Development and Techno-Economic Evaluation of Crystallization Techniques for GABA Purification from Fermentation Broth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of Cooling Crystallization Desalination
2.2. Optimization of the Process Conditions of “Antisolvent–Cooling” Coupled Crystallization
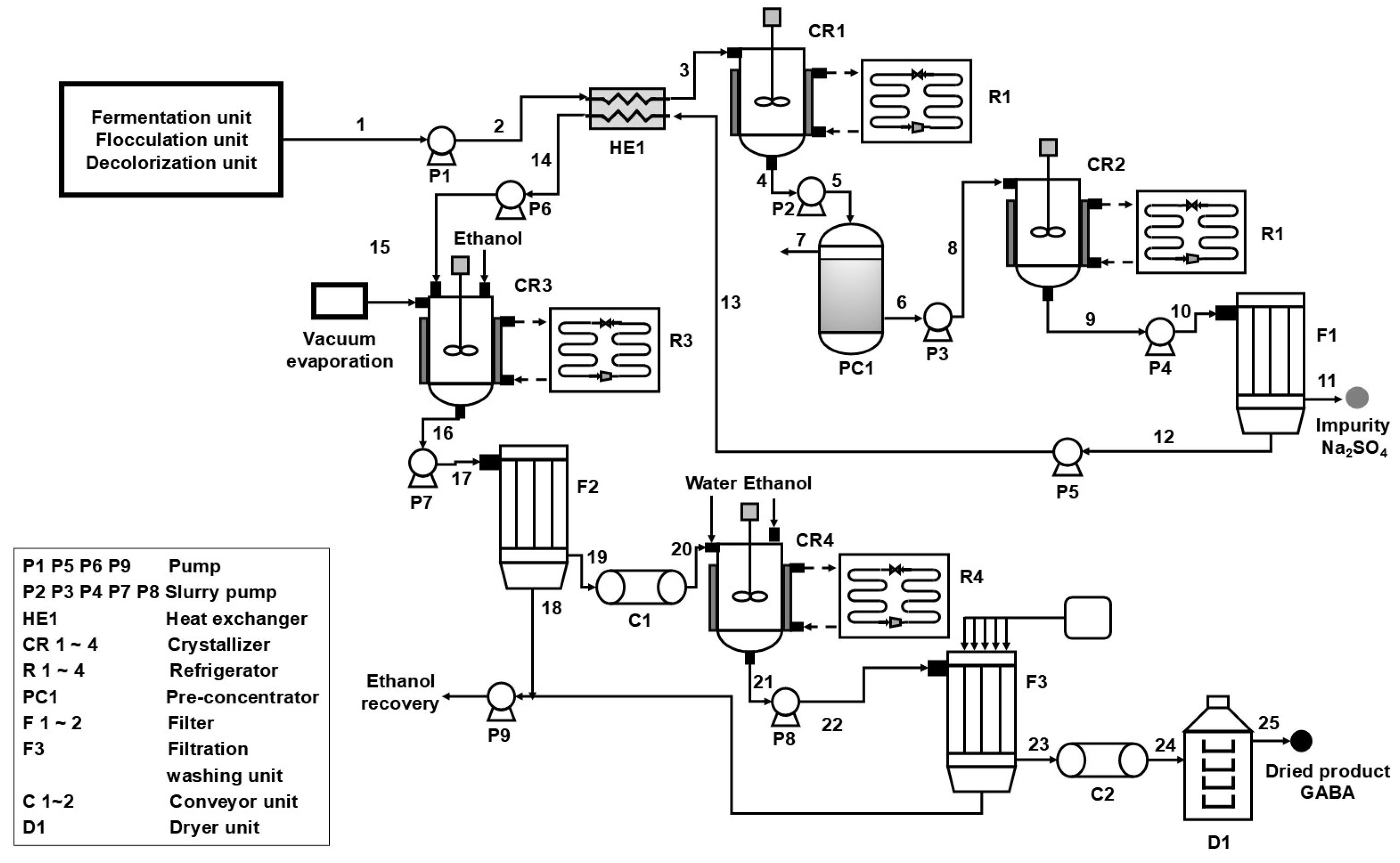
2.3. Scale-Up Test of Purification of GABA from Fermentation Broth
2.4. Comparison Between Traditional Methods and Crystallization-Based Techniques for GABA Purification
2.5. Techno-Economic Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Fermentation Processes and Pretreatment Methods
3.3. Cooling Crystallization of GABA-Na2SO4 Solution and Actual Fermentation Broth
3.4. Response Surface Optimization (RSM) for Cooling Crystallization Desalination
3.5. Comparison with Ethanol Desalination Method
3.6. Optimization of the Process Conditions of “Antisolvent–Cooling” Crystallization for GABA
3.7. Enlargement of the Crystallization Method to a 3.2 L System
3.8. Analytical Method
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, J.R.; Zhao, X.L.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, P.; Gu, Q. Microbial-Derived γ-Aminobutyric Acid: Synthesis, Purification, Physiological Function, and Applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 14931–14946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, Z.; Gao, L.; Id, O.; Chen, X.; Id, O. Unraveling the Potential of γ-Aminobutyric Acid: Insights into Its Biosynthesis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, H.Y.; Bao, D.P.; Tan, Y.S.; Zhong, Y.J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.Y. Recent advances of γ-aminobutyric acid: Physiological and immunity function. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1076223. [Google Scholar]
- Zareba, P.; Gryzlo, B.; Mazur, G.; Malawska, B. Development, Recent Achievements and Current Directions of Research into GABA Uptake Inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 750–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.Q.; Barberis, A.; Higley, M.J. Preserving the balance: Diverse forms of long-term GABAergic synaptic plasticity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 20, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perucca, E.; White, H.S.; Bialer, M. New GABA-Targeting Therapies for the Treatment of Seizures and Epilepsy: II. Treatments in Clinical Development. CNS Drugs 2023, 37, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schousboe, A.; Madsen, K.K.; Barker-Haliski, M.L.; White, H.S. The GABA Synapse as a Target for Antiepileptic Drugs: A Historical Overview Focused on GABA Transporters. Neurochem. Res. 2014, 39, 1980–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felice, D.; Cryan, J.F.; O’Leary, O.F. GABAB Receptors: Anxiety and Mood Disorders. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 52, 241–265. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.J.; Ouyang, J.Y.; Hu, Z.Y.; Yang, J.; Chu, Y.; Huang, S.W.; Yang, Y.C.; Liu, C.H. Intervention mechanism of repeated oral GABA administration on anxiety like behaviors induced by emotional stress in rats. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 271, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Marques, T. Cardioprotective role of GABA-B receptor activation on ventricular arrhythmia following myocardial infarction. Rev. Port. Cardiol. 2023, 42, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Watanabe, K.; Ma, M.L.; Hirayama, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Oyama, H.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Kanda, M.; Kodama, M.; Aizawa, Y. The Effects of γ-Aminobutyric Acid, Vinegar, and Dried Bonito on Blood Pressure in Normotensive and Mildly or Moderately Hypertensive Volunteers. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2009, 45, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryo, I.; Miyako, U.; Atsushi, Y.; Mujo, K.; Yoshinori, K.; Id, O. Exosome-Mediated Activation of Neuronal Cells Triggered by γ-Aminobutyric Acid. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kickinger, S.; Hellsberg, E.; Frolund, B.; Schousboe, A.; Ecker, G.F.; Wellendorph, P. Structural and molecular aspects of betaine-GABA transporter 1 (BGT1) and its relation to brain function. Neuropharmacology 2019, 161, 107644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Ren, L.W.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhang, S.; Ge, B.B.; Yang, H.; Du, G.H.; Tang, B.; Wang, H.Q.; et al. GABAergic signaling as a potential therapeutic target in cancers. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, E.A.; Meisters, A. Electrochemical Synthesis of Amino Acids by Reductive Amination of Keto Acids. I. Reduction at Mercury Electrodes. Aust. J. Chem. 1978, 31, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khwanchai, P.; Chinprahast, N.; Pichyangkura, R.; Chaiwanichsiri, S. Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid and Glutamic Acid Contents, and the GAD Activity in Germinated Brown Rice (Oryza sativa L.): Effect of Rice Cultivars. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.B.; Lee, M.K.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, H.H.; Chung, E.; Lee, J.H.; Park, S.U. Accumulation of γ-aminobutyric acid and transcription of glutamate decarboxylase in Brassica juncea (L.) Czern. Plant Omics 2013, 6, 263–267. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q.; Xie, K.; Wang, H.; Shao, X.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, S.; Cao, M.; Chen, J.; Xu, F. Calcium Involved in the Enrichment of γ-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) in Broccoli Sprouts under Fructose Treatment. Plants 2023, 12, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atefe, G.N.; Sayed, M.; Farideh, T.Y.; Mahboobe, S.J. Optimization of Gamma Aminobutyric Acid Production Using High Pressure Processing (HPP) by Lactobacillus brevis PML1. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 8540736. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.Z.; Liu, Z.; Xie, F.; Bilal, M.; Liu, L.N.; Yang, R.L.; Wang, Z.Y. Microbial production of gamma-aminobutyric acid: Applications, state-of-the-art achievements, and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2021, 41, 491–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.X.; Qiu, T.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.S. Separation of gamma-aminobutyric acid from fermented broth. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 38, 1955–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Duan, Q.; Wang, D.P.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zheng, C.Y. Separation and Purification of γ-Aminobutyric Acid from Fermentation Broth by Flocculation and Chromatographic Methodologies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 1914–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Ding, J.J.; Wu, M.; Liu, B.C.; Song, H.W.; You, S.P.; Qi, W.; Su, R.X.; He, Z.M. Development of an integrated process for the production of high-purity γ-aminobutyric acid from fermentation broth. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 50, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, S.; Ropel, D.; Vogt, D. Sodium ethoxide as an environmentally benign and cost-effective catalyst for chemical depolymerization of post-consumer PET waste. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 1442–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Lu, H.J.; Wang, J.K.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, Y.N.; Bao, Y.; Hao, H.X. Recent progress of continuous crystallization. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 54, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seider, W.D.; Lewin, D.R. Annual Costs, Earnings, and Profitability Analysis. In Product and Process Design Principles: Synthesis, Analysis, and Evaluation, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 17, pp. 697–932. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.J.; Ba, W.Y.; You, S.P.; Qi, W.; Su, R.X. Development of an oil-sealed anaerobic fermentation process for high production of γ-aminobutyric acid with Lactobacillus brevis isolated by directional colorimetric screening. Biochem. Eng. J. 2023, 194, 108893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, X.C.; Ding, J.J.; Ba, W.Y.; You, S.P.; Qi, W.; Su, R.X. High Production of γ-Aminobutyric Acid by Activating the xyl Operon of Lactobacillus brevis. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 8101–8109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Ding, J.J.; Zhang, Z.F.; You, S.P.; Qi, W.; Su, R.X.; He, Z.M. Kinetic modeling of gamma-aminobutyric acid production by Lactobacillus brevis based on pH-dependent model and rolling correction. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 50, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.N.; Wang, Y.L.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, H.J.; Lou, Y.J.; Huang, J.J.; He, M.; Li, Y.; Hao, H.X. Mechanism of Influence of Organic Impurity on Crystallization of Sodium Sulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 1705–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 13025.8-2012; General Test Method in Salt Industry—Determination of Sulfate. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2012.
