RNA-Binding Motif Protein 22 Induces Apoptosis via c-Myc Pathway in Colon Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
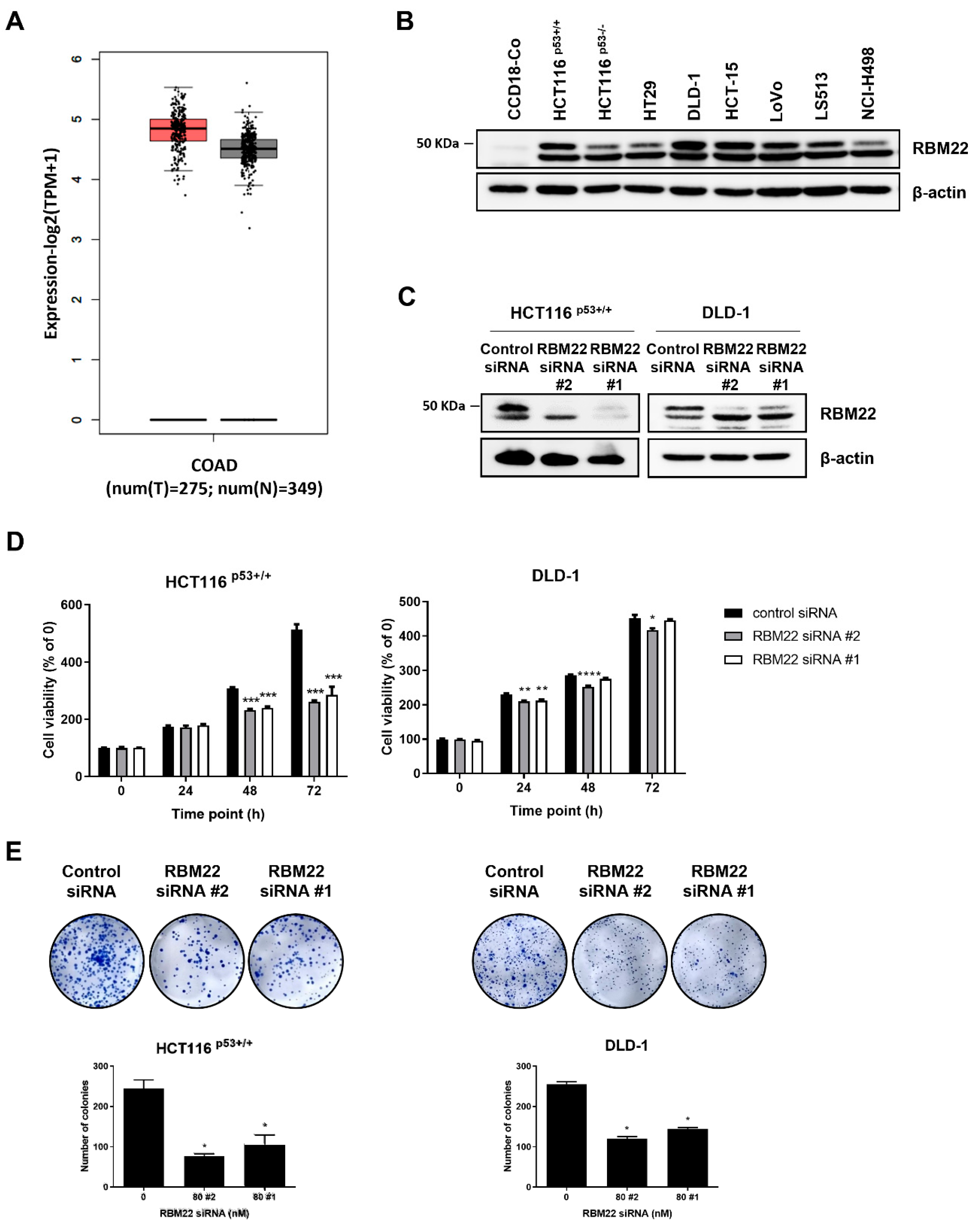
2.1. RBM22 Depletion Reduces Cytotoxicity and Proliferation in Colon Cancer Cells
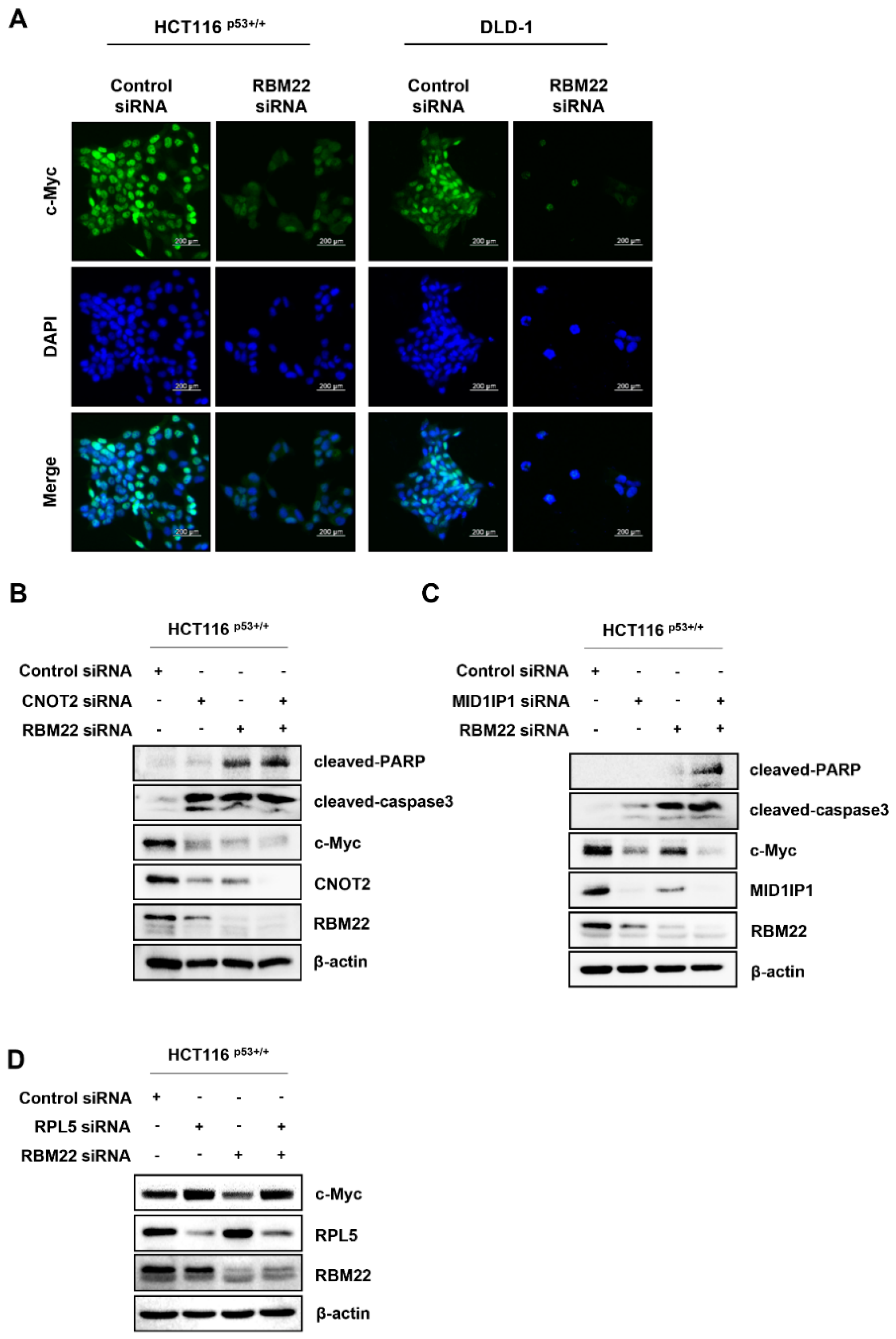
2.2. Knockdown of RBM22 Triggers Apoptosis
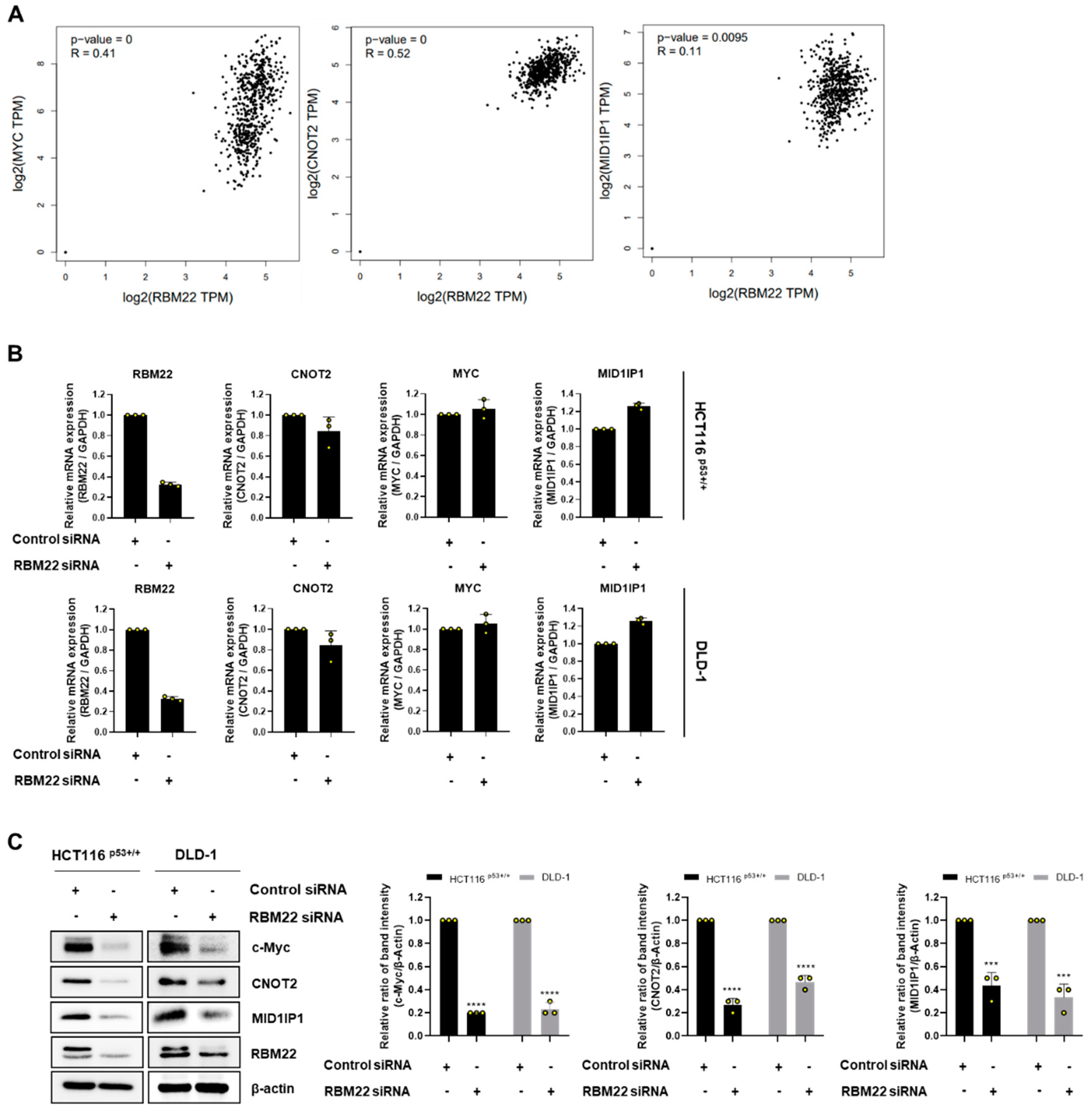
2.3. RBM22 Is Regulated by Oncogene c-Myc
2.4. RBM22 Modulates c-Myc Through CNOT2 and MID1IP1, Enhancing Apoptosis
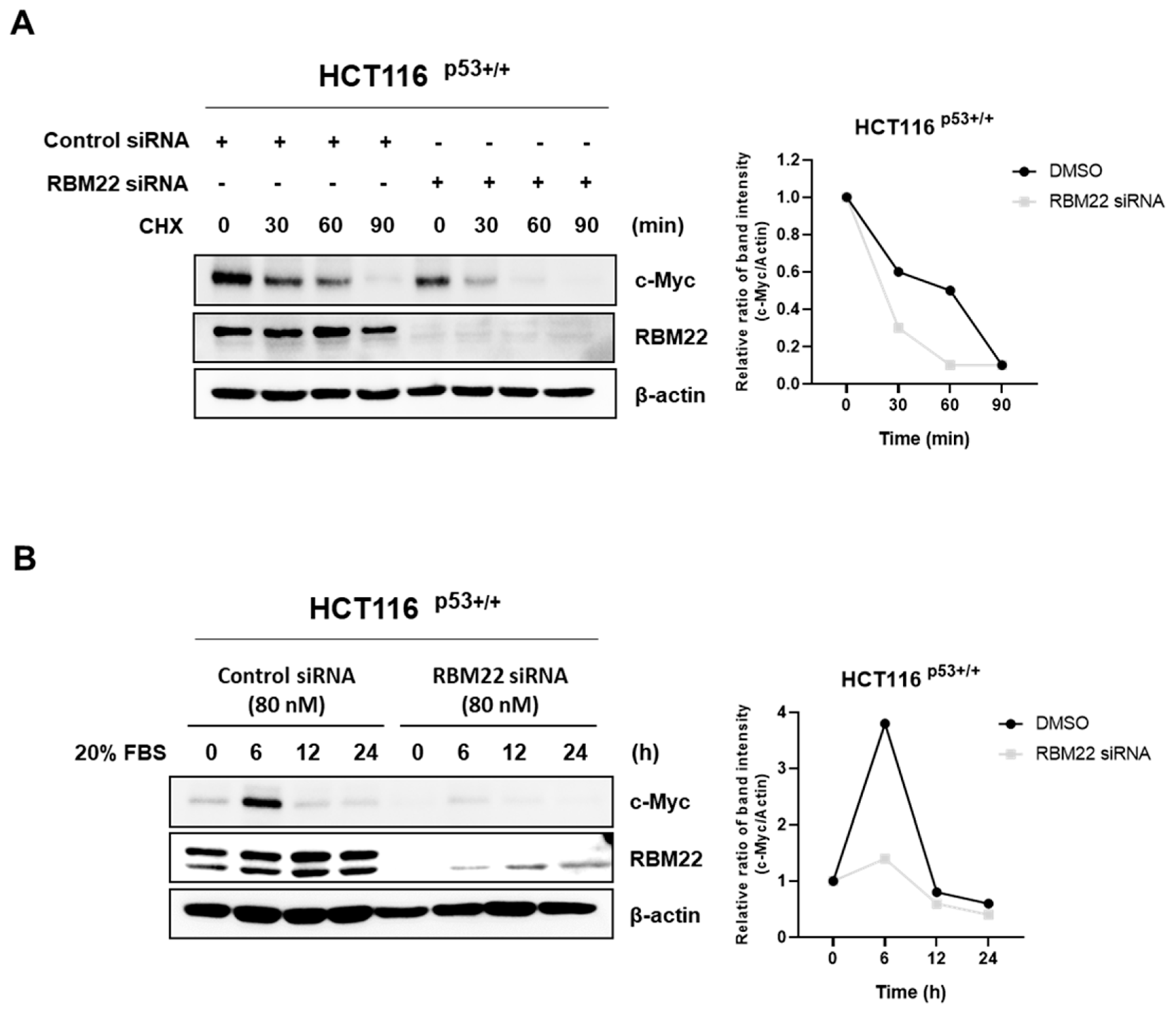
2.5. RBM22 Attenuates c-Myc Stability and Sensitivity to Serum Stimulation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture and Gene Silencing Using Small Interfering RNA (siRNA)
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Colony Formation Assay
4.5. Annexin V/Propidium Iodide (PI) Assay Using Flow Cytometry
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. Immunofluorescence
4.8. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.9. Cycloheximide (CHX) Chase Assay
4.10. Serum Stimulation for c-Myc Induction
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xia, C.; Dong, X.; Li, H.; Cao, M.; Sun, D.; He, S.; Yang, F.; Yan, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, N.; et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: Profiles, trends, and determinants. Chin. Med. J. 2022, 135, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, K.; Ghias, K. ; Ghias, K. Colorectal cancer