A Comprehensive Review of the Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Other Applications of Euphorbiae Humifusae Herba
Abstract
1. Introduction
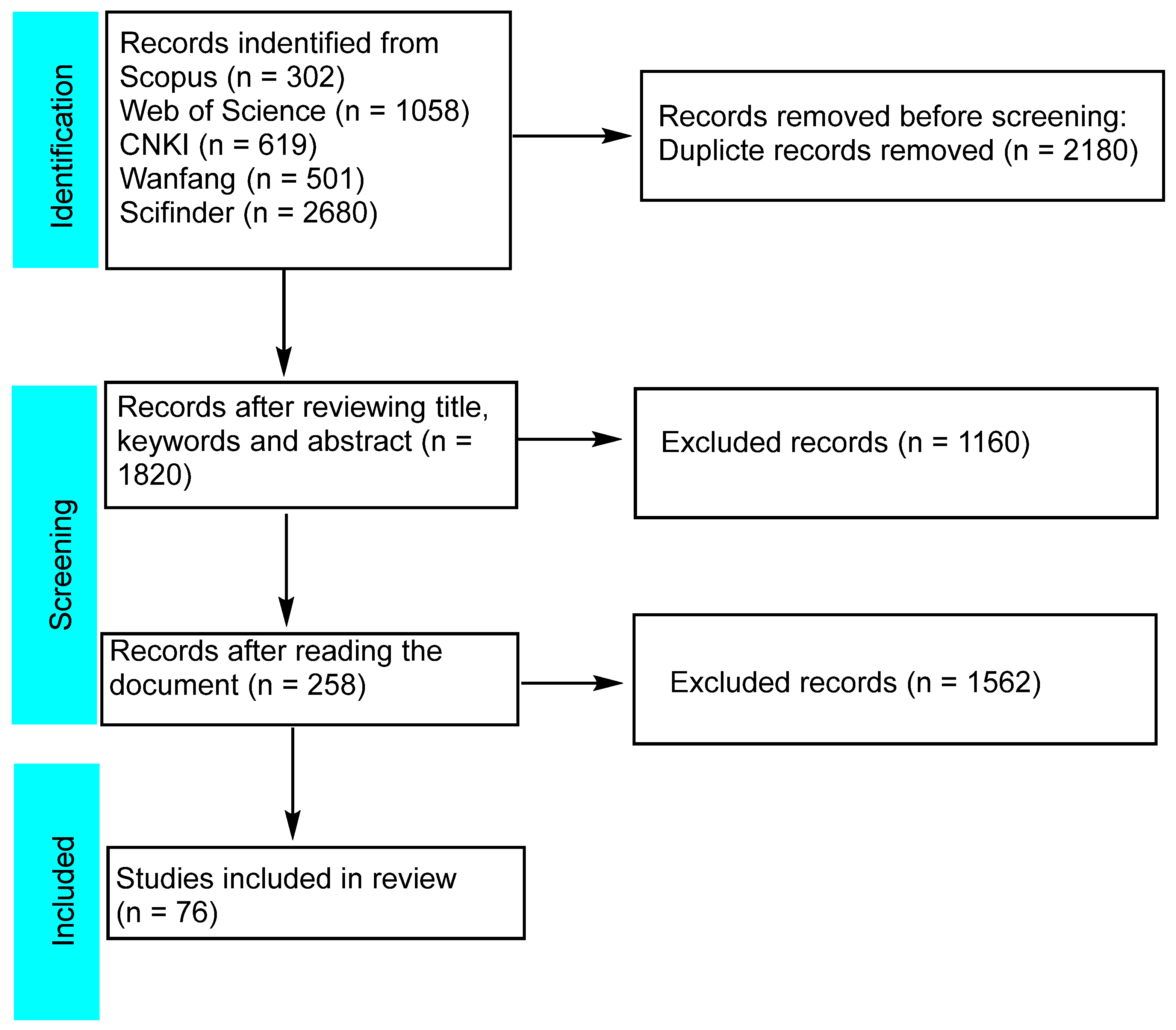
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Exclusion Criteria
- Studies carried out in vitro, in animal clinical studies and used as food
- Studies utilizing the fresh, dried or extracts of EHH
- Phytochemical studies on EHH
- Duplication of data
- The title or the abstract does not meet the inclusion criteria
- The document does not meet the inclusion criteria
3. Botany
4. Traditional Uses
5. Phytochemistry
5.1. Triterpenoids
5.2. Flavonoids
5.3. Phenolic Acids and Tannins
5.4. Alkaloids
5.5. Sterols
5.6. Lactones and Coumarins
5.7. Other Compounds
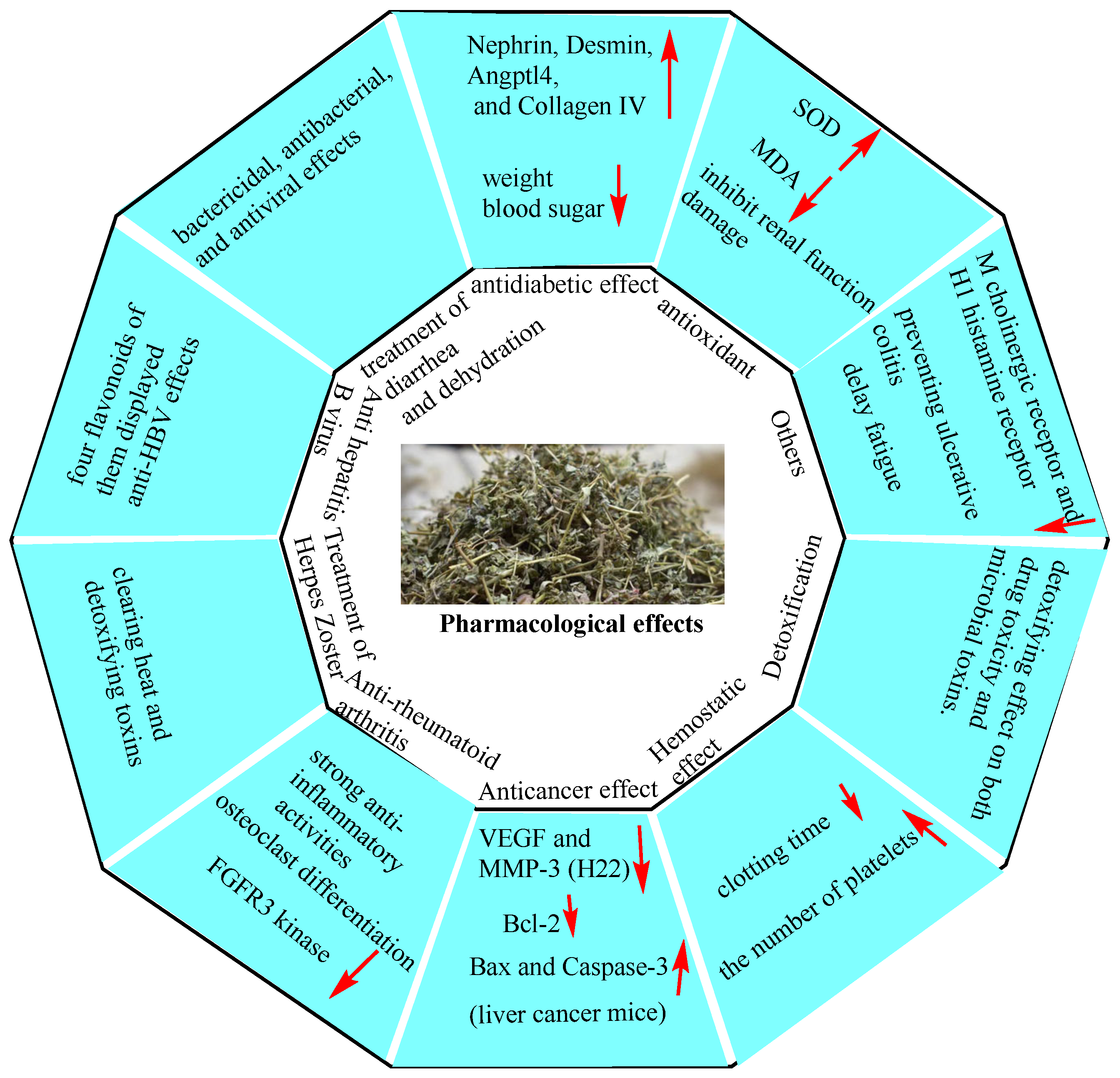
6. Pharmacological Effects
6.1. Hypoglycemic Effect (Diabetes and Diabetic Nephropathy)
6.2. Antioxidant Properties
6.3. Treatment of Diarrhea and Dehydration
6.4. Anti-Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Effects
6.5. Treatment of Herpes Zoster (HZ)
6.6. Anti-Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
6.7. Anticancer Effects
6.8. Hemostatic Effects
6.9. Detoxification
6.10. Others
7. Summary and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AP-1 | Activator protein 1 |
| CHB | Chronic hepatitis B |
| CNKI | China National Knowledge Infrastructure |
| CXCL1 | (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 protein |
| CXCL5 | (C-X-C motif) ligand 5 protein |
| DGGlc | 2,3-Digalloyglucosyl |
| DJC | Dijincao |
| DKD | Diabetic kidney disease |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| EHH | Euphorbiae Humifusae Herba |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| FvGFR3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptors |
| Gal | Galactosyl |
| GGlc | 2-Galloyglucosyl |
| GRham | 2-Galloylrhamosyl |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| IL-1 | Interleukin-1 |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| IL-17 | Interleukin-17 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| IL-2 | Interleukin-2 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-8 | Interleukin-8 |
| IP-10 | Inducible Protein 10 |
| LTB4 | Leukotriene B4 |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| MMP9 | Matrix metalloproteinase 9 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-κB |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandin E2 |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| PKC | Protein kinase C |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| Rut | Rutinosyl |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| SPF | Specific pathogen-free |
| TCM | Traditional Chinese medicine |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor-β |
| Th17 | T helper cell 17 |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| VZV | Varicella-zoster virus |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Wang, L.; Huo, Z.T.; Xu, W.B.; Zhou, P.N.; Nan, W.X.; Guo, H.J.; Zhang, Q.W.; Yang, P.; Alolga, R.N.; Yin, X.J.; et al. Comparative plastomes of eight subgenus Chamaesyce plants and system authentication of Euphorbiae Humifusae Herba. Food Chem. 2024, 447, 139039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medical Science Publisher: Beijing, China, 2020; Volume 1, p. 131. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, S.; Jung, H.; Jung, Y.; Lee, J.; Shin, S.Y.; Yoongho, L.; Lee, Y.H. Identification of the active components inhibiting the expression of matrix metallopeptidase-9 by TNFα in ethyl acetate extract of Euphorbia humifusa Willd. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2019, 62, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyen, B.T.T.; Tai, B.H.; Thao, N.P.; Eun, K.J.; Cha, J.Y.; Xin, M.J.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, Y.H. Anti-inflammatory components of Euphorbia humifusa Willd. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 1895–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, N.; Zhao, J.B.; Chang, S.Q.; Li, S.S.; Liu, S.W.; Wang, C. In vitro fecal fermentation of Euphorbia humifusa-derived polysaccharides and their protective effect against ulcerative colitis in mice. Foods 2023, 12, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Mckenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An undated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2021, 74, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Board, E. Flora of China; Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.J.; Gulnar, D.; Silafu, A. Research progress on the Uighur herb Euphorbia humifusa. J. Med. Pharm. Chin. Minor. 2008, 8, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Shi, M.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y. HPLC fingerprint spectrum of Uighur herb Euphorbiae humifusae. Chin. Wild Plant Resour. 2011, 30, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- An, H.; Gulnar, D.; Li, Z.J.; Silafu, A. Active component of Euphorbia humifusa antifungal activity and mechanism. Chin. