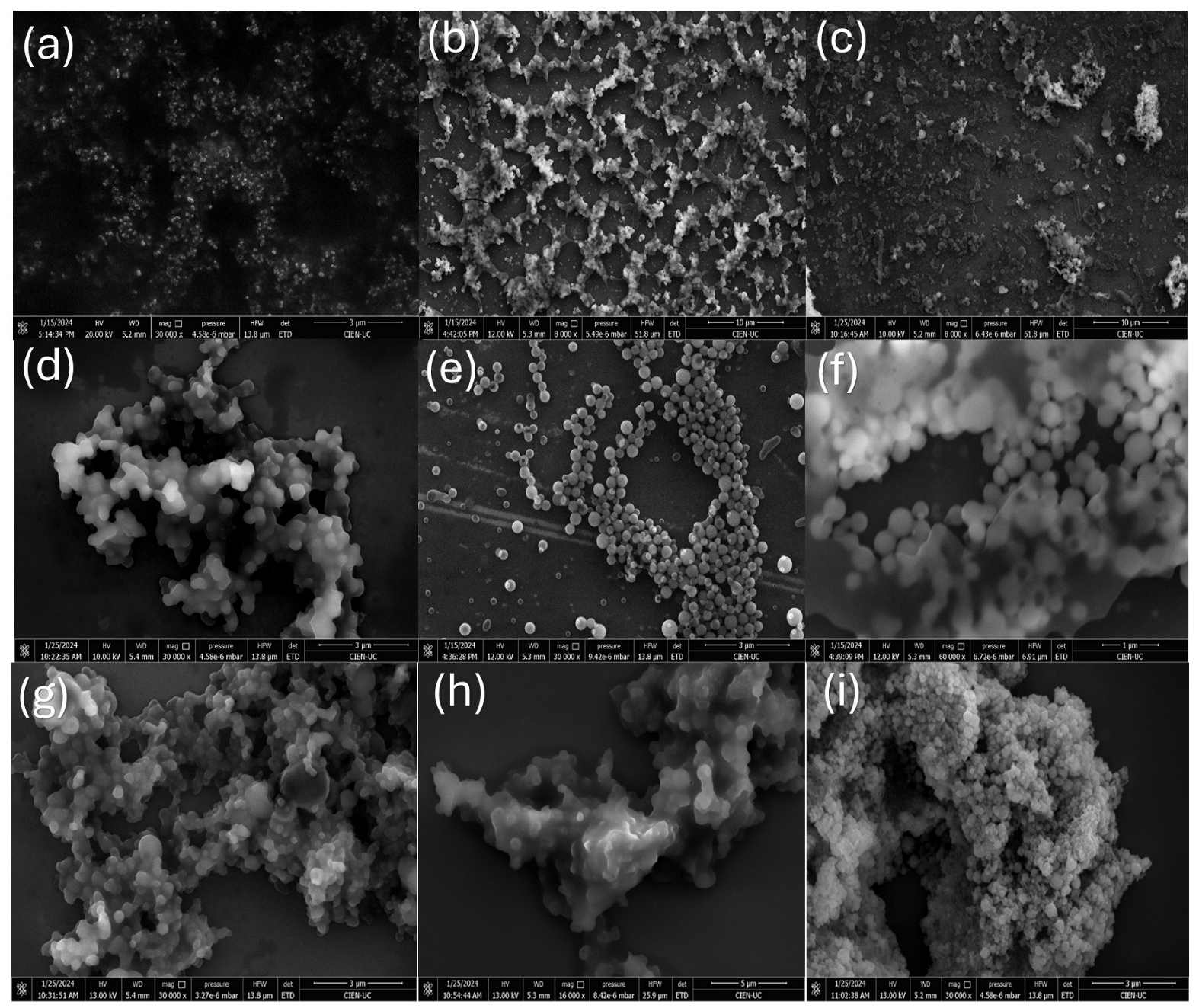
2.3. Characterization of Fractions with CQD Obtained by CPC:
2.3.1. Analysis of UV-VIS Spectra for CQD Fractions Obtained by CPC
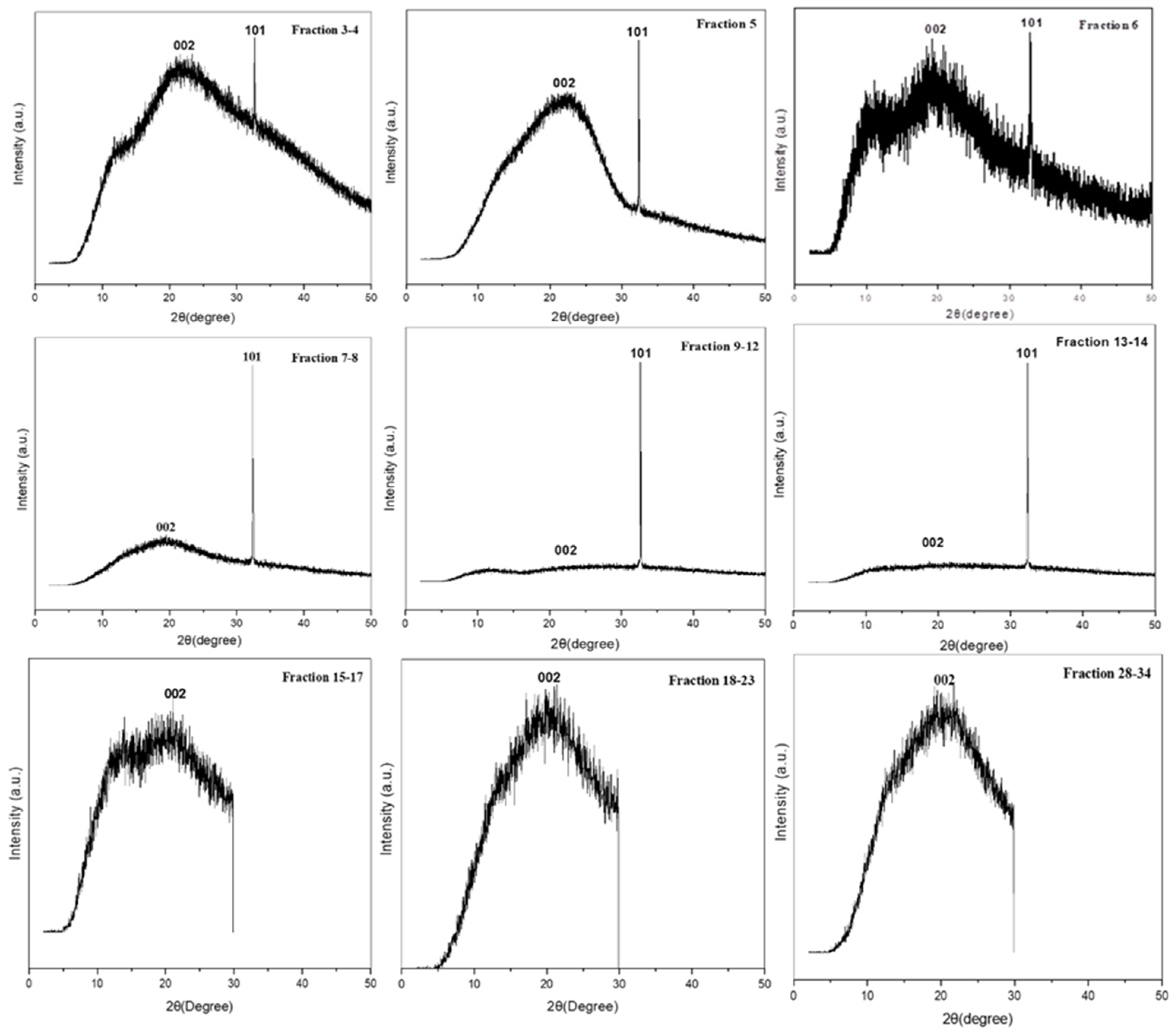
2.3.2. FE-SEM and XRD Analysis for CQD Fractions Obtained by CPC
2.3.3. FT-IR Analysis for CQD Fractions Obtained by CPC
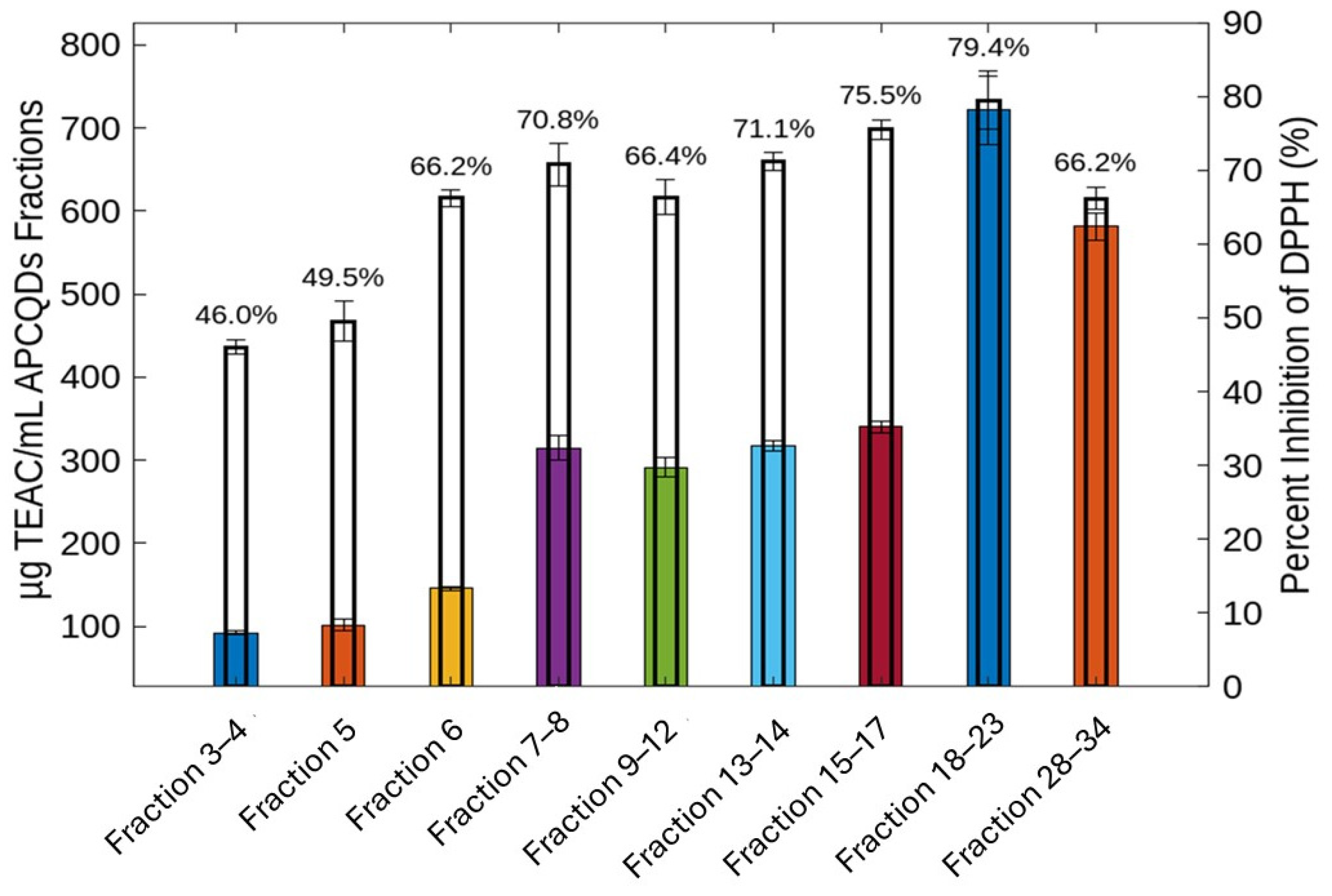
2.4. Antioxidant Activity
2.5. Antimicrobial Properties
2.5.1. Antibacterial Properties of CPC CQD Fractions
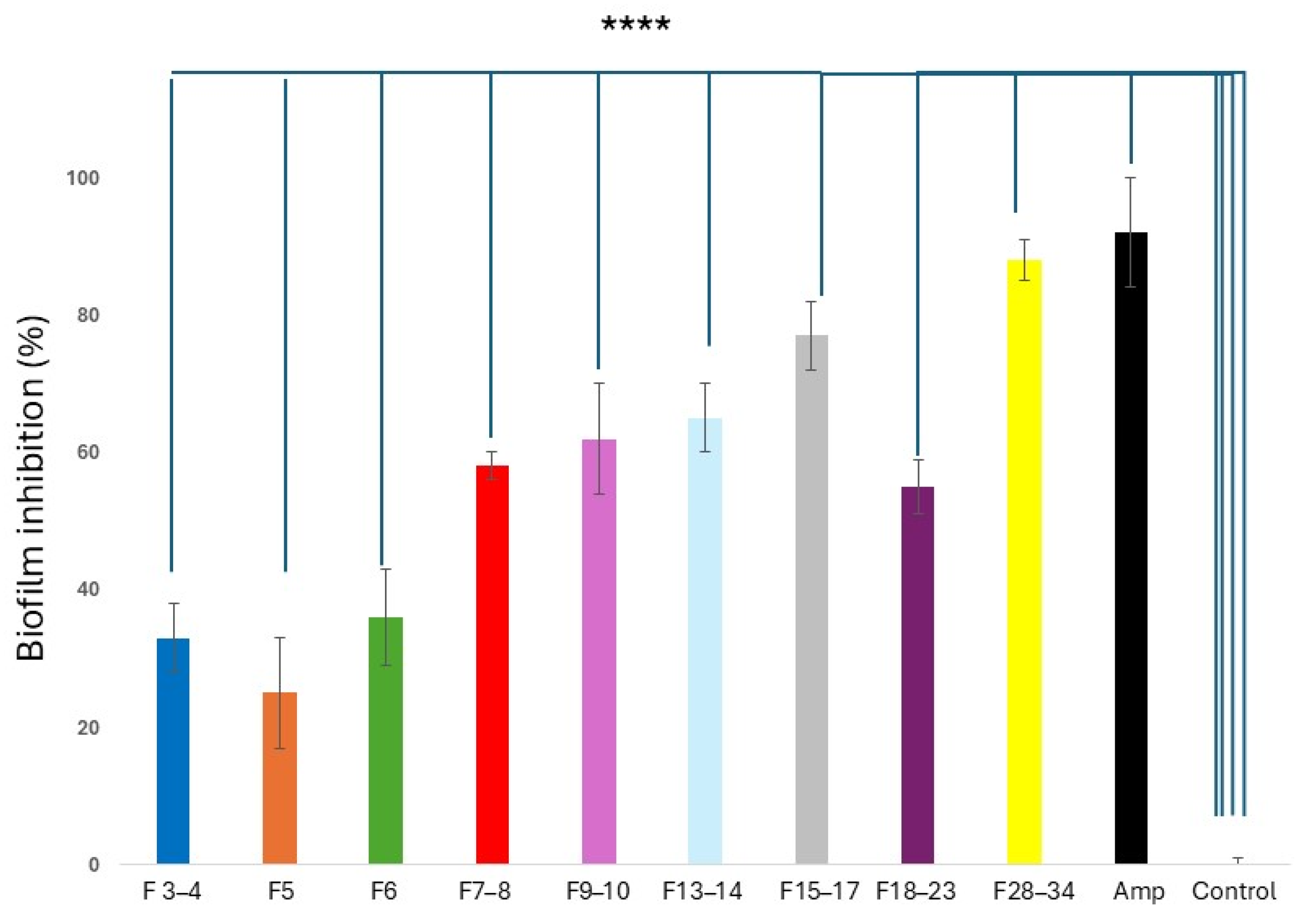
2.5.2. Anti-Biofilm Properties of CPC CQD Fractions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Proximate Analysis of Avocado Peel
3.3. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots (CQD) from Avocado Peels and Phloroglucinol
3.4. Characterization of Carbon Quantum Dot Fractions Derived from Avocado Peels
3.5. CPC Separation Procedure
3.6. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC-UV)
3.7. Antioxidant Activity: DPPH Radical Inhibition
3.8. Microbial Culture and Maintenance
3.9. Screening Disk and Well-Diffusion Test Susceptibility
3.10. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
3.11. Biofilm Test on Biofilm Formation
4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yadav, S.; Malik, K.; Moore, J.M.; Kamboj, B.R.; Malik, S.; Malik, V.K.; Arya, S.; Singh, K.; Mahanta, S.; Bishnoi, D.K. Valorisation of Agri-Food Waste for Bioactive Compounds: Recent Trends and Future Sustainable Challenges. Molecules 2024, 29, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshome, E.; Teka, T.A.; Nandasiri, R.; Rout, J.R.; Harouna, D.V.; Astatkie, T.; Urugo, M.M. Fruit By-Products and Their Industrial Applications for Nutritional Benefits and Health Promotion: A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, F.; Ali, Z.; Arshad, M.; Mubeen, K.; Ghazala, A. Exploration of Novel Eco-Friendly Techniques to Utilize Bioactive Compounds from Household Food Waste: Special Reference to Food Applications. Front. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 4, 1388461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, D.J.; Alsherbiny, M.A.; Perera, S.; Low, M.; Basu, A.; Devi, O.A.; Barooah, M.S.; Li, C.G.; Papoutsis, K. The Odyssey of Bioactive Compounds in Avocado (Persea americana) and Their Health Benefits. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akan, S. Phytochemicals in Avocado Peel and Their Potential Uses. Food Health 2021, 7, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, R.G.; Rodríguez-Jasso, R.M.; Ruíz, H.A.; Govea-Salas, M.; Pintado, M.; Aguilar, C.N. Recovery of Bioactive Components from Avocado Peels Using Microwave-Assisted Extraction. Food Bioprod. Process. 2021, 127, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Janaswamy, S. Strong and Biodegradable Films from Avocado Peel Fiber. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 201, 116926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, R.; Yang, B. Carbon Dots: A New Type of Carbon-Based Nanomaterial with Wide Applications. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 2179–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Ren, X.; Sun, M.; Liu, H.; Xia, L. Carbon Dots: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferjani, H.; Abdalla, S.; Oyewo, O.A.; Onwudiwe, D.C. Facile Synthesis of Carbon Dots by the Hydrothermal Carbonization of Avocado Peels and Evaluation of the Photocatalytic Property. