Integrated Biological and Chemical Investigation of Indonesian Marine Organisms Targeting Anti-Quorum-Sensing, Anti-Biofilm, Anti-Biofouling, and Anti-Biocorrosion Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
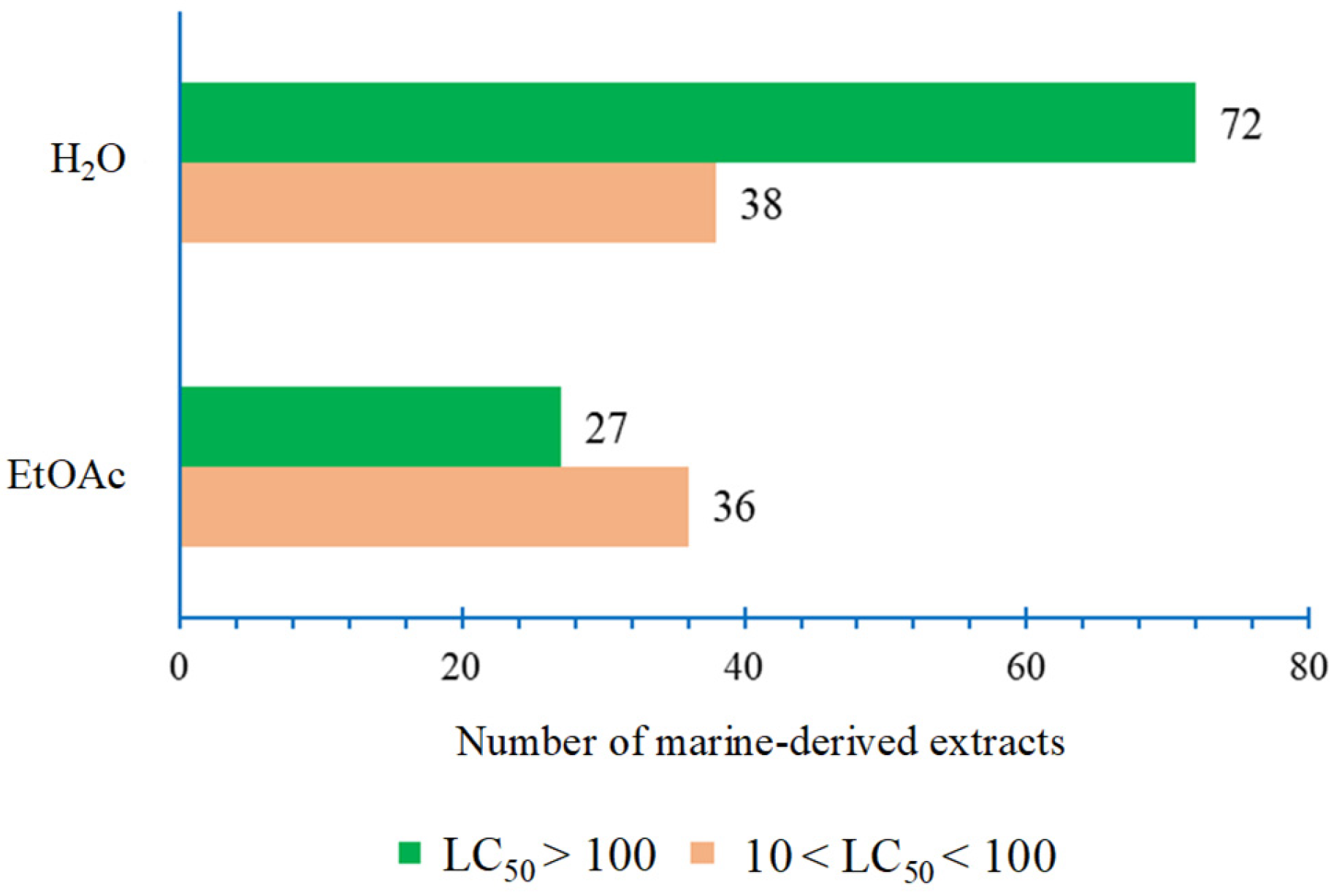
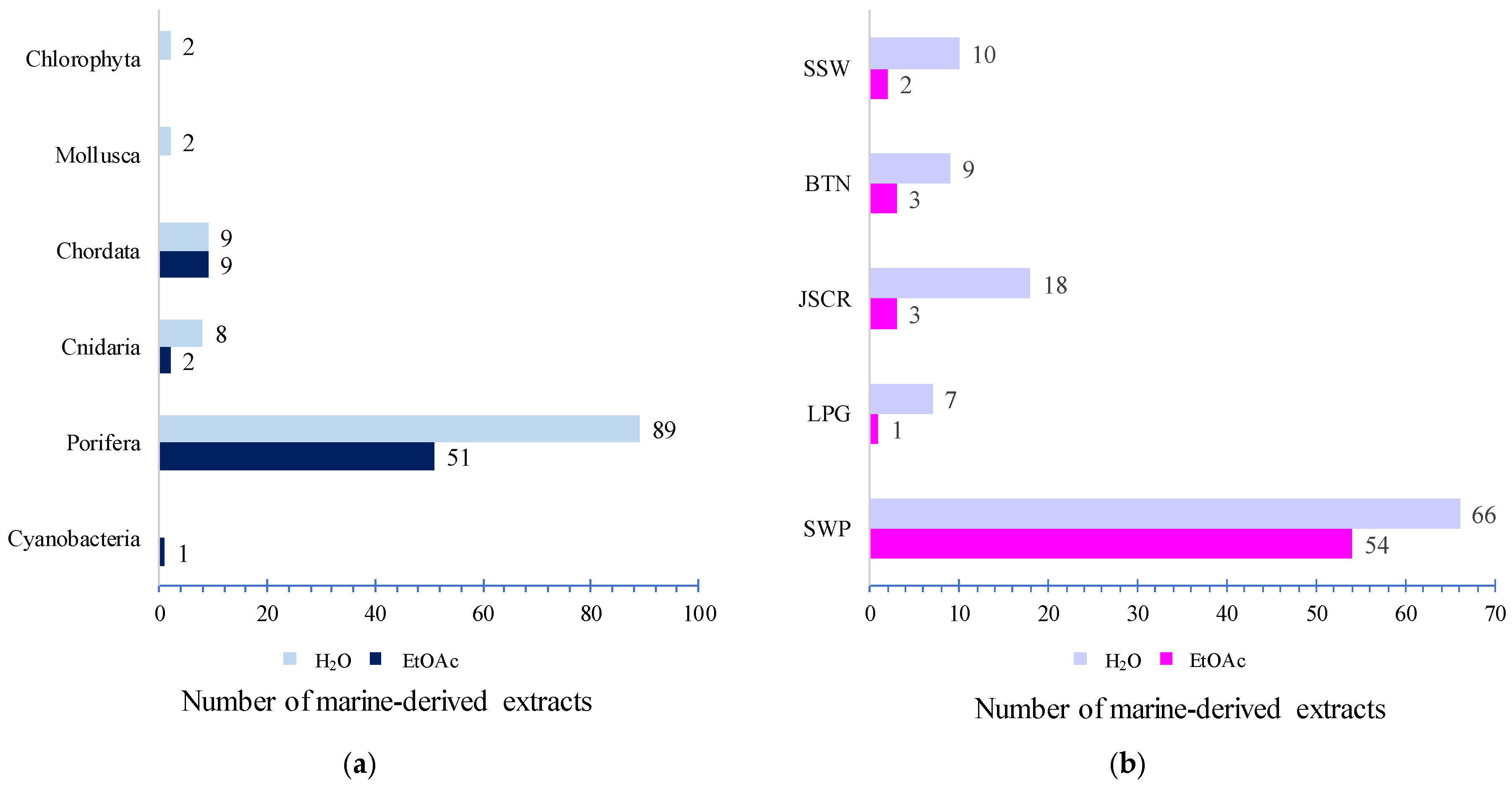
2.1. Toxicity of Marine-Derived Extracts Based on the Brine Shrimp (Artemia salina) Lethality Assay
2.2. Antibacterial Activity of Marine-Derived Extracts Against S. aureus and P. aeruginosa
2.3. Biosurfactant Properties of Marine-Derived Extracts
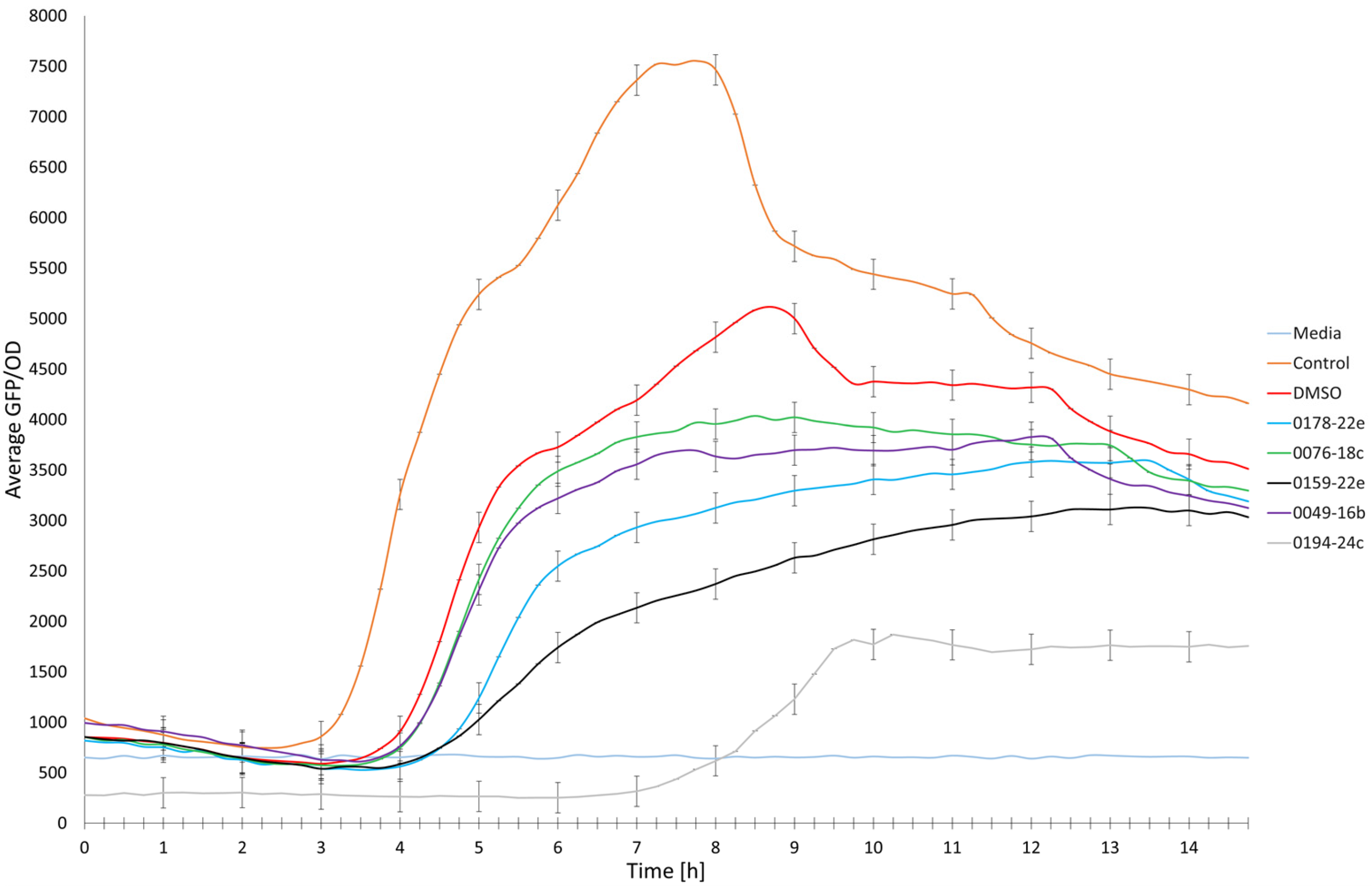
2.4. Anti-QS Activity of Selected Marine-Derived Extracts
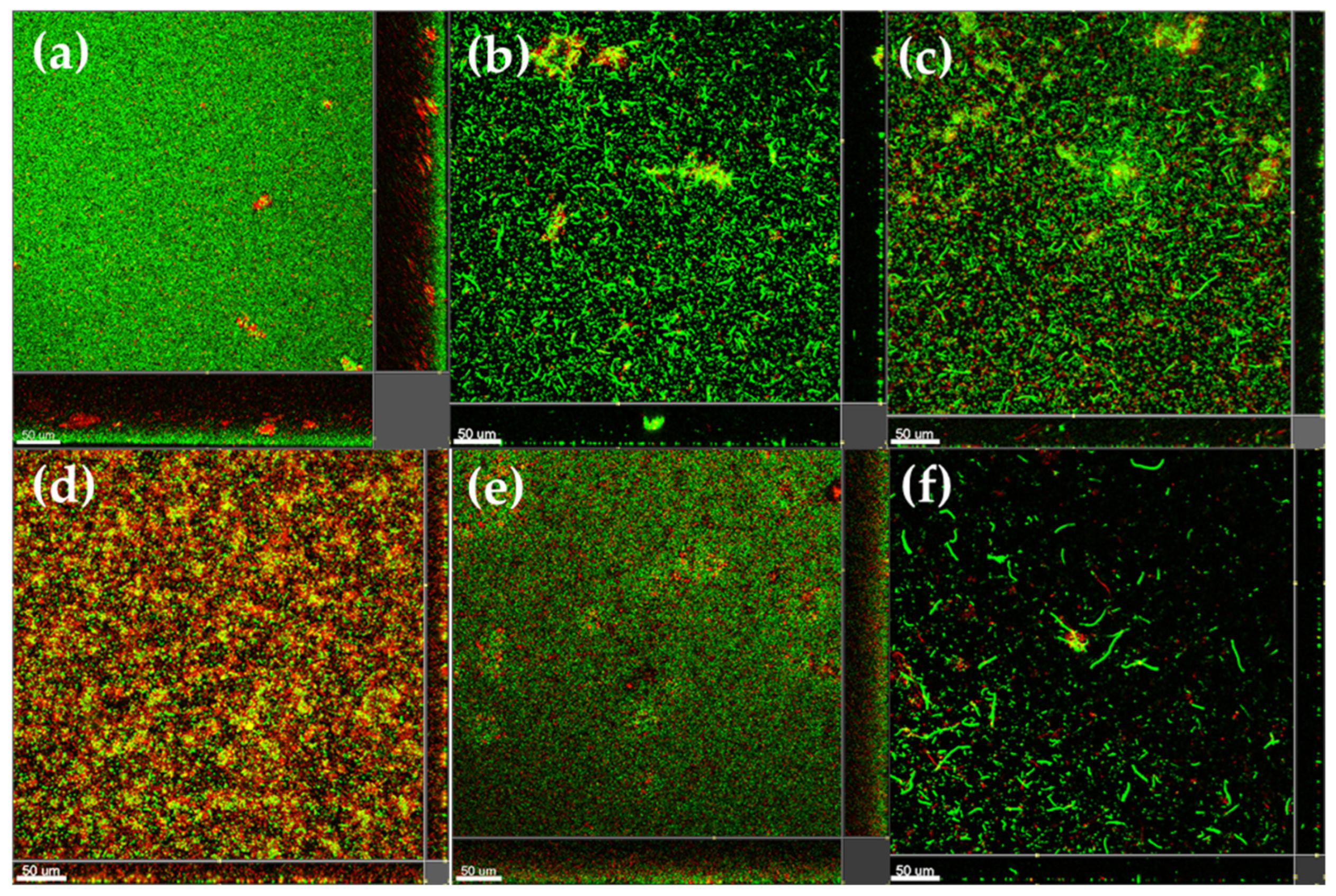
2.5. Anti-Biofilm Activity of Marine-Derived Extracts
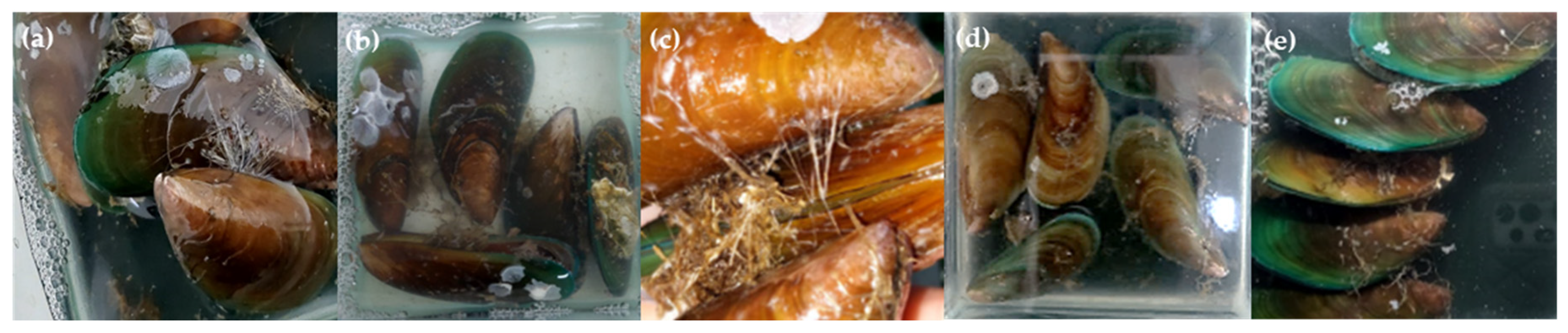
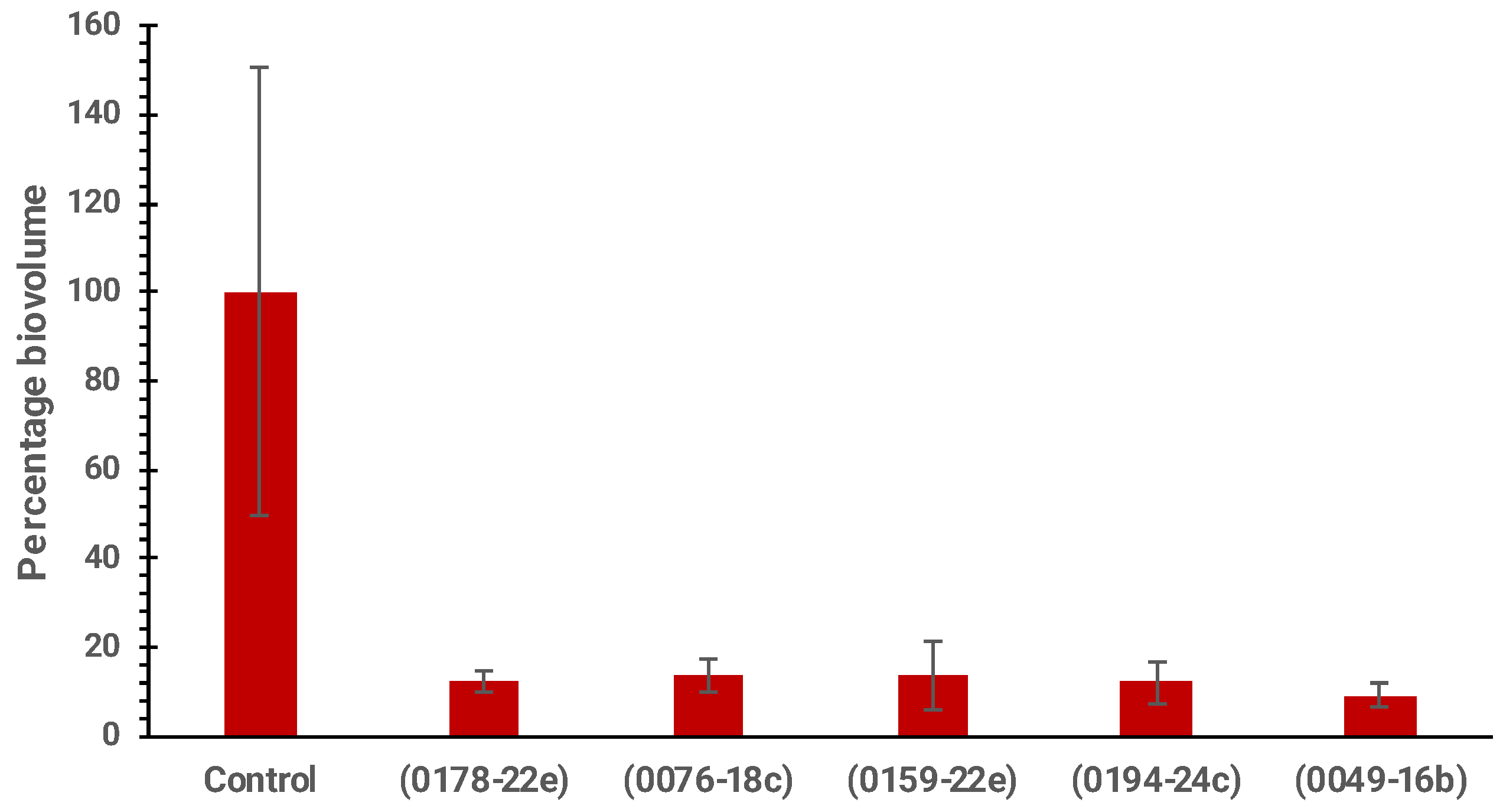
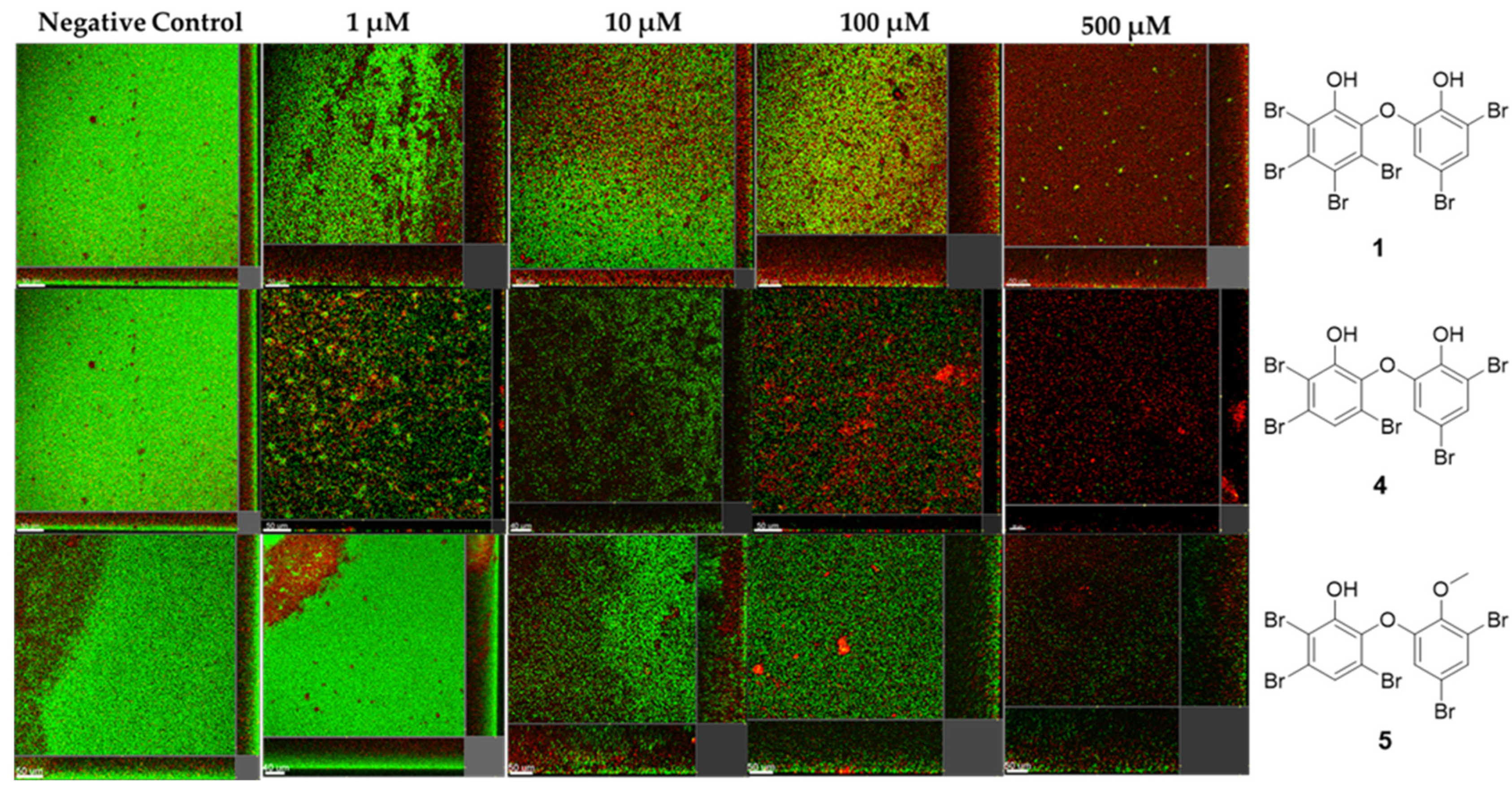
2.6. Anti-Biofouling Activity of Marine-Derived Extracts
2.7. Anti-Biocorrosion of Marine-Derived Extracts
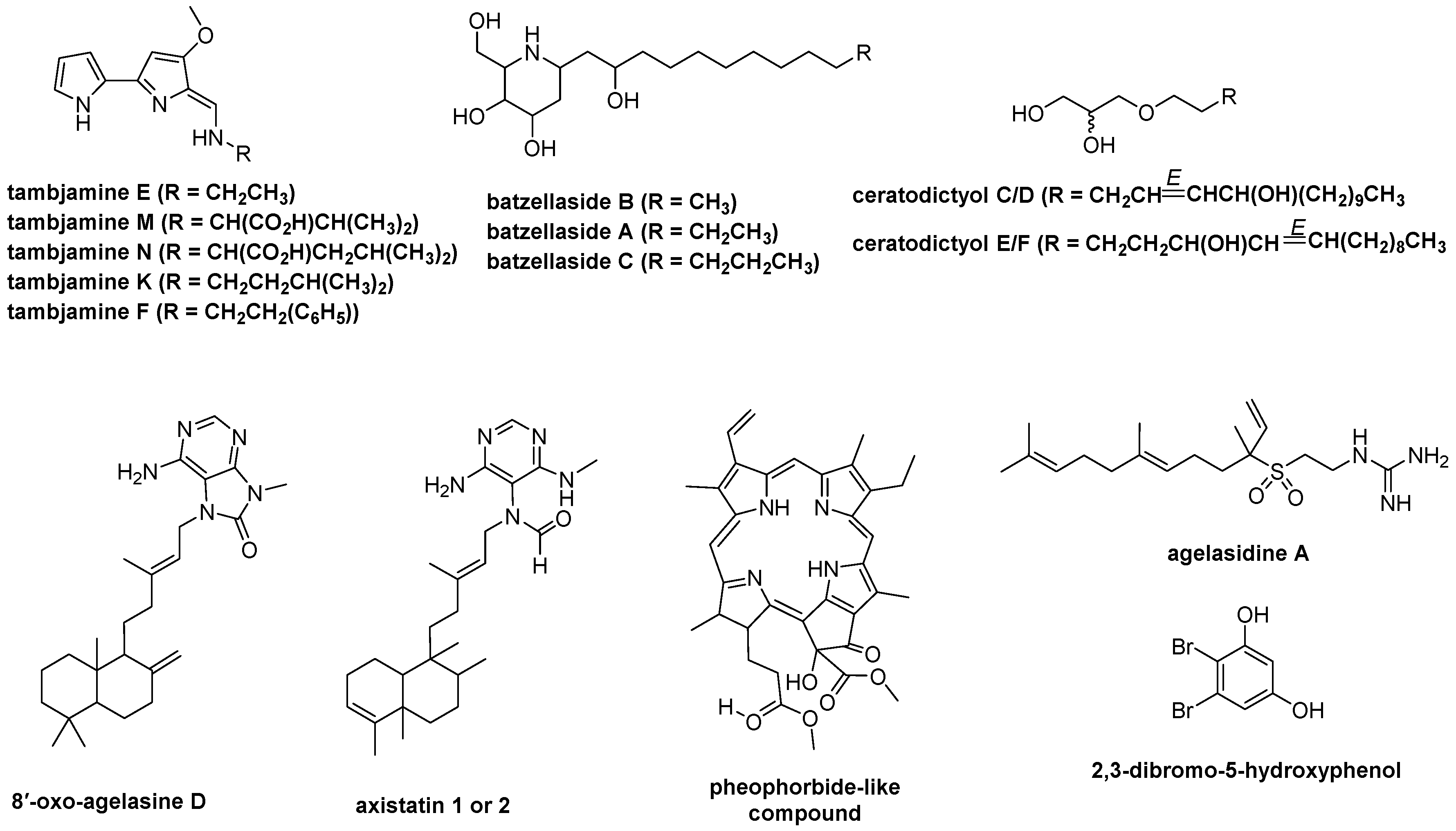
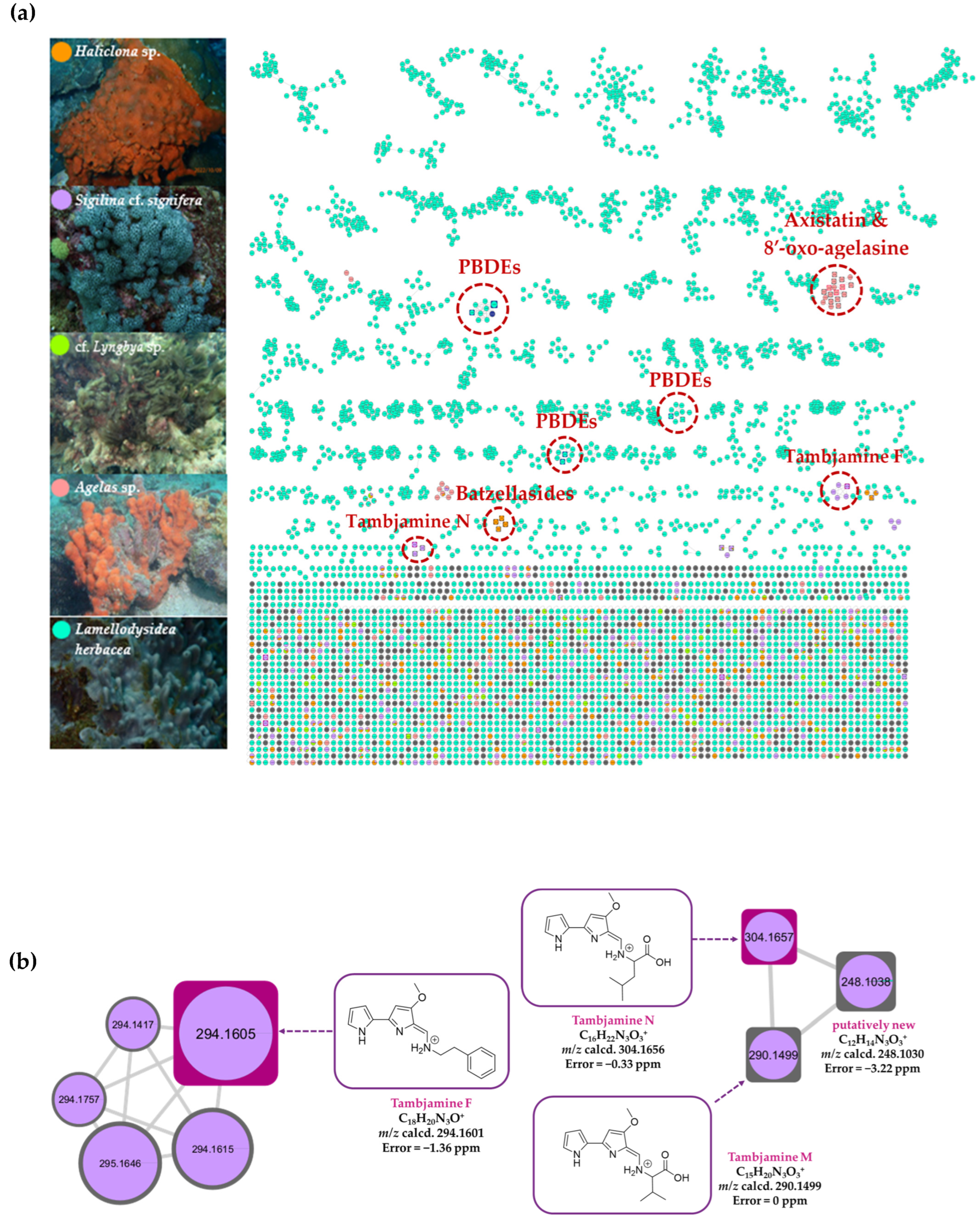
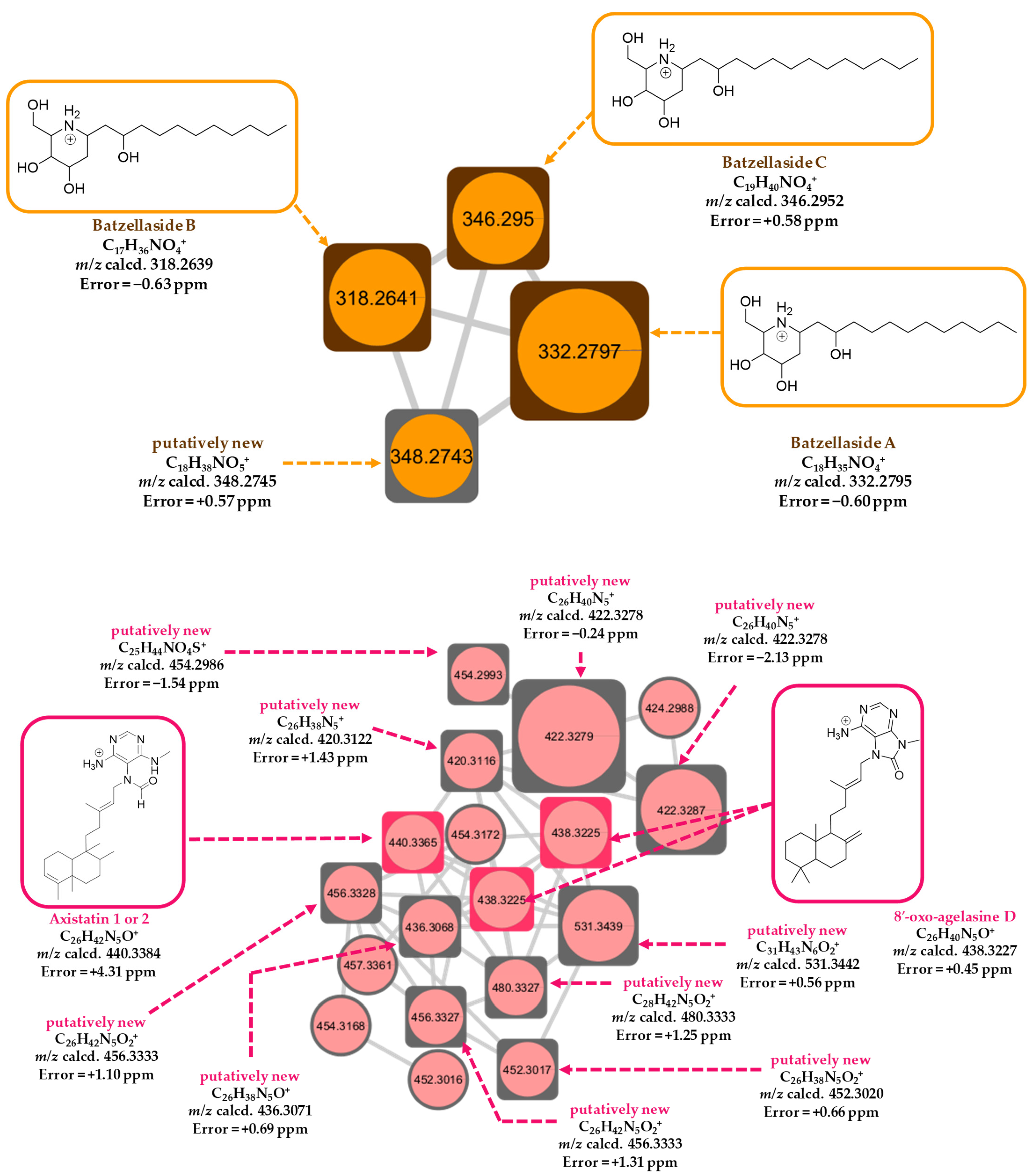
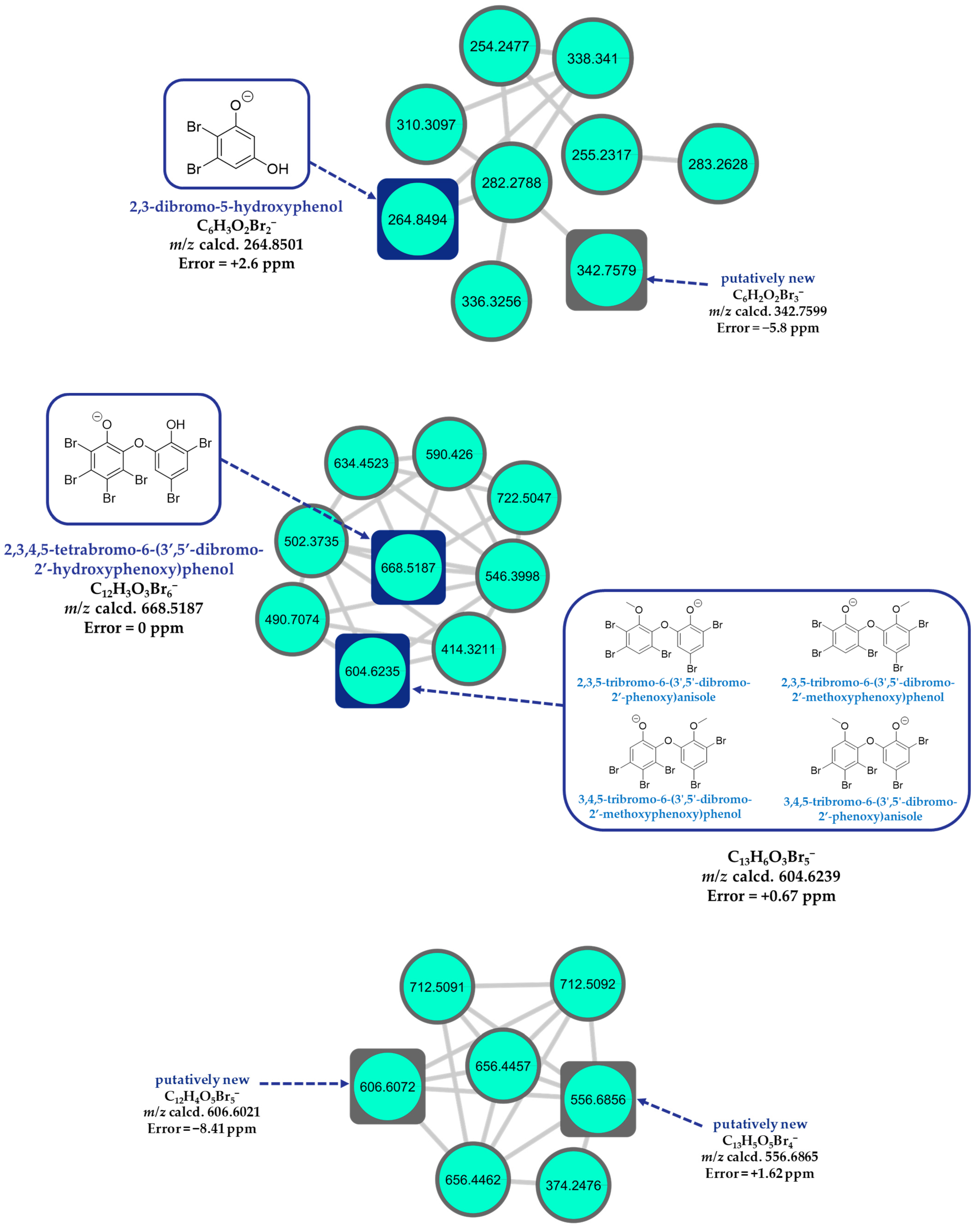
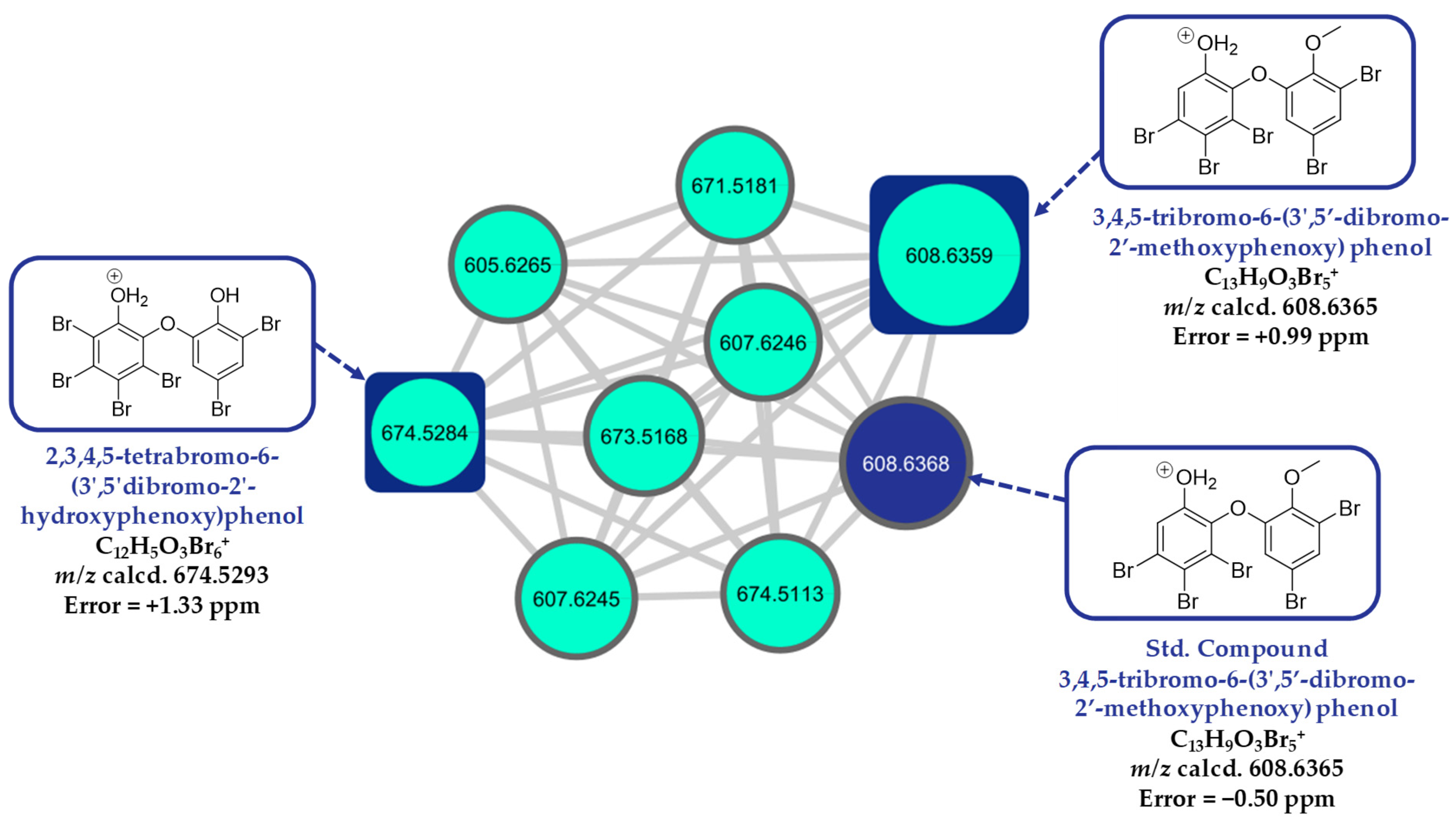
2.8. LC-HR-MS/MS, HRMS-Based Molecular Networking, and Chemoinformatic Database Analyses
2.9. PBDEs as New Anti-QS and Anti-Biofilm Agents
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Biological Material
3.2. Chemical Material
3.3. Extraction and Partition
3.4. Brine Shrimp (Artemia salina) Lethality Assay
3.5. Agar-Plate Diffusion Assay
3.6. Biosurfactant Assay
3.7. Quorum-Sensing Inhibition (QSI) Assay
3.8. Anti-Biofilm Assay
3.9. Anti-Biofouling Assay
3.10. Anti-Biocorrosion Assay
3.11. LC-HR-MS/MS Analysis
3.12. MZmine 4.30 Data Pre-Processing, Feature-Based Molecular Networking, and Chemoinformatic Database Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cahill, P.L.; Moodie, L.W.K.; Hertzer, C.; Pinori, E.; Pavia, E.; Pavia, H.; Hellio, C.; Brimble, M.A.; Svenson, J. Creating new antifoulants using the tools and tactics of medicinal chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2024, 57, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Wang, J.; Tian, L.; Gao, M.; Zhao, J.; Ren, L. Recent advances in emerging integrated antifouling and anticorrosion coatings. Mater. Des. 2022, 213, 110307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Banderas, J. Marine natural products: A promising source of environmentally friendly antifouling agents for the maritime industries. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 858757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.T.; Solanki, J.D.; Patel, K.C.; Nataraj, M. Application of biosurfactants as antifouling agent. In Green Sustainable Process for Chemical Environmental Engineering and Science; Inamuddin, Adetunji, C.O., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglisi, M.; Sneed, J.; Ritson-Williams, R.; Young, R. Marine chemical ecology in benthic environments. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 410–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusetani, N. Antifouling marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, P.Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Fusetani, N. Mini-review: Marine natural products and their synthetic analogs as antifouling compounds: 2009–2014. Biofouling 2015, 31, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.L.; Wu, C.H.; Qian, P.Y. Marine natural products as antifouling molecules—A mini review (2014–2020). Biofouling 2020, 36, 1210–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusetani, N. Biofouling and antifouling. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2004, 21, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tintillier, F.; Moriou, C.; Petek, S.; Fauchon, M.; Hellio, C.; Saulnier, D.; Ekins, M.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Al-Mourabit, A.; Debitus, C. Quorum sensing inhibitory and antifouling activities of new bromotyrosine metabolites from the Polynesian sponge Pseudoceratina n. sp. Mar. Drugs 2022, 18, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.; Almeida, J.R.; Cidade, H.; Correia-da-Silva, M. Proof of concept of natural and synthetic antifouling agents in coatings. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleman-vega, M.; Lozano, I.S.; Guerrero, C.J.H.; Hellio, C.; Quintana, E.T. Exploring antifouling activity of biosurfactants producing marine bacteria isolated from Gulf of California. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.H.; Eom, H.J.; Kim, M.; Jung, J.H.; Rhee, J.S. Nontarget effects of antifouling agents on mortality, hatching success, and acetylcholinesterase activity in the brine shrimp Artemia salina. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2017, 9, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortlepp, S.; Pedpradap, S.; Dobretsov, S.; Proksch, P. Antifouling activity of sponge-derived polybrominated diphenyl ethers and synthetic analogues. Biofouling 2008, 24, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentzer, M.; Riedel, K.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Heydorn, A.; Andersen, J.B.; Parsek, M.R.; Rice, S.A.; Ebert, L.; Molein, S.; Høiby, N.; et al. Inhibition of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm bacteria by a halogenated furanone compound. Microbiology 2002, 148, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.A.; Singh, A.K.; Nerurkar, A. Bacteria associated with marine macroorganisms as potential source of quorum-sensing antagonists. J Basic Microbiol. 2020, 60, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertiani, T.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Ortlepp, S.; van Soest, R.W.; de Voogd, N.J.; Wray, V.; Hentschel, U.; Kozytska, S.; Muller, W.E.; Proksch, P. From anti-fouling to biofilm inhibition: New cytotoxic secondary metabolites from two Indonesian Agelas sponges. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 1297–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.T.; Salleh, N.F. Marine cyanobacteria: A rich source of structurally unique anti-infectives for drug development. Molecules 2024, 29, 5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, V.J.; Lindquist, N.; Fenical, W. Chemical defenses of the tropical ascidian Atapozoa sp. and its nudibranch predators Nembrotha spp. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1990, 59, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathallah, N.; Tamer, A.; Ibrahim, R.; Kamal, M.; El-Kes, M. The marine sponge genus Dysidea sp: The biological and chemical aspects—A review. Futur J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Lozano, I.; Hernández-Guerrero, C.J.; Muñoz-Ochoa, M.; Hellio, C. Biomimetic approaches for the development of new antifouling solutions: Study of incorporation of macroalgae and sponge extracts for the development of new environmentally-friendly coatings. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júnior, A.C.V.; de Castro Nogueira Diniz Pontes, M.; Barbosa, J.P.; Höfling, F.; Araújo, R.M.; Boniek, D.; de Resende Stoianoff, M.A.; Andrande, V.S. Antibiofilm and anti-candidal activities of the extract of the marine sponge Agelas dispar. Mycopathologia 2021, 186, 819–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pech-Puch, D.; Pérez-Povedano, M.; Martinez-Guitian, M.; Lasarte-Monterrubio, C.; Vázquez-Ucha, J.C.; Bou, G.; Rodríguez, J.; Beceiro, A.; Jimenez, C. In vitro and in vivo assessment of the efficacy of bromoageliferin, an alkaloid isolated from the sponge Agelas dilatata, against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhakumari, S.; Kannappan, A.; Pandian, S.K.; Thajuddin, N.; Rajendran, R.B.; Ravi, A.V. Inhibitory effect of marine cyanobacterial extract on biofilm formation and virulence factor production of bacterial pathogens causing vibriosis in aquaculture. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepas, V.; López, Y.; Gabasa, Y.; Martins, C.B.; Ferreira, J.D.; Correia, M.J.; Santos, L.M.A.; Oliveira, F.; Ramos, V.; Reis, M.; et al. Inhibition of bacterial and fungal biofilm formation by 675 extracts from microalgae and cyanobacteria. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, K.E.; Beamish, H.; Garson, M.J.; Skilleter, G.A.; Degnan, B.M. Convergent antifouling activities of structurally distinct bioactive compounds synthesized within two sympatric Haliclona demosponges. Mar. Biotechnol. 2009, 11, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mol, V.L.; Raveendran, T.V.; Parameswaran, P.S. Antifouling activity exhibited by secondary metabolites of the marine sponge, Haliclona exigua (Kirkpatrick). Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2009, 63, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.; Mujad, S.M.; Zulkifli, M.F.R.; Izionworu, V.O.; Ghazali, M.J. A review on application of marine algae as green corrosion inhibitors in acid medium. Vietnam J. Chem. 2022, 60, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royani, A.; Hanafi, M.; Manaf, A. Prospect of plant extracts as eco-friendly biocides for microbiologically influenced corrosion: A review. Int. J. Corros. Scale Inhib. 2022, 11, 862–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Sharad, A.; Usupb, G.; Sahrani, F.K.; Ahmad, A. Bioactivity of natural compounds produced by marine Alcaligenes faecalis as antimicrobial, antibiofilm formation and anti-biocorrosion effect against Desulfovibrio sp. isolated from crude oil fluid. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Tech. Res. 2018, 6, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindquist, N.; Fenical, W. New tamjamine class alkaloids from the marine ascidian Atapozoa sp. and its nudibranch predators. Origin of the tambjamines in Atapozoa. Experientia 1991, 47, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaki, M.; Freire, V.F.; Nicacio, K.J.; Bertonha, A.F.; Nagashima, N.; Sarpong, R.; Padula, V.; Ferreira, A.G.; Berlinck, R.G. Metabolomics reveals minor tambjamines in a marine invertebrate food chain. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 84, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, M.; Irace, C.; Costagliola, F.; Castelluccio, F.; Villani, G.; Calado, G.; Padula, V.; Cimino, G.; Cervera, J.L.; Santamaria, R.; et al. A new cytotoxic tambjamine alkaloid from the Azorean nudibranch Tambja ceutae. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 20, 2668–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segraves, N.L.; Crews, P. A Madagascar sponge Batzella sp. as a source of alkylated iminosugars. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, T.; Ueoka, R.; van Soest, R.W.; Matsunaga, S. Ceratodictyols, 1-glyceryl ethers from the red alga—Sponge association Ceratodictyon spongiosum/Haliclona cymaeformis. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1552–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, L.; Song, W.; Tang, X.; de Voogd, N.J.; Chu, M.; Li, P.; Li, G. Alkaloids and polyketides from the South China Sea sponge Agelas aff. nemoechinata. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14323–14329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Hamann, M.T.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, M.Y.; Gong, X.B.; Xiao, J.R.; Chen, W.S.; Lin, H.W. Antimicrobial metabolites from the Paracel Islands sponge Agelas mauritiana. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.W.; Lin, Y.C.; Chiou, S.F.; Huang, T.Y.; Yang, Y.J.; Wu, S.H.; Chen, S.L.; Lin, C.C.; Wang, H.C.; Yu, M.C.; et al. 2-Guanidinoethanesulfonyl sesquiterpenes from the marine sponge Agelas nakamurai. Tetrahedron Lett. 2022, 103, 153964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, M.A.; Lourenço, A.; Tavares, M.R.; Curto, M.J.M.; Feio, S.S.; Roseiro, J.C. (–)-Agelasidine A from Agelas clathrodes. Z. Für Naturforschung C 2006, 61, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Wu, H.; Kobayashi, J.; Ohizumi, Y.; Hirata, Y.; Higashijima, T.; Miyazawa, T. Agelasidine-A, a novel sesquiterpene possessing antispasmodic activity from the Okinawa Sea sponge Agelas sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1983, 24, 4105–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, G.R.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Bourne, G.T.; Arm, C.A.; Leet, J.E.; Knight, J.C.; Pettit, R.K.; Chapuis, J.C.; Doubek, D.L.; et al. Isolation and structures of axistatins 1–3 from the Republic of Palau marine sponge Agelas axifera Hentschel. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, S.; Ono, F.; Shiomi, Y.; Nakao, T.; Aozasa, O.; Nagate, T.; Kitamura, K.; Yamaguchi, S.; Nishi, M.; Miyata, H. Anti-herpes simplex virus substances produced by the marine green alga, Dunaliella primolecta. J. Appl. Phycol. 1998, 10, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Schmitz, F.J.; Govindan, M.; Abbas, S.A.; Hanson, K.M.; Horton, P.A.; Crews, P.; Laney, M.; Schatzman, R.C. Enzyme inhibitors: New and known polybrominated phenols and diphenyl ethers from four Indo-Pacific Dysidea sponges. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, N.; Tanaka, J.; Setiawan, A.; Trianto, A.; de Voogd, N.J.; Murni, A.; Tanaka, C.; Higa, T. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers from the Indonesian sponge Lamellodysidea herbacea. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calcul, L.; Chow, R.; Oliver, A.G.; Tenney, K.; White, K.N.; Wood, A.W.; Fiorilla, C.; Crews, P. NMR strategy for unraveling structures of bioactive sponge-derived oxy-polyhalogenated diphenyl ethers. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carté, B.; Faulkner, D.J. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers from Dysidea herbacea, Dysidea chlorea and Phyllospongia foliascens. Tetrahedron 1981, 37, 2335–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, R.S.; Croft, K.D.; Wells, R.J. Polybrominated oxydiphenol derivatives from the sponge Dysidea herbacea: Structure determination by analysis of 13C spin-lattice relaxation data for quaternary carbons and 13C-1H coupling constants. Tetrahedron 1981, 37, 2341–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handayani, D.; Edrada, R.A.; Proksch, P.; Wray, V.; Witte, L.; Van Soest, R.W.; Kunzmann, A.; Soedarsono. Four new bioactive polybrominated diphenyl ethers of the sponge Dysidea herbacea from West Sumatra, Indonesia. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Schmitz, F.J. New brominated diphenyl ether from an unidentified species of Dysidea sponge. 13C NMR data for some brominated diphenyl ethers. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 1102–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Skildum, A.; Stromquist, E.; Rose-Hellekant, T.; Chang, L.C. Bioactive polybrominated diphenyl ethers from the marine sponge Dysidea sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 262–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, A.S.; Cheney, K.L.; Urquhart, H.H.; Blanchfield, J.T.; Garson, M.J. The sequestration of oxy-polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the nudibranchs Miamira magnifica and Miamira miamirana. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Namikoshi, M.; Meguro, S.; Nagai, H.; Kobayashi, H.; Yao, X. Isolation and characterization of polybrominated diphenyl ethers as inhibitors of microtubule assembly from the marine sponge Phyllospongia dendyi collected at Palau. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 472–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanif, N.; Tyas, T.A.; Hidayati, L.; Dinelsa, F.F.; Provita, D.; Kinnary, N.R.; Prasetiawan, F.M.; Khalik, G.A.; Mubarok, Z.; Tohir, D.; et al. Oxy-polybrominated diphenyl ethers from the Indonesian marine sponge, Lamellodysidea herbacea: X-ray, SAR, and computational studies. Molecules 2021, 26, 6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai-Kawada, F.E.; Ip, C.G.; Hagiwara, K.A.; Awaya, J.D. Biosynthesis and bioactivity of prodiginine analogs in marine bacteria, Pseudoalteromonas: A mini review. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, K.; Borborah, S.; Chatterjee, A.; Ghosh, M.; Bhattacharya, A. A comprehensive profiling of quorum quenching by bacterial pigments identifies quorum sensing inhibition and antibiofilm action of prodigiosin against Acinetobacter baumannii. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Xiao, H.; Li, H.; Lu, X.; Yan, J.; Nie, H.; Yin, Q. Prodigiosin as an antibiofilm agent against the bacterial biofilm-associated infection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Pathogens 2024, 13, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugnon, M.; Röhrig, U.F.; Goullieux, M.; Perez, M.A.S.; Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissDock 2024: Major enhancements for small-molecule docking with Attracting Cavities and AutoDock Vina. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W324–W332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röhrig, U.F.; Goullieux, M.; Bugnon, M.; Zoete, V. Attracting Cavities 2.0: Improving the flexibility and robustness for small-molecule docking. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2023, 63, 3925–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strus, M.; Mikołajczyk, D.; Machul, A.; Heczko, P.B.; Chronowska, A.; Stochel, G.; Gallienne, E.; Nicolas, C.; Martin, O.R.; Kyziol, A. Effects of the selected iminosugar derivatives on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation. Microb. Drug Resist. 2016, 22, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottomley, M.J.; Muraglia, E.; Bazzo, R.; Carfì, A. Molecular insights into quorum sensing in the human pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa from the structure of the virulence regulator LasR bound to its autoinducer. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 13592–13600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballo, J.L.; Hernández-Inda, Z.; Pérez, P.; García-Grávalos, M.D. A comparison between two brine shrimp assays to in vitro cytotoxicity in marine natural products. BMC Biotechnol. 2002, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, N.; Murni, A.; Tanaka, C.; Tanaka, J. Marine natural products from Indonesian waters. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanif, N.; Safriana, B.S.; Ohlinger, W.S.; Tyas, T.A.; Yanti, H.D.; Dinelsa, F.F.; Tohir, D.; Setiawan, A.; Tanaka, J. Stereochemical assignment of varicosenone, a merosteroid flexible side chain, from the Indonesian sea slug Phyllidia varicosa using NMR and DFT-based NMR calculations. J. App. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 14, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.B.; Sternberg, C.; Poulsen, L.K.; Bjørn, S.P.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S. New unstable variants of green fluorescent protein for studies of transient gene expression in bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1988, 64, 2240–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, D.J.; Maaløe, O. DNA replication and the division cycle in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 1967, 23, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, M.C.; Maclean, B.; Burke, R.; Amodei, D.; Ruderman, D.L.; Neumann, S.; Gatto, L.; Fischer, B.; Pratt, B.; Egertson, J.; et al. A cross-platform toolkit for mass spectrometry and proteomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 918–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, R.; Heuckeroth, S.; Korf, A.; Smirnov, A.; Myers, O.; Dyrlund, T.S.; Bushuiev, R.; Murray, K.J.; Hoffmann, N.; Lu, M.; et al. Integrative analysis of multimodal mass spectrometry data in MZmine 3. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with GNPS. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