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 26, 1162–1165. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.Z.; Gao, Y.C.; Zhang, X.H.; He, X.L. Study on one step granulation process for Euphorbia humifusa granular. J. Tradit. Chin. Vet. Med. 2016, 35, 54–56. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Sun, L.L.; Tang, M.Y.; Feng, B.M.; Pei, Y.H.; Yasukawa, K. Triterpenoids from Euphorbia maculata and their anti-inflammatory effects. Molecules 2018, 23, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.G.; Wu, Q.X.; Shi, Y.P. Triterpenoids and other constituents from Euphorbia humifusa. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2007, 54, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.Z.; Yang, H.Y.; Zhang, L.J.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, K. Anti-inflammatory activities of triterpenoids from Euphorbia humifusa willd. Phytochem. Lett. 2023, 54, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.F.; Su, J.C.; Yu, J.; Zha, H.J.; Wu, J.L.; Fu, X.N.; Cai, Q.; Wan, L.S. Anti-inflammatory lanostane triterpenoids with rearranged spirobi[indene] scaffold and their biogenetically related analogues from Euphorbia maculata. Phytochemistry 2023, 211, 113682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Sun, L.M.; Liu, X.Q.; Li, B.; Wang, Q.; Dong, J.X. Anti-HBV active flavone glucosides from Euphorbia humifusa Willd. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 799–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luyen, B.T.T.; Tai, B.H.; Thao, N.P.; Lee, S.H.; Jang, H.D.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, Y.H. Evaluation of the anti-osteoporosis and antioxidant activities of phenolic compounds from Euphorbia maculata. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2014, 57, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, A.; Rhim, T.J.; Choi, M.Y.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, M.S.; Park, H.J. Simultaneous analysis and peroxynitrite-scavenging activity of galloylated flavonoid glycosides and ellagic acid in Euphorbia supina. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2014, 37, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakotondrabe, T.F.; Fan, M.; Guo, M. Exploring potential antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory flavonoids from Euphorbia humifusa with an integrated strategy. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 980945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y. Studies on the Chemical Constituents and Quality Control of Euphorbia humifusa. Master’s Thesis, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.Z.; He, Y.Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, B. The separation and identification of flavonoids in the Euphorbia humifusa. J. Beijing Med. Coll. 1983, 15, 72–74. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, F.; Tang, N.; Xu, J.; Shi, Y.H.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, J.S. New α-pyrrolidinonoids and glycosides from Euphorbia humifusa. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2008, 10, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.H.; Wang, H.B.; Kong, L.Y. Studies on chemical constituents of Euphorbia humifusa. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2001, 32, 107–108. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. Study on the Material Basis of Anti-Dermatophytes of Euphorbiae Humifusae Herba. Master’s Thesis, Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.Y.; Sun, D.J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.N.; Li, G.Y.; Zhang, K.; Wang, L.; Huang, J.; Chen, L.X. Growth inhibitory effect of paratocarpin E, a prenylated chalcone isolated from Euphorbia humifusa Wild., by induction of autophagy and apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. Bioorg. Chem. 2016, 69, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Amakura, Y.; Liu, Y.Z. Tannins and related polyphenols of Euphorbiaceous plants. XI. three new hydrolyzable tannins and a polyphenol glucoside from Euphorbia humifusa. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1994, 42, 1803–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshiaki, A.; Keita, K.; Tsutomu, H.; Takuo, O.; Takashi, Y.; Isao, A.; Takeshi, S.; Sansei, N. Four new hydrolyzable tannins and an acylated flavonol glycoside from Euphorbia maculata. Can. J. Chem. 1997, 75, 727–733. [Google Scholar]