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 160, 111866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, Z.; Khan, A.; Rhim, J.-W.; Shin, G.H.; Kim, J.T. Sustainable Packaging Film Based on Cellulose Nanofibres/Pullulan Impregnated with Zinc-Doped Carbon Dots Derived from Avocado Peel to Extend the Shelf Life of Chicken and Tofu. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 129302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, P.D.; Mehta, V.N.; Prajapati, V.S.; Patel, S.; Rohit, J.V. Bottom-up Approaches for the Preparation of Carbon Dots. In Carbon Dots in Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 15–29. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Shang, L.; He, P.; Dong, H.; Wang, G.; Ding, G. Fabrication of Carbon-Based Quantum Dots via a “Bottom-Up” Approach: Topology, Chirality, and Free Radical Processes in “Building Blocks”. Small 2023, 19, 2205957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansi, M.; Bhikhu, M.; Gaurav, S. Synthesis and Applications of Carbon Dots from Waste Biomass. In Carbon Dots in Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 319–328. [Google Scholar]
- Abu, N.; Chinnathambi, S.; Kumar, M.; Etezadi, F.; Bakhori, N.M.; Zubir, Z.A.; Md Salleh, S.N.; Shueb, R.H.; Karthikeyan, S.; Thangavel, V.; et al. Development of Biomass Waste-Based Carbon Quantum Dots and Their Potential Application as Non-Toxic Bioimaging Agents. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 28230–28249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khairol Anuar, N.K.; Tan, H.L.; Lim, Y.P.; So’aib, M.S.; Abu Bakar, N.F. A Review on Multifunctional Carbon-Dots Synthesized From Biomass Waste: Design/Fabrication, Characterization and Applications. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 626549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travlou, N.A.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Algarra, M.; Labella, A.M.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Bandosz, T.J. S- and N-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots: Surface Chemistry Dependent Antibacterial Activity. Carbone 2018, 135, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essner, J.B.; Kist, J.A.; Polo-Parada, L.; Baker, G.A. Artifacts and Errors Associated with the Ubiquitous Presence of Fluorescent Impurities in Carbon Nanodots. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 1878–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Seivert, O.; Tang, Y.; Karahan, H.E.; Bianco, A. Carbon Dot Synthesis and Purification: Trends, Challenges and Recommendations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202412341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, F.; Shi, L.; Zhao, S.; Wan, M.; Zhang, X. Carbon Quantum Dots: Properties, Preparation, and Applications. Molecules 2024, 29, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomei, B.; Prato, M. The Importance of the Purification Step and the Characterization of the Products in the Synthesis of Carbon Nanodots. Small 2023, 19, 2206714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullal, N.; Mehta, R.; Sunil, D. Separation and Purification of Fluorescent Carbon Dots—An Unmet Challenge. Analyst 2024, 149, 1680–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-L.; Bai, L.