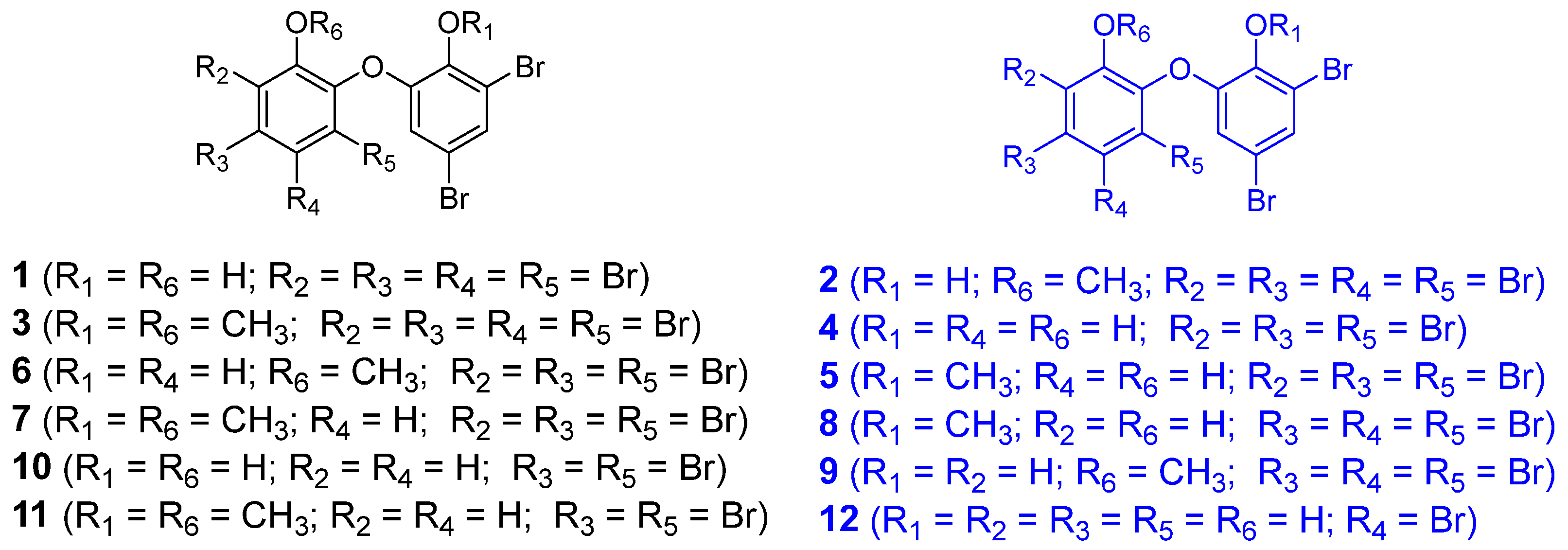
| No. | Sample Code Name | Specimen | Phylum | Brine Shrimp Lethality Assay LC50 (µg/mL) | Antibacterial Assay 100 µg/Disk (EtOAc Extract) (φ, mm ± SD) | Antibacterial Assay 200 µg/Disk (H2O Extract) (φ, mm ± SD) | Location | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EtOAc Extract | H2O Extract | S. aureus | P. aeruginosa | S. aureus | P. aeruginosa | |||||
| 1 | 0178-22e | Haliclona sp. | Porifera | 51.72 | 8.05 | 1.68 ± 0.06 | 3.00 ± 1.41 | NT | NT | SWP |
| 2 | 0065-22e | Plakortis sp. | Porifera | >100 | >100 | 3.49 ± 0.58 | 1.50 ± 0.71 | 3.26 ± 0.58 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | SWP |
| 3 | 0194-24c | Lamellodysidea herbacea | Porifera | 38.35 | >100 | 3.33 ± 0.35 | NA | NA | NA | BTN |
| 4 | 0036-22e | Agelas sp. | Porifera | >100 | >100 | NA | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 2.11 ± 0.18 | 7.50 ± 0.71 | SWP |
| 5 | 0002-22e | Niphates sp. | Porifera | 2.04 | 30.94 | NT | NT | 1.79 ± 0.59 | 5.75 ± 0.35 | SWP |
| 6 | 0001-22e | Achanthostrongylophora ingens | Porifera | 0.76 | >100 | NT | NT | 2.66 ± 1.16 | 3.50 ± 0.71 | SWP |
| 7 | 0021-22e | Neopetrosia sp. | Porifera | 23.61 | 63.59 | NT | NT | 3.19 ± 0.08 | 2.50 ± 0.71 | SWP |
| 8 | 0107-18d | Haliclona sp. | Porifera | 13.50 | 22.95 | NT | NT | 1.25 ± 0.07 | 2.50 ± 0.71 | SSW |
| 9 | 0049-16b | Agelas sp. | Porifera | 6.95 | >100 | NT | NT | 3.44 ± 0.08 | 2.50 ± 0.71 | JSCR |
| 10 | 0015-22e | Haliclona sp. | Porifera | 7.91 | >100 | NT | NT | 3.07 ± 0.06 | 2.25 ± 0.35 | SWP |
| 11 | 0027-22e | Clathria sp. | Porifera | >100 | >100 | NA | 2.00 ± 0.00 | 2.38 ± 0.11 | 2.00 ± 0.00 | SWP |
| 12 | 0041-16b | Achanthostrongylophora ingens | Porifera | 0.16 | >100 | NT | NT | 3.86 ± 0.06 | 3.30 ± 1.41 | JSCR |
| 13 | 0159-22e | Sigilina cf. signifera | Chordata | 41.44 | >100 | 2.24 ± 0.02 | 1.50 ± 0.71 | NT | NT | SWP |
| 14 | 0126-22e | Unidentified | Chordata | >100 | >100 | NT | NT | 3.09 ± 1.21 | 3.75 ± 1.41 | SWP |
| 15 | 0076-18c | cf. Lyngbya sp. | Cyanobacteria | >100 | 1.89 | 2.00 ± 0.53 | 2.50 ± 0.71 | NT | NT | BTN |
| 16 | Swinholide A | - | - | 0.14 ± 0.06 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 17 | Paclitaxel | - | - | 0.08 ± 0.01 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 18 | Manzamine A | - | - | 0.03 ± 0.01 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 19 | Oxacilin | - | - | - | 26.58 ± 0.14 (S. aureus) (5 μg/disk) | - | ||||
| 20 | Chloramphenicol | - | - | - | 17.82 ± 1.24 (S. aureus) (50 μg/disk) | - | ||||
| 21 | Gentamicin | - | - | - | 11.75 ± 0.35 (P. aeruginosa) (1000 μg/disk) | - | ||||
| No. | Sample Code Name | Specimen | Phylum | Extract | Drop-Collapse Assay | Oil Displacement Assay | Location | Biosurfactant Properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Time (s) | Mineral Oil | Olive Oil | ||||||||||
| Mineral Oil | Olive Oil | Average Time (s) | Average φ (cm) | Average Time (s) | Average φ (cm) | |||||||
| 1 | 0178-22e | Haliclona sp. | Porifera | EtOAc | 1.3 | 13.6 | 1 | 8.6 | 1 | 9 | SWP | ++ |
| 2 | 0194-24c | Lamellodysidea herbacea | Porifera | EtOAc | 3.3 | 7.6 | 1 | 8.6 | 1 | irregular | BTN | ++ c |
