Screening Refractory Dye Degradation by Different Advanced Oxidation Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
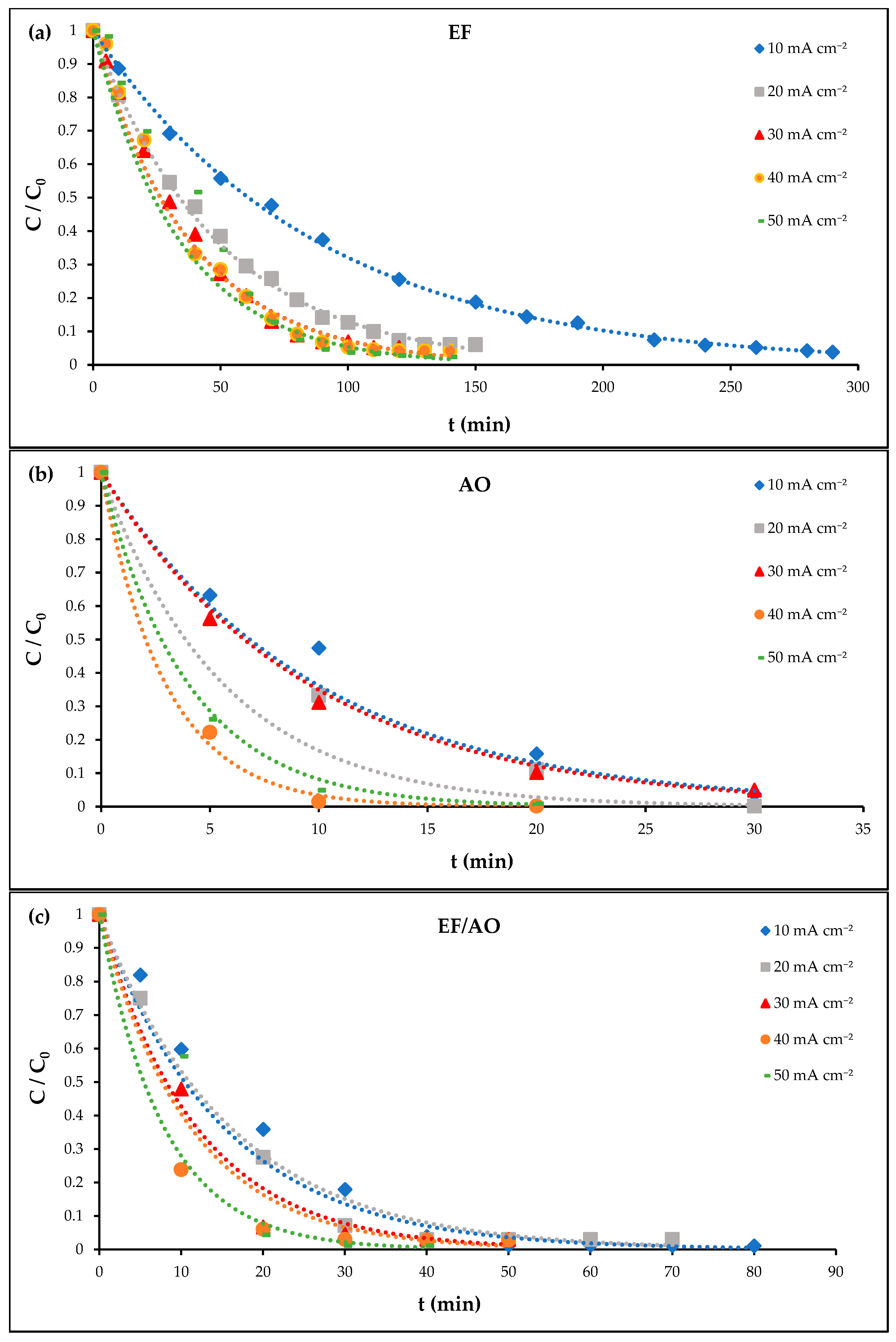
2.1. Current Density Effect
2.2. Effect of RhB Concentration
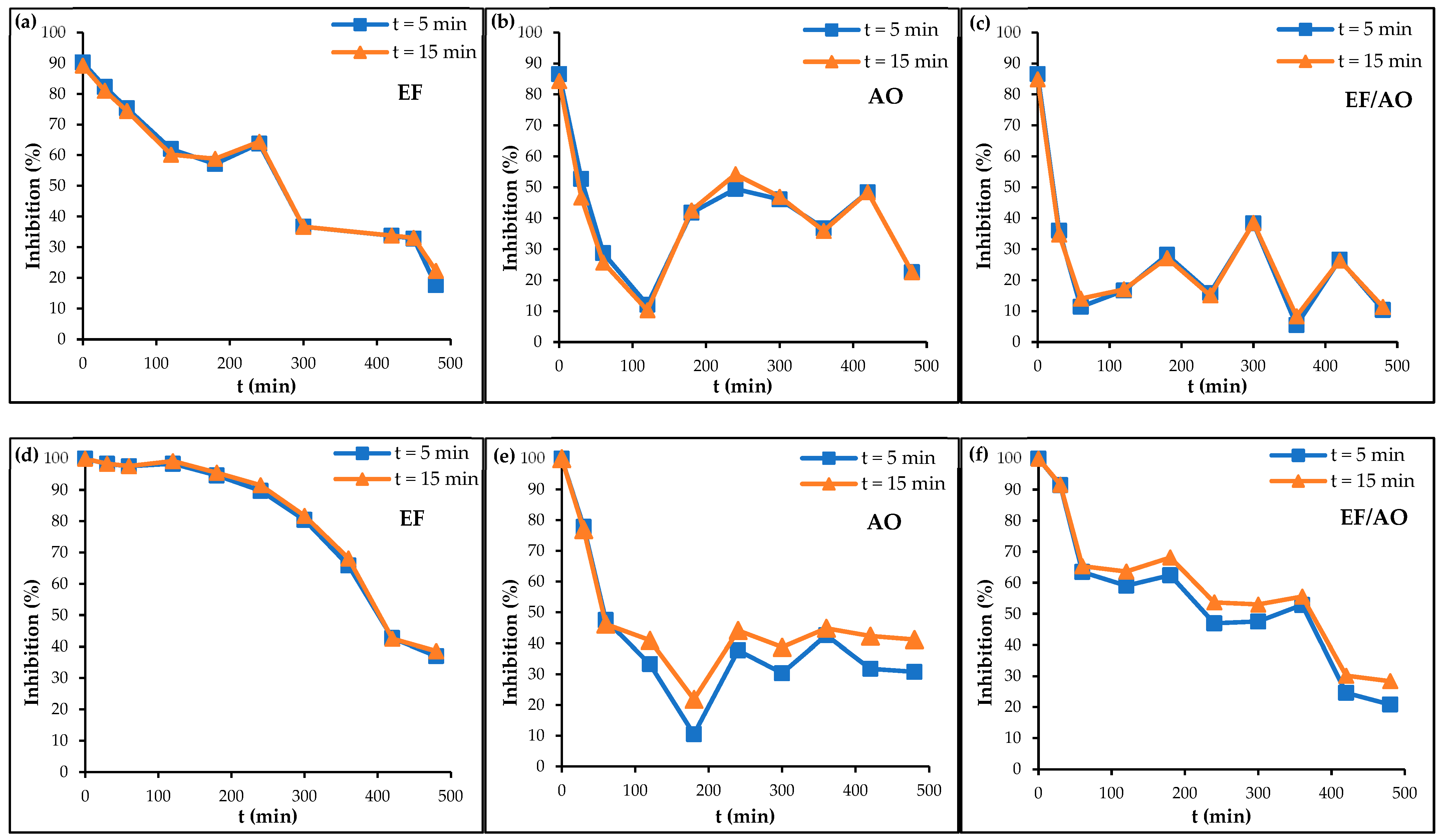
2.3. Toxicity Monitoring During RhB Degradation
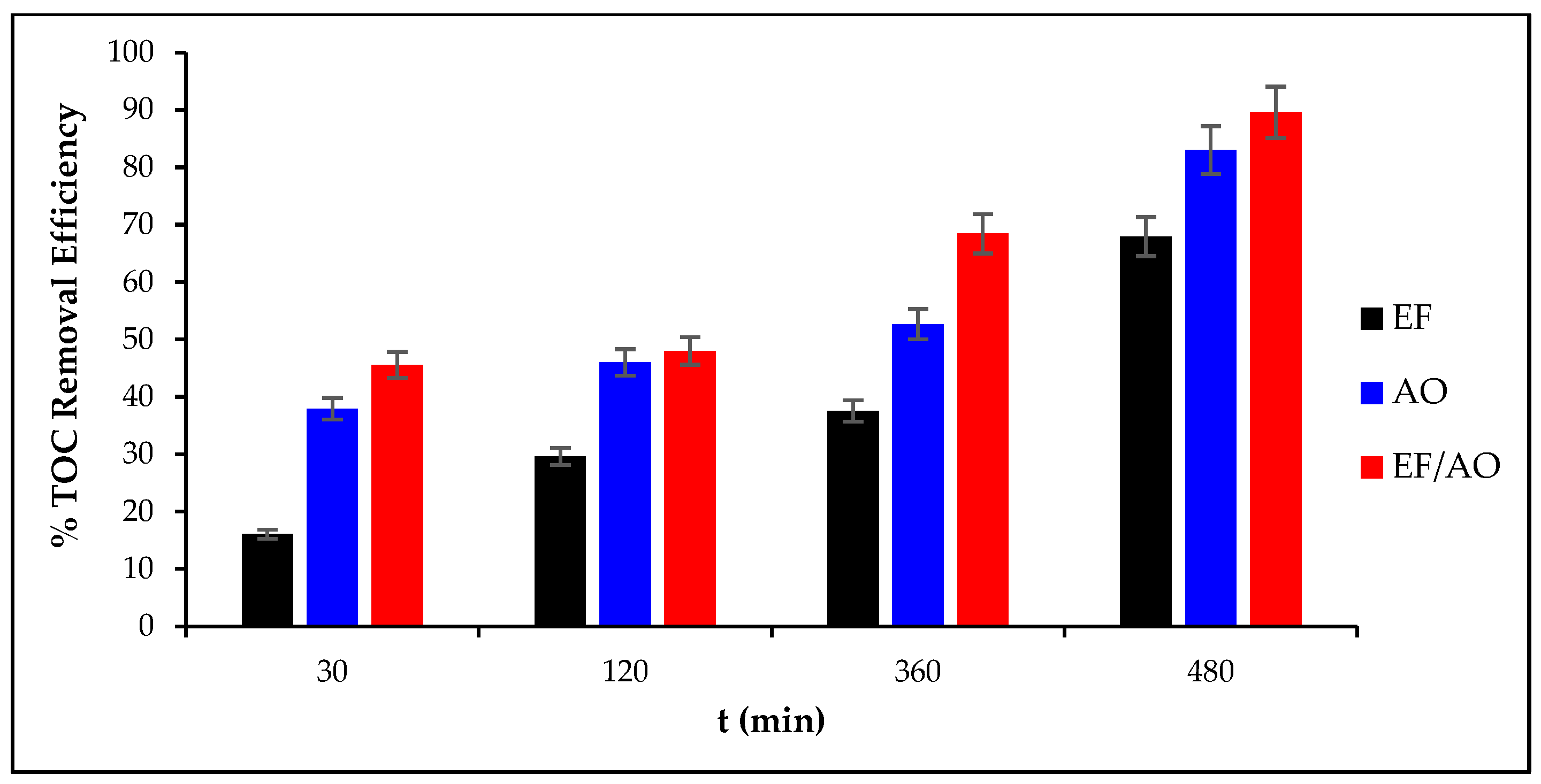
2.4. Total Organic Carbon Removal Efficiency
2.5. Mineralization Current Efficiency (MCE) and Energy Consumption (EC)
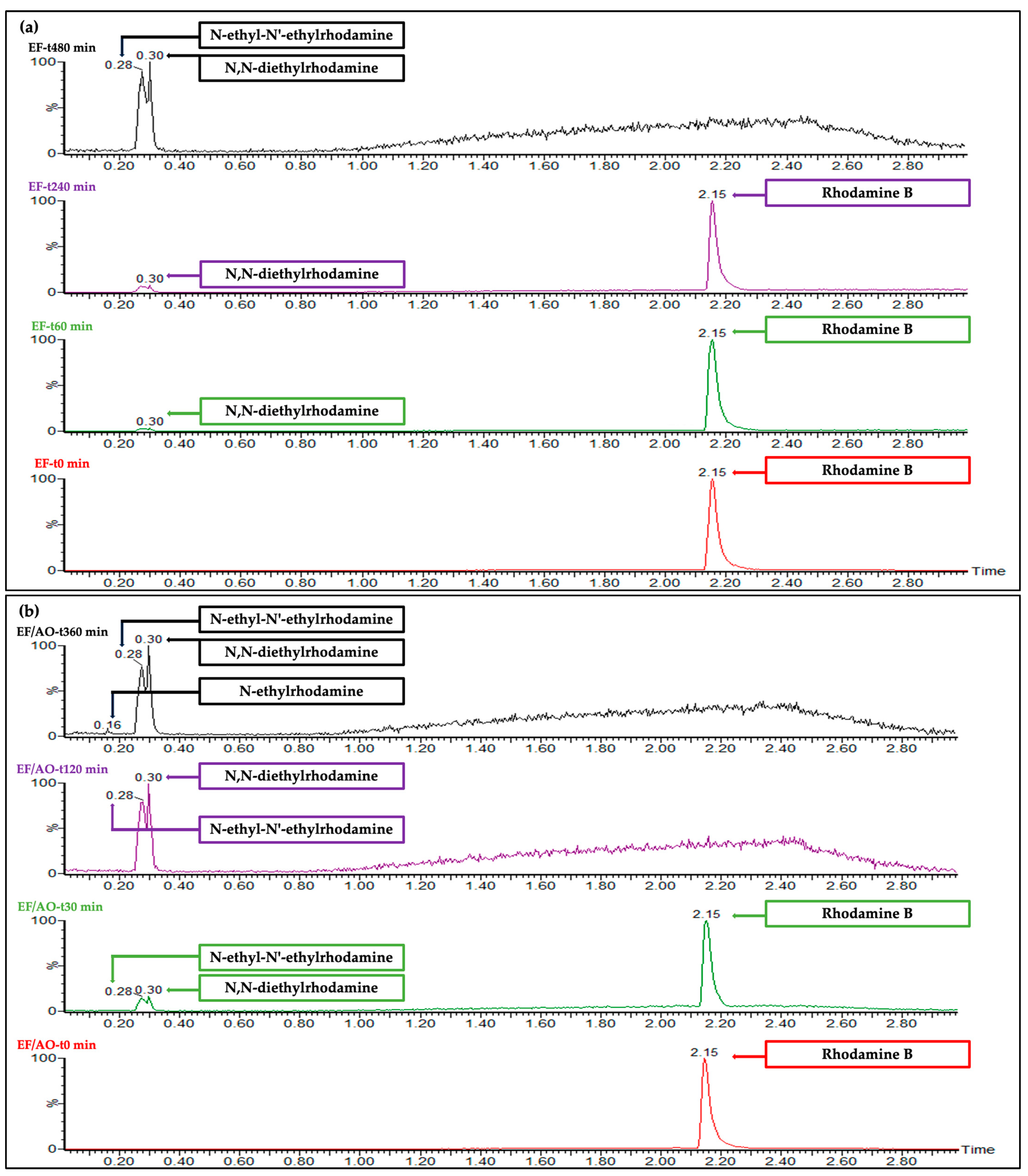
2.6. RhB and By-Product Identification by UHPLC-HRMS
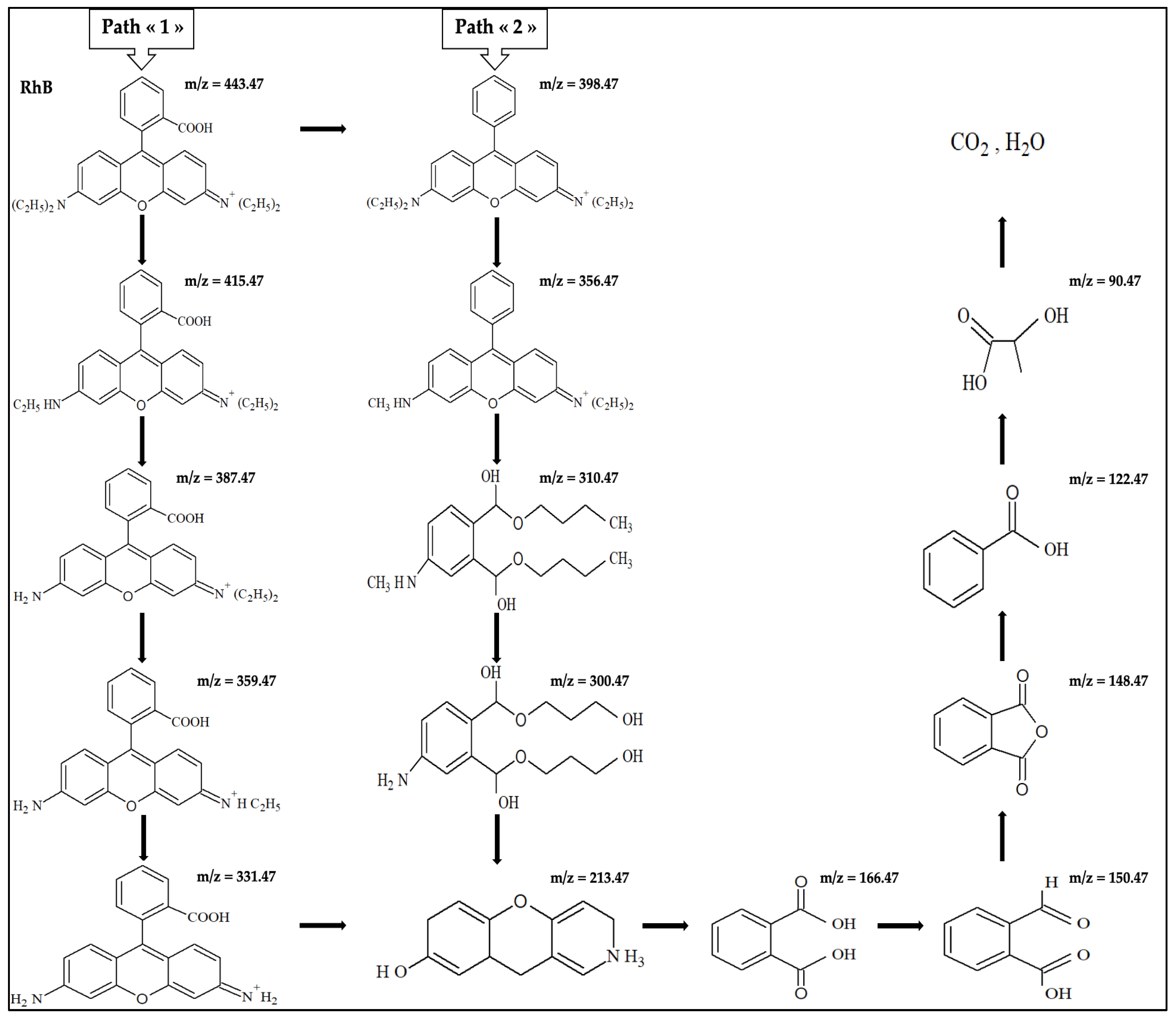
2.7. Possible RhB Degradation Pathways
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
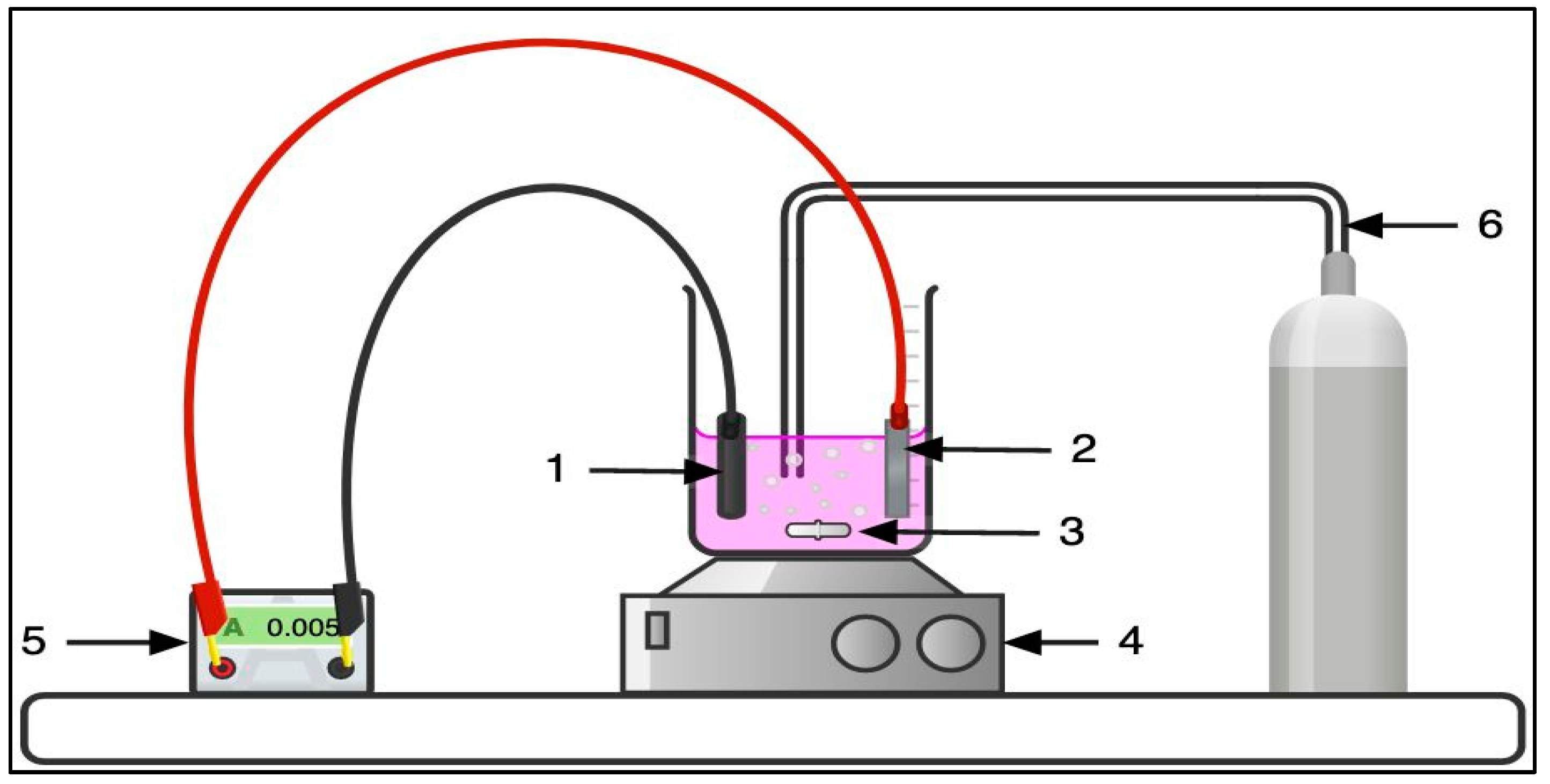
3.2. Electrochemical Cell
3.3. Performance Indicators of RhB Degradation and Associated Analytical Methods
3.3.1. Color Removal (UV–Visible Spectrophotometry Analysis)
3.3.2. RhB Degradation Kinetic Constants
3.3.3. Toxicity Test
3.3.4. Total Organic Carbon (TOC) Removal
3.3.5. RhB and By-Product Identification (UHPLC-HRMS Analysis)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouyakoub, A.Z.; Kacha, S.; Ouhib, R.; Bellebia, S.; Lartiges, B. Combined treatment of a textile effluent containing reactive dyes by coagulation-flocculation and electroflotation. J. Water Sci. 2010, 23, 89–103. [Google Scholar]
- Zongo, I.; Joseph, W.; Belkacem, M.; Amadou, H.; Lapicque, F.; Jean-Pierre, L. Electrocoagulation treatment of two textile effluents and a simulated tannery effluent: Energetic study and effect of operating parameters on pollutant treatment. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2011, 62, 216–235. [Google Scholar]
- Papić, S.; Koprivanac, N.; Božić, A.L.; Meteš, A. Removal of some reactive dyes from synthetic wastewater by combined Al (III) coagulation/carbon adsorption process. Dyes Pigm. 2004, 62, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuraman, G.; Teng, T.T. Extraction and recovery of Rhodamine B, methyl violet and methylene blue from industrial wastewater using D2EHPA as an extractant. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2009, 15, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartasun, P.; Cieśliński, H.; Bujacz, A.; Wierzbicka-Woś, A.; Kur, J. A study on the interaction of Rhodamine B with methylthioadenosine phosphorylase protein sourced from an Antarctic soil metagenomic library. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oplatowska, M.; Elliott, C.T. Development and validation of rapid disequilibrium enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for the detection of Methyl Yellow and Rhodamine B dyes in foods. Analyst 2011, 136, 2403–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratiwi, R.; Auliya As, N.N.; Yusar, R.F.; Shofwan, A.A.A. Analysis of prohibited and restricted ingredients in cosmetics. J. Cosmetics 2022, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigma-Aldrich. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/TN/en/sds/sigma/r6626?userType=anonymous (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- Skjolding, L.M.; Dyhr, K.; Köppl, C.; McKnight, U.; Bauer-Gottwein, P.; Mayer, P.; Bjerg, P.; Baun, A. Assessing the aquatic toxicity and environmental safety of tracer compounds Rhodamine B and Rhodamine WT. J. Water Res. 2021, 197, 117109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, T.L.; Orimolade, B.O.; Masekela, D.; Mamba, B.; Mabuba, N. The application of photoelectrocatalysis in the degradation of Rhodamine B in aqueous solutions: A review. J. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 26176–26191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooh, M.R.R.; Lim, L.B.; Lim, L.H.; Dahri, M.K. Separation of toxic rhodamine B from aqueous solution using an efficient low-cost material, Azolla pinnata, by adsorption method. J. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pera-Titus, M.; García-Molina, V.; Baños, M.A.; Giménez, J.; Esplugas, S. Degradation of chlorophenols by means of advanced oxidation processes: A general review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2004, 47, 219–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petala, A.; Noe, A.; Frontistis, Z.; Drivas, C.; Kennou, S.; Mantzavinos, D.; Kondarides, D.I. Synthesis and characterization of CoOx/BiVO4 photocatalysts for the degradation of propyl paraben. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 372, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.Y.; Hou, Y.Z.; Lin, Y.L.; Li, A.P.; Deng, Y.G. Degradation kinetics of diatrizoate during UV photolysis and UV/chlorination. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audino, F.; Conte, L.O.; Schenone, A.V.; Pérez-Moya, M.; Graells, M.; Alfano, O.M. A kinetic study for the Fenton and photo-Fenton paracetamol degradation in an annular photoreactor. Enviro. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 4312–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Yi, P.; Zhang, H. Degradation of clofibric acid by UV, O3 and UV/O3 processes: Performance comparison and degradation pathways. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 379, 120771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Segura, S.; Brillas, E. Applied photoelectrocatalysis on the degradation of organic pollutants in wastewaters. J. Photoch. Photobio. C 2017, 31, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orimolade, B.O.; Zwane, B.N.; Koiki, B.A.; Rivallin, M.; Bechelany, M.; Mabuba, N.; Lesage, G.; Cretin, M.; Arotiba, O.A. Coupling cathodic electro-fenton with anodic photo-electrochemical oxidation: A feasibility study on the mineralization of paracetamol. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oturan, M.A.; Aaron, J.J. Advanced oxidation processes in water/wastewater treatment: Principles and applications. A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 2577–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwane, B.N.; Orimolade, B.O.; Koiki, B.A.; Mabuba, N.; Gomri, C.; Petit, E.; Bonniol, V.; Lesage, G.; Rivallin, M.; Cretin, M. Combined electro-Fenton and anodic oxidation processes at a sub-stoichiometric titanium oxide (Ti4O7) ceramic electrode for the degradation of tetracycline in water. Water 2021, 13, 2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizza, M.; Brillas, E.; Comninellis, C. Application of boron-doped diamond electrodes for wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Eng. Manag. 2008, 18, 139–153. [Google Scholar]
- Ganiyu, S.O.; Oturan, N.; Raffy, S.; Esposito, G.; Van Hullebusch, E.D.; Cretin, M.; Oturan, M.A. Use of sub-stoichiometric titanium oxide as a ceramic electrode in anodic oxidation and electro-Fenton degradation of the beta-blocker propranolol: Degradation kinetics and mineralization pathway. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 242, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. Recent advances in the electrochemical oxidation water treatment: Spotlight on byproduct control. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2020, 14, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudoh, M.; Kitaguchi, H.; Koide, K. Electrochemical production of hydrogen peroxide by reduction of oxygen. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1985, 18, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azri, Y.M.; Zerouali, D. Treatment of Petrochemical Effluents by Electro-Fenton Processes: Electrochemical Study on the Oxygen Reduction Reaction for Hydrogen Peroxide Generation. J. Renew. Energy 2013, 16, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kesraoui-Abdessalem, A. Degradation of