-F.; Geng, Z.-R.; Chen, H.; Xu, L.-T.; Xie, Y.-C.; Wang, D.-J.; Gu, H.-W.; Wang, X.-M. Carbon Quantum Dots: Preparation, Optical Properties, and Biomedical Applications. Mater. Today Adv. 2023, 18, 100376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-D.; Li, J.; Niu, J.-N.; Bao, X.-P.; Zhao, H.-D.; Tan, M. Fluorescent Carbon Dots Derived from Urine and Their Application for Bio-Imaging. Methods 2019, 168, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubetskaya, O.E.; Trubetskoj, O.A.; Richard, C.; Vervald, A.M.; Burikov, S.A.; Marchenkov, V.V.; Shenderova, O.A.; Patsaeva, S.V.; Dolenko, T.A. High-Performance Size Exclusion Chromatography with Online Fluorescence and Multi-Wavelength Absorbance Detection for Isolation of High-Purity Carbon Dots Fractions, Free of Non-Fluorescent Material. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1650, 462251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zeng, J.; Quan, T.; Liu, S.; Deng, L.; Kang, X.; Xia, Z.; Gao, D. Liquid-Liquid Extraction and Purification of Oil Red O Derived Nitrogen-Doped Highly Photoluminescent Carbon Dots and Their Application as Multi-Functional Sensing Platform for Cu2+ and Tetracycline Antibiotics. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Pan, C.; Wei, Z.; Liu, J.; Song, Z.; Ma, W.; Wang, M.; Mao, L. One-Step Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped Multi-Emission Carbon Dots and Their Fluorescent Sensing in HClO and Cellular Imaging. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y. Golden Rules and Pitfalls in Selecting Optimum Conditions for High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1065, 145–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesen, J.B.; McAlpine, J.B.; Chen, S.-N.; Pauli, G.F. Countercurrent Separation of Natural Products: An Update. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1765–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Vargas, M.C.; Contreras, M.d.M.; Castro, E. Avocado-Derived Biomass as a Source of Bioenergy and Bioproducts. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez, F.; Aranda, M.; García, A.; Pastene, E. Los Polifenoles Antioxidantes Extraídos Del Epicarpio de Palta (Persea americana Var. Hass) Inhiben La Ureasa de Helicobacter Pylori. Bol. Latinoam. Caribe Plantas Med. Aromat. 2011, 10, 265–280. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Opoku, H.; Tang, S.; Edman, L.; Wang, J. Carbon Dots: A Review with Focus on Sustainability. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2405472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, H.; Xiao, D. Separation of Carbon Quantum Dots on a C18 Column by Binary Gradient Elution via HPLC. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 8124–8128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthod, A.; Hassoun, M.; Ruiz-Angel, M.J. Alkane Effect in the Arizona Liquid Systems Used in Countercurrent Chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 383, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerschick, T.; Vetter, W. Online Hyphenation of Centrifugal Partition Chromatography with Countercurrent Chromatography (CPC-CCC) and Its Application to the Separation of Saturated Alkylresorcinols. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 5043–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezold, F.; Minceva, M. A Water-Free Solvent System Containing an L-Menthol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent for Centrifugal Partition Chromatography Applications. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1587, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, R.; Minceva, M. Liquid–Liquid Chromatography: Current Design Approaches and Future Pathways. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2021, 12, 495–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Yuan, T.; Sui, L.; Wang, Z.; Xi, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, L.; Tan, Z.; Chen, A.; et al. Engineering Triangular Carbon Quantum Dots with Unprecedented Narrow Bandwidth Emission for Multicolored LEDs. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.; Le, P.A.; Phung, V.B.T. Facile Green Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots and Biomass-Derived Activated Carbon from Banana Peels: Synthesis and Investigation. Biomass Convers. Biorefi. 2022, 12, 2407–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Qiu, J. Unveil the Fluorescence of Carbon Quantum Dots. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2015, 17, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, A.; Biswas, S.; Kumbhakar, P. Solvatochromism in Highly Luminescent Environmental Friendly Carbon Quantum Dots for Sensing Applications: Conversion of Bio-Waste into Bio-Asset. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 191, 498–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yin, H.; Cole, I.; Houshyar, S.; Wang, L. Carbon Dots Derived from Non-Biomass Waste: Methods, Applications, and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2024, 29, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad-Jafarieh, P.; Salamat-Ahangari, R.; Pourhassan-Moghaddam, M.; Akbarzadeh, A. An Insight into the Solvatochromic and Photophysical Behaviours of Biowaste-Origin Carbon Nanodots. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 336, 116360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Sato, R.; Iso, Y.; Isobe, T. Surface Modification Strategy for Fluorescence Solvatochromism of Carbon Dots Prepared from p-Phenylenediamine. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 2174–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, N.; Mandal, D. Solvatochromic Response of Carbon Dots: Evidence of Solvent Interaction with Different Types of Emission Centers. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 18732–18741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, Y.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Lu, S. Aggregation in Carbon Dots. Aggregate 2022, 3, e296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansay, V.; Sharma, V.D.; Chandan, G.; Sharma, I.; Chakrabarti, S.; Bera, M.K. Sustainable Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots Derived from Cissus Quadrangularis for Biomarker Applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 296, 127237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thulasi, S.; Kathiravan, A.; Asha Jhonsi, M. Fluorescent Carbon Dots Derived from Vehicle Exhaust Soot and Sensing of Tartrazine in Soft Drinks. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 7025–7031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.; Ezati, P.; Yoon, K.S.; Rhim, J.-W. Gelatin/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)-Based Functional Films Integrated with Spent Coffee Ground-Derived Carbon Dots and Grapefruit Seed Extract for Active Packaging Application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 231, 123493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phull, M.; Ali, A.; Maity, B. Sustainable Synthesis of Carbon Dots from Ananas Comosus as Renewable Biomass: Nanomolar Level Detection of Glutathione. RSC Sustain. 2024, 2, 1599–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Lan, M.; Zhu, X.; Xue, H.; Ng, T.-W.; Meng, X.; Lee, C.-S.; Wang, P.; Zhang, W. Green Synthesis of Bifunctional Fluorescent Carbon Dots from Garlic for Cellular Imaging and Free Radical Scavenging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 17054–17060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Varillas, S.; Fontanil, T.; Obaya, Á.J.; Fernández-González, A.; Murru, C.; Badía-Laíño, R. Biocompatibility and Antioxidant Capabilities of Carbon Dots Obtained from Tomato (Solanum Lycopersicum). Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murru, C.; Badía-Laíño, R.; Díaz-García, M.E. Synthesis and Characterization of Green Carbon Dots for Scavenging Radical Oxygen Species in Aqueous and Oil Samples. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Innocenzi, P.; Stagi, L. Carbon Dots as Oxidant-Antioxidant Nanomaterials, Understanding the Structure-Properties Relationship. A Critical Review. Nano Today 2023, 50, 101837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yu, L.; Zhu, R.; Wei, X.; Fan, X.; Hu, H.; Yang, D.; Du, H.; Zhao, M.; Li, L.; et al. Malting Barley Carbon Dots-Mediated Oxidative Stress Promotes Insulin Resistance in Mice via NF-ΚB Pathway and MAPK Cascade. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Itkor, P.; Lee, M.; Saenjaiban, A.; Lee, Y.S. Synergistic Integration of Carbon Quantum Dots in Biopolymer Matrices: An Overview of Current Advancements in Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Active Packaging. Molecules 2024, 29, 5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamon, M.; Bierne, H.; Cossart, P. Listeria Monocytogenes: A Multifaceted Model. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farber, J.M.; Zwietering, M.; Wiedmann, M.; Schaffner, D.; Hedberg, C.W.; Harrison, M.A.; Hartnett, E.; Chapman, B.; Donnelly, C.W.; Goodburn, K.E.; et al. Alternative Approaches to the Risk Management of Listeria Monocytogenes in Low Risk Foods. Food Control 2021, 123, 107601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlaneto, M.C.; Furlaneto-Maia, L. Antimicrobial Nanoparticle-Containing Food Packaging Films for controlling Listeria Spp.: An Overview. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2025, 427, 110959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, S.; Xie, X.; Shi, Q. Pseudomonas Putida Actively Forms Biofilms to Protect the Population under Antibiotic Stress. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 270, 116261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashajyothi, M.; Balamurugan, A.; Patel, A.; Krishnappa, C.