- Isao, A.; Tsutomu, H.; Yoko, N.; Sugaya, T.; Nishibe, S.; Yoshida, T.; Okuda, T. Tannins and related polyphenols of Euphorbiaceous Plants. VIII. Eumaculin A and Eusupinin A, and accompanying polypbnols from Euphorbia maculata L. and E. Supina Rafin. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1991, 39, 881–883. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Ma, G.L.; Chen, H.W.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Zhu, Z.P.; Xiong, J.; Yang, G.X.; Hu, J.F. Antibacterial and antibiofilm efficacy of the preferred fractions and compounds from Euphorbia humifusa (herba Euphorbiae humifusae) against Staphylococcus aureus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 306, 116177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.G.; Liu, W.X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, X.; Upur, H. Development and validation of a high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detector method for the simultaneous determination of six phenolic compounds in abnormal savda munziq decoction. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2015, 11, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Lu, Y.; Gu, X.Z.; Kang, W.Y. Volatile compounds from Euphorbia humifusa. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2012, 18, 66–68. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Rouzimaimait, R.; Hasan, A.; Zang, D.; Aisa, H.A. A new anti-vitiligo unsaturated fatty glycoside from Euphorbia humifusa Willd. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 37, 2225–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Cai, M.Z.; Wang, H.; Yu, R.P.; Cheng, C.X. Analysis and comparison of trace elements of herba Euphorbiae humifusae in different periods by microwave digestion-atomic absorption spectroscopy. Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 2010, 30, 1975–1978. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Y.; Tian, Y.F.; Liu, C.; Chen, S.; Fan, F.Y.; Zhang, C.; Wu, X. Effect of Euphorbiae humifusa on expression of glomerular podocyte-related proteins in diabetickidney disease rats. Chin. J. Comp. Med. 2023, 33, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.Y. Diabetes Mellitus; Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers: Shanghai, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.L.; Fu, H.; Li, W.W.; Song, F.J.; Song, Y.X.; Yu, Q.; Liu, G.X.; Wang, X.M. Study of effect of Euphorbia Humifuse herb on alleviating insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic model KK-Ay mice. J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2015, 40, 1994–1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.M.; Gao, Z.G.; Zhou, Z.Y. Effect of Euphorbiae Humifusae herba on pancreatic islet beta cells on oxidative stress and apoptosis in diabetic mice. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2015, 21, 120–123. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. Research progress on α-glucosidase inhibitors. Strait Pharm. J. 2009, 21, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, L.; Qin, X.X.; Du, L.X.; Cui, Y.Y.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, C.M. Effects of total flavonoids from Euphorbia humifusa on growth performance, immune function, antioxidant capacity and cecal microbiota of Ross 308 Broilers. China Poult. 2023, 8, 1732–1734. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.X.; Chen, W.Y.; Gong, X.C.; Zhong, X.H. Study on the antioxidant effect of Dijincao on different tissues of mice. Heilongjiang Anim. Sci. Veter. Med. 2008, 6, 91–92. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.T.; Wu, R.Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J. Experimental study on the antioxidant effect of Dijincao and its protective effect on renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Chin. J. Tradit. Med. Sci. Technol. 1999, 6, 892–905. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.S.; Wu, R.N.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ba, G.N.; Sun, F.X.; Wang, Z.M.; Zhao, Z.X. Effects of five traditional Mongolian medicines on scavenging free radical. Shizhen J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 1997, 8, 308–309. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, R.Z.; Zhang, W.; She, J.K.; Qiao, W.; Xue, Y. Effects of total flavonoids from Dijincao on serum aging indexes in aging model mice. Chin. J. Gerontol. 2008, 6, 562–563. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.L. Experience of Cha Ansheng in treating recurrent ulcerative colitis. J. Anhui TCM Coll. 2013, 32, 53–54. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, D.B.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Shi, S.C. Study on influences of ethanol extract from Euphorbia humifusa (EEEH) on smooth muscle of isolated small intestine in rabbits and its mechanism. Chin. Hosp. Pharm. J. 2015, 35, 1371–1375. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.T.; Wen, J.F.; Jin, S.N. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Euphorbia humifusa. J. Taishan Med. Coll. 2012, 8, 628–631. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.H.; Yan, Y.B.; Wang, F. Research progress of Pueraria Mirifica and Dijincao in the treatment of diarrhea dehydration. Electr. J. Clin. Med. Liter 2015, 2, 4061. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.Z.; Gao, Y.M. Treatment of 290 cases of lung cancer with “Lung Dan” series of Chinese patent medicines. Chin. J. Civil Med. 1996, 8, 222–223. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.H.; Liu, C.C.; Zhang, M.M.; Yu, H.L.; Zhao, D.; Bai, X.; Zheng, M.; Liu, Y.; Ji, J.C.; Li, R.; et al. Prediction modelling for gastroesophageal variceal bleeding in patients with chronic hepatitis B using four-dimensional flow MRI. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2025, 15, 102403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, W.W.; Qiao, L.P.; Wang, J. Professor Tong Xiaolin’s experience in the treatment of herpes zoster. Jilin J. Chin. Med. 2022, 42, 1132–1160. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Liu, R.H.; Huang, S.B.; Zhou, M.; Li, L.M.; He, J.W. Progress of research on pathogenesis and therapeutic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis. China. Pharm. 2021, 32, 2154–2159. [Google Scholar]
