Synthesis, Structure and Iodine Adsorption Properties of a Ni Cluster-Based Supramolecular Framework
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
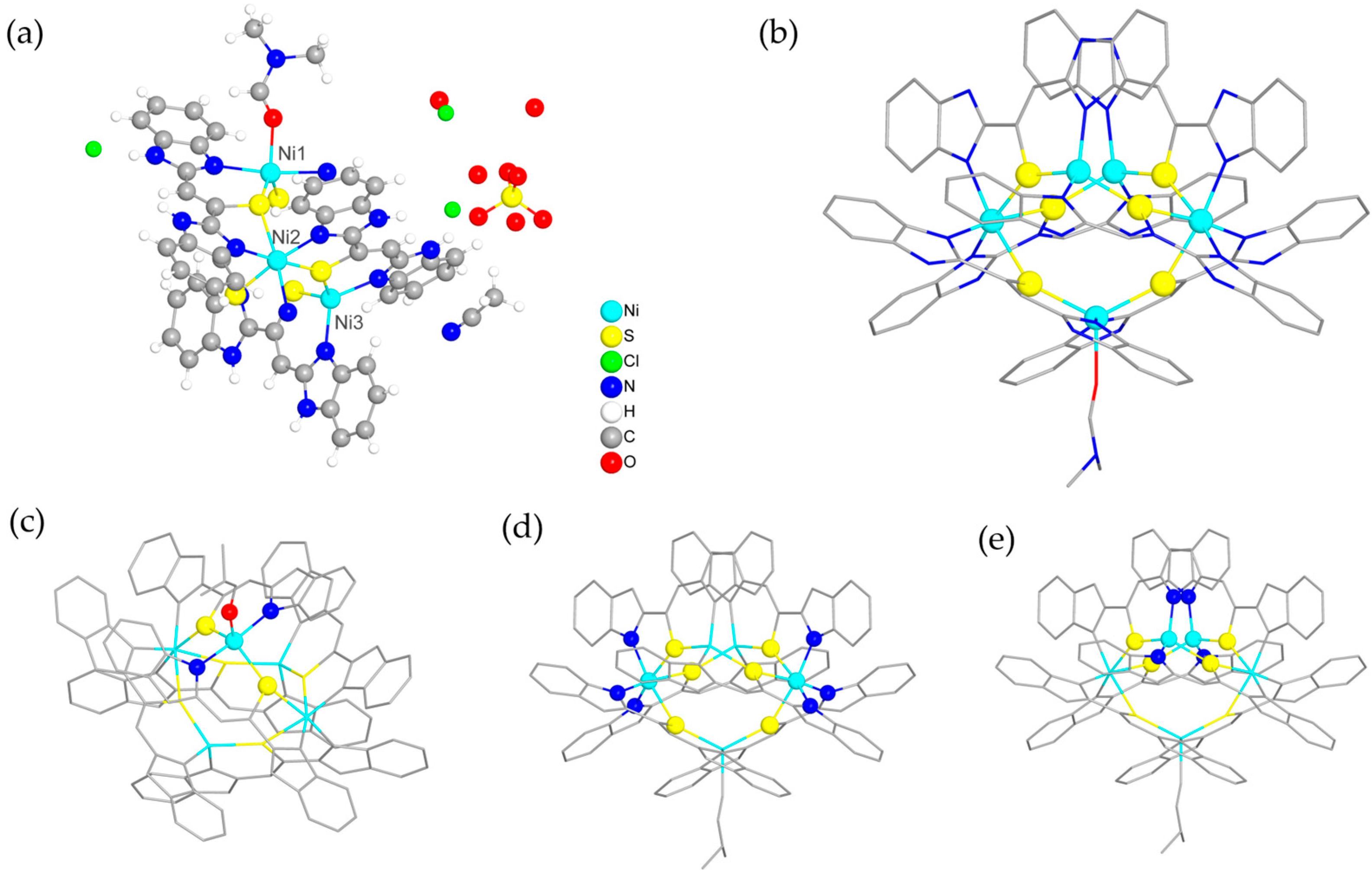
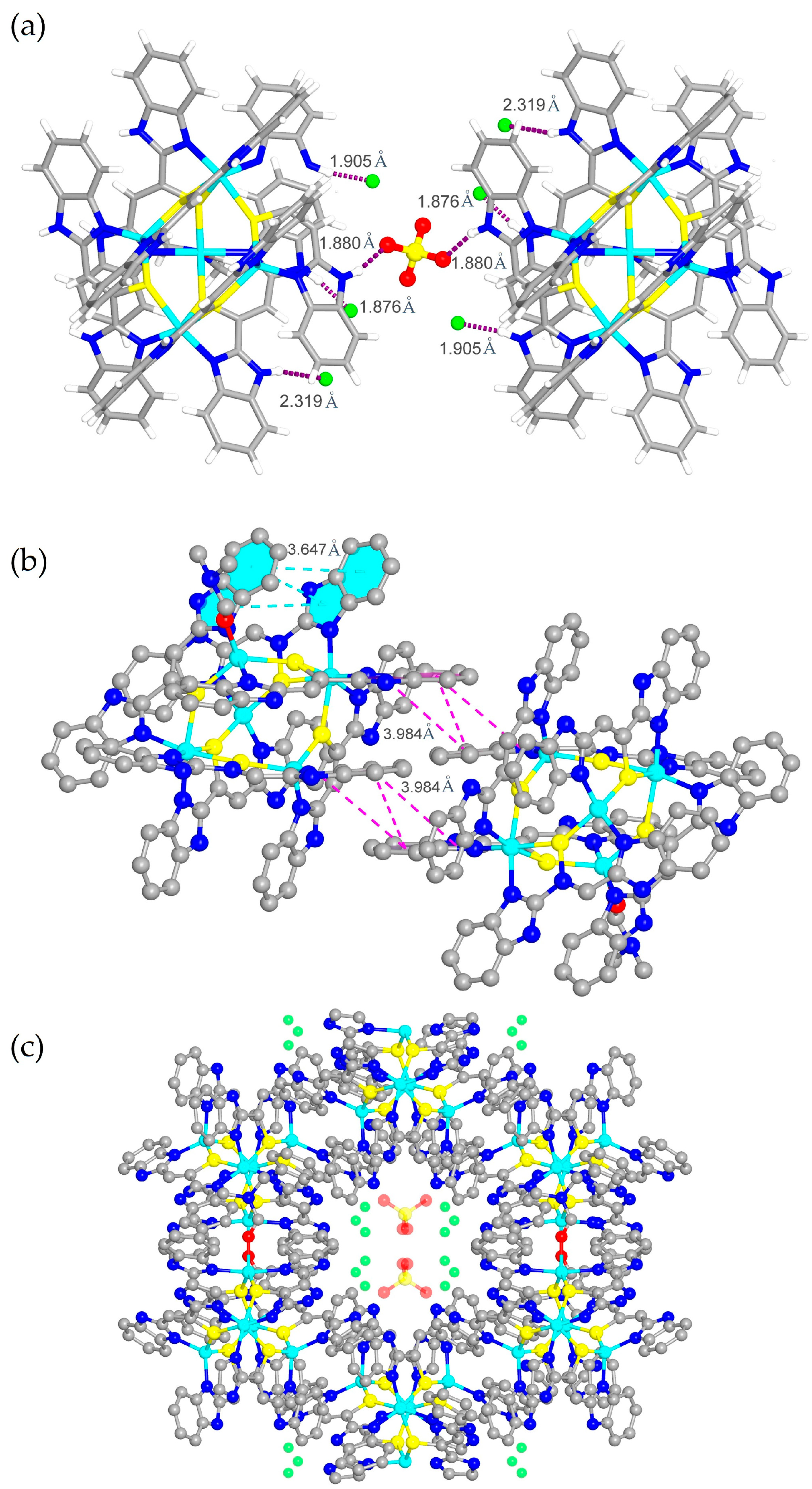
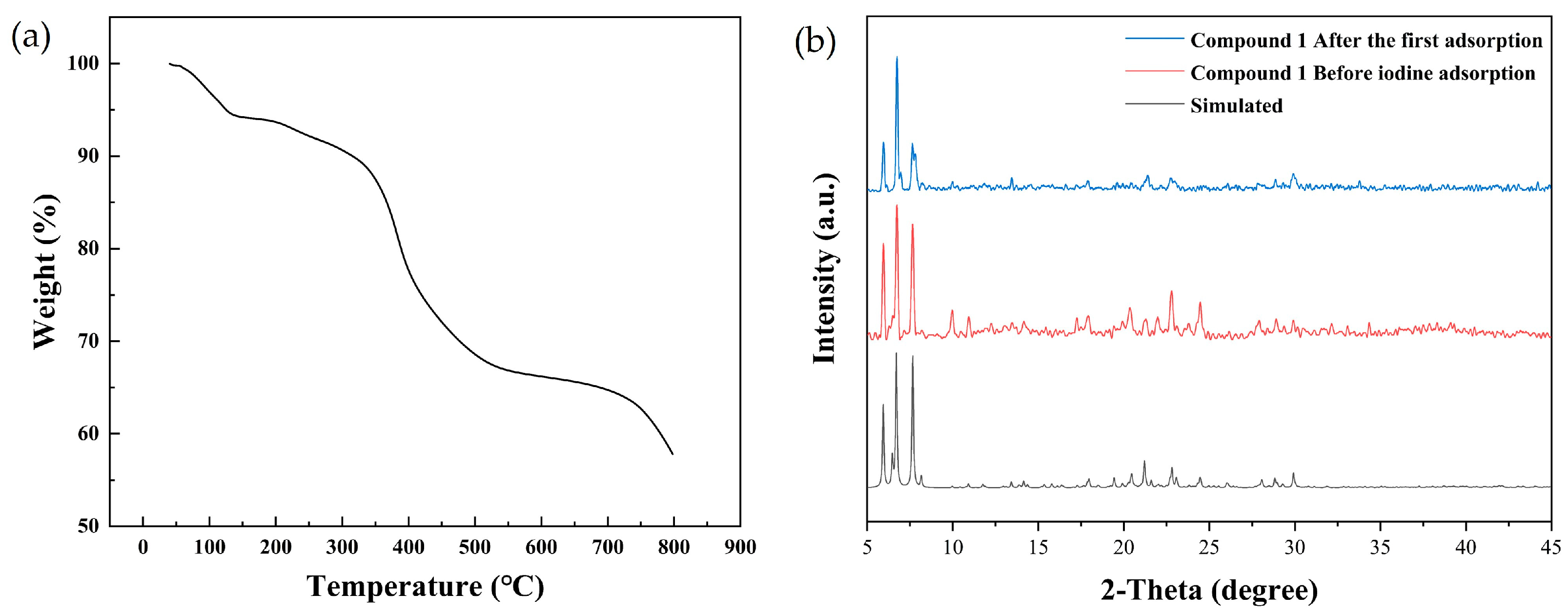
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Compound 1
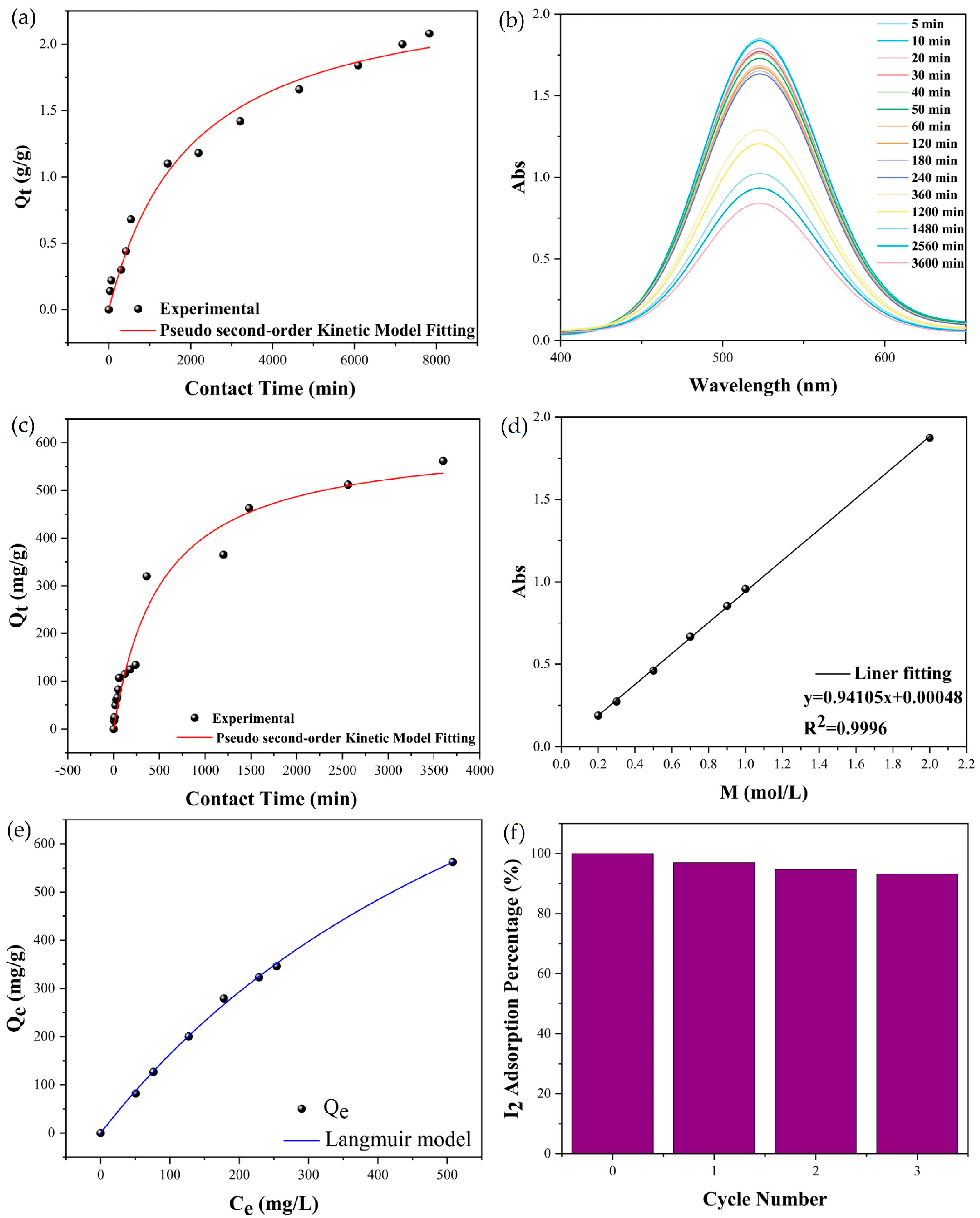
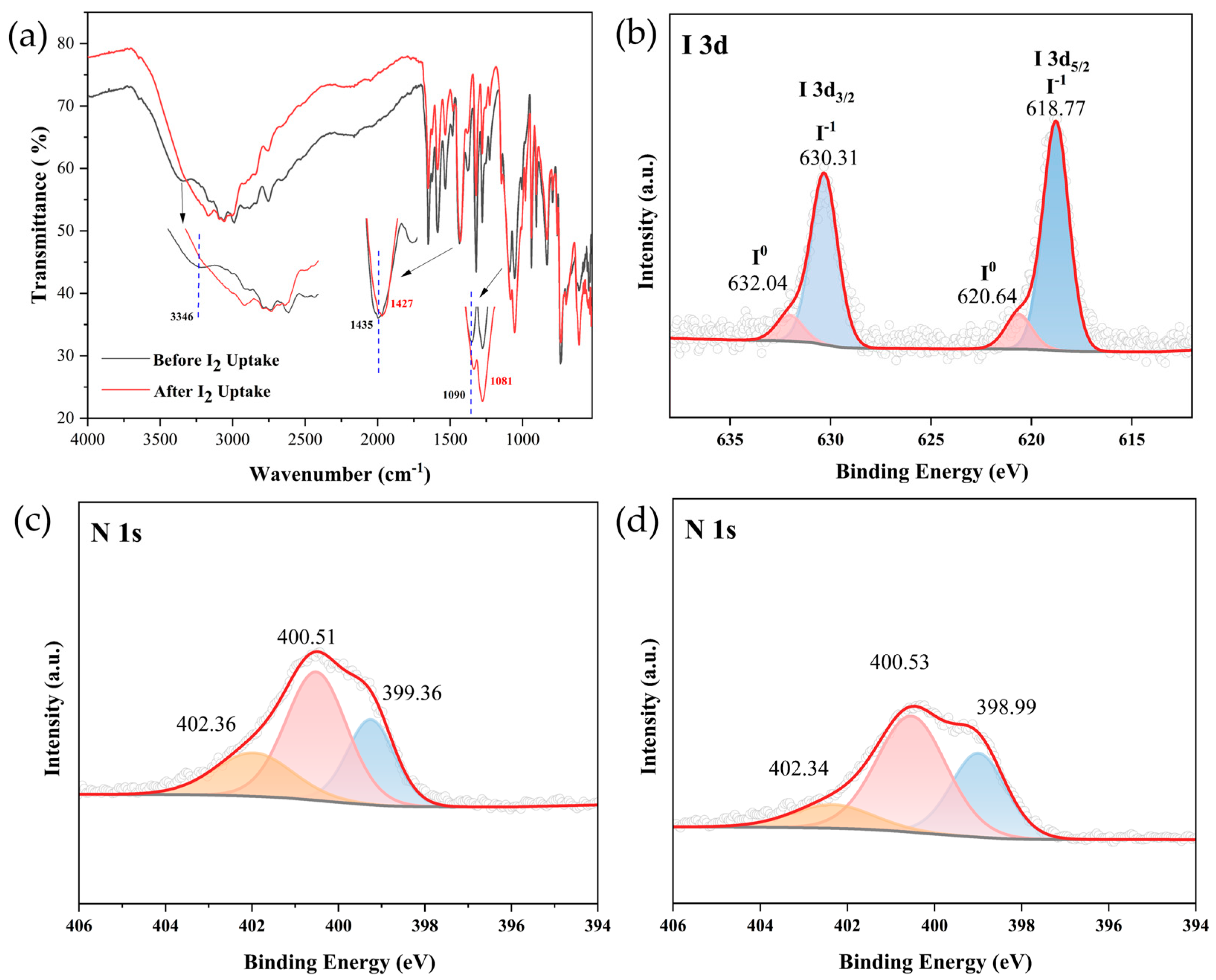
2.2. Iodine Adsorption of Compound 1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of Compound 1
4.2. Characterization
4.3. Crystallography
4.4. Iodine Adsorption Study
4.5. Iodine Adsorption Experiments
4.5.1. Gaseous Iodine Adsorption of Compound 1
4.5.2. Iodine Adsorption in Solution of Compound 1
4.5.3. Iodine Release and Recyclability of Compound 1
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michaelides, E.E.; Michaelides, D.N. Impact of nuclear energy on fossil fuel substitution. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2020, 366, 110742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Cui, D.; Zhang, S.R.; Xu, Y.H.; Jiang, D.L. Iodine capture in porous organic polymers and metal-organic frameworks materials. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 1571–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, B.J.; Vienna, J.D.; Strachan, D.M.; McCloy, J.S.; Jerden, J.L. Materials and processes for the effective capture and immobilization of radioiodine: A review. J. Nucl. Mater. 2016, 470, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhauser, G. Fukushima’s Forgotten Radionuclides: A Review of the Understudied Radioactive Emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4649–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denning, R.; Mubayi, V. Insights into the Societal Risk of Nuclear Power Plant Accidents. Risk Anal. 2017, 37, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eales, J.G. The relationship between ingested thyroid hormones, thyroid homeostasis and iodine metabolism in humans and teleost fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2019, 208, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, A.P.; Benin, A.I.; Ockwig, N.W.; O’Keeffe, M.; Matzger, A.J.; Yaghi, O.M. Porous, crystalline, covalent organic frameworks. Science 2005, 310, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.L.