carcinogenesis: A review of mechanisms. Cancer Biol. Med. 2016, 13, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soubise, B.; Jiang, Y. RBM22, a Key Player of Pre-mRNA Splicing and Gene Expression Regulation, is Altered in Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.; Sridhar, P.; Kirchner, R.; Lock, Y.J.; Herbert, Z.; Buonamici, S.; Smith, P.; Lieberman, J.; Petrocca, F. Basal-A triple-negative breast cancer cells selectively rely on RNA splicing for survival. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 2849–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes-Fayos, A.C.; Vázquez-Borrego, M.C.; Jiménez-Vacas, J.M.; Bejarano, L.; Pedraza-Arévalo, S.; L.-López, F.; Blanco-Acevedo, C.; Sánchez-Sánchez, R.; Reyes, O.; Ventura, S.; et al. Splicing machinery dysregulation drives glioblastoma development/aggressiveness: Oncogenic role of SRSF3. Brain 2020, 143, 3273–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurumayum, S.; Jiang, P.; Hao, X.; Campos, T.L.; Young, N.D.; Korhonen, P.K.; Gasser, R.B.; Bork, P.; Zhao, X.-M.; He, L.-J.; et al. OGEE v3: Online GEne Essentiality database with increased coverage of organisms and human cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D998–D1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudino, T.A.; McKay, C.; Pendeville-Samain, H.; Nilsson, J.A.; Maclean, K.H.; White, E.L.; Davis, A.C.; Ihle, J.N.; Cleveland, J.L. c-Myc is essential for vasculogenesis and angiogenesis during development and tumor progression. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 2530–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.M.; Thomas, S.D.; Islam, A.; Muench, D.; Sedoris, K. c-Myc and cancer metabolism. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5546–5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.-M.; Zhou, X.; Gatignol, A.; Lu, H. Ribosomal proteins L5 and L11 co-operatively inactivate c-Myc via RNA-induced silencing complex. Oncogene 2014, 33, 4916–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, E.J.; Jung, D.-B.; Lee, H.; Han, I.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.-H. CNOT2 promotes proliferation and angiogenesis via VEGF signaling in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2018, 412, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Jung, J.H.; Hwang, J.; Park, J.E.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, W.Y.; Suh, J.Y.; Kim, S.-H. CNOT2 is critically involved in atorvastatin induced apoptotic and autophagic cell death in non-small cell lung cancers. Cancers 2019, 11, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.H.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Sim, D.Y.; Im, E.; Kim, S.; Chang, S.; Kim, S.-H. Colocalization of MID1IP1 and c-Myc is critically involved in liver cancer growth via regulation of ribosomal protein L5 and L11 and CNOT2. Cells 2020, 9, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.E.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, H.; Sim, D.Y.; Im, E.; Park, W.Y.; Shim, B.S.; Ko, S.; Kim, S. Ribosomal protein L5 mediated inhibition of c-Myc is critically involved in sanggenon G induced apoptosis in non-small lung cancer cells. Phytotherapy Res. 2021, 35, 1080–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, H.M.; Jee, W.; Lee, D.; Jang, H.-J.; Jung, J.H. Ophiopogonin D increase apoptosis by activating p53 via ribosomal protein L5 and L11 and inhibiting the expression of c-Myc via CNOT2. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 974468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ołdak, Ł.; Zielińska, Z.; Gorodkiewicz, E. Methods of PARP-1 Determination and its Importance in Living Organisms. Protein Pept. Lett. 2022, 29, 496–504. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Li, F.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Shi, W.; Liu, F.-F.; O’Sullivan, B.; He, Z.; Peng, Y.; Tan, A.-C.; et al. Caspase 3–mediated stimulation of tumor cell repopulation during cancer radiotherapy. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.-C.; Yang, S.-F.; Chiou, H.-L.; Hsieh, S.-C.; Wen, S.-H.; Lu, K.-H.; Hsieh, Y.-H. Licochalcone A-Induced Apoptosis Through the Activation of p38MAPK Pathway Mediated Mitochondrial Pathways of Apoptosis in Human Osteosarcoma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. Cells 2019, 8, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.H.; Lee, D.; Ko, H.M.; Jang, H.