- Haleagrahara, N.; Miranda-Hernandez, S.; Alim, M.A.; Hayes, L.; Bird, G.; Ketheesan, N. Therapeutic effect of quercetin in collagen-induced arthritis. Biom. Pharm. 2017, 90, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P. Study on the Effect of Quercetin on Apoptosis of Human Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes and Its Mechanism. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, K.; Zhu, Q.Q.; Lu, Q.Y.; Jiang, H.X.; Zhu, M.M.; Li, X.H.; Huang, G.R.; Xu, A.L. Quercetin alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting neutrophil inflammatory activities. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 84, 108454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Weitzmann, M.N. Quercetin, a potent suppressor of NF-κB and Smad activation in osteoblasts. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 28, 521–525. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.R.; Kim, B.M.; Won, J.Y.; Lee, K.A.; Ko, H.M.; Kang, Y.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, K.W. Quercetin, a plant polyphenol, has potential for the prevention of bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Med. Food 2019, 22, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.J.; Lin, Y.; Huang, S.S.; Zhang, H.L.; Diao, Y.P.; Li, K. Quercetin: A potential natural drug for adjuvant treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 10, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.X.; Peng, Q.Z.; Zhang, J.J.; Li, X.; Huang, J.R.; Duan, S.; Zhang, W.S. Quercetin prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced experimental preterm labor in mice and increases offspring survival rate. Reprod. Sci. 2020, 27, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.J.; Moon, S.J.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, S.; Lee, M.H.; Yoo, S.M.; Lee, H.S.; Kang, H.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, W.S.; et al. Kaempferol targeting on the fibroblast growth factor receptor 3-ribosomal S6 kinase 2 signaling axis prevents the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.F. Isolation of Chemical Constituents from Pantheria camphorata and Screening of Its In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Immunological Activity. Master’s Thesis, Anhui Medical University, Hefei, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.L.; Liu, J.X.; Dong, W.; Li, P.; Li, L.; Hou, J.C.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Lin, C.R.; Ren, J.G. Protective effect of kaempferol on LPS plus ATP-induced inflammatory response in cardiac fibroblasts. Inflammation 2015, 38, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.J.; Hu, J.X.; Wang, X.M.; Gao, Z.G. Effect of Euphorbiae humifusae herb on expression of VEGF, MMP-9 on H22 cells bearing Mice. Chin. J. Mod. Med. 2013, 23, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Z.J.; Liu, H.Y.; Gao, Z.G.; Wang, X.M. Antitumor effect of Euphorbiae Humifusae Herb on H22 tumor-bearing mice and its mechanism. Chin. J. Cancer Prev. Treat. 2014, 21, 903–908. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Z.J.; Liu, H.Y.; Wang, X.M. Influence of herba Euphorbiae humifusae on anti-tumor effect and apoptosis protein expression in transplanted liver cancer mice. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2013, 19, 241–245. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.X.; Xi, X.T.; Wang, X.M.; Zou, Z.J. Mechanism of Humifuse euphorbia in regulating tumor angiogenesis by NF-κB/VEGF signal pathway. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2018, 24, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, G.X.; Wei, H.; Chen, H.L.; Shi, M.H.; Li, Q.W. Study on the inhibitory effect of water extract of Dijincao on cervical cancer in mice. Heilongjiang Anim. Sci. Veter. Med. 2013, 12, 152–154. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Zhou, B.; Fu, D.; Li, M. Effects of Euphorbia humifusa on proliferation, apoptosis of Hela cervical cancer cells. Mod. Chin. Med. 2017, 19, 1713–1716. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, X.L.; Fan, W.Y.; Lou, L.Y.; Liu, J.H. Pharmacological studies of Dijin. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Medica Res. 2001, 12, 193–194. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, P.; Zhou, P.; Guo, L.F. Effect of herba Euphorbiae humifusae on platelet count, aggregation. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 1998, 18, 330–332. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.J.; Sang, Y.Z.; Si, Z.Z. Alleviation of histopathologic toxicity of hexachlorobenzene by Dijincao in mice. Chin. J. Mod. Appl. Pharm. 1987, 4, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.H.; Gao, Y.S.; Xu, J.H.; Lv, J.; Qi, R.F.; Wang, L.J. Effect of Euphorbia humifusa herb on serum myocardial enzyme activity in rats with myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Chin. J. Ethnomed. Ethnophar. 2016, 25, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.J. Extraction, Isolation, In Vitro Fermentation of Polysaccharides from Euphorbia humifusa and Its Protective Effect on Ulcerative Colitis; Southern Medical University: Guangzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H. Study on the Extraction Technology and Anti-Fatigue of Polysaccharide from Herba Euphorbiae humifusae. Master’s Thesis, Agricultural University of Hunan, Changsha, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.L.; Wen, D.W.; Xiao, H.L.; Meng, F.L.; Li, Z.H.; Yu, H.H.; Liu, Y.J. Experimental study on the analgesic effect of Euphorbia humifusa decoction in mice. Chin. Hosp. Pharm. J. 2009, 29, 193–1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.J. The Preparation of Polysaccharides from Euphorbia humifusa and Its Immune-Enhancing Activity in Mice. Ph.D. Thesis, College of Veterinary Medicine Northwest A & F University, Xianyang, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.J.; Yang, X.Z.; Gao, Y.C. Acute and subacute toxicity tests of Euphorbia humifusa granule. Shandong Agric. Sci. 2014, 46, 128–130. [Google Scholar]


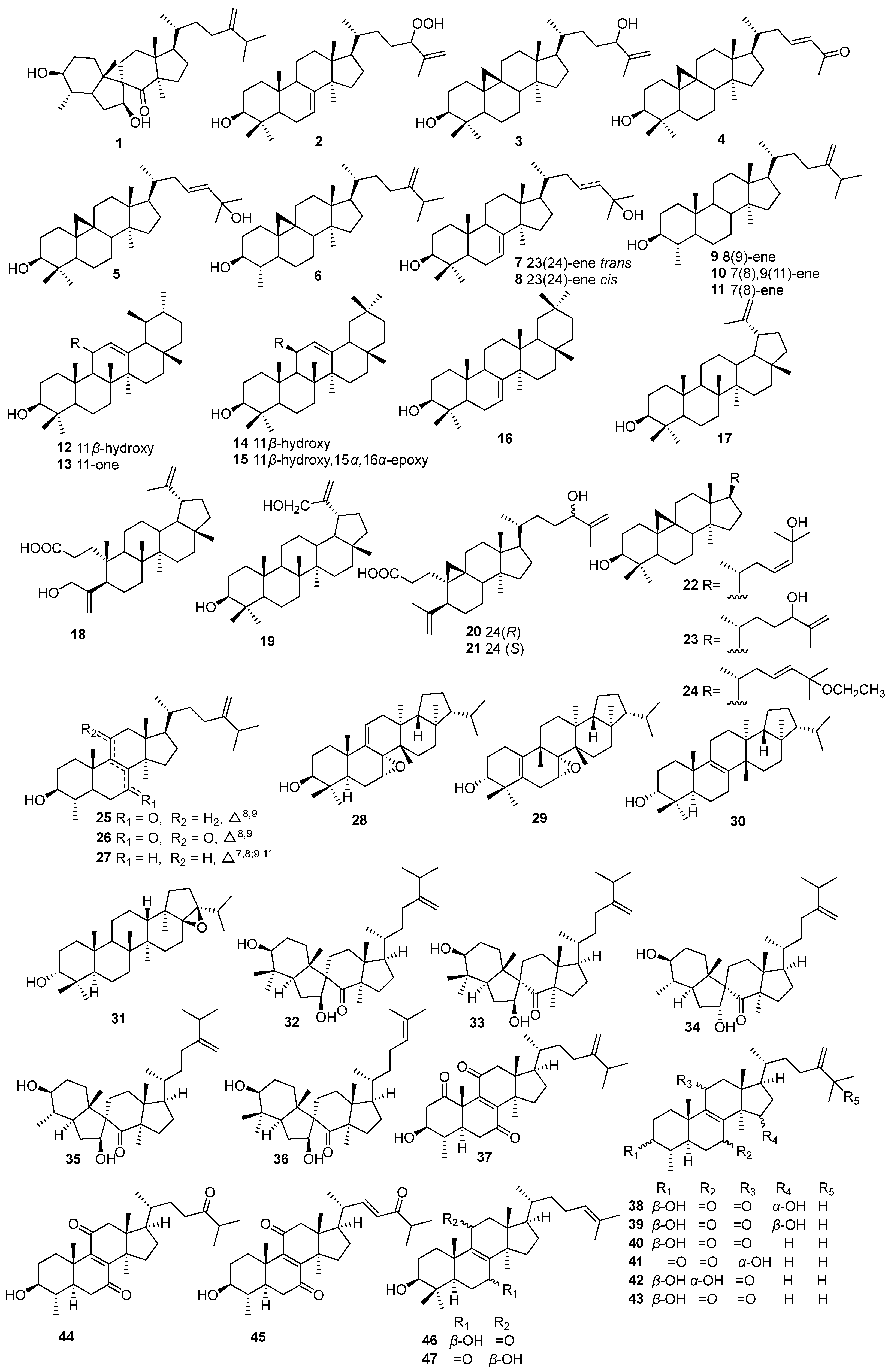
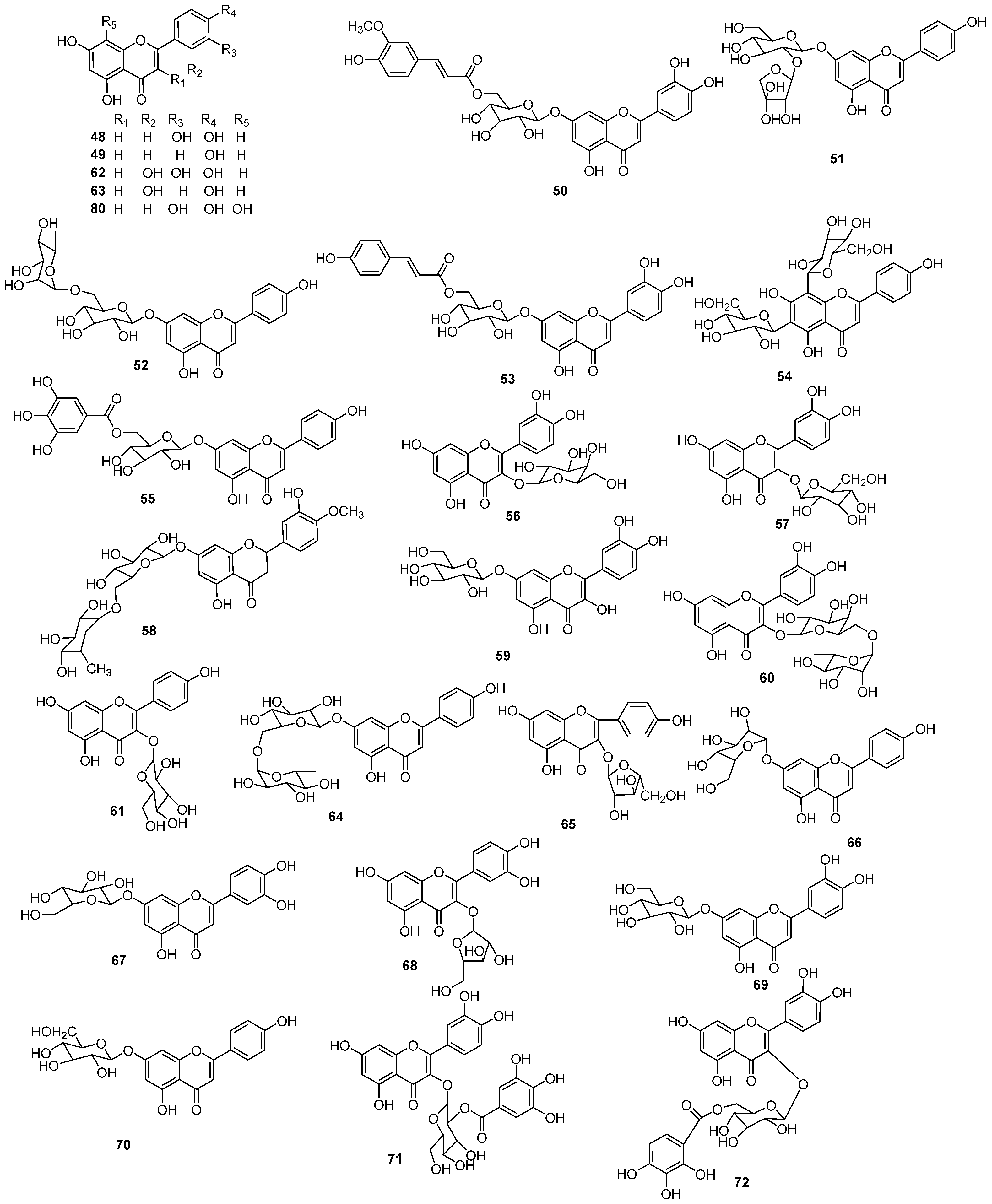
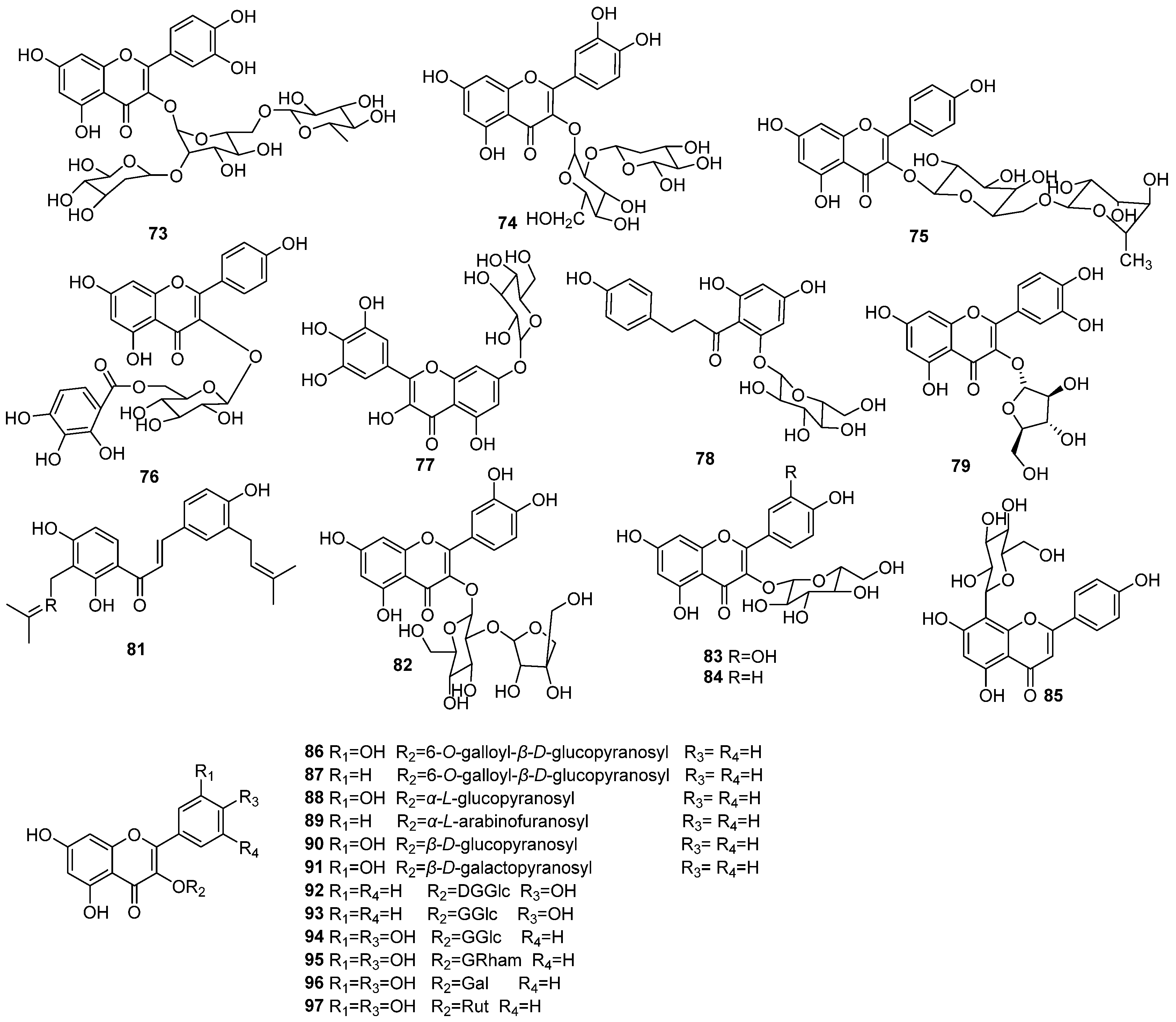
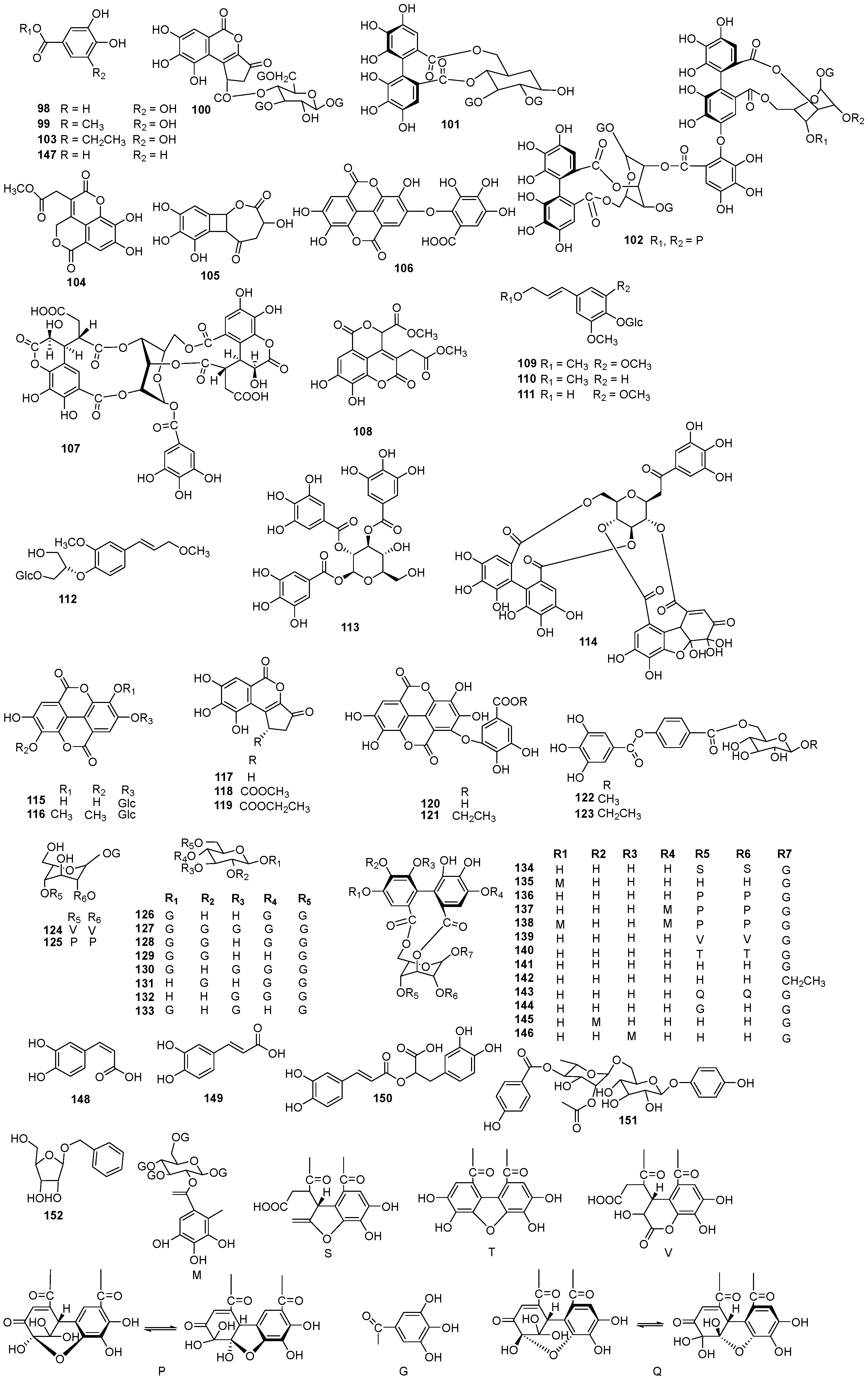


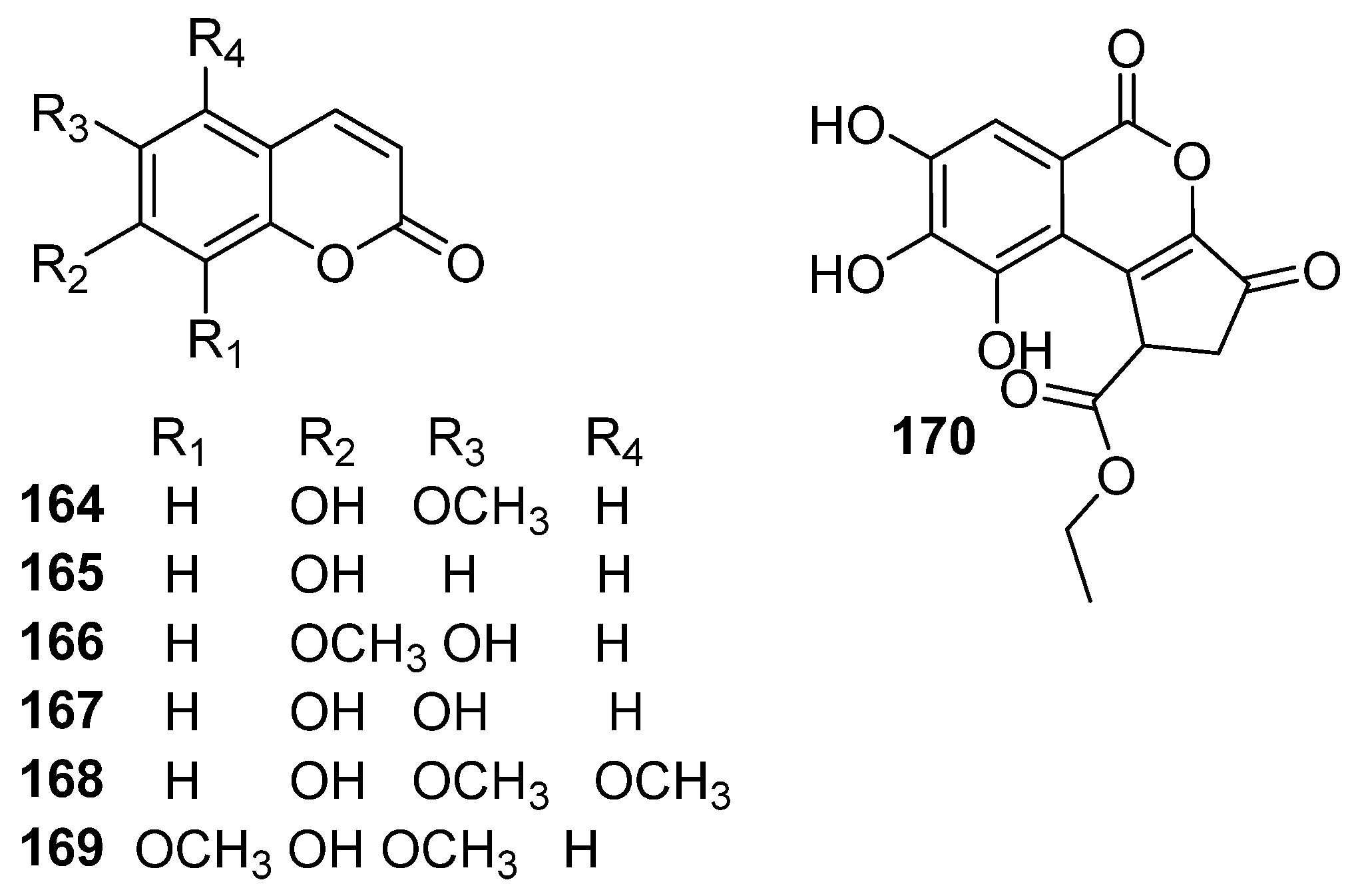
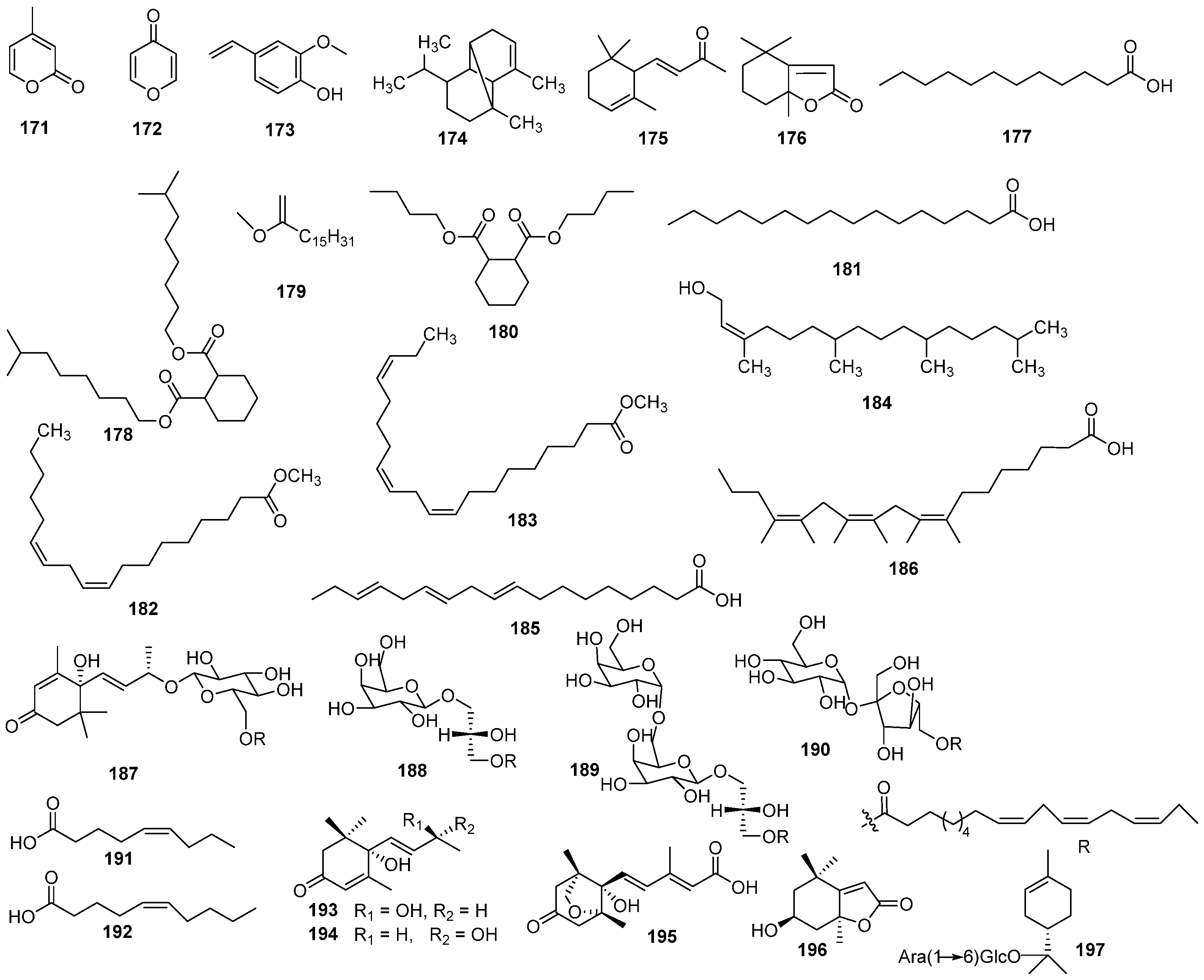
| NO. | Name | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight | Source | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (3S,4S,7S,9R)-4-methyl-3,7-dihydroxy-7(8→9) abeo-lanost-24(28)-en-8-one | C30H50O3 | 458.73 | E. maculata | [12] |
| 2 | 24-hydroperoxylanost-7,25-dien-3β-ol | C30H50O3 | 458.73 | E. maculata | [12] |
| 3 | cycloart-23Z-en-3β, 25-diol | C30H50O2 | 442.73 | E. maculata | [12] |
| 4 | 3β-hydroxy-26-nor-9,19-cyclolanost-23-en-25-one | C29H46O2 | 426.69 | E. maculata | [12] |
| 5 | cycloart-23en-3β,25-diol | C30H50O2 | 442.73 | E. maculata | [12] |
| 6 | cycloeucalenol | C30H50O | 426.73 | E. maculata | [12] |
| 7 | (23E)-3β,25-dihydroxytirucalla-7,23-diene | C30H50O2 | 442.73 | E. maculata | [12] |
| 8 | (23Z)-3β, 25-dihydroxy-tirucalla-7,23-diene | C30H50O2 | 442.73 | E. maculata | [12] |
| 9 | obtusifoliol | C30H50O | 426.73 | E. maculata | [12] |
| 10 | 4α, l4α-dimethyl-5α-ergosta-7,9(11), 24(28)-trien-3β-ol | C30H48O | 424.71 | E. maculata | [12] |
| 11 | gramisterol | C30H50O | 426.73 | E. maculata | [12] |
| 12 | urs-12-ene-3β, 11α-diol | C30H50O2 | 442.73 | E. maculata | [12] |
| 13 | neoilexonol | C30H48O2 | 440.71 | E. maculata | [12] |
| 14 | 12-oleanene-3β,11β-diol | C30H50O2 | 442.73 | E. maculata | [12] |
| 15 | (3β,15α, 16α)-15,16-epoxy, olean-12-en-3-ol | C30H48O2 | 440.71 | E. maculata | [12] |
| 16 | multiflorenol | C30H50O | 426.73 | E. maculata | [12] |
| 17 | lupeol | C30H50O | 426.73 | E. maculata | [12] |
| 18 | 3,4-seco-lupa-4(23),20(29)-dien-24-hydroxy-3-oic acid | C30H48O3 | 456.71 | E. humifusa | [13] |
| 19 | lup-20(29)-ene-3,30-diol | C30H50O2 | 442.73 | E. humifusa | [13] |
| 20 | 24(R)-3,4-secocycloart-4(29),25-dien-24-hydroxy-3-oic acid | C30H48O3 | 456.71 | E. humifusa | [13] |
| 21 | 24(S)-3,4-seco-cycloart-4(29),25-dien-24-hydroxy-3-oic acid | C30H48O3 | 456.71 | E. humifusa | [13] |
| 22 | 23(Z)-cycloart-23-en-3,25-diol | C30H50O2 | 442.73 | E. humifusa | [13] |
| 23 | 24(S)-cycloart-25-en-3,24-diol | C30H50O2 | 442.73 | E. humifusa | [13] |
| 24 | 23(E)-cycloart-23-en-25-ethoxy-3-ol | C32H54O2 | 470.78 | E. humifusa | [13] |
| 25 | 3-hydroxy-4,14-dimethyl-5-ergosta-8,24(28)-dien-7-one | C30H48O2 | 440.71 | E. humifusa | [13] |
| 26 | 3-hydroxy-4,14-dimethyl-5-ergosta-8,24(28)-dien-7,11-dione | C30H46O3 | 454.70 | E. humifusa | [13] |
| 27 | 3-hydroxy-4,14-dimethyl-5-ergosta-7,9(11),24(28)-trien | C30H48O | 424.71 | E. humifusa | [13] |
| 28 | (3S,5R,7R,8S,10S,13S,14S,17R,18R,21R)−7α,8α-epoxyfern-9(11)-en-3β-ol | C30H48O2 | 440.71 | E. humifusa | [14] |
| 29 | (3R,7R,8S,9S,13S,14S,17R,18R,21R)−7α,8α-epoxyadian-5(10)-en-3α-ol | C30H48O2 | 440.71 | E. humifusa | [14] |
| 30 | fern-8(9)-en-3β-ol | C30H50O | 426.73 | E. humifusa | [14] |
| 31 | 17β,21β-epoxyhopan-3β-ol | C30H50O2 | 442.73 | E. humifusa | [14] |
| 32 | spiromaculatol A | C31H52O3 | 472.75 | E. maculate | [15] |
| 33 | spiromaculatol B | C31H52O3 | 472.75 | E. maculate | [15] |
| 34 | spiromaculatol C | C30H50O3 | 458.73 | E. maculate | [15] |
| 35 | spiropedroxodiol | C30H50O3 | 458.73 | E. maculate | [15] |