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Shui, F.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Wang, J.H.; Yi, M.; You, Z.F.; Yang, S.Q.; Yang, R.F.; et al. Porous Organic Cage as an Efficient Platform for Industrial Radioactive Iodine Capture. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 136, e202411342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.Y.; Lou, Z.C.; Hu, L.R.; Dou, W.T.; Zhao, X.L.; Li, X.D.; Fang, J.F.; Qian, X.H.; Yang, H.B.; Xu, L. Metal-organic cages for efficient capture and convenient detection of iodine from vapor and aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 154091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurisingal, J.F.; Yun, H.; Hong, C.S. Porous organic materials for iodine adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 458, 131835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.R.; Maddock, J.; Nenoff, T.M.; Denecke, M.A.; Yang, S.H.; Schröder, M. Adsorption of iodine in metal-organic framework materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 3243–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Lin, Q.; Gao, Y.; Ji, X.; Sessler, J.L.; Wang, H. Recent advances in iodine adsorption from water. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 511, 215860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.Y.; Fang, W.H.; Sun, Y.Y.; Wang, S.T.; Zhang, J. Mesoporous Assembly of Aluminum Molecular Rings for Iodine Capture. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 2325–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suebphanpho, J.; Wannapaiboon, S.; Youngme, S.; Boonmak, J. Bifunctional Dinuclear Complexes Based on Iminodiacetate and 1,2-Di(4-pyridyl)ethylene: Crystal Structures, Vapochromism, and Iodine Adsorption. Cryst. Growth Des. 2021, 20, 