-J. Inhibition of CNOT2 Induces Apoptosis via MID1IP1 in Colorectal Cancer Cells by Activating p53. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.R.; Jee, W. Acetylcorynoline Induces Apoptosis and G2/M Phase Arrest through the c-Myc Signaling Pathway in Colon Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, Y.-R.; Park, S.-M.; Kim, N.; Jung, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, K.-I.; Jang, H.-J. RNA-Binding Motif Protein 22 Induces Apoptosis via c-Myc Pathway in Colon Cancer Cells. Molecules 2025, 30, 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061227
Park Y-R, Park S-M, Kim N, Jung J, Kim S, Kim K-I, Jang H-J. RNA-Binding Motif Protein 22 Induces Apoptosis via c-Myc Pathway in Colon Cancer Cells. Molecules. 2025; 30(6):1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061227
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Ye-Rin, So-Mi Park, Nanyeong Kim, Jihoon Jung, Seokwoo Kim, Kwan-Il Kim, and Hyeung-Jin Jang. 2025. "RNA-Binding Motif Protein 22 Induces Apoptosis via c-Myc Pathway in Colon Cancer Cells" Molecules 30, no. 6: 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061227
APA StylePark, Y.-R., Park, S.-M., Kim, N., Jung, J., Kim, S., Kim, K.-I., & Jang, H.-J. (2025). RNA-Binding Motif Protein 22 Induces Apoptosis via c-Myc Pathway in Colon Cancer Cells. Molecules, 30(6), 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061227