| 36 | spiroinonotsuoxodiol | C30H50O3 | 458.73 | E. maculate | [15] |
| 37 | euphomaculatoid A | C30H44O4 | 468.68 | E. maculate | [15] |
| 38 | euphomaculatoid B | C30H46O4 | 470.69 | E. maculate | [15] |
| 39 | euphomaculatoid C | C30H46O4 | 470.69 | E. maculate | [15] |
| 40 | euphomaculatoid D | C30H46O3 | 454.70 | E. maculate | [15] |
| 41 | euphomaculatoid E | C30H46O3 | 454.70 | E. maculate | [15] |
| 42 | 3β, 7α-dihydroxy-4α,14α-dimethyl-5α-ergosta-8,24 (28)-dien-11-one | C30H48O3 | 456.71 | E. maculate | [15] |
| 43 | 3β-hydroxy-4α,14α-dimethyl-5α-ergosta-8,24 (28)-diene-7,11-dione | C30H46O3 | 454.70 | E. maculate | [15] |
| 44 | euphomaculatoid F | C29H44O4 | 456.67 | E. maculate | [15] |
| 45 | euphomaculatoid G | C29H42O4 | 454.65 | E. maculate | [15] |
| 46 | euphomaculatoid H | C30H48O3 | 456.71 | E. maculate | [15] |
| 47 | 3β,11β-3,11-dihydroxylanosta-8,24-dien-7-one | C30H48O3 | 456.71 | E. maculate | [15] |
| NO. | Name | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight | Source | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 48 | luteolin | C15H10O6 | 286.24 | E. humifusa | [16,25] |
| 49 | apigenin | C15H10O5 | 270.24 | E. humifusa | [16] |
| 50 | luteolin-7-O-(6″-O-trans-feruloyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside | C31H28O14 | 624.55 | E. humifusa | [16] |
| 51 | luteolin-7-O-(6″-O-coumaroyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside | C25H26O14 | 550.47 | E. humifusa | [16] |
| 52 | apigenin-7-O-β-D-lutinoside | C27H30O14 | 578.52 | E. humifusa | [16] |
| 53 | apigenin-7-O-β-D-apiofuranosyl(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside | C30H26O13 | 594.14 | E. humifusa | [16] |
| 54 | 6,8-di-C-β-D-glucopyranosyl apigenin | C27H30O15 | 594.52 | E. humifusa | [16] |
| 55 | apigenin-7-O-(6″-O-galloyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside | C28H24O14 | 584.49 | E. humifusa | [16] |
| 56 | quercetin-3-O-β-D-galactoside | C21H20O12 | 464.38 | E. humifusa | [16] |
| 57 | quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside | C21H20O12 | 464.38 | E. humifusa | [16] |
| 58 | hesperidin | C29H36O14 | 608.59 | E. humifusa | [16] |
| 59 | quercetin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside | C21H20O12 | 464.38 | E. humifusa | [20] |
| 60 | quercetin-3-O-α-L-rhamnosyl(1→6)-β-D-galactoside | C27H30O16 | 610.52 | E. humifusa | [20] |
| 61 | kaempferol-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside | C21H20O11 | 448.38 | E. humifusa | [20] |
| 62 | quercetin | C15H10O7 | 302.24 | E. humifusa | [20] |
| 63 | kaempferol | C15H10O6 | 286.24 | E. humifusa | [21] |
| 64 | isorhoifolin | C27H30O14 | 578.52 | E. humifusa | [22] |
| 65 | kaempferol-3-O-α-L-arabinoforanoside | C20H18O10 | 418.35 | E. humifusa | [22] |
| 66 | apigenin-7-O-glucoside | C21H20O10 | 432.38 | E. humifusa | [23] |
| 67 | luteolin-7-O-glucoside | C21H20O11 | 448.38 | E. humifusa | [23] |
| 68 | quercetin-3-O-arabinoside | C20H18O11 | 434.35 | E. humifusa | [22] |
| 69 | luteolin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside | C21H20O11 | 448.38 | E. humifusa | [24] |
| 70 | apigenin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside | C21H20O10 | 432.38 | E. humifusa | [24] |
| 71 | quercetin-3-O-(2″,3″-di-O-galloyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside | C28H24O16 | 616.48 | E. humifusa | [24] |
| 72 | quercetin-3-O-(6″-O-galloyl)-glucopyranoside | C28H24O16 | 616.48 | E. humifusa | [24] |
| 73 | quercetin-3-O-{rhamnosyl-(1→6)-[xylosyl-(1→2)]-galactoside} | C32H38O20 | 742.64 | E. humifusa | [24] |
| 74 | quercetin-3-O-β-D-xylosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside | C26H28O16 | 596.49 | E. humifusa | [24] |
| 75 | nicotiflorin | C27H30O15 | 594.52 | E. humifusa | [24] |
| 76 | kaempferol-3-O-(6″-O-galloyl)-β-D-galactoside | C28H24O15 | 600.49 | E. humifusa | [24] |
| 77 | isomyricitrin | C21H20O13 | 480.38 | E. humifusa | [24] |
| 78 | phlorizin | C21H24O10 | 436.41 | E. humifusa | [24] |
| 79 | quercetin-3-O-α-L-arabinofuranoside | C20H18O11 | 434.35 | E. humifusa | [3] |
| 80 | 8-hydroxyluteolin | C15H10O7 | 302.24 | E. humifusa | [25] |
| 81 | paratocarpin E | C25H28O4 | 392.50 | E. humifusa | [25] |
| 82 | quercetin-3-O-apiosyl (1–2) galactoside | C26H28O16 | 596.49 | E. humifusa | [19] |
| 83 | quercetin-3-O-glucoside | C21H20O11 | 448.38 | E. humifusa | [19] |
| 84 | astragalin | C21H20O12 | 464.38 | E. humifusa | [3,19] |
| 85 | vitexin | C21H20O10 | 432.38 | E. humifusa | [19] |
| 86 | isoquercitrin 6″-O-gallate | C28H24O16 | 616.48 | E. maculata | [18] |
| 87 | astragalin 6″-O-gallate | C28H24O15 | 600.48 | E. maculata | [18] |
| 88 | avicularin | C20H18O11 | 434.35 | E. maculata | [18] |
| 89 | juglanin | C20H18O10 | 418.35 | E. maculata | [18] |
| 90 | isoquercitrin | C21H20O12 | 464.38 | E. maculata | [18] |
| 91 | hyperoside | C21H20O12 | 464.38 | E. maculata | [18] |
| 92 | astragalin 2″,3″-O-digallate | C36H30O19 | 766.62 | E. humifusa | [4] |
| 93 | astragalin 2″-O-gallate | C29H26O15 | 614.51 | E. humifusa | [4] |