7439–7449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.T.; Tu, C.Z.; Yin, H.J.; Liu, J.J.; Cheng, F.X.; Luo, F. Molecular Iodine Capture by Covalent Organic Frameworks. Molecules 2022, 27, 9045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falaise, C.; Volkringer, C.; Facqueur, J.; Bousquet, T.; Gasnot, L.; Loiseau, T. Capture of iodine in highly stable metal-organic frameworks: A systematic study. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 10320–10322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Z.L.; Wang, Y.; Wei, C.T.; Ai, K.L.; Lu, L.H. Hydrogen bond-mediated strong adsorbent-I3-interactions enable high-efficiency radioiodine capture. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.R.; da Silva, I.; Fazzi, R.; Sheveleva, A.M.; Han, X.; Spencer, B.F.; Sapchenko, S.A.; Tuna, F.; McInnes, E.J.L.; Li, M.; et al. Iodine Adsorption in a Redox-Active Metal-Organic Framework: Electrical Conductivity Induced by Host-Guest Charge-Transfer. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 14145–14150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, P.; Ai, Z.T.; Hu, H.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.L.; Gao, X.P.; Qian, J.Y.; Su, X.F.; Xiao, S.T.; Xu, H.J.; et al. Synthesis of Electron-Rich Porous Organic Polymers via Schiff-Base Chemistry for Efficient Iodine Capture. Molecules 2022, 27, 5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Ge, R.L.; Song, X.D.; Xing, X.Q.; Jiang, Q.K.; Lu, H.; Hao, C.; Guo, X.W.; Gao, Y.A.; et al. A 3D Covalent Organic Framework with Exceptionally High Iodine Capture Capability. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, D.N.; Deng, S.B.; He, C.H.; Li, J.; Wang, H.B.; Jiang, C.X.; Yu, G.; Wiesner, M.R. Intercalation of rigid molecules between carbon nanotubes for adsorption enhancement of typical pharmaceuticals. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 332, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachuri, Y.; Bisht, K.K.; Parmar, B.; Suresh, E. Luminescent MOFs comprising mixed tritopic linkers and Cd (II)/Zn (II) nodes for selective detection of organic nitro compounds and iodine capture. J. Solid State Chem. 2015, 223, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.X.; Zhao, C.W.; Wang, J.C.; Li, Y.A.; Dong, Y.B. Micro-Cu4I4-MOF: Reversible iodine adsorption and catalytic properties for tandem reaction of Friedel-Crafts alkylation of indoles with acetals. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 12702–12705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Zhao, C.W.; Ma, J.P.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Q.K.; Dong, Y.B. A Ni(II)-MOF: Reversible guest adsorption and heterogeneous catalytic properties for silylcyanation of aromatic aldehydes. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 839–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlana, G.; Ramon, G.; Bourne, S.A. A 4-fold interpenetrated diamondoid metal-organic framework with large channels exhibiting solvent sorption properties and high iodine capture. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 231, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Sun, L.X.; Xing, Y.H.; Bai, F.Y. A double-walled thorium-based metal-organic framework as a promising dual-function absorbent for efficiently capturing iodine and dyes. Cryst. Growth Des. 2019, 19, 5686–5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, P.; Mandal, N.; Roopesh, M.; Gopalakrishnan, H.; Datta, A.; Mandal, S. Enhancement in electrical conductivity of a porous indium based metal-organic framework upon I2 uptake: Combined experimental and theoretical investigations. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 4836–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arici, M.; Yesilel, O.Z.; Tas, M.; Demiral, H. Effect of solvent molecule in pore for flexible porous coordination polymer upon gas adsorption and iodine encapsulation. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 11283–11291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valizadeh, B.; Nguyen, T.N.; Smit, B.; Stylianou, K.C. Porous metal-organic framework@polymer beads for iodine capture and recovery using a gas-sparged column. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1801596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBoer, G.; Burnett, J.W.; Young, M.A. Molecular product formation from the charge-transfer state of C6H6-I2. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1996, 259, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammal, S.S.C.; Ananthavel, S.P.; Venuvanalingam, P.; Hegde, M.S. UVPES and ab initio molecular orbital studies on the electron donor-acceptor complexes of bromine with methylamines. J. Phys. Chem. A 1997, 101, 1155–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harijan, D.K.L.; Chandra, V.; Yoon, T.; Kim, K.S. Radioactive iodine capture and storage from water using magnetite nanoparticles encapsulated in polypyrrole. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, S.H.; Tang, X.; Pan, C.Y.; Li, L.; Tang, J.T.; Yu, G.P. Carbazole-bearing porous organic polymers with a mulberry-like morphology for efficient iodine capture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 27335–27342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Mageed, H.R.; Mustafa, F.M.; Abdel-Latif, M.K. Boron nitride nanoclusters, nanoparticles and nanotubes as a drug carrier for isoniazid anti-tuberculosis drug, computational chemistry approaches. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 40, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Sugimoto, H.; Hishinuma, M. Electrical conductivity of iodine adducts of nylon-6 and other nonconjugated polymers. J. Mater. Sci. 1986, 21, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.B.; Li, C.; Grätzel, M.; Kostecki, R.; Mao, S.S. Nanomaterials for renewable energy production and storage. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7909–7937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, P.K. Infrared depletion spectroscopy suggests mode-specific vibrational dynamics in the hydrogen-bonded aniline-diethyl ether (C6H5-NH2•••OC4H10) complex. J. Phys. Chem. A 2000, 104, 7233–7238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, K.D. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy as a tool for identifying the unique characteristic bands of lipid in oilseed components: Confirmed via Ethiopian indigenous desert date fruit. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, R.L.; Gerakines, P.A. Infrared spectra and interstellar sulfur: New laboratory results for H2S and four malodorous thiol ices. Astrophys. J. 2018, 867, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daulay, A.; Astuti, W.; Mufakhir, F.R.; Prasetia, H.; Samada, L.H. Chitosan grafted alginate and polyvinylpyrrolidone as the binder for porous silicon nanoparticles from coal fly ash in lithium-ion batteries. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 952, 117984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheshmani, S.; Mardali, M. Harnessing the synergistic potential of ZnS nanoparticle-interfacing chitosan for enhanced photocatalytic degradation in aqueous media and textile wastewater. J. Polym. Environ. 2024, 32, 5783–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhujel, R.; Rai, S.; Biswas, J.; Swain, B.P. Investigation of structural, chemical bonding and electrochemical performance of rGO-PEDOT: PSS nanocomposites. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2024, 46, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, T.M.; Zhu, Z.M.; Zhang, W.Y.; Wang, Y. A nitrogen-rich fluorescent conjugated microporous polymer with triazine and triphenylamine units for high iodine capture and nitro aromatic compound detection. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 7612–7617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nour, H.F.; El Malah, T.; Khattab, T.A.; Olson, M.A. Template-assisted hydrogelation of a dynamic covalent polyviologen-based supramolecular architecture via donor-acceptor interactions. Mater. Today Chem. 2020, 17, 100289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Zhang, D.S.; Cheng, K.; Li, Z.Y.; Li, P.Z. Effective iodine adsorption by nitrogen-rich nanoporous covalent organic frameworks. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Mabuchi, H.; Irie, T.; Sasaki, K.; Nozaki, M.; Tomioka, R.; Wen, D.; Zhao, Y.; Ben, T.; Negishi, Y. 3D covalent organic framework with “the” topology. Small 2024, 20, 2307666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, L.L.; Garcia-Esparza, A.T.; Sokaras, D.; Qin, J.S.; Feng, L.; Day, G.S.; Chen, W.M.; Drake, H.F.; et al. Exposed Equatorial Positions of Metal Centers via Sequential Ligand Elimination and Installation in MOFs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 10814–10819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Wang, B.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Sun, H.X.; Ren, F.; Mu, P.; Ma, C.H.; Liang, W.D.; Li, A. Novel N-rich porous organic polymers with extremely high uptake for capture and reversible storage of volatile iodine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 338, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Z.; Xie, W.; Yao, C.; Xu, G.J.; Zhang, S.R.; Xu, Y.H. Preparation of sulfur-containing conjugated microporous polymer for adsorbing iodine and Fe3+ sensing. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.R.; Do, X.H.; Cho, K.Y.; Jeong, K.; Baek, K.Y. Amine-functionalized zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) nanocrystals for adsorption of radioactive iodine. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 9852–9861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, J. Interpretation of infrared spectra, a practical approach. Encycl. Anal. Chem. 2006, 12, 10815–10837. [Google Scholar]
- Milosev, I.; Taheri, P.; Kapun, B.; Kozlica, D.K.; Mol, A.; Kokalj, A. The effect of molecular structure of imidazole-based compounds on corrosion inhibition of Cu, Zn, and Cu-Zn alloys. Corros. Sci. 2024, 240, 112328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morizet, Y.; Soudani, S.; Hamon, J.; Paris, M.; Carole, L.; Gautron, E. Iodine dissolution mechanisms in high-pressure aluminoborosilicate glasses and their relationship to oxygen speciation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 22891–22905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, A.