Pesticides Chlortoluron, Carbofuran and Bentazone in Aqueuos Medium by Advanced Oxidation Processes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Paris-Est-Marne-la-Vallée, Champs-sur-Marne, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Le, T.X.H.; Bechelany, M.; Cretin, M. Carbon felt based-electrodes for energy and environmental applications: A review. Carbon 2017, 122, 564–591. [Google Scholar]
- Hammami, S.; Bellakhal, N.; Oturan, N.; Oturan, M.A.; Dachraoui, M. Degradation of Acid Orange 7 by electrochemically generated HO• radicals in acidic aqueous medium using a boron-doped diamond or platinum anode: A mechanistic study. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drogui, P.; Blais, J.F.; Mercier, G. Review of electrochemical technologies for environmental applications. Recent Pat. Eng. 2007, 1, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Adil, M.; Ehtisham-ul-Haque, S.; Munir, B.; Yameen, M.; Ghaffar, A.; Shar, G.A.; Tahir, M.A.; Iqbal, M. Vibrio fischeri bioluminescence inhibition assay for ecotoxicity assessment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 1295–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yediler, A.; Lienert, D.; Wang, Z.; Kettrup, A. Toxicity evaluation of reactive dyestuffs, auxiliaries and selected effluents in textile finishing industry to luminescent bacteria Vibrio fischeri. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, E.C.; Brown, B.J.T.; Snook, R.D. Water toxicity monitoring using Vibrio fischeri: A method free of interferences from colour and turbidity. J. Environ. Monit. 2004, 6, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.X.H.; Van Nguyen, T.; Yacouba, Z.A.; Zoungrana, L.; Avril, F.; Petit, E.; Mendret, J.; Bonniol, V.; Bechelany, M.; Lacour, S. Toxicity removal assessments related to degradation pathways of azo dyes: Toward an optimization of electro-Fenton treatment. Chemosphere 2016, 161, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganiyu, S.O.; Oturan, N.; Raffy, S.; Cretin, M.; Causserand, C.; Oturan, M.A. Efficiency of plasma elaborated sub-stoichiometric titanium oxide (Ti4O7) ceramic electrode for advanced electrochemical degradation of paracetamol in different electrolyte media. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 208, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eladeb, B.; Bonnet, C.; Favre, E.; Lapicque, F. Electrochemical extraction of oxygen using PEM electrolysis technology. J. Electrochem. Sci. Eng. 2012, 2, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Niu, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Jin, F.; Luo, Q.; Huang, Q. Development of macroporous Magnéli phase Ti4O7 ceramic materials: As an efficient anode for mineralization of poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.U.H.; Gul, N.S.; Sabahat, S.; Sun, J.; Tahir, K.; Shah, N.S.; Muhammad, N.; Rahim, A.; Imran, M.; Iqbal, J. Removal of organic pollutants through hydroxyl radical-based advanced oxidation processes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 267, 115564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Zhao, J.; Olajuyin, A.M.; Sharshar, M.M.; Mu, T.; Yang, M.; Xing, J. Effective degradation of Rhodamine B by electro-Fenton process, using ferromagnetic nanoparticles loaded on modified graphite felt electrode as reusable catalyst: In neutral pH condition and without external aeration. J. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 15471–15482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhao, C.; Chen, Q.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, B.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X. Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton-Catalyzed Degradation of Rhodamine B by Nano-Calcined Pyrite. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganzenko, O.; Sistat, P.; Trellu, C.; Bonniol, V.; Rivallin, M.; Cretin, M. Reactive electrochemical membrane for the elimination of carbamazepine in secondary effluent from wastewater treatment plant. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 419, 129467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kateb, M.; Trellu, C.; Darwich, A.; Rivallin, M.; Bechelany, M.; Nagarajan, S.; Lacour, S.; Bellakhal, N.; Lesage, G.; Heran, M. Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes using novel electrode materials for mineralization and biodegradability enhancement of nanofiltration concentrate of landfill leachates. Water Res. 2019, 162, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouarda, Y.; Trellu, C.; Lesage, G.; Rivallin, M.; Drogui, P.; Cretin, M. Electro-oxidation of secondary effluents from various wastewater plants for the removal of acetaminophen and dissolved organic matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 140352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brillas, E.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A. Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods. An updated review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 166, 603–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, T.S.; Thomas, M.; Natarajan, K.; Bajaj, H.C.; Tayade, R.J. Study on UV-LED/TiO2 process for degradation of Rhodamine B dye. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 169, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zewde, A.A.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Odey, E.A. A review of the application of sonophotocatalytic process based on advanced oxidation process for degrading organic dye. Rev. Environ. Health 2019, 34, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.S.; Mollah, M.Y.A.; Susan, M.A.B.H.; Islam, M.M. Role of in situ electrogenerated reactive oxygen species towards degradation of organic dye in aqueous solution. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 344, 136146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ruan, J.; Wang, X.; Shao, W.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Gu, C.; Qiao, W.; Li, J. Selective oxidation of organic pollutants based on reactive oxygen species and the molecular structure: Degradation behavior and mechanism analysis. Water Res. 2023, 246, 120697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Fang, W.; Yi, Q.; Zhang, J. A comprehensive review on reactive oxygen species (ROS) in advanced oxidation processes (AOPs). Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Reactive species in advanced oxidation processes: Formation, identification and reaction mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 401, 126158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.Y.; Zhao, L.; Guo, L.H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, F.J.; Yu, W.C. Roles of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the photocatalytic degradation of pentachlorophenol and its main toxic intermediates by TiO2/UV. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Sun, C.; Yang, S.; Ding, Y.; He, H.; Wang, Z. Photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B by Bi2WO6 with electron accepting agent under microwave irradiation: Mechanism and pathway. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, H.A.L.; Vo, T.K.; Nguyen, D.T.; Huynh, H.K.; Pham, Q.T.S.; Nguyen, V.C. Facile synthesis of bismuth terephthalate metal–organic frameworks and their visible-light-driven photocatalytic activities toward Rhodamine B dye. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2022, 15, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, B.R.; Correa, D.N.; Eberlin, M.N.; Vendramini, P. Fragmentation reactions of Rhodamine B and 6G as revealed by high accuracy orbitrap tandem mass spectrometry. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2017, 28, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaviska, F.; Drogui, P.; Mercier, G.; Blais, J.-F. Advanced oxidation processes for waters and wastewaters treatment: Application to degradation of refractory pollutants. J. Water Sci. 2009, 22, 535–564. [Google Scholar]