| 94 | isoquercitin 2″-O-gallate | C29H26O16 | 630.51 | E. humifusa | [4] |
| 95 | quercitrin 2″-O-gallate | C29H26O15 | 614.51 | E. humifusa | [4] |
| 96 | hyperin | C21H20O12 | 464.38 | E. humifusa | [4] |
| 97 | rutin | C27H30O16 | 616.49 | E. humifusa | [4] |
| NO. | Name | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight | Source | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 98 | gallic acid | C7H6O5 | 170.12 | E. humifusa | [18] |
| 99 | methyl gallate | C8H8O5 | 184.15 | E. humifusa | [18] |
| 100 | 1,3,6-tri-O-galloyl-2-O-brevifolincarboxyl-β-D-glucose | C40H30O25 | 910.66 | E. humifusa | [26] |
| 101 | tellimagrandin I | C35H28O21 | 784.11 | E. humifusa | [26] |
| 102 | excoecarianin | C82H56O53 | 1888.17 | E. humifusa | [26] |
| 103 | ethyl gallate | C9H10O5 | 198.17 | E. humifusa | [16] |
| 104 | phyllanthussin E methyl ester | C14H10O8 | 306.4 | E. humifusa | [16] |
| 105 | humifusaone | C12H10O7 | 266.21 | E. humifusa | [16] |
| 106 | valoneaic aciddilactone | C21H10O13 | 470.30 | E. humifusa | [27] |
| 107 | eumaculin E | C41H32O28 | 972.68 | E. maculata | [16] |
| 108 | dehydropicrorhiza acid methyl diester | C16H12O10 | 364.26 | E. humifusa | [4] |
| 109 | methylsyringin | C18H26O9 | 386.16 | E. humifusa | [4] |
| 110 | syringin | C17H24O8 | 356.15 | E. humifusa | [4] |
| 111 | methylconiferin | C17H24O9 | 372.14 | E. humifusa | [4] |
| 112 | sphaerophyside SC | C16H22O7 | 326.35 | E. humifusa | [4] |
| 113 | 1,2,3-tri-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose | C27H24O18 | 636.47 | E. maculata | [28] |
| 114 | granatin B | C42H30O26 | 950.68 | E. maculata | [27] |
| 115 | ellagic acid-4-O-β-D-glucopyranoside | C20H16O13 | 464.34 | E. humifusa | [26] |
| 116 | 3,3′-di-O-methyl ellagic acid-4-O-β-D-glucopyranoside | C22H20O13 | 492.39 | E. humifusa | [22] |
| 117 | brevifolin carboxylic acid | C12H8O6 | 248.19 | E. humifusa | [4] |
| 118 | methyl brevifolin carboxylate | C14H10O8 | 306.23 | E. humifusa | [16] |
| 119 | ethyl brevifolin carboxylate | C15H12O8 | 320.25 | E. humifusa | [16] |
| 120 | sanguisorbicacid dilactone | C21H10O13 | 470.30 | E. humifusa | [16] |
| 121 | 7”-ethyl-sanguisorbic acid dilactone | C23H14O13 | 498.35 | E. humifusa | [16] |
| 122 | 1-O-methyl-6-O-p-digalloyl-α-D-glucopyranoside | C21H22O12 | 466.40 | E. humifusa | [12] |
| 123 | 1-O-ethyl-6-O-p-digalloyl-α-D-glucopyranoside | C22H24O12 | 480.42 | E. humifusa | [16] |
| 124 | chebulanin | C27H24O19 | 652.47 | E. humifusa | [16] |
| 125 | furosin | C27H22O19 | 650.45 | . humifusa | [16] |
| 126 | 1,3,4,6-tetra-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose | C27H24O18 | 636.47 | E. humifusa | [26] |
| 127 | Euphormisin M3 | C41H32O26 | 940.68 | E. humifusa | [26] |
| 128 | 1,2,4,6-tetra-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose | C34H28O22 | 788.58 | E. humifusa | [26] |
| 129 | 1,2,6-tri-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose | C27H24O18 | 636.47 | E. humifusa | [26] |
| 130 | 1,3,4,6-tetra-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose | C34H28O22 | 788.58 | E. humifusa | [26] |
| 131 | 2,4,6-tri-O-galloyl-D-glucose | C27H24O18 | 636.47 | E. humifusa | [26] |
| 132 | 3,4,6-tri-O-galloyl-D-glucose | C27H24O18 | 636.47 | E. humifusa | [26] |
| 133 | 1,3,6-tri-O-galloyl-D-glucose | C27H24O18 | 636.47 | E. humifusa | [26] |
| 134 | euphormisin M2 | C41H30O25 | 922.67 | E. maculata | [28] |
| 135 | eumaculinA | C69H54O43 | 1571.15 | E. maculata | [28] |
| 136 | geraniin | C41H28O27 | 952.65 | E. maculata | [28] |
| 137 | euphorbin B | C83H60O52 | 1889.34 | E. maculata | [28] |
| 138 | euphorbin A | C125H92O77 | 2826.03 | E. maculata | [28] |
| 139 | chebulagic acid | C41H30O27 | 954.66 | E. maculata | [28] |
| 140 | mallotusinin | C41H26O25 | 918.63 | E. maculata | [27] |
| 141 | corilagin | C27H22O18 | 634.46 | E. maculata | [27] |
| 142 | 1-O-ethyl-3,6-O-(R)-hexahydroxydiphenoyl-(1C4)-β-D-glucose | C22H22O14 | 510.40 | E. maculata | [27] |
| 143 | 1,3,4,6-tetra-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose | C41H28O27 | 952.65 | E. maculata | [27] |
| 144 | tercatain | C34H26O22 | 786.56 | E. maculata | [27] |
| 145 | eumaculin B | C69H54O43 | 1571.15 | E. maculata | [27] |
| 146 | eumaculin D | C69H54O43 | 1571.15 | E. maculata | [27] |
| 147 | protocatechuic acid | C7H6O4 | 154.12 | E. humifusa | [29] |
| 148 | cis-caffeic acid | C9H8O4 | 180.16 | E. humifusa | [29] |
| 149 | trans-caffeic acid | C9H8O4 | 180.16 | E. humifusa | [29] |
| 150 | rosmarinic | C18H16O8 | 360.32 | E. humifusa | [30] |
| 151 | euphorbinoside | C27H32O14 | 580.54 | E. humifusa | [4] |
| 152 | benzyl β-D-ribofuranoside | C12H16O5 | 240.26 | E. humifusa | [4] |
| NO. | Name | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight | Source | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 153 | 5-β-methoxy-4β-hydroxy-3-methylene-α-pyrrolidinone | C6H9NO3 | 143.14 | E. humifusa | [22] |
| 154 | 5-β-methoxy-4α-hydroxy-3-methylene-α-pyrrolidinone | C6H9NO3 | 143.14 | E. humifusa | [22] |