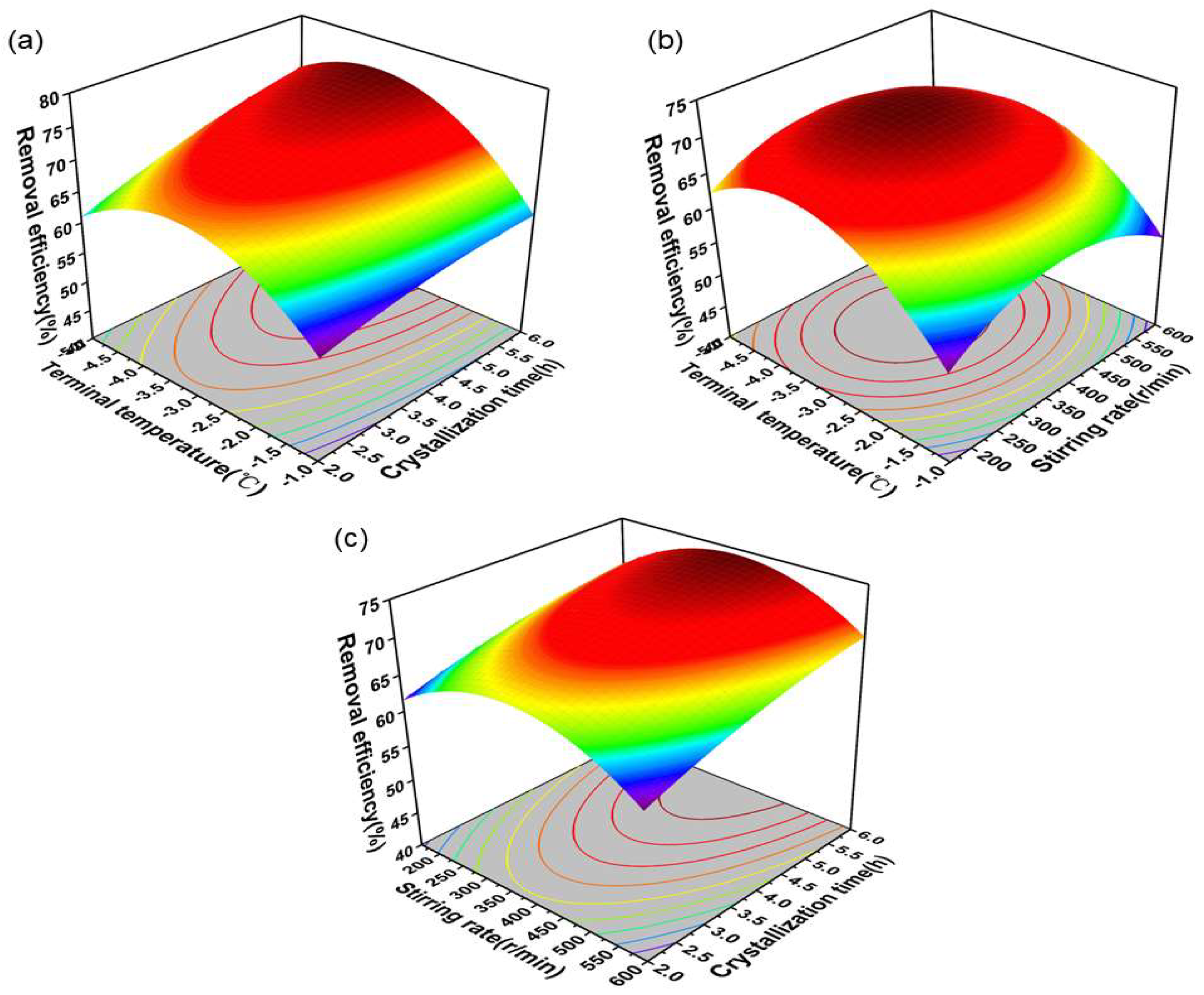

| Source | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 1036.4 | 9 | 115.16 | 40.80 | <0.0001 |
| A | 155.55 | 1 | 155.55 | 55.11 | <0.0001 |
| B | 5.39 | 1 | 5.39 | 1.91 | 0.1972 |
| C | 56.79 | 1 | 56.79 | 20.12 | 0.0012 |
| AB | 1.28 | 1 | 1.28 | 0.4535 | 0.5159 |
| AC | 1.19 | 1 | 1.19 | 0.4201 | 0.5315 |
| BC | 0.98 | 1 | 0.98 | 0.3472 | 0.5688 |
| A2 | 197.80 | 1 | 197.80 | 70.08 | <0.0001 |
| B2 | 40.36 | 1 | 40.36 | 14.30 | 0.0036 |
| C2 | 13.38 | 1 | 13.38 | 4.74 | 0.0545 |
| Residual | 28.23 | 10 | 2.82 | ||
| Lack of Fit | 15.34 | 5 | 3.07 | 1.19 | 0.4267 |
| Pure Error | 12.89 | 5 | 2.58 | ||
| Cor Total | 1064.63 | 19 |
|
Simulated Fermentation Solution | Removal Efficiency/% |
Actual Fermentation Broth | Yield of GABA/% | Purity of GABA/% |
| 800 mL system | 90.79 | 800 mL system | 64.36 | 98.73 |
| 3.2 L system | 92.58 | 3.2 L system | 67.32 | 98.66 |
| Stages | Methods | Removal Efficiency/% | GABA Loss Rate a/% | Purity of GABA /% | Yield of GABA /% | Ethanol Dosage b/% | Process Steps |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Desalination | Cooling crystallization | 90.79 | <5 | - | - | 0 | 1 |
| Ethanol desalination | 75 | 10~20 | - | - | 230 | 2 | |
| Treatment of GABA | Coupled crystallization | - | - | 98.66 | 67.32 | 300 | 2 |
| Ion Exchange [21] | - | - | 98.66 | 50 | unknow | 4 | |
| Ethanol Precipitation [23] | - | - | 98.69 | 60 | >900 | 4 |
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Annual production/t | 74.16 |
| Annual sales revenue/USD | 828,183.29 |
| Total capital investment/USD | 585,395.60 |
| Total working capital/USD | 531,776.22 |
| Payback period/years | 1.98 |
| Return on capital investment/% | 50.63 |
| Break-even point/% | 48.65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jing, Y.; Zhang, J.; You, S.; Wang, M.; Su, R.; Qi, W. Development and Techno-Economic Evaluation of Crystallization Techniques for GABA Purification from Fermentation Broth. Molecules 2025, 30, 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040897
Jing Y, Zhang J, You S, Wang M, Su R, Qi W. Development and Techno-Economic Evaluation of Crystallization Techniques for GABA Purification from Fermentation Broth. Molecules. 2025; 30(4):897. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040897
Chicago/Turabian StyleJing, Yu, Jinxu Zhang, Shengping You, Mengfan Wang, Rongxin Su, and Wei Qi. 2025. "Development and Techno-Economic Evaluation of Crystallization Techniques for GABA Purification from Fermentation Broth" Molecules 30, no. 4: 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040897
APA StyleJing, Y., Zhang, J., You, S., Wang, M., Su, R., & Qi, W. (2025). Development and Techno-Economic Evaluation of Crystallization Techniques for GABA Purification from Fermentation Broth. Molecules, 30(4), 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040897