- Mousset, E.; Diamand, A. Water treatment by advanced oxidation processes—Anodic oxidation. Tech. Inge. 2019, J3952, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazou, H.; Afanga, H.; Akhouairi, S.; Ouchtak, H.; Addi, A.A.; Akbour, R.A.; Assabbane, A.; Douch, J.; Elmchaouri, A.; Duplay, J. Treatment of textile industry wastewater by electrocoagulation coupled with electrochemical advanced oxidation process. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 28, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhou, M.; Oturan, N.; Bechelany, M.; Cretin, M.; Oturan, M.A. Highly efficient and stable FeIIFeIII LDH carbon felt cathode for removal of pharmaceutical ofloxacin at neutral pH. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, Z.; Pelalak, R.; Zhou, M. A critical review on the recent progress in application of electro-Fenton process for decontamination of wastewater at near-neutral pH. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, R.A. The integrated antioxidant system. Nutr. Res. 1995, 15, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, A.; Santos, A.; Tojo, J.; Rodríguez, A. Toxicity and biodegradability of imidazolium ionic liquids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 151, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillas, E.; Sirés, I.; Oturan, M.A. Electro-Fenton process and related electrochemical technologies based on Fenton’s reaction chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 6570–6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Olajuyin, A.M.; Mu, T.; Yang, M.; Xing, J. Efficient degradation of Rhodamine B using modified graphite felt gas diffusion electrode by electro-Fenton process. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 11574–11583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, P.; Ruparelia, J. Influence of supporting electrolytes on electrochemical treatability of Reactive Black 5 using dimensionally stable anode. J. Inst. Eng. 2019, 100, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Molecular Structure | Physicochemical Characteristics | |
|---|---|---|
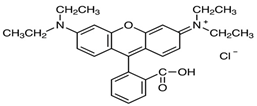 | Chemical formula of RhB as a chloride salt | C28H31ClN2O3 |