| 155 | 5β-butoxy-4α-hydroxy-3-methylene-α-pyrrolidinone | C9H15NO3 | 185.22 | E. humifusa | [22] |
| 156 | 3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-5-(1-O-glucopyranosyloxy)-indole | C16H21NO7 | 339.34 | E. humifusa | [22] |
| 157 | 1-(2′,3′,4′,5′-tetrahydroxypentyl)-6,7-dimethyl-guinoxaline-2,3-(1H,4H)-dione | C15H20N2O6 | 324.33 | E. humifusa | [16] |
| 158 | uinoxadione | C8H6N2O | 146.15 | E. humifusa | [26] |
| 159 | (−)-neoechinulin A | C19H21N3O2 | 323.40 | E. humifusa | [29] |
| NO. | Name | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight | Source | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 160 | β-sitosterol | C29H50O | 414.72 | E. humifusa | [24] |
| 161 | β-daucosterol | C35H60O6 | 576.85 | E. humifusa | [24] |
| 162 | stigmaster-5-ene-3-O-(6-linoyl-114yl)-β-D-glucopyranoside | C35H60O7 | 592.85 | E. humifusa | [24] |
| 163 | 7β-hydroxy-sitosterol | C29H50O2 | 430.72 | E. humifusa | [24] |
| NO. | Name | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight | Source | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 164 | scopoletin | C10H8O4 | 192.17 | E. humifusa | [24] |
| 165 | umbelliferone | C9H6O3 | 162.14 | E. humifusa | [23] |
| 166 | 7-methoxy-6-hydroxyl-coumarin | C10H8O4 | 192.17 | E. humifusa | [13] |
| 167 | esculetin | C9H6O4 | 178.14 | E. humifusa | [29] |
| 168 | 5-methoxyscopoletin | C11H10O5 | 222.20 | E. humifusa | [29] |
| 169 | isofraxidin | C11H10O5 | 222.20 | E. humifusa | [29] |
| 170 | ethyl brevifolincarboxylate | C15H12O8 | 320.25 | E. humifusa | [13] |
| NO. | Name | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight | Source | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 171 | α-pyrone | C6H6O2 | 110.04 | E. humifusa | [31] |
| 172 | γ-pyrone | C5H4O2 | 96.09 | E. humifusa | [31] |
| 173 | 2-methoxy-4-vinylphenol | C9H10O2 | 150.18 | E. humifusa | [31] |
| 174 | desogestrel | C15H24 | 204.36 | E. humifusa | [31] |
| 175 | α-ionone | C13H20O | 192.30 | E. humifusa | [31] |
| 176 | dihydroactinidiolide | C11H16O2 | 180.25 | E. humifusa | [31] |
| 177 | lauric acid | C12H24O2 | 200.32 | E. humifusa | [31] |
| 178 | isononyl phthalate | C26H48O4 | 424.67 | E. humifusa | [31] |
| 179 | methyl hexadecanoate | C18H36O | 268.49 | E. humifusa | [31] |
| ]180 | dibutyl phthalate | C16H28O4 | 284.40 | E. humifusa | [31] |
| 181 | palmitic acid | C16H32O2 | 256.43 | E. humifusa | [31] |
| 182 | methyl linoleate | C19H34O2 | 294.48 | E. humifusa | [31] |
| 183 | 9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid, methyl ester | C21H36O2 | 320.52 | E. humifusa | [31] |
| 184 | phytol | C20H40O | 296.54 | E. humifusa | [31] |
| 185 | linoleic acid | C18H30O2 | 278.44 | E. humifusa | [31] |
| 186 | α-linolenic acid | C24H42O2 | 362.60 | E. humifusa | [31] |
| 187 | humionoactoside A | C38H60O9 | 660.89 | E. humifusa | [32] |
| 188 | (2S)-3-O-octadeca-9Z,12Z,15Z-trienoylglyceryl-O-β-D-galactopyranoside | C28H48O9 | 528.68 | E. humifusa | [32] |
| 189 | gingerglycolipid A | C34H58O14 | 690.82 | E. humifusa | [32] |
| 190 | 6′-O-linolenoylsucrose | C31H52O12 | 616.75 | E. humifusa | [32] |
| 191 | (5Z)-nonenoic acid | C9H16O2 | 156.23 | E. humifusa | [29] |
| 192 | (5Z)-undecenoic acid | C10H18O2 | 170.25 | E. humifusa | [29] |
| 193 | corchoionol C | C13H20O3 | 224.30 | E. humifusa | [29] |
| 194 | vomifoliol | C13H20O3 | 224.30 | E. humifusa | [29] |
| 195 | (−)-phaseic acid | C15H20O5 | 280.32 | E. humifusa | [29] |
| 196 | isololiiolide | C11H16O3 | 196.25 | E. humifusa | [29] |
| 197 | (4S)-α-terpineol 8-O-[α-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside] | C21H36O10 | 448.51 | E. humifusa | [4] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, J.; Gu, H.; Zhang, J.; Xue, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, H.; Fan, B.; Wang, W. A Comprehensive Review of the Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Other Applications of Euphorbiae Humifusae Herba. Molecules 2025, 30, 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051094
Xiao J, Gu H, Zhang J, Xue Y, Chen Y, Zhu W, Zhang H, Fan B, Wang W. A Comprehensive Review of the Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Other Applications of Euphorbiae Humifusae Herba. Molecules. 2025; 30(5):1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051094
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Jian, Hong Gu, Jiaqing Zhang, Yuqian Xue, Yunyi Chen, Weizhong Zhu, Hong Zhang, Boyi Fan, and Wenli Wang. 2025. "A Comprehensive Review of the Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Other Applications of Euphorbiae Humifusae Herba" Molecules 30, no. 5: 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051094
APA StyleXiao, J., Gu, H., Zhang, J., Xue, Y., Chen, Y., Zhu, W., Zhang, H., Fan, B., & Wang, W. (2025). A Comprehensive Review of the Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Other Applications of Euphorbiae Humifusae Herba. Molecules, 30(5), 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051094