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, A. Cell Wall Polysaccharides of Endophytic Pseudomonas Putida Elicit Defense against Rice Blast Disease. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxac042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, W.; Sun, H.; Yan, Z.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Programmed Bacteria Death Induced by Carbon Dots with Different Surface Charge. Small 2016, 12, 4713–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhonsi, M.A.; Ananth, D.A.; Nambirajan, G.; Sivasudha, T.; Yamini, R.; Bera, S.; Kathiravan, A. Antimicrobial Activity, Cytotoxicity and DNA Binding Studies of Carbon Dots. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 196, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Du, J.; Yao, Q.; Ge, H.; Li, H.; Xu, F.; Gao, F.; Xian, L.; Fan, J.; Peng, X. Precise Photodynamic Therapy: Penetrating the Nuclear Envelope with Photosensitive Carbon Dots. Carbone N. Y. 2020, 159, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, D.; Wang, G.; Zhang, M.; Sun, Y.; Ding, J. Antibacterial Carbon Dots. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 30, 101383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Li, P.; Huang, R.; Xu, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Gong, X.; Xing, X. Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Mechanisms of Carbon Dots: A Review. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 734–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.-H.; Gao, G.; Chen, X.; Jia, H.-R.; Li, Y.-H.; Chen, Z.; Wu, F.-G. Carbon Dot-Based Platform for Simultaneous Bacterial Distinguishment and Antibacterial Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32170–32181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussen, N.H.; Hasan, A.H.; FaqiKhedr, Y.M.; Bogoyavlenskiy, A.; Bhat, A.R.; Jamalis, J. Carbon Dot Based Carbon Nanoparticles as Potent Antimicrobial, Antiviral, and Anticancer Agents. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 9849–9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Abbas, K.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Tedesco, A.C.; Bi, H. Photodynamic Anti-Bacteria by Carbon Dots and Their Nano-Composites. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Liu, G.; Hu, C.; Lei, B.; Liu, Y. The Structural Characteristics and Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Carbon Dots: A Mini Review. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 7726–7741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getachew, G.; Korupalli, C.; Rasal, A.S.; Chang, J.-Y. ROS Generation/Scavenging Modulation of Carbon Dots as Phototherapeutic Candidates and Peroxidase Mimetics to Integrate with Polydopamine Nanoparticles/GOx towards Cooperative Cancer Therapy. Compos. B Eng. 2021, 226, 109364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Shen, X.; Xing, D. Carbon Quantum Dots as ROS-Generator and -Scavenger: A Comprehensive Review. Dye Pigment 2023, 208, 110784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Shi, H.; Qi, Y.; Li, J.; Jing, A.; Liu, Q.; Feng, W.; Li, G.; Gao, S. Specific Anti-Biofilm Activity of Carbon Quantum Dots by Destroying P. Gingivalis Biofilm Related Genes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 5473–5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Yin, C.; Mo, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Li, G.; Zhou, Q. Recent Progress in Carbon Dots for Anti-Pathogen Applications in Oral Cavity. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1251309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Yi, B.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Wu, Z.; Ji, J.; Tang, J.; Yu, D.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Carbon Dots Induce Pathological Damage to the Intestine via Causing Intestinal Flora Dysbiosis and Intestinal Inflammation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.S. Proximate Assays in Food Analysis. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of Total Phenolics with Phosphomolybdic-Phosphotungstic Acid Reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehrer, S.; Minceva, M. Characterization of a Centrifugal Partition Chromatographic Column with Spherical Cell Design. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019, 143, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezold, F.; Roehrer, S.; Minceva, M. Ionic Liquids as Modifying Agents for Protein Separation in Centrifugal Partition Chromatography. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2019, 42, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Seriche, S.; Jerez-Morales, A.; Smith, C.T.; Sánchez-Alonzo, K.; García-Cancino, A. Candida Albicans, a Reservoir of Listeria Monocytogenes? Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 90, 104779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebel-Gerber, S.; García-Cancino, A.; Urbina, A.; Simirgiotis, M.J.; Echeverría, J.; Bustamante-Salazar, L.; Sáez-Carrillo, K.; Alarcón, J.; Pastene-Navarrete, E. Chilean Rhubarb, Gunnera Tinctoria (Molina) Mirb. (Gunneraceae): UHPLC-ESI-Orbitrap-MS Profiling of Aqueous Extract and Its Anti-Helicobacter Pylori Activity. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 583961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, R. Inhibition Effects of Low Concentrations of Epigallocatechin Gallate on the Biofilm Formation and Hemolytic Activity of Listeria Monocytogenes. Food Control 2018, 85, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrios-Henríquez, B.; Venegas-Toloza, M.; Reyes-Fuentes, M.; Zúñiga-Arbalti, F.; Bustamante, L.; García-Cancino, A.; Alarcón-Enos, J.; Pastene-Navarrete, E. Synthesis and Isolation of Phenol- and Thiol-Derived Epicatechin Adducts Prepared from Avocado Peel Procyanidins Using Centrifugal Partition Chromatography and the Evaluation of Their Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activity. Molecules 2024, 29, 2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Quitian, A.G.; Hernandez-Moreno, L.V.; Pabon-Baquero, L.C.; Prieto-Rodriguez, J.A.; Patiño-Ladino, O.J. Antiquorum and Antibiofilm Activities of Piper Bogotense C. DC. against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and Identification of Bioactive Compounds. Plants 2023, 12, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastene, E.; Speisky, H.; Troncoso, M.; Alarcón, J.; Figueroa, G. In Vitro Inhibitory Effect of Apple Peel Extract on the Growth of Helicobacter Pylori and Respiratory Burst Induced on Human Neutrophils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 7743–7749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| % | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Ash | 3.7 ± 0.59 |