| Molecular weight | 479.01 g/mol | |
| Class | Xanthene | |
| Maximum absorption wavelength | 546–556 nm | |
| Process | Current Density (mA cm−2) | kapp (min−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| EF | 10 | 0.0111 ± 0.0011 | 0.9983 |
| 20 | 0.0206 ± 0.0021 | 0.9947 | |
| 30 | 0.0277 ± 0.0028 | 0.9804 | |
| 40 | 0.0284 ± 0.0028 | 0.9863 | |
| 50 | 0.0293 ± 0.0059 | 0.9288 | |
| AO | 10 | 0.0703 ± 0.0070 | 0.9942 |
| 20 | 0.1100 ± 0.0110 | 1.0000 | |
| 30 | 0.1340 ± 0.0134 | 0.9880 | |
| 40 | 0.2152 ± 0.0430 | 0.9785 | |
| 50 | 0.2501 ± 0.0500 | 0.9732 | |
| EF/AO | 10 | 0.0448 ± 0.0090 | 0.9538 |
| 20 | 0.0872 ± 0.0087 | 0.9914 | |
| 30 | 0.1127 ± 0.0225 | 0.9500 | |
| 40 | 0.1409 ± 0.0282 | 0.9998 | |
| 50 | 0.1519 ± 0.0304 | 0.9988 |
| Dye | Process | Anode | Cathode | RhB Initial Concentration (mM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 0.1 | ||||||
| kapp (min−1) | R2 | kapp (min−1) | R2 | ||||
| RhB | EF | Ti/Pt | CF | 0.0277 | 0.9804 | 0.0057 | 0.9846 |
| AO | Ti4O7 | CF | 0.1340 | 0.9880 | 0.0210 | 0.9647 | |
| EF/AO | Ti4O7 | CF | 0.1127 | 0.9500 | 0.0252 | 0.9701 | |
| Identification Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|
| m/z | tR (min) | Molecule |
| 443.47 | 2.15 | Rhodamine B ion |
| 415.47 | 0.30 | N,N-diethylrhodamine |
| 387.47 | 0.28 | N-ethyl-N′-ethylrhodamine |
| 359.47 | 0.16 | N-ethylrhodamine |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouagued, I.; Cretin, M.; Petit, E.; Lesage, G.; Djafer, A.; Ouagued, A.; Lacour, S. Screening Refractory Dye Degradation by Different Advanced Oxidation Processes. Molecules 2025, 30, 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030712
Ouagued I, Cretin M, Petit E, Lesage G, Djafer A, Ouagued A, Lacour S. Screening Refractory Dye Degradation by Different Advanced Oxidation Processes. Molecules. 2025; 30(3):712. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030712
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuagued, Imane, Marc Cretin, Eddy Petit, Geoffroy Lesage, Abderrahmane Djafer, Abdallah Ouagued, and Stella Lacour. 2025. "Screening Refractory Dye Degradation by Different Advanced Oxidation Processes" Molecules 30, no. 3: 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030712
APA StyleOuagued, I., Cretin, M., Petit, E., Lesage, G., Djafer, A., Ouagued, A., & Lacour, S. (2025). Screening Refractory Dye Degradation by Different Advanced Oxidation Processes. Molecules, 30(3), 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030712