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Nagarkar, S.S.; Joarder, B.; Ghosh, S.K. Bi-porous metal-organic framework with hydrophilic and hydrophobic channels: Selective gas sorption and reversible iodine uptake studies. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 9465–9471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.F.; Hu, H.C.; Deng, S.Q.; Cai, S.L.; Fan, J.; Zhang, W.G.; Zheng, S.R. A Ni(ii) metal-organic framework with helical channels for the capture of iodine via guest exchange induced amorphization. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 7144–7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Xie, Q.Y.; Ma, C.F.; Zhang, G.Z. Fouling resistant silicone coating with self-healing induced by metal coordination. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 126870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, J.; Tang, L.; Nan, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhuo, Z.; Zhang, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L. Synthesis, Structure and Iodine Adsorption Properties of a Ni Cluster-Based Supramolecular Framework. Molecules 2025, 30, 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30050989
Qiu J, Tang L, Nan Z, Liu L, Li Q, Wang W, Zhuo Z, Zhang D, Huang Y, Zhang L. Synthesis, Structure and Iodine Adsorption Properties of a Ni Cluster-Based Supramolecular Framework. Molecules. 2025; 30(5):989. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30050989
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Jingyi, Linxia Tang, Ziang Nan, Luyao Liu, Qing Li, Wei Wang, Zhu Zhuo, Dongwei Zhang, Yougui Huang, and Liangliang Zhang. 2025. "Synthesis, Structure and Iodine Adsorption Properties of a Ni Cluster-Based Supramolecular Framework" Molecules 30, no. 5: 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30050989
APA StyleQiu, J., Tang, L., Nan, Z., Liu, L., Li, Q., Wang, W., Zhuo, Z., Zhang, D., Huang, Y., & Zhang, L. (2025). Synthesis, Structure and Iodine Adsorption Properties of a Ni Cluster-Based Supramolecular Framework. Molecules, 30(5), 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30050989