| Protein | 7.9 ± 0.39 |
| Moisture | 71.6 ± 0.73 |
| Fat | 18.1 ± 0.63 |
| Crude fiber | 39.0 ± 0.02 |
| Carbohydrates | 3.1 ± 1.41 |
| Polyphenols (g/100 g) * | 3.3 ± 0.52 |
| Solvent Systems | Peak 3 | Peak 4 | Peak 6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1.60 | 1.63 | 4.19 |
| C | 1.25 | 1.38 | 2.88 |
| G | 1.06 | 1.22 | 2.67 |
| K | 0.48 | 1.05 | 1.92 |
| N | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.29 |
| CQDs CPC Fractions | P. putida Inhibition Zone (Mean ± SD, mm) | L. monocytogenes Inhibition Zone (Mean ± SD, mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 3–4 | 10.83 ± 0.40 bcd | 17.47 ± 0.78 de |
| 5 | 10.97 ± 0.21 bcd | 16.43 ± 0.14 bc |
| 6 | 11.13 ± 0.83 bcd | 15.73 ± 0.14 b |
| 7–8 | 11.70 ± 0.46 b | 17.33 ± 0.64 cd |
| 9–10 | 11.20 ± 0.36 cd | 17.07 ± 0.64 cd |
| 13–14 | 10.60 ± 0.26 bc | 15.97 ± 0.57 b |
| 15–17 | 9.50 ± 0.26 a | 17.37 ± 0.21 cde |
| 18–23 | 10.27 ± 0.78 ab | 18.50 ± 0.07 e |
| 28–34 | 10.87 ± 0.40 bcd | 19.96 ± 0.61 f |
| Azithromycin | 13.30 ± 0.14 b | 12.97 ± 1.34 a |
| Ampicillin | - | 23.27 ± 0.61 g |
| CQDs CPC Fractions | P. putida mg/mL | L. monocytogenes mg/mL |
|---|---|---|
| 3–4 | >500 | 124.32 ± 0.95 f |
| 5 | >500 | 125.48 ± 0.87 f |
| 6 | >500 | 126.35 ± 0.40 f |
| 7–8 | >500 | 88.46 ± 1.71 e |
| 9–10 | >500 | 82.26 ± 0.95 d |
| 13–14 | >500 | 83.49 ± 0.79 d |
| 15–17 | >500 | 64.28 ± 1.83 b |
| 18–23 | >500 | 72.85 ± 1.74 c |
| 28–34 | >500 | 33.61 ± 1.05 a |
| Amoxicillin | >500 | 1.22 ± 0.80 g |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fiallos, N.; Acuña, S.; Correa-Otero, D.; Venegas-Toloza, M.; Beldarrain, T.; Burgos, J.; Fuentes, F.; Bustamante, F.; Christiansen, G.; Roa, V.; et al. Centrifugal Partition Chromatography Is a Powerful Tool for the Isolation of Antibiofilm Quantum Carbon Dots Synthesized by Hydrothermal Treatment of Avocado Peels. Molecules 2025, 30, 1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071525
Fiallos N, Acuña S, Correa-Otero D, Venegas-Toloza M, Beldarrain T, Burgos J, Fuentes F, Bustamante F, Christiansen G, Roa V, et al. Centrifugal Partition Chromatography Is a Powerful Tool for the Isolation of Antibiofilm Quantum Carbon Dots Synthesized by Hydrothermal Treatment of Avocado Peels. Molecules. 2025; 30(7):1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071525
Chicago/Turabian StyleFiallos, Nandis, Sergio Acuña, Diana Correa-Otero, Matías Venegas-Toloza, Tatiana Beldarrain, Josefina Burgos, Francisca Fuentes, Francisco Bustamante, Girlenne Christiansen, Vanesa Roa, and et al. 2025. "Centrifugal Partition Chromatography Is a Powerful Tool for the Isolation of Antibiofilm Quantum Carbon Dots Synthesized by Hydrothermal Treatment of Avocado Peels" Molecules 30, no. 7: 1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071525
APA StyleFiallos, N., Acuña, S., Correa-Otero, D., Venegas-Toloza, M., Beldarrain, T., Burgos, J., Fuentes, F., Bustamante, F., Christiansen, G., Roa, V., Schott, E., Alarcón-Enos, J., & Pastene-Navarrete, E. (2025). Centrifugal Partition Chromatography Is a Powerful Tool for the Isolation of Antibiofilm Quantum Carbon Dots Synthesized by Hydrothermal Treatment of Avocado Peels. Molecules, 30(7), 1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071525