| 3 | 0036-22e | Agelas sp. | Porifera | H2O | 2 | 13.6 | - | - | - | - | SWP | ++ |
| 4 | 0002-22e | Niphates sp. | Porifera | H2O | 1.3 | 1.6 | 4.3 | 8.6 | 1 | 7.5 | SWP | ++ |
| 5 | 0021-22e | Neopetrosia sp. | Porifera | H2O | 2.6 | 6 | 4 | 8.6 | 8.6 | 5.6 | SWP | ++ |
| 6 | 0049-16b | Agelas sp. | Porifera | H2O | 3.3 | 14.3 | 6 | 9 | 1 | 9 | JSCR | ++ |
| 7 | 0015-22e | Haliclona sp. | Porifera | H2O | 2.3 | 12.6 | 4 | 8.6 | 1 | 9 | SWP | ++ |
| 8 | 0159-22e | Sigilina cf. signifera | Chordata | EtOAc | 3.6 | 4.3 | 3 | 9 | 1 | 8.1 | SWP | ++ |
| 9 | 0076-18c | cf. Lyngbya sp. | Cyanobacteria | EtOAc | 3 | 12 | 2.6 | 8.6 | 1 | 8.8 | BTN | ++ |
| 10 | 1.42% SDS | 6.3 | 17 | 7 | 6.2 | 1 | 1–5 a | - | + | |||
| 11 | 60% aqueous MeOH | 22 | 72 | 62.66 | 7.2 | 1 | ≤1 b | - | - | |||
| No. | Sample Code | Specimen | Phylum | Corrosion Rate (mpy) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 35 µg/mL | 70 µg/mL | ||||
| 1 | 0178-22e | Haliclona sp. | Porifera | 14.10 ± 0.71 | 7.33 ± 1.19 |
| 2 | 0076-18c | cf. Lyngbya sp. | Cyanobacteria | 14.85 ± 1.70 | 9.22 ± 1.83 |
| 3 | 0159-22e | Sigilina cf. signifera | Chordata | 10.70 ± 1.70 | 7.72 ± 1.74 |
| 4 | 0194-24c | Lamellodysidea herbacea | Porifera | 7.87 ± 0.86 | 4.64 ± 0.52 |
| 5 | 0049-16b | Agelas sp. | Porifera | 12.54 ± 0.74 | 8.18 ± 1.70 |
| 6 | Tetracorr CI-2915 | positive control | 13.60 ± 1.70 | 12.00 ± 1.70 | |
| 7 | Seawater | negative control | 15.60 ± 2.12 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hanif, N.; Miftah, J.A.; Yanti, H.D.; Oluwabusola, E.T.; Zahra, V.A.; Salleh, N.F.; Kundukad, B.; Tan, L.T.; Voogd, N.J.d.; Rachmania, N.; et al. Integrated Biological and Chemical Investigation of Indonesian Marine Organisms Targeting Anti-Quorum-Sensing, Anti-Biofilm, Anti-Biofouling, and Anti-Biocorrosion Activities. Molecules 2025, 30, 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061202
Hanif N, Miftah JA, Yanti HD, Oluwabusola ET, Zahra VA, Salleh NF, Kundukad B, Tan LT, Voogd NJd, Rachmania N, et al. Integrated Biological and Chemical Investigation of Indonesian Marine Organisms Targeting Anti-Quorum-Sensing, Anti-Biofilm, Anti-Biofouling, and Anti-Biocorrosion Activities. Molecules. 2025; 30(6):1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061202
Chicago/Turabian StyleHanif, Novriyandi, Jihan Azmi Miftah, Henny Dwi Yanti, Emmanuel Tope Oluwabusola, Vira Amanda Zahra, Nurul Farhana Salleh, Binu Kundukad, Lik Tong Tan, Nicole J. de Voogd, Nisa Rachmania, and et al. 2025. "Integrated Biological and Chemical Investigation of Indonesian Marine Organisms Targeting Anti-Quorum-Sensing, Anti-Biofilm, Anti-Biofouling, and Anti-Biocorrosion Activities" Molecules 30, no. 6: 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061202
APA StyleHanif, N., Miftah, J. A., Yanti, H. D., Oluwabusola, E. T., Zahra, V. A., Salleh, N. F., Kundukad, B., Tan, L. T., Voogd, N. J. d., Rachmania, N., Jaspars, M., Kjelleberg, S., Noviendri, D., Murni, A., & Tanaka, J. (2025). Integrated Biological and Chemical Investigation of Indonesian Marine Organisms Targeting Anti-Quorum-Sensing, Anti-Biofilm, Anti-Biofouling, and Anti-Biocorrosion Activities. Molecules, 30(6), 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061202








